In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Furo[3,2-c]coumarins as Cholinesterases and Monoamine Oxidases Inhibitors
Abstract
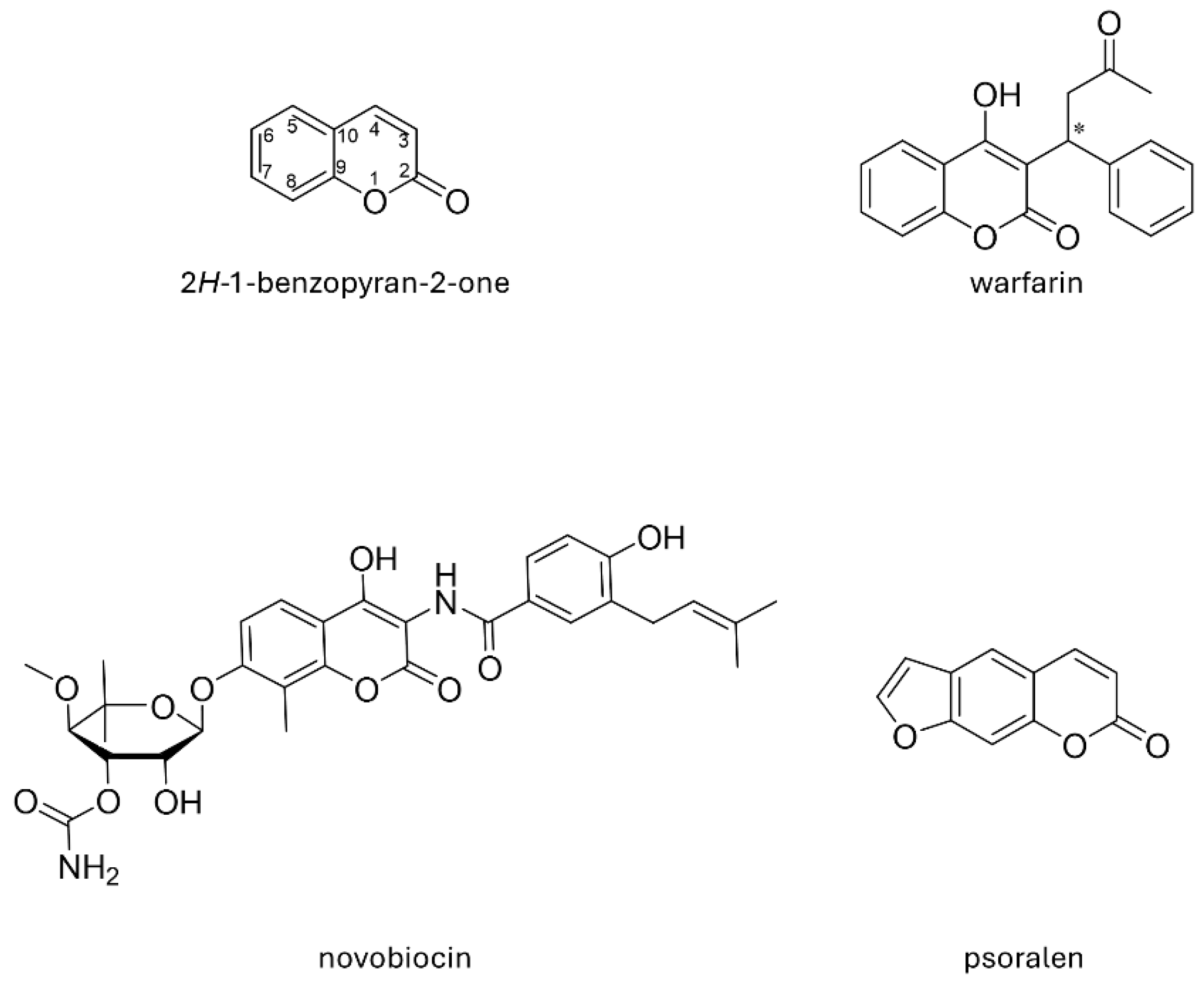
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
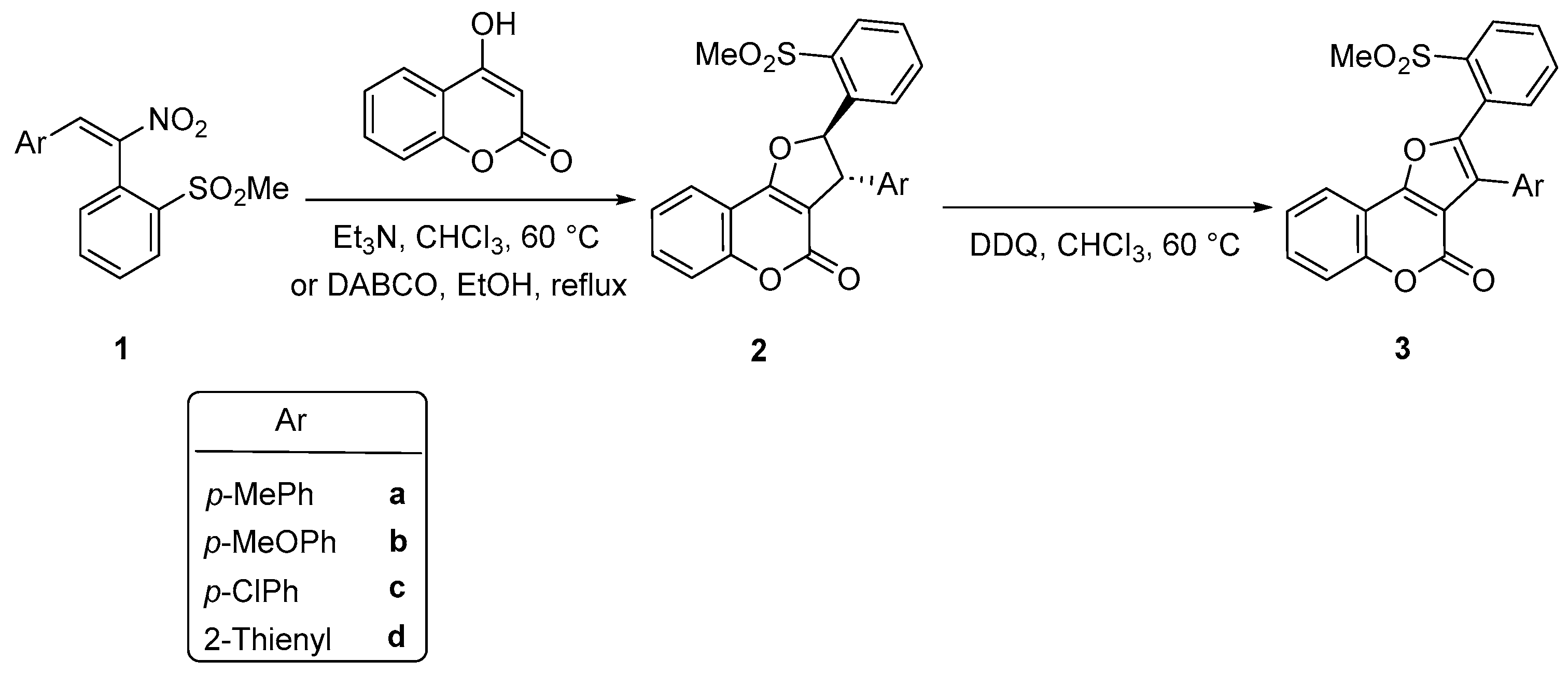
2.1. Synthesis of Dihydrofuro[3,2-c]coumarins 2 and Furo[3,2-c]coumarins 3
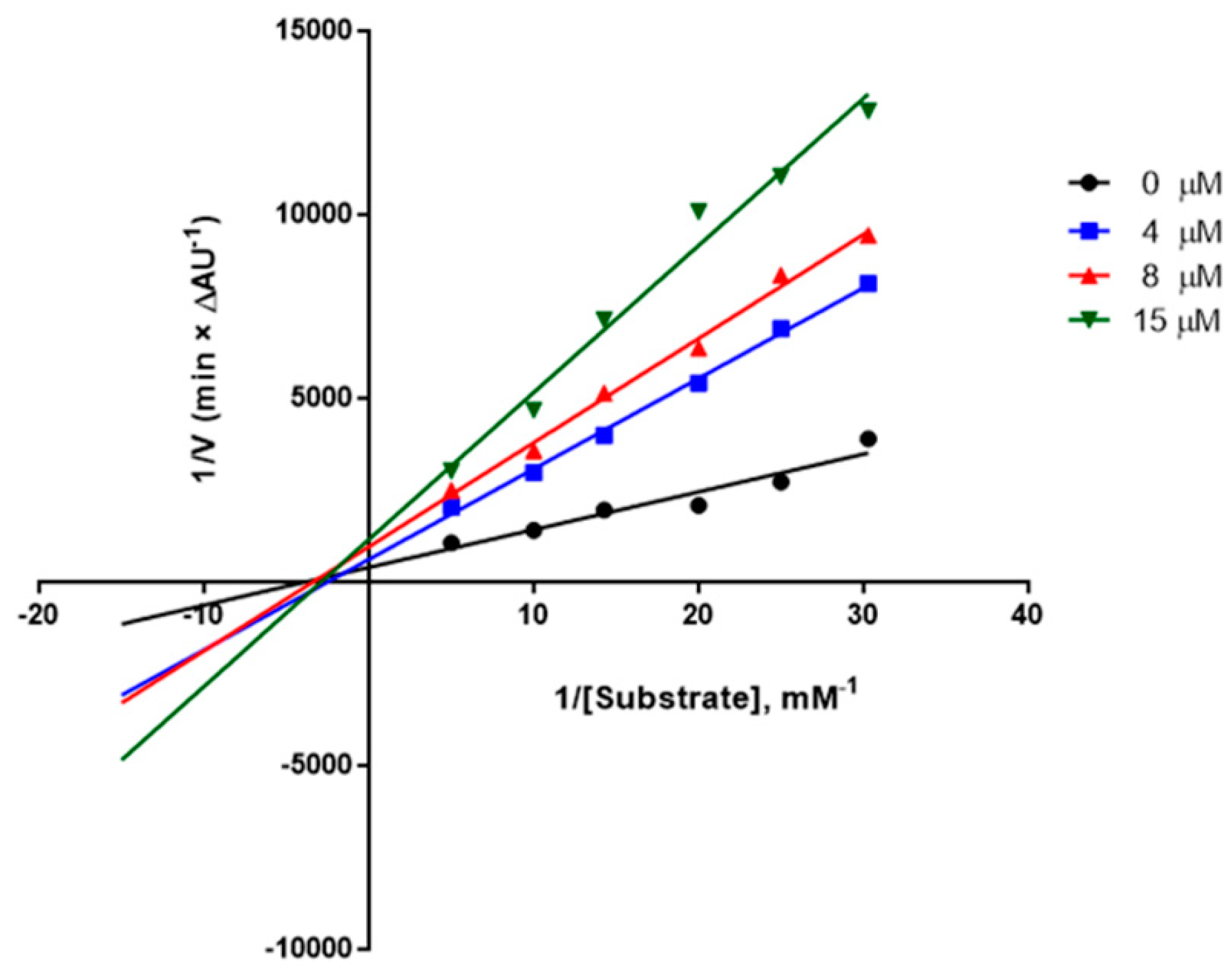
2.2. In Vitro Biological Evaluation
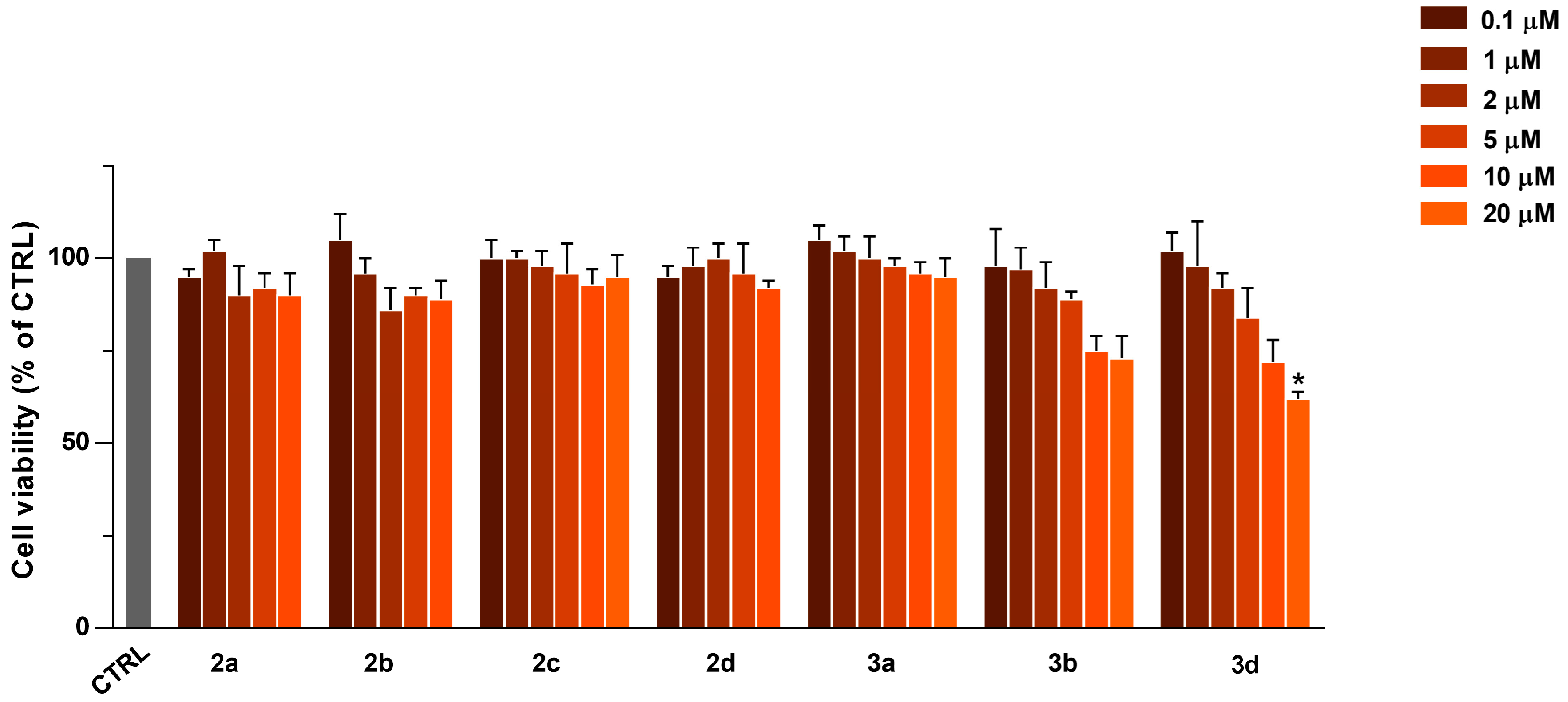
2.3. Cytotoxicity
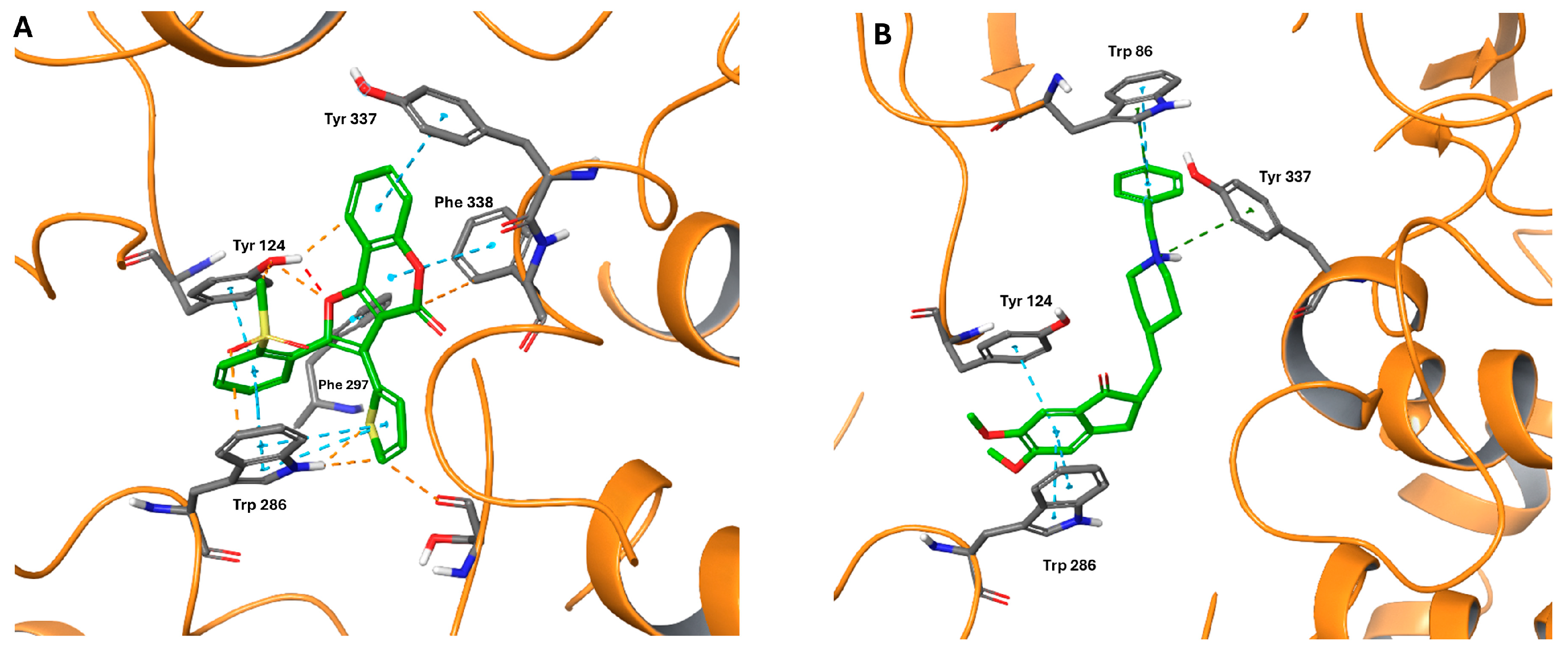
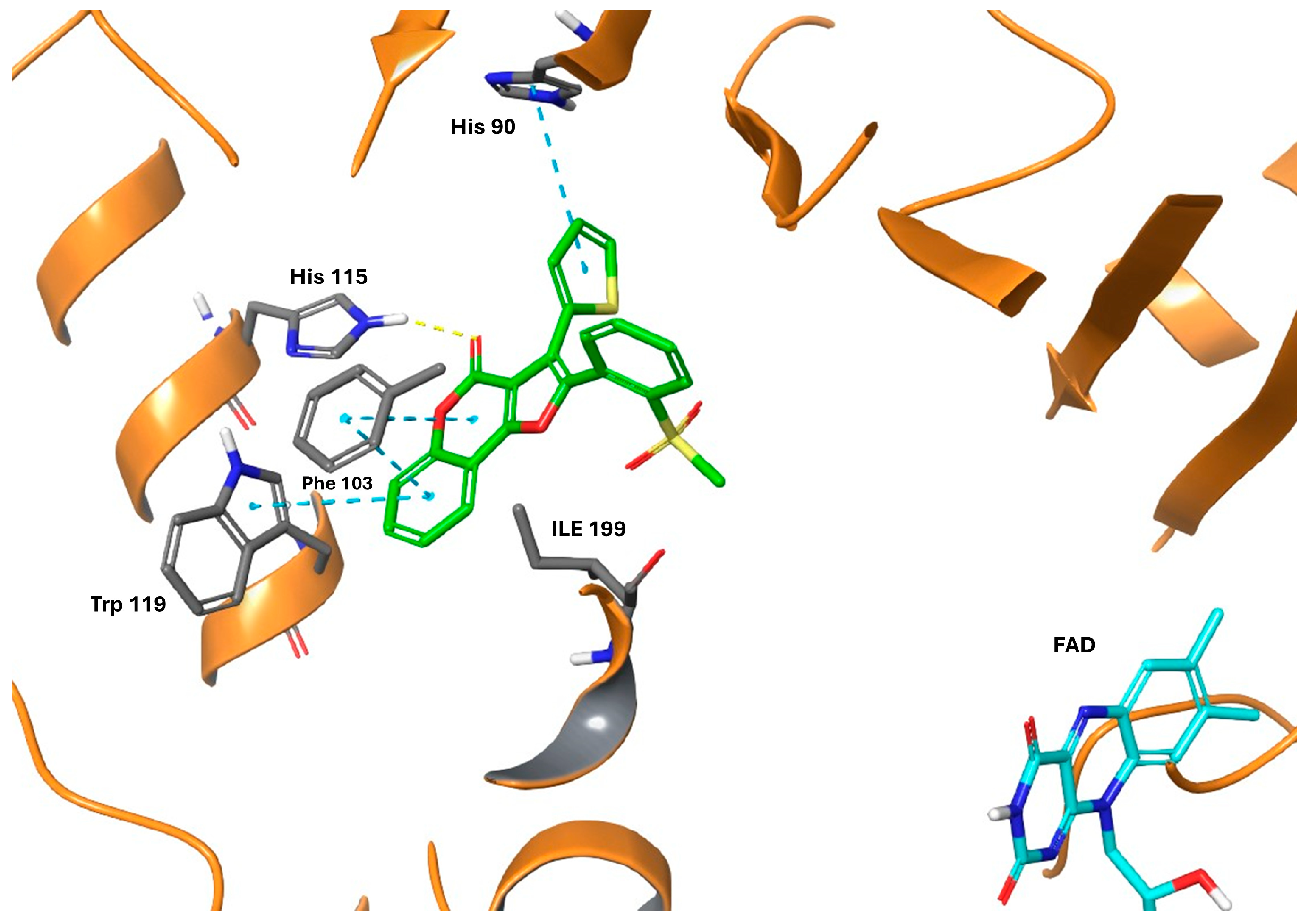
2.4. Computational Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Reaction of Substrates 1d with 4-Hydroxycoumarin
3.1.2. Aromatization of 2d with DDQ
3.2. In Vitro Enzymatic Inhibition Assays
3.3. Molecular Docking Simulations
3.4. Cell-Based Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, R.D.H. Coumarins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1995, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoult, J.R.S.; Payá, M. Pharmacological and Biochemical Actions of Simple Coumarins: Natural Products with Therapeutic Potential. Gen. Pharmacol. 1996, 27, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, T. Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lončar, M.; Jakovljević, M.; Šubarić, D.; Pavlić, M.; Služek, V.B.; Cindrić, I.; Molnar, M. Coumarins in Food and Methods of Their Determination. Foods 2020, 9, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, M.J.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Abreu, O.A.; Molina, E.; Yordi, E.G. Coumarins—An Important Class of Phytochemicals. In Phytochemicals-Isolation, Characterisation and Role in Human Health; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, A. Darstellung von Benzoesäure Aus Der Tonka-Bohne Und Aus Den Meliloten-Oder Steinklee-Blumen. Ann. Phys. 1820, 64, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, J.M.; Owens, T.W.; Mandler, M.D.; Simpson, B.W.; Lazarus, M.B.; Sherman, D.J.; Davis, R.M.; Okuda, S.; Massefski, W.; Ruiz, N.; et al. The Antibiotic Novobiocin Binds and Activates the ATPase That Powers Lipopolysaccharide Transport. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17221–17224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperkiewicz, K.; Ponczek, M.B.; Owczarek, J.; Guga, P.; Budzisz, E. Antagonists of Vitamin K-Popular Coumarin Drugs and New Synthetic and Natural Coumarin Derivatives. Molecules 2020, 25, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Cui, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, F.; Huang, W.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Bowman, G.R.; Sadler, J.E.; et al. Warfarin Traps Human Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase in an Intermediate State during Electron Transfer. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, F.G.; Marrero, J.G.; Macías-Alonso, M.; González, M.C.; Córdova-Guerrero, I.; Teissier García, A.G.; Osegueda-Robles, S. Coumarin Heterocyclic Derivatives: Chemical Synthesis and Biological Activity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 1472–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanachi, A.; Leonetti, F.; Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; Carotti, A. Coumarin: A Natural, Privileged and Versatile Scaffold for Bioactive Compounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Kaneko, Y.; Miyazaki, H.; Harayama, T. A Convenient Synthesis of a Simple Coumarin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 3100–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fringuelli, F.; Piermatti, O.; Pizzo, F. One-Pot Synthesis of 3-Carboxycoumarins via Consecutive Knoevenagel and Pinner Reactions in Water. Synthesis 2003, 15, 2331–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setena, S.M.; Shah, N.M. The Chemistry of Coumarins. Chem. Rev. 1945, 36, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, P. Adventures in Coumarin Chemistry. Synlett 2023, 36, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, F.; Pinna, C.; Dallavalle, S.; Tamborini, L.; Pinto, A. An Overview of Coumarin as a Versatile and Readily Accessible Scaffold with Broad-Ranging Biological Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rullo, M.; Niso, M.; Pisani, L.; Carrieri, A.; Colabufo, N.A.; Cellamare, S.; Altomare, C.D. 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline/2H-Chromen-2-One Conjugates as Nanomolar P-Glycoprotein Inhibitors: Molecular Determinants for Affinity and Selectivity over Multidrug Resistance Associated Protein 1. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; De Palma, A.; Farina, R.; Cellamare, S.; Altomare, C.D. Discovery of Potent Dual Binding Site Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors via Homo- and Heterodimerization of Coumarin-Based Moieties. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsinghorst, P.W.; Wille, T.; Barić, D.; Mertens, M.D.; Baumann, M.; Küppers, J.; Gütschow, M. Aminoalkoxy-Substituted Coumarins: Synthesis and Evaluation for Reactivation of Inhibited Human Acetylcholinesterase. Arch. Pharm. 2022, 355, e2200208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Yu, W.; Song, D.; Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Zhu, J.; Ren, Y.; Kong, L. Discovery of Fluorescent Coumarin-Benzo[b]Thiophene 1, 1-Dioxide Conjugates as Mitochondria-Targeting Antitumor STAT3 Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 174, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovino, L.G.; Manzella, N.; Resta, J.; Vanoni, M.A.; Rotilio, L.; Pisani, L.; Edmondson, D.E.; Parini, A.; Mattevi, A.; Mialet-Perez, J.; et al. Rational Redesign of Monoamine Oxidase A into a Dehydrogenase to Probe ROS in Cardiac Aging. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 1795–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.J.; Novo, P.; Mayán, L.; Torres, I.; Uriarte, E.; Yáñez, M.; Fontenla, J.Á.; Ortuso, F.; Alcaro, S.; Procopio, F.; et al. 8-Amide and 8-Carbamate Substitution Patterns as Modulators of 7-Hydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin’s Antidepressant Profile: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Docking Studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 248, 115091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresca, A.; Temperini, C.; Vu, H.; Pham, N.B.; Poulsen, S.A.; Scozzafava, A.; Quinn, R.J.; Supuran, C.T. Non-Zinc Mediated Inhibition of Carbonic Anhydrases: Coumarins Are a New Class of Suicide Inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3057–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanachi, A.; Hanke, N.; Pisani, L.; Leonetti, F.; Nicolotti, O.; Catto, M.; Cellamare, S.; Hartmann, R.W.; Carotti, A. Discovery of New 7-Substituted-4-Imidazolylmethyl Coumarins and 4′-Substituted-2-Imidazolyl Acetophenones Open Analogues as Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Steroid-11β-Hydroxylase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bras, G.; Radanyi, C.; Peyrat, J.F.; Brion, J.D.; Alami, M.; Marsaud, V.; Stella, B.; Renoir, J.M. New Novobiocin Analogues as Antiproliferative Agents in Breast Cancer Cells and Potential Inhibitors of Heat Shock Protein 90. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 6189–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochet, L.; Frederick, R.; Masereel, B. Coumarin and Isocoumarin as Serine Protease Inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 10, 3781–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rullo, M.; Cipolloni, M.; Catto, M.; Colliva, C.; Miniero, D.V.; Latronico, T.; de Candia, M.; Benicchi, T.; Linusson, A.; Giacchè, N.; et al. Probing Fluorinated Motifs onto Dual AChE-MAO B Inhibitors: Rational Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Early-ADME Studies. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 3962–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, L.; Rullo, M.; Catto, M.; de Candia, M.; Carrieri, A.; Cellamare, S.; Altomare, C.D. Structure-Property Relationship Study of the HPLC Enantioselective Retention of Neuroprotective 7-[(1-Alkylpiperidin-3-Yl)Methoxy]Coumarin Derivatives on an Amylose-Based Chiral Stationary Phase. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Spada, G.; Miniero, D.V.; Rullo, M.; Cipolloni, M.; Delre, P.; Colliva, C.; Colella, M.; Leonetti, F.; Liuzzi, G.M.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; et al. Structure-Based Design of Multitargeting ChEs-MAO B Inhibitors Based on Phenyl Ring Bioisosteres: AChE/BChE Selectivity Switch and Drug-like Characterization. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 274, 116511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rullo, M.; Catto, M.; Carrieri, A.; de Candia, M.; Altomare, C.D.; Pisani, L. Chasing ChEs-MAO B Multi-Targeting 4-Aminomethyl-7-Benzyloxy-2H-Chromen-2-Ones. Molecules 2019, 24, 4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, R.; Barreca, D.; Protti, M.; Brighenti, V.; Righetti, L.; Anceschi, L.; Mercolini, L.; Benvenuti, S.; Gattuso, G.; Pellati, F. Botanical Sources, Chemistry, Analysis, and Biological Activity of Furanocoumarins of Pharmaceutical Interest. Molecules 2019, 24, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehian, F.; Nadri, H.; Jalili-Baleh, L.; Youseftabar-Miri, L.; Abbas Bukhari, S.N.; Foroumadi, A.; Tüylü Küçükkilinç, T.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Khoobi, M. A Review: Biologically Active 3,4-Heterocycle-Fused Coumarins. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 212, 113034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fylaktakidou, K.C.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.J.; Litinas, K.E.; Nicolaides, D.N. Natural and Synthetic Coumarin Derivatives with Anti-Inflammatory/Antioxidant Activities. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 3813–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzi, A.; Bianchi, L.; Giorgi, G.; Maccagno, M.; Petrillo, G.; Spinelli, D.; Tavani, C. An Easy Access to Furan-Fused Polyheterocyclic Systems. Molecules 2022, 27, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzi, A.; Bianchi, L.; Giorgi, G.; Lentini, G.; Maccagno, M.; Marcantoni Taddei, G.; Petrillo, G.; Tavani, C. An Appealing, Robust Access to Furo-Fused Heteropolycycles. Molecules 2025, 30, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youkwan, J.; Sutthivaiyakit, S.; Sutthivaiyakit, P. Citrusosides A-D and Furanocoumarins with Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activity from the Fruit Peels of Citrus Hystrix. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1879–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Peng, Q.; Shao, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Pu, X.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.M.; Chan, A.S.C.; Gu, L. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Functionalized Coumarins as Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 40, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Reconsideration of Anticholinesterase Therapeutic Strategies against Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Alzheimer Disease: An Update on Pathobiology and Treatment Strategies. Cell 2019, 179, 312–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertini, C.; Salerno, A.; de Sena Murteira Pinheiro, P.; Bolognesi, M.L. From Combinations to Multitarget-Directed Ligands: A Continuum in Alzheimer’s Disease Polypharmacology. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 2606–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, R.; Munari, F.; Angioni, R.; Venegas, F.; Agnellini, A.; Castro-Gil, M.P.; Castegna, A.; Luisetto, R.; Viola, A.; Canton, M. Targeting Monoamine Oxidase to Dampen NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Inflammation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1311–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, G.; Benzi, A.; Bianchi, L.; Maccagno, M.; Pagano, A.; Tavani, C.; Spinelli, D. Recent Advances in the Use of Conjugated Nitro or Dinitro-1,3-Butadienes as Building-Blocks for the Synthesis of Heterocycles. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 152297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Qin, Z.; Cheng, X.; Liu, D.; Peng, Y.; Huang, H.; Song, B.; Bian, J.; Li, Z. Copper(II)-Catalyzed Tandem Reaction: Synthesis of Furo[3,2-c]Coumarin Derivatives and Evaluation for Photophysical Properties. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 12537–12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolita, S.; Borah, P.; Naidu, P.S.; Bhuyan, P.J. DMSO and Iodine Mediated Reaction of 4-Hydroxycoumarins and Aldehydes/Aryl Methyl Ketones: Synthesis of Furo[3,2-c]Coumarins. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zeng, P.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X. Lewis-Acid-Mediated One-Pot Tandem Reactions for Synthesis of Structurally Diverse Furo[3,2-c]Coumarins. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 4539–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerru, N.; Lalitha Gummidi, M.; Kumar Gangu, K.; Maddila, S.; Jonnalagadda, S.B. Synthesis of Novel Furo[3,2-c]Coumarin Derivatives through Multicomponent [4+1] Cycloaddition Reaction Using ZnO/FAp as a Sustainable Catalyst. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 4104–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rullo, M.; Pisani, L. 4-Hydroxycoumarins as Michael Donors in Asymmetric Routes to Polycyclic Coumarins (Microreview). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2018, 54, 394–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Hajra, A. DABCO-Promoted One-Pot Facile Synthesis of Angularly Fused Furoquinolinones and Furocoumarins. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 2015, 7836–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Feather-Stone, R.M. A New and Rapid Colorimetric Determination of Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colletier, J.P.; Fournier, D.; Greenblatt, H.M.; Stojan, J.; Sussman, J.L.; Zaccai, G.; Silman, I.; Weik, M. Structural Insights into Substrate Traffic and Inhibition in Acetylcholinesterase. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2746–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordentlich, A.; Barak, D.; Kronman, C.; Flashner, Y.; Leitner, M.; Segall, Y.; Ariel, N.; Cohen, S.; Velan, B.; Shafferman, A. Dissection of the Human Acetylcholinesterase Active Center Determinants of Substrate Specificity. Identification of Residues Constituting the Anionic Site, the Hydrophobic Site, and the Acyl Pocket. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 17083–17095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inestrosa, N.C.; Dinamarca, M.C.; Alvarez, A. Amyloid-Cholinesterase Interactions. Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rullo, M.; La Spada, G.; Miniero, D.V.; Gottinger, A.; Catto, M.; Delre, P.; Mastromarino, M.; Latronico, T.; Marchese, S.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; et al. Bioisosteric Replacement Based on 1,2,4-Oxadiazoles in the Discovery of 1H-Indazole-Bearing Neuroprotective MAO B Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 255, 115352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, L.; Rullo, M.; Catto, M.; de Candia, M.; Carrieri, A.; Cellamare, S.; Altomare, C.D. Targeting Monoamine Oxidases with Multipotent Ligands: An Emerging Strategy in the Search of New Drugs against Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 41, 4568–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finberg, J.P.M.; Gillman, K. Selective Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase Type B and the “Cheese Effect”. In International Review of Neurobiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 100, pp. 169–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ekström, F.; Gottinger, A.; Forsgren, N.; Catto, M.; Iacovino, L.G.; Pisani, L.; Binda, C. Dual Reversible Coumarin Inhibitors Mutually Bound to Monoamine Oxidase B and Acetylcholinesterase Crystal Structures. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2024-4: Maestro; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- Schrödinger Release 2024-4: Glide; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- Schrödinger Release 2024-4: Prime; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- Schrödinger Release 2024-4: Force Fields; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- Schrödinger Release 2024-4: LigPrep; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
| Compound | Ar | IC50 (μM) or % Inhibition at 10 μM a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hAChE b | hBChE c | hMAO A d | hMAO B d | ||
| 2a | 4-MePh | 5.5 ± 0.7 | 27 ± 12% | 47 ± 3% | 40 ± 8% |
| 2b | 4-MeOPh | 6.1 ± 0.3 | 29 ± 11% | 45 ± 1% | 39 ± 6% |
| 2c | 4-ClPh | 4.0 ± 0.7 | n.i. e | 16 ± 14% | 11 ± 6% |
| 2d | 2-Thienyl | 4.0 ± 0.5 | n.i. e | 42 ± 4% | 17 ± 10% |
| 3a | 4-MePh | 4.4 ± 0.5 | n.i. e | n.i. e | 32 ± 0% |
| 3b | 4-MeOPh | 5.7 ± 1.0 | 19 ± 9% | n.i. e | 43 ± 1% |
| 3d | 2-Thienyl | 4.1 ± 0.7 | 21 ± 3% | n.i. e | 0.561 ± 0.085 |
| donepezil | 0.017 ± 0.004 | ||||
| tacrine | 0.032 ± 0.011 | ||||
| clorgyline | 0.020 ± 0.003 | ||||
| safinamide | 0.037 ± 0.001 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rullo, M.; Benzi, A.; Bianchi, L.; Maccagno, M.; Marcantoni Taddei, G.; Miniero, D.V.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Lentini, G.; Pisani, L.; Petrillo, G.; et al. In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Furo[3,2-c]coumarins as Cholinesterases and Monoamine Oxidases Inhibitors. Molecules 2025, 30, 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081830
Rullo M, Benzi A, Bianchi L, Maccagno M, Marcantoni Taddei G, Miniero DV, Mangiatordi GF, Lentini G, Pisani L, Petrillo G, et al. In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Furo[3,2-c]coumarins as Cholinesterases and Monoamine Oxidases Inhibitors. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081830
Chicago/Turabian StyleRullo, Mariagrazia, Alice Benzi, Lara Bianchi, Massimo Maccagno, Guglielmo Marcantoni Taddei, Daniela Valeria Miniero, Giuseppe Felice Mangiatordi, Giovanni Lentini, Leonardo Pisani, Giovanni Petrillo, and et al. 2025. "In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Furo[3,2-c]coumarins as Cholinesterases and Monoamine Oxidases Inhibitors" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081830
APA StyleRullo, M., Benzi, A., Bianchi, L., Maccagno, M., Marcantoni Taddei, G., Miniero, D. V., Mangiatordi, G. F., Lentini, G., Pisani, L., Petrillo, G., & Tavani, C. (2025). In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Furo[3,2-c]coumarins as Cholinesterases and Monoamine Oxidases Inhibitors. Molecules, 30(8), 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081830











