Long Non-Coding RNAs as Master Regulators in Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Representative Classes of LncRNAs

3. Global Mechanisms of LncRNA Functions

4. Identification of LncRNAs as Major Regulators in Human Disease
5. LncRNAs in Cardiovascular Development
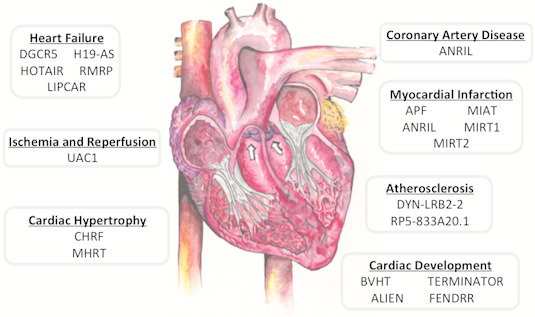
| Disease | LncRNA Name | Effect * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atherosclerosis | CDKNA/B | ↑ | [38] |
| DYN-LRB2-2 | ↑ | [39] | |
| RP5-833A20.1 | ↑ | [40] | |
| Cardiac Hypertrophy | CHRF | ↑ | [10] |
| MHRT | ↑ | [41] | |
| Heart Failure | LIPCAR | ↓/↑ | [42] |
| Coronary Artery Disease | ANRIL | Unknown | [43] |
| Ischemia and Reperfusion | UAC1 | ↓ | [44] |
| Cardiac Development | BVHT | ↑ | [9] |
| TERMINATOR | ↓ | [45] | |
| ALIEN | Unknown | [45] | |
| AK143260 | Unknown | [45] | |
| FENDRR | Unknown | [46] | |
| Myocardial Infarction | MIAT | Unknown | [47] |
| APF | ↑ | [48] | |
| ANRIL | Unknown | [43] | |
| MIRT1 | ↑ | [49] | |
| MIRT2 | ↑ | [49] |

6. LncRNAs and Cardiovascular Disease
6.1. Roles of LncRNAs in Myocardial Infarction
6.2. Roles of LncRNAs in Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury
6.3. Roles of LncRNAs in Cardiac Hypertrophy and Heart Failure
6.4. Roles of LncRNAs in Atherosclerosis
6.5. Abnormal Regulation of LncRNAs in Veins
7. Circulating LncRNAs as Novel Biomarkers for Heart Disease
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ezkurdia, I.; Juan, D.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Frankish, A.; Diekhans, M.; Harrow, J.; Vazquez, J.; Valencia, A.; Tress, M.L. The shrinking human protein coding complement: Are there now fewer than 20,000 genes? Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1312.7111 (accessed on 1 July 2015).
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, W.; Huang, L.; Feng, D.; Cai, B. Long non-coding RNAs, a new important regulator of cardiovascular physiology and pathology. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 188, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoki, H.; Sato, T.; Endo, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Sugatani, J.; Ikari, A. Quercetin decreases claudin-2 expression mediated by up-regulation of microRNA miR-16 in Lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4578–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, N.; Dasaradhi, P.V.N.; Mohmmed, A.; Malhotra, P.; Bhatnagar, R.K.; Mukherjee, S.K. RNA interference: Biology, mechanism, and applications. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 657–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.S.; Ponting, C.P. Identification and function of long non-coding RNAs. Essays Biochem. 2013, 54, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaikkonen, M.U.; Lam, M.T.Y.; Glass, C.K. Non-coding RNAs as regulators of gene expression and epigenetics. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 90, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klattenhoff, C.A.; Scheuermann, J.C.; Surface, L.E.; Bradley, R.K.; Fields, P.A.; Steinhauser, M.L.; Ding, H.; Butty, V.L.; Torrey, L.; Haas, S. Braveheart, a long noncoding RNA required for cardiovascular lineage commitment. Cell 2013, 152, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Liu, F.; Zhou, L.Y.; Long, B.; Yuan, S.M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, P.F. The long noncoding RNA CHRF regulates cardiac hypertrophy by targeting miR-489. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, V.A.; Perera, R.J.; Khalil, A.M. Emerging functional and mechanistic paradigms of mammalian long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 6391–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Bajic, V.B.; Zhang, Z. On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birney, E.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J.A.; Dutta, A.; Guigó, R.; Gingeras, T.; Margulies, E.H.; Weng, Z.; Snyder, M.; Dermitzakis, E.T.; Thurman, R.E.; et al. Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature 2007, 447, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prensner, J.R.; Iyer, M.K.; Balbin, O.A.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Cao, Q.; Brenner, J.C.; Laxman, B.; Asangani, I.A.; Grasso, C.S.; Kominsky, H.D.; et al. Transcriptome sequencing across a prostate cancer cohort identifies PCAT-1, an unannotated lincRNA implicated in disease progression. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Kapranov, P.; Drenkow, J.; Dike, S.; Brubaker, S.; Patel, S.; Long, J.; Stern, D.; Tammana, H.; Helt, G. Transcriptional maps of 10 human chromosomes at 5-nucleotide resolution. Science 2005, 308, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Garber, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Donaghey, J.; Robinson, J.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Koziol, M.J.; Gnirke, A.; Nusbaum, C. Ab initio reconstruction of cell type-specific transcriptomes in mouse reveals the conserved multi-exonic structure of lincRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Rice, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhong, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Klibanski, A. Maternally expressed gene 3 (MEG3) noncoding ribonucleic acid: Isoform structure, expression, and functions. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Sunkin, S.M.; Mehler, M.F.; Mattick, J.S. Specific expression of long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carninci, P.; Kasukawa, T.; Katayama, S.; Gough, J.; Frith, M.C.; Maeda, N.; Oyama, R.; Ravasi, T.; Lenhard, B.; Wells, C. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science 2005, 309, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leygue, E. Steroid receptor RNA activator (SRA1): Unusual bifaceted gene products with suspected relevance to breast cancer. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2007, 5, e006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campalans, A.; Kondorosi, A.; Crespi, M. Enod40, a short open reading frame-containing mRNA, induces cytoplasmic localization of a nuclear RNA binding protein in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Sun, S.; Lee, J.T. The long noncoding RNA, Jpx, is a molecular switch for X chromosome inactivation. Cell 2010, 143, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penny, G.D.; Kay, G.F.; Sheardown, S.A.; Rastan, S.; Brockdorff, N. Requirement for Xist in X chromosome inactivation. Nature 1996, 379, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, T.; Wang, Y.; Lin, M.F.; Koegel, A.K.; Kotake, Y.; Grant, G.D.; Horlings, H.M.; Shah, N.; Umbricht, C.; Wang, P. Extensive and coordinated transcription of noncoding RNAs within cell-cycle promoters. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonasio, R.; Tu, S.; Reinberg, D. Molecular signals of epigenetic states. Science 2010, 330, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitale, R.C.; Tsai, M.C.; Chang, H.Y. RNA templating the epigenome: Long noncoding RNAs as molecular scaffolds. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, K. Physiological assembly and activity of human telomerase complexes. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2008, 129, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.L.; Greider, C.W. Template boundary definition in mammalian telomerase. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2747–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappulla, D.C.; Cech, T.R. Yeast telomerase RNA: A flexible scaffold for protein subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10024–10029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Su, H.; Liu, C.; Skogerbø, G.; He, H.; He, D.; Zhu, X.; Liu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, R. MicroRNA-encoding long non-coding RNAs. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Long, B.; Zhou, L.Y.; Liu, F.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Fan, Y.Y.; Li, P.F. CARL lncRNA inhibits anoxia-induced mitochondrial fission and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by impairing miR-539-dependent PHB2 downregulation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirasawa, S.; Harada, H.; Furugaki, K.; Akamizu, T.; Ishikawa, N.; Ito, K.; Ito, K.; Tamai, H.; Kuma, K.; Kubota, S. SNPs in the promoter of a B cell-specific antisense transcript, SAS-ZFAT, determine susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 2221–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharap, A.; Pokrzywa, C.; Vemuganti, R. Increased binding of stroke-induced long non-coding RNAs to the transcriptional corepressors Sin3A and coREST. ASN Neuro 2013, 5, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonrock, N.; Harvey, R.P.; Mattick, J.S. Long noncoding RNAs in cardiac development and pathophysiology. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, R.; Akhade, V.S.; Pal, D.; Rao, S.M. Long noncoding RNAs in development and cancer: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Mol. Cell. Ther. 2015, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, A.; Rinn, J.L.; Schier, A.F. Non-coding RNAs as regulators of embryogenesis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, J.S.; Gaughwin, P.M.; Lim, B.; Robson, P.; Lipovich, L. Conserved long noncoding RNAs transcriptionally regulated by Oct4 and Nanog modulate pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. RNA 2010, 16, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congrains, A.; Kamide, K.; Oguro, R.; Yasuda, O.; Miyata, K.; Yamamoto, E.; Kawai, T.; Kusunoki, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Takeya, Y. Genetic variants at the 9p21 locus contribute to atherosclerosis through modulation of ANRIL and CDKN2A/B. Atherosclerosis 2012, 220, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.W.; Yang, J.Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.P.; Hu, Y.R.; Zhao, J.Y.; Li, S.F.; Qiu, Y.R.; Lu, J.B.; Wang, Y.C. A lincRNA-DYNLRB2-2/GPR119/GLP-1R/ABCA1-dependent signal transduction pathway is essential for the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.W.; Zhao, J.Y.; Li, S.F.; Huang, J.L.; Qiu, Y.R.; Ma, X.; Wu, S.G.; Chen, Z.P.; Hu, Y.R.; Yang, J.Y. RP5-833A20.1/miR-382-5p/NFIA-dependent signal transduction pathway contributes to the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis and inflammatory reaction. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Li, W.; Lin, C.H.; Yang, J.; Shang, C.; Nurnberg, S.T.; Jin, K.K.; Xu, W.; Lin, C.Y.; Lin, C.J.; et al. A long noncoding RNA protects the heart from pathological hypertrophy. Nature 2014, 514, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarswamy, R.; Bauters, C.; Volkmann, I.; Maury, F.; Fetisch, J.; Holzmann, A.; Lemesle, G.; de Groote, P.; Pinet, F.; Thum, T. Circulating long noncoding RNA, LIPCAR, predicts survival in patients with heart failure. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadbent, H.M.; Peden, J.F.; Lorkowski, S.; Goel, A.; Ongen, H.; Green, F.; Clarke, R.; Collins, R.; Franzosi, M.G.; Tognoni, G. Susceptibility to coronary artery disease and diabetes is encoded by distinct, tightly linked SNPs in the ANRIL locus on chromosome 9p. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Song, G.; Zhou, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, M.; Nie, J.; Lu, S.; Wu, X.; Cao, Y.; Tao, L. Compared analysis of LncRNA expression profiling in pdk1 gene knockout mice at two time points. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurian, L.; Aguirre, A.; Sancho-Martinez, I.; Benner, C.; Hishida, T.; Nguyen, T.B.; Reddy, P.; Nivet, E.; Krause, M.N.; Nelles, D.A. Identification of novel long noncoding RNAs underlying vertebrate cardiovascular development. Circulation 2015, 131, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grote, P.; Wittler, L.; Hendrix, D.; Koch, F.; Währisch, S.; Beisaw, A.; Macura, K.; Bläss, G.; Kellis, M.; Werber, M. The tissue-specific lncRNA Fendrr is an essential regulator of heart and body wall development in the mouse. Dev. Cell 2013, 24, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, N.; Ozaki, K.; Sato, H.; Mizuno, H.; Saito, S.; Takahashi, A.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ikegawa, S.; Kamatani, N.; Hori, M. Identification of a novel non-coding RNA, MIAT, that confers risk of myocardial infarction. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 51, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhou, L.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, M.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, W.K.; Xu, S.J.; Fan, L.H.; Zhang, X.J.; et al. APF lncRNA regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting miR-188-3p. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangrando, J.; Zhang, L.; Vausort, M.; Maskali, F.; Marie, P.Y.; Wagner, D.R.; Devaux, Y. Identification of candidate long non-coding RNAs in response to myocardial infarction. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondue, A.; Lapouge, G.; Paulissen, C.; Semeraro, C.; Iacovino, M.; Kyba, M.; Blanpain, C. Mesp1 acts as a master regulator of multipotent cardiovascular progenitor specification. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thum, T.; Condorelli, G. Long noncoding RNAs and microRNAs in cardiovascular pathophysiology. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattick, J.S. Challenging the dogma: The hidden layer of non-protein-coding RNAs in complex organisms. Bioessays 2003, 25, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Arora, P. Long noncoding Mhrt RNA molecular crowbar unravel insights into heart failure treatment. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2015, 8, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sara, J.D.; Eleid, M.F.; Gulati, R.; Holmes, D.R. Sudden cardiac death from the perspective of coronary artery disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemirani, H.; Nayeri-Torshizi, E. Electrocardiographic characteristics of posterior myocardial infarction in comparison to angiographic findings. ARYA Atheroscler. 2015, 11, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Visscher, P.M.; Brown, M.A.; McCarthy, M.I.; Yang, J. Five years of GWAS discovery. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, R.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Kavaslar, N.; Stewart, A.; Roberts, R.; Cox, D.R.; Hinds, D.A.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Folsom, A.R. A common allele on chromosome 9 associated with coronary heart disease. Science 2007, 316, 1488–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuno, K.; Bilguvar, K.; Bijlenga, P.; Low, S.K.; Krischek, B.; Auburger, G.; Simon, M.; Krex, D.; Arlier, Z.; Nayak, N. Genome-wide association study of intracranial aneurysm identifies three new risk loci. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, C.; Ahmed, S.; Morrison, J.; Pernet, D.; Renwick, A.; Maranian, M.; Seal, S.; Ghoussaini, M.; Hines, S.; Healey, C.S. Genome-wide association study identifies five new breast cancer susceptibility loci. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shete, S.; Hosking, F.J.; Robertson, L.B.; Dobbins, S.E.; Sanson, M.; Malmer, B.; Simon, M.; Marie, Y.; Boisselier, B.; Delattre, J.Y. Genome-wide association study identifies five susceptibility loci for glioma. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacey, S.N.; Sulem, P.; Masson, G.; Gudjonsson, S.A.; Thorleifsson, G.; Jakobsdottir, M.; Sigurdsson, A.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Sigurgeirsson, B.; Benediktsdottir, K.R. New common variants affecting susceptibility to basal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, A.S.; Mozaffarian, D.; Roger, V.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Berry, J.D.; Borden, W.B.; Bravata, D.M.; Dai, S.; Ford, E.S.; Fox, C.S. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2013 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2013, 127, e6–e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groyer, E.; Caligiuri, G.; Laschet-Khallou, J.; Nicoletti, A. Immunological aspects of atherosclerosis. Presse Med. 2006, 35, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.J.; Tabas, I. Macrophages in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell 2011, 145, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, B.; Rotllan, N.; Fernández-Hernando, C. Noncoding RNAs and atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2014, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, K.S.; Le, N.T.; Cushman, H.J.; Giancursio, C.J.; Chang, E.; Woo, C.H.; Sullivan, M.A.; Taunton, J.; Yeh, E.T.H.; Fujiwara, K. Disturbed flow-activated p90RSK kinase accelerates atherosclerosis by inhibiting SENP2 function. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deneen, B.; Ho, R.; Lukaszewicz, A.; Hochstim, C.J.; Gronostajski, R.M.; Anderson, D.J. The transcription factor NFIA controls the onset of gliogenesis in the developing spinal cord. Neuron 2006, 52, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronostajski, R.M. Analysis of nuclear factor I binding to DNA using degenerate oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986, 14, 9117–9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waki, H.; Nakamura, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Wakabayashi, K.I.; Yu, J.; Hirose-Yotsuya, L.; Take, K.; Sun, W.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M. Global mapping of cell type-specific open chromatin by FAIRE-seq reveals the regulatory role of the NFI family in adipocyte differentiation. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Lammers, B.; Zhao, Y.; Meurs, I.; van Berkel, T.J.; van Eck, M. ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1, HDL metabolism, cholesterol efflux, and inflammation: Important targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callam, M.J. Epidemiology of varicose veins. Br. J. Surg. 1994, 81, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Jiang, X.Y.; Ge, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, G.J.; Xu, L.; Xie, D.Y.; Yuan, T.Y.; Zhang, D.S.; Zhang, H. Aberrantly expressed lncRNAs in primary varicose great saphenous veins. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, G.; Yang, J.; Fan, X.; Gong, Y.; Xu, G.; Cui, Q.; Geng, B. Transcriptome analysis reveals distinct patterns of long noncoding RNAs in heart and plasma of mice with heart failure. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Archer, K.; Broskova, Z.; Bayoumi, A.S.; Teoh, J.-p.; Davila, A.; Tang, Y.; Su, H.; Kim, I.-m. Long Non-Coding RNAs as Master Regulators in Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 23651-23667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161023651
Archer K, Broskova Z, Bayoumi AS, Teoh J-p, Davila A, Tang Y, Su H, Kim I-m. Long Non-Coding RNAs as Master Regulators in Cardiovascular Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(10):23651-23667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161023651
Chicago/Turabian StyleArcher, Krystal, Zuzana Broskova, Ahmed S. Bayoumi, Jian-peng Teoh, Alec Davila, Yaoliang Tang, Huabo Su, and Il-man Kim. 2015. "Long Non-Coding RNAs as Master Regulators in Cardiovascular Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 10: 23651-23667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161023651
APA StyleArcher, K., Broskova, Z., Bayoumi, A. S., Teoh, J.-p., Davila, A., Tang, Y., Su, H., & Kim, I.-m. (2015). Long Non-Coding RNAs as Master Regulators in Cardiovascular Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(10), 23651-23667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161023651