A Novel Role of Medicago truncatula KNAT3/4/5-like Class 2 KNOX Transcription Factors in Drought Stress Tolerance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
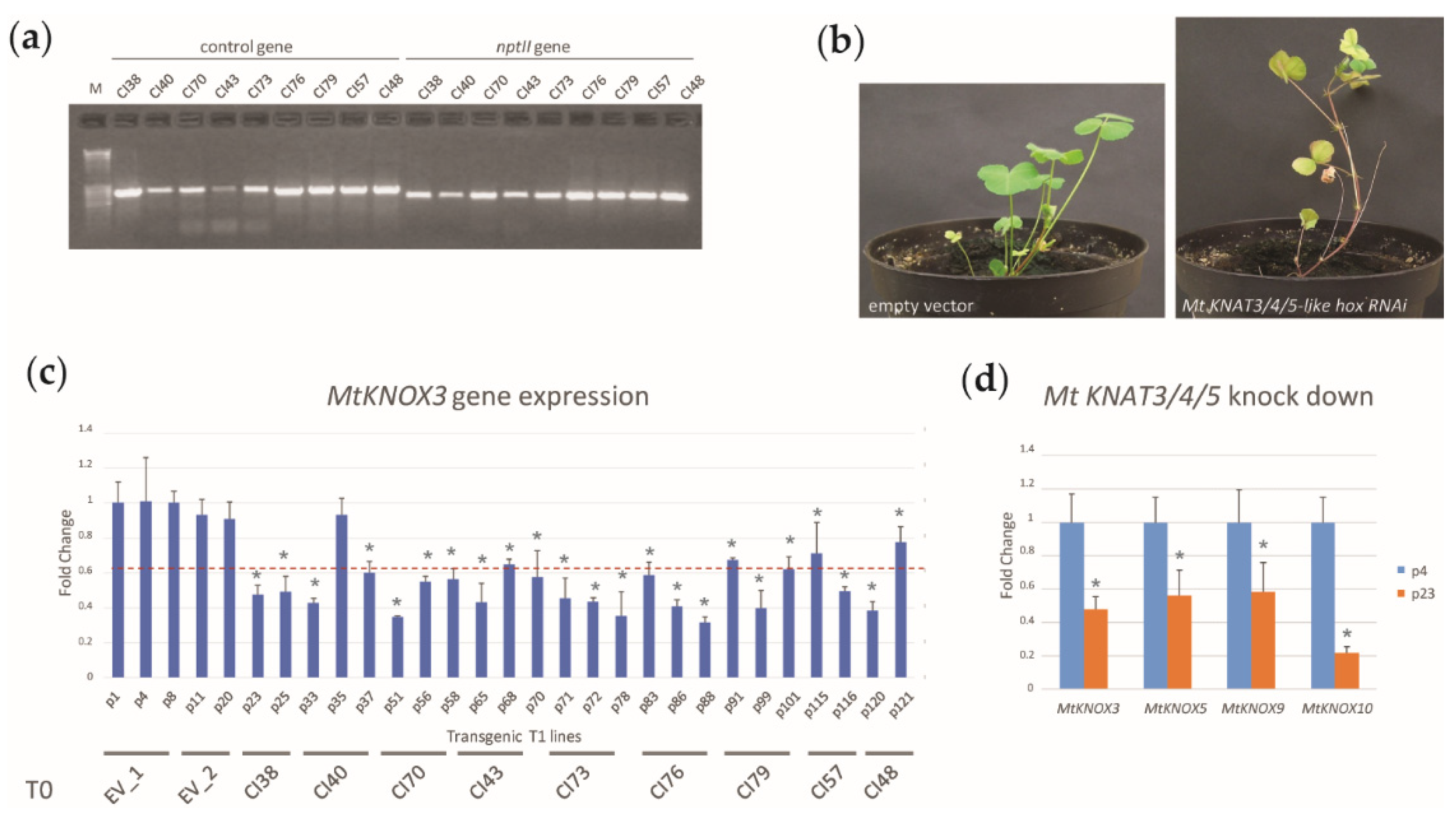
2.1. Generation and Selection of MtKNOX3-like RNAi Transgenic Lines
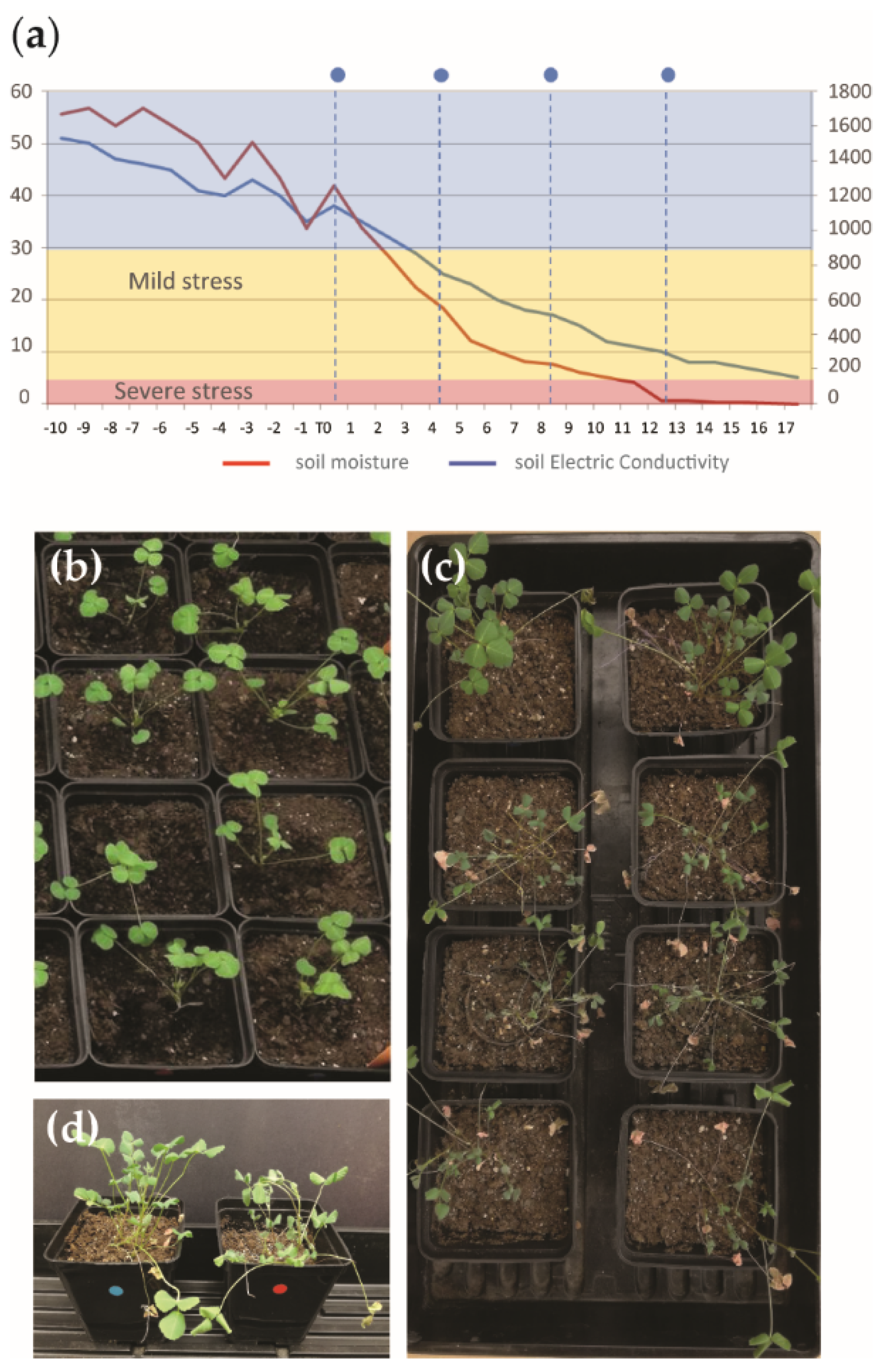
2.2. Physiological Characterization of MtKNAT3/4/5-like RNAi Transgenic Lines
2.3. Silencing of Mt KNAT3/4/5-like Transcription Factors Decreases Tolerance to Drought Stress
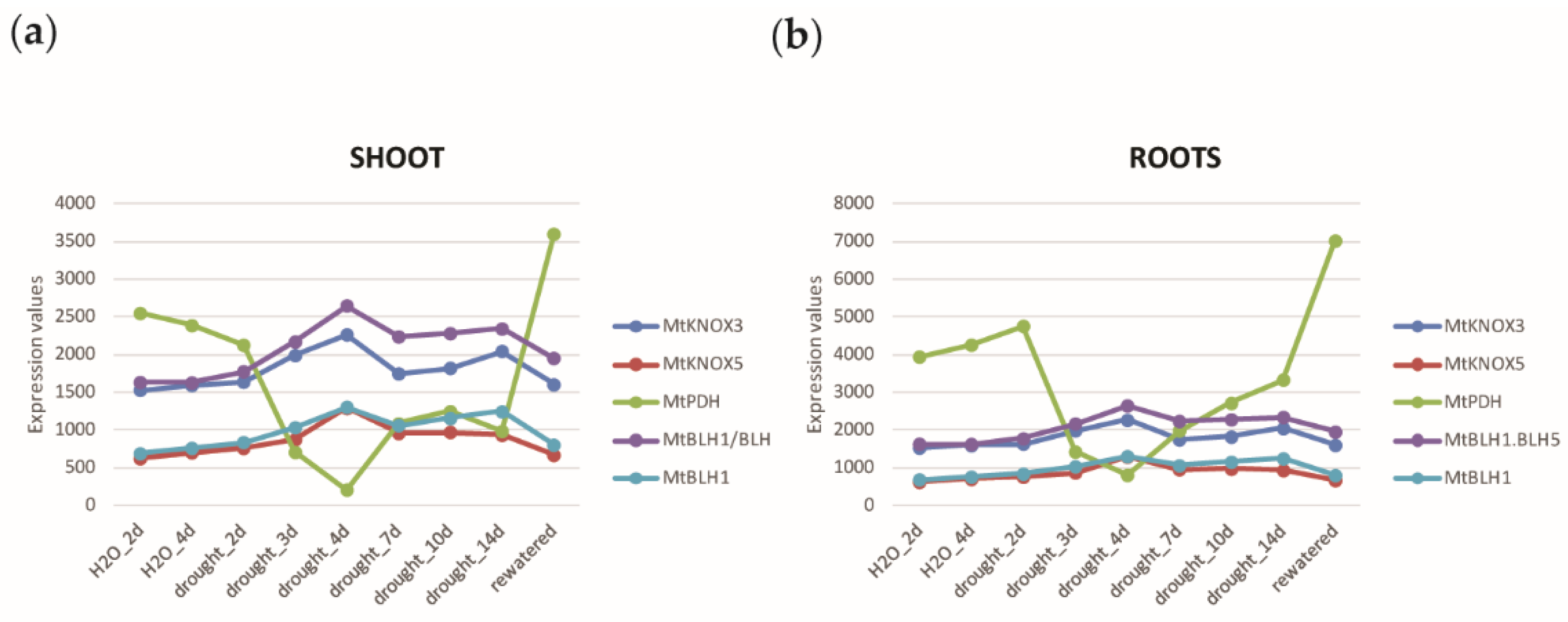
2.4. Meta-Analysis of a M. truncatula Drought Stress Transcriptomic Experiment Identifies MtKNOX3-like Genes as Rapidly Induced during Drought Stress
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis to Validate Clustering and GCN Analysis Predictions
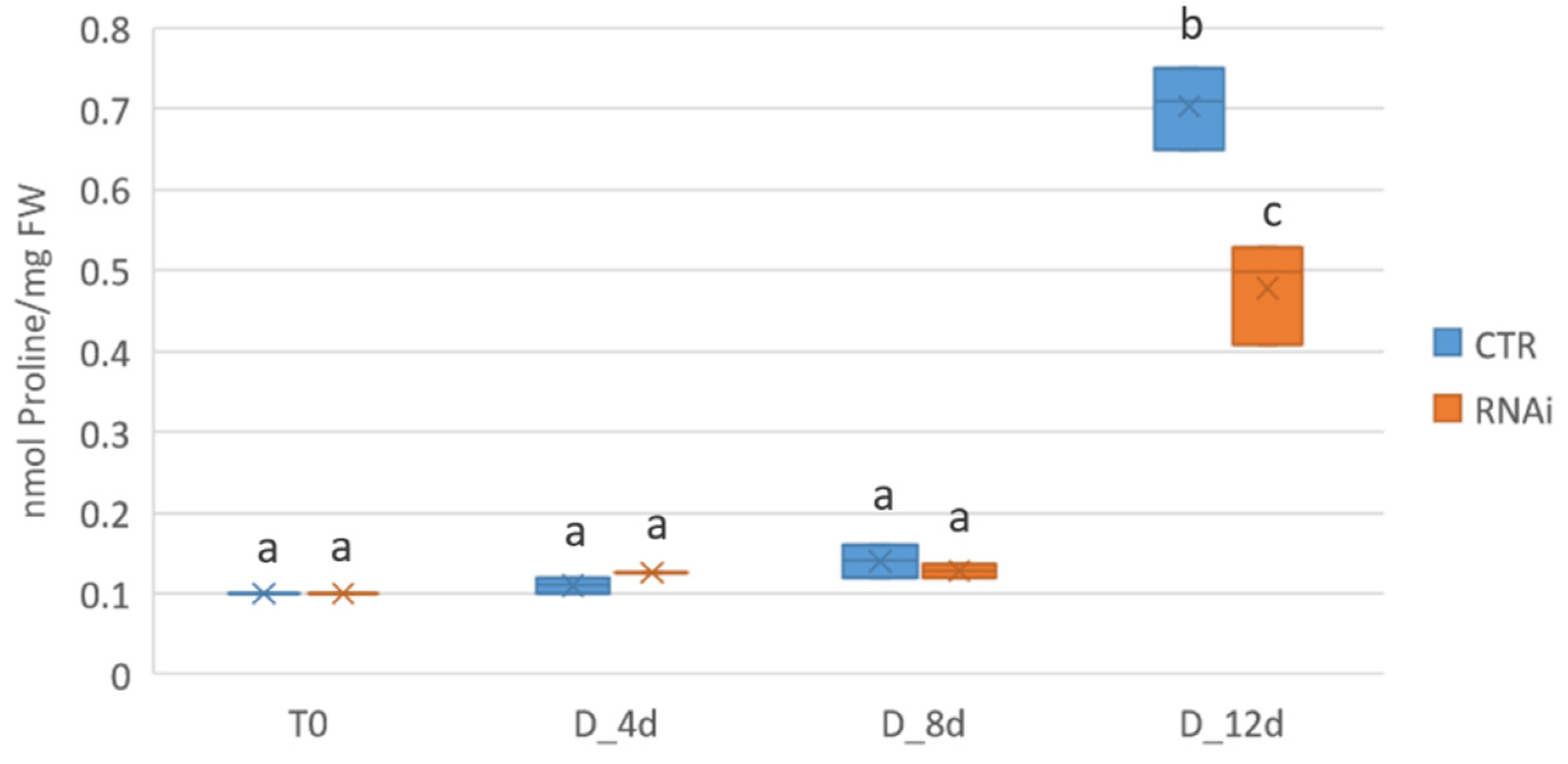
2.6. Mt KNAT3/4/5 like-RNAi Plants Accumulate Less Proline during Drought Stress
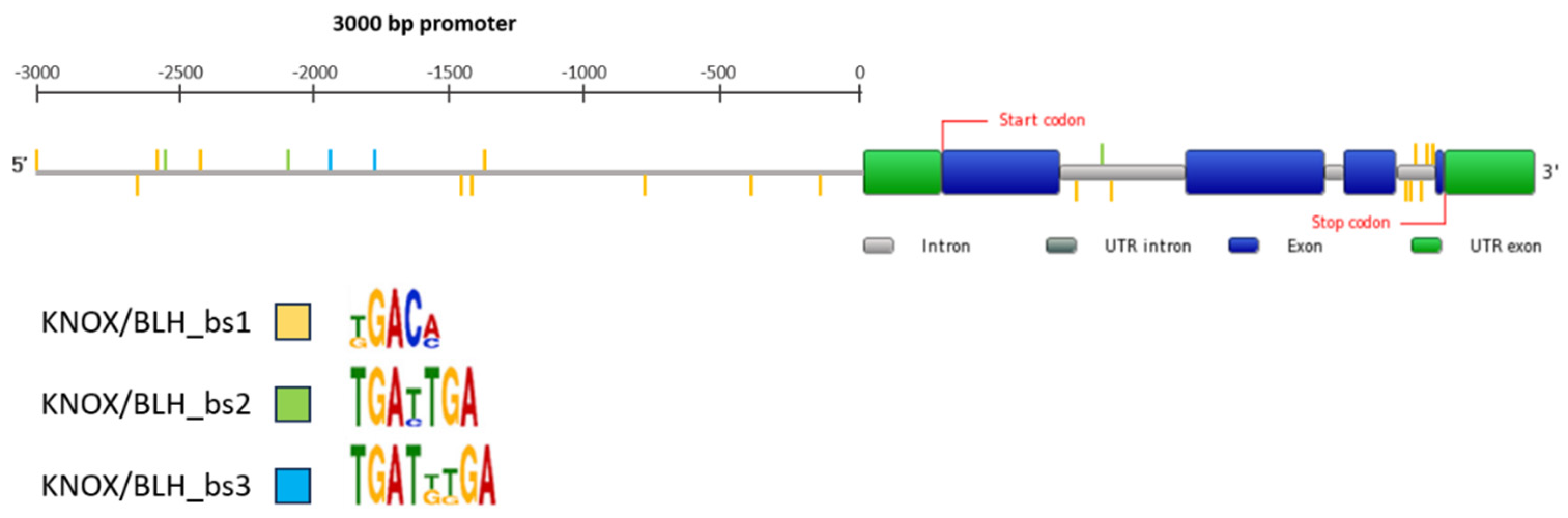
2.7. KNOX/BLH Binding Site Motifs in the MtPDH Regulatory Sequences
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material, Growth Conditions, and Stress Treatment
4.2. Plasmid Construction and Plant Transformation
4.3. Plant Genotyping and Selection of Transgenic Plants
4.4. Physiological and Biochemical Measurements
4.5. Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis of Gene Expression
4.6. Gene Expression Meta-Analyses and Microarray Pathway Annotation
4.7. Correlation Analysis and Gene Co-Expression Networks
4.8. KNOX/BLH Binding Sites Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, A.; Rico-Medina, A.; Caño-Delgado, A.I. The Physiology of Plant Responses to Drought. Science 2020, 368, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.-K. Thriving under Stress: How Plants Balance Growth and the Stress Response. Dev. Cell 2020, 55, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, K.; Muneer, S. Drought Stress-Induced Physiological Mechanisms, Signaling Pathways and Molecular Response of Chloroplasts in Common Vegetable Crops. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 41, 669–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, T.B.; Ribas, A.F.; de Souza, S.G.H.; Budzinski, I.G.F.; Domingues, D.S. Physiological Responses to Drought, Salinity, and Heat Stress in Plants: A Review. Stresses 2022, 2, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fàbregas, N.; Fernie, A.R. The Metabolic Response to Drought. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blum, A. Osmotic Adjustment Is a Prime Drought Stress Adaptive Engine in Support of Plant Production: Osmotic Adjustment and Plant Production. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi Alagoz, S.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; Ghorbanpour, M. Proline and Soluble Carbohydrates Biosynthesis and Their Roles in Plants under Abiotic Stresses. In Plant Stress Mitigators; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 169–185. ISBN 978-0-323-89871-3. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, S.; Hayat, Q.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wani, A.S.; Pichtel, J.; Ahmad, A. Role of Proline under Changing Environments: A Review. Plant. Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claeys, H.; Inzé, D. The Agony of Choice: How Plants Balance Growth and Survival under Water-Limiting Conditions. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waadt, R.; Seller, C.A.; Hsu, P.-K.; Takahashi, Y.; Munemasa, S.; Schroeder, J.I. Plant Hormone Regulation of Abiotic Stress Responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2022, 23, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhu, J.-K. Abiotic Stress Responses in Plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Wani, S.H.; Singh, B.; Bohra, A.; Dar, Z.A.; Lone, A.A.; Pareek, A.; Singla-Pareek, S.L. Transcription Factors and Plants Response to Drought Stress: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimotho, B.; Xu, Z. Transcription Factors Associated with Abiotic and Biotic Stress Tolerance and Their Potential for Crops Improvement. Genes 2019, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldoni, E.; Frugis, G.; Martinelli, F.; Benny, J.; Paffetti, D.; Buti, M. A Comparative Transcriptomic Meta-Analysis Revealed Conserved Key Genes and Regulatory Networks Involved in Drought Tolerance in Cereal Crops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, M.; Thakur, T.; Chirom, O.; Mandlik, R.; Deshmukh, R.; Salvi, P. Transcription Factors as Key Molecular Target to Strengthen the Drought Stress Tolerance in Plants. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 847–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirona, R.; Frugis, G.; Locatelli, F.; Mattana, M.; Genga, A.; Baldoni, E. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Gene Regulatory Networks Involved in Leaf and Root Response to Osmotic Stress in Tomato. Front. Plant. Sci. 2023, 14, 1155797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Ghorai, M.; Anand, U.; Samanta, D.; Kant, N.; Mishra, T.; Rahman, M.H.; Jha, N.K.; Jha, S.K.; Lal, M.K.; et al. Cytokinin and Abiotic Stress Tolerance -What Has Been Accomplished and the Way Forward? Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 943025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, N.N.; Chuong, N.N.; Tu, N.H.C.; Kisiala, A.; Hoang, X.L.T.; Thao, N.P. Role and Regulation of Cytokinins in Plant Response to Drought Stress. Plants 2020, 9, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hake, S.; Smith, H.M.S.; Holtan, H.; Magnani, E.; Mele, G.; Ramirez, J. The Role of Knox Genes in Plant Development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 125–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, A.; Tsiantis, M. KNOX Genes: Versatile Regulators of Plant Development and Diversity. Development 2010, 137, 3153–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Giacomo, E.; Iannelli, M.A.; Frugis, G. TALE and Shape: How to Make a Leaf Different. Plants 2013, 2, 317–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Paolis, A.D.; Frugis, G.; Giannino, D.; Iannelli, M.A.; Mele, G.; Rugini, E.; Silvestri, C.; Sparvoli, F.; Testone, G.; Mauro, M.L.; et al. Plant Cellular and Molecular Biotechnology: Following Mariotti’s Steps. Plants 2019, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, K.; Brocchieri, L.; Burglin, T.R. A Comprehensive Classification and Evolutionary Analysis of Plant Homeobox Genes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 2775–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furumizu, C.; Alvarez, J.P.; Sakakibara, K.; Bowman, J.L. Antagonistic Roles for KNOX1 and KNOX2 Genes in Patterning the Land Plant Body Plan Following an Ancient Gene Duplication. PLoS Genet 2015, 11, e1004980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Cho, Y.; Ryu, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, T.-H.; Hwang, I. BLH1 and KNAT3 Modulate ABA Responses during Germination and Early Seedling Development in Arabidopsis. Plant. J. 2013, 75, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Wu, W.; Abrams, S.R.; Cutler, A.J. The Relationship of Drought-Related Gene Expression in Arabidopsis Thaliana to Hormonal and Environmental Factors. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 2991–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Giacomo, E.; Sestili, F.; Iannelli, M.A.; Testone, G.; Mariotti, D.; Frugis, G. Characterization of KNOX Genes in Medicago Truncatula. Plant. Mol. Biol. 2008, 67, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giacomo, E.; Laffont, C.; Sciarra, F.; Iannelli, M.A.; Frugier, F.; Frugis, G. KNAT3/4/5-like Class 2 KNOX Transcription Factors Are Involved in Medicago Truncatula Symbiotic Nodule Organ Development. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 822–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Cruz DE Carvalho, M.H.; Torres-Jerez, I.; Kang, Y.; Allen, S.N.; Huhman, D.V.; Tang, Y.; Murray, J.; Sumner, L.W.; Udvardi, M.K. Global Reprogramming of Transcription and Metabolism in Medicago Truncatula during Progressive Drought and after Rewatering. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 2553–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nadeem, M.; Li, J.; Yahya, M.; Sher, A.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Qiu, L. Research Progress and Perspective on Drought Stress in Legumes: A Review. IJMS 2019, 20, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Gene Networks Involved in Drought Stress Response and Tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 58, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, T.; Zhu, L.; Arfan, M.; Zou, L.; Lin, H. Medicago Truncatula Genotypes Jemalong A17 and R108 Show Contrasting Variations under Drought Stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 109, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.H.; Ratet, P.; Kondorosi, E.; Durand, P.; Kamaté, K.; Bauer, P.; Kondorosi, A. Rapid and Efficient Transformation of Diploid Medicago Truncatula and Medicago Sativa Ssp. Falcata Lines Improved in Somatic Embryogenesis. Plant. Cell Rep. 1998, 17, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluch-Lubawa, E.; Stolarska, E.; Sobieszczuk-Nowicka, E. Dark-Induced Barley Leaf Senescence—A Crop System for Studying Senescence and Autophagy Mechanisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 635619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Ali, N.; Akmal, M.; Alotaibi, M.; Refay, Y.; Dindaroglu, T.; Abdul-Wajid, H.H.; Battaglia, M.L. Drought Stress Impacts on Plants and Different Approaches to Alleviate Its Adverse Effects. Plants 2021, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Tian, F.; Yang, D.-C.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Kong, L.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. PlantTFDB 4.0: Toward a Central Hub for Transcription Factors and Regulatory Interactions in Plants. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1040–D1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Testone, G.; Baldoni, E.; Iannelli, M.A.; Nicolodi, C.; Di Giacomo, E.; Pietrini, F.; Mele, G.; Giannino, D.; Frugis, G. Transcription Factor Networks in Leaves of Cichorium Endivia: New Insights into the Relationship between Photosynthesis and Leaf Development. Plants 2019, 8, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.; Mishra, B.; Athar, M.; Mukhtar, S. Inference of Gene Regulatory Network from Single-Cell Transcriptomic Data Using PySCENIC. In Modeling Transcriptional Regulation; Mukhtar, S., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 2328, pp. 171–182. ISBN 978-1-07-161533-1. [Google Scholar]
- AbuQamar, S.F.; El-Tarabily, K.A.; Sham, A. Co-Expression Networks in Predicting Transcriptional Gene Regulation. In Modeling Transcriptional Regulation; Mukhtar, S., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 2328, pp. 1–11. ISBN 978-1-07-161533-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zainal-Abidin, R.-A.; Harun, S.; Vengatharajuloo, V.; Tamizi, A.-A.; Samsulrizal, N.H. Gene Co-Expression Network Tools and Databases for Crop Improvement. Plants 2022, 11, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; Huang, J. RiceTFtarget: A Rice Transcription Factor-Target Prediction Server Based on Co-Expression and Machine Learning. Plant Physiol. 2023, kiad332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome. Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.X.; Thomas, C.E.; Brunak, S. Network Biology Concepts in Complex Disease Comorbidities. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencivenga, S.; Serrano-Mislata, A.; Bush, M.; Fox, S.; Sablowski, R. Control of Oriented Tissue Growth through Repression of Organ Boundary Genes Promotes Stem Morphogenesis. Dev. Cell 2016, 39, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Bel, M.; Silvestri, F.; Weitz, E.M.; Kreft, L.; Botzki, A.; Coppens, F.; Vandepoele, K. PLAZA 5.0: Extending the Scope and Power of Comparative and Functional Genomics in Plants. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1468–D1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Fu, D. The Roles of BLH Transcription Factors in Plant Development and Environmental Response. IJMS 2022, 23, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, I.S.; Marcotte, E.M.; Roshan, U. Diametrical Clustering for Identifying Anti-Correlated Gene Clusters. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarez, M.E.; Savouré, A.; Szabados, L. Proline Metabolism as Regulatory Hub. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerabagu, M.; Kirchler, T.; Elgass, K.; Stadelhofer, B.; Stahl, M.; Harter, K.; Mira-Rodado, V.; Chaban, C. The Interaction of the Arabidopsis Response Regulator ARR18 with BZIP63 Mediates the Regulation of Proline Dehydrogenase Expression. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1560–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hosseinifard, M.; Stefaniak, S.; Ghorbani Javid, M.; Soltani, E.; Wojtyla, Ł.; Garnczarska, M. Contribution of Exogenous Proline to Abiotic Stresses Tolerance in Plants: A Review. IJMS 2022, 23, 5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, M.; Divyanshu, K.; Kumar, S.; Swapnil, P.; Zehra, A.; Shukla, V.; Yadav, M.; Upadhyay, R.S. Regulation of L-Proline Biosynthesis, Signal Transduction, Transport, Accumulation and Its Vital Role in Plants during Variable Environmental Conditions. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hood, E.E.; Helmer, G.L.; Fraley, R.T.; Chilton, M.D. The Hypervirulence of Agrobacterium Tumefaciens A281 Is Encoded in a Region of PTiBo542 Outside of T-DNA. J. Bacteriol. 1986, 168, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Hsu, C.-C.; Du, Y.; Sang, T.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Satheesh, V.; et al. A RAF-SnRK2 Kinase Cascade Mediates Early Osmotic Stress Signaling in Higher Plants. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasajima, I. Difference in Oxidative Stress Tolerance between Rice Cultivars Estimated with Chlorophyll Fluorescence Analysis. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.R.; Kim, C.S.; Park, T.; Choi, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-H. Optimization of the Ninhydrin Reaction and Development of a Multiwell Plate-Based High-Throughput Proline Detection Assay. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 556, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrere, S.; Verdier, J.; Gamas, P. MtExpress, a Comprehensive and Curated RNAseq-Based Gene Expression Atlas for the Model Legume Medicago Truncatula. Plant Cell Physiol. 2021, 62, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedito, V.A.; Torres-Jerez, I.; Murray, J.D.; Andriankaja, A.; Allen, S.; Kakar, K.; Wandrey, M.; Verdier, J.; Zuber, H.; Ott, T.; et al. A Gene Expression Atlas of the Model Legume Medicago Truncatula. Plant J. 2008, 55, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodstein, D.M.; Shu, S.; Howson, R.; Neupane, R.; Hayes, R.D.; Fazo, J.; Mitros, T.; Dirks, W.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; et al. Phytozome: A Comparative Platform for Green Plant Genomics. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1178–D1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.T.; Contreras-Moreira, B.; Castro-Mondragon, J.A.; Santana-Garcia, W.; Ossio, R.; Robles-Espinoza, C.D.; Bahin, M.; Collombet, S.; Vincens, P.; Thieffry, D.; et al. RSAT 2018: Regulatory Sequence Analysis Tools 20th Anniversary. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2018, 46, W209–W214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iannelli, M.A.; Nicolodi, C.; Coraggio, I.; Fabriani, M.; Baldoni, E.; Frugis, G. A Novel Role of Medicago truncatula KNAT3/4/5-like Class 2 KNOX Transcription Factors in Drought Stress Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612668
Iannelli MA, Nicolodi C, Coraggio I, Fabriani M, Baldoni E, Frugis G. A Novel Role of Medicago truncatula KNAT3/4/5-like Class 2 KNOX Transcription Factors in Drought Stress Tolerance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(16):12668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612668
Chicago/Turabian StyleIannelli, Maria Adelaide, Chiara Nicolodi, Immacolata Coraggio, Marco Fabriani, Elena Baldoni, and Giovanna Frugis. 2023. "A Novel Role of Medicago truncatula KNAT3/4/5-like Class 2 KNOX Transcription Factors in Drought Stress Tolerance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 16: 12668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612668
APA StyleIannelli, M. A., Nicolodi, C., Coraggio, I., Fabriani, M., Baldoni, E., & Frugis, G. (2023). A Novel Role of Medicago truncatula KNAT3/4/5-like Class 2 KNOX Transcription Factors in Drought Stress Tolerance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(16), 12668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612668






