Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Diagnosis, Management, and Activity Criteria for SLE
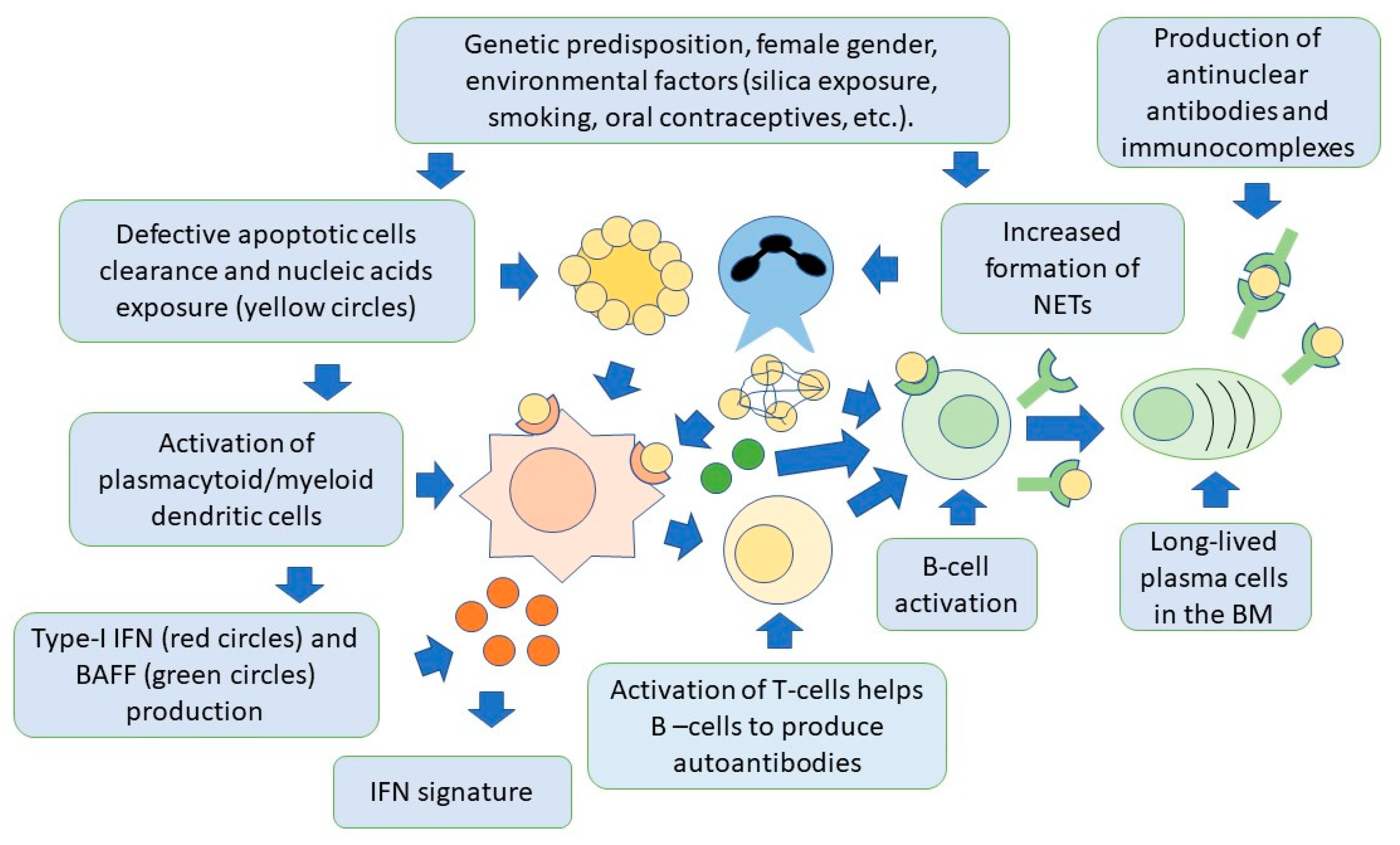
4. SLE Pathogenesis
4.1. The Role of Adaptive Immunity
4.1.1. B Cells and Autoantibodies in SLE
4.1.2. T Cells in SLE Pathogenesis
4.2. The Role of Innate Immunity
4.2.1. Role of Neutrophils in SLE
4.2.2. Role of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells
4.3. The Role of Mitochondria
4.4. The Role of Apoptosis
4.5. The Role of Interferons in SLE
5. SLE Treatment
5.1. The EULAR/ACR Recommendations
5.2. Rituximab
5.3. Belimumab
5.4. Anifrolumab
5.5. Voclosporin
6. Future Therapies
6.1. Targeting of Plasma Cells
6.2. Cell-Based Therapies
6.2.1. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
6.2.2. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells
6.3. Other Promising Therapies
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fava, A.; Petri, M. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Diagnosis and clinical management. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 96, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justiz Vaillant, A.A.; Goyal, A.; Varacallo, M. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Barrat, F.J.; Crow, M.K.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Interferon target-gene expression and epigenomic signatures in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Alunno, A.; Aringer, M.; Bajema, I.; Boletis, J.N.; Cervera, R.; Doria, A.; Gordon, C.; Govoni, M.; et al. 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Tziolos, N.; Bertsias, G.; Boumpas, D.T. Update omicronn the diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, F.; Doherty, M.; Grainge, M.J.; Lanyon, P.; Zhang, W. The worldwide incidence and prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1945–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewold, T.B. Advances in lupus genetics. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2015, 27, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado-Galicia, N.A.; Hernandez-Dono, S.; Ruiz-Gomez, D.; Jakez-Ocampo, J.; Zuniga, J.; Vargas-Alarcon, G.; Acuna, V.; Hernandez, M.T.; Marquez-Garcia, J.E.; Garcia-Lechuga, M.; et al. The role of socioeconomic status in the susceptibility to develop systemic lupus erythematosus in Mexican patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danchenko, N.; Satia, J.A.; Anthony, M.S. Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: A comparison of worldwide disease burden. Lupus 2006, 15, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojan, G.; Petri, M. Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: An update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Piraquive, V.; Nieto-Aristizabal, I.; Canas, C.A.; Tobon, G.J. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: Causes, predictors and interventions. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Choi, S.J.; Ji, J.D.; Song, G.G. Overall and cause-specific mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: An updated meta-analysis. Lupus 2016, 25, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauderon, A.; Roux-Lombard, P.; Spoerl, D. Antinuclear Antibodies With a Homogeneous and Speckled Immunofluorescence Pattern Are Associated With Lack of Cancer While Those With a Nucleolar Pattern With the Presence of Cancer. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Applbaum, E.; Lichtbroun, A. Novel Sjogren’s autoantibodies found in fibromyalgia patients with sicca and/or xerostomia. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, J.M., 3rd; Moore, T.L.; Osborn, T.G.; Nesher, G.; Madson, K.L.; Kinsella, M.B. Autoantibody studies in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 22, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisetsky, D.S.; Lipsky, P.E. New insights into the role of antinuclear antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, M.A.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Buyon, J.; Levy, R.A.; Navarra, S.V.; Cervera, R.; Zhong, Z.J.; Freimuth, W.W.; Bliss; Groups, B.-S. Baseline predictors of systemic lupus erythematosus flares: Data from the combined placebo groups in the phase III belimumab trials. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2143–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoro, N.; Kanayama, Y.; Takeda, T.; Amatsu, K.; Koda, S.; Inoue, Y.; Kim, T.; Okamura, M.; Inoue, T. Clinical significance of U1-RNP immune complexes in mixed connective tissue disease and systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 1987, 7, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, G.V.; Marques, M.; Balbi, V.; Gormezano, N.W.; Kozu, K.; Sakamoto, A.P.; Pereira, R.M.; Terreri, M.T.; Magalhaes, C.S.; Guariento, A.; et al. Anti-RO/SSA and anti-La/SSB antibodies: Association with mild lupus manifestations in 645 childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, G.A.; Canti, V.; Del Rosso, S.; Erra, R.; Moiola, L.; Magnoni, M.; Bozzolo, E.P.; Manfredi, A.A.; Rovere-Querini, P. Diagnostic performance of aPS/PT antibodies in neuropsychiatric lupus and cardiovascular complications of systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity 2020, 53, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unlu, O.; Zuily, S.; Erkan, D. The clinical significance of antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 3, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikdashi, J.; Nived, O. Measuring disease activity in adults with systemic lupus erythematosus: The challenges of administrative burden and responsiveness to patient concerns in clinical research. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladman, D.D.; Ibanez, D.; Urowitz, M.B. Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 288–291. [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg, D.A.; Rahman, A.; Allen, E.; Farewell, V.; Akil, M.; Bruce, I.N.; D’Cruz, D.; Griffiths, B.; Khamashta, M.; Maddison, P.; et al. BILAG 2004. Development and initial validation of an updated version of the British Isles Lupus Assessment Group’s disease activity index for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladman, D.; Ginzler, E.; Goldsmith, C.; Fortin, P.; Liang, M.; Urowitz, M.; Bacon, P.; Bombardieri, S.; Hanly, J.; Hay, E.; et al. The development and initial validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology damage index for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijten, K.M.; Tekstra, J.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Bijl, M. The Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Responder Index (SRI); a new SLE disease activity assessment. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, R. Distinct B cell receptor functions are determined by phosphorylation. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemazee, D. Mechanisms of central tolerance for B cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikherman, J.; Parameswaran, R.; Weiss, A. Endogenous antigen tunes the responsiveness of naive B cells but not T cells. Nature 2012, 489, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, D.L.; Langley, D.B.; Schofield, P.; Hermes, J.R.; Chan, T.D.; Jackson, J.; Bourne, K.; Reed, J.H.; Patterson, K.; Porebski, B.T.; et al. Germinal center antibody mutation trajectories are determined by rapid self/foreign discrimination. Science 2018, 360, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, F.; Schneider, P. Cracking the BAFF code. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.W.; Davidson, A. BAFF inhibition in SLE-Is tolerance restored? Immunol. Rev. 2019, 292, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.R.; Shupe, J.; Nickerson, K.; Kashgarian, M.; Flavell, R.A.; Shlomchik, M.J. Toll-like receptor 7 and TLR9 dictate autoantibody specificity and have opposing inflammatory and regulatory roles in a murine model of lupus. Immunity 2006, 25, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berland, R.; Fernandez, L.; Kari, E.; Han, J.H.; Lomakin, I.; Akira, S.; Wortis, H.H.; Kearney, J.F.; Ucci, A.A.; Imanishi-Kari, T. Toll-like receptor 7-dependent loss of B cell tolerance in pathogenic autoantibody knockin mice. Immunity 2006, 25, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.R.; Kashgarian, M.; Alexopoulou, L.; Flavell, R.A.; Akira, S.; Shlomchik, M.J. Toll-like receptor 9 controls anti-DNA autoantibody production in murine lupus. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lartigue, A.; Courville, P.; Auquit, I.; Francois, A.; Arnoult, C.; Tron, F.; Gilbert, D.; Musette, P. Role of TLR9 in anti-nucleosome and anti-DNA antibody production in lpr mutation-induced murine lupus. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, S.L.; Hodgkin, P.D.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Corcoran, L.M. The generation of antibody-secreting plasma cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinuesa, C.G.; Sanz, I.; Cook, M.C. Dysregulation of germinal centres in autoimmune disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, O.; Shlomchik, M.J. A new role for B cells in systemic autoimmunity: B cells promote spontaneous T cell activation in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, O.T.; Hannum, L.G.; Haberman, A.M.; Madaio, M.P.; Shlomchik, M.J. A novel mouse with B cells but lacking serum antibody reveals an antibody-independent role for B cells in murine lupus. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koffler, D.; Schur, P.H.; Kunkel, H.G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Exp. Med. 1967, 126, 607–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenstein, M.R.; Katz, D.R.; Griffiths, M.H.; Papadaki, L.; Winkler, T.H.; Kalden, J.R.; Isenberg, D.A. Human IgG anti-DNA antibodies deposit in kidneys and induce proteinuria in SCID mice. Kidney Int. 1995, 48, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannik, M.; Merrill, C.E.; Stamps, L.D.; Wener, M.H. Multiple autoantibodies form the glomerular immune deposits in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Izmirly, P.M.; Rivera, T.L.; Buyon, J.P. Neonatal lupus syndromes. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 33, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, D.; Kiran, R.; Wanchu, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Oxidative stress in systemic lupus erythematosus: Relationship to Th1 cytokine and disease activity. Immunol. Lett. 2010, 129, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Morimoto, S.; Kaneko, H.; Nozawa, K.; Tokano, Y.; Takasaki, Y.; Hashimoto, H. Decreased IL-4 producing CD4+ T cells in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus-relation to IL-12R expression. Autoimmunity 2002, 35, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paroli, M.; Caccavale, R.; Fiorillo, M.T.; Spadea, L.; Gumina, S.; Candela, V.; Paroli, M.P. The Double Game Played by Th17 Cells in Infection: Host Defense and Immunopathology. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, P.; Rodriguez-Carrio, J.; Caminal-Montero, L.; Mozo, L.; Suarez, A. A pathogenic IFNalpha, BLyS and IL-17 axis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zickert, A.; Amoudruz, P.; Sundstrom, Y.; Ronnelid, J.; Malmstrom, V.; Gunnarsson, I. IL-17 and IL-23 in lupus nephritis—association to histopathology and response to treatment. BMC Immunol. 2015, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonelli, M.; Savitskaya, A.; von Dalwigk, K.; Steiner, C.W.; Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S.; Scheinecker, C. Quantitative and qualitative deficiencies of regulatory T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, T.; Sattler, A.; Templin, L.; Kohler, S.; Gross, C.; Meisel, A.; Sawitzki, B.; Burmester, G.R.; Arnold, R.; Radbruch, A.; et al. Foxp3+ Helios+ regulatory T cells are expanded in active systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Cava, A. Tregs in SLE: An Update. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.M.; Tsokos, G.C. T Cell Abnormalities in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: An Update. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2021, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liarski, V.M.; Kaverina, N.; Chang, A.; Brandt, D.; Yanez, D.; Talasnik, L.; Carlesso, G.; Herbst, R.; Utset, T.O.; Labno, C.; et al. Cell distance mapping identifies functional T follicular helper cells in inflamed human renal tissue. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 230ra246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comte, D.; Karampetsou, M.P.; Yoshida, N.; Kis-Toth, K.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Tsokos, G.C. Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule Family Member 7 Engagement Restores Defective Effector CD8+ T Cell Function in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, E.F.; Lee, J.C.; Jayne, D.R.; Lyons, P.A.; Smith, K.G. T-cell exhaustion, co-stimulation and clinical outcome in autoimmunity and infection. Nature 2015, 523, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuyama, E.; Suarez-Fueyo, A.; Bradley, S.J.; Mizui, M.; Marin, A.V.; Mulki, L.; Krishfield, S.; Malavasi, F.; Yoon, J.; Sui, S.J.H.; et al. The CD38/NAD/SIRTUIN1/EZH2 Axis Mitigates Cytotoxic CD8 T Cell Function and Identifies Patients with SLE Prone to Infections. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 112–123.e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kang, N.; Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Wei, W.; Cui, L.; Ba, D.; He, W. Generation of human regulatory gammadelta T cells by TCRgammadelta stimulation in the presence of TGF-beta and their involvement in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 6693–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, E.; Niewiadomska, H.; Robak, T.; Bartkowiak, J.; Blonski, J.Z.; Wozniacka, A.; Pomorski, L.; Sysa-Jedrezejowska, A. Lymphocyctes Tgammadelta in clinically normal skin and peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and their correlation with disease activity. Mediat. Inflamm. 2001, 10, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, L.; Hedberg, H. Impaired phagocytosis by peripheral blood granulocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand. J. Haematol. 1969, 6, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, S.; Roake, W.; Brown, S.; Young, P.; Naik, H.; Wordsworth, P.; Isenberg, D.A.; Reid, K.B.; Eggleton, P. Impaired recognition of apoptotic neutrophils by the C1q/calreticulin and CD91 pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lood, C.; Blanco, L.P.; Purmalek, M.M.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; De Ravin, S.S.; Smith, C.K.; Malech, H.L.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Elkon, K.B.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophil extracellular traps enriched in oxidized mitochondrial DNA are interferogenic and contribute to lupus-like disease. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hom, G.; Graham, R.R.; Modrek, B.; Taylor, K.E.; Ortmann, W.; Garnier, S.; Lee, A.T.; Chung, S.A.; Ferreira, R.C.; Pant, P.V.; et al. Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, L.M.; Johansson, A.C.; Gullstrand, B.; Jonsen, A.; Saevarsdottir, S.; Ronnblom, L.; Leonard, D.; Wettero, J.; Sjowall, C.; Svenungsson, E.; et al. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the NCF1 gene leading to reduced oxidative burst is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C.O.; Eisenstein, M.; Dinauer, M.C.; Ming, W.; Liu, Q.; John, S.; Quismorio, F.P., Jr.; Reiff, A.; Myones, B.L.; Kaufman, K.M.; et al. Lupus-associated causal mutation in neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 (NCF2) brings unique insights to the structure and function of NADPH oxidase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E59–E67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindau, D.; Mussard, J.; Rabsteyn, A.; Ribon, M.; Kotter, I.; Igney, A.; Adema, G.J.; Boissier, M.C.; Rammensee, H.G.; Decker, P. TLR9 independent interferon alpha production by neutrophils on NETosis in response to circulating chromatin, a key lupus autoantigen. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 2199–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanichamy, A.; Bauer, J.W.; Yalavarthi, S.; Meednu, N.; Barnard, J.; Owen, T.; Cistrone, C.; Bird, A.; Rabinovich, A.; Nevarez, S.; et al. Neutrophil-mediated IFN activation in the bone marrow alters B cell development in human and murine systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Sagar, D.; Hanna, R.N.; Lightfoot, Y.L.; Mistry, P.; Smith, C.K.; Manna, Z.; Hasni, S.; Siegel, R.M.; Sanjuan, M.A.; et al. Low-density granulocytes activate T cells and demonstrate a non-suppressive role in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, A.; Beresford, M.W. Increased expression of low density granulocytes in juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus patients correlates with disease activity. Lupus 2016, 25, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, M.F.; Yalavarthi, S.; Zhao, W.; Thacker, S.G.; Anderson, M.; Sandy, A.R.; McCune, W.J.; Kaplan, M.J. A distinct subset of proinflammatory neutrophils isolated from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus induces vascular damage and synthesizes type I IFNs. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3284–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeltz, S.; Amini, P.; Anders, H.J.; Andrade, F.; Bilyy, R.; Chatfield, S.; Cichon, I.; Clancy, D.M.; Desai, J.; Dumych, T.; et al. To NET or not to NET:current opinions and state of the science regarding the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, F.; Zychlinsky, A.; Kenny, E.F. The role of neutrophil extracellular traps in rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odqvist, L.; Jevnikar, Z.; Riise, R.; Oberg, L.; Rhedin, M.; Leonard, D.; Yrlid, L.; Jackson, S.; Mattsson, J.; Nanda, S.; et al. Genetic variations in A20 DUB domain provide a genetic link to citrullination and neutrophil extracellular traps in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.H.; Dwivedi, N.; Nicholas, A.P.; Ho, I.C. The W620 Polymorphism in PTPN22 Disrupts Its Interaction With Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type 4 and Enhances Citrullination and NETosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2323–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Matta, B.; Song, S.; Nelson, V.; Diggins, K.; Simpfendorfer, K.R.; Gregersen, P.K.; Linsley, P.; Barnes, B.J. IRF5 genetic risk variants drive myeloid-specific IRF5 hyperactivation and presymptomatic SLE. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e124020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, R.R.; Nakabo, S.; Dizon, B.L.P.; Urban, A.; Waldman, M.; Howard, L.; Darnell, D.; Buhaya, M.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Hasni, S.; et al. Lupus-like autoimmunity and increased interferon response in patients with STAT3-deficient hyper-IgE syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 746–749.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlenberg, J.M.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Smith, C.K.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophil extracellular trap-associated protein activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome is enhanced in lupus macrophages. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisirak, V.; Ganguly, D.; Lewis, K.L.; Couillault, C.; Tanaka, L.; Bolland, S.; D’Agati, V.; Elkon, K.B.; Reizis, B. Genetic evidence for the role of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, N.; Castellano, G.; Blasi, A.; Capobianco, C.; Loverre, A.; Montinaro, V.; Netti, S.; Torres, D.; Manno, C.; Grandaliano, G.; et al. Immature myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells infiltrate renal tubulointerstitium in patients with lupus nephritis. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, K.; Nakayamada, S.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kubo, S.; Ishii, A.; Nakano, K.; Tanaka, Y. Up-Regulation of TLR7-Mediated IFN-alpha Production by Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bave, U.; Magnusson, M.; Eloranta, M.L.; Perers, A.; Alm, G.V.; Ronnblom, L. Fc gamma RIIa is expressed on natural IFN-alpha-producing cells (plasmacytoid dendritic cells) and is required for the IFN-alpha production induced by apoptotic cells combined with lupus IgG. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 3296–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Romo, G.S.; Caielli, S.; Vega, B.; Connolly, J.; Allantaz, F.; Xu, Z.; Punaro, M.; Baisch, J.; Guiducci, C.; Coffman, R.L.; et al. Netting neutrophils are major inducers of type I IFN production in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjorton, K.; The DISSECT consortium; Hagberg, N.; Israelsson, E.; Jinton, L.; Berggren, O.; Sandling, J.K.; Thörn, K.; Mo, J.; Eloranta, M.-L.; et al. Cytokine production by activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells and natural killer cells is suppressed by an IRAK4 inhibitor. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corzo, C.A.; Varfolomeev, E.; Setiadi, A.F.; Francis, R.; Klabunde, S.; Senger, K.; Sujatha-Bhaskar, S.; Drobnick, J.; Do, S.; Suto, E.; et al. The kinase IRAK4 promotes endosomal TLR and immune complex signaling in B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaaz1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiecki, M.; Colonna, M. The multifaceted biology of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jego, G.; Palucka, A.K.; Blanck, J.P.; Chalouni, C.; Pascual, V.; Banchereau, J. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells induce plasma cell differentiation through type I interferon and interleukin 6. Immunity 2003, 19, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, C.; Perez, O.A.; Voss, W.N.; Pucella, J.N.; Serpas, L.; Mehl, J.; Ching, K.L.; Goike, J.; Georgiou, G.; Ippolito, G.C.; et al. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and Type I Interferon Promote Extrafollicular B Cell Responses to Extracellular Self-DNA. Immunity 2020, 52, 1022–1038.e1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.; Charles, N.; Escoubet, B.; Guedj, K.; Chauveheid, M.P.; Caligiuri, G.; Nicoletti, A.; Papo, T.; Sacre, K. CD4+CXCR3+ T cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells drive accelerated atherosclerosis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 63, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.H.; Lande, R.; Gregorio, J.; Perng, O.A.; Qin, X.F.; Liu, Y.J.; Gilliet, M. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells prime IL-10-producing T regulatory cells by inducible costimulator ligand. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahrsdorfer, B.; Vollmer, A.; Blackwell, S.E.; Maier, J.; Sontheimer, K.; Beyer, T.; Mandel, B.; Lunov, O.; Tron, K.; Nienhaus, G.U.; et al. Granzyme B produced by human plasmacytoid dendritic cells suppresses T-cell expansion. Blood 2010, 115, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseman, E.A.; Liang, X.; Dawson, A.J.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Krieg, A.M.; Liu, Y.J.; Blazar, B.R.; Chen, W. Human plasmacytoid dendritic cells activated by CpG oligodeoxynucleotides induce the generation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4433–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M.; Blair, P.A.; Isenberg, D.A.; Mauri, C. A Regulatory Feedback between Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and Regulatory B Cells Is Aberrant in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunity 2016, 44, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, J.P.; Leslie, A.G.; Lutter, R.; Walker, J.E. Structure at 2.8 A resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature 1994, 370, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, K.; Moinuddin; Jabeen, S. Immunogenicity of mitochondrial DNA modified by hydroxyl radical. Cell. Immunol. 2007, 247, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Duvvuri, B.; Grigull, J.; Jamnik, R.; Wither, J.E.; Wu, G.E. Experimental evidence that mutated-self peptides derived from mitochondrial DNA somatic mutations have the potential to trigger autoimmunity. Hum. Immunol. 2014, 75, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lopez, L.; Nieves-Plaza, M.; Castro Mdel, R.; Font, Y.M.; Torres-Ramos, C.A.; Vila, L.M.; Ayala-Pena, S. Mitochondrial DNA damage is associated with damage accrual and disease duration in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2014, 23, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Raoof, M.; Chen, Y.; Sumi, Y.; Sursal, T.; Junger, W.; Brohi, K.; Itagaki, K.; Hauser, C.J. Circulating mitochondrial DAMPs cause inflammatory responses to injury. Nature 2010, 464, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyshkina, T.; Sylvester, A.; Sadiq, S.; Bonilla, E.; Canter, J.A.; Perl, A.; Kalman, B. Association of common mitochondrial DNA variants with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 129, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsen, A.; Yu, X.; Truedsson, L.; Nived, O.; Sturfelt, G.; Ibrahim, S.; Bengtsson, A. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility and phenotype of systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2009, 18, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Yang, M.; Zhong, K.; Du, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gui, M. Association of mtDNA M/N haplogroups with systemic lupus erythematosus: A case-control study of Han Chinese women. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wester-Rosenlof, L.; Gimsa, U.; Holzhueter, S.A.; Marques, A.; Jonas, L.; Hagenow, K.; Kunz, M.; Nizze, H.; Tiedge, M.; et al. The mtDNA nt7778 G/T polymorphism affects autoimmune diseases and reproductive performance in the mouse. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4689–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caielli, S.; Athale, S.; Domic, B.; Murat, E.; Chandra, M.; Banchereau, R.; Baisch, J.; Phelps, K.; Clayton, S.; Gong, M.; et al. Oxidized mitochondrial nucleoids released by neutrophils drive type I interferon production in human lupus. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, Y.; Marcoux, G.; Allaeys, I.; Julien, A.S.; Loignon, R.C.; Benk-Fortin, H.; Rollet-Labelle, E.; Rauch, J.; Fortin, P.R.; Boilard, E. Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Target Mitochondrial RNA. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisirak, V.; Sally, B.; D’Agati, V.; Martinez-Ortiz, W.; Ozcakar, Z.B.; David, J.; Rashidfarrokhi, A.; Yeste, A.; Panea, C.; Chida, A.S.; et al. Digestion of Chromatin in Apoptotic Cell Microparticles Prevents Autoimmunity. Cell 2016, 166, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mayouf, S.M.; Sunker, A.; Abdwani, R.; Abrawi, S.A.; Almurshedi, F.; Alhashmi, N.; Al Sonbul, A.; Sewairi, W.; Qari, A.; Abdallah, E.; et al. Loss-of-function variant in DNASE1L3 causes a familial form of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1186–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, J.; Serpas, L.; Wang, Y.; Rashidfarrokhi, A.; Perez, O.A.; Sally, B.; Sisirak, V.; Soni, C.; Khodadadi-Jamayran, A.; Tsirigos, A.; et al. Autoantibody-mediated impairment of DNASE1L3 activity in sporadic systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20201138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawane, K.; Fukuyama, H.; Kondoh, G.; Takeda, J.; Ohsawa, Y.; Uchiyama, Y.; Nagata, S. Requirement of DNase II for definitive erythropoiesis in the mouse fetal liver. Science 2001, 292, 1546–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Okabe, Y.; Kawane, K.; Fukuyama, H.; Nagata, S. Lethal anemia caused by interferon-beta produced in mouse embryos carrying undigested DNA. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieves, J.L.; Fye, J.M.; Harvey, S.; Grayson, J.M.; Hollis, T.; Perrino, F.W. Exonuclease TREX1 degrades double-stranded DNA to prevent spontaneous lupus-like inflammatory disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5117–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, Y.J.; Hayward, B.E.; Parmar, R.; Robins, P.; Leitch, A.; Ali, M.; Black, D.N.; van Bokhoven, H.; Brunner, H.G.; Hamel, B.C.; et al. Mutations in the gene encoding the 3′-5′ DNA exonuclease TREX1 cause Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome at the AGS1 locus. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, R.; Hezaveh, K.; Halaby, M.J.; Kloetgen, A.; Chakravarthy, A.; da Silva Medina, T.; Deol, R.; Manion, K.P.; Baglaenko, Y.; Eldh, M.; et al. Apoptotic cell-induced AhR activity is required for immunological tolerance and suppression of systemic lupus erythematosus in mice and humans. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravishankar, B.; Liu, H.; Shinde, R.; Chandler, P.; Baban, B.; Tanaka, M.; Munn, D.H.; Mellor, A.L.; Karlsson, M.C.; McGaha, T.L. Tolerance to apoptotic cells is regulated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3909–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravishankar, B.; Liu, H.; Shinde, R.; Chaudhary, K.; Xiao, W.; Bradley, J.; Koritzinsky, M.; Madaio, M.P.; McGaha, T.L. The amino acid sensor GCN2 inhibits inflammatory responses to apoptotic cells promoting tolerance and suppressing systemic autoimmunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10774–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaux, D.L.; Flavell, R.A. Apoptosis genes and autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2000, 12, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, P.M.; Hume, D.A. Apoptotic cell removal in development and tissue homeostasis. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devitt, A.; Parker, K.G.; Ogden, C.A.; Oldreive, C.; Clay, M.F.; Melville, L.A.; Bellamy, C.O.; Lacy-Hulbert, A.; Gangloff, S.C.; Goyert, S.M.; et al. Persistence of apoptotic cells without autoimmune disease or inflammation in CD14-/- mice. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 167, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, R.; Ganguly, D.; Facchinetti, V.; Frasca, L.; Conrad, C.; Gregorio, J.; Meller, S.; Chamilos, G.; Sebasigari, R.; Riccieri, V.; et al. Neutrophils activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells by releasing self-DNA-peptide complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, M.K.; Wohlgemuth, J. Microarray analysis of gene expression in lupus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2003, 5, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B. IFNgamma: Signalling, epigenetics and roles in immunity, metabolism, disease and cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Baldridge, M.T. Interferon-Lambda: A Potent Regulator of Intestinal Viral Infections. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyuan, I.T.; Tzeng, H.T.; Chen, J.Y. Signaling Pathways of Type I and Type III Interferons and Targeted Therapies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Cells 2019, 8, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J. IPC: Professional type 1 interferon-producing cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 275–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petro, T.M. IFN Regulatory Factor 3 in Health and Disease. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegal, F.P.; Kadowaki, N.; Shodell, M.; Fitzgerald-Bocarsly, P.A.; Shah, K.; Ho, S.; Antonenko, S.; Liu, Y.J. The nature of the principal type 1 interferon-producing cells in human blood. Science 1999, 284, 1835–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoggins, J.W. Interferon-Stimulated Genes: What Do They All Do? Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, G.R.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty. Immunity 2012, 36, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, A.D.; Baron, S.; Talal, N. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand mice, I. Induction of antinucleic acid antibodies by polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1969, 63, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okanoue, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Itoh, Y.; Minami, M.; Yasui, K.; Sakamoto, M.; Nishioji, K.; Katagishi, T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tada, H.; et al. Side effects of high-dose interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 1996, 25, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gota, C.; Calabrese, L. Induction of clinical autoimmune disease by therapeutic interferon-alpha. Autoimmunity 2003, 36, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewold, T.B. Interferon alpha-induced lupus: Proof of principle. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 14, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewold, T.B.; Swedler, W.I. Systemic lupus erythematosus arising during interferon-alpha therapy for cryoglobulinemic vasculitis associated with hepatitis C. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 24, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, L.E.; Widman, D.; Dikman, S.H.; Gorevic, P.D. Autoimmune disease complicating antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus infection. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 32, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, R.R.; Kozyrev, S.V.; Baechler, E.C.; Reddy, M.V.; Plenge, R.M.; Bauer, J.W.; Ortmann, W.A.; Koeuth, T.; Gonzalez Escribano, M.F.; the Argentine and Spanish Collaborative Groups; et al. A common haplotype of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) regulates splicing and expression and is associated with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Consortium for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Genetics (SLEGEN); Harley, J.B.; Alarcon-Riquelme, M.E.; Criswell, L.A.; Jacob, C.O.; Kimberly, R.P.; Moser, K.L.; Tsao, B.P.; Vyse, T.J.; Langefeld, C.D.; et al. Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessard, C.J.; Adrianto, I.; Ice, J.A.; Wiley, G.B.; Kelly, J.A.; Glenn, S.B.; Adler, A.J.; Li, H.; Rasmussen, A.; Williams, A.H.; et al. Identification of IRF8, TMEM39A, and IKZF3-ZPBP2 as susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus in a large-scale multiracial replication study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodke-Puranik, Y.; Niewold, T.B. Genetics of the type I interferon pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int. J. Clin. Rheumtol. 2013, 8, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vollenhoven, R.; Askanase, A.D.; Bomback, A.S.; Bruce, I.N.; Carroll, A.; Dall’Era, M.; Daniels, M.; Levy, R.A.; Schwarting, A.; Quasny, H.A.; et al. Conceptual framework for defining disease modification in systemic lupus erythematosus: A call for formal criteria. Lupus Sci. Med. 2022, 9, e000634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vollenhoven, R.; Voskuyl, A.; Bertsias, G.; Aranow, C.; Aringer, M.; Arnaud, L.; Askanase, A.; Balazova, P.; Bonfa, E.; Bootsma, H.; et al. A framework for remission in SLE: Consensus findings from a large international task force on definitions of remission in SLE (DORIS). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklyn, K.; Lau, C.S.; Navarra, S.V.; Louthrenoo, W.; Lateef, A.; Hamijoyo, L.; Wahono, C.S.; Chen, S.L.; Jin, O.; Morton, S.; et al. Definition and initial validation of a Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Brasil, C.C.; Hanly, J.G.; Urowitz, M.; Clarke, A.E.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Gordon, C.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Petri, M.; Ginzler, E.M.; Wallace, D.J.; et al. Flares after hydroxychloroquine reduction or discontinuation: Results from the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) inception cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinjo, S.K.; Bonfa, E.; Wojdyla, D.; Borba, E.F.; Ramirez, L.A.; Scherbarth, H.R.; Brenol, J.C.; Chacon-Diaz, R.; Neira, O.J.; Berbotto, G.A.; et al. Antimalarial treatment may have a time-dependent effect on lupus survival: Data from a multinational Latin American inception cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Ramos-Casals, M.; Brito-Zeron, P.; Khamashta, M.A. Clinical efficacy and side effects of antimalarials in systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Mak, A.; Leong, J.; Dharmadhikari, B.; Kow, N.Y.; Reategui-Sokolova, C.; Elera-Fitzcarrald, C.; Aranow, C.; Arnaud, L.; Askanase, A.D.; et al. Impact of glucocorticoids on the incidence of lupus-related major organ damage: A systematic literature review and meta-regression analysis of longitudinal observational studies. Lupus Sci. Med. 2021, 8, e000590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderka, M.T.; Lin, A.E.; Abuelo, D.N.; Mitchell, A.A.; Rasmussen, S.A. Reviewing the evidence for mycophenolate mofetil as a new teratogen: Case report and review of the literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2009, 149A, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssiau, F.A.; Vasconcelos, C.; D’Cruz, D.; Sebastiani, G.D.; Garrido, E.D.R.; Danieli, M.G.; Abramovicz, D.; Blockmans, D.; Mathieu, A.; Direskeneli, H.; et al. Immunosuppressive therapy in lupus nephritis: The Euro-Lupus Nephritis Trial, a randomized trial of low-dose versus high-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadi, A.; Jones, R.J.; Brodsky, R.A. Cyclophosphamide and cancer: Golden anniversary. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, T.; Furie, R. Novel paradigms in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 2019, 393, 2344–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, J.T.; Neuwelt, C.M.; Wallace, D.J.; Shanahan, J.C.; Latinis, K.M.; Oates, J.C.; Utset, T.O.; Gordon, C.; Isenberg, D.A.; Hsieh, H.J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in moderately-to-severely active systemic lupus erythematosus: The randomized, double-blind, phase II/III systemic lupus erythematosus evaluation of rituximab trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Furie, R.; Latinis, K.; Looney, R.J.; Fervenza, F.C.; Sanchez-Guerrero, J.; Maciuca, R.; Zhang, D.; Garg, J.P.; Brunetta, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active proliferative lupus nephritis: The Lupus Nephritis Assessment with Rituximab study. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.K.; Levarht, E.W.; Toes, R.E.; Huizinga, T.W.; van Laar, J.M. Residual inflammation after rituximab treatment is associated with sustained synovial plasma cell infiltration and enhanced B cell repopulation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijpe, J.; Meijer, J.M.; Bootsma, H.; van der Wal, J.E.; Spijkervet, F.K.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Vissink, A.; Ihrler, S. Clinical and histologic evidence of salivary gland restoration supports the efficacy of rituximab treatment in Sjogren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, R.; Richardson, N.; Neeli, I.; Khawaja, S.; Chamberlain, D.; Ghani, M.; Ghani, Q.U.; Balazs, L.; Beranova-Giorgianni, S.; Giorgianni, F.; et al. Sustained B cell depletion by CD19-targeted CAR T cells is a highly effective treatment for murine lupus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez Mendez, L.M.; Cascino, M.D.; Garg, J.; Katsumoto, T.R.; Brakeman, P.; Dall’Era, M.; Looney, R.J.; Rovin, B.; Dragone, L.; Brunetta, P. Peripheral Blood B Cell Depletion after Rituximab and Complete Response in Lupus Nephritis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.; Evers, M.; Jansen, J.H.M.; Buijs, J.; Broek, B.; Reitsma, S.E.; Moerer, P.; Amini, M.; Kretschmer, A.; Ten Broeke, T.; et al. New insights in Type I and II CD20 antibody mechanisms-of-action with a panel of novel CD20 antibodies. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, A.D.; Wang, H.; Bastacky, S.I.; van Puijenbroek, E.; Schindler, T.; Speziale, D.; Perro, M.; Klein, C.; Nickerson, K.M.; Shlomchik, M.J. The Type II Anti-CD20 Antibody Obinutuzumab (GA101) Is More Effective Than Rituximab at Depleting B Cells and Treating Disease in a Murine Lupus Model. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mysler, E.F.; Spindler, A.J.; Guzman, R.; Bijl, M.; Jayne, D.; Furie, R.A.; Houssiau, F.A.; Drappa, J.; Close, D.; Maciuca, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ocrelizumab in active proliferative lupus nephritis: Results from a randomized, double-blind, phase III study. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2368–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarra, S.V.; Guzman, R.M.; Gallacher, A.E.; Hall, S.; Levy, R.A.; Jimenez, R.E.; Li, E.K.; Thomas, M.; Kim, H.Y.; Leon, M.G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.; Petri, M.; Zamani, O.; Cervera, R.; Wallace, D.J.; Tegzova, D.; Sanchez-Guerrero, J.; Schwarting, A.; Merrill, J.T.; Chatham, W.W.; et al. A phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of belimumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B lymphocyte stimulator, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3918–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Petri, M.A.; Cervera, R.; Roth, D.A.; Ji, B.N.; Kleoudis, C.S.; Zhong, Z.J.; Freimuth, W. Belimumab in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: High disease activity predictors of response. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urowitz, M.B.; Ohsfeldt, R.L.; Wielage, R.C.; Kelton, K.A.; Asukai, Y.; Ramachandran, S. Organ damage in patients treated with belimumab versus standard of care: A propensity score-matched comparative analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.A.; Wallace, D.J.; Aranow, C.; Fettiplace, J.; Wilson, B.; Mistry, P.; Roth, D.A.; Gordon, D. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Belimumab in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Continuation of a Seventy-Six-Week Phase III Parent Study in the United States. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Navarra, S.V.; Levy, R.A.; Thomas, M.; Heath, A.; Lustine, T.; Adamkovic, A.; Fettiplace, J.; Wang, M.L.; Ji, B.; et al. Long-term safety and limited organ damage in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus treated with belimumab: A Phase III study extension. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, W.; Schwarting, A.; Okada, M.; Scheinberg, M.; Doria, A.; Hammer, A.E.; Kleoudis, C.; Groark, J.; Bass, D.; Fox, N.L.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Subcutaneous Belimumab in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Fifty-Two-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, H.I.; Abud-Mendoza, C.; Viola, D.O.; Calvo Penades, I.; Levy, D.; Anton, J.; Calderon, J.E.; Chasnyk, V.G.; Ferrandiz, M.A.; Keltsev, V.; et al. Safety and efficacy of intravenous belimumab in children with systemic lupus erythematosus: Results from a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.; Rovin, B.H.; Houssiau, F.; Malvar, A.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Contreras, G.; Amoura, Z.; Yu, X.; Mok, C.C.; Santiago, M.B.; et al. Two-Year, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Belimumab in Lupus Nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Furie, R.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Contreras, G.; Malvar, A.; Yu, X.; Ji, B.; Green, Y.; Gonzalez-Rivera, T.; Bass, D.; et al. A secondary analysis of the Belimumab International Study in Lupus Nephritis trial examined effects of belimumab on kidney outcomes and preservation of kidney function in patients with lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2022, 101, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Tummala, R. Anifrolumab, a monoclonal antibody to the type I interferon receptor subunit 1, for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: An overview from clinical trials. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.; Khamashta, M.; Merrill, J.T.; Werth, V.P.; Kalunian, K.; Brohawn, P.; Illei, G.G.; Drappa, J.; Wang, L.; Yoo, S.; et al. Anifrolumab, an Anti-Interferon-alpha Receptor Monoclonal Antibody, in Moderate-to-Severe Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.A.; Morand, E.F.; Bruce, I.N.; Manzi, S.; Kalunian, K.C.; Vital, E.M.; Ford, T.L.; Gupta, R.; Hiepe, F.; Santiago, M. Type I interferon inhibitor anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus (TULIP-1): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019, 1, e208–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, E.F.; Furie, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Bruce, I.N.; Askanase, A.D.; Richez, C.; Bae, S.C.; Brohawn, P.Z.; Pineda, L.; Berglind, A.; et al. Trial of Anifrolumab in Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.; Morand, E.F.; Askanase, A.D.; Vital, E.M.; Merrill, J.T.; Kalyani, R.N.; Abreu, G.; Pineda, L.; Tummala, R. Anifrolumab reduces flare rates in patients with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2021, 30, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, E.M.; Merrill, J.T.; Morand, E.F.; Furie, R.A.; Bruce, I.N.; Tanaka, Y.; Manzi, S.; Kalunian, K.C.; Kalyani, R.N.; Streicher, K.; et al. Anifrolumab efficacy and safety by type I interferon gene signature and clinical subgroups in patients with SLE: Post hoc analysis of pooled data from two phase III trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayne, D.; Rovin, B.; Mysler, E.F.; Furie, R.A.; Houssiau, F.A.; Trasieva, T.; Knagenhjelm, J.; Schwetje, E.; Chia, Y.L.; Tummala, R.; et al. Phase II randomised trial of type I interferon inhibitor anifrolumab in patients with active lupus nephritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, Y.A. Voclosporin: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Ginzler, E.M.; Arriens, C.; Caster, D.J.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Gibson, K.; Kaplan, J.; Lisk, L.; Navarra, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of voclosporin versus placebo for lupus nephritis (AURORA 1): A double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovin, B.H.; Solomons, N.; Pendergraft, W.F., 3rd; Dooley, M.A.; Tumlin, J.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Lysenko, L.; Navarra, S.V.; Huizinga, R.B.; Group, A.-L.S. A randomized, controlled double-blind study comparing the efficacy and safety of dose-ranging voclosporin with placebo in achieving remission in patients with active lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.L.; Crowley, J.E.; Tomayko, M.M.; Steinel, N.; O’Neill, P.J.; Quinn, W.J., 3rd; Goenka, R.; Miller, J.P.; Cho, Y.H.; Long, V.; et al. BLyS inhibition eliminates primary B cells but leaves natural and acquired humoral immunity intact. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15517–15522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, K.; Meister, S.; Moser, K.; Weisel, F.; Maseda, D.; Amann, K.; Wiethe, C.; Winkler, T.H.; Kalden, J.R.; Manz, R.A.; et al. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib depletes plasma cells and protects mice with lupus-like disease from nephritis. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Kawakami, A.; Saito, K.; Ichinose, K.; Fujii, H.; Shirota, Y.; Shirai, T.; Fujita, Y.; Watanabe, R.; et al. Multicenter double-blind randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of bortezomib as a treatment for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Mod. Rheumatol. 2018, 28, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladi, E.; Everett, C.; Stivala, C.E.; Daniels, B.E.; Durk, M.R.; Harris, S.F.; Huestis, M.P.; Purkey, H.E.; Staben, S.T.; Augustin, M.; et al. Design and Evaluation of Highly Selective Human Immunoproteasome Inhibitors Reveal a Compensatory Process That Preserves Immune Cell Viability. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7032–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.C. Progress and Paradigms in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5419–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostendorf, L.; Burns, M.; Durek, P.; Heinz, G.A.; Heinrich, F.; Garantziotis, P.; Enghard, P.; Richter, U.; Biesen, R.; Schneider, U.; et al. Targeting CD38 with Daratumumab in Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenks, S.A.; Cashman, K.S.; Zumaquero, E.; Marigorta, U.M.; Patel, A.V.; Wang, X.; Tomar, D.; Woodruff, M.C.; Simon, Z.; Bugrovsky, R.; et al. Distinct Effector B Cells Induced by Unregulated Toll-like Receptor 7 Contribute to Pathogenic Responses in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunity 2018, 49, 725–739.e726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, R.F.; Labopin, M.; Bader, P.; Basak, G.W.; Bonini, C.; Chabannon, C.; Corbacioglu, S.; Dreger, P.; Dufour, C.; Gennery, A.R.; et al. Indications for haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for haematological diseases, solid tumours and immune disorders: Current practice in Europe, 2019. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019, 54, 1525–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, T.; Greco, R.; Snowden, J.A. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Autoimmune Disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2021, 72, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zand, M.S.; Vo, T.; Pellegrin, T.; Felgar, R.; Liesveld, J.L.; Ifthikharuddin, J.J.; Abboud, C.N.; Sanz, I.; Huggins, J. Apoptosis and complement-mediated lysis of myeloma cells by polyclonal rabbit antithymocyte globulin. Blood 2006, 107, 2895–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, T.; Arnold, R.; Hiepe, F.; Radbruch, A. Resetting the immune system with immunoablation and autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Swart, J.F.; Delemarre, E.M.; van Wijk, F.; Boelens, J.J.; Kuball, J.; van Laar, J.M.; Wulffraat, N.M. Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for autoimmune diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifa, I.; Hazlewood, G.S.; Durand, C.; Barr, S.G.; Mydlarski, P.R.; Beck, P.L.; Burton, J.M.; Khan, F.M.; Jamani, K.; Osman, M.; et al. Efficacy of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Autoimmune Diseases. Transpl. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 489.e1–489.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, R.K.; Han, X.; Gozdziak, P.; Yaung, K.; Morgan, A.; Clendenan, A.M.; Henry, J.; Calvario, M.A.; Datta, S.K.; Helenowski, I.; et al. Five year follow-up after autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for refractory, chronic, corticosteroid-dependent systemic lupus erythematosus: Effect of conditioning regimen on outcome. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2018, 53, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorshid, O.; Hosing, C.; Bibawi, S.; Ueno, N.; Reveille, J.; Mayes, M.D.; Champlin, R.E. Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplant in a patient with advanced systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 2513–2516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Lu, L.; Niu, X.; Guo, Y.; Parino, G.R.; Liu, D. Non-myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplant in a patient with refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2006, 37, 979–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmont, A.M.; Bacigalupo, A.; Gualandi, F.; Bregante, S.; van Lint, M.T.; Geroldi, S. Systemic lupus erythematosus complicated with thymoma and pure red cell aplasia (PCRA). CR of both complications following thymectomy and allogeneic haematopoietic SCT (HSCT), but persistence of antinuclear antibodies (ANA). Bone Marrow Transpl. 2014, 49, 982–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, R.; Labopin, M.; Badoglio, M.; Veys, P.; Furtado Silva, J.M.; Abinun, M.; Gualandi, F.; Bornhauser, M.; Ciceri, F.; Saccardi, R.; et al. Allogeneic HSCT for Autoimmune Diseases: A Retrospective Study From the EBMT ADWP, IEWP, and PDWP Working Parties. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshhar, Z.; Waks, T.; Gross, G.; Schindler, D.G. Specific activation and targeting of cytotoxic lymphocytes through chimeric single chains consisting of antibody-binding domains and the gamma or zeta subunits of the immunoglobulin and T-cell receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; Carpenter, T.J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, R.; Davis, H.M.; Heald, D.L.; Wang, W. Development of a Target cell-Biologics-Effector cell (TBE) complex-based cell killing model to characterize target cell depletion by T cell redirecting bispecific agents. MAbs 2018, 10, 876–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellebrecht, C.T.; Bhoj, V.G.; Nace, A.; Choi, E.J.; Mao, X.; Cho, M.J.; Di Zenzo, G.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Seykora, J.T.; Cotsarelis, G.; et al. Reengineering chimeric antigen receptor T cells for targeted therapy of autoimmune disease. Science 2016, 353, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadelain, M.; Riviere, I.; Riddell, S. Therapeutic T cell engineering. Nature 2017, 545, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudecek, M.; Sommermeyer, D.; Kosasih, P.L.; Silva-Benedict, A.; Liu, L.; Rader, C.; Jensen, M.C.; Riddell, S.R. The nonsignaling extracellular spacer domain of chimeric antigen receptors is decisive for in vivo antitumor activity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casucci, M.; Falcone, L.; Camisa, B.; Norelli, M.; Porcellini, S.; Stornaiuolo, A.; Ciceri, F.; Traversari, C.; Bordignon, C.; Bonini, C.; et al. Extracellular NGFR Spacers Allow Efficient Tracking and Enrichment of Fully Functional CAR-T Cells Co-Expressing a Suicide Gene. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, P.J.; Roddie, C.; Bader, P.; Basak, G.W.; Bonig, H.; Bonini, C.; Chabannon, C.; Ciceri, F.; Corbacioglu, S.; Ellard, R.; et al. Management of adults and children receiving CAR T-cell therapy: 2021 best practice recommendations of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) and the Joint Accreditation Committee of ISCT and EBMT (JACIE) and the European Haematology Association (EHA). Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mougiakakos, D.; Kronke, G.; Volkl, S.; Kretschmann, S.; Aigner, M.; Kharboutli, S.; Boltz, S.; Manger, B.; Mackensen, A.; Schett, G. CD19-Targeted CAR T Cells in Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackensen, A.; Muller, F.; Mougiakakos, D.; Boltz, S.; Wilhelm, A.; Aigner, M.; Volkl, S.; Simon, D.; Kleyer, A.; Munoz, L.; et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarczak, D.; Nierhaus, A. Cytokine Storm-Definition, Causes, and Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.M.R.; Muller, Y.D.; Bluestone, J.A.; Tang, Q. Next-generation regulatory T cell therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 749–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffin, C.; Vo, L.T.; Bluestone, J.A. T(reg) cell-based therapies: Challenges and perspectives. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.; Werth, V.P.; Merola, J.F.; Stevenson, L.; Reynolds, T.L.; Naik, H.; Wang, W.; Christmann, R.; Gardet, A.; Pellerin, A.; et al. Monoclonal antibody targeting BDCA2 ameliorates skin lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Qin, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X.; Gao, X.; Chen, W.; Sun, L. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy induces FLT3L and CD1c(+) dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.S.; Subramanian, V.; O’Dell, A.A.; Yalavarthi, S.; Zhao, W.; Smith, C.K.; Hodgin, J.B.; Thompson, P.R.; Kaplan, M.J. Peptidylarginine deiminase inhibition disrupts NET formation and protects against kidney, skin and vascular disease in lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C. The Jakinibs in systemic lupus erythematosus: Progress and prospects. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.; Thomas, R. Potential for Antigen-Specific Tolerizing Immunotherapy in Systematic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 654701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Drug | Target | Molecular Structure | Trial | Dosing | Primary Endpoint (PE) | Result | FDA Approval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rituximab | Pan-B-cell marker CD20 | Chimeric mAb | EXPLORER | 1000 mg or placebo on days 1, 15, 168, and 182 | BILAG response versus placebo at week 52 | PE not met | No |
| Rituximab | _ | _ | LUNAR | 1000 mg or placebo on days 1, 15, 168, and 182 | Complete or partial response at week 52 in LN patients | PE not met | No |
| Belimumab | BAFF | Human mAb IgG-1 lamba | BLISS-52 | 10 mg/kg or 1 mg/kg or placebo every 4 weeks | SRI-4 response versus placebo at week 52 | PE met | _ |
| Belimumab | _ | _ | BLISS-76 | 10 mg/kg or 1 mg/kg i.v. or placebo every 4 weeks | SRI-4 response versus placebo at week 52 | PE met | Yes (adults with ANA+, active SLE plus standard therapy) |
| Belimumab | _ | _ | BLISS-SC | 200 mg s.c. weekly | SRI-4 response versus placebo at week 52 | PE met | Yes (adults with ANA+, active SLE plus standard therapy) |
| Belimumab | _ | _ | BLISS-LN | 10 mg/kg i.v. or placebo every 4 weeks | PERR at week 104 in patients with active LN | PE met | Yes (adults with active LN plus standard therapy) |
| Belimumab | _ | _ | PLUTO | 10 mg/kg i.v. or placebo every 4 weeks | SRI-4 response versus placebo at week 52 in children aged 5 to 17 years | PE met | Yes (children 5 years and older with SLE and LN plus standard therapy) |
| Anifrolumab | Type-I IFNR subunit 1 | Human mAb IgG-1 kappa | TULIP-1 | 300 mg or 150 mg or placebo every 4 weeks | SRI-4 response of anifrolumab 300 mg versus placebo at week 52 | PE not met | _ |
| Anifrolumab | _ | _ | TULIP-2 | 300 mg or placebo every 4 weeks | BICLA response of anifrolumab 300 mg versus placebo at week 52 | PE met | Yes (adults with moderate to severe SLE plus standard therapy) |
| Voclosporin | T-cell inhibition and kidney podocytes stabilization | Calcineurin inhibition | AURORA | Voclosporin 23.7 mg twice daily + MM 1 g daily or MM 1 g daily | CRR in voclosporin + MM versus MM alone at week 52 | PE met | Yes (adults with active LN plus standard therapy) |
| Drug | Mechanism of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Ocrelizumab | CD20+ B-cell depletion | [158] |
| Bortezomib | Proteasome inhibition of LLPCs | [181] |
| CAR T cells | CD19+ B-cell depletion | [205] |
| BDCA2 | Anti-pDC antibody | [209] |
| IL-2 | Treg enhancement | [208] |
| JAK inhibitors | Type-I and type-II IFN signaling inhibition | [212] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Accapezzato, D.; Caccavale, R.; Paroli, M.P.; Gioia, C.; Nguyen, B.L.; Spadea, L.; Paroli, M. Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076578
Accapezzato D, Caccavale R, Paroli MP, Gioia C, Nguyen BL, Spadea L, Paroli M. Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076578
Chicago/Turabian StyleAccapezzato, Daniele, Rosalba Caccavale, Maria Pia Paroli, Chiara Gioia, Bich Lien Nguyen, Luca Spadea, and Marino Paroli. 2023. "Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076578
APA StyleAccapezzato, D., Caccavale, R., Paroli, M. P., Gioia, C., Nguyen, B. L., Spadea, L., & Paroli, M. (2023). Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076578






