Characterization of the ddt1 Mutant in Rice and Its Impact on Plant Height Reduction and Water Use Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phenotypic Analysis of ddt1
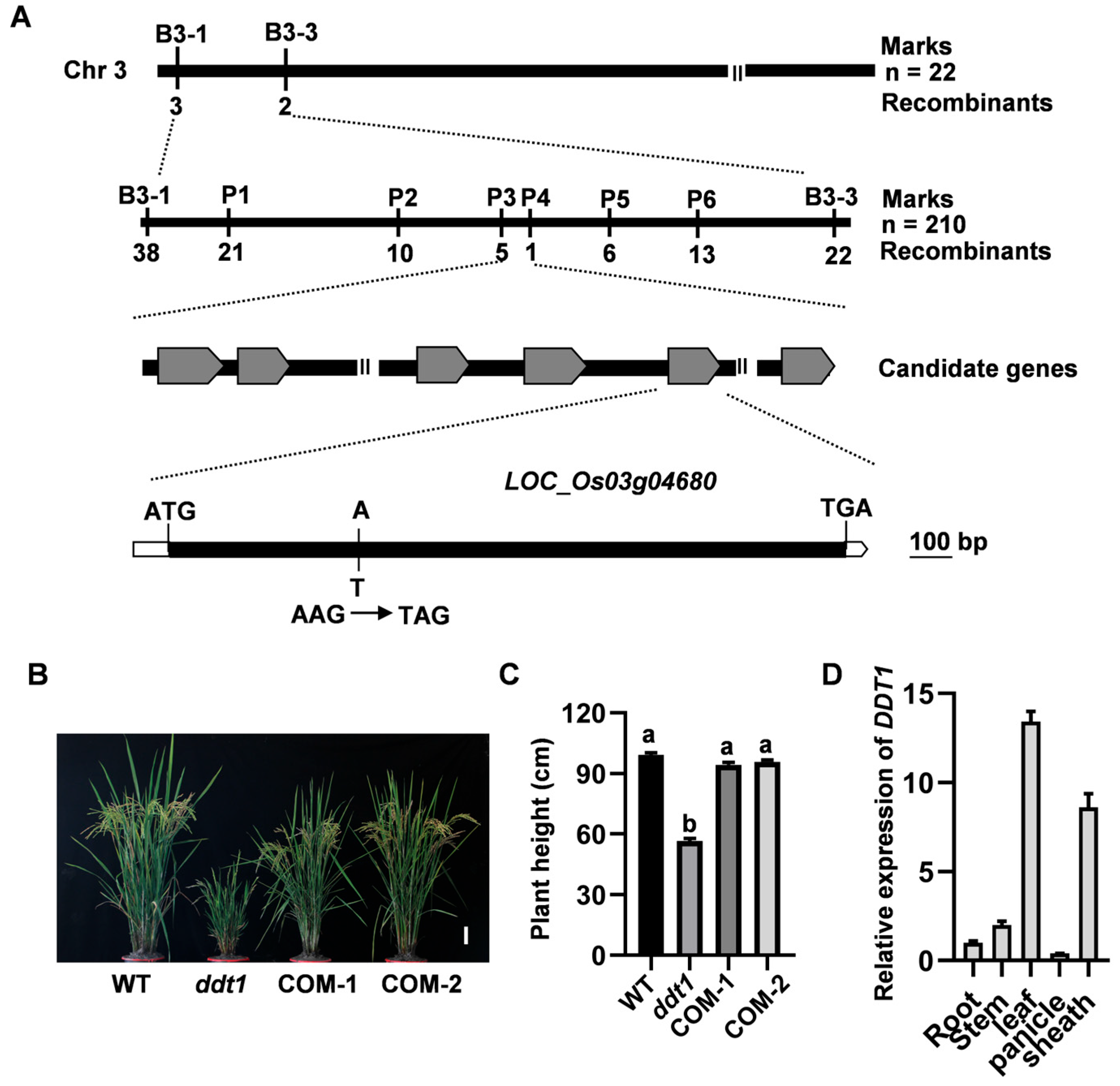
2.2. Map-Based Cloning of DDT1
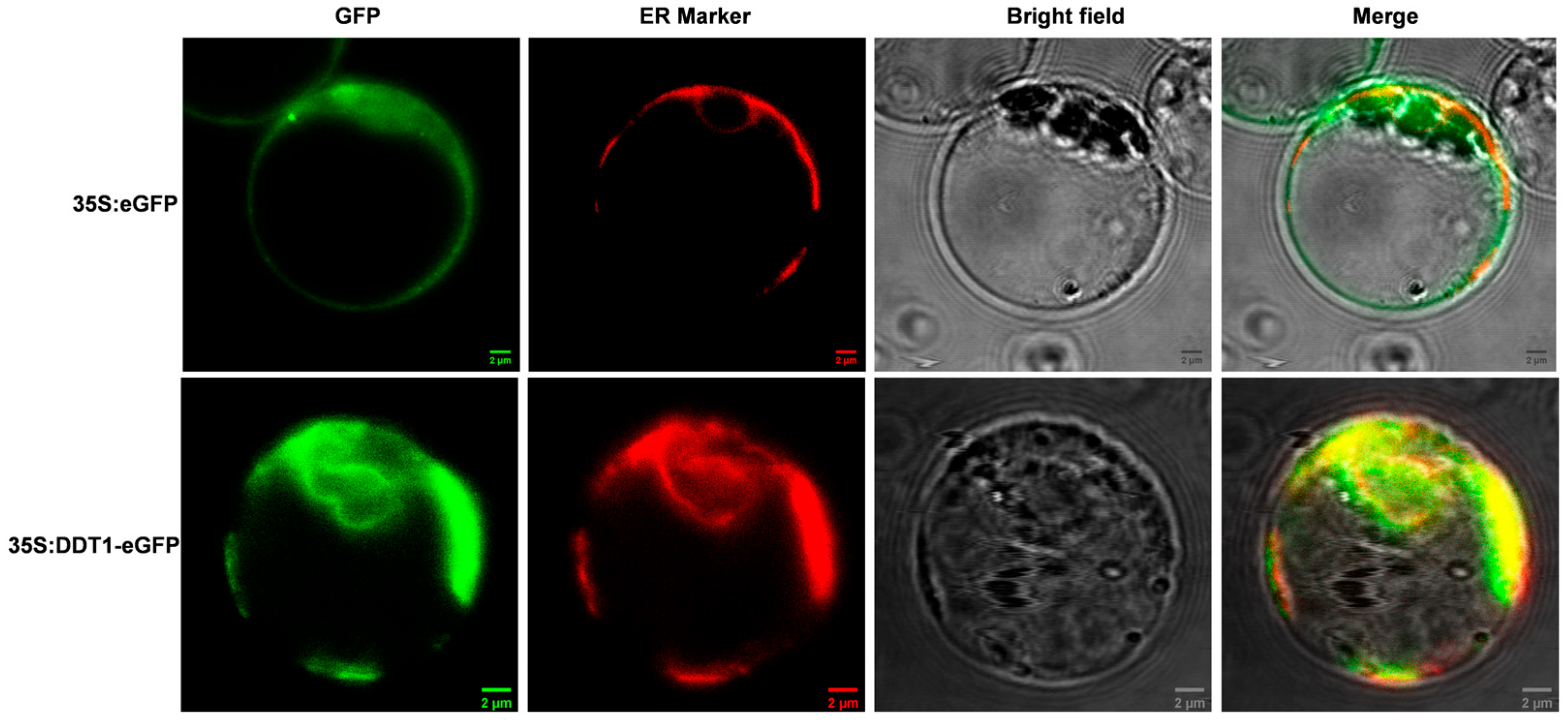
2.3. Subcellular Localization of DDT1
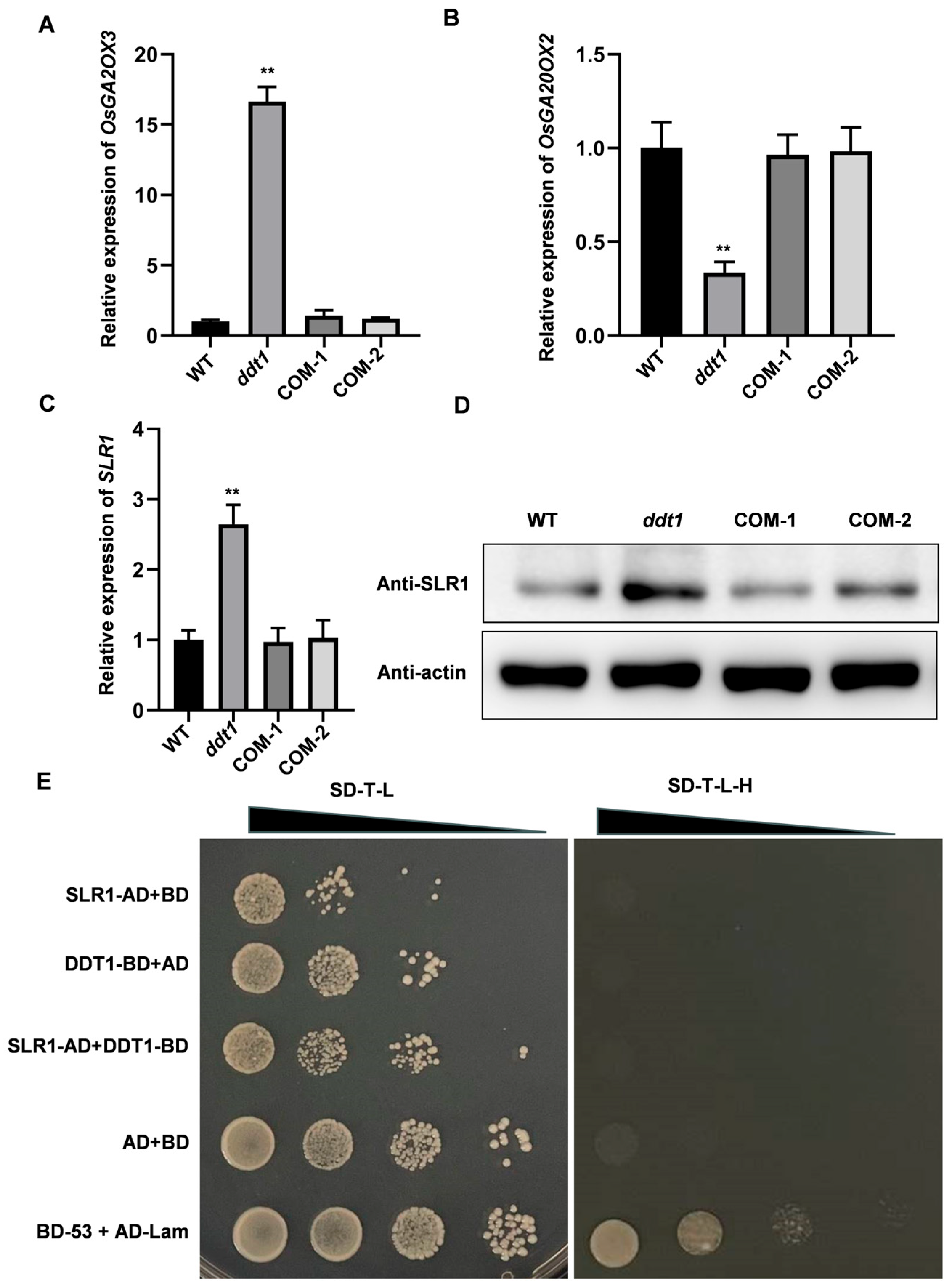
2.4. Unveiling the Role of DDT1 in Plant Height Regulation
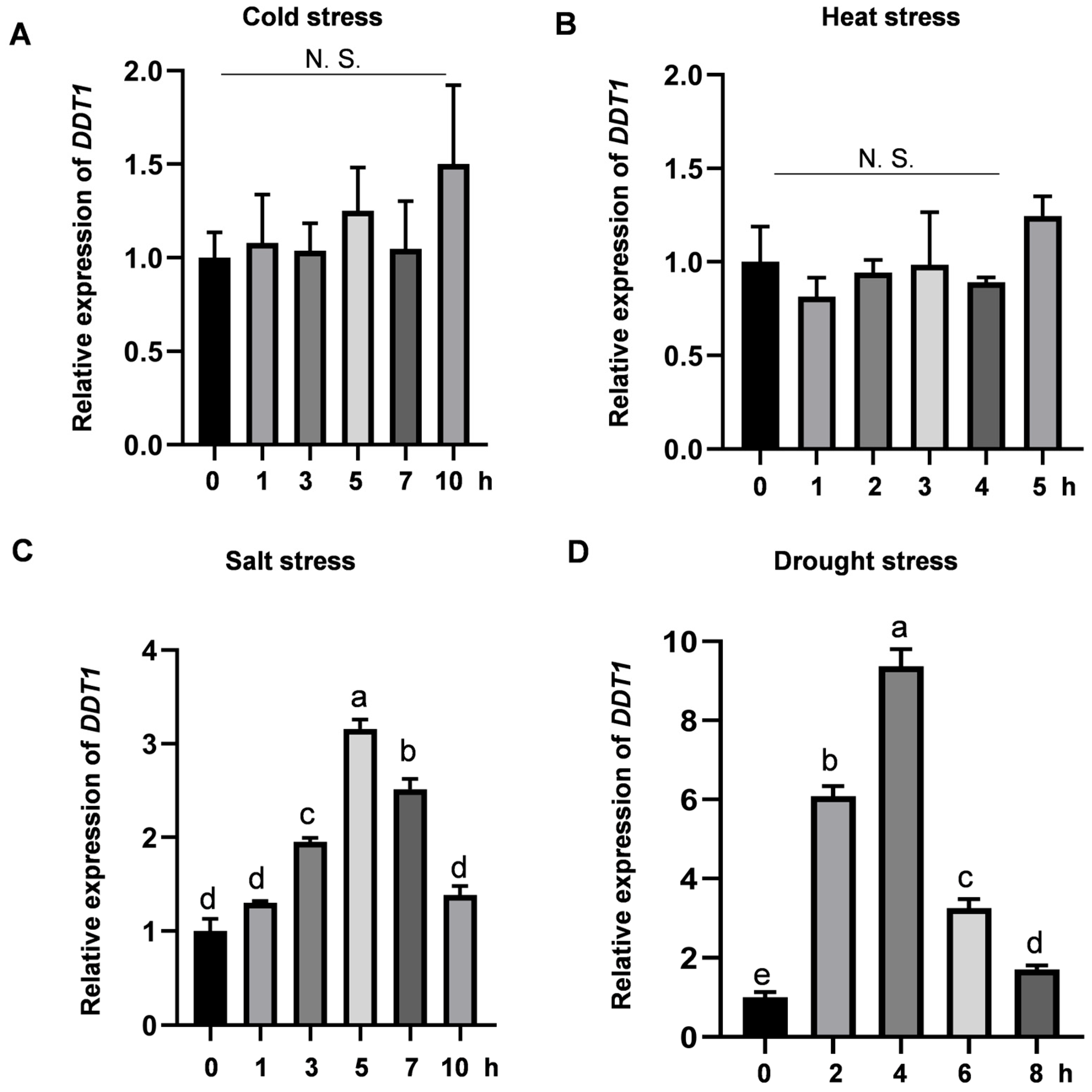
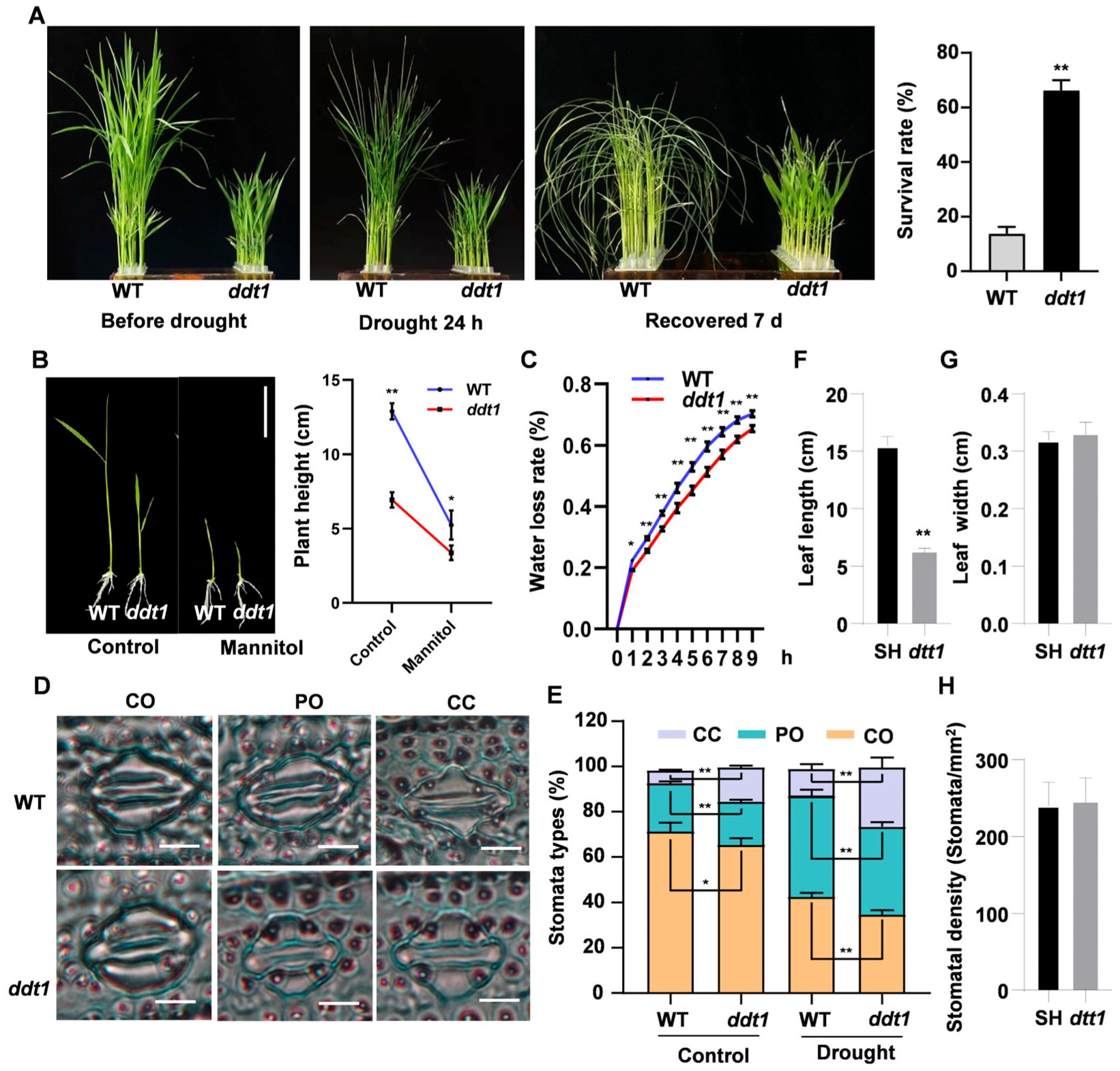
2.5. Role of the DDT1 in Enhancing Drought Stress Tolerance in Rice
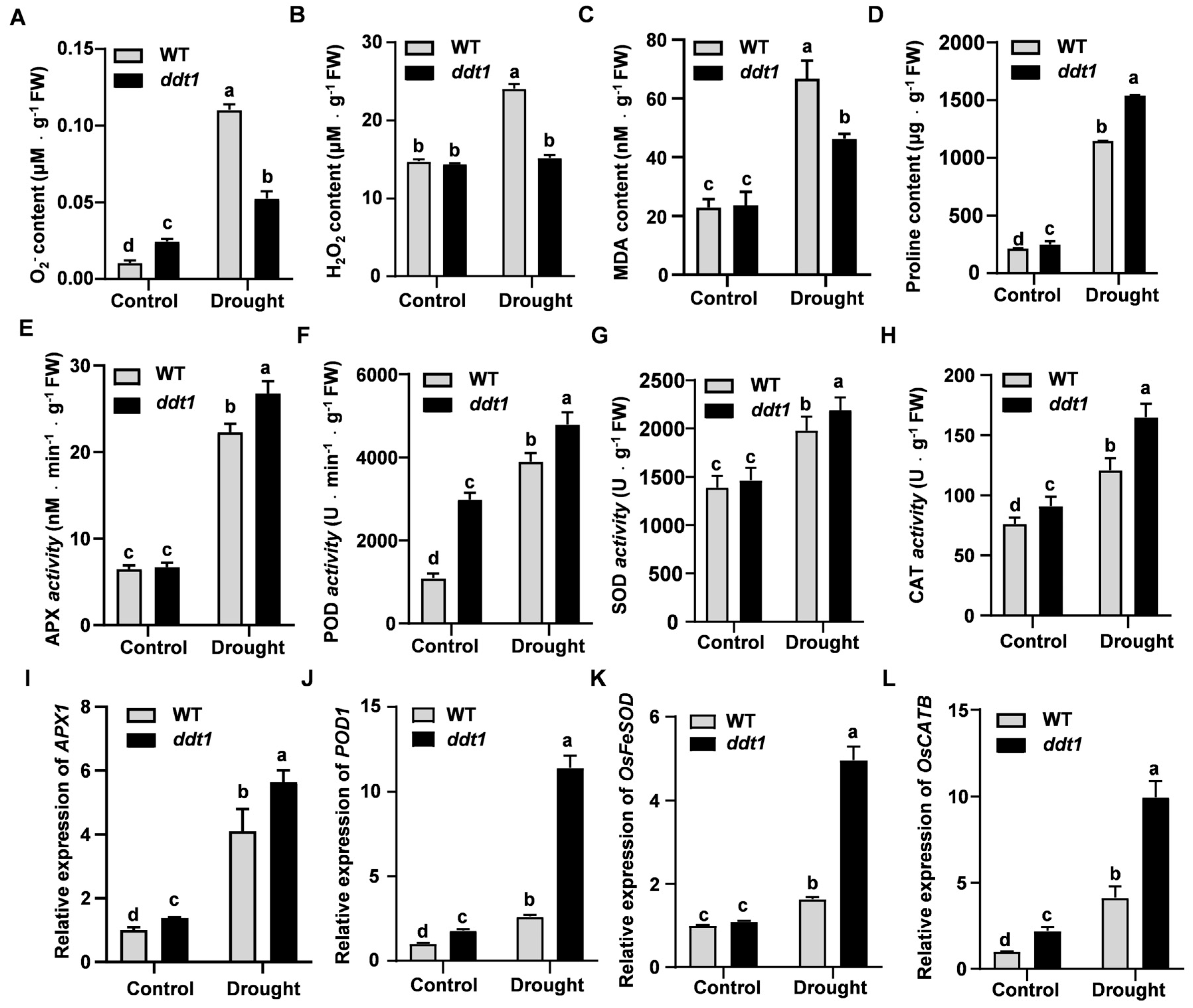
2.6. Enhancing Drought Tolerance through Antioxidant Capacity Modulation in ddt1 Mutant
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
4.2. Genetic Mapping and Mutant Analysis
4.3. Characterization of DDT1
4.4. Phenotypic Assessments
4.5. qRT-PCR Analyses
4.6. Subcellular Localization of DDT1
4.7. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay
4.8. SDS–PAGE and Western Blot Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, C.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Huang, A.; Li, H.; Zhao, T. OsMPH1 regulates plant height and improves grain yield in rice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Huang, Y.; Qi, P.; Lian, G.; Hu, X.; Han, N.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Qian, Q.; Bian, H. Functional analysis of auxin receptor OsTIR1/OsAFB family members in rice grain yield, tillering, plant height, root system, germination, and auxinic herbicide resistance. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 2676–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Shu, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; Ying, J.; et al. OsABF1 represses gibberellin biosynthesis to regulate plant height and seed germination in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Lin, J.; Chen, J.; Wei, M.; Liu, L.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, F.; Jiang, L.; et al. Natural variation of the BRD2 allele affects plant height and grain size in rice. Planta 2022, 256, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jia, L.; Li, Y.; Tian, W.; Chen, H.; Zhu, X.; et al. A very-long-chain fatty acid synthesis gene, SD38, influences plant height by activating ethylene biosynthesis in rice. Plant J. 2022, 112, 1084–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, Y.; Li, F.; Tan, J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; et al. Rice OsUBR7 modulates plant height by regulating histone H2B monoubiquitination and cell proliferation. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.R.; Jang, Y.H.; Kim, E.G.; Hur, S.S.; Kim, K.M. Quantitative trait loci mapping identified candidate genes involved in plant height regulation in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Gong, G.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhu, H.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.; et al. qGLF5 from Oryza rufipogon Griff. improves kernel shape, plant architecture, and yield in rice, TAG. Theoretical and applied genetics. Theor. Angew. Genet. 2023, 136, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Luo, R.; Man, J.; Long, Q.; Xu, N. OsHLS1 regulates plant height and development by controlling active gibberellin accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci. 2023, 326, 111508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monna, L.; Kitazawa, N.; Yoshino, R.; Suzuki, J.; Masuda, H.; Maehara, Y.; Tanji, M.; Sato, M.; Nasu, S.; Minobe, Y. Positional cloning of rice semidwarfing gene, sd-1: Rice “green revolution gene” encodes a mutant enzyme involved in gibberellin synthesis. DNA Res. 2002, 9, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.; Ashikari, M.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Itoh, H.; Nishimura, A.; Swapan, D.; Ishiyama, K.; Saito, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Khush, G.S.; et al. Green revolution: A mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice. Nature 2002, 416, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmeyer, W.; Ellis, M.H.; Chandler, P.M. Semidwarf (sd-1), “green revolution” rice, contains a defective gibberellin 20-oxidase gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9043–9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamuro, C.; Ihara, Y.; Wu, X.; Noguchi, T.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Ashikari, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1591–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterou, M.; Dubois, F.; Schaller, H.; Aubanelle, L.; Vilcot, B.; Sangwan-Norreel, B.S.; Sangwan, R.S. Brassinosteroids, microtubules and cell elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecular, I.; cellular and physiological characterization of the Arabidopsis bull mutant, defective in the delta 7-sterol-C5-desaturation step leading to brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Planta 2001, 212, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Umemura, K.; Uozu, S.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Ashikari, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2900–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ashikari, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. The Rice brassinosteroid-deficient dwarf2 mutant, defective in the rice homolog of Arabidopsis DIMINUTO/DWARF1, is rescued by the endogenously accumulated alternative bioactive brassinosteroid, dolichosterone. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, S.; Ashikari, M.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Yano, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Fujisawa, Y.; et al. A novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant, dwarf11, with reduced seed length. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, A.; Fujioka, S.; Sunohara, H.; Kamiya, N.; Hong, Z.; Inukai, Y.; Miura, K.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; et al. The role of OsBRI1 and its homologous genes, OsBRL1 and OsBRL3, in rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Morinaka, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Sunohara, H.; Fujioka, S.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Mizutani, M.; Sakata, K.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency increase biomass production and grain yield in rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Liu, J.; Yan, B.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Shen, R. BRASSINOSTEROID-SIGNALING KINASE1-1, a positive regulator of brassinosteroid signalling, modulates plant architecture and grain size in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Yu, B.; Sun, Y.; Huang, J. OsNAC016 regulates plant architecture and drought tolerance by interacting with the kinases GSK2 and SAPK8. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 1296–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, D.; Lu, S.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Y.; Yu, D.; Yang, X. Molecular characterization reveals that OsSAPK3 improves drought tolerance and grain yield in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Jin, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhan, C.; Tang, S.; Qin, T.; Liu, N.; Huang, J. OsNAC120 balances plant growth and drought tolerance by integrating GA and ABA signaling in rice. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishor, P.; Hong, Z.; Miao, G.H.; Hu, C.; Verma, D. Overexpression of [delta]-Pyrroline-5-Carboxylate Synthetase Increases Proline Production and Confers Osmotolerance in Transgenic Plants. Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, K.; Hirt, H. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.R.; Schuler, M.A.; Paquette, S.M.; Werck-Reichhart, D.; Bak, S. Comparative genomics of rice and Arabidopsis. Analysis of 727 cytochrome P450 genes and pseudogenes from a monocot and a dicot. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 756–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.; Seebeck, T.; Schrenker, D.; Yu, O. CYP709B3, a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase gene involved in salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, A.; Singh, R.; Shirke, P.A.; Tripathi, R.D.; Trivedi, P.K.; Chakrabarty, D. Expression of Rice CYP450-Like Gene (Os08g01480) in Arabidopsis Modulates Regulatory Network Leading to Heavy Metal and Other Abiotic Stress Tolerance. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138574. [Google Scholar]
- Tamiru, M.; Undan, J.R.; Takagi, H.; Abe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Undan, J.Q.; Natsume, S.; Uemura, A.; Saitoh, H.; Matsumura, H.; et al. A cytochrome P450, OsDSS1, is involved in growth and drought stress responses in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol. Biol. 2015, 88, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancoş, S.; Nomura, T.; Sato, T.; Molnár, G.; Bishop, G.J.; Koncz, C.; Yokota, T.; Nagy, F.; Szekeres, M. Regulation of transcript levels of the Arabidopsis cytochrome p450 genes involved in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, J.; Fujioka, S.; Dilkes, B.P.; Choe, S. Brassinosteroids regulate plant growth through distinct signaling pathways in Selaginella and Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, S.; Kahn, R.A.; Nielsen, H.L.; Moller, B.L.; Halkier, B.A. Cloning of three A-type cytochromes P450, CYP71E1, CYP98, and CYP99 from Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench by a PCR approach and identification by expression in Escherichia coli of CYP71E1 as a multifunctional cytochrome P450 in the biosynthesis of the cyanogenic glucoside dhurrin. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 36, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bak, S.; Tax, F.E.; Feldmann, K.A.; Galbraith, D.W.; Feyereisen, R. CYP83B1, a cytochrome P450 at the metabolic branch point in auxin and indole glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, M.; Ohta, D. Diversification of P450 genes during land plant evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.; Werck-Reichhart, D. A P450-centric view of plant evolution. Plant J. 2011, 66, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, R.; Jiang, S.Y.; Ramachandran, S. Oryza sativa cytochrome P450 family member OsCYP96B4 reduces plant height in a transcript dosage dependent manner. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Cheng, Z.; Li, C. The rice semi-dwarf mutant sd37, caused by a mutation in CYP96B4, plays an important role in the fine-tuning of plant growth. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Jianyu, L.; Xu, T.; Noman, M.; Jameel, A.; Na, Y.; Yuanyuan, D.; Nan, W.; Xiaowei, L.; Fawei, W.; et al. Overexpression of a novel cytochrome P450 promotes flavonoid biosynthesis and osmotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Genes 2019, 10, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Chu, C. Functional specificities of brassinosteroid and potential utilization for crop improvement. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. The transcriptional regulatory network in the drought response and its crosstalk in abiotic stress responses including drought, cold, and heat. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedden, P.; Kamiya, Y. Gibberellin biosynthesis: Enzymes, genes and their regulation. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1997, 48, 431–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Chen, Q.; Xin, P.; Yuan, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Chu, J.; Peters, R.J.; Wang, G. CYP72A enzymes catalyse 13-hydrolyzation of gibberellins. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamski, N.; Anastasiou, E.; Eriksson, S.; O’Neill, C.M.; Lenhard, M. Local maternal control of seed size by KLUH/CYP78A5-dependent growth signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20115–20120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magome, H.; Nomura, T.; Hanada, A.; Takeda-Kamiya, N.; Ohnishi, T.; Shinma, Y.; Katsumata, T.; Kawaide, H.; Kamiya, Y.; Yamaguchi, S. CYP714B1 and CYP714B2 encode gibberellin 13-oxidases that reduce gibberellin activity in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1947–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, S. Gibberellin metabolism and its regulation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M. Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Damage, and Antioxidative Defense Mechanism in Plants under Stressful Conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 217037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Hashimoto, T. Stress-induced expression of NADP-cytochrome P450 reductase genes in Nicotiana sylvestris. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Gao, C. CRISPR/Cas genome editing and precision plant breeding in agriculture. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 667–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, M.; Langridge, P. Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science 2010, 327, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.; Hua, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, B.; Ren, D.; Liu, C.; Yang, S.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, H.; Yu, H.; et al. OsACL-A2 negatively regulates cell death and disease resistance in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruan, B.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, M.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wu, L. Characterization of the ddt1 Mutant in Rice and Its Impact on Plant Height Reduction and Water Use Efficiency. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147629
Ruan B, Jiang Y, Ma Y, Zhou M, Chen F, Zhang Y, Yu Y, Wu L. Characterization of the ddt1 Mutant in Rice and Its Impact on Plant Height Reduction and Water Use Efficiency. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(14):7629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147629
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuan, Banpu, Yaohuang Jiang, Yingying Ma, Menghao Zhou, Fei Chen, Yanli Zhang, Yanchun Yu, and Limin Wu. 2024. "Characterization of the ddt1 Mutant in Rice and Its Impact on Plant Height Reduction and Water Use Efficiency" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 14: 7629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147629
APA StyleRuan, B., Jiang, Y., Ma, Y., Zhou, M., Chen, F., Zhang, Y., Yu, Y., & Wu, L. (2024). Characterization of the ddt1 Mutant in Rice and Its Impact on Plant Height Reduction and Water Use Efficiency. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(14), 7629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147629





