Exploration of the Graphene Quantum Dots-Blue Light Combination: A Promising Treatment against Bacterial Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
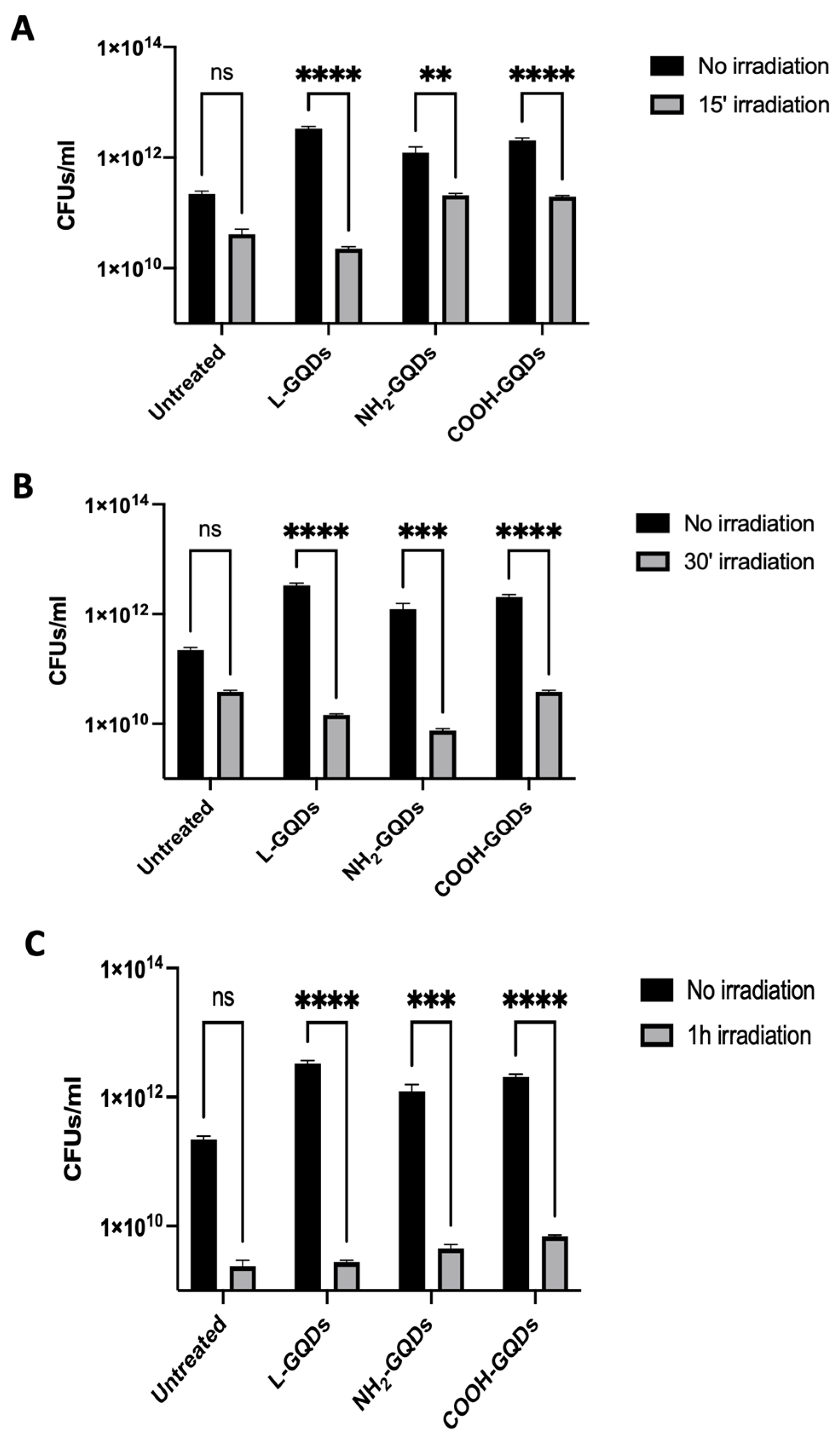
2.1. Stimulation of Graphene Quantum Dots Enhances Their Antibacterial Activity against E. coli
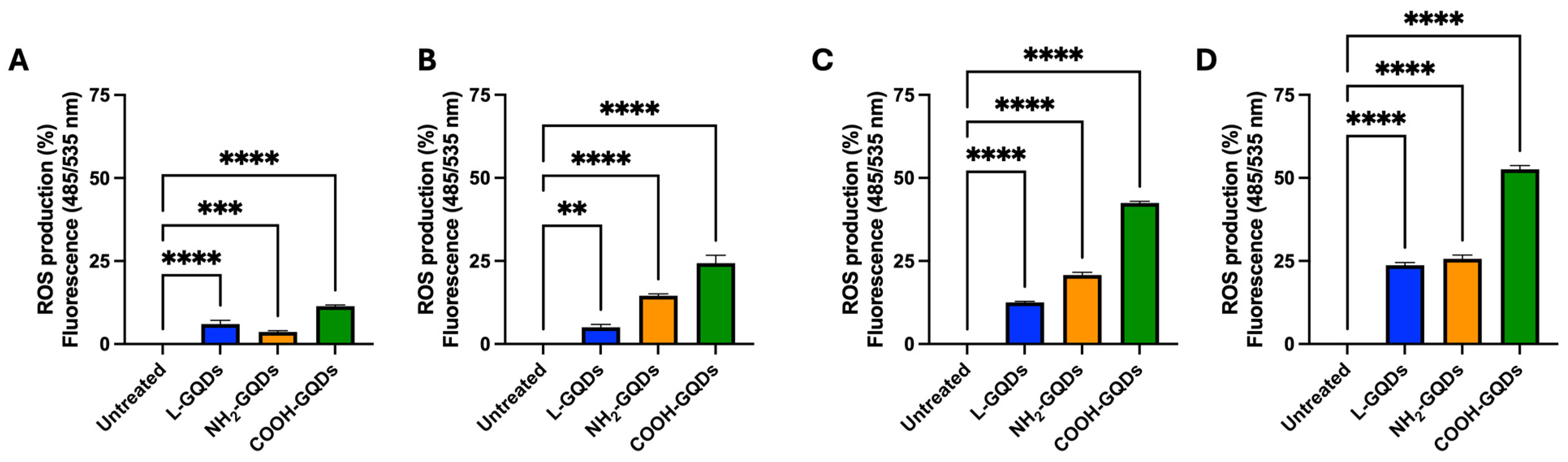
2.2. Stimulated Graphene Quantum Dots Impair E. coli Metabolic Activity
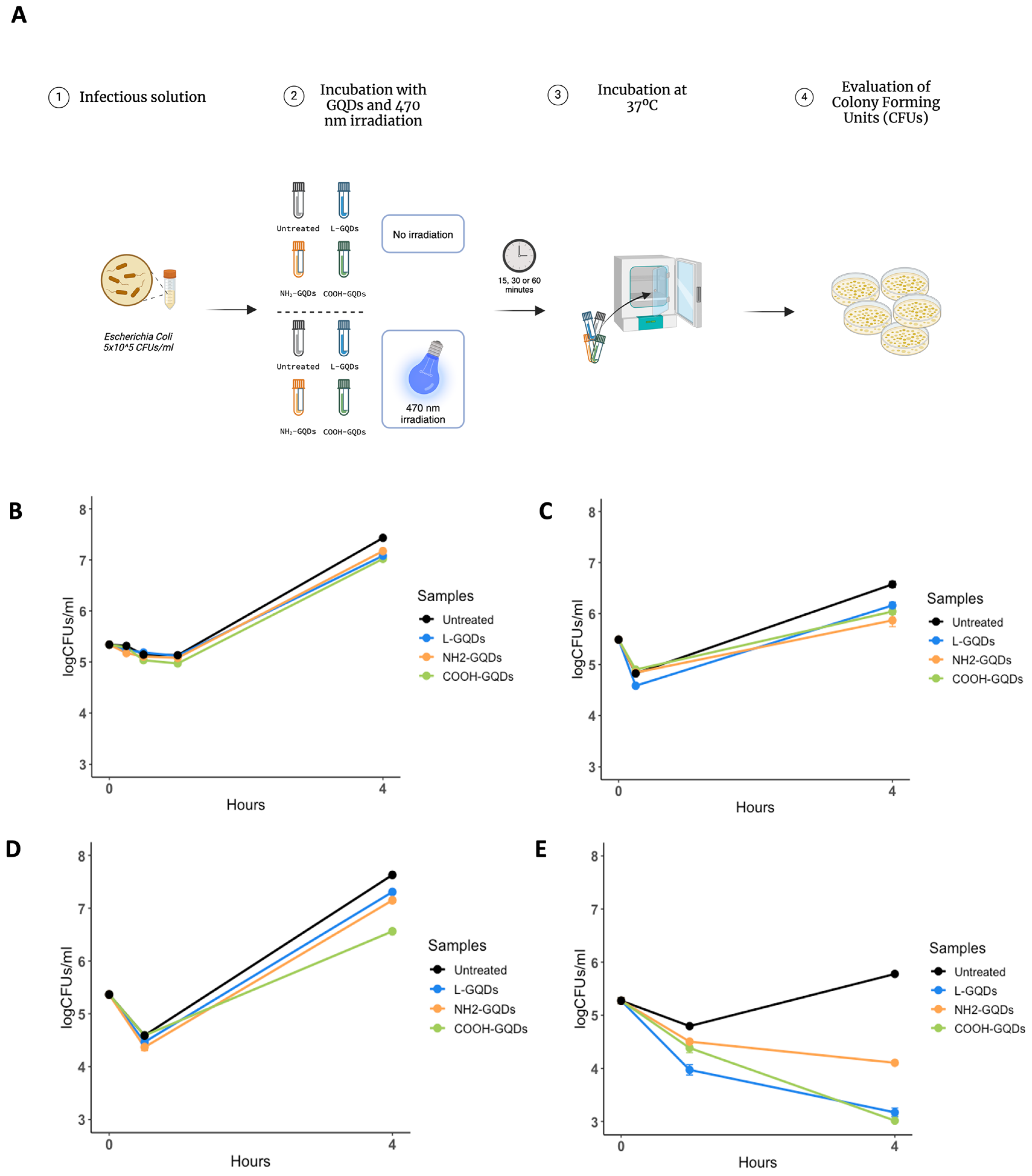
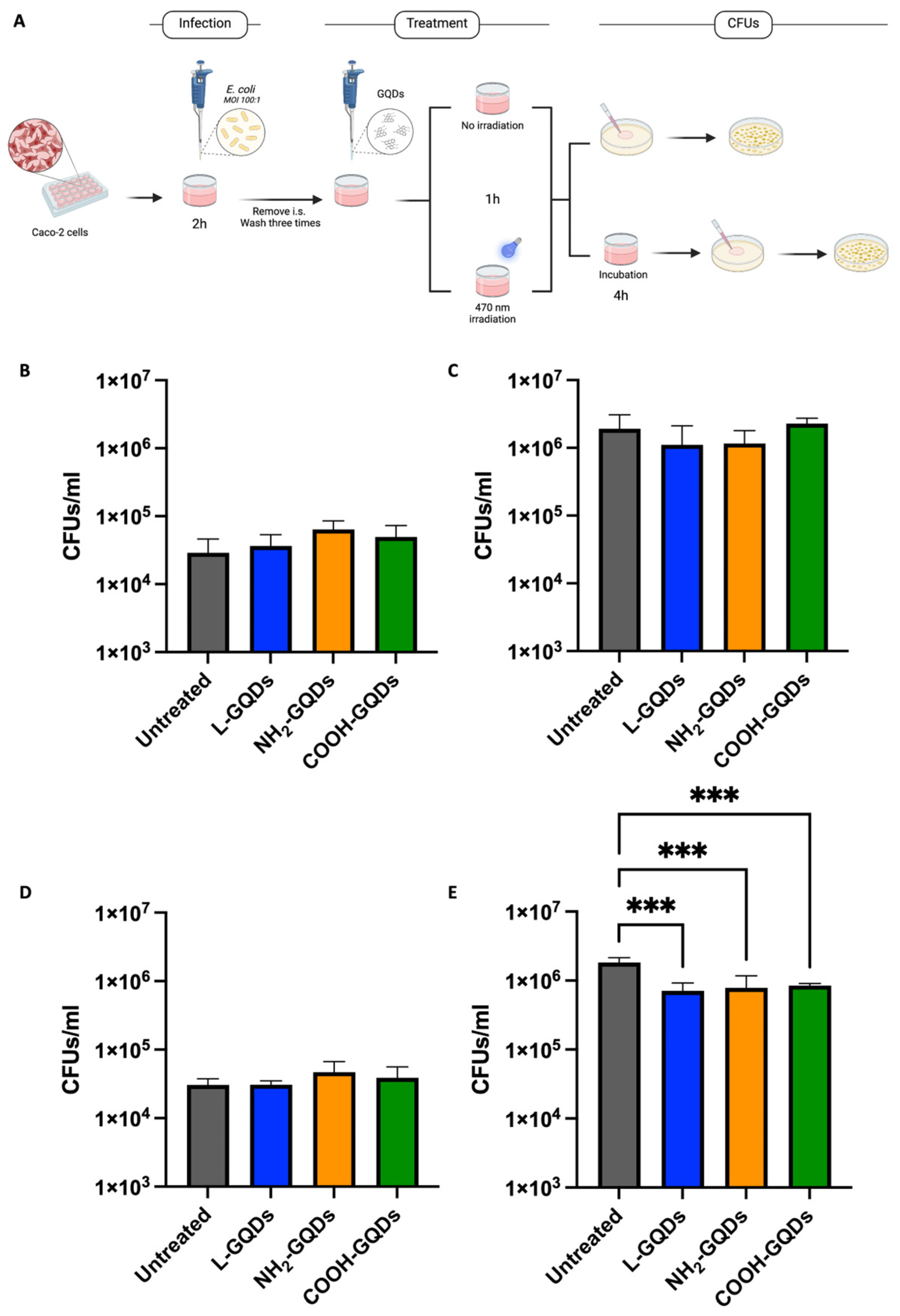
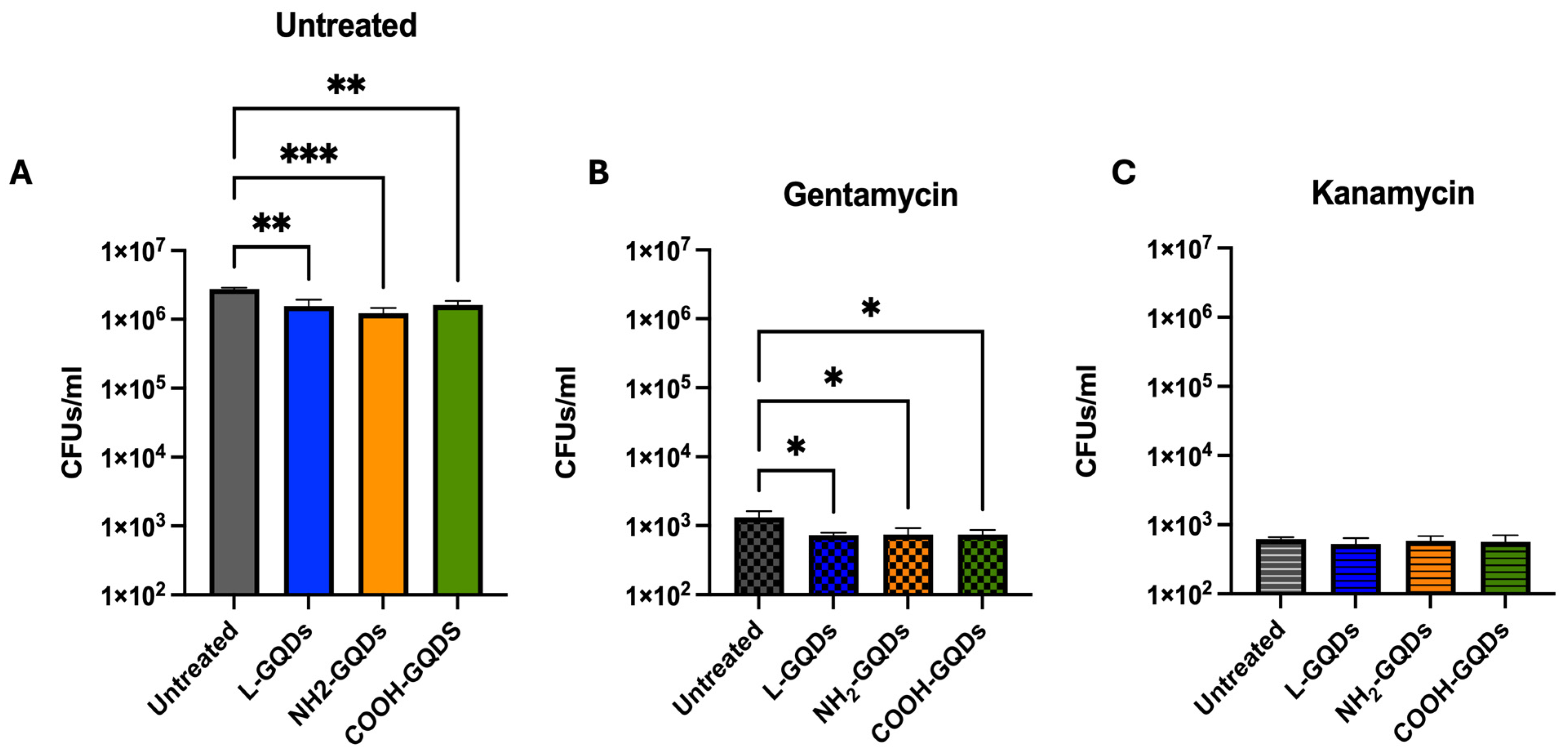
2.3. Graphene Quantum Dots Exert Extracellular Antibacterial Activity during Infection of Epithelial Cells
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Bacterial Manipulation
4.2. Graphene Quantum Dots Features
4.3. In Vitro Antimicrobial Assay
4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.5. Graphene Quantum Dots Effect on E. coli Metabolic Activity
4.6. Assessment of ROS Generation in E. coli Culture
4.7. Caco-2 Cells Culture and Infection
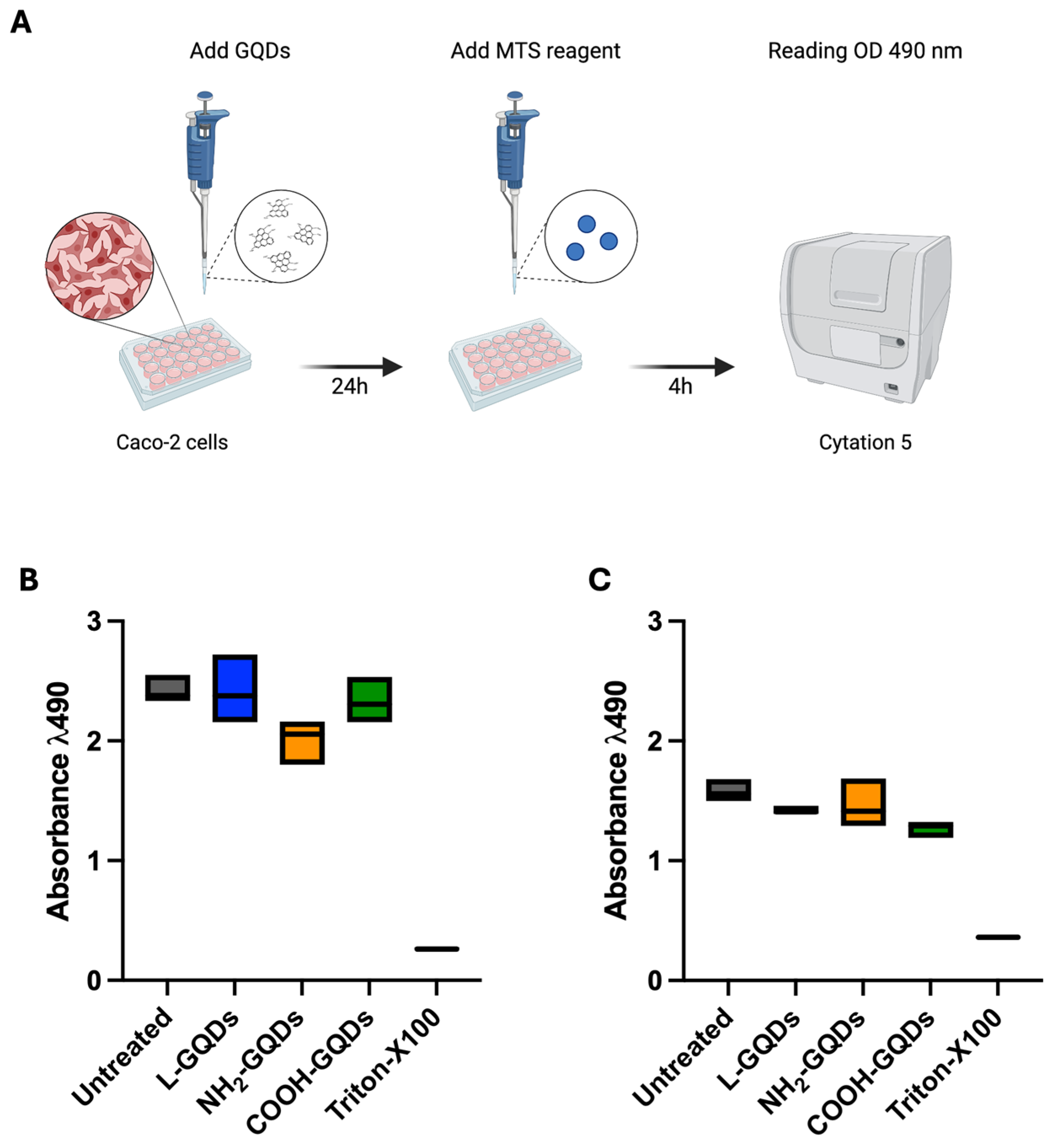
4.8. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity on Caco-2 Cells
4.9. Assessment of ROS Generation in Human Epithelial Cells
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, C.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, N.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Mohammadniaei, M.; Zhang, M.; et al. Synthesis of graphene quantum dots and their applications in drug delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Graphene quantum dots: Emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarelli, G.; Perini, G.; Salustri, A.; Palucci, I.; Rosato, R.; Palmieri, V.; Iacovelli, C.; Bellesi, S.; Sali, M.; Sanguinetti, M.; et al. Unraveling the potential of graphene quantum dots against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1395815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Cui, L.; Losic, D. Graphene and graphene oxide as new nanocarriers for drug delivery applications. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9243–9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Lao, J.; He, H.; Cheng, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Huang, F. Multifunctional graphene quantum dots for simultaneous targeted cellular imaging and drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 122, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, J.; Pan, D.; Chen, Y.; et al. N-Heterocycle Modified Graphene Quantum Dots as Topoisomerase Targeted Nanoantibiotics for Combating Microbial Infections. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2302659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, H.E.; Wiraja, C.; Xu, C.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y. Graphene Materials in Antimicrobial Nanomedicine: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1701406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Lan, M.; Zhou, B.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q.; Niu, G.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.Y.; Yu, X.H.; Wang, K.; Yin, Y.J.; Tang, Y.J.; Tang, Y.L.; Liang, X.H. Graphene quantum dots (GQDs)-based nanomaterials for improving photodynamic therapy in cancer treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Sen Gupta, R.; Bose, S. A comprehensive review on singlet oxygen generation in nanomaterials and conjugated polymers for photodynamic therapy in the treatment of cancer. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 3243–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, Z.M.; Ristic, B.Z.; Arsikin, K.M.; Klisic, D.G.; Harhaji-Trajkovic, L.M.; Todorovic-Markovic, B.M.; Kepic, D.P.; Kravic-Stevovic, T.K.; Jovanovic, S.P.; Milenkovic, M.M.; et al. Graphene quantum dots as autophagy-inducing photodynamic agents. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7084–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hu, C.; Gu, Z.; Dai, L. Understanding of catalytic ROS generation from defect-rich graphene quantum-dots for therapeutic effects in tumor microenvironment. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.J.; Fang, Y.; Yao, M. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 159157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristic, B.Z.; Milenkovic, M.M.; Dakic, I.R.; Todorovic-Markovic, B.M.; Milosavljevic, M.S.; Budimir, M.D.; Paunovic, V.G.; Dramicanin, M.D.; Markovic, Z.M.; Trajkovic, V.S. Photodynamic antibacterial effect of graphene quantum dots. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4428–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisch, T. A new strategy to destroy antibiotic resistant microorganisms: Antimicrobial photodynamic treatment. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh, S.; Koshi, E.; Philip, K.; Mohan, A. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy: An overview. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2011, 15, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuo, W.S.; Chen, H.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, P.C.; Hou, Y.I.; Shao, Y.T.; Kao, H.F.; Lilian Hsu, C.L.; Chen, Y.C.; et al. Graphene quantum dots with nitrogen-doped content dependence for highly efficient dual-modality photodynamic antimicrobial therapy and bioimaging. Biomaterials 2017, 120, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Huo, P.; Zhang, R.; Liu, B. Antibacterial Properties of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, M.T.C. Escherichia coli Infection; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Ren, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, H.; Xia, L. Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Andrade, M.D.; Nguyen, T.A.; Mistler, W.P.; Armas, J.; Lu, J.E.; Roseman, G.; Hollingsworth, W.R.; Nichols, F.; Millhauser, G.L.; Ayzner, A.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of graphene oxide quantum dots: Impacts of chemical reduction. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Gao, N.; Dong, K.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Graphene quantum dots-band-aids used for wound disinfection. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6202–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Maio, F.; Palmieri, V.; De Spirito, M.; Delogu, G.; Papi, M. Carbon nanomaterials: A new way against tuberculosis. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2019, 16, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, V.; Bugli, F.; Lauriola, M.C.; Cacaci, M.; Torelli, R.; Ciasca, G.; Conti, C.; Sanguinetti, M.; Papi, M.; De Spirito, M. Bacteria Meet Graphene: Modulation of Graphene Oxide Nanosheet Interaction with Human Pathogens for Effective Antimicrobial Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Maio, F.; Palmieri, V.; Salustri, A.; Perini, G.; Sanguinetti, M.; De Spirito, M.; Delogu, G.; Papi, M. Graphene oxide prevents mycobacteria entry into macrophages through extracellular entrapment. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Maio, F.; Palmieri, V.; Santarelli, G.; Perini, G.; Salustri, A.; Palucci, I.; Sali, M.; Gervasoni, J.; Primiano, A.; Ciasca, G.; et al. Graphene Oxide-Linezolid Combination as Potential New Anti-Tuberculosis Treatment. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Maio, F.; Palmieri, V.; Babini, G.; Augello, A.; Palucci, I.; Perini, G.; Salustri, A.; Spilman, P.; De Spirito, M.; Sanguinetti, M.; et al. Graphene nanoplatelet and graphene oxide functionalization of face mask materials inhibits infectivity of trapped SARS-CoV-2. iScience 2021, 24, 102788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.; Revia, R.A.; Zhang, M. Graphene Quantum Dots and Their Applications in Bioimaging, Biosensing, and Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e1904362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, A.; Debnath, D.; Dharmadhikari, B.; Patra, P. Graphene Quantum Dots: Synthesis and Applications. Methods Enzymol. 2018, 609, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.L.L.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, C. A Review of Advances in Graphene Quantum Dots: From Preparation and Modification Methods to Application. J. Carbon Res. 2024, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.W.G.; Xiaopei, Q.; Hong, Z.; Lianhua, L.; Liao, P.; Weiling, F.; Luo, Y. Graphene quantum dots in biomedical applications: Recent advances and future challenges. In Handbook of Nanomaterials in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Kalashgrani, M.Y.; Omidifar, N.; Bahrani, S.; Vijayakameswara Rao, N.; Babapoor, A.; Gholami, A.; Chiang, W.H. Bioactive Graphene Quantum Dots Based Polymer Composite for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.S.; He, D.; Chai, M.; Wu, Z.; Yao, X.; Yang, Y. Antibacterial property of graphene quantum dots-modified TiO2 nanorods on titanium dental implant. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2023, 33, 2395–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, N.B.M.; Siffalovic, P.; Kotlar, M.; Micusik, M.; Spitalsky, Z.; Danko, M.; Milivojevic, D.; Kleinova, A.; Kubat, P.; Capakova, Z.; et al. Antibacterial and Antibiofouling Properties of Light Triggered Fluorescent Hydrophobic Carbon Quantum Dots Langmuir-Blodgett Thin Films. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4154–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoblauch, R.; Geddes, C.D. Carbon Nanodots in Photodynamic Antimicrobial Therapy: A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haridas, D.; Atreya, C.D. The microbicidal potential of visible blue light in clinical medicine and public health. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 905606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.X.F.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, P.; Xu, J.; Luo, R.; Xiang, Z.; Rommens, P.; Liu, M.; Ritz, U. Nanomaterials-based photothermal therapies for antibacterial applications. Mater. Des. 2023, 233, 112231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadyan, P.; Thillai Arasu, P.; Kataria, S.K. Graphene Quantum Dots: Green Synthesis, Characterization, and Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Potential. Int. J. Biomater. 2024, 2024, 2626006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Qin, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, S.; Meng, F.; Zhang, M. Based on multi-omics technology study the antibacterial mechanisms of pH-dependent N-GQDs beyond ROS. J. Hazard Mater. 2023, 441, 129954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, B.Z.Q.; Ouyang, P.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, S. Graphene quantum dots enhance the biological nitrogen fixation by up-regulation of cellular metabolism and electron transport. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Gudda, F.O.; Ling, W.; Qin, C.; Gao, Y. Graphene Quantum Dots Nonmonotonically Influence the Horizontal Transfer of Extracellular Antibiotic Resistance Genes via Bacterial Transformation. Small 2023, 19, e2301177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Murray, C.K.; Hamblin, M.R.; Hooper, D.C.; Dai, T. Antimicrobial blue light inactivation of pathogenic microbes: State of the art. Drug Resist. Updates 2017, 33–35, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jao, Y.; Ding, S.J.; Chen, C.C. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy for the treatment of oral infections: A systematic review. J. Dent. Sci. 2023, 18, 1453–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barneck, M.D.; Rhodes, N.L.R.; de la Presa, M.; Allen, J.P.; Poursaid, A.E.; Nourian, M.M.; Firpo, M.A.; Langell, J.T. Violet 405-nm light: A novel therapeutic agent against common pathogenic bacteria. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 206, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, N.L.; de la Presa, M.; Barneck, M.D.; Poursaid, A.; Firpo, M.A.; Langell, J.T. Violet 405 nm light: A novel therapeutic agent against beta-lactam-resistant Escherichia coli. Lasers Surg. Med. 2016, 48, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Tiwari, M.; Donelli, G.; Tiwari, V. Strategies for combating bacterial biofilms: A focus on anti-biofilm agents and their mechanisms of action. Virulence 2018, 9, 522–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupel, K.; Zupin, L.; Ottaviani, G.; Bertani, I.; Martinelli, V.; Porrelli, D.; Vodret, S.; Vuerich, R.; Passos da Silva, D.; Bussani, R.; et al. Blue laser light inhibits biofilm formation in vitro and in vivo by inducing oxidative stress. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, J.; Rahban, D.; Aghamiri, S.; Teymouri, A.; Bahador, A. Photosensitizers in antibacterial photodynamic therapy: An overview. Laser Ther. 2018, 27, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatansever, F.; de Melo, W.C.; Avci, P.; Vecchio, D.; Sadasivam, M.; Gupta, A.; Chandran, R.; Karimi, M.; Parizotto, N.A.; Yin, R.; et al. Antimicrobial strategies centered around reactive oxygen species--bactericidal antibiotics, photodynamic therapy, and beyond. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 955–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Laguna, V.; Garcia-Luque, I.; Ballesta, S.; Rezusta, A.; Gilaberte, Y. Photodynamic Therapy Combined with Antibiotics or Antifungals against Microorganisms That Cause Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: A Planktonic and Biofilm Approach to Overcome Resistances. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, R.; Hoenes, K.; Meurle, T.; Hessling, M.; Spellerberg, B. The effects of violet and blue light irradiation on ESKAPE pathogens and human cells in presence of cell culture media. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Dai, T.; Avci, P.; Jorge, A.E.; de Melo, W.C.; Vecchio, D.; Huang, Y.Y.; Gupta, A.; Hamblin, M.R. Light based anti-infectives: Ultraviolet C irradiation, photodynamic therapy, blue light, and beyond. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 731–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.P.A.; Karthikeyan, C.; Kumar, D.; Khan, R. Multifunctional GQDs for receptor targeting, drug delivery, and bioimaging in pancreatic cancer. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 14698–14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannazzo, D.; Celesti, C.; Espro, C. Recent Advances on Graphene Quantum Dots as Multifunctional Nanoplatforms for Cancer Treatment. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 16, e1900422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maio, F.; Battah, B.; Palmieri, V.; Petrone, L.; Corrente, F.; Salustri, A.; Palucci, I.; Bellesi, S.; Papi, M.; Rubino, S.; et al. PE_PGRS3 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is specifically expressed at low phosphate concentration, and its arginine-rich C-terminal domain mediates adhesion and persistence in host tissues when expressed in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Cell Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Kumar, A.; Bekyarova, E.; Al-Hadeethi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Ansari, M.S.; Cochis, A.; Rimondini, L. Antimicrobial Mechanisms and Effectiveness of Graphene and Graphene-Functionalized Biomaterials. A Scope Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senel, B.; Demir, N.; Buyukkoroglu, G.; Yildiz, M. Graphene quantum dots: Synthesis, characterization, cell viability, genotoxicity for biomedical applications. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 846–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Ji, Y.; Jin, M.; Wang, X. Cellular distribution and cytotoxicity of graphene quantum dots with different functional groups. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacon, N.; Lo Cascio, E.; Pennacchietti, V.; De Maio, F.; Santarelli, G.; Sibilia, D.; Tiberio, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Lattanzi, W.; Toto, A.; et al. PDZ2-conjugated-PLGA nanoparticles are tiny heroes in the battle against SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosato, R.; Santarelli, G.; Augello, A.; Perini, G.; De Spirito, M.; Sanguinetti, M.; Papi, M.; De Maio, F. Exploration of the Graphene Quantum Dots-Blue Light Combination: A Promising Treatment against Bacterial Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158033
Rosato R, Santarelli G, Augello A, Perini G, De Spirito M, Sanguinetti M, Papi M, De Maio F. Exploration of the Graphene Quantum Dots-Blue Light Combination: A Promising Treatment against Bacterial Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158033
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosato, Roberto, Giulia Santarelli, Alberto Augello, Giordano Perini, Marco De Spirito, Maurizio Sanguinetti, Massimiliano Papi, and Flavio De Maio. 2024. "Exploration of the Graphene Quantum Dots-Blue Light Combination: A Promising Treatment against Bacterial Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158033
APA StyleRosato, R., Santarelli, G., Augello, A., Perini, G., De Spirito, M., Sanguinetti, M., Papi, M., & De Maio, F. (2024). Exploration of the Graphene Quantum Dots-Blue Light Combination: A Promising Treatment against Bacterial Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158033








