Membrane Localization of RNase Y Is Important for Global Gene Expression in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
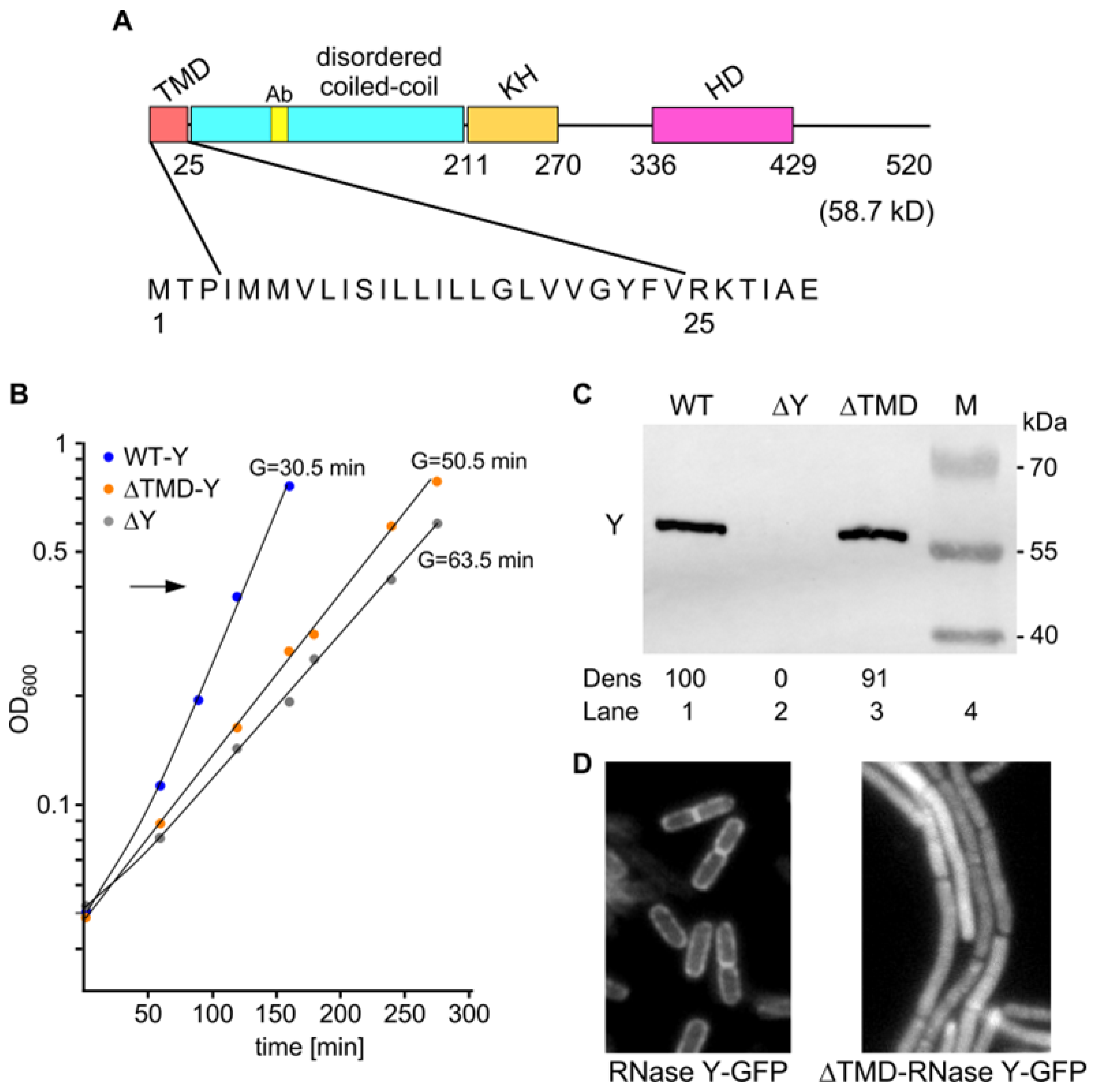
2.1. Effects of Cytoplasmic RNase Y on Cell Morphology and Fitness
2.2. Cytoplasmic Localization of RNase Y Affects Gene Expression on a Genome-Wide Scale
2.3. Modulation of Specific Transcript Levels by Cytoplasmic RNase Y
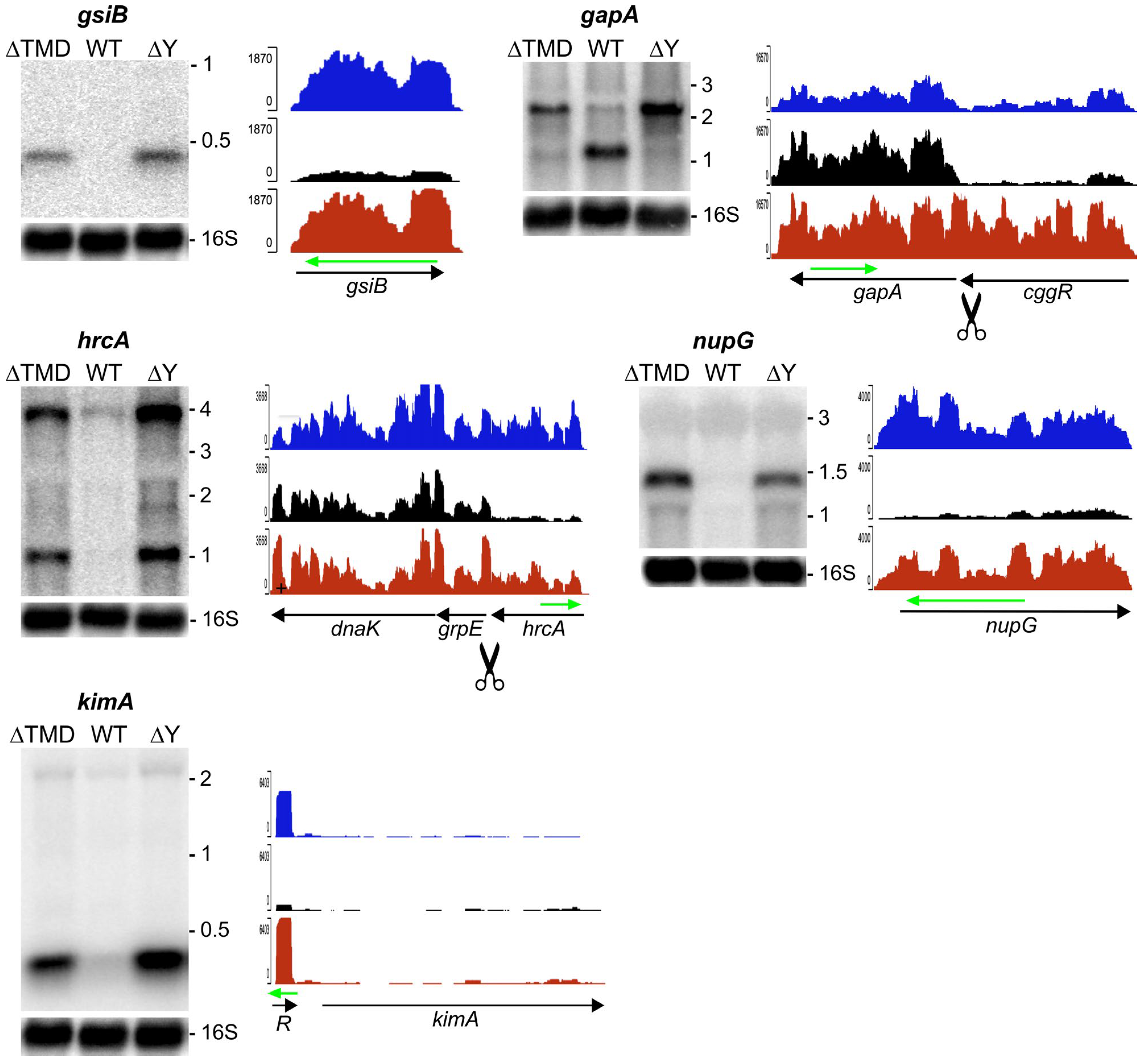
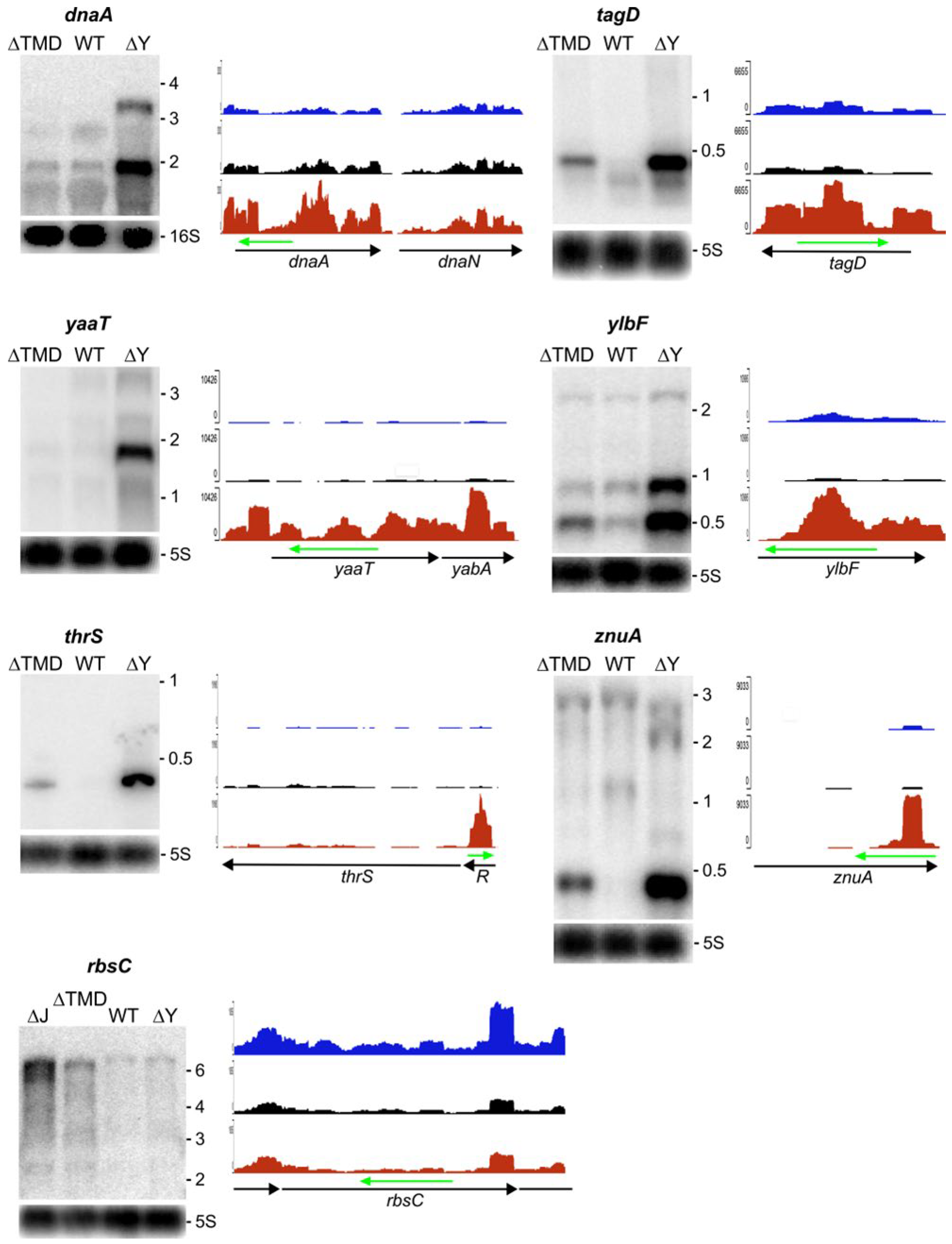
2.3.1. RNA Substrates that Require Membrane Localization of RNase Y
2.3.2. RNA Substrates not Sensitive to RNase Y Localization
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Plasmid Constructs
4.3. Epi-Fluorescence Microscopy
4.4. Northern Blot
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Transcriptome Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laalami, S.; Zig, L.; Putzer, H. Initiation of mRNA decay in bacteria. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2014, 71, 1799–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbabian, K.; Jamalli, A.; Zig, L.; Putzer, H. RNase Y, a novel endoribonuclease, initiates riboswitch turnover in Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 3523–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnik-Habrink, M.; Schaffer, M.; Mader, U.; Diethmaier, C.; Herzberg, C.; Stulke, J. RNA processing in Bacillus subtilis: Identification of targets of the essential RNase Y. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 81, 1459–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, S.; Gilet, L.; Bessieres, P.; Nicolas, P.; Condon, C. Three essential ribonucleases-RNase Y, J1, and III-control the abundance of a majority of Bacillus subtilis mRNAs. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laalami, S.; Bessieres, P.; Rocca, A.; Zig, L.; Nicolas, P.; Putzer, H. Bacillus subtilis RNase Y activity in vivo analysed by tiling microarrays. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Itzek, A.; Malke, H.; Ferretti, J.J.; Kreth, J. Multiple Roles of RNase Y in Streptococcus pyogenes mRNA Processing and Degradation. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2585–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khemici, V.; Prados, J.; Linder, P.; Redder, P. Decay-Initiating Endoribonucleolytic Cleavage by RNase Y Is Kept under Tight Control via Sequence Preference and Sub-cellular Localisation. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marincola, G.; Wolz, C. Downstream element determines RNase Y cleavage of the saePQRS operon in Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 5980–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLoughery, A.; Lalanne, J.B.; Losick, R.; Li, G.W. Maturation of polycistronic mRNAs by the endoribonuclease RNase Y and its associated Y-complex in Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5585–E5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broglia, L.; Lecrivain, A.L.; Renault, T.T.; Hahnke, K.; Ahmed-Begrich, R.; Le Rhun, A.; Charpentier, E. An RNA-seq based comparative approach reveals the transcriptome-wide interplay between 3’-to-5’ exoRNases and RNase Y. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, J.C.; Lalanne, J.-B.; Durand, S.; Braun, F.; Condon, C.; Li, G.-W. A high-resolution view of RNA endonuclease cleavage in Bacillus subtilis. bioRxiv 2023, 2023-03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commichau, F.M.; Rothe, F.M.; Herzberg, C.; Wagner, E.; Hellwig, D.; Lehnik-Habrink, M.; Hammer, E.; Völker, U.; Stülke, J. Novel activities of glycolytic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: Interactions with essential proteins involved in mRNA processing. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2009, 8, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnik-Habrink, M.; Pfortner, H.; Rempeters, L.; Pietack, N.; Herzberg, C.; Stülke, J. The RNA degradosome in Bacillus subtilis: Identification of CshA as the major RNA helicase in the multiprotein complex. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, I.U.; Muller, P.; Brantl, S. A comprehensive study of the interactions in the B. subtilis degradosome with special emphasis on the role of the small proteins SR1P and SR7P. Mol. Microbiol. 2024, 121, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, J.A.; Hewitt, L.; Rodrigues, C.; Solovyova, A.S.; Harwood, C.R.; Lewis, R.J. Dissection of the network of interactions that links RNA processing with glycolysis in the Bacillus subtilis degradosome. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 416, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascante-Estepa, N.; Gunka, K.; Stulke, J. Localization of Components of the RNA-Degrading Machine in Bacillus subtilis. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redder, P. Molecular and genetic interactions of the RNA degradation machineries in Firmicute bacteria. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2018, 9, e1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLoughery, A.; Dengler, V.; Chai, Y.; Losick, R. Biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis requires an endoribonuclease-containing multisubunit complex that controls mRNA levels for the matrix gene repressor SinR. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adusei-Danso, F.; Khaja, F.T.; DeSantis, M.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Dubnau, E.; Demeler, B.; Neiditch, M.B.; Dubnau, D. Structure-Function Studies of the Bacillus subtilis Ric Proteins Identify the Fe-S Cluster-Ligating Residues and Their Roles in Development and RNA Processing. mBio 2019, 10, e01841-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabetta, V.J.; Tanner, A.W.; Greco, T.M.; Defrancesco, M.; Cristea, I.M.; Dubnau, D. A complex of YlbF, YmcA and YaaT regulates sporulation, competence and biofilm formation by accelerating the phosphorylation of Spo0A. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 88, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouche, L.; Billaudeau, C.; Rocca, A.; Chastanet, A.; Ngo, S.; Laalami, S.; Putzer, H. Dynamic Membrane Localization of RNase Y in Bacillus subtilis. mBio 2020, 11, e03337-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, A.; Rawlins, J.P.; Thomaides, H.B.; Errington, J. Functional analysis of 11 putative essential genes in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 2006, 152, 2895–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khemici, V.; Poljak, L.; Luisi, B.F.; Carpousis, A.J. The RNase E of Escherichia coli is a membrane-binding protein. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strahl, H.; Turlan, C.; Khalid, S.; Bond, P.J.; Kebalo, J.M.; Peyron, P.; Poljak, L.; Bouvier, M.; Hamoen, L.; Luisi, B.F.; et al. Membrane recognition and dynamics of the RNA degradosome. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1004961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, P.J.; Thaker, S.D.; Errington, J. Compartmentalization of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascarenhas, J.; Weber, M.H.; Graumann, P.L. Specific polar localization of ribosomes in Bacillus subtilis depends on active transcription. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjeras, L.; Poljak, L.; Bouvier, M.; Morin-Ogier, Q.; Canal, I.; Cocaign-Bousquet, M.; Girbal, L.; Carpousis, A.J. Detachment of the RNA degradosome from the inner membrane of Escherichia coli results in a global slowdown of mRNA degradation, proteolysis of RNase E and increased turnover of ribosome-free transcripts. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 1715–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoya, S.; Asai, K.; Ogasawara, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Sato, T. Mutation in yaaT leads to significant inhibition of phosphorelay during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 5545–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Heijne, G. Membrane protein structure prediction. Hydrophobicity analysis and the positive-inside rule. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 225, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. The HD domain defines a new superfamily of metal-dependent phosphohydrolases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnik-Habrink, M.; Newman, J.; Rothe, F.M.; Solovyova, A.S.; Rodrigues, C.; Herzberg, C.; Commichau, F.M.; Lewis, R.J.; Stulke, J. RNase Y in Bacillus subtilis: A Natively disordered protein that is the functional equivalent of RNase E from Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 5431–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardouin, P.; Velours, C.; Bou-Nader, C.; Assrir, N.; Laalami, S.; Putzer, H.; Durand, D.; Golinelli-Pimpaneau, B. Dissociation of the Dimer of the Intrinsically Disordered Domain of RNase Y upon Antibody Binding. Biophys. J. 2018, 115, 2102–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Stulke, J. SubtiWiki in 2018: From genes and proteins to functional network annotation of the model organism Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, D743–D748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul, B.; Volker, U.; Riethdorf, S.; Engelmann, S.; Hecker, M. sigma B-dependent regulation of gsiB in response to multiple stimuli in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1995, 248, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homuth, G.; Mogk, A.; Schumann, W. Post-transcriptional regulation of the Bacillus subtilis dnaK operon. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 32, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulhbacher, J.; Lafontaine, D.A. Ligand recognition determinants of guanine riboswitches. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 5568–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.W.; Sudarsan, N.; Furukawa, K.; Weinberg, Z.; Wang, J.X.; Breaker, R.R. Riboswitches in eubacteria sense the second messenger c-di-AMP. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundlach, J.; Herzberg, C.; Kaever, V.; Gunka, K.; Hoffmann, T.; Weiss, M.; Gibhardt, J.; Thurmer, A.; Hertel, D.; Daniel, R.; et al. Control of potassium homeostasis is an essential function of the second messenger cyclic di-AMP in Bacillus subtilis. Sci. Signal 2017, 10, eaal3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Helmann, J.D. Molecular logic of the Zur-regulated zinc deprivation response in Bacillus subtilis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laalami, S.; Cavaiuolo, M.; Roque, S.; Chagneau, C.; Putzer, H. Escherichia coli RNase E can efficiently replace RNase Y in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 4643–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even, S.; Pellegrini, O.; Zig, L.; Labas, V.; Vinh, J.; Brechemmier-Baey, D.; Putzer, H. Ribonucleases J1 and J2: Two novel endoribonucleases in B. subtilis with functional homology to E. coli RNase E. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2141–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodson, K.; Devine, K.M. Analysis of a ribose transport operon from Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 1994, 140 Pt 8, 1829–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, L.; Ngo, S.; Laalami, S.; Putzer, H. In Vitro Study of the Major Bacillus subtilis Ribonucleases Y and J. Methods Enzymol. 2018, 612, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogk, A.; Homuth, G.; Scholz, C.; Kim, L.; Schmid, F.X.; Schumann, W. The GroE chaperonin machine is a major modulator of the CIRCE heat shock regulon of Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 4579–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, Y.; Imai, Y.; Ogasawara, N.; Moriya, S. Autoregulation of the dnaA-dnaN operon and effects of DnaA protein levels on replication initiation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 3833–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Santa Maria, J.P., Jr.; Walker, S. Wall teichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, L.; Graumann, P.L. Real-Time Messenger RNA Dynamics in Bacillus subtilis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 760857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorke, B.; Rak, B. Efficient transcriptional antitermination from the Escherichia coli cytoplasmic membrane. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 308, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Husini, N.; Tomares, D.T.; Bitar, O.; Childers, W.S.; Schrader, J.M. alpha-Proteobacterial RNA Degradosomes Assemble Liquid-Liquid Phase-Separated RNP Bodies. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 1027–1039.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laalami, S.; Putzer, H. mRNA degradation and maturation in prokaryotes: The global players. Biomol. Concepts 2011, 2, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäder, U.; Zig, L.; Kretschmer, J.; Homuth, G.; Putzer, H. mRNA processing by RNases J1 and J2 affects Bacillus subtilis gene expression on a global scale. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jester, B.C.; Romby, P.; Lioliou, E. When Ribonucleases Come into Play in Pathogens: A Survey of Gram-Positive Bacteria. Int. J. Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 592196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, R.G.; Casinhas, J.; Barria, C.; Dos Santos, R.F.; Silva, I.J.; Arraiano, C.M. The Role of Ribonucleases and sRNAs in the Virulence of Foodborne Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanisch-Perron, C.; Vieira, J.; Messing, J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: Nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 1985, 33, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horinouchi, S.; Weisblum, B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J. Bacteriol. 1982, 150, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, M.; Chastanet, A.; Debarbouille, M. New vector for efficient allelic replacement in naturally nontransformable, low-GC-content, gram-positive bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6887–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudner, D.Z.; Breger, K.S.; Rio, D.C. Molecular genetic analysis of the heterodimeric splicing factor U2AF: The RS domain on either the large or small Drosophilasubunit is dispensable in vivo. Genes. Dev. 1998, 12, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobeinikova, A.; Laalami, S.; Berthy, C.; Putzer, H. RNase Y Autoregulates Its Synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaiuolo, M.; Chagneau, C.; Laalami, S.; Putzer, H. Impact of RNase E and RNase J on Global mRNA Metabolism in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC6803. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
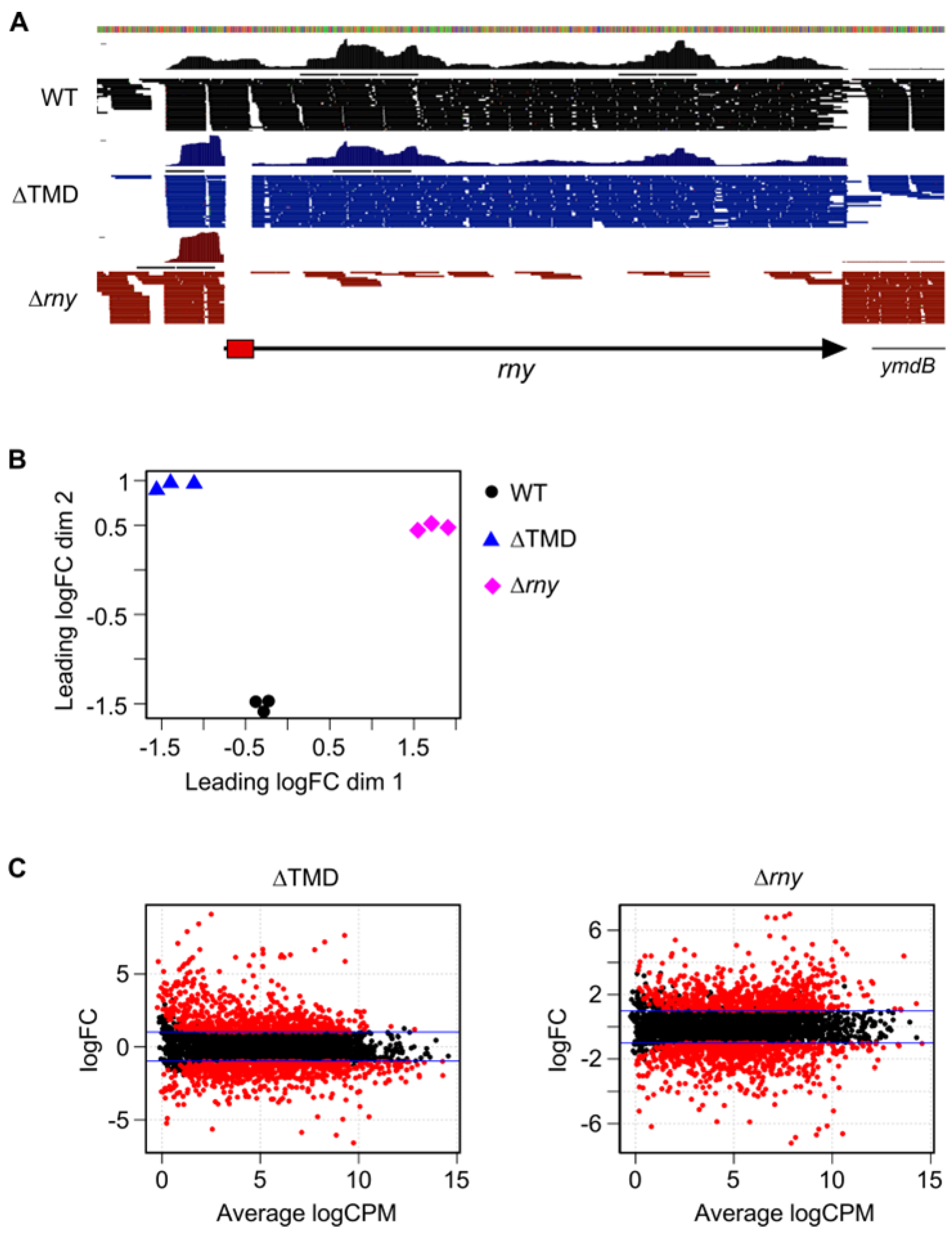
| Strain, Relevant Genotype | No. Upregulated Transcripts | No. Downregulated Transcripts |
|---|---|---|
| SSB574, ∆TMD-RNase Y | 665 | 652 |
| SSB508, ∆rny | 712 | 751 |
| B. subtilis Strain | Relevant Genotype | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| SSB1002 | Wild-type strain | Lab stock |
| SSB507 | ∆amyE::pDR160T | This work |
| SSB508 | ∆rny::cat, ∆amyE::pDR160T | This work |
| SSB574 | ∆rny::cat, ∆amyE::pHMD40 | This work |
| Oligonucleotide | Sequence 5′-3′ |
|---|---|
| HP1696 | GACTCGAGCCGTAGAGTATGCAAAATAAAGGATCCTATC |
| HP1827 | AATGATTAATTAACAACAACCAAGTTCATAGCAAGAGGAGGTGAAAGTATGCGTAAAACCATTGCCGAAGCG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laalami, S.; Cavaiuolo, M.; Oberto, J.; Putzer, H. Membrane Localization of RNase Y Is Important for Global Gene Expression in Bacillus subtilis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158537
Laalami S, Cavaiuolo M, Oberto J, Putzer H. Membrane Localization of RNase Y Is Important for Global Gene Expression in Bacillus subtilis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158537
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaalami, Soumaya, Marina Cavaiuolo, Jacques Oberto, and Harald Putzer. 2024. "Membrane Localization of RNase Y Is Important for Global Gene Expression in Bacillus subtilis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158537
APA StyleLaalami, S., Cavaiuolo, M., Oberto, J., & Putzer, H. (2024). Membrane Localization of RNase Y Is Important for Global Gene Expression in Bacillus subtilis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158537







