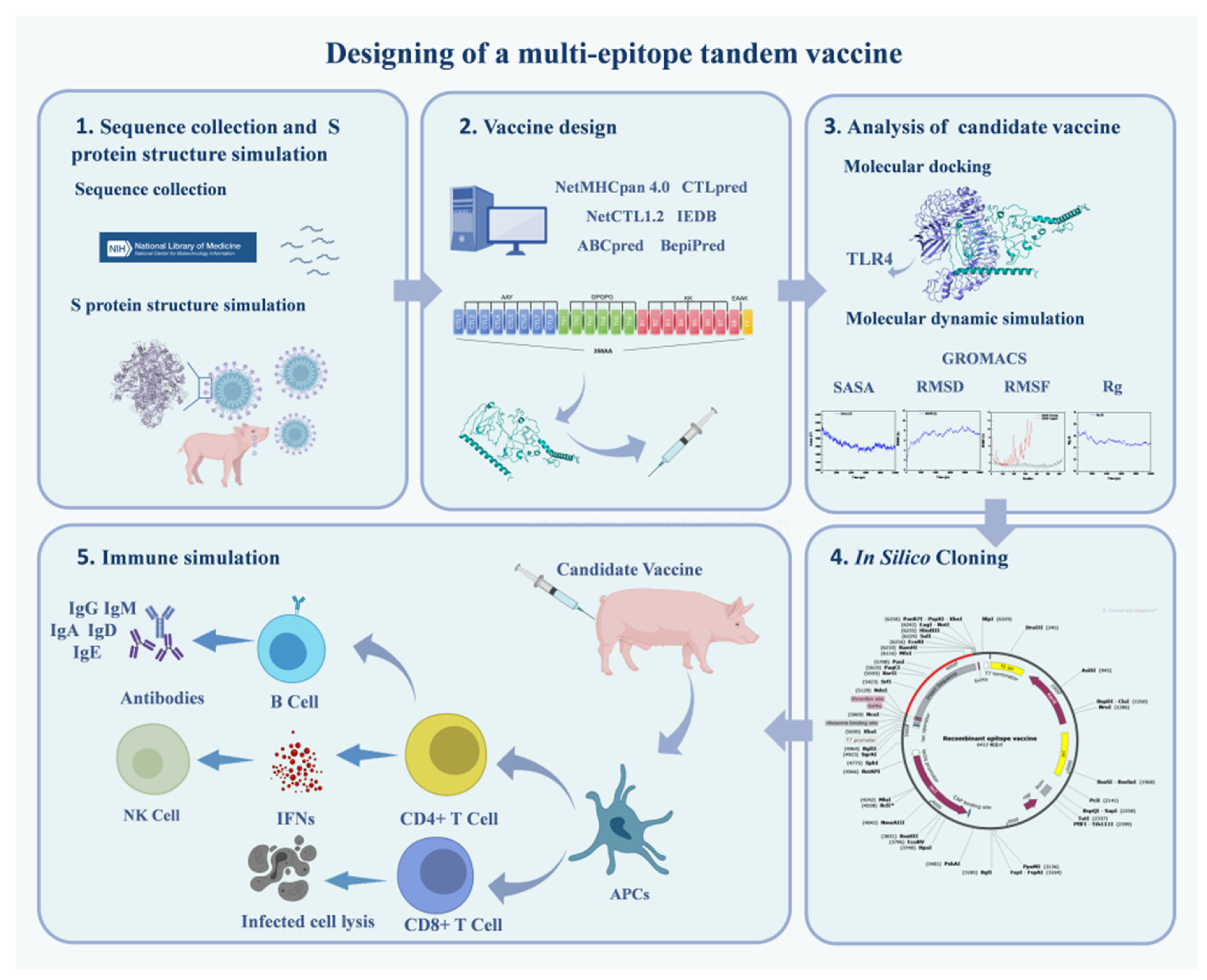
Designing a Candidate Multi-Epitope Vaccine against Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus Based on Immunoinformatic and Molecular Dynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
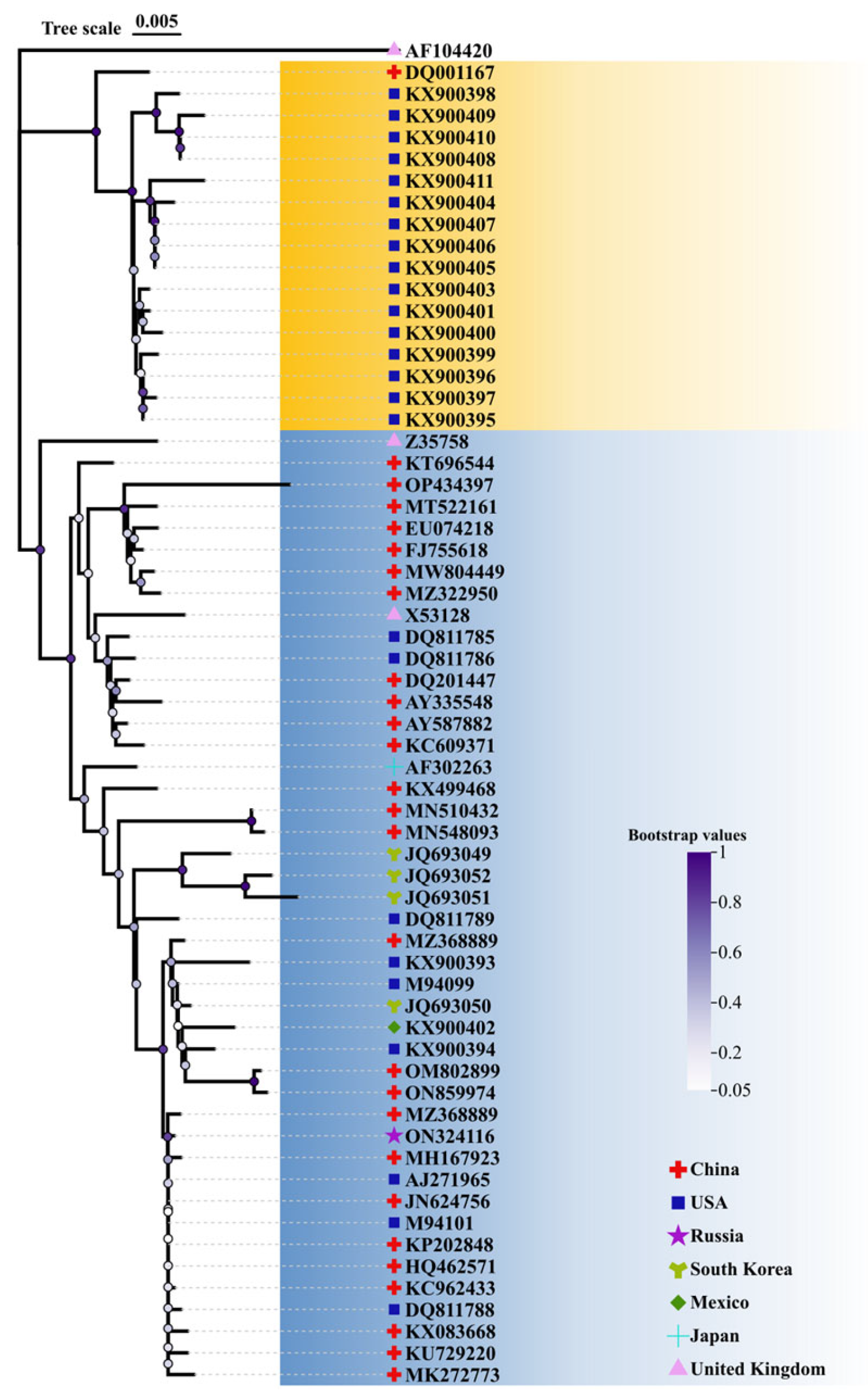
2.1. Conservative Analysis of TGEV S Protein and Selection of Vaccine Strain
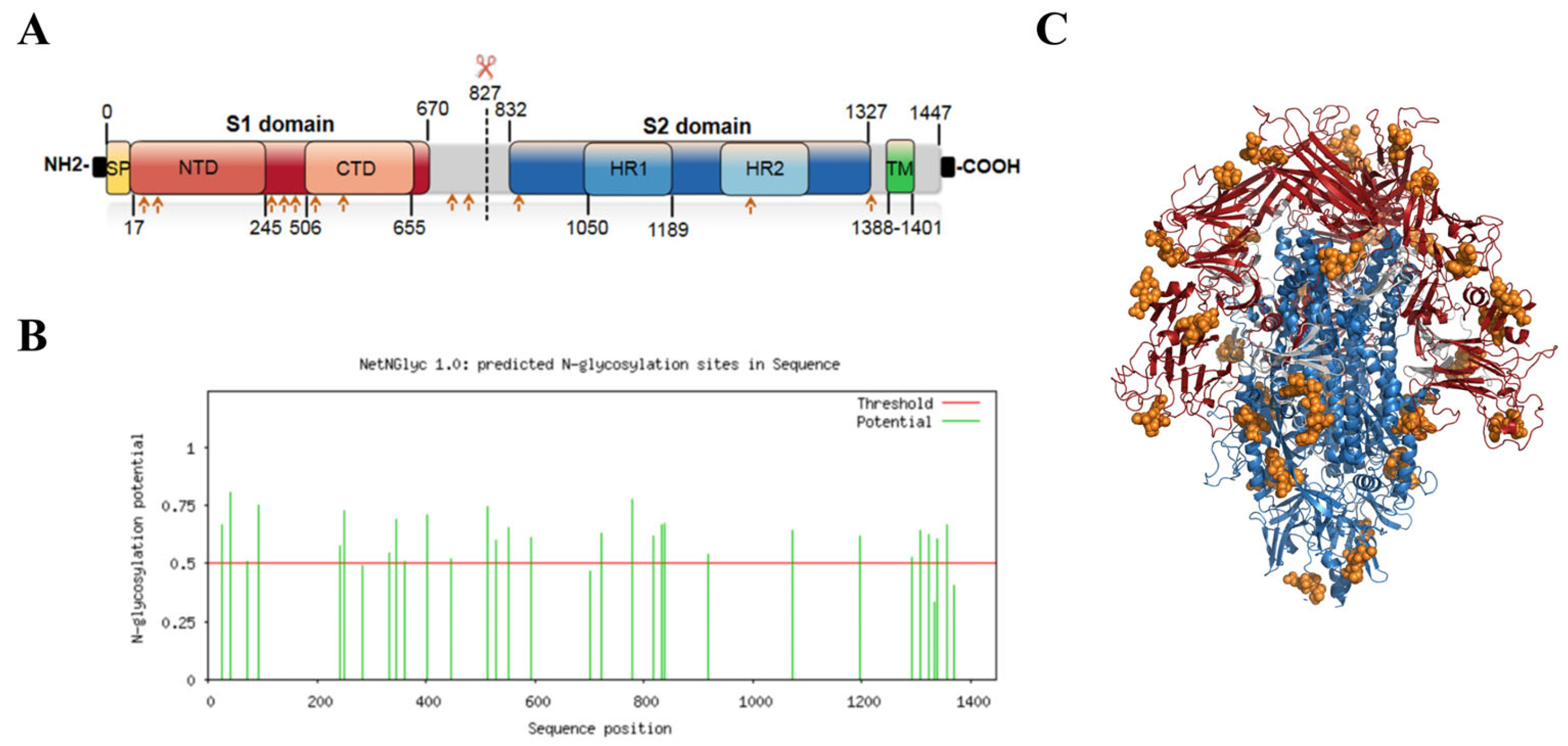
2.2. S Protein Structure Simulation and Glycosylation Site Prediction
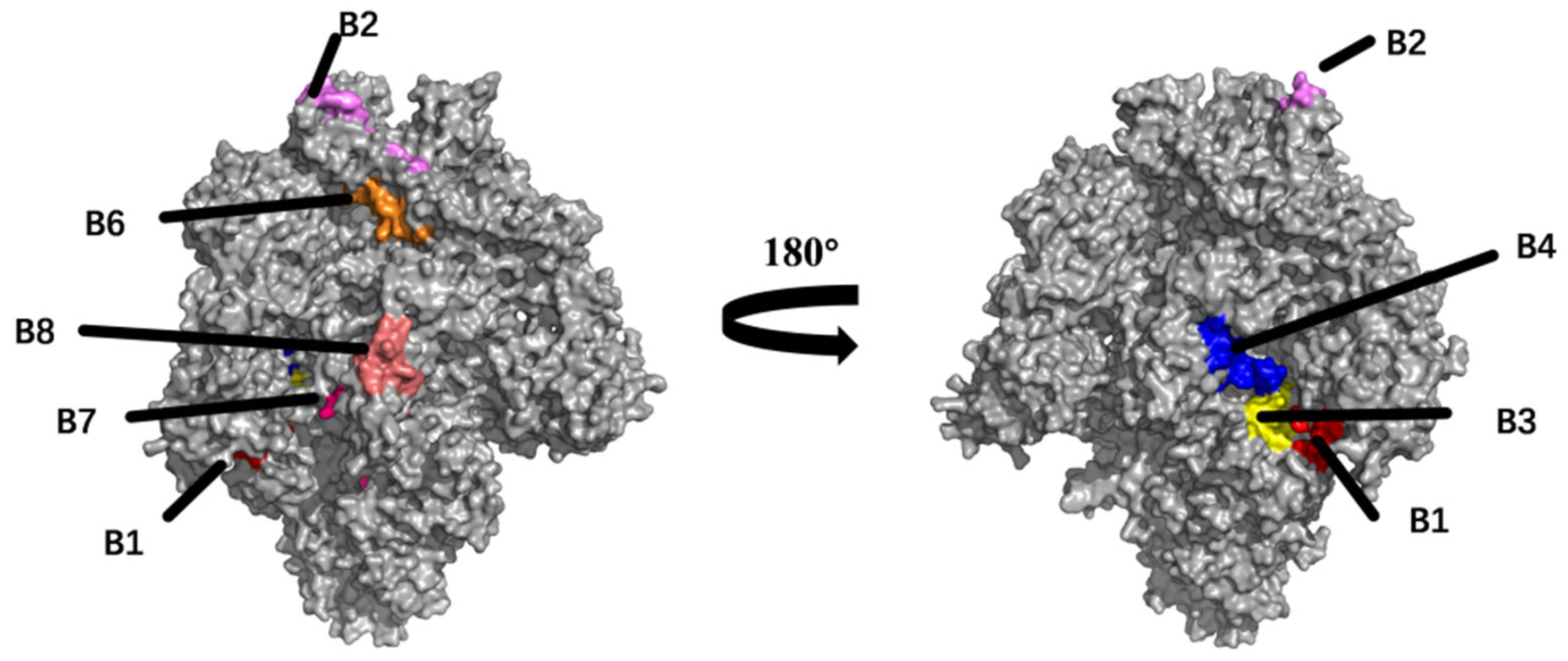
2.3. Prediction and Analysis of B Cell Epitopes
2.4. T Cell Epitopes Prediction
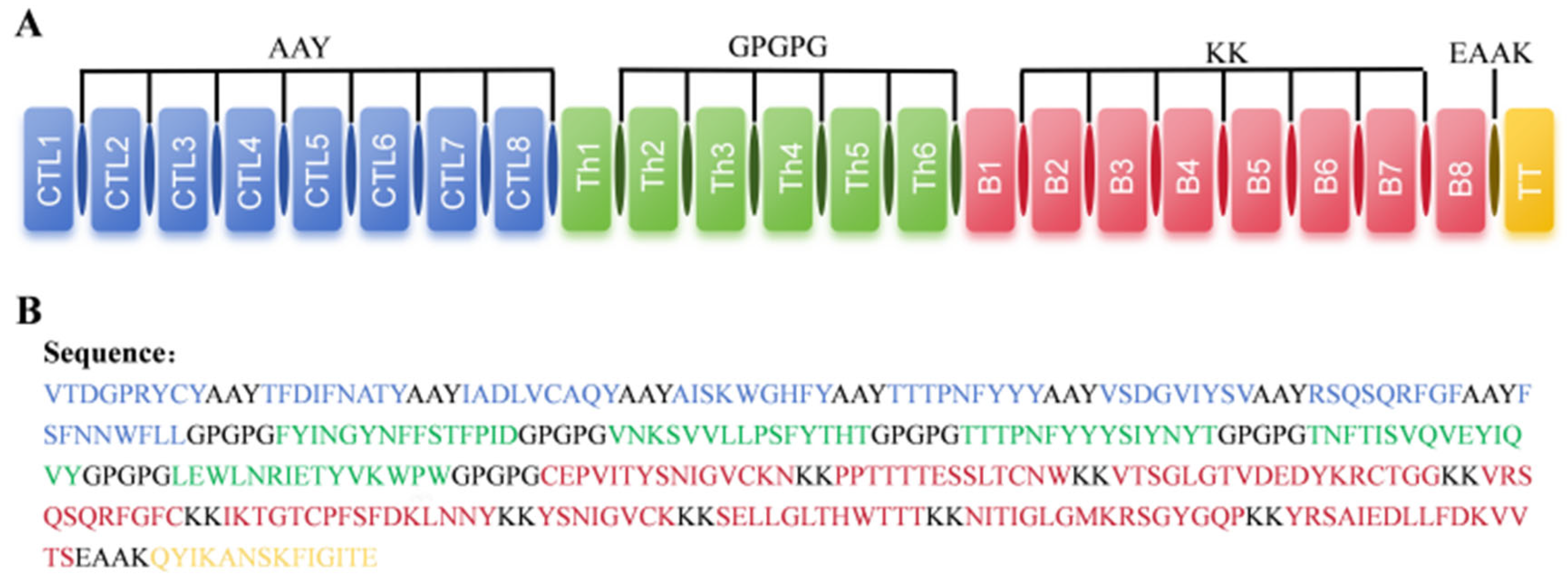
2.5. Design of Multi-Epitope Vaccine Candidate
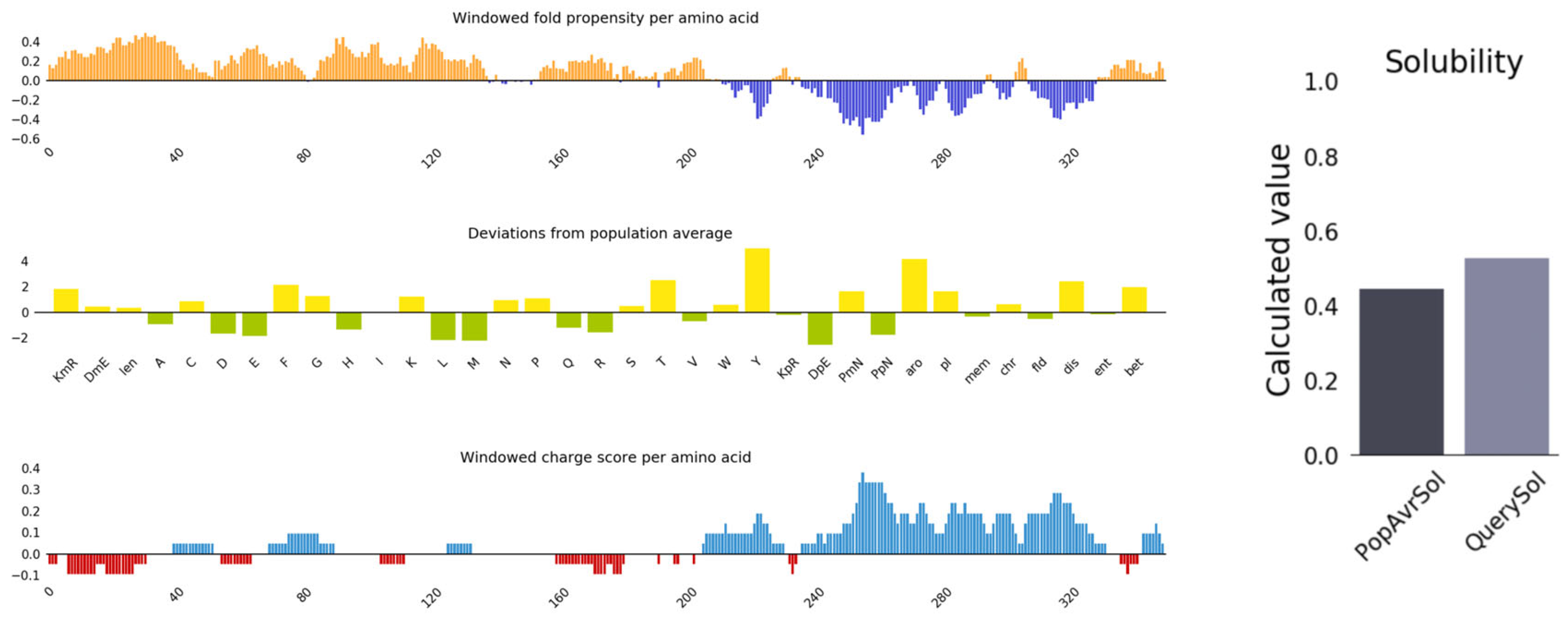
2.6. Antigenicity, Allergenicity, and Physicochemical Properties Evaluation of Vaccine Candidate
2.7. Secondary and Tertiary Structure Prediction of Vaccine
2.8. Prediction of Conformational B Cell Epitopes
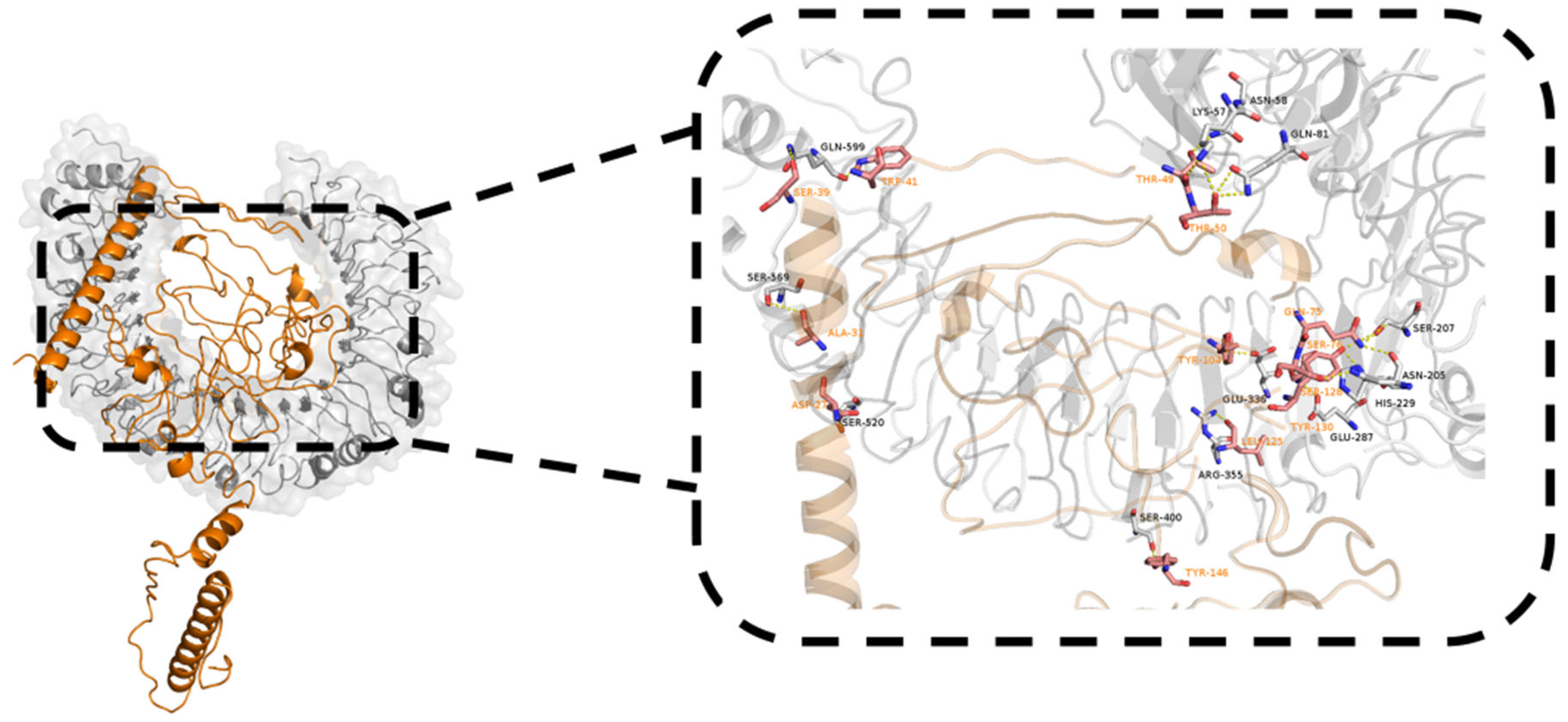
2.9. Molecular Docking with TLR4
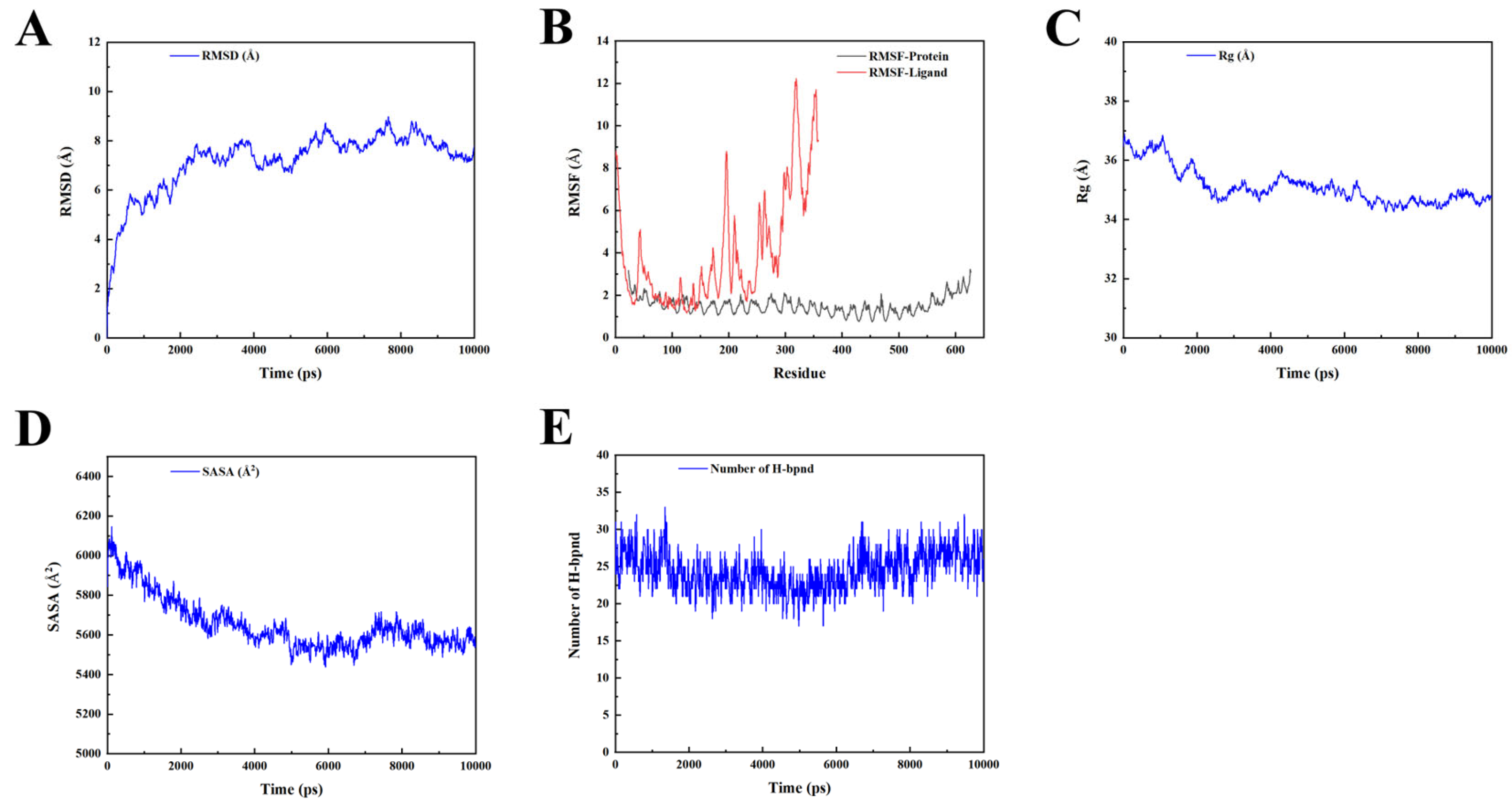
2.10. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
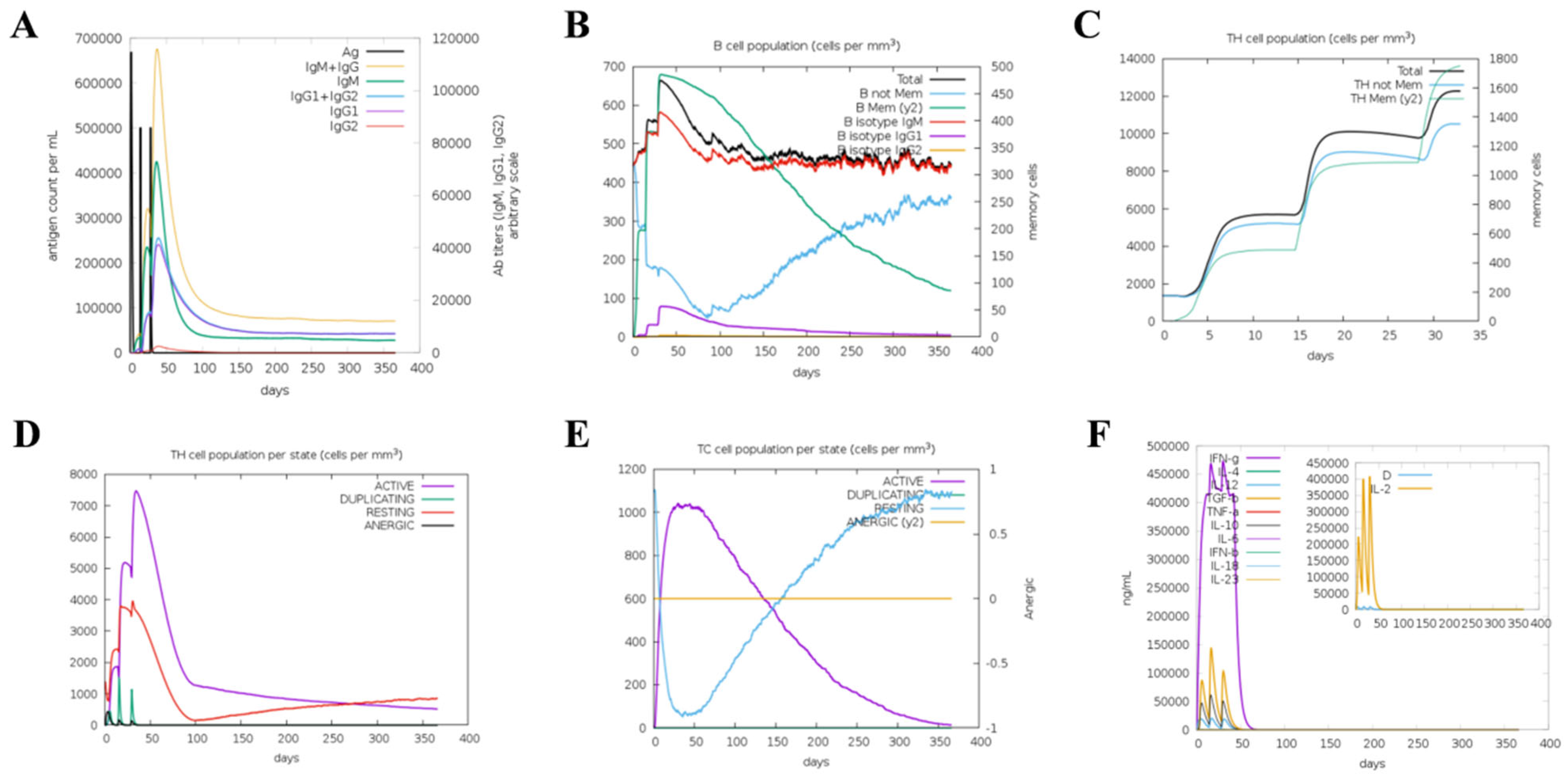
2.11. Simulation of Immune Responses
2.12. Optimization of Codons and In Silico Cloning
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sequence Datasets and Phylogenetic Tree Analysis
4.2. Tertiary Structure Simulation and N-Glycosylation Site Prediction of TGEV S Protein
4.3. Prediction of B Cell Epitopes
4.4. T Cell Epitope Prediction
4.5. Molecular Docking of CD8 T Cell Epitopes with SLA Alleles
4.6. Antigenicity, Allergenicity, Toxicity, and Conservation Analysis
4.7. Construction of the Vaccine, Structure Modelling, and Validation
4.8. Secondary and Tertiary Structure Prediction
4.9. Prediction of Conformational B Cell Epitopes
4.10. Molecular Docking of Vaccine with TLR4 and Molecular Dynamic Simulation
4.11. Simulation of Immune Responses against Designed Vaccines
4.12. Codon Optimization and In Silico Cloning
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.P.; Hutchings, L.M. A transmissible gastroenteritis in pigs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1946, 108, 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, H.Y. Porcine enteric coronaviruses: An updated overview of the pathogenesis, prevalence, and diagnosis. Vet. Res. Commun. 2021, 45, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlewicz-Podbielska, H.; Pomorska-Mól, M. Porcine Coronaviruses: Overview of the State of the Art. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yount, B.; Curtis, K.M.; Baric, R.S. Strategy for systematic assembly of large RNA and DNA genomes: Transmissible gastroenteritis virus model. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10600–10611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garwes, D.J.; Pocock, D.H.; Pike, B.V. Isolation of subviral components from transmissible gastroenteritis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1976, 32, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, B.J.; van der Zee, R.; de Haan, C.A.; Rottier, P.J. The coronavirus spike protein is a class I virus fusion protein: Structural and functional characterization of the fusion core complex. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8801–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belouzard, S.; Millet, J.K.; Licitra, B.N.; Whittaker, G.R. Mechanisms of coronavirus cell entry mediated by the viral spike protein. Viruses 2012, 4, 1011–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, M.L.; Sánchez, C.M.; Enjuanes, L. Two amino acid changes at the N-terminus of transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus spike protein result in the loss of enteric tropism. Virology 1997, 227, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, B.; Gelfi, J.; L’Haridon, R.; Vogel, L.K.; Sjöström, H.; Norén, O.; Laude, H. Aminopeptidase N is a major receptor for the entero-pathogenic coronavirus TGEV. Nature 1992, 357, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.M.; Saif, L.J.; Marthaler, D.; Wang, Q. Evolution, antigenicity and pathogenicity of global porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleman, M.; Asad, U.; Arshad, S.; Rahman, A.U.; Akbar, F.; Khan, H.; Hussain, Z.; Ali, S.S.; Mohammad, A.; Khan, A.; et al. Screening of immune epitope in the proteome of the Dabie bandavirus, SFTS, to design a protein-specific and proteome-wide vaccine for immune response instigation using an immunoinformatics approaches. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 148, 105893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleman, M.; Khan, S.H.; Rashid, F.; Khan, A.; Hussain, Z.; Zaman, N.; Rehman, S.U.; Zhai, J.; Xue, M.; Zheng, C. Designing a multi-epitopes subunit vaccine against human herpes virus 6A based on molecular dynamics and immune stimulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danazumi, A.U.; Iliyasu Gital, S.; Idris, S.; Bs Dibba, L.; Balogun, E.O.; Górna, M.W. Immunoinformatic design of a putative multi-epitope vaccine candidate against Trypanosoma brucei gambiense. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 5574–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cui, X.; Yan, Z.; Tao, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Y.; Shi, L. Design and evaluation of a multi-epitope DNA vaccine against HPV16. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2024, 20, 2352908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennerz, V.; Gross, S.; Gallerani, E.; Sessa, C.; Mach, N.; Boehm, S.; Hess, D.; von Boehmer, L.; Knuth, A.; Ochsenbein, A.F.; et al. Immunologic response to the survivin-derived multi-epitope vaccine EMD640744 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2014, 63, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Xue, Y.; Wang, J.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Gong, W. Evaluation of the consistence between the results of immunoinformatics predictions and real-world animal experiments of a new tuberculosis vaccine MP3RT. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1047306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eickhoff, C.S.; Terry, F.E.; Peng, L.; Meza, K.A.; Sakala, I.G.; Van Aartsen, D.; Moise, L.; Martin, W.D.; Schriewer, J.; Buller, R.M.; et al. Highly conserved influenza T cell epitopes induce broadly protective immunity. Vaccine 2019, 37, 5371–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Popova, L.; Kwinn, L.; Haynes, L.M.; Jones, L.P.; Tripp, R.A.; Walsh, E.E.; Freeman, M.W.; Golenbock, D.T.; Anderson, L.J.; et al. Pattern recognition receptors TLR4 and CD14 mediate response to respiratory syncytial virus. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Sen Gupta, P.S.; Panda, S.K.; Rana, M.K.; Mukherjee, S. Designing AbhiSCoVac—A single potential vaccine for all ‘corona culprits’: Immunoinformatics and immune simulation approaches. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 351, 118633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, B.; Yoo, D.; Qin, T.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Y.; Cui, S. Animal coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1097–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdts, V.; Zakhartchouk, A. Vaccines for porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and other swine coronaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Ma, L.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Ouyang, H.; Yuan, H.; Pang, D. Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus: An Update Review and Perspective. Viruses 2023, 15, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir Ul Qamar, M.; Saleem, S.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Bari, A.; Anwar, F.; Alqahtani, S. Epitope-based peptide vaccine design and target site depiction against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus: An immune-informatics study. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, L.; Gaieb, Z.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hjorth, C.K.; Dommer, A.C.; Harbison, A.M.; Fogarty, C.A.; Barros, E.P.; Taylor, B.C.; McLellan, J.S.; et al. Beyond Shielding: The Roles of Glycans in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Xiong, X.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Snijder, J.; Quispe, J.; Cameroni, E.; Gopal, R.; Dai, M.; Lanzavecchia, A.; et al. Unexpected Receptor Functional Mimicry Elucidates Activation of Coronavirus Fusion. Cell 2019, 176, 1026–1039.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Feng, L.; Shi, H.; Chen, J.; Cui, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Tong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tong, G. Identification of two novel B cell epitopes on porcine epidemic diarrhea virus spike protein. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 131, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zaro, J.L.; Shen, W.C. Fusion protein linkers: Property, design and functionality. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, S.K.; Vir, P.; Raghava, G.P. Designing of interferon-gamma inducing MHC class-II binders. Biol. Direct 2013, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, D.; Jones, G.; Pirson, C.; Malone, K.; Rue-Albrecht, K.; Chubb, A.J.; Vordermeier, M.; Gordon, S.V. Integrated computational prediction and experimental validation identifies promiscuous T cell epitopes in the proteome of Mycobacterium bovis. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwede, T.; Kopp, J.; Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL: An automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3381–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, R.; Overton, J.A.; Greenbaum, J.A.; Ponomarenko, J.; Clark, J.D.; Cantrell, J.R.; Wheeler, D.K.; Gabbard, J.L.; Hix, D.; Sette, A.; et al. The immune epitope database (IEDB) 3.0. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D405–D412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P. Prediction of continuous B-cell epitopes in an antigen using recurrent neural network. Proteins 2006, 65, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhasin, M.; Raghava, G.P. Prediction of CTL epitopes using QM, SVM and ANN techniques. Vaccine 2004, 22, 3195–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, S.K.; Gupta, S.; Vir, P.; Raghava, G.P. Prediction of IL4 inducing peptides. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 263952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajda, S.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Bohnuud, T.; Mottarella, S.E.; Xia, B.; Hall, D.R.; Kozakov, D. New additions to the ClusPro server motivated by CAPRI. Proteins 2017, 85, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, I.; Bangov, I.; Flower, D.R.; Doytchinova, I. AllerTOP v.2—A server for in silico prediction of allergens. J. Mol. Model. 2014, 20, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kapoor, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Gautam, A.; Kumar, R.; Raghava, G.P. In silico approach for predicting toxicity of peptides and proteins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. VaxiJen: A server for prediction of protective antigens, tumour antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.H.; Sidney, J.; Li, W.; Fusseder, N.; Sette, A. Development of an epitope conservancy analysis tool to facilitate the design of epitope-based diagnostics and vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchan, D.W.; Minneci, F.; Nugent, T.C.; Bryson, K.; Jones, D.T. Scalable web services for the PSIPRED Protein Analysis Workbench. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W349–W357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, L.; Park, H.; Seok, C. GalaxyRefine: Protein structure refinement driven by side-chain repacking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W384–W388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, S.N.; Li, K. Toll-like receptors in antiviral innate immunity. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 1246–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, P.; Li, B.; Huang, S.Y. HDOCK: A web server for protein-protein and protein-DNA/RNA docking based on a hybrid strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W365–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, M.; Nagashima, U. Particle mesh Ewald method for three-dimensional systems with two-dimensional periodicity. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2001, 340, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, A.; Hiller, K.; Scheer, M.; Münch, R.; Nörtemann, B.; Hempel, D.C.; Jahn, D. JCat: A novel tool to adapt codon usage of a target gene to its potential expression host. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W526–W531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Epitope | Length | Position | Sequence | Toxin | Identity (62 Isolates) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 14 | 137–150 | PPTTTTESSLTCNW | Non-Toxin | 87.09% (55/62) |
| B2 | 16 | 530–545 | NITIGLGMKRSGYGQP | Non-Toxin | 96.77% (60/62) |
| B3 | 12 | 955–970 | YRSAIEDLLFDKVVTS | Non-Toxin | 93.54% (58/62) |
| B4 | 18 | 968–985 | VTSGLGTVDEDYKRCTGG | Non-Toxin | 91.93% (57/62) |
| B5 | 11 | 1186–1196 | VRSQSQRFGFC | Non-Toxin | 96.77% (60/62) |
| B6 | 16 | 603–618 | IKTGTCPFSFDKLNNY | Non-Toxin | 85.48% (53/62) |
| B7 | 8 | 802–809 | YSNIGVCK | Non-Toxin | 100.00% (62/62) |
| B8 | 12 | 757–768 | SELLGLTHWTTT | Non-Toxin | 98.38% (61/62) |
| Epitope | Length | Position | Sequence | Score | Rank | TAP Score | Proteasome Score | MHC Ⅰ IC50 (nM) | Toxin | Identity (62 Isolates) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTL1 | 9 | 275–283 | FSFNNWFLL | 0.90876 | 0.15 | 0.43 | 1.79 | 307.9 | Non-Toxin | 100.00% (62/62) |
| CTL2 | 9 | 391–399 | VTDGPRYCY | 0.968509 | 0.02 | 1.2 | 2.75 | 62.2 | Non-Toxin | 93.54% (58/62) |
| CTL3 | 9 | 421–429 | AISKWGHFY | 0.871218 | 0.07 | 1.39 | 2.68 | 42.3 | Non-Toxin | 96.77% (60/62) |
| CTL4 | 9 | 724–732 | VSDGVIYSV | 0.776052 | 0.23 | 1.25 | 1.32 | 210.6 | Non-Toxin | 100.00% (62/62) |
| CTL5 | 9 | 766–774 | TTTPNFYYY | 0.745044 | 0.17 | 1.21 | 1.54 | 67.7 | Non-Toxin | 100.00% (62/62) |
| CTL6 | 9 | 988–996 | IADLVCAQY | 0.880338 | 0.06 | 1.17 | 1.46 | 90.8 | Non-Toxin | 100.00% (62/62) |
| CTL7 | 9 | 1187–1195 | RSQSQRFGF | 0.418621 | 0.04 | 1.15 | 1.22 | 148.8 | Non-Toxin | 100.00% (62/62) |
| CTL8 | 9 | 1329–1337 | TFDIFNATY | 0.818436 | 0.12 | 1.35 | 1.28 | 98 | Non-Toxin | 96.77% (60/62) |
| Epitope | Length | Position | Sequence | Rank | IL-4 | IFN | MHC Ⅱ IC50 (nM) | Toxin | Identity (62 Isolates) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th1 | 15 | 428–442 | FYINGYNFFSTFPID | 0.84 | IL4-inducer | Positive | 45.63 | Non-Toxin | 91.93% (57/62) |
| Th2 | 15 | 513–527 | VNKSVVLLPSFYTHT | 0.37 | IL4-inducer | Positive | 32.82 | Non-Toxin | 85.48% (53/62) |
| Th3 | 15 | 766–780 | TTTPNFYYYSIYNYT | 2.9 | IL4-inducer | Positive | 160.09 | Non-Toxin | 100.00% (62/62) |
| Th4 | 15 | 796–810 | CEPVITYSNIGVCKN | 1.1 | IL4-inducer | Positive | 31.1 | Non-Toxin | 100.00% (62/62) |
| Th5 | 15 | 837–851 | TNFTISVQVEYIQVY | 3.9 | IL4-inducer | Positive | 192.33 | Non-Toxin | 98.38% (61/62) |
| Th6 | 15 | 1375–1389 | LEWLNRIETYVKWPW | 5 | IL4-inducer | Positive | 63.01 | Non-Toxin | 100.00% (62/62) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D. Designing a Candidate Multi-Epitope Vaccine against Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus Based on Immunoinformatic and Molecular Dynamics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25168828
Bai Y, Zhou M, Wang N, Yang Y, Wang D. Designing a Candidate Multi-Epitope Vaccine against Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus Based on Immunoinformatic and Molecular Dynamics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(16):8828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25168828
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Yihan, Mingxia Zhou, Naidong Wang, Yi Yang, and Dongliang Wang. 2024. "Designing a Candidate Multi-Epitope Vaccine against Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus Based on Immunoinformatic and Molecular Dynamics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 16: 8828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25168828
APA StyleBai, Y., Zhou, M., Wang, N., Yang, Y., & Wang, D. (2024). Designing a Candidate Multi-Epitope Vaccine against Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus Based on Immunoinformatic and Molecular Dynamics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(16), 8828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25168828






