A New Look at Immunogenetics of Pregnancy: Maternal Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Educates Uterine Natural Killer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. NK Cell Function, Diversity, and Education
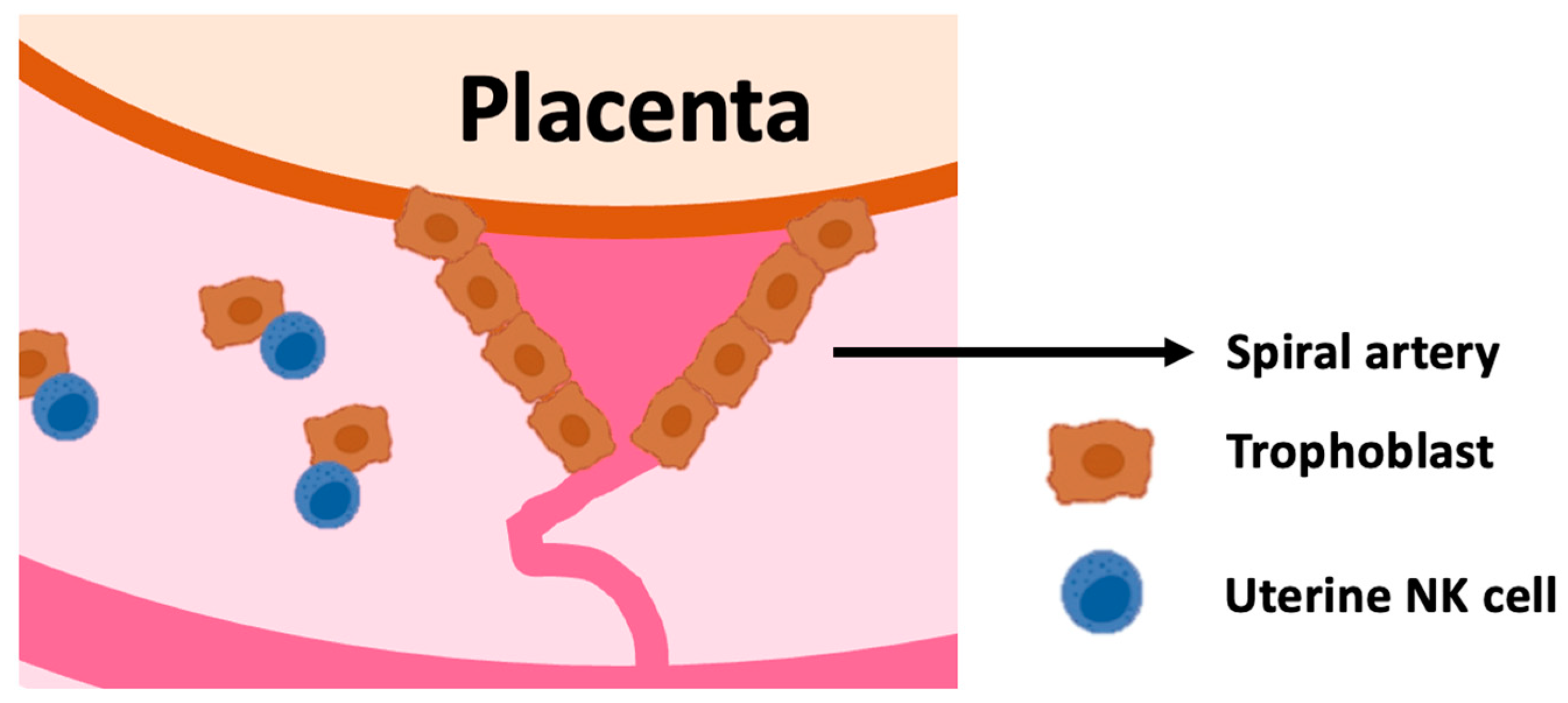
2.2. Uterine NK Cells
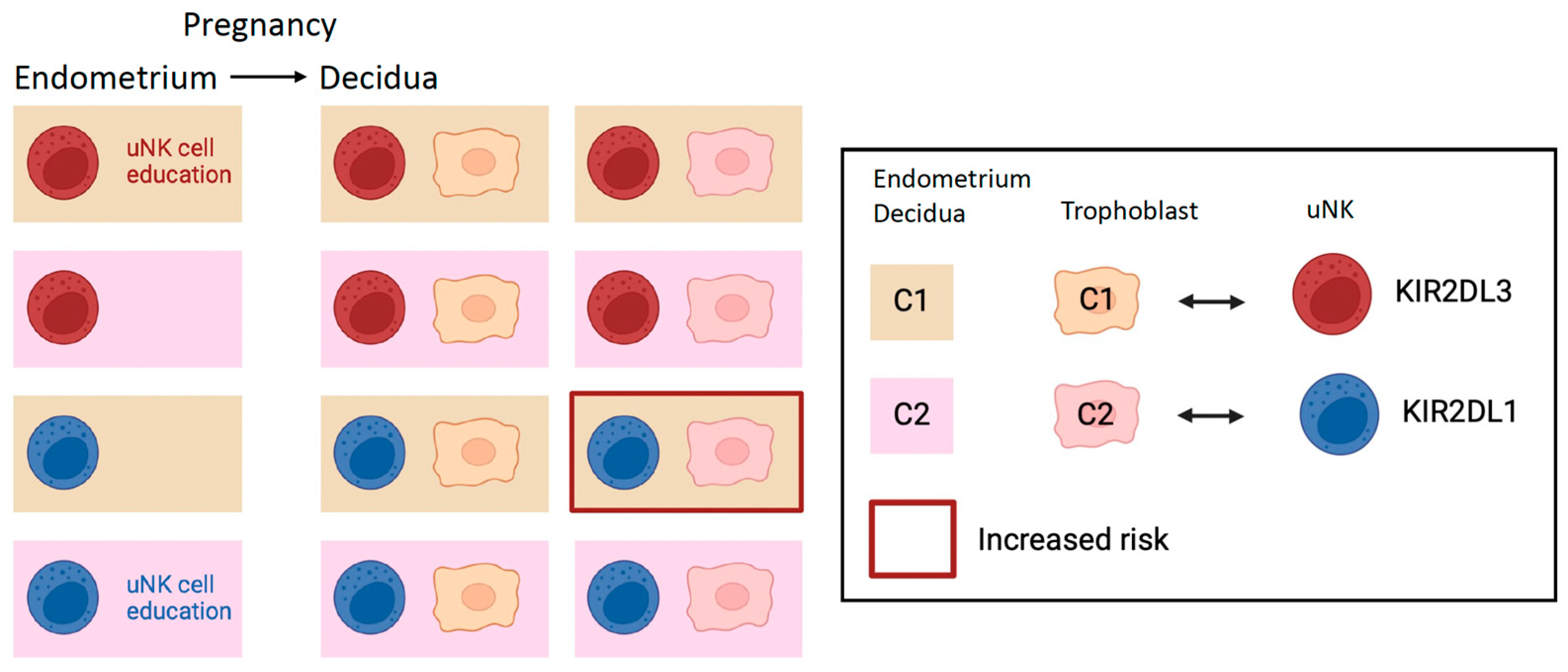
2.3. Education of uNK Cells by KIR and HLA-C
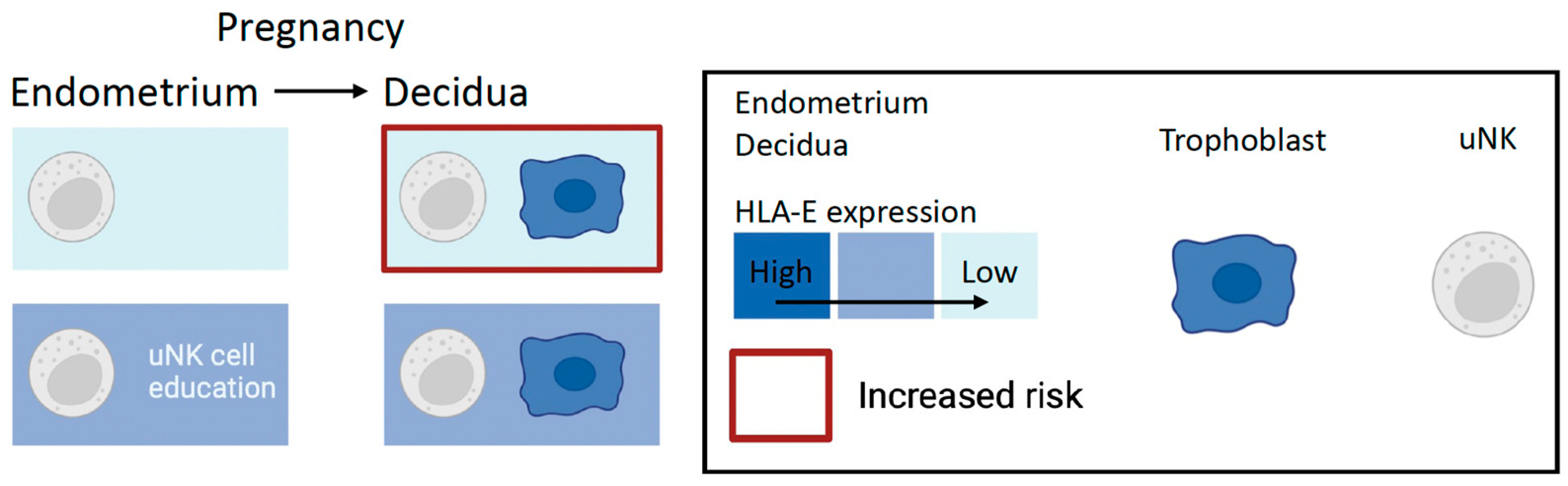
2.4. A New Look: NKG2A and Maternal HLA-E
2.5. Transplantation, Tumor Immunology, and the MFI
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Search Methods
4.2. Selection of Papers
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moffett, A.; Loke, Y.W. The immunological paradox of pregnancy: A reappraisal. Placenta 2004, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, W.; Wachholz, G.E.; de Pereda, J.M.; Kapur, R.; van der Schoot, E.; Margadant, C. Fetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia: Current pathophysiological insights and perspectives for future diagnostics and treatment. Blood Rev. 2022, 59, 101038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, F. The role of KIR and HLA interactions in pregnancy complications. Immunogenetics 2017, 69, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, A.; Colucci, F. Co-evolution of NK receptors and HLA ligands in humans is driven by reproduction. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 267, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shreeve, N.; Depierreux, D.; Hawkes, D.; Traherne, J.A.; Sovio, U.; Huhn, O.; Jayaraman, J.; Horowitz, A.; Ghadially, H.; Perry, J.R.B.; et al. The CD94/NKG2A inhibitory receptor educates uterine NK cells to optimize pregnancy outcomes in humans and mice. Immunity 2021, 54, 1231–1244.e1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiessling, R.; Klein, E.; Pross, H.; Wigzell, H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. II. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Characteristics of the killer cell. Eur. J. Immunol. 1975, 5, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herberman, R.B.; Nunn, M.E.; Holden, H.T.; Lavrin, D.H. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic tumors. II. Characterization of effector cells. Int. J. Cancer 1975, 16, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E. What is natural in natural killer cells? Immunol. Lett. 2006, 107, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piontek, G.E.; Taniguchi, K.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Grönberg, A.; Kiessling, R.; Klein, G.; Kärre, K. YAC-1 MHC class I variants reveal an association between decreased NK sensitivity and increased H-2 expression after interferon treatment or in vivo passage. J. Immunol. 1985, 135, 4281–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlhofer, F.M.; Ribaudo, R.K.; Yokoyama, W.M. MHC class I alloantigen specificity of Ly-49+ IL-2-activated natural killer cells. Nature 1992, 358, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagtmann, N.; Biassoni, R.; Cantoni, C.; Verdiani, S.; Malnati, M.S.; Vitale, M.; Bottino, C.; Moretta, L.; Moretta, A.; Long, E.O. Molecular clones of the p58 NK cell receptor reveal immunoglobulin-related molecules with diversity in both the extra- and intracellular domains. Immunity 1995, 2, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.C.; Seaman, W.E. Ligand interactions by activating and inhibitory Ly-49 receptors. Immunol. Rev. 2001, 181, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, R.E.; Kraft, J.R.; Altman, J.D.; Jensen, P.E.; Raulet, D.H. Mouse CD94/NKG2A is a natural killer cell receptor for the nonclassical major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule Qa-1(b). J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braud, V.M.; Allan, D.S.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Söderström, K.; D’Andrea, A.; Ogg, G.S.; Lazetic, S.; Young, N.T.; Bell, J.I.; Phillips, J.H.; et al. HLA-E binds to natural killer cell receptors CD94/NKG2A, B and C. Nature 1998, 391, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, A.M.; Yang, C.; Thakar, M.S.; Malarkannan, S. Natural Killer Cells: Development, Maturation, and Clinical Utilization. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfossi, N.; André, P.; Guia, S.; Falk, C.S.; Roetynck, S.; Stewart, C.A.; Breso, V.; Frassati, C.; Reviron, D.; Middleton, D.; et al. Human NK cell education by inhibitory receptors for MHC class I. Immunity 2006, 25, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Tian, Z. NK cell education via nonclassical MHC and non-MHC ligands. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, N.C.; Treiner, E.; Vance, R.E.; Jamieson, A.M.; Lemieux, S.; Raulet, D.H. A subset of natural killer cells achieves self-tolerance without expressing inhibitory receptors specific for self-MHC molecules. Blood 2005, 105, 4416–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Qualls, A.E.; Marques-Fernandez, L.; Colucci, F. Biology and pathology of the uterine microenvironment and its natural killer cells. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2101–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whettlock, E.M.; Woon, E.V.; Cuff, A.O.; Browne, B.; Johnson, M.R.; Male, V. Dynamic Changes in Uterine NK Cell Subset Frequency and Function Over the Menstrual Cycle and Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 880438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkar, A.A.; Di Santo, J.P.; Croy, B.A. Interferon gamma contributes to initiation of uterine vascular modification, decidual integrity, and uterine natural killer cell maturation during normal murine pregnancy. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.; Goldman-Wohl, D.; Hamani, Y.; Avraham, I.; Greenfield, C.; Natanson-Yaron, S.; Prus, D.; Cohen-Daniel, L.; Arnon, T.I.; Manaster, I.; et al. Decidual NK cells regulate key developmental processes at the human fetal-maternal interface. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, A.; Colucci, F. Uterine NK cells: Active regulators at the maternal-fetal interface. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1872–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunz, B.; Bister, J.; Jönsson, H.; Filipovic, I.; Crona-Guterstam, Y.; Kvedaraite, E.; Sleiers, N.; Dumitrescu, B.; Brännström, M.; Lentini, A.; et al. Continuous human uterine NK cell differentiation in response to endometrial regeneration and pregnancy. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabb7800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sojka, D.K.; Yang, L.; Plougastel-Douglas, B.; Higuchi, D.A.; Croy, B.A.; Yokoyama, W.M. Cutting Edge: Local Proliferation of Uterine Tissue-Resident NK Cells during Decidualization in Mice. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, D.K. Uterine Natural Killer Cell Heterogeneity: Lessons From Mouse Models. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vento-Tormo, R.; Efremova, M.; Botting, R.A.; Turco, M.Y.; Vento-Tormo, M.; Meyer, K.B.; Park, J.E.; Stephenson, E.; Polański, K.; Goncalves, A.; et al. Single-cell reconstruction of the early maternal-fetal interface in humans. Nature 2018, 563, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhn, O.; Ivarsson, M.A.; Gardner, L.; Hollinshead, M.; Stinchcombe, J.C.; Chen, P.; Shreeve, N.; Chazara, O.; Farrell, L.E.; Theorell, J.; et al. Distinctive phenotypes and functions of innate lymphoid cells in human decidua during early pregnancy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamliel, M.; Goldman-Wohl, D.; Isaacson, B.; Gur, C.; Stein, N.; Yamin, R.; Berger, M.; Grunewald, M.; Keshet, E.; Rais, Y.; et al. Trained Memory of Human Uterine NK Cells Enhances Their Function in Subsequent Pregnancies. Immunity 2018, 48, 951–962.e955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackmon, R.; Pinnaduwage, L.; Zhang, J.; Lye, S.J.; Geraghty, D.E.; Dunk, C.E. Definitive class I human leukocyte antigen expression in gestational placentation: HLA-F, HLA-E, HLA-C, and HLA-G in extravillous trophoblast invasion on placentation, pregnancy, and parturition. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 77, e12643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, H. Roles of HLA-G in the Maternal-Fetal Immune Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 592010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, P. The genetic and evolutionary balances in human NK cell receptor diversity. Semin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khakoo, S.I.; Thio, C.L.; Martin, M.P.; Brooks, C.R.; Gao, X.; Astemborski, J.; Cheng, J.; Goedert, J.J.; Vlahov, D.; Hilgartner, M.; et al. HLA and NK cell inhibitory receptor genes in resolving hepatitis C virus infection. Science 2004, 305, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiby, S.E.; Apps, R.; Chazara, O.; Farrell, L.E.; Magnus, P.; Trogstad, L.; Gjessing, H.K.; Carrington, M.; Moffett, A. Maternal KIR in combination with paternal HLA-C2 regulate human birth weight. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5069–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiby, S.E.; Walker, J.J.; O’Shaughnessy, K.M.; Redman, C.W.; Carrington, M.; Trowsdale, J.; Moffett, A. Combinations of maternal KIR and fetal HLA-C genes influence the risk of preeclampsia and reproductive success. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittman, A.B.; Wall, L.L. The evolutionary origins of obstructed labor: Bipedalism, encephalization, and the human obstetric dilemma. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2007, 62, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, A.; Chazara, O.; Colucci, F.; Johnson, M.H. Variation of maternal KIR and fetal HLA-C genes in reproductive failure: Too early for clinical intervention. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2016, 33, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Porter, C.B.M.; Ashenberg, O.; Lee, J.; Riesenfeld, S.J.; Hofree, M.; Aggelakopoulou, M.; Subramanian, A.; Kuttikkatte, S.B.; Attfield, K.E.; et al. Mouse fetal growth restriction through parental and fetal immune gene variation and intercellular communications cascade. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depierreux, D.M.; Kieckbusch, J.; Shreeve, N.; Hawkes, D.A.; Marsh, B.; Blelloch, R.; Sharkey, A.; Colucci, F. Beyond Maternal Tolerance: Education of Uterine Natural Killer Cells by Maternal MHC Drives Fetal Growth. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 808227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieckbusch, J.; Gaynor, L.M.; Moffett, A.; Colucci, F. MHC-dependent inhibition of uterine NK cells impedes fetal growth and decidual vascular remodelling. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björkström, N.K.; Riese, P.; Heuts, F.; Andersson, S.; Fauriat, C.; Ivarsson, M.A.; Björklund, A.T.; Flodström-Tullberg, M.; Michaëlsson, J.; Rottenberg, M.E.; et al. Expression patterns of NKG2A, KIR, and CD57 define a process of CD56dim NK-cell differentiation uncoupled from NK-cell education. Blood 2010, 116, 3853–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.; Allan, D.S.; Bowen, M.; Powis, S.J.; Joseph, S.; Verma, S.; Hiby, S.E.; McMichael, A.J.; Loke, Y.W.; Braud, V.M. HLA-E is expressed on trophoblast and interacts with CD94/NKG2 receptors on decidual NK cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastidas-Legarda, L.Y.; Khakoo, S.I. Conserved and variable natural killer cell receptors: Diverse approaches to viral infections. Immunology 2019, 156, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Goodlett, D.R.; Ishitani, A.; Marquardt, H.; Geraghty, D.E. HLA-E surface expression depends on binding of TAP-dependent peptides derived from certain HLA class I signal sequences. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 4951–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, A.; Djaoud, Z.; Nemat-Gorgani, N.; Blokhuis, J.; Hilton, H.G.; Béziat, V.; Malmberg, K.J.; Norman, P.J.; Guethlein, L.A.; Parham, P. Class I HLA haplotypes form two schools that educate NK cells in different ways. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, eaag1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallner, A.; Bernson, E.; Hussein, B.A.; Ewald Sander, F.; Brune, M.; Aurelius, J.; Martner, A.; Hellstrand, K.; Thorén, F.B. The HLA-B -21 dimorphism impacts on NK cell education and clinical outcome of immunotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2019, 133, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeja, Z.; Yadi, H.; Apps, R.; Boulenouar, S.; Roper, S.J.; Gardner, L.; Moffett, A.; Colucci, F.; Hemberger, M. Paternal MHC expression on mouse trophoblast affects uterine vascularization and fetal growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4012–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papúchová, H.; Meissner, T.B.; Li, Q.; Strominger, J.L.; Tilburgs, T. The Dual Role of HLA-C in Tolerance and Immunity at the Maternal-Fetal Interface. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, C.C. The genetics of tissue transplantation in mammals. J. Cancer Res. 1924, 8, 75–95. [Google Scholar]
- Cudkowicz, G.; Stimpfling, J.H. Hybrid Resistance to Parental Marrow Grafts: Association with the K Region of H-2. Science 1964, 144, 1339–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.; Yu, Y.Y.; Stoneman, E.; Rembecki, R.M.; Mathew, P.A.; Lindahl, K.F.; Kumar, V. Hybrid resistance: ‘negative’ and ‘positive’ signaling of murine natural killer cells. Semin. Immunol. 1995, 7, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, E.J.; Huang, X.J.; Miller, J.S. HLA-haploidentical stem cell transplantation for hematologic malignancies. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, S57–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ruggeri, L.; Capanni, M.; Urbani, E.; Perruccio, K.; Shlomchik, W.D.; Tosti, A.; Posati, S.; Rogaia, D.; Frassoni, F.; Aversa, F.; et al. Effectiveness of donor natural killer cell alloreactivity in mismatched hematopoietic transplants. Science 2002, 295, 2097–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, V.; Bardelli, A.; Siena, S.; Abrignani, S. Exploring the links between cancer and placenta development. Open Biol. 2018, 8, 180081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseaux, S.; Debernardi, A.; Jacquiau, B.; Vitte, A.L.; Vesin, A.; Nagy-Mignotte, H.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Brichon, P.Y.; Lantuejoul, S.; Hainaut, P.; et al. Ectopic activation of germline and placental genes identifies aggressive metastasis-prone lung cancers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 186ra166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochan, G.; Escors, D.; Breckpot, K.; Guerrero-Setas, D. Role of non-classical MHC class I molecules in cancer immunosuppression. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e26491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Zuo, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, X.; Guo, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Immune checkpoint HLA-E:CD94-NKG2A mediates evasion of circulating tumor cells from NK cell surveillance. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 272–287.e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, P.; Denis, C.; Soulas, C.; Bourbon-Caillet, C.; Lopez, J.; Arnoux, T.; Bléry, M.; Bonnafous, C.; Gauthier, L.; Morel, A.; et al. Anti-NKG2A mAb Is a Checkpoint Inhibitor that Promotes Anti-tumor Immunity by Unleashing Both T and NK Cells. Cell 2018, 175, 1731–1743.e1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bos, M.; Colucci, F. A New Look at Immunogenetics of Pregnancy: Maternal Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Educates Uterine Natural Killer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25168869
Bos M, Colucci F. A New Look at Immunogenetics of Pregnancy: Maternal Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Educates Uterine Natural Killer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(16):8869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25168869
Chicago/Turabian StyleBos, Manon, and Francesco Colucci. 2024. "A New Look at Immunogenetics of Pregnancy: Maternal Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Educates Uterine Natural Killer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 16: 8869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25168869
APA StyleBos, M., & Colucci, F. (2024). A New Look at Immunogenetics of Pregnancy: Maternal Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Educates Uterine Natural Killer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(16), 8869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25168869






