BMP4-Induced Suppression of Breast Cancer Metastasis Is Associated with Inhibition of Cholesterol Biosynthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Alteration in the Transcriptome by BMP4
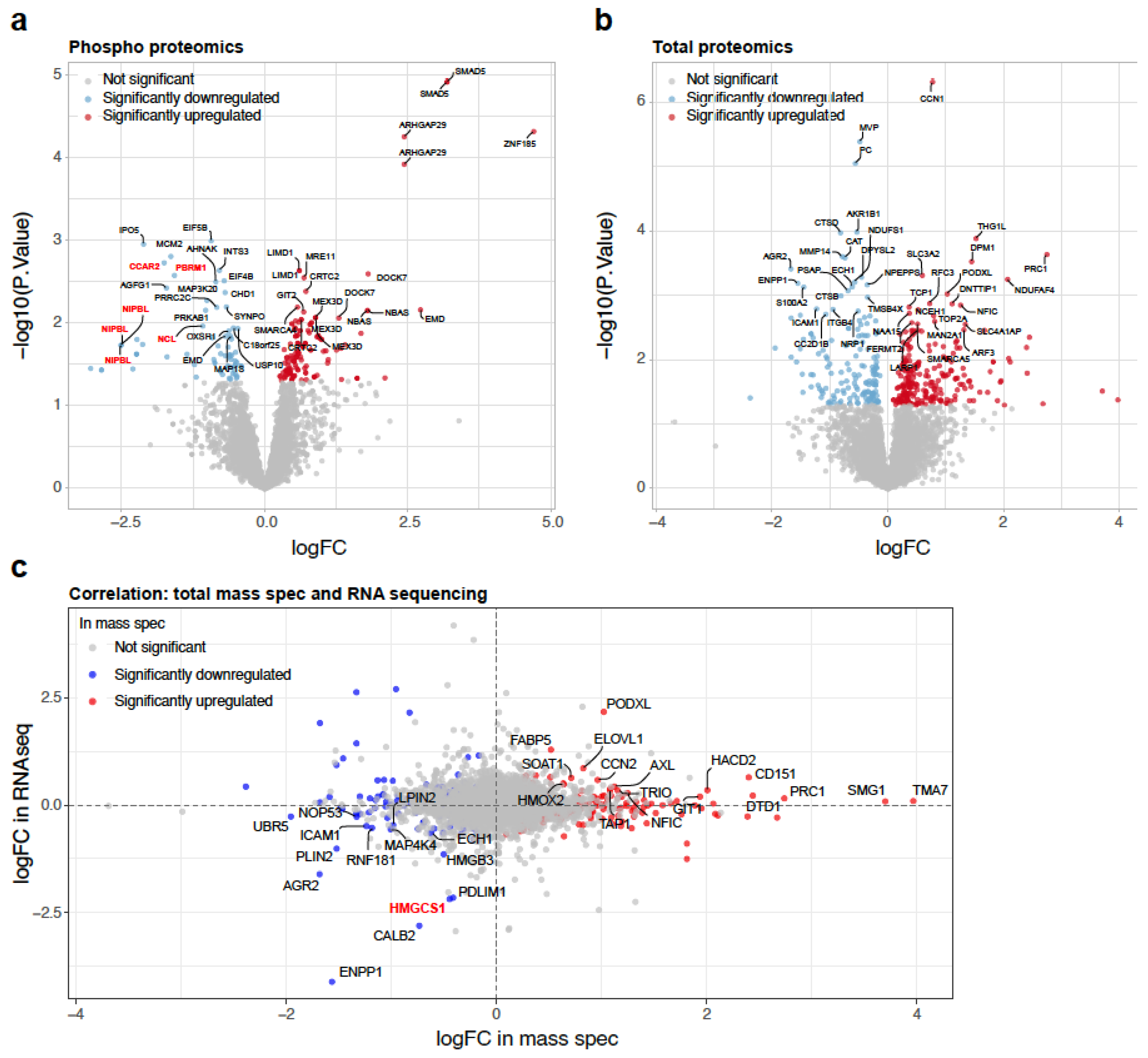
2.2. Alteration in the Proteome by BMP4
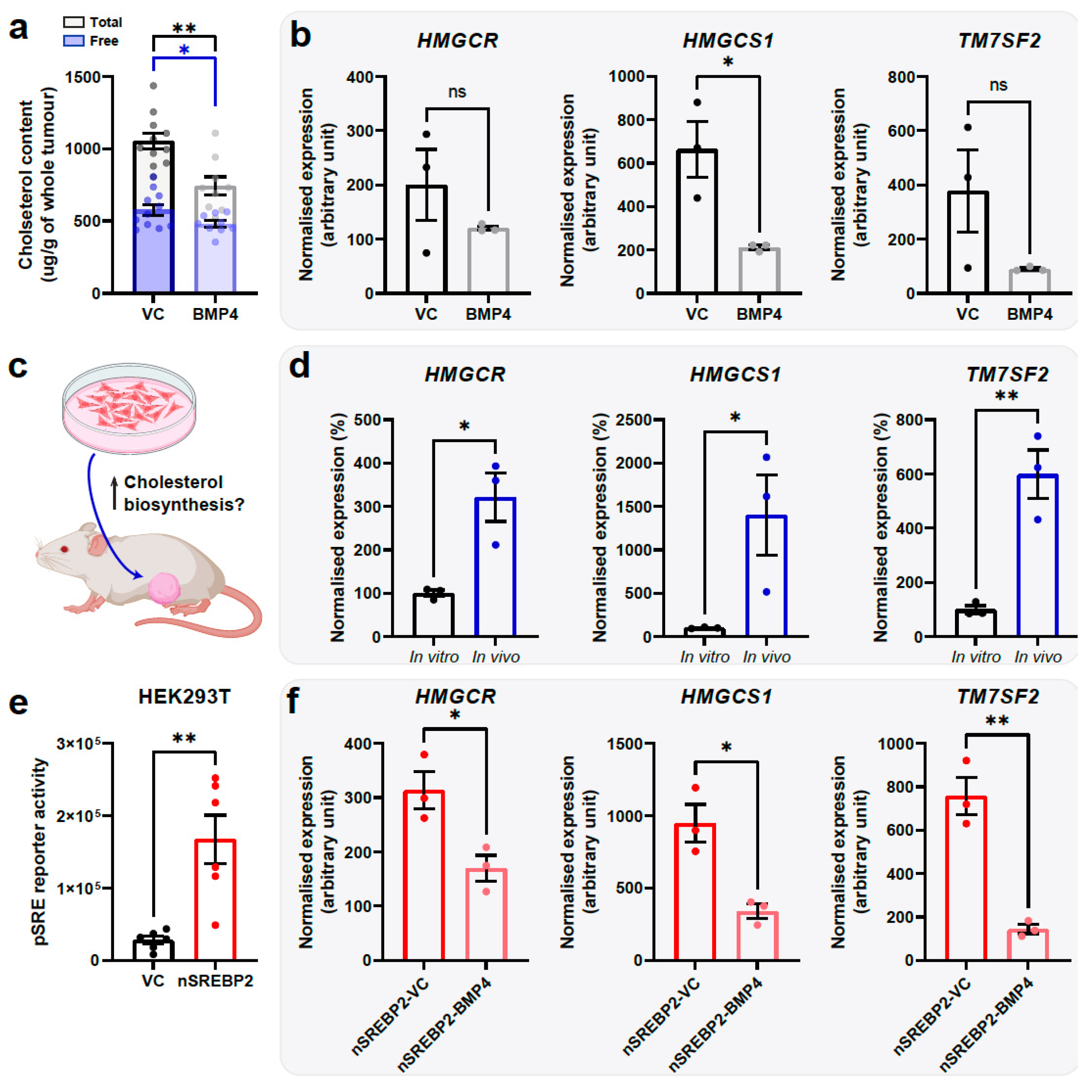
2.3. BMP4 Suppresses Cholesterol Biosynthesis
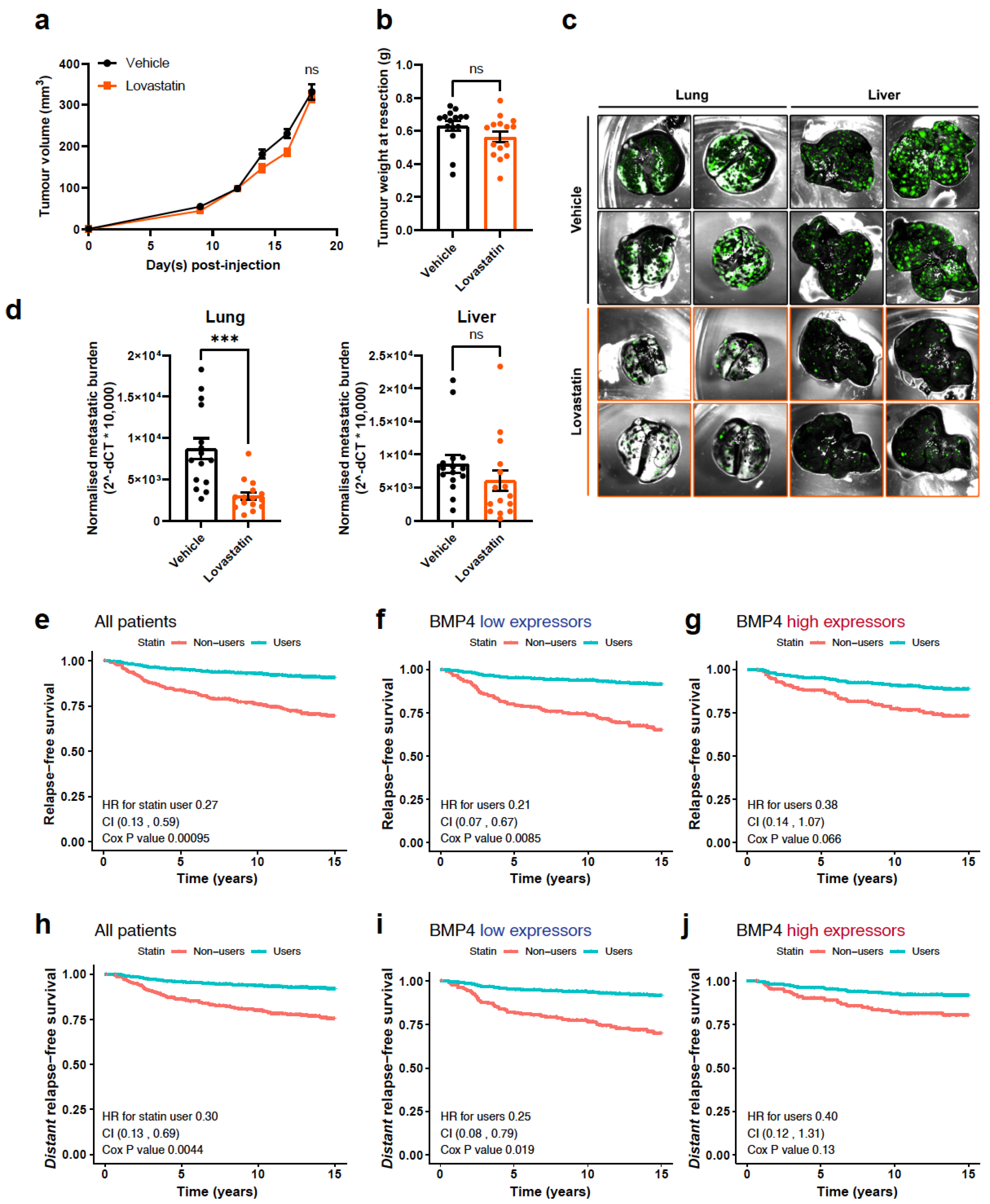
2.4. Inhibition of Cholesterol Biosynthesis Suppresses Metastasis
2.5. The Relationship between BMP4 and Statin Use in Breast Cancer Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and In Vitro Assays
4.2. Western Blotting
4.3. Bioinformatics and Patient Dataset Analyses
4.4. Mass Spectrometric Analysis
4.5. Cholesterol Quantitation
4.6. Quantitative Reverse-Transcription PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.7. Plasmid Cloning and Promoter Activity Assay
4.8. Mouse Experiments
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Miller, K.D.; Kramer, J.L.; Newman, L.A.; Minihan, A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 524–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Zhao, F.; Goldstein, L.J.; Cella, D.; Basik, M.; Golshan, M.; Julian, T.B.; Pockaj, B.A.; Lee, C.A.; Razaq, W.; et al. Early Local Therapy for the Primary Site in De Novo Stage IV Breast Cancer: Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial (EA2108). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Slaney, C.Y.; Bidwell, B.N.; Parker, B.S.; Johnstone, C.N.; Rautela, J.; Eckhardt, B.L.; Anderson, R.L. BMP4 inhibits breast cancer metastasis by blocking myeloid-derived suppressor cell activity. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5091–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckhardt, B.L.; Cao, Y.; Redfern, A.D.; Chi, L.H.; Burrows, A.D.; Roslan, S.; Sloan, E.K.; Parker, B.S.; Loi, S.; Ueno, N.T.; et al. Activation of Canonical BMP4-SMAD7 Signaling Suppresses Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.H.; Redfern, A.D.; Roslan, S.; Street, I.P.; Burrows, A.D.; Anderson, R.L. Loss of tumor-derived SMAD4 enhances primary tumor growth but not metastasis following BMP4 signalling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, P.; Pickup, M.W.; Novitskiy, S.V.; Chytil, A.; Gorska, A.E.; Aakre, M.E.; West, J.; Moses, H.L. Disruption of bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2 (BMPR2) in mammary tumors promotes metastases through cell autonomous and paracrine mediators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2814–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollaire, J.; Machuca-Gayet, I.; Lavaud, J.; Bellanger, A.; Bouazza, L.; El Moghrabi, S.; Treilleux, I.; Coll, J.L.; Peyruchaud, O.; Josserand, V.; et al. The Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Inhibitor LDN-193189 Enhances Metastasis Development in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, M.W.; Hover, L.D.; Guo, Y.; Gorska, A.E.; Chytil, A.; Novitskiy, S.V.; Moses, H.L.; Owens, P. Deletion of the BMP receptor BMPR1a impairs mammary tumor formation and metastasis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22890–22904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampuja, M.; Alarmo, E.L.; Owens, P.; Havunen, R.; Gorska, A.E.; Moses, H.L.; Kallioniemi, A. The impact of bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) on breast cancer metastasis in a mouse xenograft model. Cancer Lett. 2016, 375, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, M.; Harris, S.E.; Mi, Z. Signal transduction and biological functions of bone morphogenetic proteins. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, J.; Mueller, T.D. Specification of BMP Signaling. Cells 2019, 8, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.E. Non-Smad Signaling Pathways of the TGF-beta Family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a022129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shee, K.; Jiang, A.; Varn, F.S.; Liu, S.; Traphagen, N.A.; Owens, P.; Ma, C.X.; Hoog, J.; Cheng, C.; Golub, T.R.; et al. Cytokine sensitivity screening highlights BMP4 pathway signaling as a therapeutic opportunity in ER(+) breast cancer. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 1644–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyedibe, K.I.; Wang, M.; Sintim, H.O. ENPP1, an Old Enzyme with New Functions, and Small Molecule Inhibitors-A STING in the Tale of ENPP1. Molecules 2019, 24, 4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piedra-Quintero, Z.L.; Serrano, C.; Villegas-Sepulveda, N.; Maravillas-Montero, J.L.; Romero-Ramirez, S.; Shibayama, M.; Medina-Contreras, O.; Nava, P.; Santos-Argumedo, L. Myosin 1F Regulates M1-Polarization by Stimulating Intercellular Adhesion in Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvermoser, M.; Pick, R.; Weckbach, L.T.; Zehrer, A.; Lohr, P.; Drechsler, M.; Sperandio, M.; Soehnlein, O.; Walzog, B. Myosin 1f is specifically required for neutrophil migration in 3D environments during acute inflammation. Blood 2018, 131, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Labouesse, M. The making of hemidesmosome structures in vivo. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler-Toprak, S.; Treeck, O.; Ortmann, O. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin and Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, N.M.; Oliveira, E.F.; Gesto, D.S.; Santos-Martins, D.; Moreira, C.; Moorthy, H.N.; Ramos, M.J.; Fernandes, P.A. Cholesterol Biosynthesis: A Mechanistic Overview. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 5483–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurabashi, A.; Wada-Hiraike, O.; Hirano, M.; Fu, H.; Isono, W.; Fukuda, T.; Morita, Y.; Tanikawa, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Oda, K.; et al. CCAR2 negatively regulates nuclear receptor LXRalpha by competing with SIRT1 deacetylase. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 149, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J.A.; Herrera, P.S.; Kaur, M.; Leo, L.; McEldrew, D.; Tintos-Hernandez, J.A.; Rajagopalan, R.; Gagne, A.; Zhang, Z.; Ortiz-Gonzalez, X.R.; et al. NIPBL(+/−) haploinsufficiency reveals a constellation of transcriptome disruptions in the pluripotent and cardiac states. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Gomez, E.C.; Chalabi-Dchar, M.; Rong, C.; Das, S.; Ugrinova, I.; Gaume, X.; Monier, K.; Mongelard, F.; Bouvet, P. Integrated analysis of mRNA and miRNA expression in HeLa cells expressing low levels of Nucleolin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, B.; Porter, E.G.; Stewart, J.C.; Ferreira, C.R.; Schipma, M.J.; Dykhuizen, E.C. PBRM1 Regulates the Expression of Genes Involved in Metabolism and Cell Adhesion in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, H.; Hu, L.; Negi, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ahmed, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, D. Binding of anterior gradient 2 and estrogen receptor-alpha: Dual critical roles in enhancing fulvestrant resistance and IGF-1-induced tumorigenesis of breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2016, 377, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, B.; Chi, Y.; Liu, L.; Chi, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Guo, R.; Si, J.; Li, L.; Xue, J.; et al. LINC02273 drives breast cancer metastasis by epigenetically increasing AGR2 transcription. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarouf, A.; Boissard, A.; Henry, C.; Leman, G.; Coqueret, O.; Guette, C.; Lelievre, E. Anterior gradient protein 2 is a marker of tumor aggressiveness in breast cancer and favors chemotherapyinduced senescence escape. Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 60, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.M.; Wardell, S.E.; Jasper, J.S.; Stice, J.P.; Safi, R.; Nelson, E.R.; McDonnell, D.P. Delineation of a FOXA1/ERalpha/AGR2 regulatory loop that is dysregulated in endocrine therapy-resistant breast cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderlaag, K.E.; Hudak, S.; Bald, L.; Fayadat-Dilman, L.; Sathe, M.; Grein, J.; Janatpour, M.J. Anterior gradient-2 plays a critical role in breast cancer cell growth and survival by modulating cyclin D1, estrogen receptor-alpha and survivin. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Subramanian, A.; Pinchback, R.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Wang, J.; Gao, B.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Zou, J.X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zou, H.; Huang, Z.; et al. RORgamma is a targetable master regulator of cholesterol biosynthesis in a cancer subtype. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, A.E.; Nelson, E.R. The Contribution of Cholesterol and Its Metabolites to the Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer. Horm. Cancer 2016, 7, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, E.R.; Chang, C.Y.; McDonnell, D.P. Cholesterol and breast cancer pathophysiology. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.L.; DeBose-Boyd, R.A.; Brown, M.S. Protein sensors for membrane sterols. Cell 2006, 124, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, J.; Sato, R.; Maeda, M. Multiple DNA elements for sterol regulatory element-binding protein and NF-Y are responsible for sterol-regulated transcription of the genes for human 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A synthase and squalene synthase. J. Biochem. 1998, 123, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, C.; Wang, X.; Briggs, M.R.; Admon, A.; Wu, J.; Hua, X.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBP-1, a basic-helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein that controls transcription of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene. Cell 1993, 75, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, M.S.; Smoot, M.; Cerami, E.; Kuchinsky, A.; Landys, N.; Workman, C.; Christmas, R.; Avila-Campilo, I.; Creech, M.; Gross, B.; et al. Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using Cytoscape. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2366–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oughtred, R.; Stark, C.; Breitkreutz, B.J.; Rust, J.; Boucher, L.; Chang, C.; Kolas, N.; O’Donnell, L.; Leung, G.; McAdam, R.; et al. The BioGRID interaction database: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D529–D541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldes, M.; Boizard, M.; Liepvre, X.L.; Feve, B.; Dugail, I.; Pairault, J. Functional antagonism between inhibitor of DNA binding (Id) and adipocyte determination and differentiation factor 1/sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (ADD1/SREBP-1c) trans-factors for the regulation of fatty acid synthase promoter in adipocytes. Biochem. J. 1999, 344, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Wen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, K.; Yao, J.; Ye, Y.; Hsiao, H.; et al. LncRNAs-directed PTEN enzymatic switch governs epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, C.; Shah, S.P.; Chin, S.F.; Turashvili, G.; Rueda, O.M.; Dunning, M.J.; Speed, D.; Lynch, A.G.; Samarajiwa, S.; Yuan, Y.; et al. The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature 2012, 486, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronich, N.; Rennert, G. Beyond aspirin-cancer prevention with statins, metformin and bisphosphonates. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Shi, D.; Fei, M.; Chen, Y.; Xie, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, P. Association Between Statin Use and Prognosis of Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 556243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, L.J.; Brown, A.J. Controlling cholesterol synthesis beyond 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 18707–18715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Q.; Sun, H.; Chen, X.; Yin, Q.; Li, Y. Hydrogen-bonded and reduction-responsive micelles loading atorvastatin for therapy of breast cancer metastasis. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7574–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckwitt, C.H.; Clark, A.M.; Ma, B.; Whaley, D.; Oltvai, Z.N.; Wells, A. Statins attenuate outgrowth of breast cancer metastases. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzu, O.F.; Noory, M.A.; Robertson, G.P. The Role of Cholesterol in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centonze, G.; Natalini, D.; Piccolantonio, A.; Salemme, V.; Morellato, A.; Arina, P.; Riganti, C.; Defilippi, P. Cholesterol and Its Derivatives: Multifaceted Players in Breast Cancer Progression. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 906670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Prijic, S.; Urban, B.C.; Tisza, M.J.; Zuo, Y.; Li, L.; Tan, Z.; Chen, X.; Mani, S.A.; Chang, J.T. Candidate Antimetastasis Drugs Suppress the Metastatic Capacity of Breast Cancer Cells by Reducing Membrane Fluidity. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2037–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Liang, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Jing, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Y.; et al. Enhanced CHOLESTEROL biosynthesis promotes breast cancer metastasis via modulating CCDC25 expression and neutrophil extracellular traps formation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabarek, B.O.; Boron, D.; Morawiec, E.; Michalski, P.; Palazzo-Michalska, V.; Pach, L.; Dziuk, B.; Swider, M.; Zmarzly, N. Crosstalk between Statins and Cancer Prevention and Therapy: An Update. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X. Complex heatmap visualization. iMeta 2022, 1, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.; Chin, S.F.; Rueda, O.M.; Vollan, H.K.; Provenzano, E.; Bardwell, H.A.; Pugh, M.; Jones, L.; Russell, R.; Sammut, S.J.; et al. The somatic mutation profiles of 2,433 breast cancers refines their genomic and transcriptomic landscapes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, S.J.; Karayel, O.; James, D.E.; Mann, M. High-throughput and high-sensitivity phosphoproteomics with the EasyPhos platform. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1897–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayer, A.; Shao, L.; Chung, M.; Joubert, L.M.; Yang, H.W.; Tsai, F.C.; Bisaria, A.; Betzig, E.; Meyer, T. Engulfed cadherin fingers are polarized junctional structures between collectively migrating endothelial cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.S.; Prashar, P.; Bandyopadhyay, A. BRITER: A BMP responsive osteoblast reporter cell line. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, L.H.; Redfern, A.D.; Lim Kam Sian, T.C.C.; Street, I.P.; Burrows, A.D.; Roslan, S.; Daly, R.J.; Anderson, R.L. BMP4-Induced Suppression of Breast Cancer Metastasis Is Associated with Inhibition of Cholesterol Biosynthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179160
Chi LH, Redfern AD, Lim Kam Sian TCC, Street IP, Burrows AD, Roslan S, Daly RJ, Anderson RL. BMP4-Induced Suppression of Breast Cancer Metastasis Is Associated with Inhibition of Cholesterol Biosynthesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(17):9160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179160
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Lap Hing, Andrew D. Redfern, Terry C. C. Lim Kam Sian, Ian P. Street, Allan D. Burrows, Suraya Roslan, Roger J. Daly, and Robin L. Anderson. 2024. "BMP4-Induced Suppression of Breast Cancer Metastasis Is Associated with Inhibition of Cholesterol Biosynthesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 17: 9160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179160
APA StyleChi, L. H., Redfern, A. D., Lim Kam Sian, T. C. C., Street, I. P., Burrows, A. D., Roslan, S., Daly, R. J., & Anderson, R. L. (2024). BMP4-Induced Suppression of Breast Cancer Metastasis Is Associated with Inhibition of Cholesterol Biosynthesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(17), 9160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179160





