Effects of Oxiris® Therapy on Cytokine Elimination after a LPS Infusion—An Experimental Animal Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Preparation
4.2. Instrumentation and Measurements
4.3. Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI) Measurements
4.4. Cytokine Analysis
4.5. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, G.S.; Mannino, D.M.; Eaton, S.; Moss, M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-García, J.; Osca-Verdegal, R.; Jávega, B.; Herrera, G.; O’Connor, J.E.; García-López, E.; Casabó-Vallés, G.; Rodriguez-Gimillo, M.; Ferreres, J.; Carbonell, N.; et al. Characterization of Early Peripheral Immune Responses in Patients with Sepsis and Septic Shock. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianaro, A.; Tersigni, M.; D’Acquisto, F. New insight in LPS antagonist. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janosevic, D.; Myslinski, J.; McCarthy, T.W.; Zollman, A.; Syed, F.; Xuei, X.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y.L.; Collins, K.S.; Cheng, Y.H.; et al. The orchestrated cellular and molecular responses of the kidney to endotoxin define a precise sepsis timeline. eLife 2021, 10, e62270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellman, T.; Uusalo, P.; Järvisalo, M.J. Renal Replacement Techniques in Septic Shock. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlot, G.; Tomasini, A.; Zanchi, S.; Moro, E. The Techniques of Blood Purification in the Treatment of Sepsis and Other Hyperinflammatory Conditions. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monard, C.; Rimmelé, T.; Ronco, C. Extracorporeal Blood Purification Therapies for Sepsis. Blood Purif. 2019, 47 (Suppl. S3), 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malard, B.; Lambert, C.; Kellum, J.A. In vitro comparison of the adsorption of inflammatory mediators by blood purification devices. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2018, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmelé, T.; Assadi, A.; Cattenoz, M.; Desebbe, O.; Lambert, C.; Boselli, E.; Goudable, J.; Etienne, J.; Chassard, D.; Bricca, G.; et al. High-volume haemofiltration with a new haemofiltration membrane having enhanced adsorption properties in septic pigs. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, L.Y.; Lee, Z.Y.; Yunos, N.M.; Atan, R.; Cove, M.E.; Lumlertgul, N.; Srisawat, N.; Hasan, M.S. Outcomes of extracorporeal blood purification with oXiris® membrane in critically ill patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Crit. Care 2024, 83, 154844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, M.O.; Muellenbach, R.M.; Rolfes, C.; Lotz, C.; Nickel, F.; Müller-Stich, B.P.; Supady, A.; Lepper, P.M.; Weigand, M.A.; Meybohm, P.; et al. Pumpless Extracorporeal Hemadsorption Technique (pEHAT): A Proof-of-Concept Animal Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurens, F.; Summerfield, A.; Nauwynck, H.; Saif, L.; Gerdts, V. The pig: A model for human infectious diseases. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vintrych, P.; Al-Obeidallah, M.; Horák, J.; Chvojka, J.; Valešová, L.; Nalos, L.; Jarkovská, D.; Matějovič, M.; Štengl, M. Modeling sepsis, with a special focus on large animal models of porcine peritonitis and bacteremia. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1094199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli-de-Figueiredo, L.F.; Garrido, A.G.; Nakagawa, N.; Sannomiya, P. Experimental models of sepsis and their clinical relevance. Shock 2008, 30 (Suppl. S1), 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyns, H.; Plessers, E.; De Backer, P.; Meyer, E.; Croubels, S. In vivo porcine lipopolysaccharide inflammation models to study immunomodulation of drugs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 166, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.P.; Heard, S.O. Laboratory models of sepsis and septic shock. J. Surg. Res. 1990, 49, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J.W.; Mellencamp, M.A.; Carroll, J.A.; Boyd, R.D.; Allee, G.L. Acute feed intake and acute-Phase protein responses following a lipopolysaccharide challenge in pigs from two dam lines. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2005, 107, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, J.A.; Carter, D.B.; Korte, S.W.; Prather, R.S. Evaluation of the acute phase response in cloned pigs following a lipopolysaccharide challenge. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2005, 29, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.N.; Collier, C.T.; Carroll, J.A.; Welsh, T.H., Jr.; Laurenz, J.C. Temporal pattern and effect of sex on lipopolysaccharide-induced stress hormone and cytokine response in pigs. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2009, 37, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urmann, A.; Mohnke, K.; Riedel, J.; Hain, J.; Renz, M.; Rissel, R.; Duenges, B.; Ruemmler, R.; Ziebart, A. Lipopolysaccharide Infusion as a Porcine Endotoxemic Shock Model. J. Vis. Exp. 2023, 66039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llamas Moya, S.; Boyle, L.A.; Lynch, P.B.; Arkins, S. Age-related changes in pro-inflammatory cytokines, acute phase proteins and cortisol concentrations in neonatal piglets. Neonatology 2007, 91, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyns, H.; Croubels, S.; Demeyere, K.; Watteyn, A.; De Backer, P.; Meyer, E. Development of a cytometric bead array screening tool for the simultaneous detection of pro-inflammatory cytokines in porcine plasma. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 151, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castegren, M.; Skorup, P.; Lipcsey, M.; Larsson, A.; Sjölin, J. Endotoxin tolerance variation over 24 h during porcine endotoxemia: Association with changes in circulation and organ dysfunction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 53221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broman, M.E.; Hansson, F.; Vincent, J.L.; Bodelsson, M. Endotoxin and cytokine reducing properties of the oXiris membrane in patients with septic shock: A randomized crossover double-blind study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 0220444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, I.; Asada, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayase, N.; Hiruma, T.; Doi, K. Changes in carbon dioxide production and oxygen uptake evaluated using indirect calorimetry in mechanically ventilated patients with sepsis. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert, J.A.; Rogers, A.J. Metabolism, Metabolomics, and Nutritional Support of Patients with Sepsis. Clin. Chest Med. 2016, 37, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, H.; Garczarek, L.; Künne, D.; Pattberg, K.; Skarabis, A.; Frank, M.; Schmidt, B.; Arends, S.; Herbstreit, F.; Brenner, T.; et al. Bedside Hyperspectral Imaging and Organ Dysfunction Severity in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients-A Prospective, Monocentric Observational Study. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, R.P.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Antonelli, M.; Foster, D.M.; Klein, D.J.; Marshall, J.C.; Palevsky, P.M.; Weisberg, L.S.; Schorr, C.A.; Trzeciak, S.; et al. Effect of Targeted Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion on 28-Day Mortality in Patients With Septic Shock and Elevated Endotoxin Level: The EUPHRATES Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 320, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schädler, D.; Pausch, C.; Heise, D.; Meier-Hellmann, A.; Brederlau, J.; Weiler, N.; Marx, G.; Putensen, C.; Spies, C.; Jörres, A.; et al. The effect of a novel extracorporeal cytokine hemoadsorption device on IL-6 elimination in septic patients: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0187015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogelmann, K.; Jarczak, D.; Scheller, M.; Drüner, M. Hemoadsorption by CytoSorb in septic patients: A case series. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, A.; Waalders, N.J.B.; van Lier, D.P.T.; Kox, M.; Pickkers, P. CytoSorb hemoperfusion markedly attenuates circulating cytokine concentrations during systemic inflammation in humans in vivo. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, K.; Scaravilli, V.; Kreyer, S.F.; Belenkiy, S.M.; Stewart, I.J.; Chung, K.K.; Cancio, L.C.; Batchinsky, A.I. Evaluation of the Cytosorb™ Hemoadsorptive Column in a Pig Model of Severe Smoke and Burn Injury. Shock 2015, 44, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffer, U.; Wade, R.G.; Gourlay, T. Cytokines in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome: A review. HSR Proc. Intensive Care Cardiovasc. Anesth. 2010, 2, 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; He, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, Z.; Deng, K.; et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy with the adsorptive oXiris filter may be associated with the lower 28-day mortality in sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, J. Comparison of the Clinical Effectiveness of AN69-oXiris versus AN69-ST Filter in Septic Patients: A Single-Centre Study. Blood Purif. 2022, 51, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Fu, P. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy With Adsorbing Filter oXiris in Acute Kidney Injury With Septic Shock: A Retrospective Observational Study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 789623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhang, C. The application value of oXiris-endotoxin adsorption in sepsis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 3839–3844. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Bonello, M.; Bordoni, V.; Ricci, Z.; D’Intini, V.; Bellomo, R.; Levin, N.W. Extracorporeal therapies in non-renal disease: Treatment of sepsis and the peak concentration hypothesis. Blood Purif. 2004, 22, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vriese, A.S.; Colardyn, F.A.; Philippé, J.J.; Vanholder, R.C.; De Sutter, J.H.; Lameire, N.H. Cytokine removal during continuous hemofiltration in septic patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heering, P.; Morgera, S.; Schmitz, F.J.; Schmitz, G.; Willers, R.; Schultheiss, H.P.; Strauer, B.E.; Grabensee, B. Cytokine removal and cardiovascular hemodynamics in septic patients with continuous venovenous hemofiltration. Intensive Care Med. 1997, 23, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, R.A.; Zainudin, S.; Ctkong, N.; Rahman, A.F.; Wafa, S.R.; Mohamad, M.; Manaf, M.R.; Ismail, R. Serum IL-6 and IL-1-ra with sequential organ failure assessment scores in septic patients receiving high-volume haemofiltration and continuous venovenous haemofiltration. Nephrology 2006, 11, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, E.; Amézaga Menéndez, R.; Vidal Cortés, P.; Escapa, M.G.; Suberviola, B.; Serrano Lázaro, A.; Marcos Neira, P.; Quintana Díaz, M.; Catalán González, M. Pharmacological treatment of COVID-19: Narrative review of the Working Group in Infectious Diseases and Sepsis (GTEIS) and the Working Groups in Transfusions and Blood Products (GTTH). Med. Intensiva 2021, 45, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchikalapati, R.; Schening, J.; Farias, A.J.; Sacco, K.A. Clinical utility of interleukin-1 inhibitors in pediatric sepsis. Shock 2024, 61, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, M.; Özdemir, B.; Gruneberg, D.; Petersen, C.; Studier-Fischer, A.; von der Forst, M.; Schmitt, F.C.F.; Fiedler, M.O.; Nickel, F.; Müller-Stich, B.P.; et al. Hyperspectral Imaging for the Evaluation of Microcirculatory Tissue Oxygenation and Perfusion Quality in Haemorrhagic Shock: A Porcine Study. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahnasawy, S.M.; Skorup, P.; Hanslin, K.; Lipcsey, M.; Friberg, L.E.; Nielsen, E.I. Predicting cytokine kinetics during sepsis; a modelling framework from a porcine sepsis model with live Escherichia coli. Cytokine 2023, 169, 156296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsted, A.; Bouchene, S.; Tano, E.; Castegren, M.; Lipcsey, M.; Sjölin, J.; Karlsson, M.O.; Friberg, L.E.; Nielsen, E.I. A non-linear mixed effect model for innate immune response: In vivo kinetics of endotoxin and its induction of the cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 0211981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardisi, M.; Thelen, K.; Groenendal, A.; Rajput, M.; Sebastian, K.; Contreras, G.A.; Moeser, A.J. Early weaning and biological sex shape long-term immune and metabolic responses in pigs. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

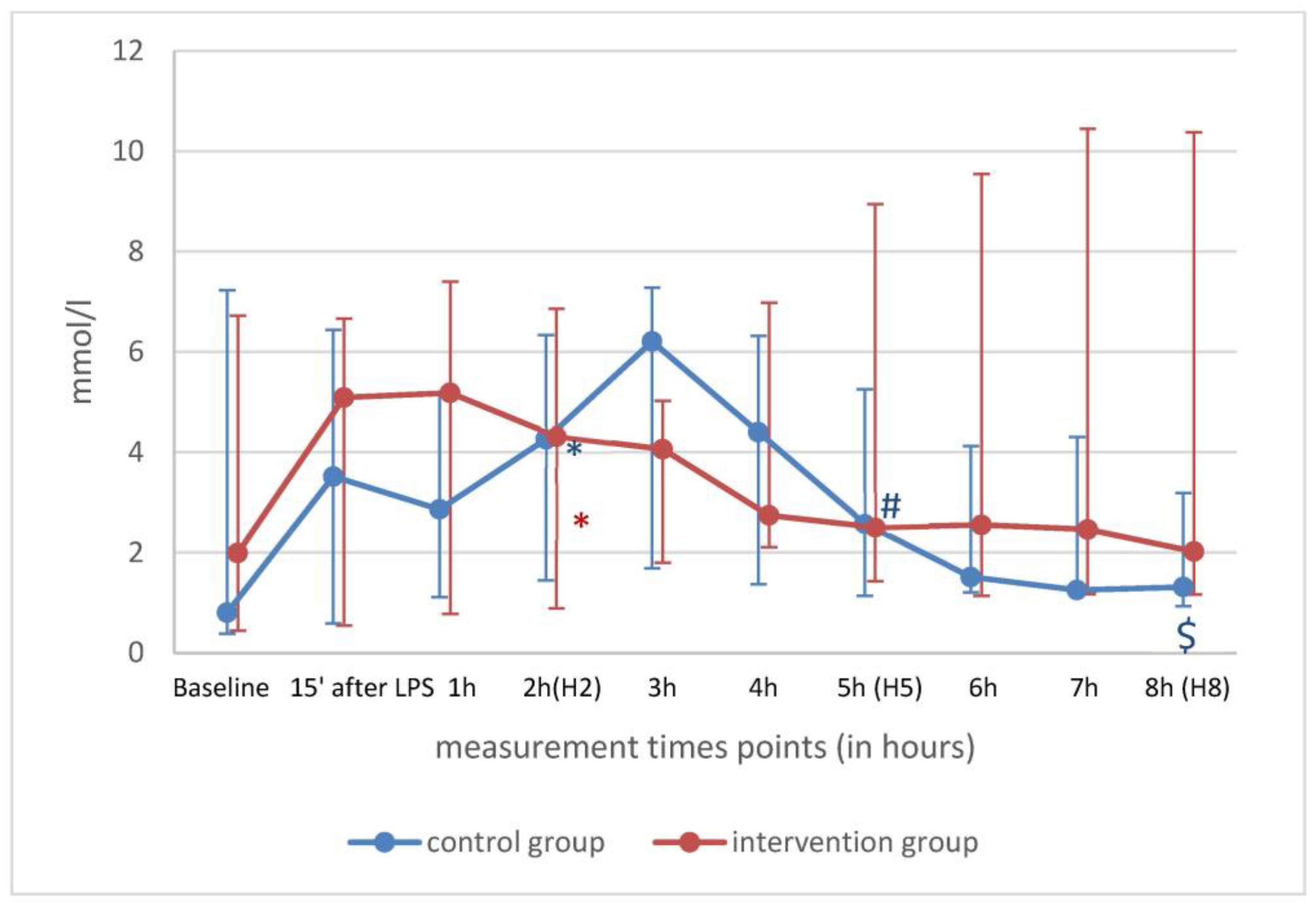
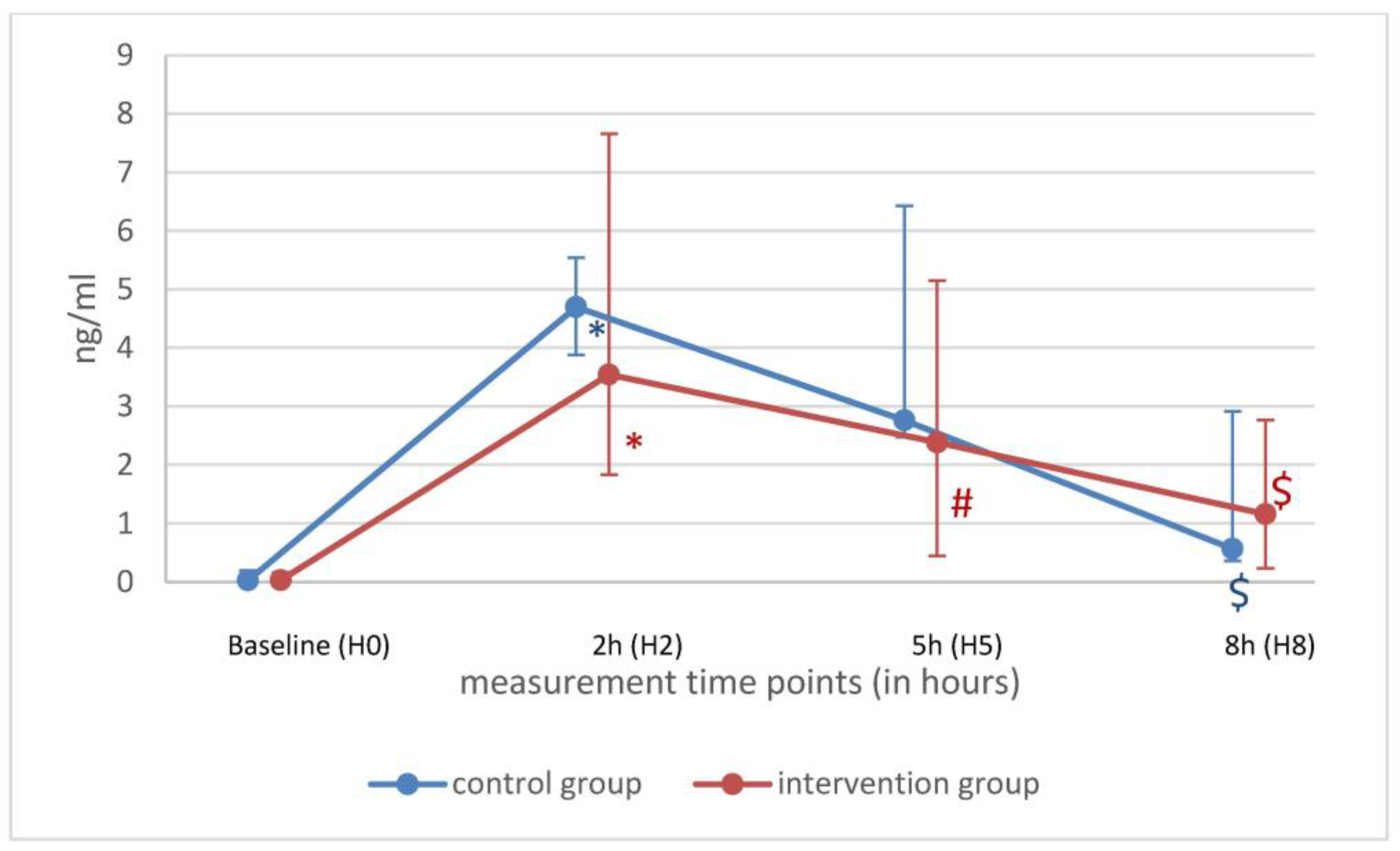
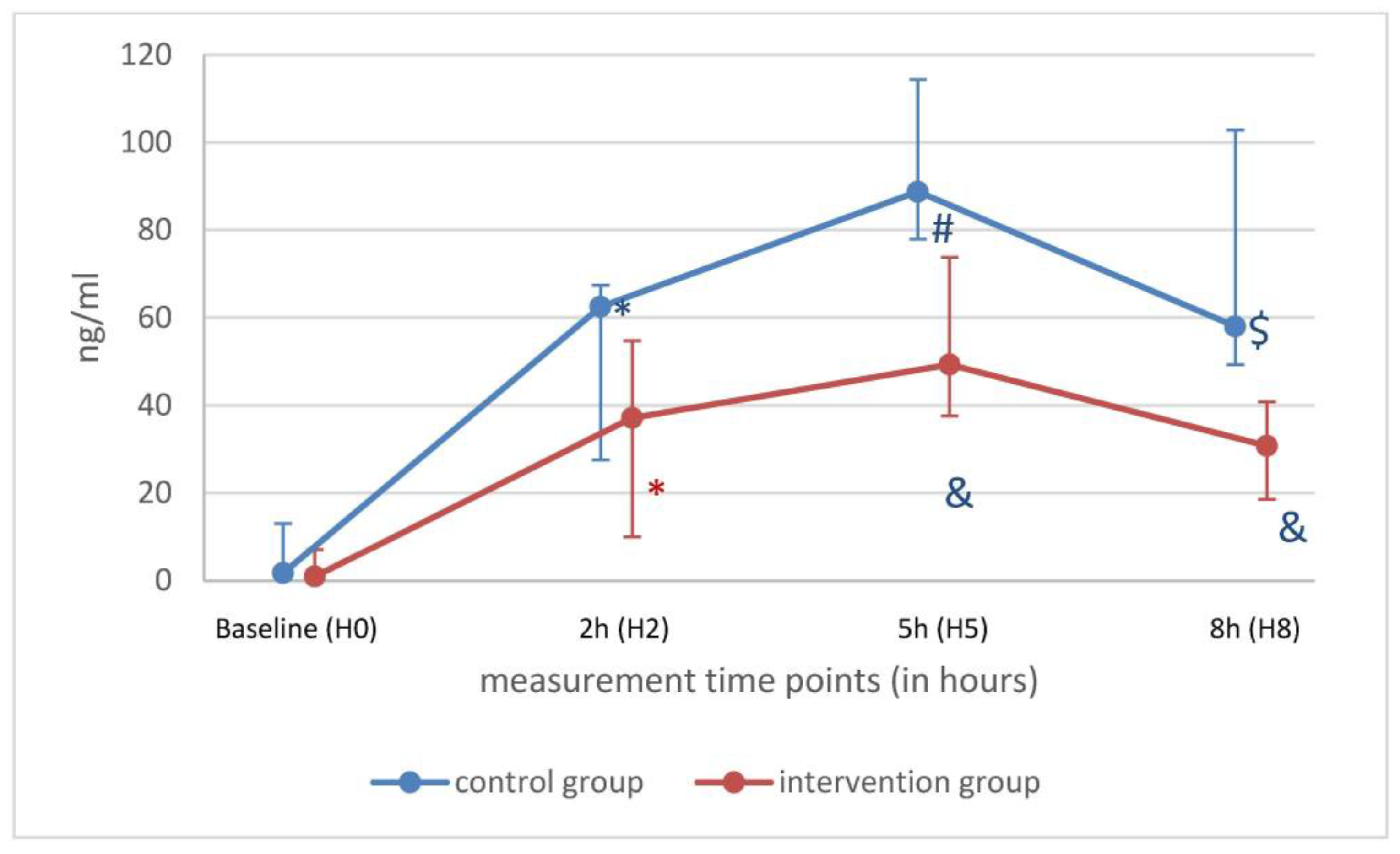

| H0 (n = 11) | H2 (n = 11) | |
|---|---|---|
| HR (bpm) | 76 (58; 133) | 102 (75; 152) * |
| MAP (mmHg) | 85 (71; 101) | 85 (71; 109) |
| CI (l/min/m2) | 7.1 (4.8; 10.7) | 8.1 (4.9; 9.9) |
| Lactate (mmol/l) | 1.56 (0.42; 4.38) | 4.26 (0.89; 6.86) * |
| mPAP (mmHg) | 23 (19; 38) | 30 (23; 39) * |
| paO2 (mmHg) | 186.5 (128.8; 210.6) | 173.1 (89.5; 195.0) |
| paCO2 (mmHg) | 48.1 (41.0; 51.2) | 49.9 (42.5; 57.0) |
| VO2/m2 (ml/min/m2) | 220 (187; 389) | 266 (237; 374) # |
| VCO2/m2 (ml/min/m2) | 210 (149; 334) | 272 (207; 352) * |
| StO2 (%) | 74.0 (63.6; 79.6) | 70.4 (48.9; 75.9) * |
| NIR (%) | 43.5 (39.7; 53.7) | 45.9 (40.2; 54.8) |
| TWI (%) | 55.5 (44.6; 58.9) | 54.9 (43.7; 58.5) |
| IL-1β (ng/mL) | 0.03 (0.00; 0.29) | 0.13 (0.06; 0.67) # |
| IL-1ra (ng/mL) | 1.20 (0.19; 13.06) | 53.06 (9.96; 67.36) # |
| IL-2 (ng/mL) | 0.06 (0.00; 0.84) | 0.09 (0.01; 0.89) # |
| IL-4 (ng/mL) | 0.15 (0.00; 1.83) | 0.24 (0.00; 1.76) |
| IL-6 (ng/mL) | 0.03 (0.00; 0.20) | 3.89 (1.83; 7.60) # |
| IL-8 (ng/mL) | 0.00 (0.00; 0.00) | 0.20 (0.03; 2.75) # |
| IL-10 (ng/mL) | 0.24 (0.01; 1.58) | 0.54 (0.21; 1.76) # |
| IL-12 (ng/mL) | 0.96 (0.41; 1.47) | 1.16 (0.42; 2.43) # |
| IL-18 (ng/mL) | 0.20 (0.05; 3.15) | 0.27 (0.08; 3.27) |
| TNF-α (ng/mL) | 0.00 (0.00; 0.24) | 1.75 (0.04; 11.00) # |
| H2 | H5 | H8 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (bpm) | A | 120 (94; 152) | 114 (77; 118) | 110 (81; 134) |
| B | 93 (75; 128) | 113 (68; 126) | 95 (79; 116) | |
| MAP (mmHg) | A | 82 (71; 85) | 95 (87; 116) # | 85 (66; 122) |
| B | 98 (78; 109) | 96 (87; 115) | 87 (80; 113) | |
| CI (L/min/m2) | A | 8.1 (6.5; 9.9) | 5.9 (5.2; 6) # | 6.4 (5.7; 7) |
| B | 7.6 (4.9; 8.3) | 6.0 (4.3; 7.9) | 5.4 (5; 7.1) | |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | A | 4.3 (1.5; 6.4) | 2.6 (1.1; 5.3) # | 1.3 (0.9; 3.2) $ |
| B | 4.3 (0.9; 6.9) | 2.5 (1.4; 8.9) | 2.0 (1.2; 10.4) | |
| mPAP (mmHg) | A | 26 (23; 32) | 30 (20; 34) # | 30 (19; 33) $ |
| B | 34 (27; 39) | 31 (25; 40) | 30 (27; 36) | |
| paO2 (mmHg) | A | 159.9 (134.6; 179.6) | 134.0 (99.9; 164.0) # | 138.3 (93.8; 173.2) $ |
| B | 179.1 (89.5; 195.0) | 154.9 (97.2; 178.7) | 157.3 (109.0; 179.1) | |
| paCO2 (mmHg) | A | 51.0 (45.1; 57.0) | 44.1 (40.4; 54.2) | 43.6 (39.9; 48.3) |
| B | 46.3 (42.5; 53.5) | 46.8 (38.3; 59.9) | 45.1 (38.5; 55.1) | |
| VO2/m2 (mL/min/m2) | A | 287 (237; 374) | 296 (200; 355) | 282 (205; 346) |
| B | 260 (244; 365) | 247 (190; 317) | 240 (207; 284) | |
| VCO2/m2 (mL/min/m2) | A | 273 (207; 352) | 262 (183; 311) | 275 (180; 286) |
| B | 264 (227; 311) | 231 (192; 297) # | 232 (202; 280) $ | |
| StO2 (%) | A | 68.5 (59.8; 73.3) | 65.4 (60.4; 69.9) | 66.6 (58.3; 72.9) |
| B | 71.3 (48.9; 75.9) | 68.1 (59.4; 76.1) | 66.3 (50.3; 73.8) | |
| NIR (%) | A | 45.9 (41.5; 54.8) | 40.2 (32.2; 48.9) | 41.6 (34.5; 50.2) |
| B | 43.8 (40.2; 49.3) | 44.6 (34.6; 51.5) | 40.2 (36.7; 48.8) | |
| TWI (%) | A | 55.5 (52.8; 57.7) | 60.8 (53.1; 62.2) | 61.3 (52.4; 63.4) |
| B | 50.1 (43.7; 58.5) | 49.8 (45.1; 63.9) | 53.1 (48.9; 66.2) |
| H2 | H5 | H8 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ (pg/mL) | A | 0.00 (0.00; 0.09) | 0.00(0.00; 0.28) | 0.00 (0.00; 0.00) |
| B | 0.05 (0.00; 0.61) | 0.14 (0.00; 0.61) | 0.05 (0.00; 0.42) | |
| IL-1α (pg/mL) | A | 0.02 (0.00; 0.04) | 0.02 (0.00; 0.05) | 0.02 (0.00; 0.04) |
| B | 0.03 (0.02; 0.14) | 0.03 (0.01; 0.16) | 0.03 (0.01; 0.13) | |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | A | 0.10 (0.06; 0.33) | 0.29 (0.13; 1.23) # | 0.23 (0.07; 1.00) $ |
| B | 0.14 (0.06; 0.67) | 0.29 (0.15; 2.07) | 0.23 (0.13; 1.39) | |
| IL-1ra (pg/mL) | A | 62.50(27.56; 67.36) | 88.78 (77.98; 114.33) # | 58.03 (49.34; 102.87) |
| B | 37.14 (9.96; 54.77) | 49.33 (37.61; 73.79) * | 30.77 (18.58; 40.87) * | |
| IL-2 (pg/mL) | A | 0.05 (0.00; 0.12) | 0.05 (0.01; 0.14) | 0.03 (0.00; 0.10) |
| B | 0.14 (0.02; 0.89) | 0.15 (0.01; 0.86) | 0.15 (0.01; 0.79) | |
| IL-4 (pg/mL) | A | 0.15 (0.00; 0.49) | 0.22 (0.03; 0.67) | 0.19 (0.00; 0.42) |
| B | 0.33 (0.00; 1.76) | 0.28(0.00; 2.04) | 0.33 (0.00; 1.81) | |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | A | 4.70 (3.88; 5.55) | 2.76 (2.50; 6.43) | 0.568 (0.359; 2.916) $ |
| B | 3.54 (1.83; 7.66) | 2.39 (0.45; 5.15) # | 1.16 (0.24; 2.77) $ | |
| IL-8 (pg/mL) | A | 0.25 (0.13; 0.66) | 0.00 (0.000; 0.02) # | 0.00 (0.00; 0.00) $ |
| B | 0.16 (0.03; 2.75) | 0.00 (0.000; 0.04) # | 0.00 (0.000; 0.01) $* | |
| IL-10 (pg/mL) | A | 0.54 (0.44; 0.89) | 0.36 (0.26 0.95) | 0.20 (0.14; 0.53) |
| B | 0.57 (0.21; 1.76) | 0.42 (0.10; 1.58) # | 0.45 (0.09; 1.44) $ | |
| IL-12 (pg/mL) | A | 1.36 (0.83; 2.43) | 1.52 (0.63; 3.86) | 1.44 (0.51; 3.24) |
| B | 1.02 (0.42; 1.83) | 0.80 (0.44; 1.43) # | 0.63 (0.34; 1.19) $ | |
| IL-18 (pg/mL) | A | 0.27 (0.22; 0.60) | 0.35 (0.23; 0.97) | 0.32 (0.20; 1.03) |
| B | 0.34 (0.08; 3.27) | 0.54 (0.12; 3.56) | 0.72 (0.18; 3.71) | |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | A | 2.57 (0.51; 11.00) | 0.26 (0.00; 0.58) # | 0.10 (0.00; 0.18) $ |
| B | 1.15 (0.04; 2.70) | 0.03 (0.00; 0.09) # | 0.02 (0.00; 0.04) $ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalenka, A.; Arens, P.; Müllenbach, R.M.; Weigand, M.A.; Brune, M.; Fiedler-Kalenka, M.O. Effects of Oxiris® Therapy on Cytokine Elimination after a LPS Infusion—An Experimental Animal Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179283
Kalenka A, Arens P, Müllenbach RM, Weigand MA, Brune M, Fiedler-Kalenka MO. Effects of Oxiris® Therapy on Cytokine Elimination after a LPS Infusion—An Experimental Animal Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(17):9283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179283
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalenka, Armin, Philipp Arens, Ralf M. Müllenbach, Markus A. Weigand, Maik Brune, and Mascha O. Fiedler-Kalenka. 2024. "Effects of Oxiris® Therapy on Cytokine Elimination after a LPS Infusion—An Experimental Animal Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 17: 9283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179283
APA StyleKalenka, A., Arens, P., Müllenbach, R. M., Weigand, M. A., Brune, M., & Fiedler-Kalenka, M. O. (2024). Effects of Oxiris® Therapy on Cytokine Elimination after a LPS Infusion—An Experimental Animal Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(17), 9283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179283







