Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum
Abstract
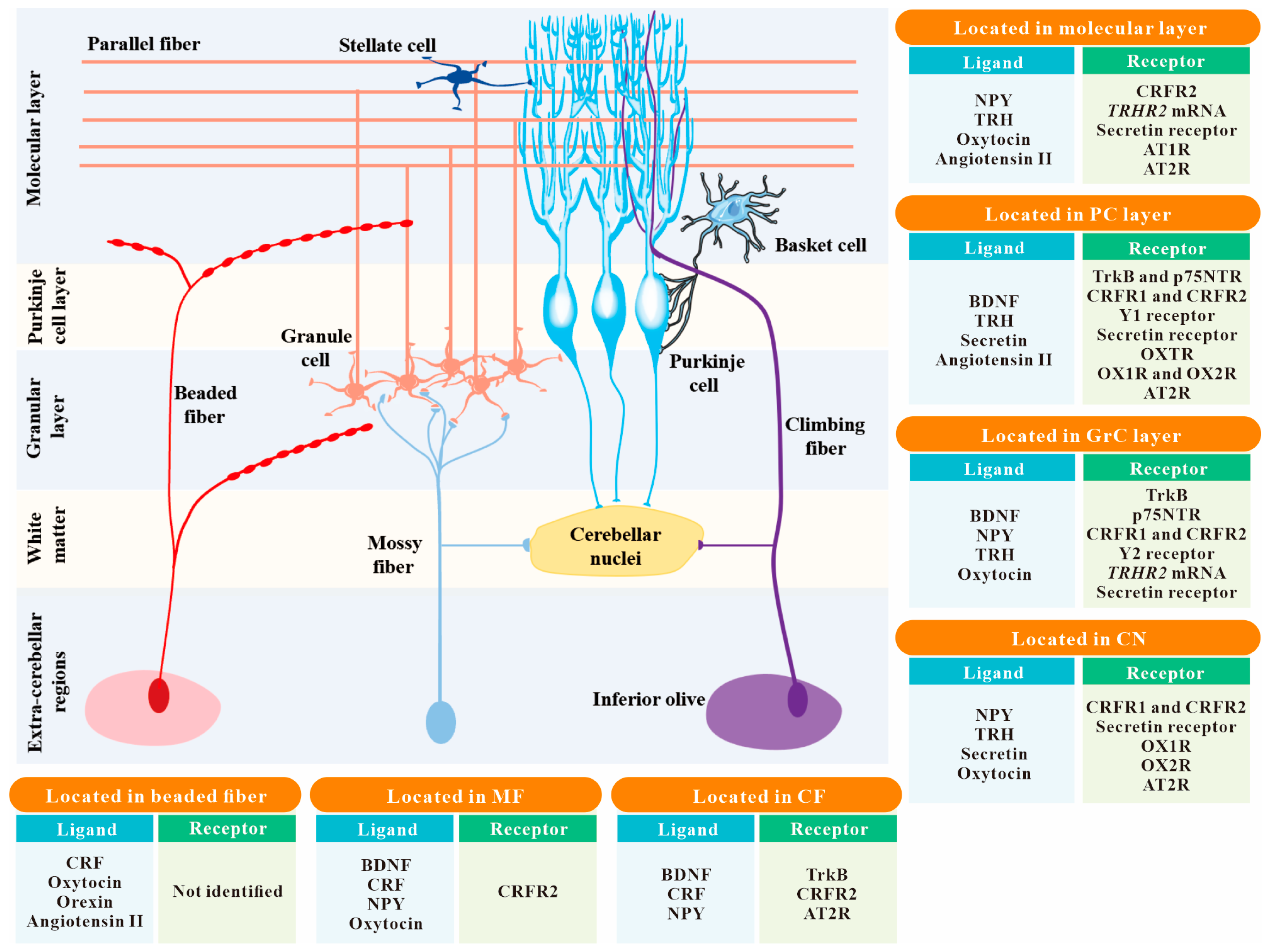
1. Introduction
2. BDNF
3. CRF
4. Angiotensin II
5. NPY
6. Orexin
7. TRH
8. Oxytocin
9. Secretin
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koziol, L.F.; Budding, D.; Andreasen, N.; D’Arrigo, S.; Bulgheroni, S.; Imamizu, H.; Ito, M.; Manto, M.; Marvel, C.; Parker, K.; et al. Consensus paper: The cerebellum’s role in movement and cognition. Cerebellum 2014, 13, 151–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibi, M.; Shimizu, T. Development of the cerebellum and cerebellar neural circuits. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 282–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Hibi, M. Development and evolution of cerebellar neural circuits. Dev. Growth Differ. 2012, 54, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzban, H.; Del Bigio, M.R.; Alizadeh, J.; Ghavami, S.; Zachariah, R.M.; Rastegar, M. Cellular commitment in the developing cerebellum. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapfhammer, J.P. Cellular and molecular control of dendritic growth and development of cerebellar Purkinje cells. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 2004, 39, 131–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzel, M.; Rook, V.; Wingate, R.J.T. Mitotic granule cell precursors undergo highly dynamic morphological transitions throughout the external germinal layer of the chick cerebellum. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galas, L.; Bénard, M.; Lebon, A.; Komuro, Y.; Schapman, D.; Vaudry, H.; Vaudry, D.; Komuro, H. Postnatal Migration of Cerebellar Interneurons. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M. Cerebellar circuitry as a neuronal machine. Prog. Neurobiol. 2006, 78, 272–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Ichikawa, R.; Kitamura, K.; Watanabe, M.; Kano, M. Translocation of a “Winner” Climbing Fiber to the Purkinje Cell Dendrite and Subsequent Elimination of “Losers” from the Soma in Developing Cerebellum. Neuron 2009, 63, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, S.E.; Hansel, C. Climbing fiber multi-innervation of mouse Purkinje dendrites with arborization common to human. Science 2023, 381, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; van Beugen, B.J.; De Zeeuw, C.I. Distributed synergistic plasticity and cerebellar learning. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M. Functional roles of neuropeptides in cerebellar circuits. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbière, A.; Walet-Balieu, M.-L.; Chan, P.; Basille-Dugay, M.; Hardouin, J.; Vaudry, D. A Peptidomic Approach to Characterize Peptides Involved in Cerebellar Cortex Development Leads to the Identification of the Neurotrophic Effects of Nociceptin. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, G.A.; King, J.S. Neuropeptides in the Cerebellum; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2023; pp. 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Barde, Y.; Edgar, D.; Thoenen, H. Purification of a new neurotrophic factor from mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1982, 1, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci-D’amato, L.; Speranza, L.; Volpicelli, F. Neurotrophic Factor BDNF, Physiological Functions and Therapeutic Potential in Depression, Neurodegeneration and Brain Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camuso, S.; La Rosa, P.; Fiorenza, M.T.; Canterini, S. Pleiotropic effects of BDNF on the cerebellum and hippocampus: Implications for neurodevelopmental disorders. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 163, 105606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.I.; Zang, K.; Masliah, E.; Reichardt, L.F. Glutamatergic axon-derived BDNF controls GABAergic synaptic differentiation in the cerebellum. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieni, S.; Rees, S. Distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB receptor proteins in the fetal and postnatal hippocampus and cerebellum of the guinea pig. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 454, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocamora, N.; García-Ladona, F.; Palacios, J.; Mengod, G. Differential expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin-3, and low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor during the postnatal development of the rat cerebellar system. Mol. Brain Res. 1993, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanin, J.P.; Verpeut, J.L.; Li, Y.; Shiflett, M.W.; Wang, S.S.-H.; Santhakumar, V.; Friedman, W.J. The p75NTR Influences Cerebellar Circuit Development and Adult Behavior via Regulation of Cell Cycle Duration of Granule Cell Progenitors. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9119–9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, D.; Dechant, G.; Heisenberg, C.; Thoenen, H. Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor is a Survival Factor for Cultured Rat Cerebellar Granule Neurons and Protects them Against Glutamate-induced Neurotoxicity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1993, 5, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, P.M.; Borghesani, P.R.; Levy, R.L.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Segal, R.A. Abnormal cerebellar development and foliation in BDNF-/- mice reveals a role for neurotrophins in CNS patterning. Neuron 1997, 19, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.Q.; Zheng, J.L.; Karihaloo, M. Neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) act at later stages of cerebellar granule cell differentiation. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 2656–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico, B.; Xu, B.; Reichardt, L.F. TrkB receptor signaling is required for establishment of GABAergic synapses in the cerebellum. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minichiello, L.; Klein, R. TrkB and TrkC neurotrophin receptors cooperate in promoting survival of hippocampal and cerebellar granule neurons. Minerva Anestesiol. 1996, 10, 2849–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Kawamura, M.; Nakazawa, T.; Zhang, J.; Tanimura, A.; Uesaka, N.; Watanabe, M.; Sakimura, K.; et al. Retrograde BDNF to TrkB signaling promotes synapse elimination in the developing cerebellum. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafitz, K.W.; Rose, C.R.; Thoenen, H.; Konnerth, A. Neurotrophin-evoked rapid excitation through TrkB receptors. Nature 1999, 401, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ko, H.; Cheung, Z.H.; Yung, K.K.; Yao, T.; Wang, J.-J.; Morozov, A.; Ke, Y.; Ip, N.Y.; Yung, W.-H. Dual actions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on GABAergic transmission in cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 233, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxall, A.R. GABAergic mIPSCs in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells are modulated by TrkB and mGluR1-mediated stimulation of Src. J. Physiol. 2000, 524, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, Y.M.; Martínez-García, M.; Llansola, M.; Felipo, V. Enhanced BDNF and TrkB Activation Enhance GABA Neurotransmission in Cerebellum in Hyperammonemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, J.-J.; Yung, W.-H. Coupling Between GABA-A Receptor and Chloride Transporter Underlies Ionic Plasticity in Cerebellar Purkinje Neurons. Cerebellum 2013, 12, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.R.; Chen, C.; Schwartz, P.M.; Segal, R.A. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Modulates Cerebellar Plasticity and Synaptic Ultrastructure. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Sato, N.; Obayashi, M.; Niimi, Y.; Ishiguro, T.; Yamada, M.; Toyoshima, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Kato, T.; et al. Reduced brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA expression and presence of BDNF-immunoreactive granules in the spinocerebellar ataxia type 6 (SCA6) cerebellum. Neuropathology 2012, 32, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourez, R.; Servais, L.; Orduz, D.; Gall, D.; Millard, I.; de Kerchove d’Exaerde, A.; Cheron, G.; Orr, H.T.; Pandolfo, M.; Schiffmann, S.N. Aminopyridines correct early dysfunction and delay neurodegeneration in a mouse model of spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 11795–11807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.; Jaramillo-Merchán, J.; Bueno, C.; Pastor, D.; Viso-León, M.; Martínez, S. Mesenchymal stem cells rescue Purkinje cells and improve motor functions in a mouse model of cerebellar ataxia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 40, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firozan, B.; Goudarzi, I.; Salmani, M.E.; Lashkarbolouki, T.; Rezaei, A.; Abrari, K. Estradiol increases expression of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor after acute administration of ethanol in the neonatal rat cerebellum. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 732, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, A.; Kato, H.; Takakura, H.; Osawa, S.; Maeda, Y.; Izawa, T. Effects of physical activity and melatonin on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and cytokine expression in the cerebellum of high-fat diet-fed rats. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2020, 40, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelucci, F.; De Bartolo, P.; Gelfo, F.; Foti, F.; Cutuli, D.; Bossù, P.; Caltagirone, C.; Petrosini, L. Increased Concentrations of Nerve Growth Factor and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Rat Cerebellum After Exposure to Environmental Enrichment. Cerebellum 2009, 8, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.S.d.S.; Santos, G.C.J.; Filgueira, T.O.; Gomes, D.A.; Barbosa, E.A.S.; dos Santos, T.M.; Câmara, N.O.S.; Castoldi, A.; Souto, F.O. Cytokines and Immune Cells Profile in Different Tissues of Rodents Induced by Environmental Enrichment: Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, W.; Spiess, J.; Rivier, C.; Rivier, J. Characterization of a 41-residue ovine hypothalamic peptide that stimulates secretion of corticotropin and beta-endorphin. Science 1981, 213, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittencourt, J.C.; Sawchenko, P.E. Do Centrally Administered Neuropeptides Access Cognate Receptors?: An Analysis in the Central Corticotropin-Releasing Factor System. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.-P.; Zhuang, Q.-X.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Li, H.-Z.; Wang, J.-J.; Zhu, J.-N. Role of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor in Cerebellar Motor Control and Ataxia. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2661–2669.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezra-Nevo, G.; Volk, N.; Ramot, A.; Kuehne, C.; Tsoory, M.; Deussing, J.; Chen, A. Inferior olive CRF plays a role in motor performance under challenging conditions. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, S.; Sharp, B.; Elde, R. Corticotropin-releasing factor in cerebellar afferent systems: A combined immunohistochemistry and retrograde transport study. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Totsune, K.; Ohneda, M.; Konno, H.; Murakami, O.; Satoh, F.; Sone, M.; Takase, S.; Itoyama, Y.; et al. Decrease in cerebellin and corticotropin-releasing hormone in the cerebellum of olivopontocerebellar atrophy and Shy-Drager syndrome. Brain Res. 1995, 686, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libster, A.M.; Title, B.; Yarom, Y. Corticotropin-releasing factor increases Purkinje neuron excitability by modulating sodium, potassium, and Ih currents. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 114, 3339–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, M.; Okada, D.; Hashimoto, K.; Kano, M.; Ito, M. Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Plays a Permissive Role in Cerebellar Long-Term Depression. Neuron 1999, 22, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmolesky, M.T.; De Ruiter, M.M.; De Zeeuw, C.I.; Hansel, C. The neuropeptide corticotropin-releasing factor regulates excitatory transmission and plasticity at the climbing fibre-Purkinje cell synapse. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.-N.; Zhang, X.-D.; Xu, Y.-H.; Li, B.-Y.; Qiu, D.-L.; Chu, C.-P. Activation CRF-R2 augments cerebellar climbing fiber-Purkinje cell synaptic transmission via presynaptic PKA pathway in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 777, 136584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.-G.; Piao, C.-J.; Wan, P.; Li, S.-Y.; Wei, Y.-X.; Zhao, G.-J.; Wu, W.-Y.; Hong, L.; Chu, C.-P.; Qiu, D.-L. Opposing actions of CRF-R1 and CB1 receptor on facial stimulation-induced MLI-PC plasticity in mouse cerebellar cortex. BMC Neurosci. 2022, 23, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezra-Nevo, G.; Prestori, F.; Locatelli, F.; Soda, T.; Brinke, M.M.T.; Engel, M.; Boele, H.-J.; Botta, L.; Leshkowitz, D.; Ramot, A.; et al. Cerebellar Learning Properties Are Modulated by the CRF Receptor. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 6751–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, O.T.; Minnebusch, D.; Daum, I. Stress impairs acquisition of delay eyeblink conditioning in men and women. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2009, 91, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, O.T.; Bauser, D.S.; Daum, I. Eyeblink conditional discrimination learning in healthy young men is impaired after stress exposure. Psychophysiology 2011, 49, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joëls, M.; Baram, T.Z. The neuro-symphony of stress. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.D.; Rammes, G.; Kraev, I.; Wolf, M.; Liebl, C.; Scharf, S.H.; Rice, C.J.; Wurst, W.; Holsboer, F.; Deussing, J.M.; et al. Forebrain CRF₁ modulates early-life stress-programmed cognitive deficits. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 13625–13634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmack, N.H.; Pettorossi, V.E. Adaptive Balance in Posterior Cerebellum. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 635259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, G.A.; King, J.S. Corticotropin Releasing Factor in the Embryonic Mouse Cerebellum. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 160, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madtes, P.; King, J.S. The temporal and spatial development of CRF binding sites in the postnatal mouse cerebellum. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 34, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.S.; Bishop, G.A. The distribution and cellular localization of CRF-R1 in the vermis of the postnatal mouse cerebellum. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 178, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounko, N.V.; Kalicharan, D.; Rybakin, V.; Gramsbergen, A.; Van Der Want, J.J.L. The dynamic developmental localization of the full-length corticotropin-releasing factor receptor type 2 in rat cerebellum. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 3217–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Shan, X.; Bishop, G.; King, J. Presynaptic localization of a truncated isoform of the type 2 corticotropin releasing factor receptor in the cerebellum. Neuroscience 2006, 138, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounko, N.V.; Gramsbergen, A.; van der Want, J.J.L. Localization and functional roles of corticotropin-releasing factor receptor type 2 in the cerebellum. Cerebellum 2008, 7, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounko, N.V.; Swinny, J.D.; Kalicharan, D.; Jafari, S.; Corteen, N.; Seifi, M.; Bakels, R.; van der Want, J.J.L. Corticotropin-releasing factor and urocortin regulate spine and synapse formation: Structural basis for stress-induced neuronal remodeling and pathology. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 18, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Swinny, J.D.; Metzger, F.; Ijkema-Paassen, J.; Gounko, N.V.; Gramsbergen, A.; Van Der Want, J.J.L. Corticotropin-releasing factor and urocortin differentially modulate rat Purkinje cell dendritic outgrowth and differentiation in vitro. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeggs, L.T.; Marsh, W.H.; Kahn, J.R.; Shumway, N.P. The existence of two forms of hypertensin. J. Exp. Med. 1954, 99, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M. Functions Of Angiotensin In The Central Nervous System. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1987, 49, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changaris, D.G.; Severs, W.B.; Keil, L.C. Localization of angiotensin in rat brain. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1978, 26, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdmann, B.; Fuxe, K.; Ganten, D. Subcellular Localization of Angiotensin II Immunoreactivity in the Rat Cerebellar Cortex. Hypertension 1996, 28, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkahloun, A.G.; Saavedra, J.M. Candesartan Neuroprotection in Rat Primary Neurons Negatively Correlates with Aging and Senescence: A Transcriptomic Analysis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 57, 1656–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ohno, N.; Terada, N.; Saitoh, Y.; Chen, J.; Ohno, S. Immunohistochemical detection of angiotensin II receptors in mouse cerebellum and adrenal gland using “in vivo cryotechnique”. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 140, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan, L.P.; Flanagan-Cato, L.M.; Yee, D.K.; Ma, L.-Y.; Sakai, R.R.; Fluharty, S.J. Immunohistochemical mapping of angiotensin type 2 (AT2) receptors in rat brain. Brain Res. 1994, 662, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jöhren, O.; Häuser, W.; Saavedra, J.M. Chemical lesion of the inferior olive reduces [125I]Sarcosine1–Angiotensin II binding to AT2 receptors in the cerebellar cortex of young rats. Brain Res. 1998, 793, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, F.; Do, T.H.; Laflamme, L.; Gallo, J.-M.; Gallo-Payet, N. Activation of the AT2 Receptor of Angiotensin II Induces Neurite Outgrowth and Cell Migration in Microexplant Cultures of the Cerebellum. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31686–31692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongroach, P.; Sanguanrungsirikul, S.; Tantisira, B.; Kunluan, P. Angiotensin II-induced depression of purkinje cell firing and possible modulatory action on GABA responses. Neurosci. Res. 1984, 1, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haspula, D.; Clark, M.A. Contrasting Roles of Ang II and ACEA in the Regulation of IL10 and IL1β Gene Expression in Primary SHR Astroglial Cultures. Molecules 2021, 26, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, A.T.; Clark, M.A. Angiotensin II induces cyclooxygenase 2 expression in rat astrocytes via the angiotensin type 1 receptor. Neuropeptides 2019, 77, 101958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervoort, V.S.; Beachem, M.A.; Edwards, P.S.; Ladd, S.; Miller, K.E.; de Mollerat, X.; Clarkson, K.; DuPont, B.; Schwartz, C.E.; Stevenson, R.E.; et al. AGTR2 Mutations in X-Linked Mental Retardation. Science 2002, 296, 2401–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.G.; Rafi, S.K.; Manzardo, A.M. High-Resolution Chromosome Ideogram Representation of Currently Recognized Genes for Autism Spectrum Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6464–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bealer, S.L.; Crowley, W.R. Angiotensin II-induced release of oxytocin: Interaction with norepinephrine and role in lactation. Regul. Pept. 2002, 111, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Kloth, A.D.; Badura, A. The cerebellum, sensitive periods, and autism. Neuron 2014, 83, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatemoto, K.; Carlquist, M.; Mutt, V. Neuropeptide Y—A novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature 1982, 296, 659–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, Y.; Fournier, A.; St-Pierre, S.; Quirion, R. Comparative characterization and autoradiographic distribution of neuropeptide Y receptor subtypes in the rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Z.; Li, X.Y.; Tong, J.J.; Qiu, Z.Y.; Zhan, H.C.; Sha, J.N.; Peng, K.M. Duck cerebellum participates in regulation of food intake via the neurotransmitters serotonin and neuropeptide Y. Nutr. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wai, S.M.; Kindler, P.M.; Lam, E.T.K.; Zhang, A.; Yew, D.T. Distribution of Neuropeptide Y-Immunoreactive Neurons in the Human Brainstem, Cerebellum, and Cortex During Development. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2004, 24, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, T.; Houtani, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Baba, K.; Ikeda, M.; Yamashita, T.; Sugimoto, T. A subpopulation of olivocerebellar projection neurons express neuropeptide Y. Brain Res. 1994, 634, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neveu, I.; Rémy, S.; Naveilhan, P. The neuropeptide Y receptors, Y1 and Y2, are transiently and differentially expressed in the developing cerebellum. Neuroscience 2002, 113, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morara, S.; Marcotti, W.; Provini, L.; Rosina, A. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) expression is up-regulated in the rat inferior olive during development. NeuroReport 1997, 8, 3743–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte-Neves, J.; Gonçalves, N.; Cunha-Santos, J.; Simões, A.T.; Dunnen, W.F.D.; Hirai, H.; Kügler, S.; Cavadas, C.; de Almeida, L.P. Neuropeptide Y mitigates neuropathology and motor deficits in mouse models of Machado–Joseph disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5451–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte-Neves, J.; Cavadas, C.; de Almeida, L.P. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) intranasal delivery alleviates Machado–Joseph disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, T.; Amemiya, A.; Ishii, M.; Matsuzaki, I.; Chemelli, R.M.; Tanaka, H.; Williams, S.C.; Richardson, J.A.; Kozlowski, G.P.; Wilson, S.; et al. Orexins and Orexin Receptors: A Family of Hypothalamic Neuropeptides and G Protein-Coupled Receptors that Regulate Feeding Behavior. Cell 1998, 92, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lecea, L.; Kilduff, T.S.; Peyron, C.; Gao, X.; Foye, P.E.; Danielson, P.E.; Fukuhara, C.; Battenberg, E.L.; Gautvik, V.T.; Bartlett, F.S., 2nd; et al. The hypocretins: Hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, T. The neural circuit of orexin (hypocretin): Maintaining sleep and wakefulness. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemelli, R.M.; Willie, J.T.; Sinton, C.M.; Elmquist, J.K.; Scammell, T.; Lee, C.; Richardson, J.A.; Williams, S.; Xiong, Y.; Kisanuki, Y.; et al. Narcolepsy in orexin Knockout Mice: Molecular Genetics of Sleep Regulation. Cell 1999, 98, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- España, R.A.; McCormack, S.L.; Mochizuki, T.; Scammell, T.E. Running Promotes Wakefulness and Increases Cataplexy in Orexin Knockout Mice. Sleep 2007, 30, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervieu, G.; Cluderay, J.; Harrison, D.; Roberts, J.; Leslie, R. Gene expression and protein distribution of the orexin-1 receptor in the rat brain and spinal cord. Neuroscience 2001, 103, 777–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluderay, J.; Harrison, D.; Hervieu, G. Protein distribution of the orexin-2 receptor in the rat central nervous system. Regul. Pept. 2001, 104, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.-N.; Wang, J.-J. Orexins Excite Neurons of the Rat Cerebellar Nucleus Interpositus Via Orexin 2 Receptors In Vitro. Cerebellum 2009, 9, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Yu, L.; He, Y.-C.; Li, H.-Z.; Zhu, J.-N.; Wang, J.-J. A Role for Orexin in Central Vestibular Motor Control. Neuron 2011, 69, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisimaru, N.; Mittal, C.; Shirai, Y.; Sooksawate, T.; Anandaraj, P.; Hashikawa, T.; Nagao, S.; Arata, A.; Sakurai, T.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. Orexin-neuromodulated cerebellar circuit controls redistribution of arterial blood flows for defense behavior in rabbits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14124–14131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, F.; Yan, J.; Yang, N.; Wang, Y.-J.; Zhu, Z.-R.; Hu, Z.-A.; Sui, J.-F.; Hu, B. Functional inactivation of orexin 1 receptors in the cerebellum disrupts trace eyeblink conditioning and local theta oscillations in guinea pigs. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 250, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Wu, W.-X.; Shen, L.-P.; Ji, M.-J.; Zhao, P.-F.; Yu, L.; Yin, J.; Xie, S.-T.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-X.; et al. A role for the cerebellum in motor-triggered alleviation of anxiety. Neuron, 2024; In press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichlin, S. TRH: Historical aspects. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1989, 553, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winokur, A.; Utiger, R.D. Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone: Regional Distribution in Rat Brain. Science 1974, 185, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, M.F.; McKelvy, J.F.; Woodward, D.J.; Loudes, C.; Joseph-Bravo, P.; Krulich, L.; Griffin, W.S. TRH in the rat cerebellum: I. Distribution and concentration. Peptides 1981, 2, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzá, L.; Giardino, L.; Ceccatelli, S.; Zanni, M.; Elde, R.; Hökfelt, T. Distribution of thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor messenger RNA in the rat brain: An in situ hybridization study. Neuroscience 1992, 51, 891–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuer, H.; Schäfer, M.K.; O’Donnell, D.; Walker, P.; Bauer, K. Expression of thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor 2 (TRH-R2) in the central nervous system of rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 428, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibusawa, N.; Hashimoto, K.; Yamada, M. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) in the cerebellum. Cerebellum 2008, 7, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, S.; Amano, I.; Koibuchi, N. The Role of Thyroid Hormone in the Regulation of Cerebellar Development. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyani, W.; Miyazaki, W.; Amano, I.; Koibuchi, N. Involvement of integrin αvβ3 in thyroid hormone-induced dendritogenesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 938596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.R. Characterization of Immunoreactive Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone in Human Fetal Cerebellum. J. Neurochem. 1981, 37, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, L.P.; Martin, J.B.; Brazeau, P. Depressant action of TRH, LH-RH and somatostatin on activity of central neurones. Nature 1975, 255, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanave, M.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Ozawa, A.; Yamada, M.; Hirai, H. Contribution of Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone to Cerebellar Long-Term Depression and Motor Learning. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, A.; Amano, I.; Kokubo, M.; Takatsuru, Y.; Ishii, S.; Hirai, H.; Hosoi, N.; Koibuchi, N. Long-term depression–inductive stimulation causes long-term potentiation in mouse Purkinje cells with a mutant thyroid hormone receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2210645119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T.; Tsutsumi, R.; Shimizu, K.; Tominaga, N.; Nagai, M.; Ugawa, Y.; Nishiyama, K.; Hanajima, R. Differential effects of thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) on motor execution and motor adaptation process in patients with spinocerebellar degeneration. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 415, 116927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muroga, T.; Adachi, K.; Konagaya, M.; Takayanagi, T.; Sobue, I. Effects of thyrotropin releasing hormone on cerebellar mutant mice—A kinesiological comparison between Rolling Mouse Nagoya, weaver and reeler. Jpn. J. Med. 1982, 21, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijiro, T.; Yaguchi, A.; Yokoyama, A.; Abe, Y.; Kiguchi, S. Ameliorating effect of rovatirelin on the ataxia in rolling mouse Nagoya. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 882, 173271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamamura, M.; Matsuoka, Y. TRH receptor agonists ameliorate 3-acetylpyridine-induced ataxia through NMDA receptors in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 343, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobue, I.; Yamamoto, H.; Konagaya, M.; Iida, M.; Takayanagi, T. Effect of thyrotropin-releasing hormone on ataxia of spinocerebellar degeneration. Lancet 1980, 315, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobue, I.; Takayanagi, T.; Nakanishi, T.; Tsubaki, T.; Uono, M.; Kinoshita, M.; Igata, A.; Miyazaki, M.; Yoshida, M.; Ando, K.; et al. Controlled trial of thyrotropin releasing hormone tartrate in ataxia of spinocerebellar degenerations. J. Neurol. Sci. 1983, 61, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekary, A.E.; Sattin, A. A resveratrol derivative modulates TRH and TRH-like peptide expression throughout the brain and peripheral tissues of male rats. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 5, e356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Vigneaud, V.; Ressler, C.; Trippett, S. The sequence of amino acids in oxytocin, with a proposal for the structure of oxytocin. J. Biol. Chem. 1953, 205, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurek, B.; Neumann, I.D. The Oxytocin Receptor: From Intracellular Signaling to Behavior. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1805–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warfvinge, K.; Krause, D.; Edvinsson, L. The distribution of oxytocin and the oxytocin receptor in rat brain: Relation to regions active in migraine. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipari, A.; Farina, E.; Gerbino, A.; Lipari, L. Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and oxytocin-expression in the adult rat and mouse cerebellum. Cerebellum Ataxias 2015, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, D.S.; Rokicki, J.; van der Meer, D.; Alnæs, D.; Kaufmann, T.; Córdova-Palomera, A.; Dieset, I.; Andreassen, O.A.; Westlye, L.T. Oxytocin pathway gene networks in the human brain. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newmaster, K.T.; Nolan, Z.T.; Chon, U.; Vanselow, D.J.; Weit, A.R.; Tabbaa, M.; Hidema, S.; Nishimori, K.; Hammock, E.A.D.; Kim, Y. Quantitative cellular-resolution map of the oxytocin receptor in postnatally developing mouse brains. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.-P.; Li, W.; Pei, L.-Z.; Yin, J.; Xie, S.-T.; Li, H.-Z.; Yan, C.; Wang, J.-J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.-Y.; et al. Oxytocin Receptor in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells Does Not Engage in Autism-Related Behaviors. Cerebellum 2022, 22, 888–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Shen, J.; Chen, Z.; Song, W.; Zheng, P.; et al. Melanopsin retinal ganglion cells mediate light-promoted brain development. Cell 2022, 185, 3124–3137.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Miao, W.; Ji, E.; Huang, S.; Jin, S.; Zhu, X.; Liu, M.-Z.; Sun, Y.-G.; Xu, F.; Yu, X. Social touch-like tactile stimulation activates a tachykinin 1-oxytocin pathway to promote social interactions. Neuron 2022, 110, 1051–1067.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Ma, X.; Geng, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, F.; Wang, J.; Markett, S.; Biswal, B.B.; Ma, Y.; Kendrick, K.M.; et al. Oxytocin differentially modulates specific dorsal and ventral striatal functional connections with frontal and cerebellar regions. NeuroImage 2018, 184, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riem, M.M.; van Ijzendoorn, M.H.; Tops, M.; Boksem, M.A.; Rombouts, S.A.; Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.J. Oxytocin effects on complex brain networks are moderated by experiences of maternal love withdrawal. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menashe, I.; Grange, P.; Larsen, E.C.; Banerjee-Basu, S.; Mitra, P.P. Co-expression Profiling of Autism Genes in the Mouse Brain. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willsey, A.J.; Sanders, S.J.; Li, M.; Dong, S.; Tebbenkamp, A.T.; Muhle, R.A.; Reilly, S.K.; Lin, L.; Fertuzinhos, S.; Miller, J.A.; et al. Coexpression Networks Implicate Human Midfetal Deep Cortical Projection Neurons in the Pathogenesis of Autism. Cell 2013, 155, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.M.; Kim, S.J.; Kistner-Griffin, E.; Guter, S.; Cook, E.H.; Jacob, S. ASD and Genetic Associations with Receptors for Oxytocin and Vasopressin-AVPR1A, AVPR1B, and OXTR. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurek, B.; Slattery, D.A.; Hiraoka, Y.; Liu, Y.; Nishimori, K.; Aguilera, G.; Neumann, I.D.; Burg, E.H.v.D. Oxytocin Regulates Stress-InducedCrfGene Transcription through CREB-Regulated Transcription Coactivator 3. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 12248–12260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Berger, I.; Winter, J.; Jurek, B. Oxytocin alters the morphology of hypothalamic neurons via the transcription factor myocyte enhancer factor 2A (MEF-2A). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 477, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, A.P.; Manzardo, A.M.; Butler, M.G. GeneAnalytics Pathways and Profiling of Shared Autism and Cancer Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assali, A.; Harrington, A.J.; Cowan, C.W. Emerging roles for MEF2 in brain development and mental disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2019, 59, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatkova, M.; Reichova, A.; Bacova, Z.; Bakos, J. Activation of the Oxytocin Receptor Modulates the Expression of Synaptic Adhesion Molecules in a Cell-Specific Manner. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 68, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayliss, W.M.; Starling, E.H. The mechanism of pancreatic secretion. J. Physiol. 1902, 28, 325–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chow, B.K.C. The Central Mechanisms of Secretin in Regulating Multiple Behaviors. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Chow, B.K.C. Secretin Modulates the Postnatal Development of Mouse Cerebellar Cortex Via PKA- and ERK-dependent Pathways. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, K.M.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, M.K.; Nam, R.H.; Lee, B.L.; Lee, K.H.; Cha, C.I. Distribution of vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide receptors (VPAC1, VPAC2, and PAC1 receptor) in the rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 476, 388–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, W.-H.; Leung, P.-S.; Ng, S.S.M.; Zhang, J.; Chan, S.C.Y.; Chow, B.K.C. Secretin Facilitates GABA Transmission in the Cerebellum. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 7063–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chung, S.K.; Chow, B.K.C. The Knockout of Secretin in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells Impairs Mouse Motor Coordination and Motor Learning. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 39, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Chow, B.K.C. Secretin Prevents Apoptosis in the Developing Cerebellum Through Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 68, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, W.-H.; Chan, Y.-S.; Chow, B.K.C.; Wang, J.-J. The role of secretin in the cerebellum. Cerebellum 2006, 5, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chen, L.; Chow, B.; Yung, W. Endogenous release and multiple actions of secretin in the rat cerebellum. Neuroscience 2005, 134, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, J.R.; Robinson, G.M.; Dean, A.M.; Schoenberg, H.E.; Williams, M.R.; Morielli, A.D.; Green, J.T. Cerebellar secretin modulates eyeblink classical conditioning. Learn. Mem. 2014, 21, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; Fuchs, J.R.; Green, J.T.; Morielli, A.D. Cellular Mechanisms and Behavioral Consequences of Kv1.2 Regulation in the Rat Cerebellum. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 9228–9237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, K.; Stefanatos, G.; Sokolski, K.N.; Wachtel, R.; Nabors, L.; Tildon, J.T. Improved social and language skills after secretin administration in patients with autistic spectrum disorders. J. Assoc. Acad. Minor. Physicians 1998, 9, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lamson, D.W.; Plaza, S.M. Transdermal secretin for autism—A case report. Altern. Med. Rev. 2001, 6, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.; Wray, J.A.; Wheeler, D.M. Intravenous secretin for autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, CD003495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.S.; Chow, B.K.; Wong, V.C. The Human Secretin Gene in Children With Autistic Spectrum Disorder: Screening for Polymorphisms and Mutations. J. Child Neurol. 2005, 20, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Order | Neuropeptide Name | Abbreviation | No. of Publications Available on PubMed in Last Two Decades (2004–2024) | Potential Clinical Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor | BDNF | 403 | SCA6, SCA1 |
| 2 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 | IGF-1 | 110 | Metabolic diseases |
| 3 | Corticotropin-releasing factor (hormone) | CRF (CRH) | 68 | Ataxias |
| 4 | Angiotensin II | Ang II | 49 | ASD |
| 5 | Somatostatin | SS | 45 | |
| 6 | Cerebellin | CBLN | 41 | |
| 7 | Neuropeptide Y | NPY | 40 | SCA3 |
| 8 | Orexin | OX | 33 | Narcolepsy-cataplexy, anxiety |
| 9 | Thyrotropin-releasing hormone | TRH | 32 | Ataxias |
| 10 | Oxytocin | OXT | 29 | ASD |
| 11 | Calcitonin-gene-related peptide | CGRP | 28 | Migraine |
| 12 | Substance P | SP | 26 | |
| 13 | Secretin | SCT | 24 | ASD |
| 14 | Cholecystokinin | CCK | 22 | |
| 15 | Dynorphin | DYN | 17 |
| Cerebellar Development | Neuronal Excitability, Synaptic Transmission, and Synaptic Plasticity | Molecular, Circuital and Behavioral Phenotype | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BDNF | Survival, migration, maturation, and arborization of GrCs ↑ [21,22,23,24,25,26] Survival of PCs ↑ [36] CF synapse elimination ↑ [27] Inhibitory synapse development ↑ [25,27] | GrC and PC excitability ↑ [28] GABAergic transmission in PCs ↑↓ [29,30,31] Ionic plasticity ↑ [32] Paired-pulse facilitation ↑ [33] | Neuroprotective effect ↑ [22,37] Neuroimmune modulation ↑ [38,39] Ataxic gait ↓ [23,36] |
| CRF | PC development ↑ [64,65] Presynaptic development in the cerebellar cortex ↑ [62,63] | Glutamatergic neuron excitability in the interposed nucleus ↑ [43] PC excitability ↑ [47] LTD of PF–PC transmission ↑ [48] LTD of CF–PC transmission ↑ [49] LTP of CF–PC transmission ↑ [50] LTD between interneuron and PC ↓ [51] LTP of MF–GrC transmission ↑ [52] | Motor control under challenging conditions ↑ [44] Motor performance ↑ [43] Motor learning ↓ [52,57] Ataxic symptoms ↓ [43] |
| Angiotensin II | IO–cerebellar pathway development ↑ [73] Neurite outgrowth and cell migration ↑ [74] | PC excitability ↓ [75] GABAergic transmission in PCs ↑ [75] | Aging- and senescence- related gene expression ↑ [70] Il-10 mRNA expression ↓ [76] Cyclooxygenase 2 expression ↑ [77] Proinflammatory effect ↑ [77] Astrocyte mitosis ↑ [77] Systemic oxytocin levels ↑ [80] |
| NPY | Cerebellar volume ↑ [89] GrC survival ↑ [89] | BDNF levels ↑ [89] Anti-inflammatory effect ↑ [89] Mutant ataxin-3 aggregates ↓ [89] Motor coordination ↑ [89,90] | |
| Orexin | CN excitability ↑ [98,102] Vestibular nuclear complex excitability ↑ [99] PC excitability ↑ [100] | Cerebellar theta oscillations ↑ [101] The timing of TEC ↑ [101] Motor performance during a motor challenge ↑ [99] Arterial blood flow redistribution ↑ [100] Anxiolytic effect ↑ [102] | |
| TRH | Migration and differentiation of GrCs ↑ [109] Dendritogenesis and neuritogenesis of PCs ↑ [109,110] Synaptogenesis ↑ [109] | Neuronal excitability in the cerebellar cortex ↓ [112] Neuronal excitability in the interposed nucleus ↑ [108] LTD of PF–PC transmission ↑ [113,114] | Bdnf mRNA levels ↑ [117] Glucose uptake ↑ [117] Motor coordination ↑ [114] Motor learning ↑ [113,114] Ataxic symptoms ↓ [115,116,117,118,119,120] |
| Oxytocin | Synaptic adhesion molecule ↑ [140] Cerebellum-putamen connectivity ↓ [131] Cerebellum-posterior cingulate cortex connectivity ↑ [132] | ||
| Secretin | Survival and arborization of PCs ↑ [143] Survival and maturation of GrC ↑ [143] Anti-apoptotic effects [147] | GABAergic transmission in PCs ↑ [145,148,149] | The acquisition phase of DEC ↑ [150,151] Motor coordination ↑ [146] Motor learning ↑ [146] Autistic-like behaviors ↓ [152,153] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.-H.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhu, J.-N. Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042332
Li Z-H, Li B, Zhang X-Y, Zhu J-N. Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(4):2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042332
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zi-Hao, Bin Li, Xiao-Yang Zhang, and Jing-Ning Zhu. 2024. "Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 4: 2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042332
APA StyleLi, Z.-H., Li, B., Zhang, X.-Y., & Zhu, J.-N. (2024). Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(4), 2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042332





