Iron Stress Affects the Growth and Differentiation of Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Iron Stress Affects the Proliferation and Invasion of Toxoplasma gondii
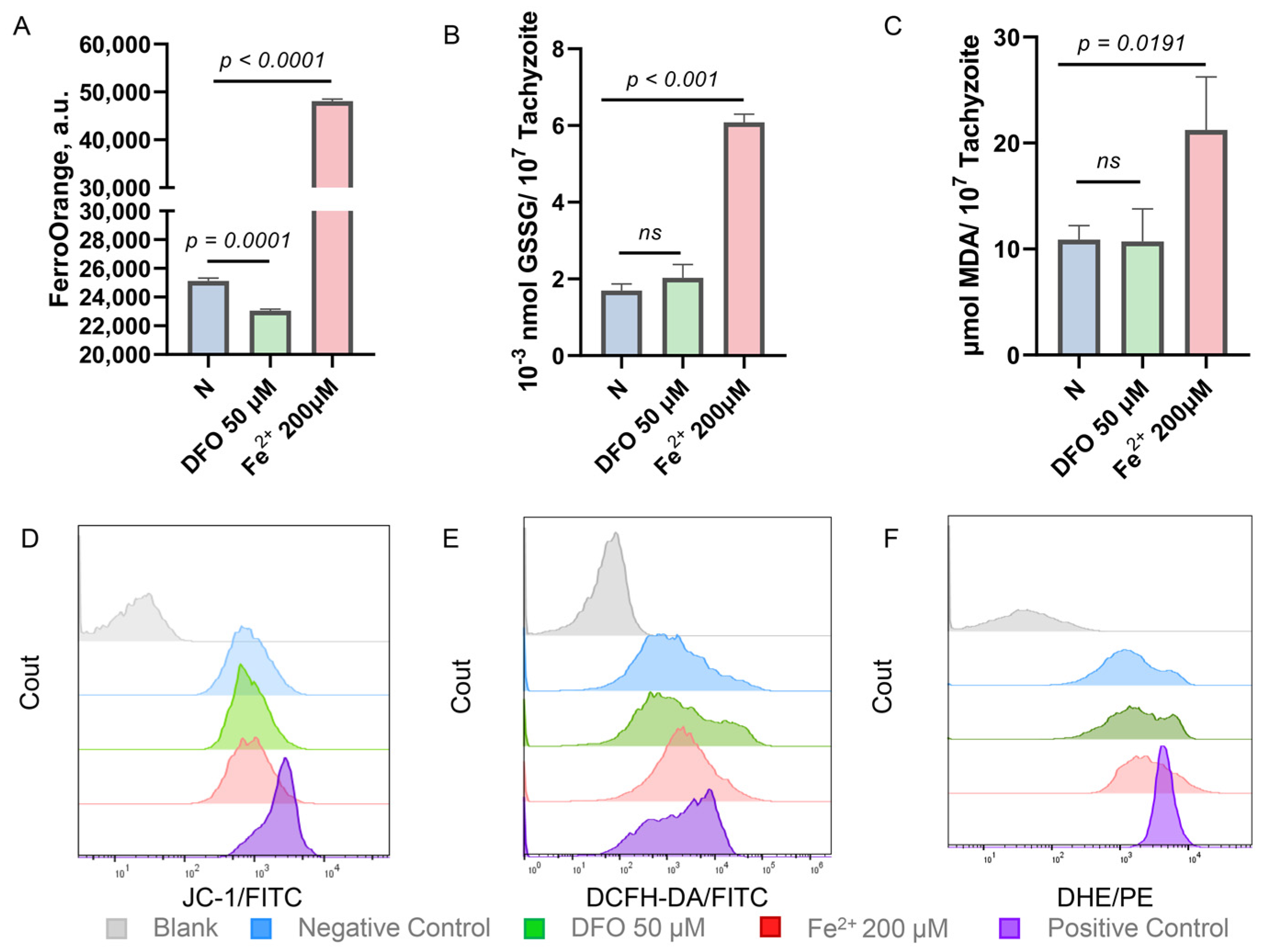
2.2. Iron Stress Affects the Oxidation-Reduction Ability of Toxoplasma gondii
2.3. Enhanced Adhesion Ability of Toxoplasma gondii in a High Iron Environment
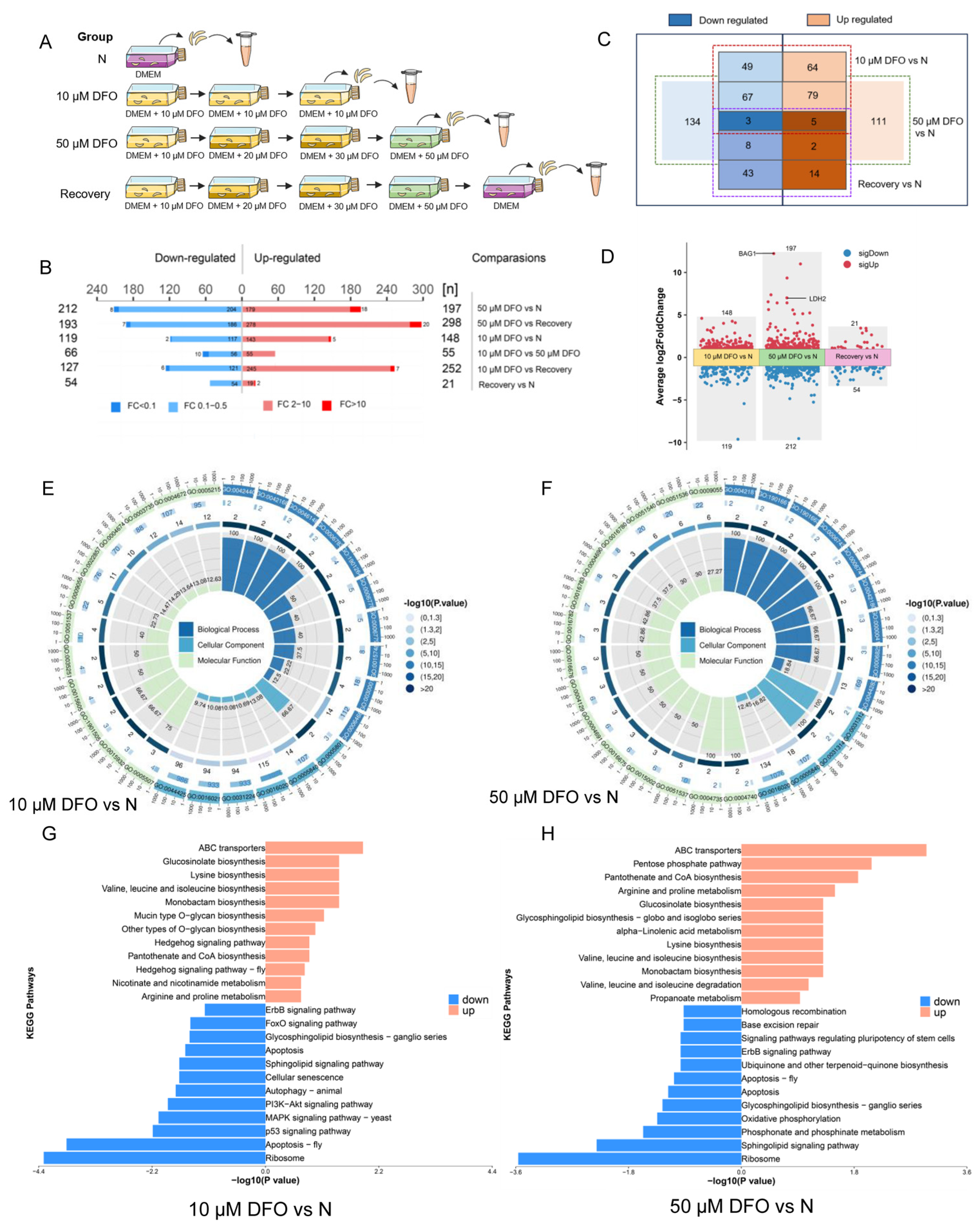
2.4. Conversion of Tachyzoites to Bradyzoites Induced by Iron Depletion
2.5. Comparative Proteomics Reveals Differentially Expressed Proteins of Toxoplasma gondii Impacted by Iron Depletion
2.6. Phosphotyrosyl Phosphatase Activator Protein Is Important for Iron Depletion-Driven Differentiation of Tachyzoites into Bradyzoites
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Host Cells and Parasite Culture
4.2. In Vitro Inhibition Assay
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. Immunofluorescence Assays
4.5. Invasion Assay
4.6. Replication Assay
4.7. Egress Assay
4.8. Plaque Assay
4.9. Detection of Iron, Reactive Oxygen Species, Superoxide Anion, and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.10. GSSG and MDA Determination
4.11. Transcriptomics Analysis
4.12. Comparative Proteomics Analysis
4.13. Mouse Infectivity Studies
4.14. Sequence Analysis, Phylogenetics and Protein Structure Prediction
4.15. CRISPR-Cas9-Mediated Conditional Knockdown
4.16. Western Blotting
4.17. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, D.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii: Transmission, diagnosis and prevention. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2002, 8, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ybañez, R.H.D.; Ybañez, A.P.; Nishikawa, Y. Review on the current trends of toxoplasmosis serodiagnosis in humans. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Ge, C.C.; Fan, Y.M.; Jin, Q.W.; Shen, B.; Huang, S.Y. The determinants regulating Toxoplasma gondii bradyzoite development. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1027073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Cuevas, Y.; Mayoral, J.; Di Cristina, M.; Lawrence, A.-L.E.; Olafsson, E.B.; Patel, R.K.; Thornhill, D.; Waldman, B.S.; Ono, A.; Sexton, J.Z.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii exploits the host ESCRT machinery for parasite uptake of host cytosolic proteins. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sangaré, L.O.; Paredes-Santos, T.C.; Saeij, J.P.J. Toxoplasma mechanisms for delivery of proteins and uptake of nutrients across the host-pathogen interface. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 74, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, C.P. Host-pathogen interactions: The role of iron. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sandaqchi, A.T.; Brignell, C.; Collingwood, J.F.; Geraki, K.; Mirkes, E.M.; Kong, K.; Castellanos, M.; May, S.T.; Stevenson, C.W.; Elsheikha, H.M. Metallome of cerebrovascular endothelial cells infected with Toxoplasma gondii using μ-XRF imaging and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Metallomics 2018, 10, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, Y.T.V.; Seidi, A.; Hayward, J.A.; Lee, J.; Makota, F.V.; Rug, M.; van Dooren, G.G. A key cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster synthesis protein localizes to the mitochondrion of Toxoplasma gondii. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 115, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, E.A.; Pamukcu, S.; Cerutti, A.; Berry, L.; Lemaire-Vieille, C.; Yamaryo-Botté, Y.; Botté, C.Y.; Besteiro, S. Disrupting the plastidic iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis pathway in Toxoplasma gondii has pleiotropic effects irreversibly impacting parasite viability. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamukcu, S.; Cerutti, A.; Bordat, Y.; Hem, S.; Rofidal, V.; Besteiro, S. Differential contribution of two organelles of endosymbiotic origin to iron-sulfur cluster synthesis and overall fitness in Toxoplasma. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjhin, E.T.; Hayward, J.A.; McFadden, G.I.; van Dooren, G.G. Characterization of the apicoplast-localized enzyme TgUroD in Toxoplasma gondii reveals a key role of the apicoplast in heme biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, A.; Floyd, K.; Key, M.; Dameron, C.; Rees, K.C.; Thornton, L.B.; Whitehead, D.C.; Hamza, I.; Dou, Z. Toxoplasma gondii requires its plant-like heme biosynthesis pathway for infection. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuh, O.A.; Elahi, R.; Prigge, S.T.; Seeber, F. The ferredoxin redox system—An essential electron distributing hub in the apicoplast of Apicomplexa. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Yang, X.; Ying, Z.; Wu, K.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q. Regulation of mitochondrial energy metabolism by glutaredoxin 5 in the apicomplexan parasite Neospora caninum. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0309122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkel, S.; Frohnecke, N.; Maus, D.; McConville, M.J.; Laue, M.; Blume, M.; Seeber, F. Toxoplasma gondii apicoplast-resident ferredoxin is an essential electron transfer protein for the MEP isoprenoid-biosynthetic pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimier, I.H.; Bout, D.T. Interferon-gamma-activated primary enterocytes inhibit Toxoplasma gondii replication: A role for intracellular iron. Immunology 1998, 94, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonis, N.; Creek, D.J.; Tilley, L. Iron and heme metabolism in Plasmodium falciparum and the mechanism of action of artemisinins. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziadek, B.; Dziadek, J.; Dlugonska, H. Identification of Toxoplasma gondii proteins binding human lactoferrin: A new aspect of rhoptry proteins function. Exp. Parasitol. 2007, 115, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziadek, B.; Dzitko, K.; Dlugonska, H. Toxoplasma gondii binds human lactoferrin but not transferrin. Exp. Parasitol. 2005, 110, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghabi, D.; Sloan, M.; Gill, G.; Hartmann, E.; Antipova, O.; Dou, Z.; Guerra, A.J.; Carruthers, V.B.; Harding, C.R. The vacuolar iron transporter mediates iron detoxification in Toxoplasma gondii. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, G.; Pantopoulos, K. Iron metabolism and toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 202, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattermann, N.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Kulozik, A.E.; Metzgeroth, G.; Hastka, J. The evaluation of iron deficiency and iron overload. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2021, 118, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.J.R.; Merlot, A.M.; Huang, M.L.H.; Bae, D.-H.; Jansson, P.J.; Sahni, S.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Richardson, D.R. Cellular iron uptake, trafficking and metabolism: Key molecules and mechanisms and their roles in disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 1130–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Conrad, M. The metabolic underpinnings of ferroptosis. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 920–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaldan, S.; Clatworthy, S.A.S.; Gamell, C.; Meggyesy, P.M.; Rigopoulos, A.-T.; Haupt, S.; Haupt, Y.; Denoyer, D.; Adlard, P.A.; Bush, A.I.; et al. Iron accumulation in senescent cells is coupled with impaired ferritinophagy and inhibition of ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recalcati, S.; Locati, M.; Gammella, E.; Invernizzi, P.; Cairo, G. Iron levels in polarized macrophages: Regulation of immunity and autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.; Ryan, F.; Jhelum, P.; Kroner, A. Ferroptosis in Neurological Disease. Neuroscientist 2023, 29, 591–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusek, P.; Hofer, T.; Alexander, J.; Roos, P.M.; Aaseth, J.O. Cerebral Iron Deposition in Neurodegeneration. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, I. Anemia, Iron supplementation and susceptibility to Plasmodium falciparum malaria. EBioMedicine 2016, 14, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.A.; Goheen, M.M.; Fulford, A.; Prentice, A.M.; Elnagheeb, M.A.; Patel, J.; Fisher, N.; Taylor, S.M.; Kasthuri, R.S.; Cerami, C. Host iron status and iron supplementation mediate susceptibility to erythrocytic stage Plasmodium falciparum. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.A.; Goheen, M.M.; Cerami, C. Influence of host iron status on Plasmodium falciparum infection. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddey, J.A.; Cowman, A.F. Plasmodium nesting: Remaking the erythrocyte from the inside out. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 243–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk-Golec, K.; Pawłowska, M.; Wesołowski, R.; Wróblewski, M.; Mila-Kierzenkowska, C. Oxidative stress as a possible target in the treatment of toxoplasmosis: Perspectives and ambiguities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, J.; Sutak, R. Iron in parasitic protists—From uptake to storage and where we can interfere. Metallomics 2020, 12, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, S.; Castro, P.; Nogué, S.; Nicolás, J.M. Acute iron intoxication: Change in urine color during chelation therapy with deferoxamine. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhang, C.; Han, L.; Xu, T.; Saeed, K.; Han, J.; Liu, J.; Klaassen, C.D.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Lu, Y.; et al. Suppressed farnesoid X receptor by iron overload in mice and humans potentiates iron-induced hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 2022, 76, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelman, A.; Wachtel, C.; Cohen, M.; Haupt, S.; Shapiro, H.; Tzur, A. JC-1: Alternative excitation wavelengths facilitate mitochondrial membrane potential cytometry. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasmuth, J.D.; Pszenny, V.; Haile, S.; Jansen, E.M.; Gast, A.T.; Sher, A.; Boyle, J.P.; Boulanger, M.J.; Parkinson, J.; Grigg, M.E. Integrated bioinformatic and targeted deletion analyses of the SRS gene superfamily identify SRS29C as a negative regulator of Toxoplasma virulence. mBio 2012, 3, e00321-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.; Lee, C.Y.-F.; Grigg, M.E. The SRS superfamily of Toxoplasma surface proteins. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, T.T.; Kim, S.-K.; Camps, M.; Boothroyd, J.C.; Knoll, L.J. The BSR4 protein is up-regulated in Toxoplasma gondii bradyzoites, however the dominant surface antigen recognised by the P36 monoclonal antibody is SRS9. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K. How does Toxoplama gondii invade host cells? J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portes, J.; Barrias, E.; Travassos, R.; Attias, M.; de Souza, W. Toxoplasma gondii mechanisms of entry into host cells. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubremetz, J.F. Host cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii. Trends Microbiol. 1998, 6, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelbaset, A.E.; Fox, B.A.; Karram, M.H.; Abd Ellah, M.R.; Bzik, D.J.; Igarashi, M. Lactate dehydrogenase in Toxoplasma gondii controls virulence, bradyzoite differentiation, and chronic infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Parmley, S.F. Toxoplasma gondii expresses two distinct lactate dehydrogenase homologous genes during its life cycle in intermediate hosts. Gene 1997, 184, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes-Santos, T.C.; Tomita, T.; Yan Fen, M.; de Souza, W.; Attias, M.; Vommaro, R.C.; Weiss, L.M. Development of dual fluorescent stage specific reporter strain of Toxoplasma gondii to follow tachyzoite and bradyzoite development in vitro and in vivo. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, D.J.P. Use of molecular and ultrastructural markers to evaluate stage conversion of Toxoplasma gondii in both the intermediate and definitive host. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.A.; Fouts, A.E.; Cummings, C.A.; Ferguson, D.J.P.; Boothroyd, J.C. A novel rhoptry protein in Toxoplasma gondii bradyzoites and merozoites. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2005, 144, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmasso, M.C.; Onyango, D.O.; Naguleswaran, A.; Sullivan, W.J., Jr.; Angel, S.O. Toxoplasma H2A variants reveal novel insights into nucleosome composition and functions for this histone family. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 392, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Xia, N.; Zhao, P.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, B.; Zhao, J. Micronemal protein 13 contributes to the optimal growth of Toxoplasma gondii under stress conditions. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, K.J.; Aliota, M.T.; Knoll, L.J. Dual transcriptional profiling of mice and Toxoplasma gondii during acute and chronic infection. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehl, A.B.; Basso, W.U.; Lippuner, C.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Okoniewski, M.; Walker, R.A.; Grigg, M.E.; Smith, N.C.; Deplazes, P. Asexual expansion of Toxoplasma gondii merozoites is distinct from tachyzoites and entails expression of non-overlapping gene families to attach, invade, and replicate within feline enterocytes. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, C.; Maier, S.; Walker, R.A.; Rehrauer, H.; Joekel, D.E.; Winiger, R.R.; Basso, W.U.; Grigg, M.E.; Hehl, A.B.; Deplazes, P.; et al. An experimental genetically attenuated live vaccine to prevent transmission of Toxoplasma gondii by cats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Brown, K.M.; Jones, N.G.; Moreno, S.N.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma bradyzoites exhibit physiological plasticity of calcium and energy stores controlling motility and egress. Elife 2021, 10, e73011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.; Xing, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Stock, J.B.; Shi, Y. Structure and mechanism of the phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activator. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Li, T.T.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Liang, Q.L.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, M.; Sibley, L.D.; Zhu, X.Q. The protein phosphatase 2A holoenzyme is a key regulator of starch metabolism and bradyzoite differentiation in Toxoplasma gondii. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licon, M.H.; Giuliano, C.J.; Chan, A.W.; Chakladar, S.; Eberhard, J.N.; Shallberg, L.A.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Waldman, B.S.; Koshy, A.A.; Hunter, C.A.; et al. A positive feedback loop controls Toxoplasma chronic differentiation. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldman, B.S.; Schwarz, D.; Wadsworth, M.H., 2nd; Saeij, J.P.; Shalek, A.K.; Lourido, S. Identification of a Master Regulator of Differentiation in Toxoplasma. Cell 2020, 180, 359–372.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutt, S.; Hamza, I.; Bartnikas, T.B. Molecular mechanisms of iron and heme metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2022, 42, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, C.E.; Mahoney, A.W. Contributions of heme and nonheme iron to human nutrition. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1992, 31, 333–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephen, L.D.; Alexa, M.; Lindsay, L.N.; Miguel, P.S.; Barbara, A.F.; David, J.B.; Jason, P.G. Theft of host transferrin receptor-1 by Toxoplasma gondii is required for infection. bioRxiv 2023, 546322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.P.O.; Ferro, E.A.V.; Briceño, M.P.P.; Oliveira, M.C.; Barbosa, B.F.; Silva, N.M. S Susceptibility of human villous (BeWo) and extravillous (HTR-8/SVneo) trophoblast cells to Toxoplasma gondii infection is modulated by intracellular iron availability. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 1559–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megan, A.S.; Adam, S.; Clare, R.H. Keeping FIT: Iron-mediated post-transcriptional regulation in Toxoplasma gondii. bioRxiv 2023, 565792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eléa, A.R.; Ambre, J.M.M.; Yann, B.; Arnault, G.; Laurence, B.; Sébastien, B. Iron depletion has different consequences on the growth and survival of Toxoplasma gondii strains. bioRxiv 2023, 572787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, F.; Nishikawa, Y. Starvation of low-density lipoprotein-derived cholesterol induces bradyzoite conversion in Toxoplasma gondii. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.C.; Coutinho, L.B.; Almeida, M.P.O.; Briceño, M.P.; Araujo, E.C.B.; Silva, N.M. The availability of iron is involved in the murine experimental Toxoplasma gondii infection outcome. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.S. Effect of deferoxamine alone and combined with pyrimethamine on acute toxoplasmosis in mice. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 791–803. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, W.; Barad, A.; Clark, A.G.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Gu, Z.; O’Brien, K.O. Ethnic differences in iron status. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1838–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.G.; Remington, J.S. Management of Toxoplasma gondii infection during pregnancy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Ying, Z.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Q. Toxoplasma gondii UBL-UBA shuttle proteins contribute to the degradation of ubiquitinylated proteins and are important for synchronous cell division and virulence. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 13711–13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Cui, X.; Fan, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Q. Comprehensive characterization of Toxoplasma acyl coenzyme A-binding protein TgACBP2 and its critical role in parasite cardiolipin metabolism. mBio 2018, 9, e01597-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ying, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, Q. Depletion of Toxoplasma adenine nucleotide translocator leads to defects in mitochondrial morphology. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Brown, K.M.; Lee, T.D.; Sibley, L.D. Efficient gene disruption in diverse strains of Toxoplasma gondii using CRISPR/CAS9. mBio 2014, 5, e01114-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Han, F.; Ge, C.; Mao, W.; Chen, L.; Hu, H.; Chen, G.; Lang, Q.; Fang, C. OmicStudio: A composable bioinformatics cloud platform with real-time feedback that can generate high-quality graphs for publication. iMeta 2023, 2, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ying, Z.; Yin, M.; Zhu, Z.; Shang, Z.; Pei, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q. Iron Stress Affects the Growth and Differentiation of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052493
Ying Z, Yin M, Zhu Z, Shang Z, Pei Y, Liu J, Liu Q. Iron Stress Affects the Growth and Differentiation of Toxoplasma gondii. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(5):2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052493
Chicago/Turabian StyleYing, Zhu, Meng Yin, Zifu Zhu, Zheng Shang, Yanqun Pei, Jing Liu, and Qun Liu. 2024. "Iron Stress Affects the Growth and Differentiation of Toxoplasma gondii" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 5: 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052493
APA StyleYing, Z., Yin, M., Zhu, Z., Shang, Z., Pei, Y., Liu, J., & Liu, Q. (2024). Iron Stress Affects the Growth and Differentiation of Toxoplasma gondii. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5), 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052493





