Silver and Gold Complexes with NHC-Ligands Derived from Caffeine: Catalytic and Pharmacological Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
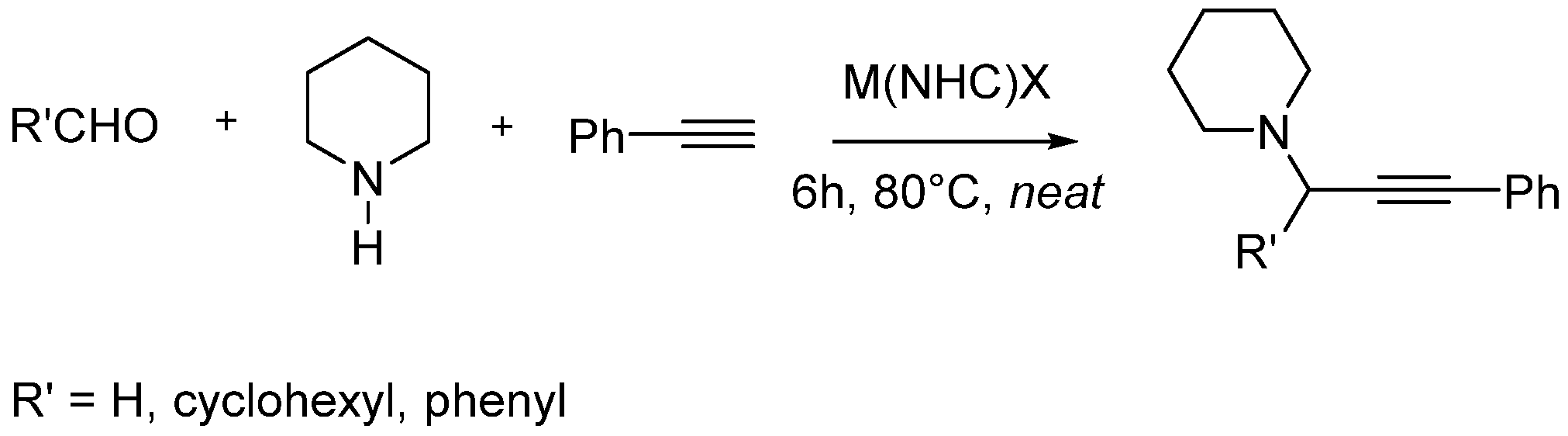
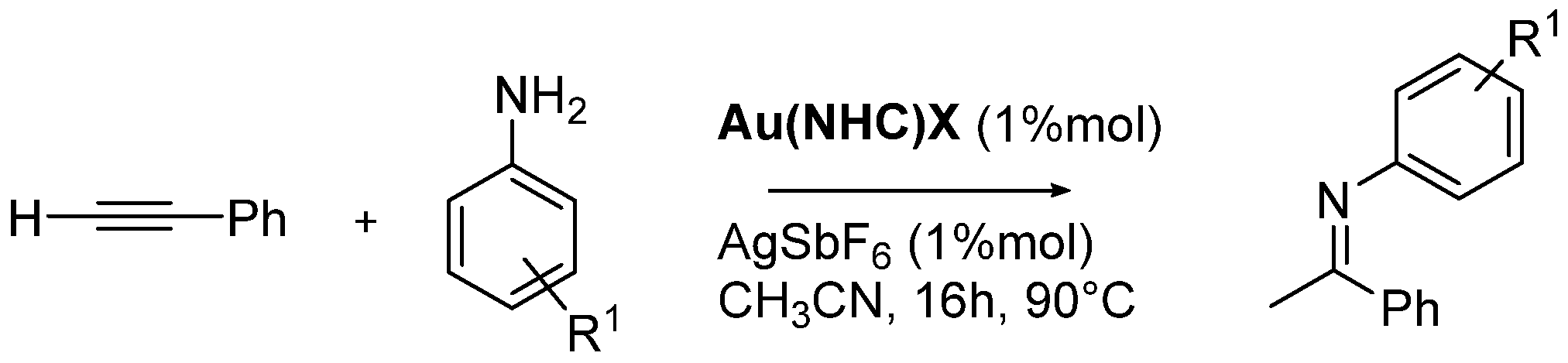
Catalytic Activity in A3-Coupling and Hydroamination Reactions
- All the reactions were carried out without the use of solvents, so they are also interesting from the point of view of environmental protection;
- All the complexes are active in this type of catalytic transformation. NHC-gold(I) iodide complexes have shown better catalytic activity than the silver acetate analogue, for all three types of aldehydes;
- AuL1OAc is more active than silver analogues, as can be observed by comparing the results of runs 1–3 vs. 13–15;
- p-formaldehyde is almost completely converted in the product, except in run 7, where the complex AgL3OAc was used as a catalyst;
- Aliphatic aldehydes are more reactive than aromatic aldehydes;
- AuL1OAc is less reactive than the iodide analogues, as can be observed by comparing the results of runs 10–12 vs. 12–15.
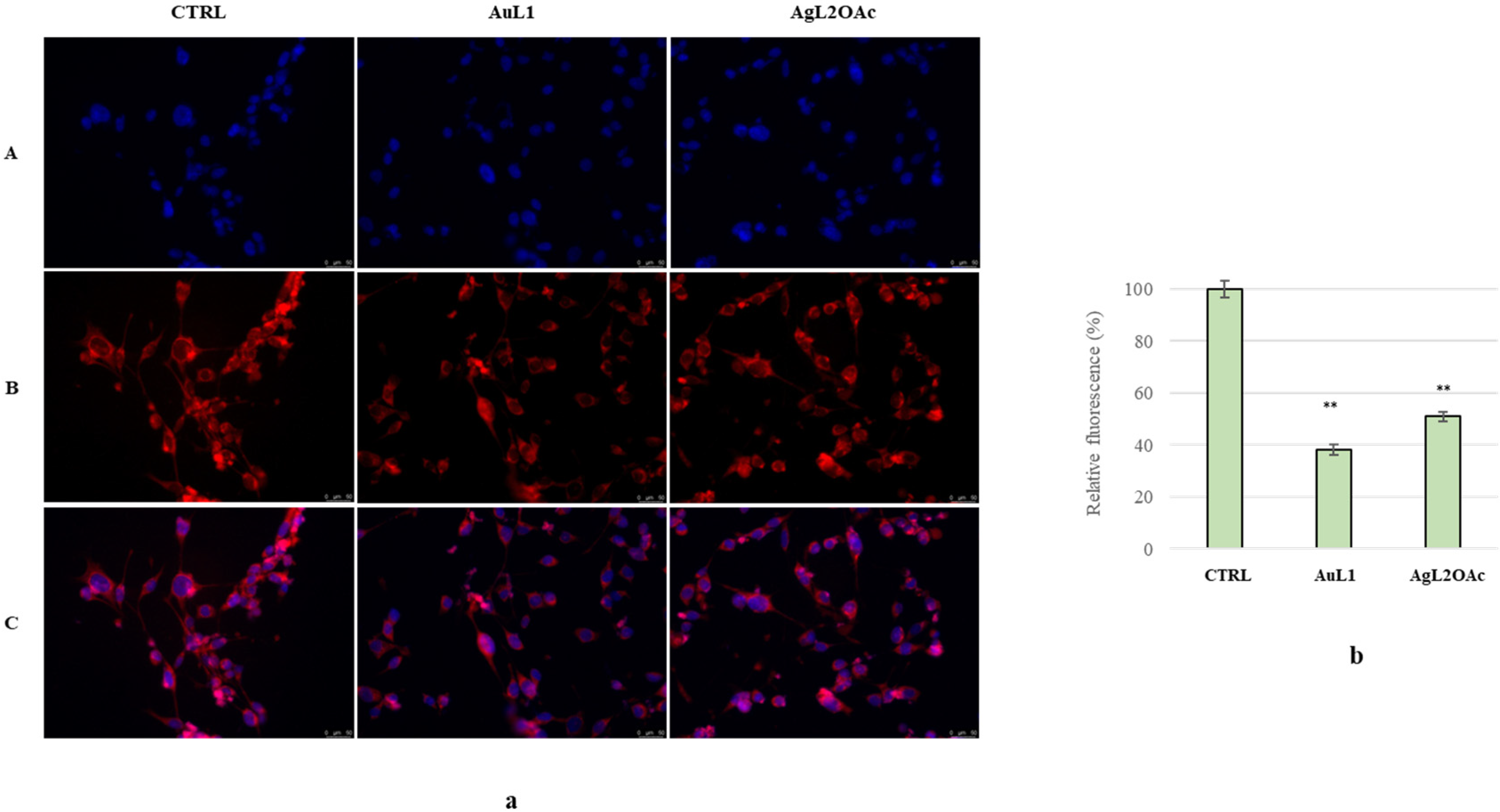
2.2. Anticancer Activity
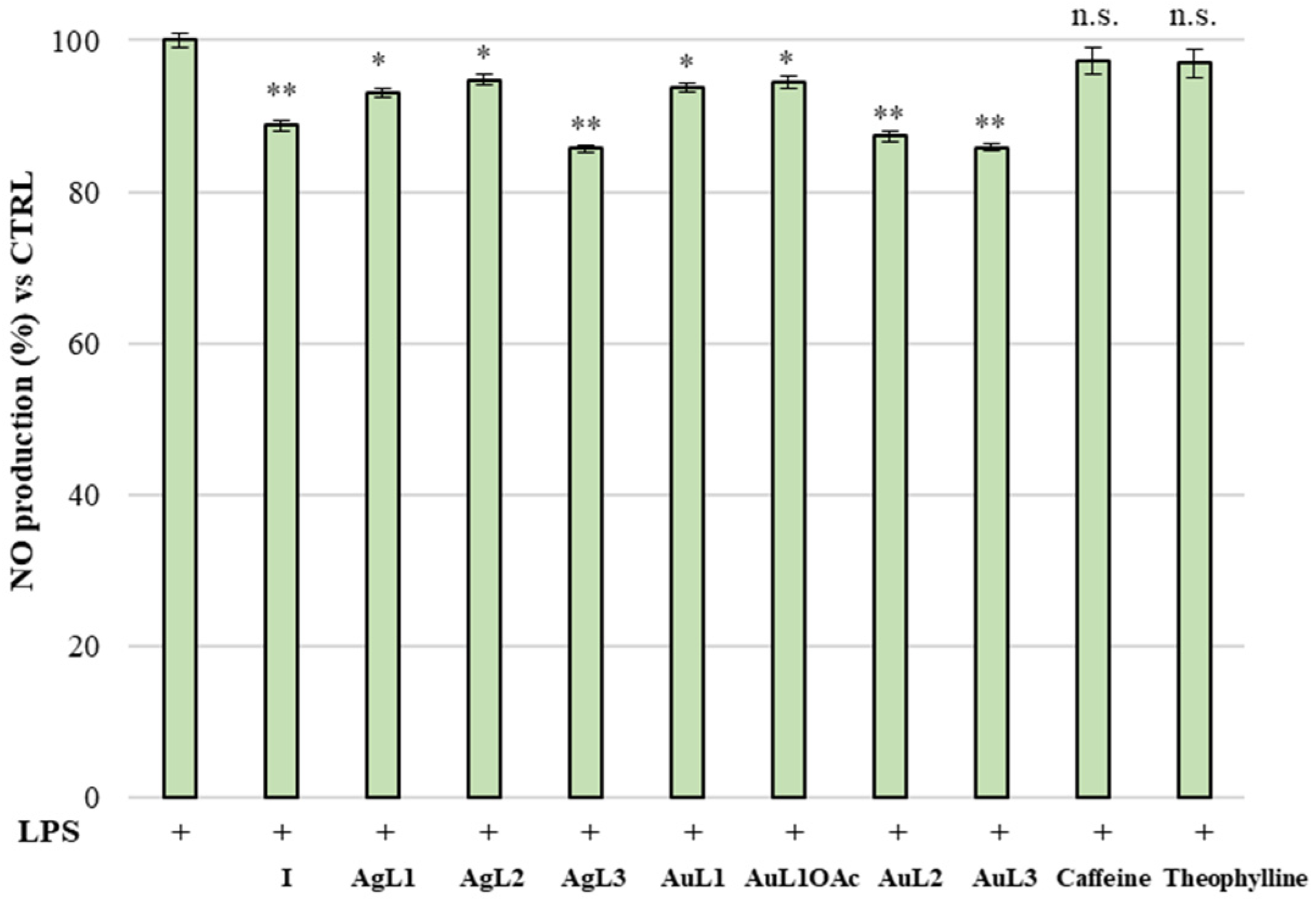
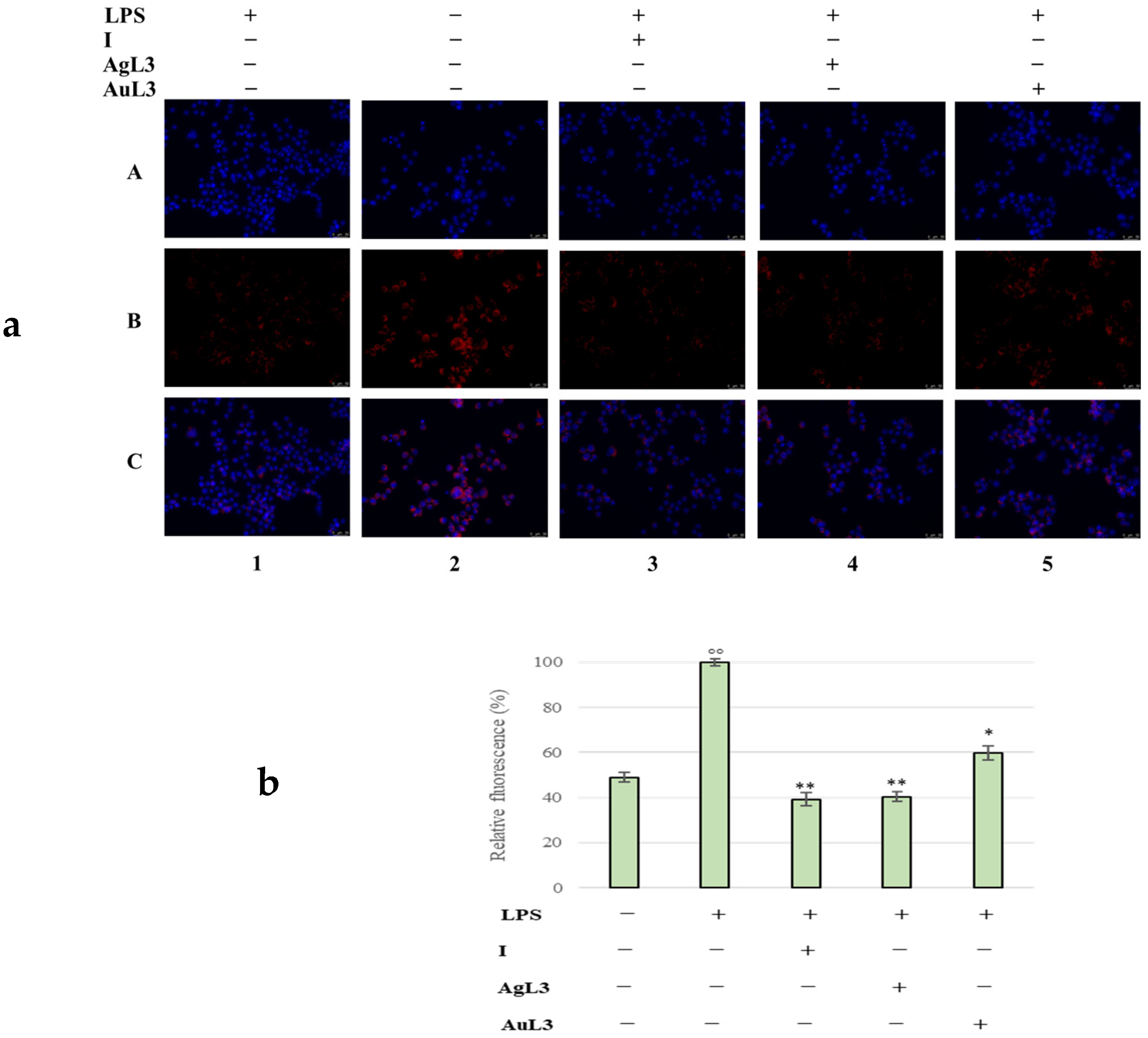
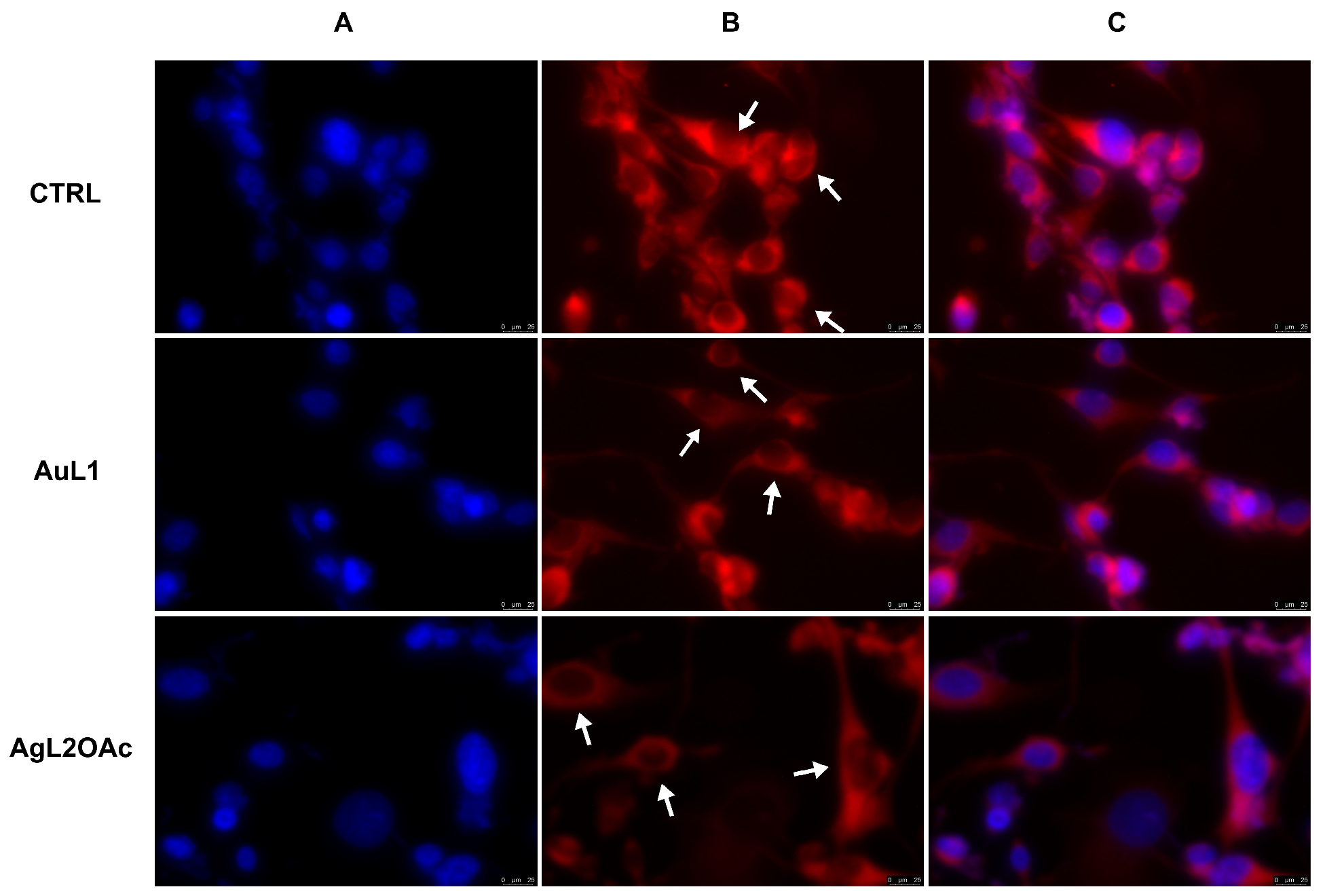
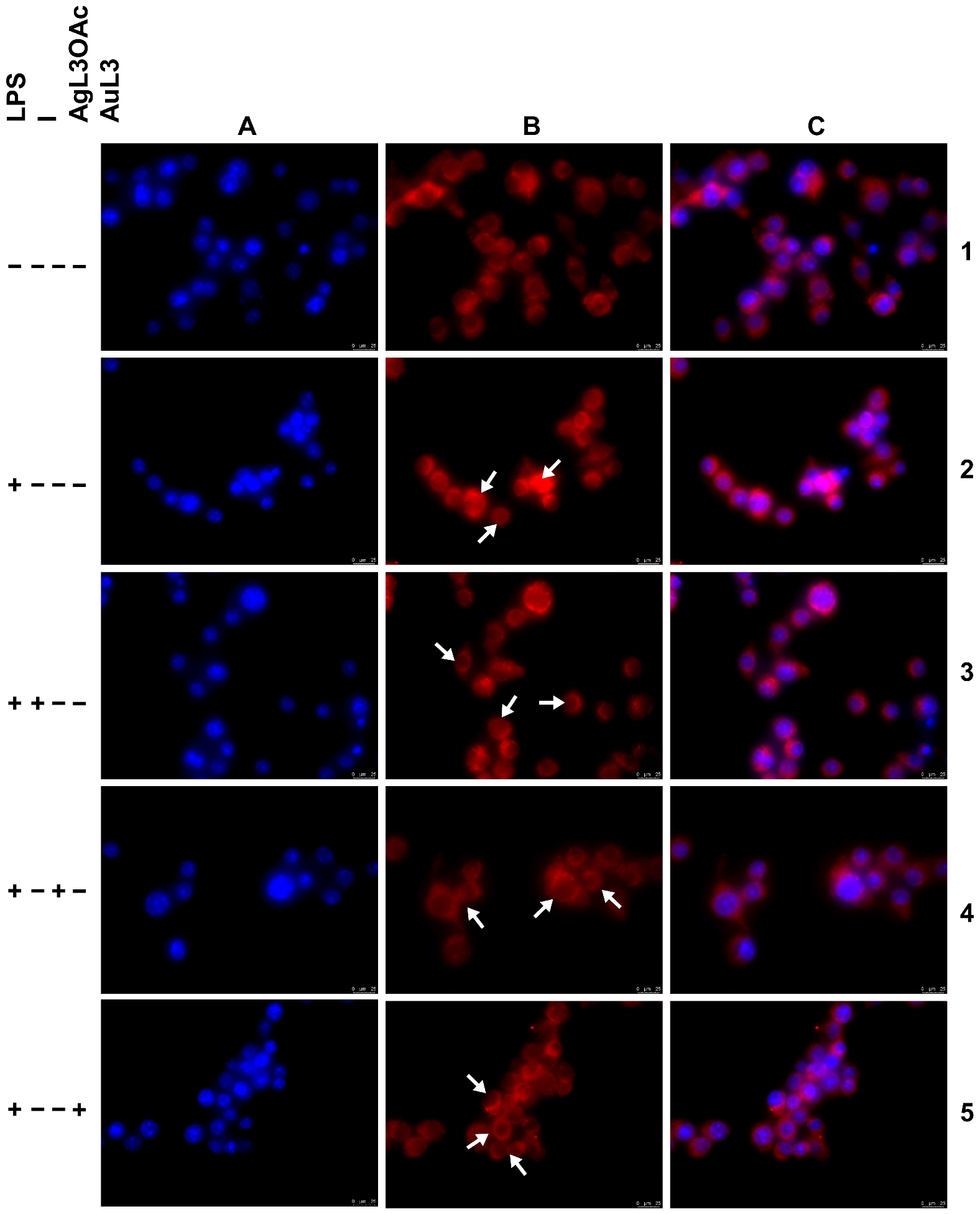
2.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
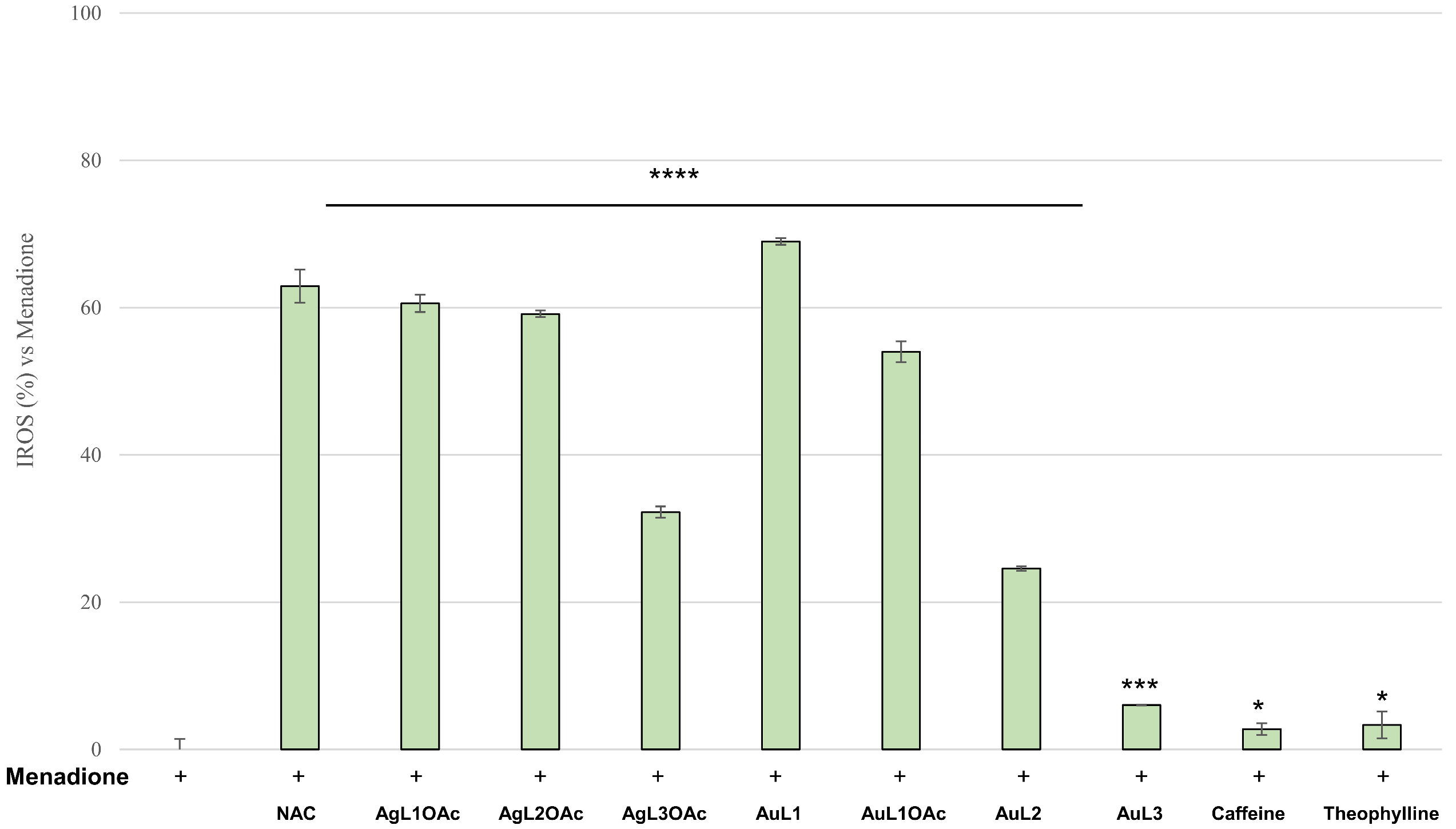
2.4. Antioxidant Activity
2.5. Antibacterial Activity
3. Materials and Methods
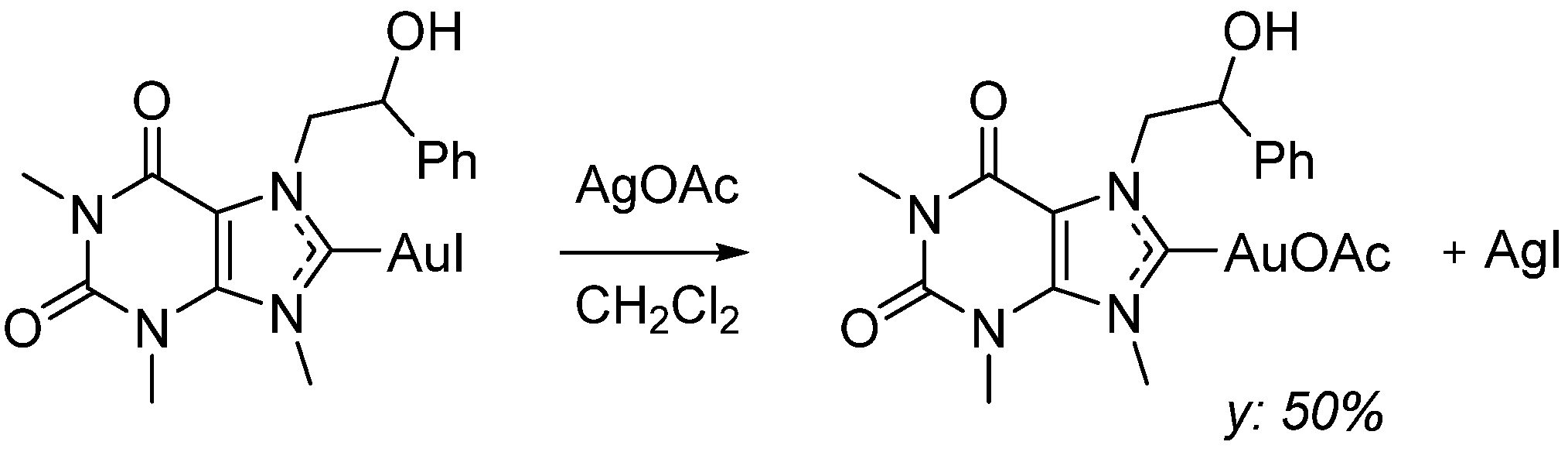
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Xanthinium Salts (P-L1, P-L2, and P-L3)
Synthesis of P-L1, 9-[(2-Hydroxy-2-phenyl)ethyl]-1,3,7-trimethylxanthinium Iodide
Synthesis of P-L2, 9-[Cyclohexan-2-ol]-1,3,7-trimethylxantinium Iodide
Synthesis of P-L3, 9-[(2-Hydroxy)ethyl)]-1,3,7-trimethylxantinium Iodide
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Caffeine-Derived N-Heterocyclic Carbene Silver Acetate Complexes (AgL1OAc, AgL2OAc, and AgL3OAc)
Synthesis of AgL1OAc, 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthin-9-[(2-hydroxy-2-phenyl)ethyl-8-ylidene]Ag(I) Acetate
Synthesis of AgL2OAc, 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthin-9-[cyclohexan-2-ol-8-ylidene]Ag(I) Acetate
Synthesis of AgL3OAc, 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthin-9-[(2-hydroxy)ethyl)-8-ylidene]Ag(I) Acetate
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Caffeine-Based N-Heterocyclic Carbene Gold Iodide Complexes (AuL1, AuL2, AuL3)
Synthesis of AuL1, 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthin-9-[(2-hydroxy-2-phenyl)ethyl-8-ylidene]Au(I) Iodide
Synthesis of AuL2, 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthin-9-[cyclohexan-2-ol-8-ylidene]Au(I) Iodide
Synthesis of AuL3, 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthin-9-[(2-hydroxy)ethyl)-8-ylidene]Au(I) Iodide
3.1.4. Synthesis of AuL1OAc, 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthin-9-[(2-hydroxy-2-phenyl)ethyl-8-ylidene]Au(I) Acetate
3.1.5. General Procedure for A3-Coupling (Aldehyde, Amine, and Alkyne) Reaction Promoted by M-NHC (M=Ag, Au) Complexes
3.1.6. General Procedure for Hydroamination reaction between Phenylacetylene and Aniline Promoted by AuNHC Complexes
3.2. Biology
3.2.1. Cell Culture
3.2.2. MTT Assay
3.2.3. TUNEL Assay
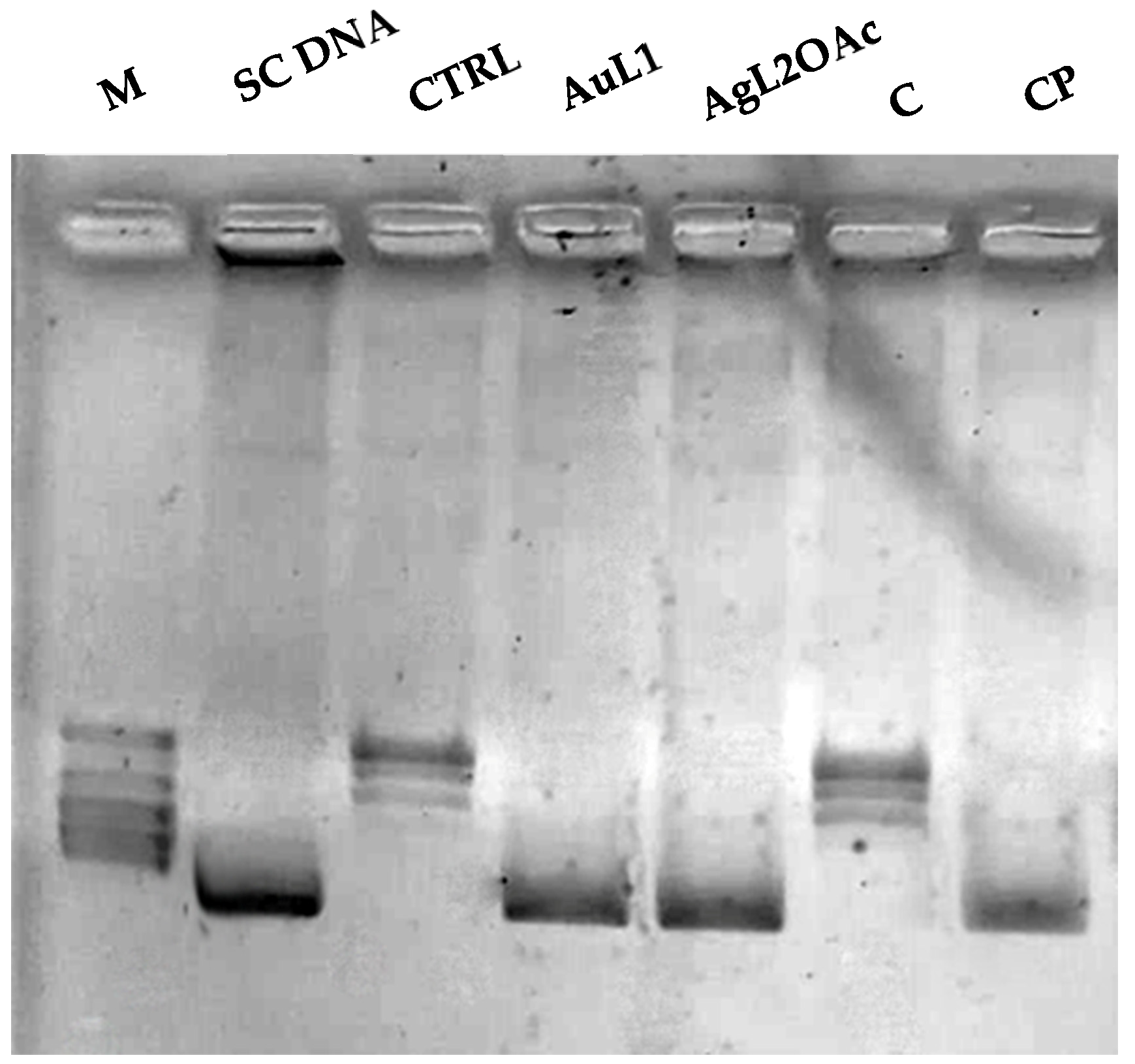
3.2.4. Human Topoisomerase I (hTopoI) Relaxation Assay
3.2.5. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3.2.6. Immunofluorescence
3.2.7. Antioxidant Activity
2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Assay
2,20-Azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) Assay
3.2.8. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) Determination
3.2.9. Statistical analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, B.; Van Camp, L.; Krigas, T. Inhibition of Cell Division in Escherichia coli by Electrolysis Products from a Platinum Electrode. Nature 1965, 205, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabik, C.A.; Dolan, M.E. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance and Toxicity Associated with Platinating Agents. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2007, 33, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, T.J.; Deblock, M.C.; Hindi, K.M.; Durmus, S.; Panzner, M.J.; Tessier, C.A.; Youngs, W.J. Synthesis and Anticancer Properties of Gold(I) and Silver(I) N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2011, 696, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, S.; Mini, E.; Landini, I.; Gabbiani, C.; Casini, A.; Messori, L. Gold Compounds as Anticancer Agents: Chemistry, Cellular Pharmacology, and Preclinical Studies. Med. Res. Rev. 2010, 30, 550–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márta Nagy, E.; Ronconi, L.; Nardon, C.; Fregona, D. Noble Metal-Dithiocarbamates Precious Allies in the Fight against Cancer. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1216–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianferrara, T.; Bratsos, I.; Alessio, E. A Categorization of Metal Anticancer Compounds Based on Their Mode of Action. Dalton Trans. 2009, 7588–7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronconi, L.; Sadler, P.J. Using Coordination Chemistry to Design New Medicines. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 1633–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalbari, F.H.; Telleria, C.M. The Gold Complex Auranofin: New Perspectives for Cancer Therapy. Discov. Oncol. 2021, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakupec, M.A.; Galanski, M.S.; Arion, V.B.; Hartinger, C.G.; Keppler, B.K. Antitumour Metal Compounds: More than Theme and Variations. Dalton Trans. 2008, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sava, G.; Bergamo, A.; Dyson, P.J. Metal-Based Antitumour Drugs in the Post-Genomic Era: What Comes Next? Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 9069–9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Rosano, C.; Mariconda, A.; Pellegrino, M.; Sirignano, M.; Saturnino, C.; Catalano, A.; Aquaro, S.; Longo, P.; et al. N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Gold(I) Complexes Targeting Actin Polymerization. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceramella, J.; Mariconda, A.; Sirignano, M.; Iacopetta, D.; Rosano, C.; Catalano, A.; Saturnino, C.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Longo, P. Novel Au Carbene Complexes as Promising Multi-Target Agents in Breast Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, R.; Keri, R.S.; Budagumpi, S.; Balakrishna, G.R.; Tacke, M. N-Heterocyclic Carbene Metal Complexes as Bio-Organometallic Antimicrobial and Anticancer Drugs. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 1305–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.A.; Hoagland, A.P.; Patil, S.A.; Bugarin, A. N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Metal Complexes as Bio-Organometallic Antimicrobial and Anticancer Drugs, an Update (2015–2020). Future Med. Chem. 2020, 12, 2239–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Frémont, P.; Marion, N.; Nolan, S.P. Cationic NHC–Gold(I) Complexes: Synthesis, Isolation, and Catalytic Activity. J. Organomet. Chem. 2009, 694, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, S.P. (Ed.) N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: Effective Tools for Organometallic Synthesis, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-527-33490-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mariconda, A.; Sirignano, M.; Troiano, R.; Russo, S.; Longo, P. N-Heterocyclic Carbene Gold Complexes Active in Hydroamination and Hydration of Alkynes. Catalysts 2022, 12, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kascatan-Nebioglu, A.; Panzner, M.J.; Garrison, J.C.; Tessier, C.A.; Youngs, W.J. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes of Silver(I) and Rhodium(I) from Caffeine. Organometallics 2004, 23, 1928–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.; Zahoor, A.F.; Faiz, S.; Javed, S.; Irfan, M. Recent Synthetic Approaches towards Biologically Potent Derivatives/Analogues of Theophylline. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2018, 55, 2447–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.A.; Lake, B.R.M.; Laing, T.; Phillips, R.M.; Willans, C.E. Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of Silver(i)–N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes Derived from the Natural Xanthine Products Caffeine, Theophylline and Theobromine. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 7563–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajare, S.P.; Bansode, P.A.; Patil, P.V.; Patil, A.D.; Pore, D.M.; Sonawane, K.D.; Dhanavade, M.J.; Khot, V.M.; Rashinkar, G.S. Anticancer, Antibacterial and Hyperthermia Studies of a Caffeine-Based N-Heterocyclic Carbene Silver Complex Anchored on Magnetic Nanoparticles. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, B.; Stefan, L.; Pirrotta, M.; Monchaud, D.; Bodio, E.; Richard, P.; Le Gendre, P.; Warmerdam, E.; de Jager, M.H.; Groothuis, G.M.M.; et al. Caffeine-Based Gold(I) N-Heterocyclic Carbenes as Possible Anticancer Agents: Synthesis and Biological Properties. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 2296–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achar, G.; Shahini, C.R.; Patil, S.A.; Budagumpi, S. Synthesis, Structural Characterization, Crystal Structures and Antibacterial Potentials of Coumarin–Tethered N–Heterocyclic Carbene Silver(I) Complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 833, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, M.; Wenzel, M.; Prochnow, P.; Pierroz, V.; Gasser, G.; Bandow, J.E.; Metzler-Nolte, N. An Organometallic Structure-Activity Relationship Study Reveals the Essential Role of a Re(CO)3 Moiety in the Activity against Gram-Positive Pathogens Including MRSA. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draviana, H.T.; Fitriannisa, I.; Khafid, M.; Krisnawati, D.I.; Widodo; Lai, C.-H.; Fan, Y.-J.; Kuo, T.-R. Size and Charge Effects of Metal Nanoclusters on Antibacterial Mechanisms. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauder, K.; Toscani, A.; Scalacci, N.; Castagnolo, D. Synthesis and Reactivity of Propargylamines in Organic Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 14091–14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manujyothi, R.; Aneeja, T.; Anilkumar, G. Solvent-Free Synthesis of Propargylamines: An Overview. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 19433–19449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshkov, V.A.; Pereshivko, O.P.; Nechaev, A.A.; Peshkov, A.A.; Van der Eycken, E.V. Reactions of Secondary Propargylamines with Heteroallenes for the Synthesis of Diverse Heterocycles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 3861–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, A.; Sirignano, M.; Russo, S.; Troiano, R.; Mariconda, A.; Longo, P. Recent Advances in N-Heterocyclic Carbene Coinage Metal Complexes in A3-Coupling and Carboxylation Reaction. Catalysts 2023, 13, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlki, F.; Doye, S. The Catalytic Hydroamination of Alkynes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2003, 32, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.E.; Hultzsch, K.C.; Yus, M.; Foubelo, F.; Tada, M. Hydroamination: Direct Addition of Amines to Alkenes and Alkynes. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3795–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirignano, M.; D’Amato, A.; Costabile, C.; Mariconda, A.; Crispini, A.; Scarpelli, F.; Longo, P. Hydroamination of Alkynes Catalyzed by NHC-Gold(I) Complexes: The Non-Monotonic Effect of Substituted Arylamines on the Catalyst Activity. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1260726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kascatan-Nebioglu, A.; Melaiye, A.; Hindi, K.; Durmus, S.; Panzner, M.J.; Hogue, L.A.; Mallett, R.J.; Hovis, C.E.; Coughenour, M.; Crosby, S.D.; et al. Synthesis from Caffeine of a Mixed N-Heterocyclic Carbene−Silver Acetate Complex Active against Resistant Respiratory Pathogens. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6811–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scattolin, T.; Caligiuri, I.; Canovese, L.; Demitri, N.; Gambari, R.; Lampronti, I.; Rizzolio, F.; Santo, C.; Visentin, F. Synthesis of New Allyl Palladium Complexes Bearing Purine-Based NHC Ligands with Antiproliferative and Proapoptotic Activities on Human Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 13616–13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, H.; Canseco-González, D.; Germán-Acacio, J.M.; Morales-Morales, D. Xanthine Based N-Heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 867, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, M.; Saturnino, C.; Cianciulli, E.I.; Varcamonti, M.; Zanfardino, A.; Tommonaro, G.; Longo, P. Silver(I) N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Activity. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 725, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caytan, E.; Roland, S. Structure of Silver–N-Heterocyclic Carbenes in Solution: Evidence of Equilibration in DMSO at Very Different Time Scales by 1H NMR Experiments. Organometallics 2014, 33, 2115–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariconda, A.; Grisi, F.; Costabile, C.; Falcone, S.; Bertolasi, V.; Longo, P. Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Behaviour of a Palladium Complex Bearing a Hydroxy-Functionalized N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligand. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Frémont, P.; Scott, N.M.; Stevens, E.D.; Nolan, S.P. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of N-Heterocyclic Carbene Gold(I) Complexes. Organometallics 2005, 24, 2411–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, A.; Gómez-Suárez, A.; Martin, A.R.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Nolan, S.P. Straightforward Synthesis of [Au(NHC)X] (NHC = N-Heterocyclic Carbene, X = Cl, Br, I) Complexes. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visbal, R.; Laguna, A.; Gimeno, M.C. Simple and Efficient Synthesis of [MCI(NHC)] (M = Au, Ag) Complexes. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, F.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Smith, R.; Streciwilk, W.; Zhu, X.; Tacke, M. Novel Ruthenium(II) and Gold(I) NHC Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of Their Anticancer Properties. Organometallics 2013, 32, 5551–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariconda, A.; Sirignano, M.; Costabile, C.; Longo, P. New NHC- Silver and Gold Complexes Active in A3-Coupling (Aldehyde-Alkyne-Amine) Reaction. Mol. Catal. 2020, 480, 110570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, C.; Mariconda, A.; Sirignano, M.; Crispini, A.; Scarpelli, F.; Longo, P. A Green Approach for A3-Coupling Reactions: An Experimental and Theoretical Study on NHC Silver and Gold Catalysts. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 18509–18517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Bi, X. Silver-Catalysed Reactions of Alkynes: Recent Advances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8124–8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teles, J.H.; Brode, S.; Chabanas, M. Cationic Gold(I) Complexes: Highly Efficient Catalysts for the Addition of Alcohols to Alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, M.; Del Zotto, A.; Segato, J.; Zuccaccia, D. Hydration of Alkynes Catalyzed by L–Au–X under Solvent- and Acid-Free Conditions: New Insights into an Efficient, General, and Green Methodology. Organometallics 2018, 37, 4685–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, M.; Baratta, W.; Belanzoni, P.; Belpassi, L.; Del Zotto, A.; Tarantelli, F.; Zuccaccia, D. Hydration and Alkoxylation of Alkynes Catalyzed by NHC–Au–OTf. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcheggiani, E.; Tubaro, C.; Biffis, A.; Graiff, C.; Baron, M. Hydroalkoxylation of Terminal and Internal Alkynes Catalyzed by Dinuclear Gold(I) Complexes with Bridging Di(N-Heterocyclic Carbene) Ligands. Catalysts 2019, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinjo, R.; Donnadieu, B.; Bertrand, G. Gold-Catalyzed Hydroamination of Alkynes and Allenes with Parent Hydrazine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5560–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, M.; Battistel, E.; Tubaro, C.; Biffis, A.; Armelao, L.; Rancan, M.; Graiff, C. Single-Step Synthesis of Dinuclear Neutral Gold(I) Complexes with Bridging Di(N-Heterocyclic Carbene) Ligands and Their Catalytic Performance in Cross Coupling Reactions and Alkyne Hydroamination. Organometallics 2018, 37, 4213–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, C.; Tinnermann, H.; Huynh, H.V. Gold(I) and Gold(III) Complexes of Expanded-Ring N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: Structure, Reactivity, and Catalytic Applications. Organometallics 2020, 39, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubaro, C.; Baron, M.; Biffis, A.; Basato, M. Alkyne Hydroarylation with Au N-Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysts. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, C.; Zeng, C.; Mousavi, B.; Chaemchuen, S.; Verpoort, F. Carboxylation of Terminal Alkynes with Carbon Dioxide Catalyzed by an In Situ Ag2O/N-Heterocyclic Carbene Precursor System. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Velázquez, H.; Wu, Z.-X.; Vandichel, M.; Verpoort, F. Inserting CO2 into Terminal Alkynes via Bis-(NHC)-Metal Complexes. Catal. Lett. 2017, 147, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, S.P. The Development and Catalytic Uses of N-Heterocyclic Carbene Gold Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshkov, V.A.; Pereshivko, O.P.; Van der Eycken, E.V. A Walk around the A3-Coupling. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, J.F. Carbon–Heteroatom Bond Formation Catalysed by Organometallic Complexes. Nature 2008, 455, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, J.L.; Hsieh, C.-M.; Chan, N.-L.; Hiasa, H. Topoisomerases as Anticancer Targets. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 373–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inkanuwat, A.; Sukaboon, R.; Reamtong, O.; Asawanonda, P.; Pattaratanakun, A.; Saisavoey, T.; Sangtanoo, P.; Karnchanatat, A. Nitric Oxide Synthesis Inhibition and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Polypeptide Isolated from Chicken Feather Meal in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huakan, Z.; Wu, L.; Guifang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Mingyue, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and Tumor Progression: Signaling Pathways and Targeted Intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, M.A.; Do, H.T.; Miley, G.P.; Silverman, R.B. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase: Regulation, Structure, and Inhibition. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 158–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Yang, L.; He, J. Plantanone C Attenuates LPS-Stimulated Inflammation by Inhibiting NF-κB/iNOS/COX-2/MAPKs/Akt Pathways in RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Rodiles, M.; Tiraloche, G.; Chadee, K. Lipopolysaccharide Modulates Cyclooxygenase-2 Transcriptionally and Posttranscriptionally in Human Macrophages Independently from Endogenous IL-1β and TNF-A1. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zong, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, J.; Yang, C.; Liu, X.; Deng, H. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Decreasing COX-2 Expression in Macrophages. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 702107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovich, A.; Johnson, C.A.; Buczynski, M.W.; Dennis, E.A. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Human U937 Macrophages Is Phosphatidic Acid Phosphohydrolase-1-Dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 32978–32987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Z.; Li, M.; Xu, J.; Howell, D.C.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.-E. Recent Development on COX-2 Inhibitors as Promising Anti-Inflammatory Agents: The Past 10 Years. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2790–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkins, T.L.; Nowell, M.; Singh, S.; Sanford, G.L. Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase-2 Decreases Breast Cancer Cell Motility, Invasion and Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatef, A.A.; Meselhy, M.R.; El-Askary, H.I.; El-mekkawy, S.; Hayakawa, Y. Anti-Metastatic Function of Triterpene Phytochemicals from Guggul by Targeting Tumor-Intrinsic NF-kB Activation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Phytomedicine Plus 2022, 2, 100345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, B.P. TNF-α/NF-κB/Snail Pathway in Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Tao, D.; Fang, Y.; Deng, C.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, J. TNF-Alpha Promotes Invasion and Metastasis via NF-Kappa B Pathway in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2017, 23, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, Y. Tumor Necrosis Factor and Cancer, Buddies or Foes? Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Janabi, A.A.H.S. Potential Activity of the Purine Compounds Caffeine and Aminophylline on Bacteria. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2011, 3, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ji, R.; Zha, X.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, S. Investigation of the Bactericidal Mechanism of Penicilazaphilone C on Escherichia Coli Based on 4D Label-Free Quantitative Proteomic Analysis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 179, 106299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-J.; Yang, S.; Lim, Y. Antibiotic Susceptibility of Staphylococcus Aureus with Different Degrees of Biofilm Formation. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Ko, K.S.; Peck, K.R.; Oh, W.S.; Song, J.-H. In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibiotic Lock Technique (ALT) for the Treatment of Catheter-Related Infections Caused by Staphylococci. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowski, P.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Pruss, A.; Łopusiewicz, Ł.; Arszyńska, N.; Wojciechowska-Koszko, I.; Kilanowicz, A.; Kot, B.; Dołęgowska, B. Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activities of Essential Oil Compounds against New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase-1-Producing Uropathogenic Klebsiella Pneumoniae Strains. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, J.; Ma, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, L. An In Vitro Study on the Effects of Nisin on the Antibacterial Activities of 18 Antibiotics against Enterococcus Faecalis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alandiyjany, M.N.; Abdelaziz, A.S.; Abdelfattah-Hassan, A.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Hassan, A.A.; Elazab, S.T.; Mohamed, E.A.A.; El-Shetry, E.S.; Saleh, A.A.; ElSawy, N.A.; et al. Novel In Vivo Assessment of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles against Salmonella Typhimurium Infection. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasir, M.; Dutta, D.; Willcox, M.D.P. Activity of Antimicrobial Peptides and Ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms. Molecules 2020, 25, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindi, K.M.; Siciliano, T.J.; Durmus, S.; Panzner, M.J.; Medvetz, D.A.; Reddy, D.V.; Hogue, L.A.; Hovis, C.E.; Hilliard, J.K.; Mallet, R.J.; et al. Synthesis, Stability, and Antimicrobial Studies of Electronically Tuned Silver Acetate N-Heterocyclic Carbenes. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzner, M.J.; Deeraksa, A.; Smith, A.; Wright, B.D.; Hindi, K.M.; Kascatan-Nebioglu, A.; Torres, A.G.; Judy, B.M.; Hovis, C.E.; Hilliard, J.K.; et al. Synthesis and in Vitro Efficacy Studies of Silver Carbene Complexes on Biosafety Level 3 Bacteria. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzner, M.J.; Hindi, K.M.; Wright, B.D.; Taylor, J.B.; Han, D.S.; Youngs, W.J.; Cannon, C.L. A Theobromine Derived Silver N-Heterocyclic Carbene: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Efficacy Studies on Cystic Fibrosis Relevant Pathogens. Dalton Trans. 2009, 7308–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinicropi, M.S.; Ceramella, J.; Vanelle, P.; Iacopetta, D.; Rosano, C.; Khoumeri, O.; Abdelmohsen, S.; Abdelhady, W.; El-Kashef, H. Novel Thiazolidine-2,4-Dione-Trimethoxybenzene-Thiazole Hybrids as Human Topoisomerases Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacopetta, D.; Rosano, C.; Puoci, F.; Parisi, O.I.; Saturnino, C.; Caruso, A.; Longo, P.; Ceramella, J.; Malzert-Fréon, A.; Dallemagne, P.; et al. Multifaceted Properties of 1,4-Dimethylcarbazoles: Focus on Trimethoxybenzamide and Trimethoxyphenylurea Derivatives as Novel Human Topoisomerase II Inhibitors. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceramella, J.; Troiano, R.; Iacopetta, D.; Mariconda, A.; Pellegrino, M.; Catalano, A.; Saturnino, C.; Aquaro, S.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Longo, P. Synthesis of Novel N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Ruthenium (II) Complexes, “Precious” Tools with Antibacterial, Anticancer and Antioxidant Properties. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopetta, D.; Carocci, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Catalano, A.; Lentini, G.; Ceramella, J.; Curcio, R.; Caroleo, M.C. Old Drug Scaffold, New Activity: Thalidomide-Correlated Compounds Exert Different Effects on Breast Cancer Cell Growth and Progression. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M100Ed33|Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd Edition. Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m100/ (accessed on 13 October 2023).


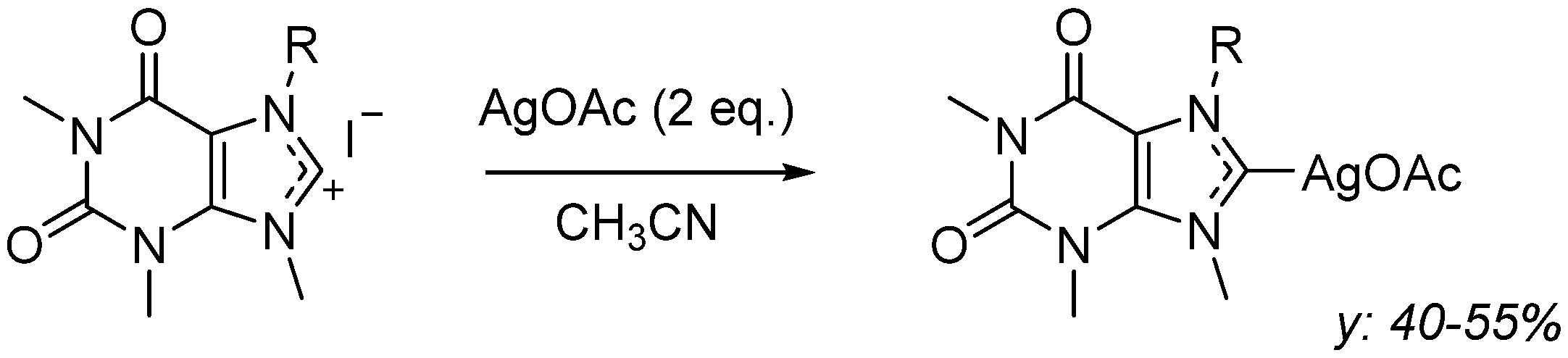
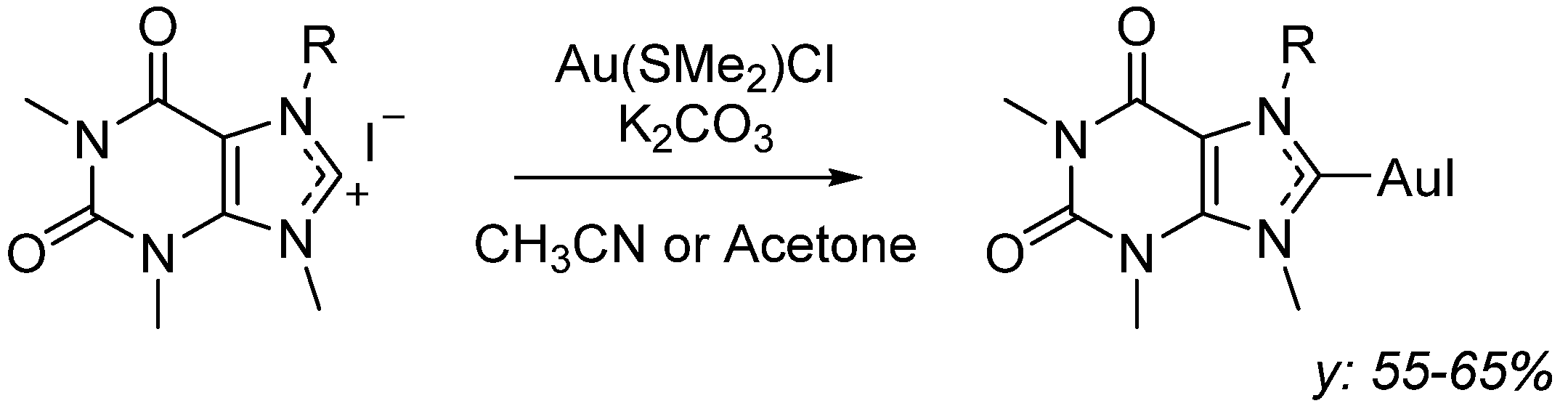



| Run [a] | Catalyst | Aldehyde | Yield (%) [b] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AgL1OAc | p-formaldehyde | 95 |
| 2 | cyclohexanecarboxaldehyde | 60 | |
| 3 | benzaldehyde | 15 | |
| 4 | AgL2OAc | p-formaldehyde | 95 |
| 5 | cyclohexanecarboxaldehyde | 50 | |
| 6 | benzaldehyde | 15 | |
| 7 | AgL3OAc | p-formaldehyde | 77 |
| 8 | cyclohexanecarboxaldehyde | 53 | |
| 9 | benzaldehyde | 20 | |
| 10 | AuL1 | p-formaldehyde | 95 |
| 11 | cyclohexanecarboxaldehyde | 88 | |
| 12 | benzaldehyde | 71 | |
| 13 | AuL1OAc | p-formaldehyde | 91 |
| 14 | cyclohexanecarboxaldehyde | 71 | |
| 15 | benzaldehyde | 54 | |
| 16 | AuL2 | p-formaldehyde | 95 |
| 17 | cyclohexanecarboxaldehyde | 80 | |
| 18 | benzaldehyde | 44 | |
| 19 | AuL3 | p-formaldehyde | 99 |
| 20 | cyclohexanecarboxaldehyde | 75 | |
| 21 | benzaldehyde | 47 |
| Run [a] | Catalyst | Arylamine | Yield (%) [b] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AuL1 | 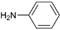 | 67 |
| 2 | AuL2 | 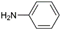 | 60 |
| 3 | AuL3 |  | 55 |
| 4 | AuL1OAc | 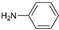 | 69 |
| 5 | AuL1OAc | 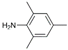 | 73 |
| 6 | AuL1OAc | 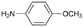 | 39 |
| 7 | AuL1OAc | 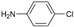 | 44 |
| IC50 (µM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | MCF-7 | MCF-10A | |
| AgL1OAc | 32.3 ± 0.9 | 39.6 ± 0.8 | >100 |
| AgL2OAc | 19.4 ± 1.0 | 28.7 ± 1.0 | >100 |
| AgL3OAc | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| AuL1 | 14.7 ± 1.1 | 73.8 ± 1.1 | >100 |
| AuL1OAc | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| AuL2 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| AuL3 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| Caffeine | >500 | >500 | >500 |
| Theophylline | >500 | >500 | >500 |
| Cisplatin | 32.2 ± 1.0 | 26.2 ± 1.1 | 78.2 ± 1.2 |
| IC50 (µM) | ||
|---|---|---|
| ABTS | DPPH | |
| AgL1OAc | 149.2 ± 0.7 | >500 |
| AgL2OAc | 145.4 ± 1.1 | >500 |
| AgL3OAc | >500 | >500 |
| AuL1 | 161.0 ± 1.0 | >500 |
| AuL1OAc | >500 | >500 |
| AuL2 | 155.5 ± 1.0 | >500 |
| AuL3 | >500 | >500 |
| Caffeine | >500 | >500 |
| Theophylline | >500 | >500 |
| Trolox | 54.49 ± 0.9 | 47.03 ± 1.2 |
| M.I.C. [µg/mL] [a]/M.B.C. [µg/mL] [b] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli [c] | S. aureus [c] | E. faecalis [d] | K. pneumoniae [d] | S. epidermidis [d] | P. aeruginosa [e] | S. typhimurium [e] | |
| AgL1OAc | 125/(>150) | 125/(>150) | 150/(>200) | 125/(>150) | 125/(>150) | 125/(>150) | 150/(>200) |
| AgL2OAc | 100/(>150) | 100/(>150) | 150/(>200) | 125/(>150) | 100/(>125) | 100/(>125) | 150/(>200) |
| AgL3OAc | 125/(>200) | 125/(>200) | 150/(>200) | 150/(>200) | 100/(>125) | 150/(>200) | 150/(>200) |
| AuL1 | 150/(>200) | 150/(>200) | 150/(>200) | 150/(>200) | 125/(>150) | 100/(>125) | 150/(>200) |
| AuL1OAc | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| AuL2 | 150/(>200) | 150/(>200) | 150/(>200) | 150/(>200) | 100/(>125) | 100/(>125) | 150/(>200) |
| AuL3 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| Caffeine | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| Theophylline | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| Ampicillin | 2/(4) [74] | 1/(1) [75] | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gentamicin | - | - | 4/(128) [78] | 1.25/(>40) [77] | 8–32/(16–64) [76] | - | - |
| Cephalosporin | - | - | - | - | - | 0.25–1/(0.5–2) [80] | 1/(2) [79] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mariconda, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Sirignano, M.; Ceramella, J.; D’Amato, A.; Marra, M.; Pellegrino, M.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Aquaro, S.; Longo, P. Silver and Gold Complexes with NHC-Ligands Derived from Caffeine: Catalytic and Pharmacological Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052599
Mariconda A, Iacopetta D, Sirignano M, Ceramella J, D’Amato A, Marra M, Pellegrino M, Sinicropi MS, Aquaro S, Longo P. Silver and Gold Complexes with NHC-Ligands Derived from Caffeine: Catalytic and Pharmacological Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(5):2599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052599
Chicago/Turabian StyleMariconda, Annaluisa, Domenico Iacopetta, Marco Sirignano, Jessica Ceramella, Assunta D’Amato, Maria Marra, Michele Pellegrino, Maria Stefania Sinicropi, Stefano Aquaro, and Pasquale Longo. 2024. "Silver and Gold Complexes with NHC-Ligands Derived from Caffeine: Catalytic and Pharmacological Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 5: 2599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052599
APA StyleMariconda, A., Iacopetta, D., Sirignano, M., Ceramella, J., D’Amato, A., Marra, M., Pellegrino, M., Sinicropi, M. S., Aquaro, S., & Longo, P. (2024). Silver and Gold Complexes with NHC-Ligands Derived from Caffeine: Catalytic and Pharmacological Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5), 2599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052599












