Isothiocyanates Potentiate Tazemetostat-Induced Apoptosis by Modulating the Expression of Apoptotic Genes, Members of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2, and Levels of Tri-Methylating Lysine 27 at Histone 3 in Human Malignant Melanoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
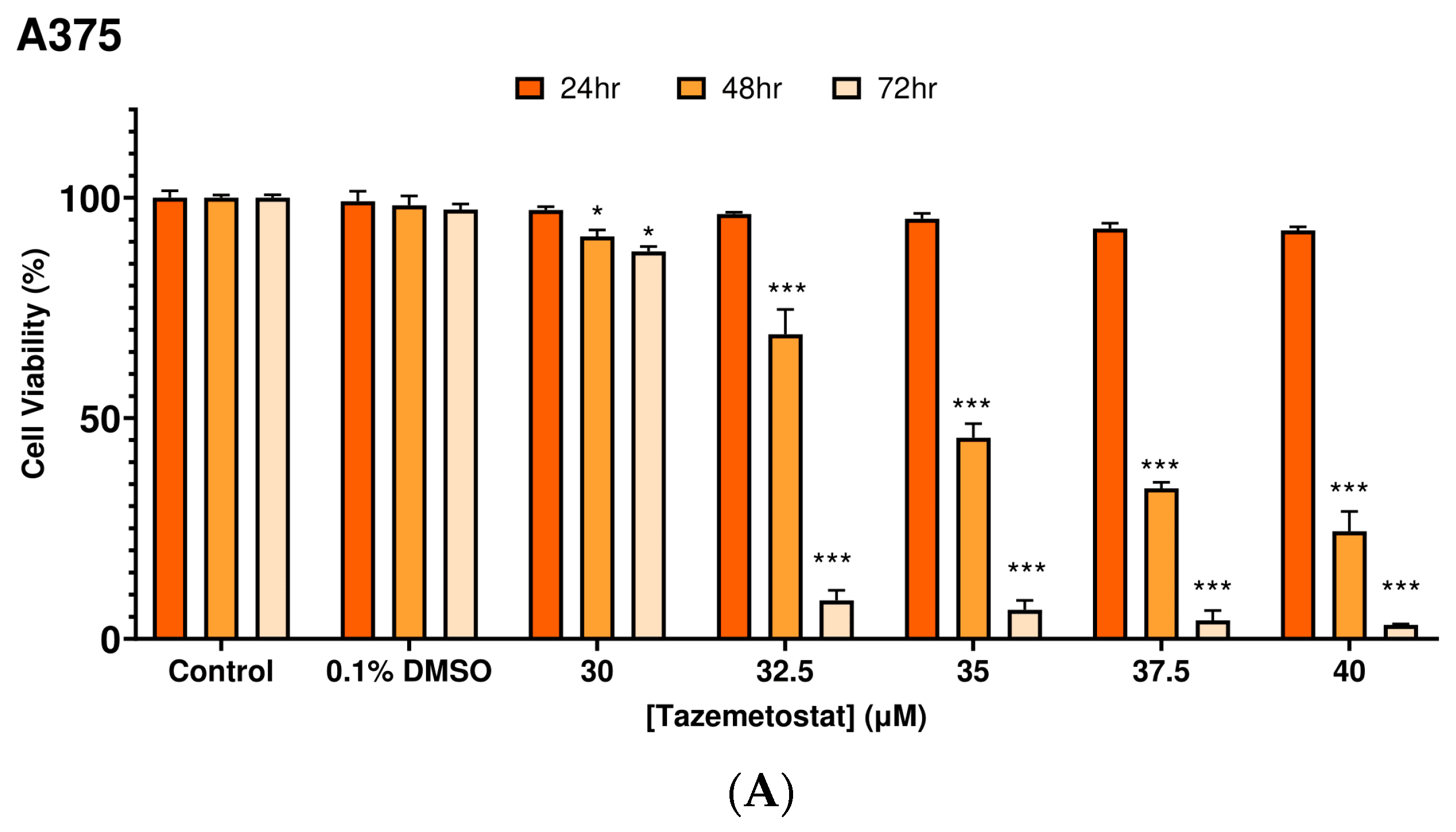
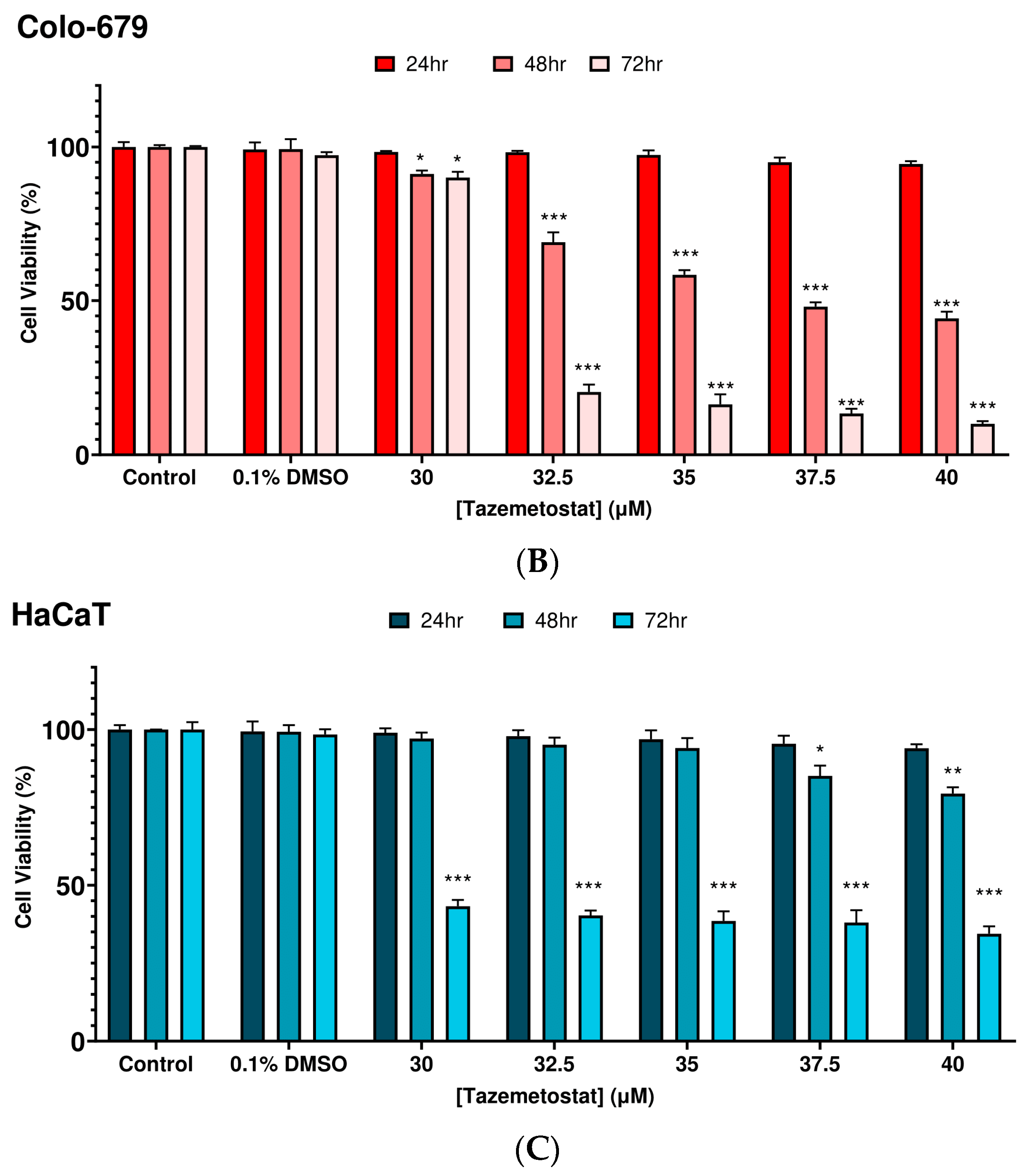
2.1. Optimization of the Experimental Exposure Model
2.2. Combination Index Analyses for Profiling Co-Exposure Interactions
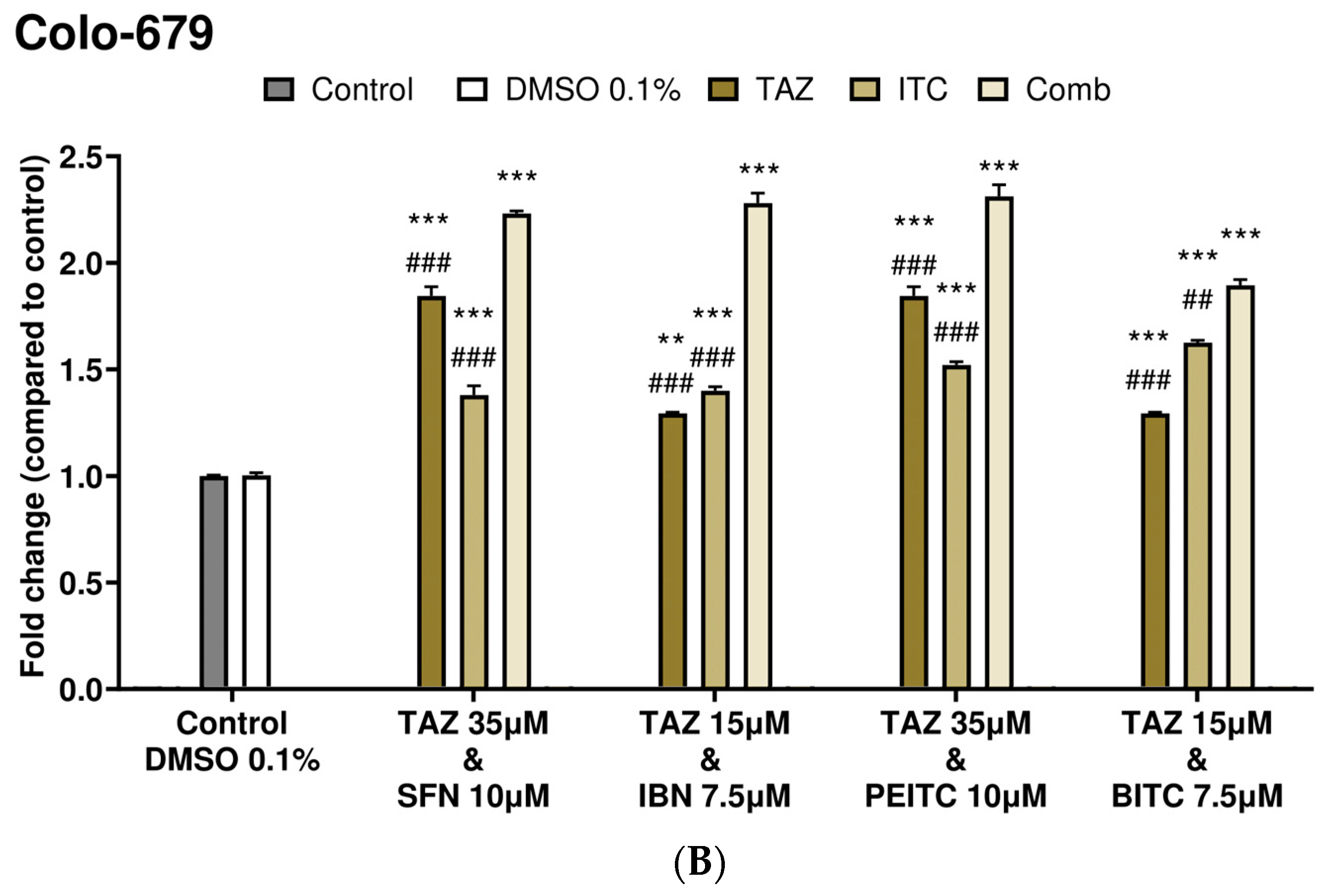
2.3. Caspase-3 Activity Levels as an Index of Apoptotic Induction
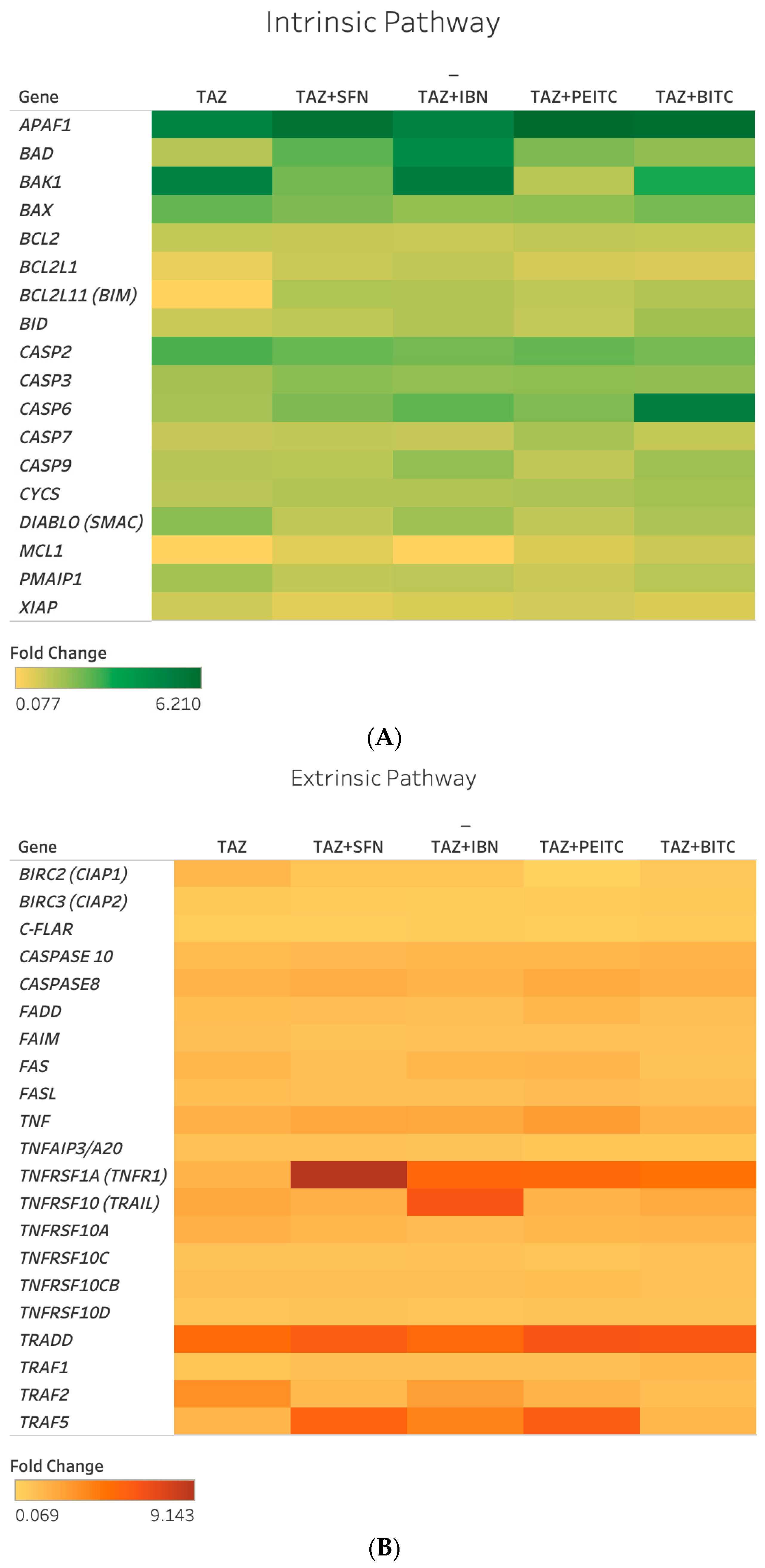
2.4. Differential Gene Expression Response of Major Apoptotic Pathways
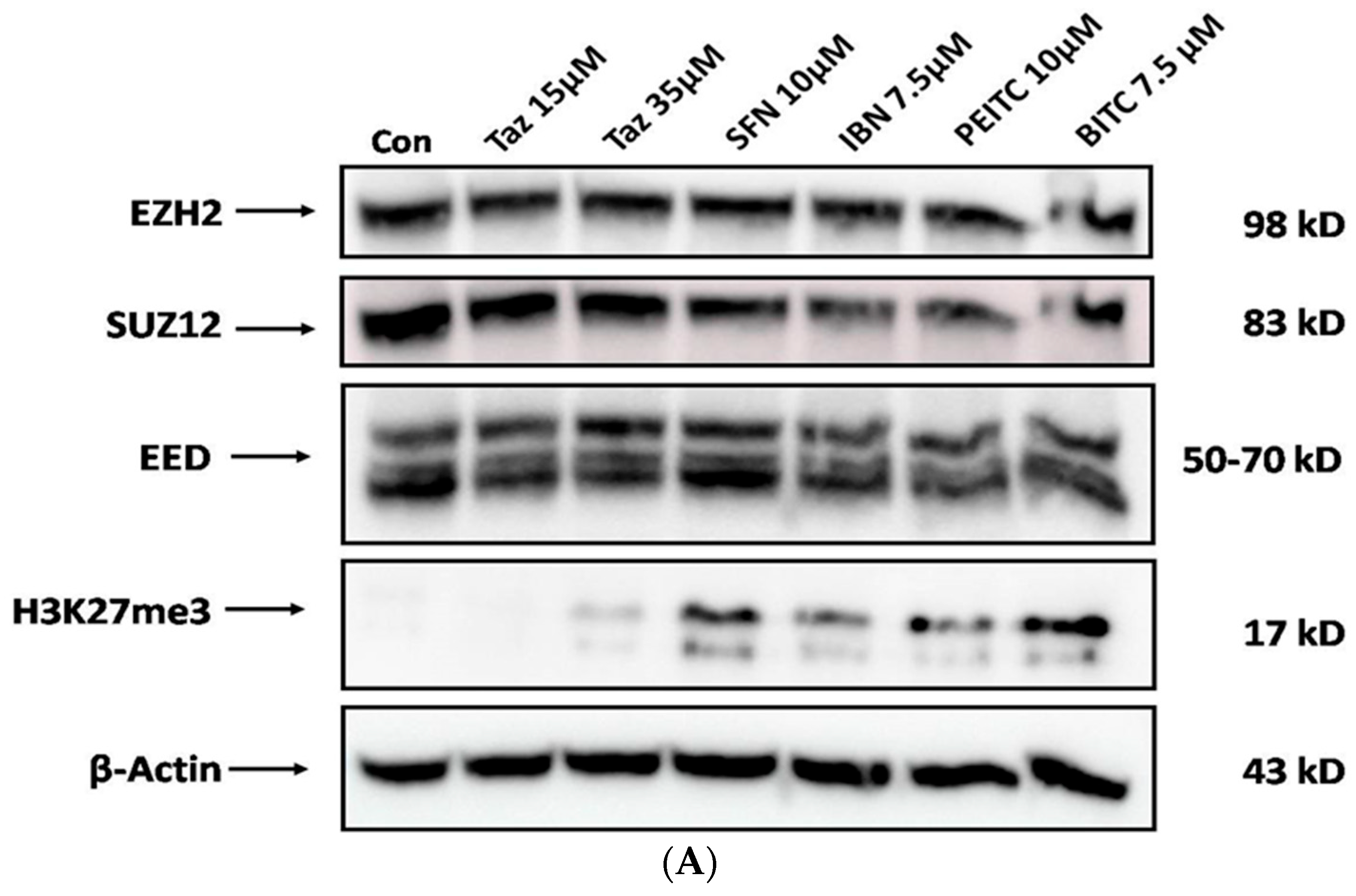
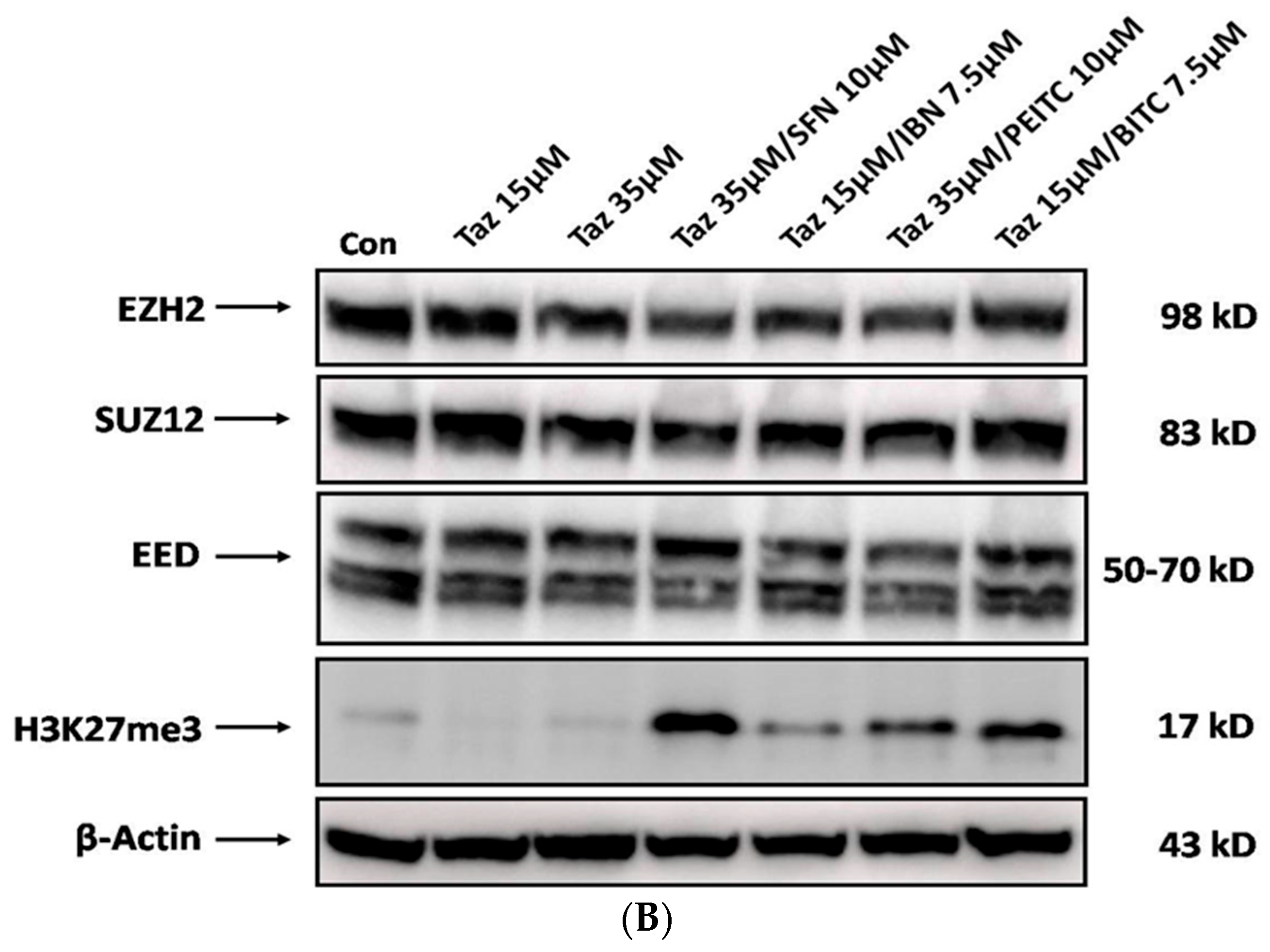
2.5. Effect of Single and/or Co-Exposures on PRC2 and H3K27me3 Protein Expression Levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.2. Determination of Cell Viability
4.3. Exposure Protocols
4.4. Combination Index Analyses
4.5. Determination of Caspase-3 Activity Levels
4.6. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Protocol
4.7. Western Immunoblotting Protocol
4.8. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eggermont, A.M.; Spatz, A.; Robert, C. Cutaneous melanoma. Lancet 2014, 383, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.J.; Mihm, M.C. Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalla, Z.; Lallas, A.; Sotiriou, E.; Lazaridou, E.; Ioannidis, D. Epidemiological trends in skin cancer. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2017, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandaru, M.; Rotte, A. Monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of melanoma: Present and future strategies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1904, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, B.; Silva, R.; Perry, A.S.; Gallagher, W.M. Epigenetics of malignant melanoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 51, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yi, X.; Sun, N.; Guo, W.; Li, C. Epigenetics regulates antitumor immunity in melanoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 868786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KaramiFath, M.; Azargoonjahromi, A.; Soofi, A.; Almasi, F.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Khalili, S.; Sheikhi, K.; Ferdousmakan, S.; Owrangi, S.; Fahimi, M.; et al. Current understanding of epigenetics role in melanoma treatment and resistance. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingg, D.; Debbache, J.; Schaefer, S.M.; Tuncer, E.; Frommel, S.C.; Cheng, P.; Arenas-Ramirez, N.; Haeusel, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bonalli, M.; et al. The epigenetic modifier EZH2 controls melanoma growth and metastasis through silencing of distinct tumour suppressors. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, D.; Arenas-Ramirez, N.; Sahin, D.; Rosalia, R.A.; Antunes, A.T.; Haeusel, J.; Sommer, L.; Boyman, O. The histone methyltransferase Ezh2 controls mechanisms of adaptive resistance to tumor immunotherapy. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, F.; Shields, B.; Makhoul, I.; Hutchins, L.F.; Shalin, S.C.; Tackett, A.J. Role of EZH2 histone methyltrasferase in melanoma progression and metastasis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Tazemetostat: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsiogianni, M.; Koutsidis, G.; Mavroudis, N.; Trafalis, D.T.; Botaitis, S.; Franco, R.; Zoumpourlis, V.; Amery, T.; Galanis, A.; Pappa, A.; et al. The role of isothiocyanates as cancer chemo-preventive, chemo-therapeutic and anti-melanoma agents. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, M.K.; R, P.; Haque, S.; Akhter, N.; Khan, S.; Ahmad, S.; Hussain, A. Dietary isothiocyanates inhibit cancer progression by modulation of epigenome. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 83, 353–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soundararajan, P.; Kim, J.S. Anti-carcinogenic glucosinolates in cruciferous vegetables and their antagonistic effects on prevention of cancers. Molecules 2018, 23, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsiogianni, M.; Anestopoulos, I.; Kyriakou, S.; Trafalis, D.T.; Franco, R.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I. Benzyl and phenethyl isothiocyanates as promising epigenetic drug compounds by modulating histone acetylation and methylation marks in malignant melanoma. Investig. New Drugs. 2021, 39, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsiogianni, M.; Trafalis, D.T.; Franco, R.; Zoumpourlis, V.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I. Sulforaphane and iberin are potent epigenetic modulators of histone acetylation and methylation in malignant melanoma. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsiogianni, M.; Mantso, T.; Trafalis, D.T.; VasanthaRupasinghe, H.P.; Zoumpourlis, V.; Franco, R.; Botaitis, S.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I. Allyl isothiocyanate regulates lysine acetylation and methylation marks in an experimental model of malignant melanoma. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 59, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, P.; Natesh, J.; Penta, D.; Meeran, S.M. Progress and promises of epigenetic drugs and epigenetic diets in cancer prevention and therapy: A clinical update. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 83, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.; Arimondo, P.B.; Rots, M.G.; Jeronimo, C.; Berdasco, M. The timeline of epigenetic drug discovery: From reality to dreams. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, D.; Jeffery, D.; Aspeslagh, S.; Almouzni, G.; Postel-Vinay, S. Combining epigenetic drugs with other therapies for solid tumours—past lessons and future promise. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maru, G.B.; Hudlikar, R.R.; Kumar, G.; Gandhi, K.; Mahimkar, M.B. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of cancer prevention by dietary phytochemicals: From experimental models to clinical trials. World J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 7, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, A.; Brazeau, D.; Amin, A.R. Perspectives on natural compounds in chemoprevention and treatment of cancer: An update with new promising compounds. Eur. J. Cancer. 2021, 149, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, B.; Li, Y.; Tollefsbol, T.O. The effects of combinatorial genistein and sulforaphane in breast tumor inhibition: Role in epigenetic regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 19, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Omari, N.; Bakrim, S.; Bakha, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Rebezov, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Aboulaghras, S.; Balahbib, A.; Khayrullin, M.; Bouyahya, A.; et al. Natural bioactive compounds targeting epigenetic pathways in cancer: A review on alkaloids, terpenoids, quinones and isothiocyanates. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekric, D.; Neureiter, D.; Ablinger, C.; Dobias, H.; Beyreis, M.; Ritter, M.; Jakab, M.; Bischof, J.; Koller, U.; Kiesslich, T.; et al. Evaluation of Taze-metostat as a Therapeutically Relevant Substance in Biliary Tract Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brach, D.; Johnston-Blackwell, D.; Drew, A.; Lingaraj, T.; Motwani, V.; Warholic, N.M.; Feldman, I.; Plescia, C.; Smith, J.J.; Copeland, R.A.; et al. EZH2 Inhibition by Tazemetostat Results in Altered Dependency on B-cell Activation Signaling in DLBCL. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2586–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, S.K.; Kawano, S.; Minoshima, Y.; Warholic, N.M.; Huang, K.C.; Xiao, Y.; Kadowaki, T.; Uesugi, M.; Kuznetsov, G.; Kumar, N.; et al. Selective inhibition of EZH2 by EPZ-6438 leads to potent antitumor activity in EZH2-mutant non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholze, H.; Stephenson, R.E.; Reynolds, R.; Shah, S.; Puri, R.; Butler, S.D.; Trujillo-Alonso, V.; Teater, M.R.; van Besien, H.; Gibbs-Curtis, D.; et al. Combined EZH2 and Bcl-2 inhibitors as precision therapy for genetically defined DLBCL subtypes. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5226–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julia, E.; Salles, G. EZH2 inhibition by tazemetostat: Mechanisms of action, safety and efficacy in relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 2127–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Mandlekar, S.; Harvey, K.J.; Ucker, D.S.; Kong, A.N. Chemopreventive isothiocyanates induce apoptosis and caspase-3-like protease activity. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Fimognari, C.; Nüsse, M.; Cesari, R.; Iori, R.; Cantelli-Forti, G.; Hrelia, P. Growth inhibition, cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in human T-cell leukemia by the isothiocyanate sulforaphane. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, S.; Tufail, S.; Sherwani, M.A.; Yusuf, N.; Islam, N. Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Induces Apoptosis Through ROS Generation and Caspase-3 Activation in Cervical Cancer Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 29, 12:673103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Lin, K.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, W. Sulforaphane induced apoptosis via promotion of mitochondrial fusion and ERK1/2-mediated 26S proteasome degradation of novel pro-survival Bim and upregulation of Bax in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. J. Cancer. 2017, 8, 2456–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantso, T.; Sfakianos, A.P.; Atkinson, A.; Anestopoulos, I.; Mitsiogianni, M.; Botaitis, S.; Perente, S.; Simopoulos, C.; Vasileiadis, S.; Franco, R.; et al. Development of a novel experimental in vitro model of isothiocyanate-induced apoptosis in human malignant melanoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 6303–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovic, L.M.; Laketic, D.; Cumic, J.; Jordanova, E.; Pantic, I. Application of artificial intelligence for detection of chemico-biological interactions associated with oxidative stress and DNA damage. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 345, 109533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the chou-talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, D.; Vale, N. Evaluation of synergism in drug combinations and reference models for future orientations in oncology. Curr. Res. Pharmacol. Drug Discov. 2022, 3, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
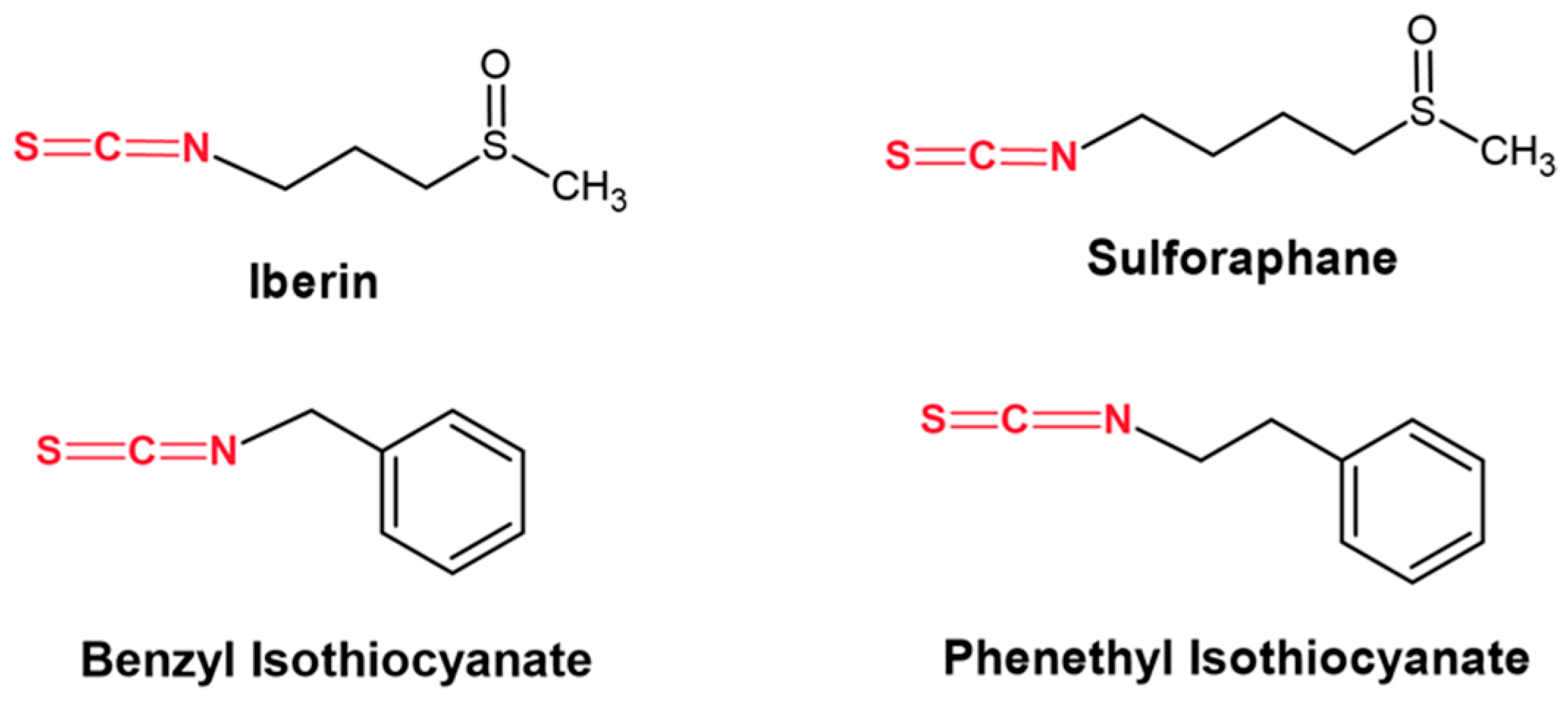
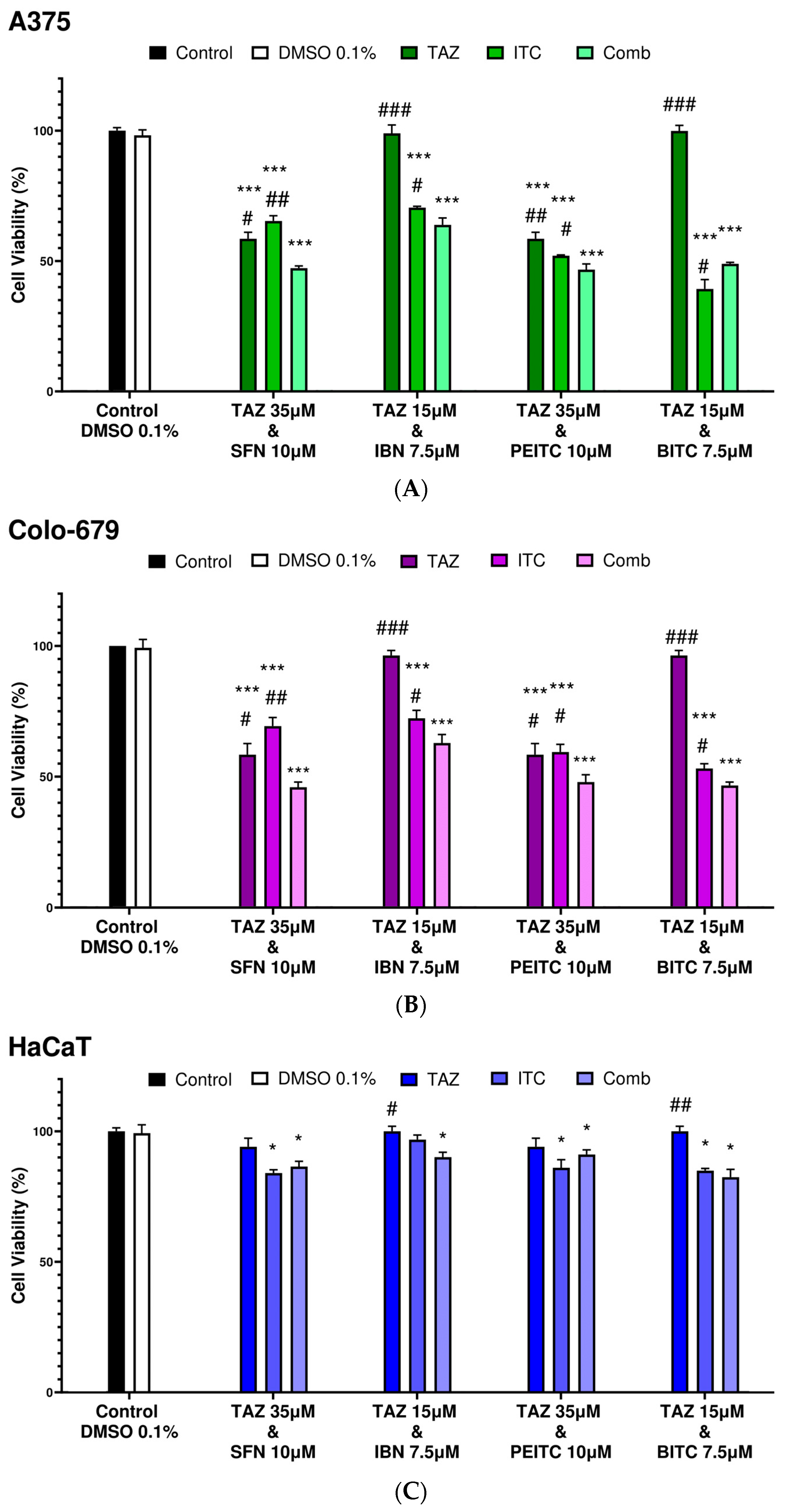


| Combinatorial Exposure | Combination Index (CI) | Agent Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| TAZ (35.0 μM) + SFN (10.0 μM) | 0.89 | Synergistic |
| TAZ (15.0 μM) + IBN (7.5 μM) | 1.02 | Additive |
| TAZ (35.0 μM) + PEITC (10.0 μM) | 0.79 | Synergistic |
| TAZ (15.0 μM) + BITC (7.5 μM) | 1.09 | Additive |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anestopoulos, I.; Paraskevaidis, I.; Kyriakou, S.; Giova, L.E.; Trafalis, D.T.; Botaitis, S.; Franco, R.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I. Isothiocyanates Potentiate Tazemetostat-Induced Apoptosis by Modulating the Expression of Apoptotic Genes, Members of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2, and Levels of Tri-Methylating Lysine 27 at Histone 3 in Human Malignant Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052745
Anestopoulos I, Paraskevaidis I, Kyriakou S, Giova LE, Trafalis DT, Botaitis S, Franco R, Pappa A, Panayiotidis MI. Isothiocyanates Potentiate Tazemetostat-Induced Apoptosis by Modulating the Expression of Apoptotic Genes, Members of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2, and Levels of Tri-Methylating Lysine 27 at Histone 3 in Human Malignant Melanoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(5):2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052745
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnestopoulos, Ioannis, Ioannis Paraskevaidis, Sotiris Kyriakou, Lambrini E. Giova, Dimitrios T. Trafalis, Sotiris Botaitis, Rodrigo Franco, Aglaia Pappa, and Mihalis I. Panayiotidis. 2024. "Isothiocyanates Potentiate Tazemetostat-Induced Apoptosis by Modulating the Expression of Apoptotic Genes, Members of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2, and Levels of Tri-Methylating Lysine 27 at Histone 3 in Human Malignant Melanoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 5: 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052745
APA StyleAnestopoulos, I., Paraskevaidis, I., Kyriakou, S., Giova, L. E., Trafalis, D. T., Botaitis, S., Franco, R., Pappa, A., & Panayiotidis, M. I. (2024). Isothiocyanates Potentiate Tazemetostat-Induced Apoptosis by Modulating the Expression of Apoptotic Genes, Members of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2, and Levels of Tri-Methylating Lysine 27 at Histone 3 in Human Malignant Melanoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5), 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052745








