Functional Divergence of the Paralog Salmonella Effector Proteins SopD and SopD2 and Their Contributions to Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. SopD and SopD2: Salmonella enterica Paralog Effectors
2.1. Discovery of SopD and Early Insights into Function
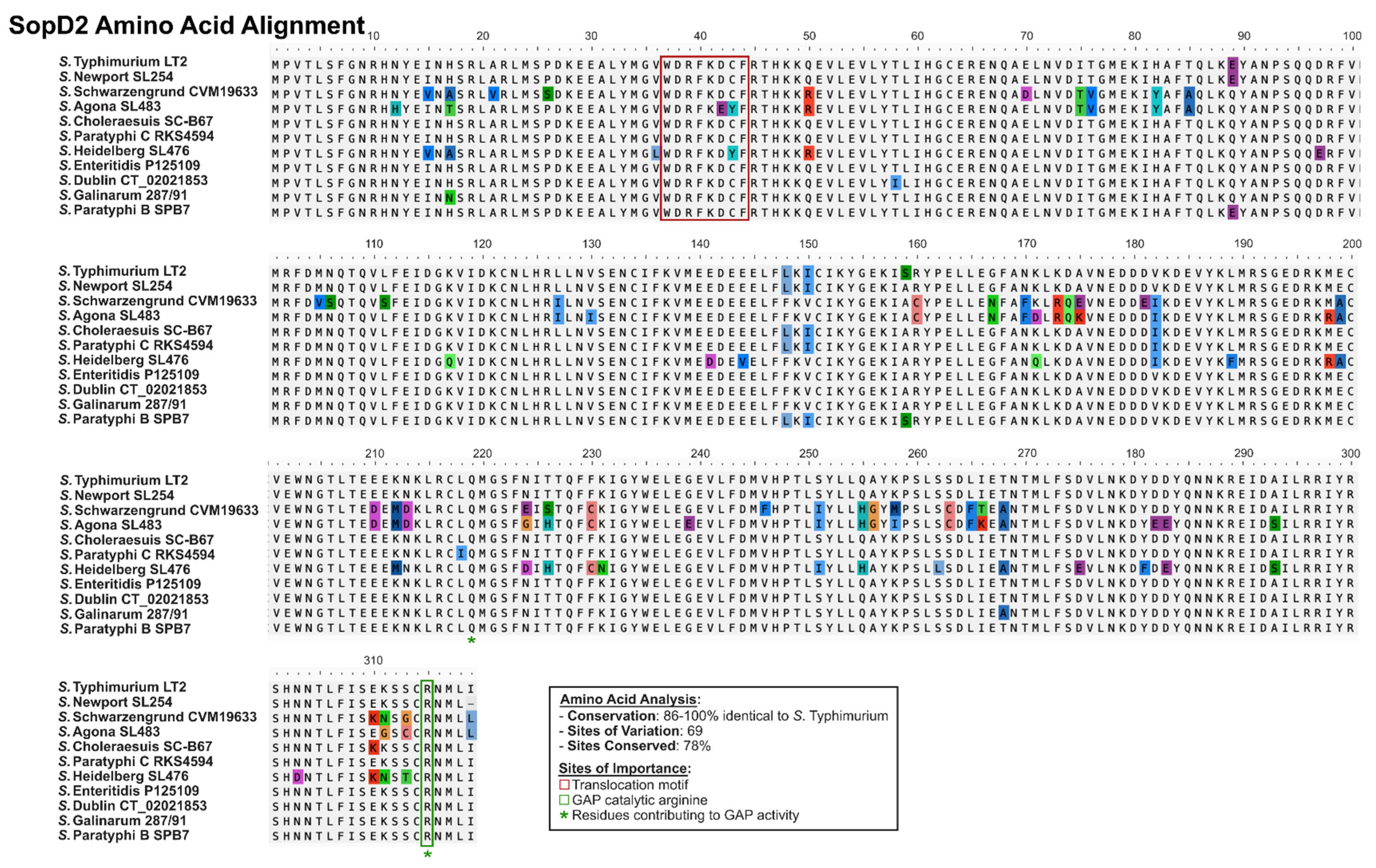
2.2. SopD2: A Paralog Effector in S. enterica
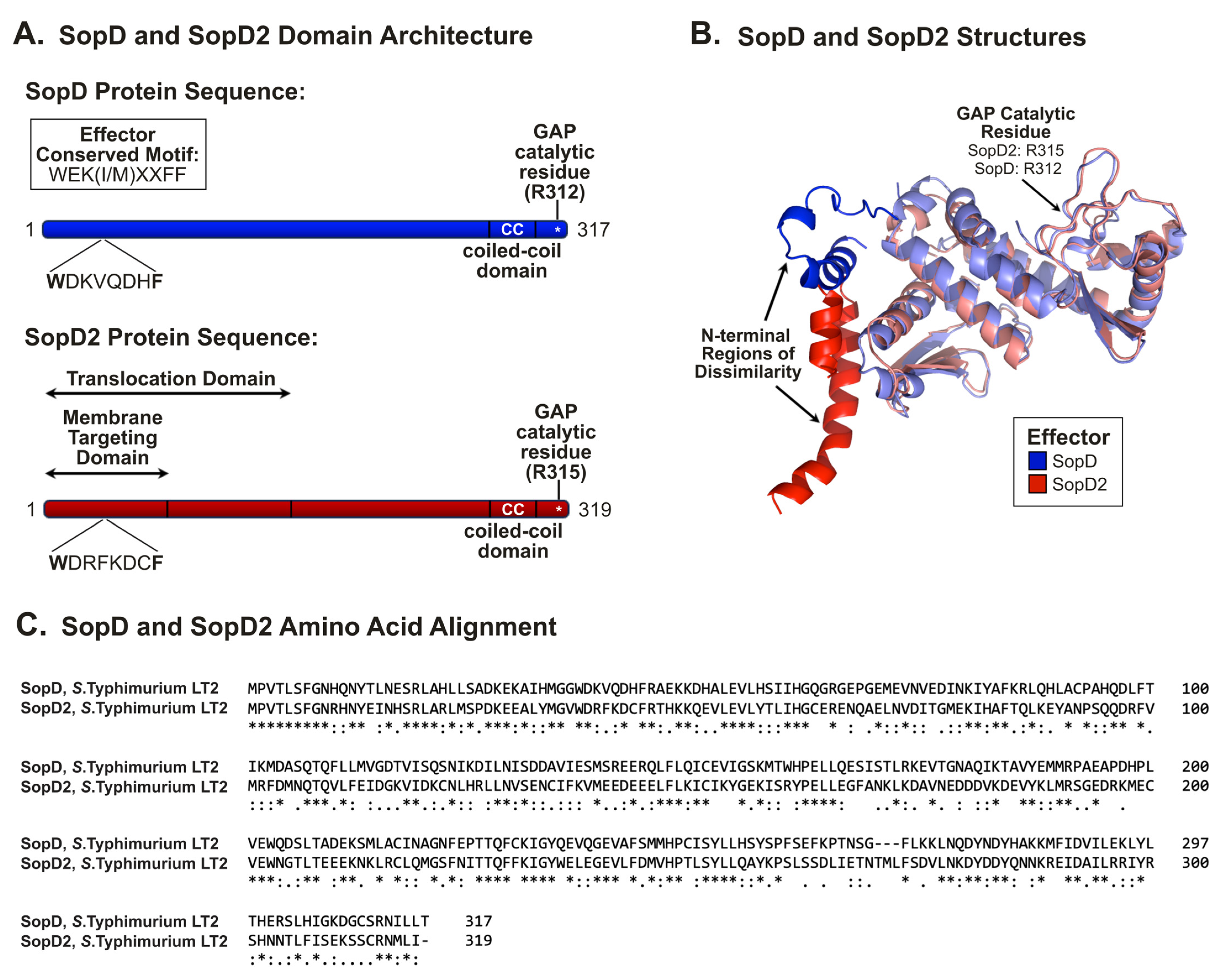
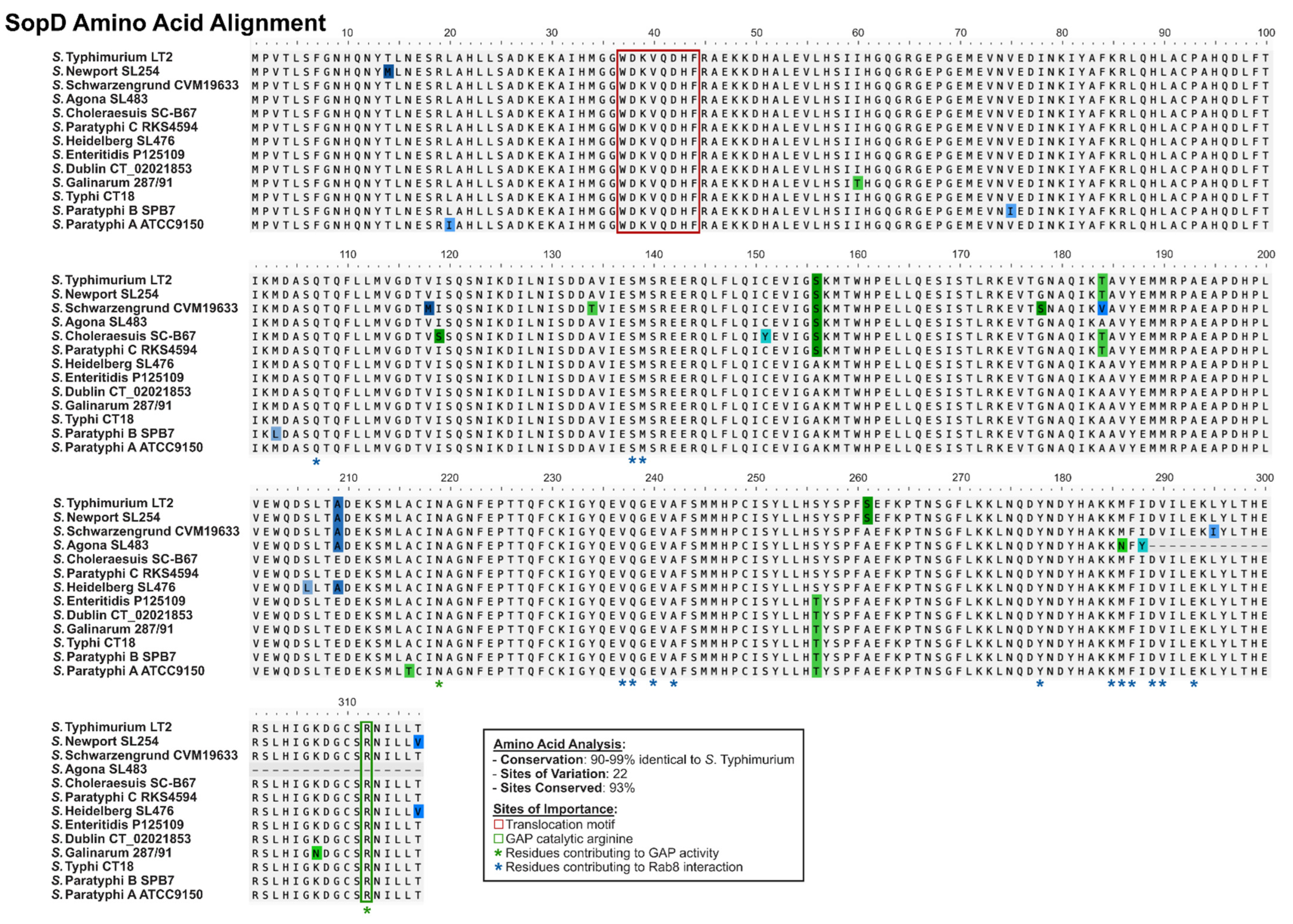
2.3. SopD and SopD2: Structure–Function Relationships
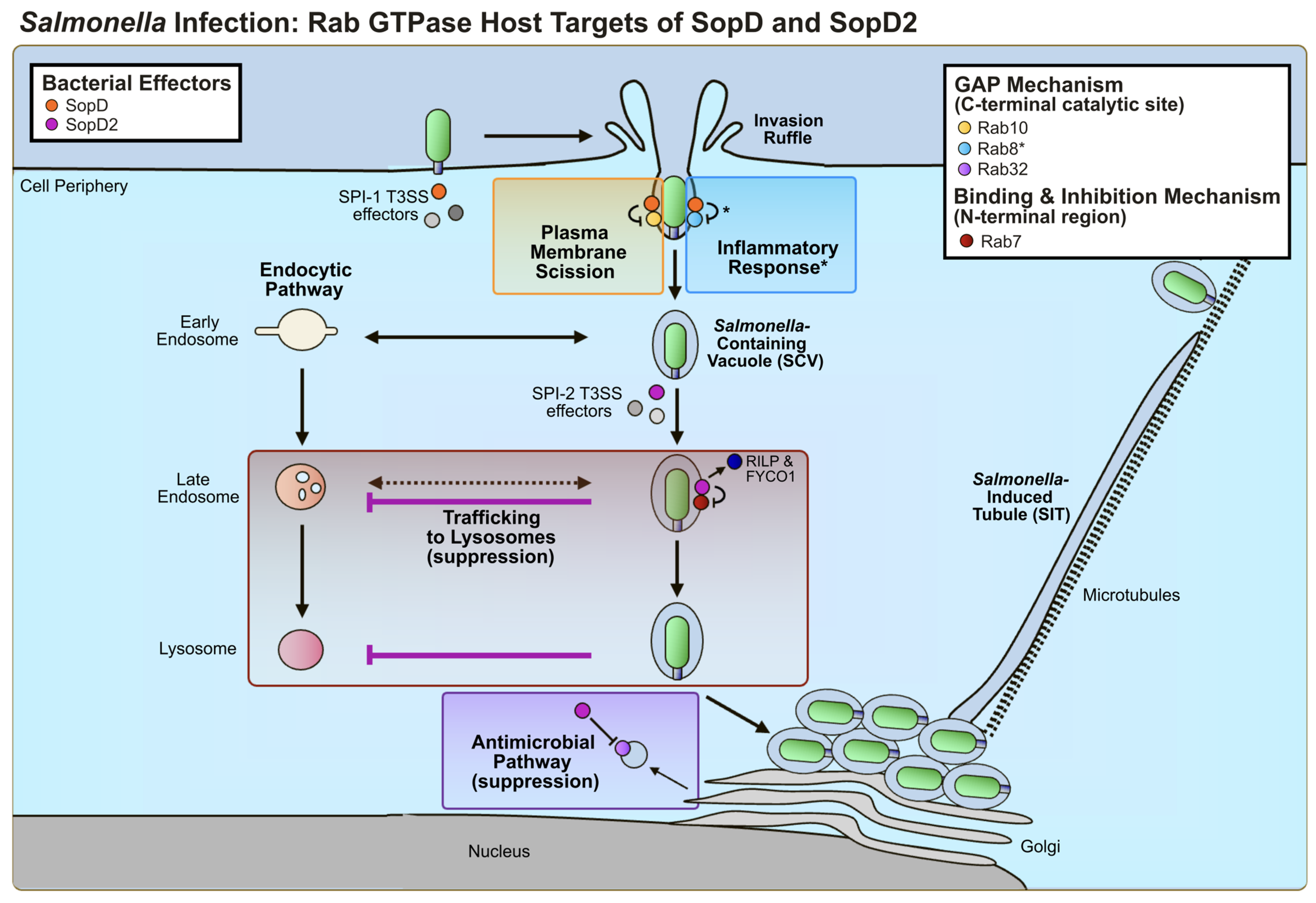
3. SopD and SopD2: Host Interactors and Molecular Mechanisms of Action
3.1. Host Cell Interaction Partners
3.2. Host Cell Targets and Effector-Mediated Manipulation of Host Function
3.2.1. SopD2: Rab GTPase Targets
3.2.2. SopD: Rab GTPase Targets
3.2.3. Other Host Targets
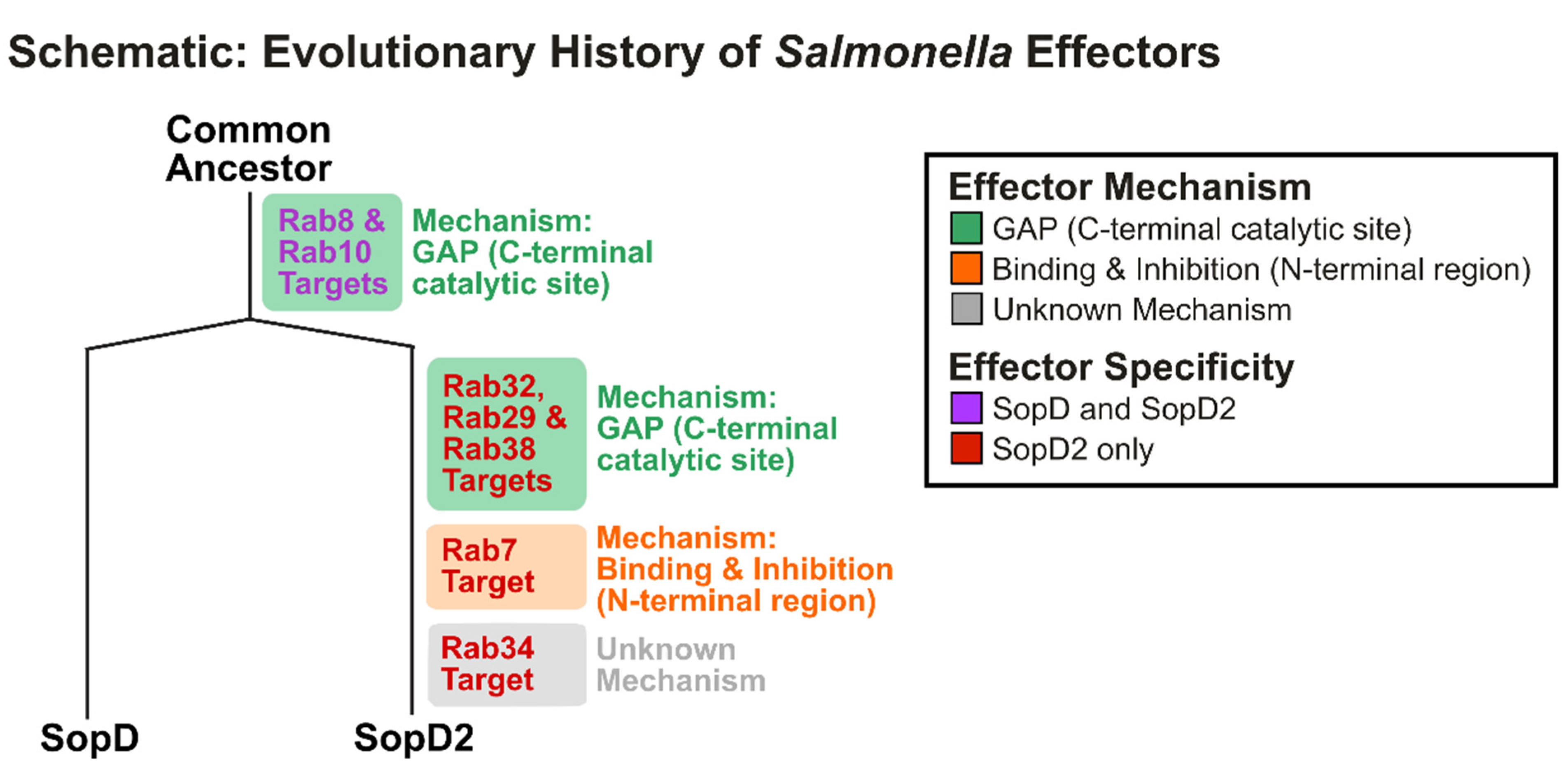
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrari, R.G.; Rosario, D.K.A.; Cunha-Neto, A.; Mano, S.B.; Figueiredo, E.E.S.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Worldwide Epidemiology of Salmonella Serovars in Animal-Based Foods: A Meta-Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00591-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, T.F.; Ingram, L.A.; Cieslak, P.R.; Vugia, D.J.; Tobin-D’Angelo, M.; Hurd, S.; Medus, C.; Cronquist, A.; Angulo, F.J. Salmonellosis Outcomes Differ Substantially by Serotype. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal-Mor, O.; Boyle, E.C.; Grassl, G.A. Same Species, Different Diseases: How and Why Typhoidal and Non-Typhoidal Salmonella enterica Serovars Differ. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M. The Global Burden of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fàbrega, A.; Vila, J. Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Skills To Succeed in the Host: Virulence and Regulation. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 308–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele-Mortimer, O. The Salmonella-Containing Vacuole—Moving with the Times. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuff, K.; Finlay, B.B. What the SIF Is Happening—The Role of Intracellular Salmonella-Induced Filaments. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, S.L.; Brumell, J.H.; Pfeifer, C.G.; Finlay, B.B. Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands: Big Virulence in Small Packages. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán, J.E. Common Themes in the Design and Function of Bacterial Effectors. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.-H.; Liu, S.-L. Salmonella Secretion Systems: Differential Roles in Pathogen-Host Interactions. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 241, 126591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, A.P.; Guttman, J.A.; Finlay, B.B. Manipulation of Host-Cell Pathways by Bacterial Pathogens. Nature 2007, 449, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, T.D.; Hettiarachchi, S.U.; Gan, J.; Diaz-Del-Olmo, I.; Yu, X.-J.; Muench, J.H.; Thurston, T.L.M.; Pearson, J.S. Speaking the Host Language: How Salmonella Effector Proteins Manipulate the Host. Microbiology 2023, 169, 001342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán, J.E.; Curtiss, R. Cloning and Molecular Characterization of Genes Whose Products Allow Salmonella Typhimurium to Penetrate Tissue Culture Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6383–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halici, S.; Zenk, S.F.; Jantsch, J.; Hensel, M. Functional Analysis of the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 2-Mediated Inhibition of Antigen Presentation in Dendritic Cells. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4924–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuff-Janzen, K.; Tupin, A.; Yurist-Doutsch, S.; Rowland, J.L.; Finlay, B.B. Multiple Salmonella-Pathogenicity Island 2 Effectors Are Required to Facilitate Bacterial Establishment of Its Intracellular Niche and Virulence. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Burford, W.B.; Pham, G.; Zhang, L.; Alto, L.T.; Ertelt, J.M.; Winter, M.G.; Winter, S.E.; Way, S.S.; Alto, N.M. Systematic Reconstruction of an Effector-Gene Network Reveals Determinants of Salmonella Cellular and Tissue Tropism. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1531–1544.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, J.E.; Hensel, M.; Gleeson, C.; Holden, D.W. Identification of a Virulence Locus Encoding a Second Type III Secretion System in Salmonella Typhimurium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2593–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, E.; Thurston, T.L.M.; Holden, D.W. Salmonella SPI-2 Type III Secretion System Effectors: Molecular Mechanisms And Physiological Consequences. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, T.D.; Schmieder, R.; Silva, G.G.Z.; Busch, J.; Cassman, N.; Dutilh, B.E.; Green, D.; Matlock, B.; Heffernan, B.; Olsen, G.J.; et al. Genomic Comparison of the Closely-Related Salmonella enterica Serovars Enteritidis, Dublin and Gallinarum. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirold, S.; Ehrbar, K.; Weissmüller, A.; Prager, R.; Tschäpe, H.; Rüssmann, H.; Hardt, W.-D. Salmonella Host Cell Invasion Emerged by Acquisition of a Mosaic of Separate Genetic Elements, Including Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 (SPI1), SPI5, and sopE2. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 2348–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Rossanese, O.W.; Brown, N.F.; Kujat-Choy, S.; Galán, J.E.; Finlay, B.B.; Brumell, J.H. The Related Effector Proteins SopD and SopD2 from Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Contribute to Virulence during Systemic Infection of Mice. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knodler, L.A.; Celli, J.; Hardt, W.-D.; Vallance, B.A.; Yip, C.; Finlay, B.B. Salmonella Effectors within a Single Pathogenicity Island Are Differentially Expressed and Translocated by Separate Type III Secretion Systems. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 43, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlson, M.B.; Huang, Z.; Alto, N.M.; Blanc, M.-P.; Dixon, J.E.; Chai, J.; Miller, S.I. Structure and Function of Salmonella SifA Indicate That Its Interactions with SKIP, SseJ, and RhoA Family GTPases Induce Endosomal Tubulation. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 4, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stender, S.; Friebel, A.; Linder, S.; Rohde, M.; Mirold, S.; Hardt, W.-D. Identification of SopE2 from Salmonella Typhimurium, a Conserved Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor for Cdc42 of the Host Cell. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 1206–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brumell, J.H.; Kujat-Choy, S.; Brown, N.F.; Vallance, B.A.; Knodler, L.A.; Finlay, B.B. SopD2 Is a Novel Type III Secreted Effector of Salmonella Typhimurium That Targets Late Endocytic Compartments Upon Delivery Into Host Cells. Traffic 2003, 4, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakowski, M.A.; Cirulis, J.T.; Brown, N.F.; Finlay, B.B.; Brumell, J.H. SopD Acts Cooperatively with SopB during Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Invasion. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2839–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitskiy, S.; Itzen, A. SopD from Salmonella Specifically Inactivates Rab8. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2021, 1869, 140661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Costa, V.M.; Braun, V.; Landekic, M.; Shi, R.; Proteau, A.; McDonald, L.; Cygler, M.; Grinstein, S.; Brumell, J.H. Salmonella Disrupts Host Endocytic Trafficking by SopD2-Mediated Inhibition of Rab7. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 1508–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddy, K.C.; Zhu, H.; D’Costa, V.M.; Xu, C.; Beyrakhova, K.; Cygler, M.; Grinstein, S.; Coyaud, E.; Laurent, E.M.N.; St-Germain, J.; et al. Salmonella Effector SopD Promotes Plasma Membrane Scission by Inhibiting Rab10. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowski, J.; Wu, J.Y.; Rueger, D.C.; Miller, B.E.; Siegel, L.M.; Kredich, N.M. Characterization of the cysJIH Regions of Salmonella Typhimurium and Escherichia Coli B. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 15726–15737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.A.; Wood, M.W.; Mullan, P.B.; Watson, P.R.; Wallis, T.S.; Galyov, E.E. Secreted Effector Proteins of Salmonella Dublin Act in Concert To Induce Enteritis. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 5799–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prager, R.; Mirold, S.; Tietze, E.; Strutz, U.; Knüppel, B.; Rabsch, W.; Hardt, W.-D.; Tschäpe, H. Prevalence and Polymorphism of Genes Encoding Translocated Effector Proteins among Clinical Isolates of Salmonella enterica. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 290, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Santos, R.L.; Tsolis, R.M.; Stender, S.; Hardt, W.D.; Bäumler, A.J.; Adams, L.G. The Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium Effector Proteins SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD, and SopE2 Act in Concert to Induce Diarrhea in Calves. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3843–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawley, T.D.; Chan, K.; Thompson, L.J.; Kim, C.C.; Govoni, G.R.; Monack, D.M. Genome-Wide Screen for Salmonella Genes Required for Long-Term Systemic Infection of the Mouse. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidwai, A.S.; Mushamiri, I.; Niemann, G.S.; Brown, R.N.; Adkins, J.N.; Heffron, F. Diverse Secreted Effectors Are Required for Salmonella Persistence in a Mouse Infection Model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffatellu, M.; Wilson, R.P.; Chessa, D.; Andrews-Polymenis, H.; Tran, Q.T.; Lawhon, S.; Khare, S.; Adams, L.G.; Bäumler, A.J. SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD, and SopE2 Contribute to Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium Invasion of Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.C.; Galán, J.E. Manipulation of the Host Actin Cytoskeleton by Salmonella—All in the Name of Entry. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, D.; Boddy, K.C.; Canadien, V.; Brabant, D.; Fairn, G.D.; D’Costa, V.M.; Coyaud, E.; Raught, B.; Pérez-Sala, D.; Park, W.S.; et al. Salmonella Exploits Host Rho GTPase Signalling Pathways through the Phosphatase Activity of SopB. Cell Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terebiznik, M.R.; Vieira, O.V.; Marcus, S.L.; Slade, A.; Yip, C.M.; Trimble, W.S.; Meyer, T.; Finlay, B.B.; Grinstein, S. Elimination of Host Cell PtdIns(4,5)P2 by Bacterial SigD Promotes Membrane Fission during Invasion by Salmonella. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, M.; Sanderson, K.E.; Spieth, J.; Clifton, S.W.; Latreille, P.; Courtney, L.; Porwollik, S.; Ali, J.; Dante, M.; Du, F.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium LT2. Nature 2001, 413, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fookes, M.; Schroeder, G.N.; Langridge, G.C.; Blondel, C.J.; Mammina, C.; Connor, T.R.; Seth-Smith, H.; Vernikos, G.S.; Robinson, K.S.; Sanders, M.; et al. Salmonella bongori Provides Insights into the Evolution of the Salmonellae. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuccio, S.-P.; Bäumler, A.J. Comparative Analysis of Salmonella Genomes Identifies a Metabolic Network for Escalating Growth in the Inflamed Gut. mBio 2014, 5, e00929-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, M.; Sanderson, K.E.; Clifton, S.W.; Latreille, P.; Porwollik, S.; Sabo, A.; Meyer, R.; Bieri, T.; Ozersky, P.; McLellan, M.; et al. Comparison of Genome Degradation in Paratyphi A and Typhi, Human-Restricted Serovars of Salmonella enterica That Cause Typhoid. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, R.; Watson, K.G.; Holden, D.W.; Helaine, S. Identification of Salmonella Pathogenicity Island-2 Type III Secretion System Effectors Involved in Intramacrophage Replication of S. enterica Serovar Typhimurium: Implications for Rational Vaccine Design. mBio 2013, 4, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, N.; Henry, T.; de Chastellier, C.; Zhao, W.; Guilhon, A.-A.; Gorvel, J.-P.; Méresse, S. The Virulence Protein SopD2 Regulates Membrane Dynamics of Salmonella-Containing Vacuoles. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, N.; Mota, L.J.; Méresse, S. Salmonella-Induced Tubular Networks. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, L.J.; Ramsden, A.E.; Liu, M.; Castle, J.D.; Holden, D.W. SCAMP3 Is a Component of the Salmonella-Induced Tubular Network and Reveals an Interaction between Bacterial Effectors and Post-Golgi Trafficking. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1236–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gorvel, J.-P.; Méresse, S. Effector Proteins Support the Asymmetric Apportioning of Salmonella during Cytokinesis. Virulence 2016, 7, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRock, D.L.; Chaudhary, A.; Miller, S.I. Salmonellae Interactions with Host Processes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szeto, J.; Namolovan, A.; Osborne, S.E.; Coombes, B.K.; Brumell, J.H. Salmonella-Containing Vacuoles Display Centrifugal Movement Associated with Cell-to-Cell Transfer in Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liss, V.; Swart, A.L.; Kehl, A.; Hermanns, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chikkaballi, D.; Böhles, N.; Deiwick, J.; Hensel, M. Salmonella enterica Remodels the Host Cell Endosomal System for Efficient Intravacuolar Nutrition. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Settembre, C.; Di Malta, C.; Polito, V.A.; Arencibia, M.G.; Vetrini, F.; Erdin, S.; Erdin, S.U.; Huynh, T.; Medina, D.; Colella, P.; et al. TFEB Links Autophagy to Lysosomal Biogenesis. Science 2011, 332, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardiello, M.; Palmieri, M.; di Ronza, A.; Medina, D.L.; Valenza, M.; Gennarino, V.A.; Di Malta, C.; Donaudy, F.; Embrione, V.; Polishchuk, R.S.; et al. A Gene Network Regulating Lysosomal Biogenesis and Function. Science 2009, 325, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inpanathan, S.; Ospina-Escobar, E.; Li, V.C.; Adamji, Z.; Lackraj, T.; Cho, Y.H.; Porco, N.; Choy, C.H.; McPhee, J.B.; Botelho, R.J. Salmonella Actively Modulates TFEB in Murine Macrophages in a Growth-Phase and Time-Dependent Manner. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 12, e04981-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingues, L.; Holden, D.W.; Mota, L.J. The Salmonella Effector SteA Contributes to the Control of Membrane Dynamics of Salmonella-Containing Vacuoles. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 2923–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.F.; Szeto, J.; Jiang, X.; Coombes, B.K.; Finlay, B.B.; Brumell, J.H. Mutational Analysis of Salmonella Translocated Effector Members SifA and SopD2 Reveals Domains Implicated in Translocation, Subcellular Localization and Function. Microbiology 2006, 152, 2323–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knodler, L.A.; Ibarra, J.A.; Pérez-Rueda, E.; Yip, C.K.; Steele-Mortimer, O. Coiled-Coil Domains Enhance the Membrane Association of Salmonella Type III Effectors. Cell. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1497–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanò, S.; Gao, X.; Hannemann, S.; Lara-Tejero, M.; Galán, J.E. A Bacterial Pathogen Targets a Host Rab-Family GTPase Defense Pathway with a GAP. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.X.; Yang, Z.; Kerr, M.C.; Luo, L.; Guo, Z.; Alexandrov, K.; Stow, J.L.; Teasdale, R.D. Salmonella Effector SopD2 Interferes with Rab34 Function. Cell Biol. Int. 2017, 41, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, H.; Jiang, K.; Tong, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Galán, J.E.; Gao, X. The Salmonella Effector Protein SopD Targets Rab8 to Positively and Negatively Modulate the Inflammatory Response. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Costa, V.M.; Coyaud, E.; Boddy, K.C.; Laurent, E.M.N.; St-Germain, J.; Li, T.; Grinstein, S.; Raught, B.; Brumell, J.H. BioID Screen of Salmonella Type 3 Secreted Effectors Reveals Host Factors Involved in Vacuole Positioning and Stability during Infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2511–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuff-Janzen, K.; Serapio-Palacios, A.; McCoy, J.; Krekhno, Z.; Moon, K.-M.; Deng, W.; Foster, L.J.; Finlay, B.B. Quantitative Proteomic Screen Identifies Annexin A2 as a Host Target for Salmonella Pathogenicity Island-2 Effectors SopD2 and PipB2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, Y.; Hiragi, S.; Fukuda, M. Rab Family of Small GTPases: An Updated View on Their Regulation and Functions. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Marlin, M.C. Rab Family of GTPases. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1298, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanò, S.; Galán, J.E. Taking Control: Hijacking of Rab GTPases by Intracellular Bacterial Pathogens. Small GTPases 2018, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, M.-P.; Müller, M.P.; Wandinger-Ness, A. Bacterial Pathogens Commandeer Rab GTPases to Establish Intracellular Niches. Traffic 2012, 13, 1565–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiya, K.; Barbieri, M.A.; Funato, K.; Shah, A.H.; Stahl, P.D.; Groisman, E.A. A Salmonella Virulence Protein That Inhibits Cellular Trafficking. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, F.; Bucci, C. Multiple Roles of the Small GTPase Rab7. Cells 2016, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantalupo, G.; Alifano, P.; Roberti, V.; Bruni, C.B.; Bucci, C. Rab-Interacting Lysosomal Protein (RILP): The Rab7 Effector Required for Transport to Lysosomes. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankiv, S.; Alemu, E.A.; Brech, A.; Bruun, J.-A.; Lamark, T.; Øvervatn, A.; Bjørkøy, G.; Johansen, T. FYCO1 Is a Rab7 Effector That Binds to LC3 and PI3P to Mediate Microtubule plus End–Directed Vesicle Transport. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanò, S.; Galán, J.E. A Rab32-Dependent Pathway Contributes to Salmonella Typhi Host Restriction. Science 2012, 338, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zou, L.; Tang, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, L.; Jia, Q.; Ni, Q.; Liu, S.; Tang, L.; et al. Analysis of the Rab GTPase Interactome in Dendritic Cells Reveals Anti-Microbial Functions of the Rab32 Complex in Bacterial Containment. Immunity 2016, 44, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, S.; Tsujimura, K.; Koide, Y. Rab GTPases Regulating Phagosome Maturation Are Differentially Recruited to Mycobacterial Phagosomes. Traffic 2011, 12, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Sun, H.; Boot, M.; Shao, L.; Chang, S.J.; Wang, W.; Lam, T.T.; Lara-Tejero, M.; Rego, E.H.; Galán, J.E. Itaconate Is an Effector of a Rab GTPase Cell-Autonomous Host Defense Pathway against Salmonella. Science 2020, 369, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachtel, R.; Bräuning, B.; Mader, S.L.; Ecker, F.; Kaila, V.R.I.; Groll, M.; Itzen, A. The Protease GtgE from Salmonella Exclusively Targets Inactive Rab GTPases. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Hong, W. Interorganellar Regulation of Lysosome Positioning by the Golgi Apparatus through Rab34 Interaction with Rab-Interacting Lysosomal Protein. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 4317–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Yamamoto, H.; Suetsugu, S.; Miki, H.; Takenawa, T.; Endo, T. Small GTPase Rah/Rab34 Is Associated with Membrane Ruffles and Macropinosomes and Promotes Macropinosome Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 4063–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenberg, N.M.; Silverman, M. Rab34 and Its Effector Munc13-2 Constitute a New Pathway Modulating Protein Secretion in the Cellular Response to Hyperglycemia. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colicelli, J. Human RAS Superfamily Proteins and Related GTPases. Sci. STKE 2004, 2004, RE13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goitre, L.; Trapani, E.; Trabalzini, L.; Retta, S.F. The Ras Superfamily of Small GTPases: The Unlocked Secrets. In Ras Signaling: Methods and Protocols; Trabalzini, L., Retta, S.F., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–18. ISBN 978-1-62703-791-4. [Google Scholar]
- Giacomodonato, M.N.; Uzzau, S.; Bacciu, D.; Caccuri, R.; Sarnacki, S.H.; Rubino, S.; Cerquetti, M.C. SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD and SopE2 Effector Proteins of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Are Synthesized at Late Stages of Infection in Mice. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streckel, W.; Wolff, A.-C.; Prager, R.; Tietze, E.; Tschäpe, H. Expression Profiles of Effector Proteins SopB, SopD1, SopE1, and AvrA Differ with Systemic, Enteric, and Epidemic Strains of Salmonella enterica. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2004, 48, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Effector | Host Interactors and/or Targets | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interactor (Assay) 1 | Target 2 | Mechanism | Infection Phenotype | ||
| SopD | Rab8A (IP-MS, CoIP, Y2H, SEC, GAP) | Yes | C-terminal GAP site 3 | Upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, downregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines 3 | [27,29,60] |
| Rab10 (IP-MS, CoIP, Y2H, GAP) | Yes | C-terminal GAP site | Suppression of Rab10, promoting plasma membrane scission (SCV formation) | [27,29] | |
| Rab8B (Y2H) | ND | --- | --- | [27] | |
| Rab14 (Y2H) | ND, NG | --- | --- | [27] | |
| Rab3D (Y2H) | ND, NG | --- | --- | [27] | |
| VPS35 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| VPS26A (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| MAP1B (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| CKAP5 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| DCTN2 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| DYNC1H1 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| KIF5B (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| KIF11 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| MYO5B (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| AP3S1 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| SCYL2 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| CLTC (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| AP2M1 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [29] | |
| SopD2 | Rab7A (IP-MS, CoIP, IVB) | Yes, NG | N-terminal inhibition | Suppression of Rab7A-mediated endocytic trafficking | [28,45] |
| Rab32 (CoIP, GAP) | Yes | C-terminal GAP site | Suppression of Rab32-mediated cell- autonomous defense pathway | [27,58,60] | |
| Rab8A (IP-MS, CoIP, GAP) | Yes | C-terminal GAP site | --- | [27,58,61] | |
| Rab10 (IP-MS, CoIP, GAP) | Yes | C-terminal GAP site | --- | [27,29,61] | |
| Rab8B (CoIP) | ND | --- | --- | [58] | |
| Rab34 (IP-MS, SEC, PD) | Yes | --- | Rab34, along with SopD2, promotes Salmonella replication in epithelial cells | [59] | |
| Rab29 (GAP) | Yes | C-terminal GAP site | --- | [27] | |
| Rab38 (GAP) | Yes | C-terminal GAP site | --- | [27] | |
| AnxA2 (IP-MS, PD) | Yes | --- | --- | [62] | |
| MYH10 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| MYL6 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| MYL12B (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| MYH9 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| RBM10 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| EIF3B (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| CYFIP1 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| PHB2 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| EIF3A (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| AP2B1 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| EIF3E (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| AP3D1 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| MYO1B (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| AP3B1 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
| AP2A1 (IP-MS) | ND | --- | --- | [61] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oke, M.T.; D’Costa, V.M. Functional Divergence of the Paralog Salmonella Effector Proteins SopD and SopD2 and Their Contributions to Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084191
Oke MT, D’Costa VM. Functional Divergence of the Paralog Salmonella Effector Proteins SopD and SopD2 and Their Contributions to Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(8):4191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084191
Chicago/Turabian StyleOke, Mosopefoluwa T., and Vanessa M. D’Costa. 2024. "Functional Divergence of the Paralog Salmonella Effector Proteins SopD and SopD2 and Their Contributions to Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 8: 4191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084191
APA StyleOke, M. T., & D’Costa, V. M. (2024). Functional Divergence of the Paralog Salmonella Effector Proteins SopD and SopD2 and Their Contributions to Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(8), 4191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084191





