Impact of Serotonergic 5HT1A and 5HT2A Receptor Activation on the Respiratory Response to Hypercapnia in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
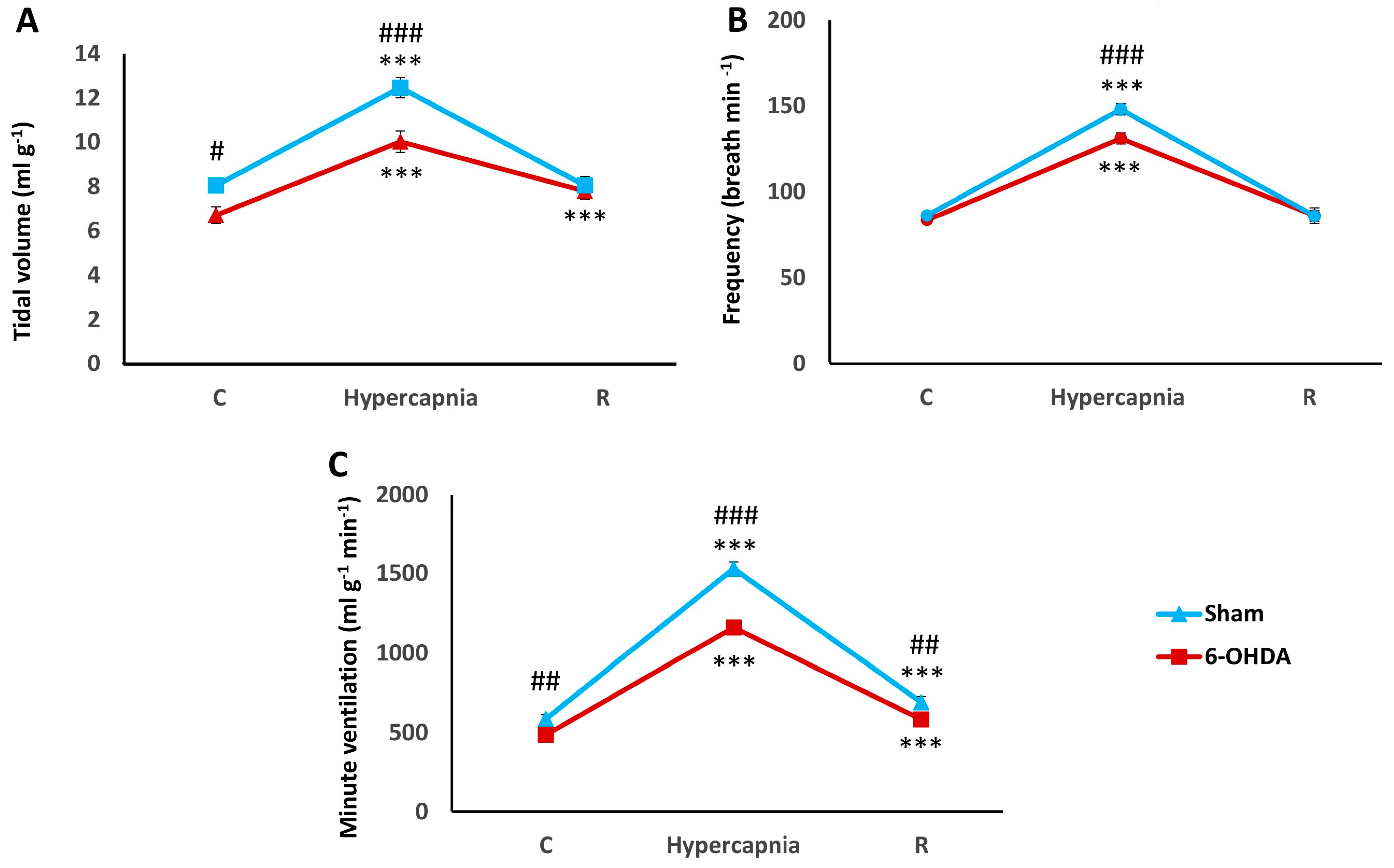
2.1. Hypercapnic Ventilatory Response (HCVR) in PD and Sham Rats
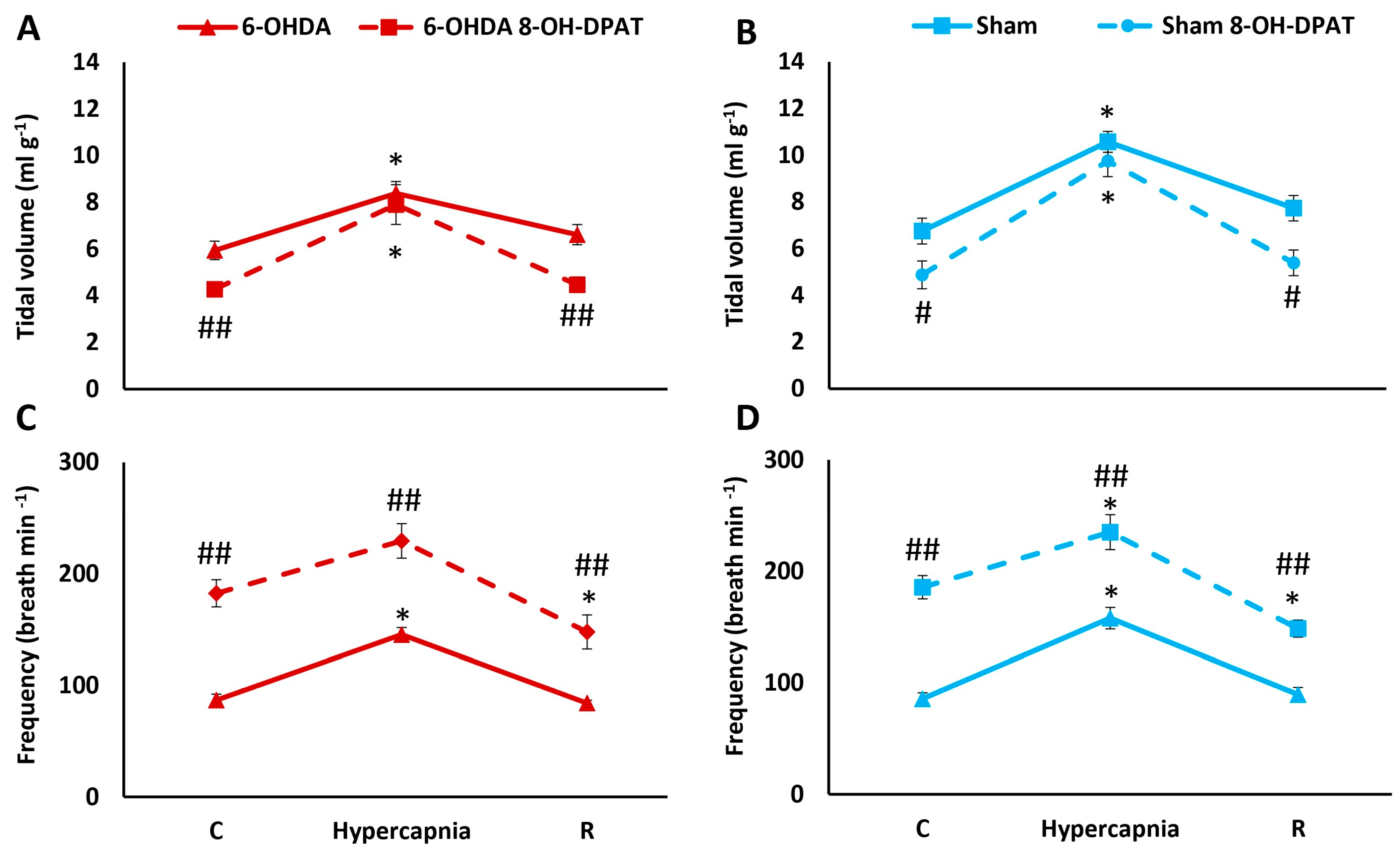
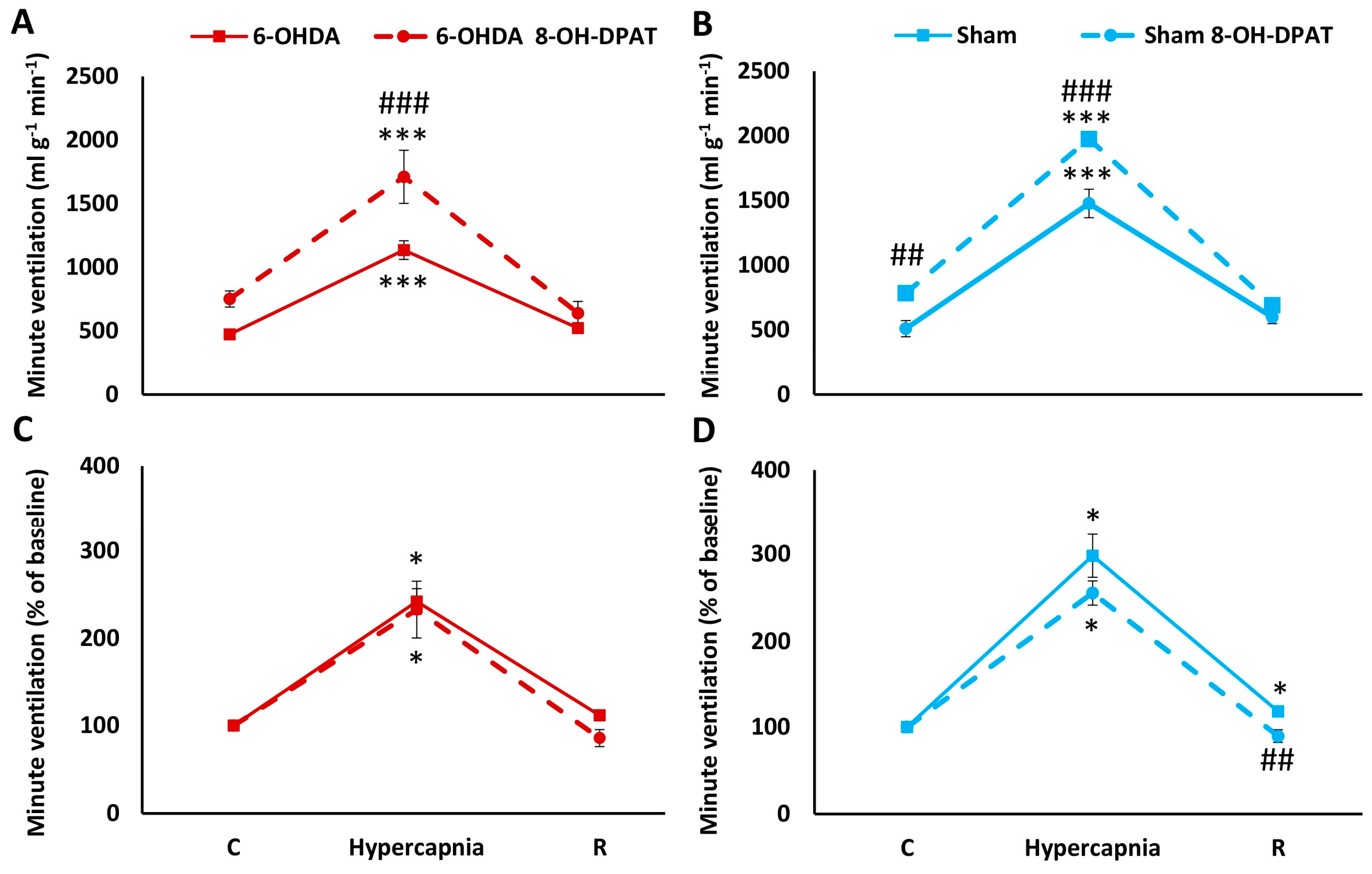
2.2. HCVR in PD and Sham Rats before and after Intraperitoneal (i.p.) Treatment with 8-OH-DPAT
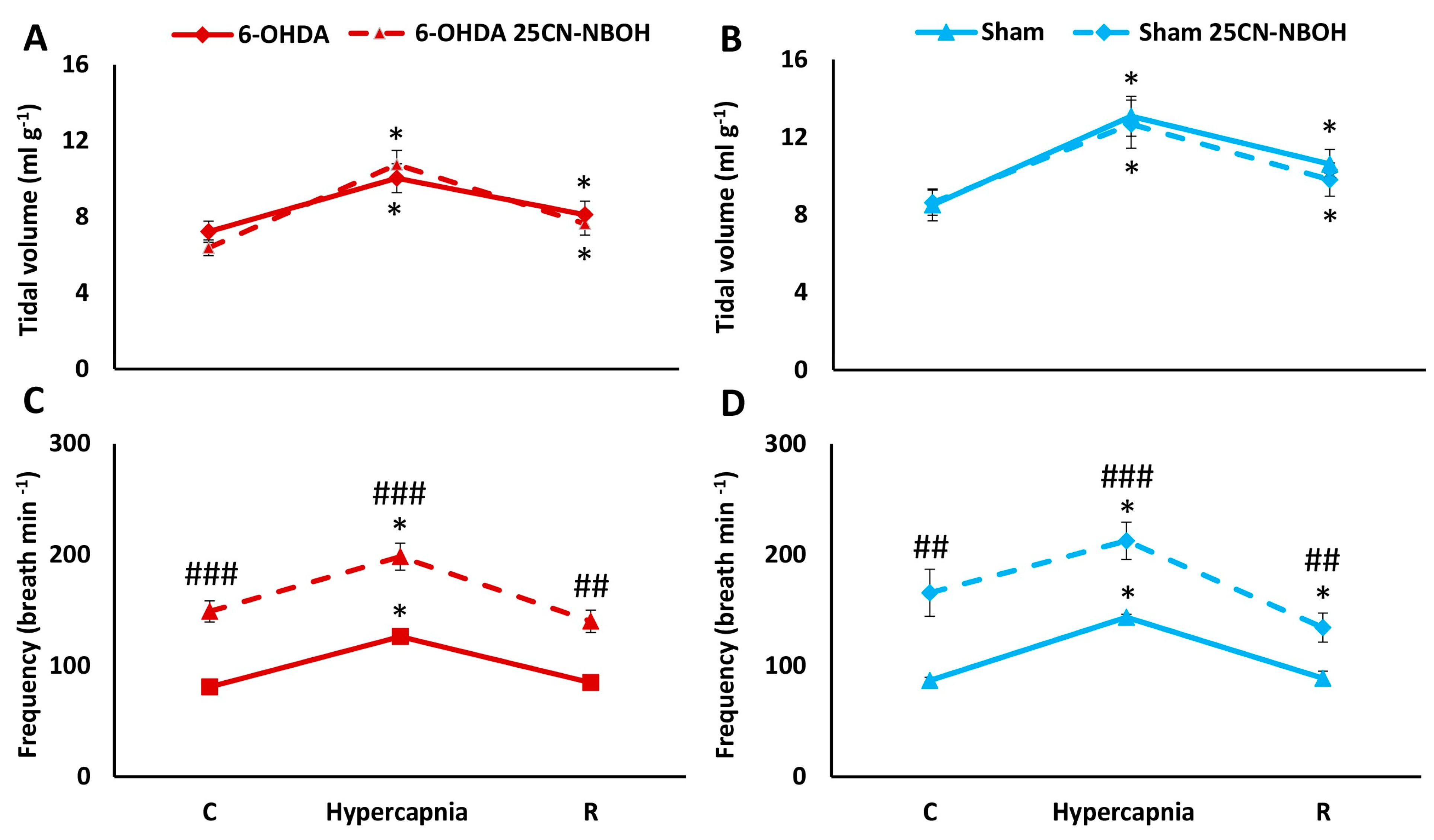
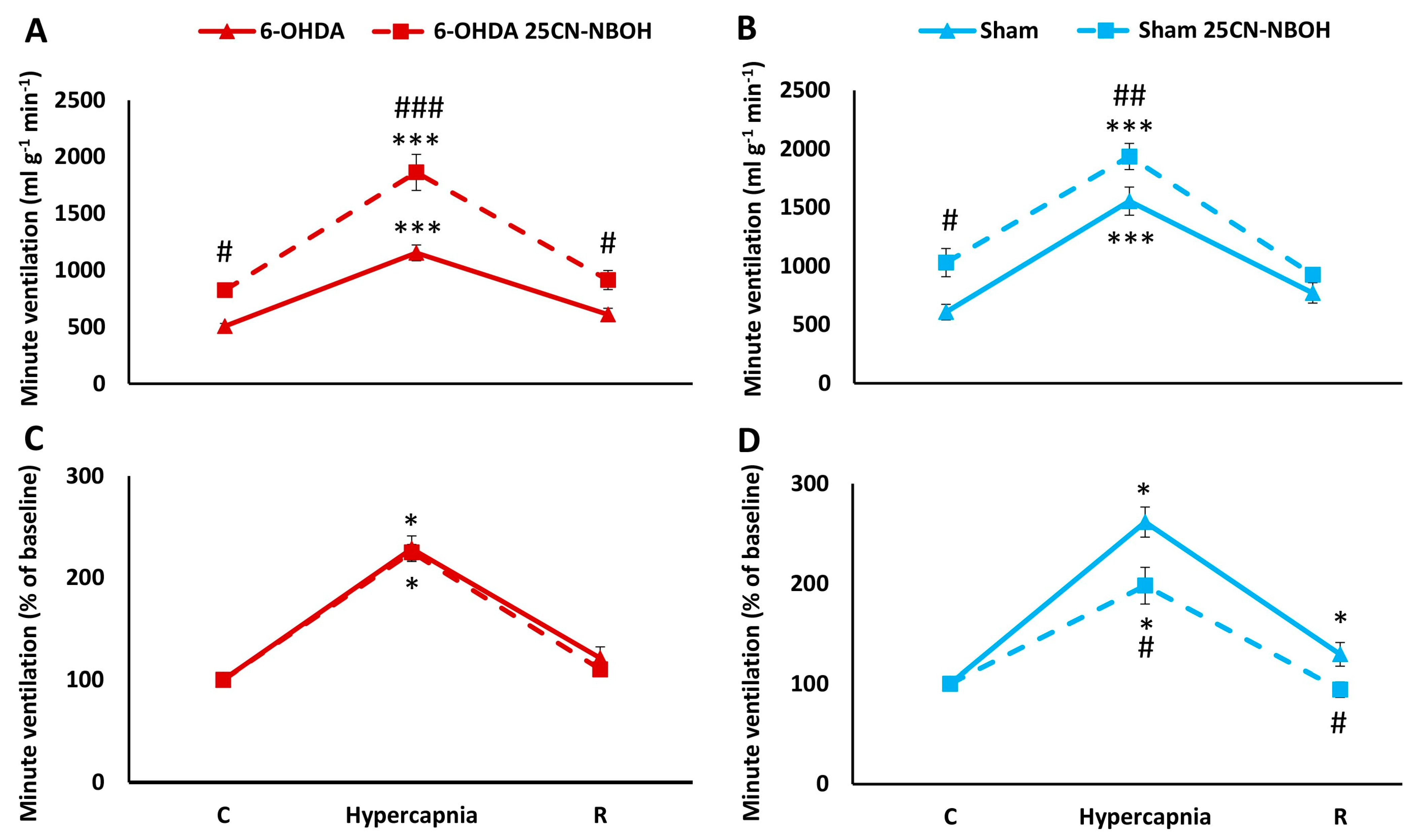
2.3. HCVR in PD and Sham Rats before and after i.p. Treatment with 25CN-NBOH
2.4. HCVR in PD and Sham Rats before and after i.p. Treatment with TCB-2
2.5. Comparison of HCVR in Sham and PD Rats after i.p. Treatment with 25CN-NBOH, TCB-2, and 8-OH-DPAT
2.6. Apnea Index Analysis
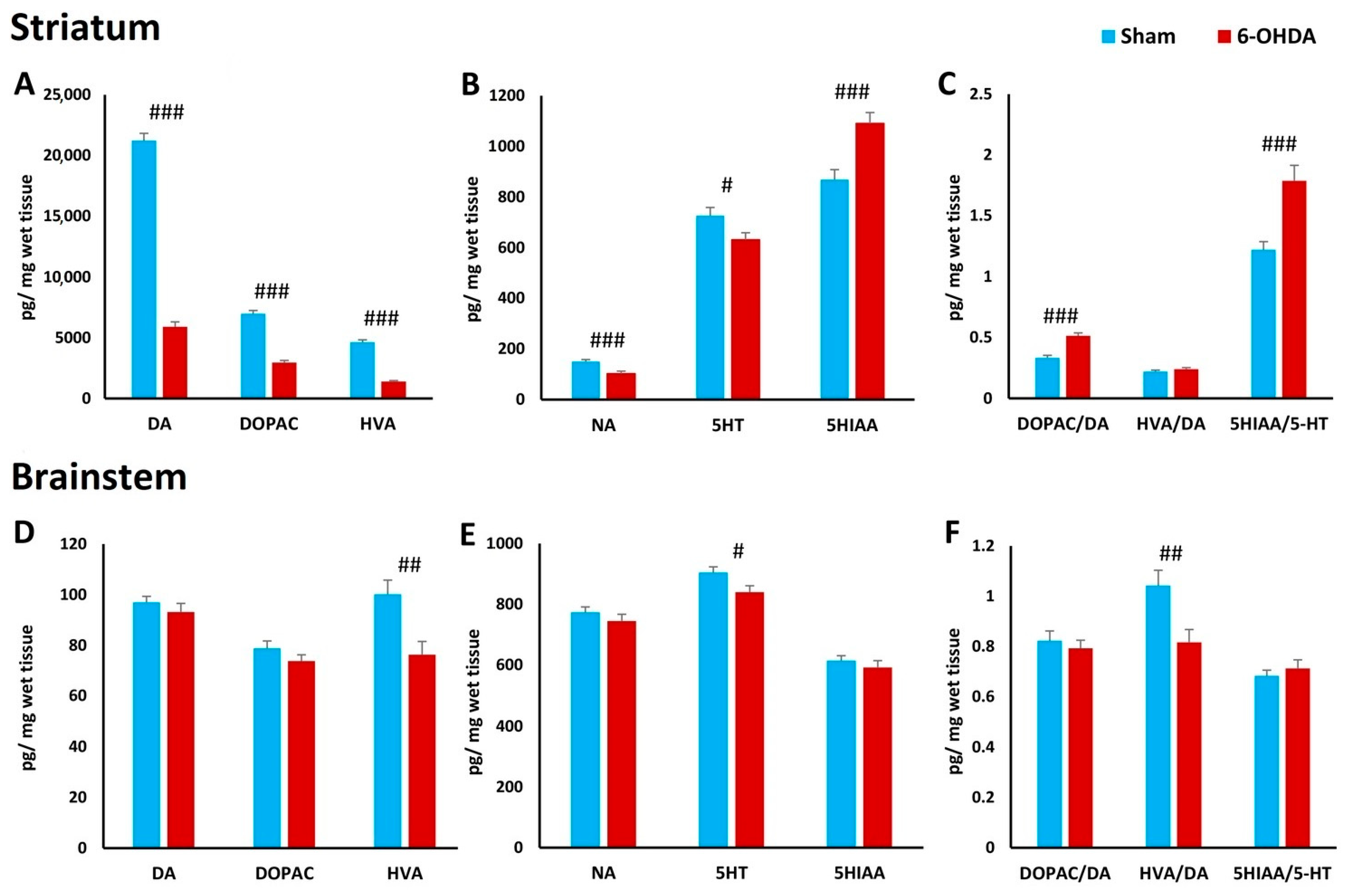
2.7. Concentration of Biogenic Amines in Striatum and Brainstem
3. Discussion
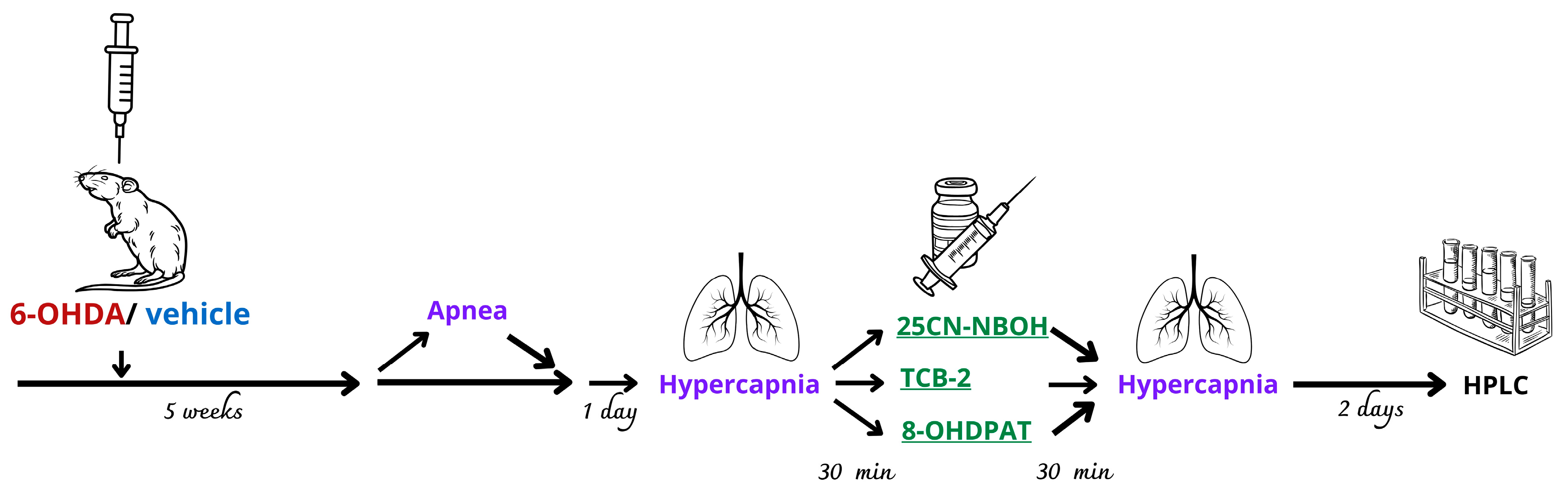
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Experimental Groups and Drug Treatment
- 25CN-NBOH at a dose of 1 mg kg−1 dissolved in water (Sham n = 7, 6-OHDA n = 7);
- TCB-2 at a dose of 1 mg kg−1 dissolved in water (Sham n = 7, 6-OHDA n = 7);
- 8-OH-DPAT at a dose of 0.5 mg kg−1 dissolved in water (Sham n = 6, 6-OHDA n = 6).
4.3. Surgery and 6-OHDA/Vehicle Injection
4.4. Ventilation Measurements
4.5. Apnea Measurement
4.6. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahsas, G.; Chisti, W.; Verma, A.; Agrawal, N.; Bansal, K. The Role of the Serotonergic System of the Brain in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem. J. 2023, 17, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, P.; Fox, S.H.; Brotchie, J.M. The serotonergic system in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 95, 163–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politis, M.; Loane, C. Serotonergic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease and its relevance to disability. Sci. World J. 2011, 11, 1726–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilaire, G.; Voituron, N.; Menuet, C.; Ichiyama, R.M.; Subramanian, H.H.; Dutschmann, M. The role of serotonin in respiratory function and dysfunction. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2010, 174, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szereda-Przestaszewska, M.; Kaczyńska, K. Serotonin and substance P: Synergy or competition in the control of breathing. Auton. Neurosci. 2020, 225, 102658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, M.R.; Richerson, G.B. Medullary serotonin neurons and their roles in central respiratory chemoreception. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2010, 173, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, M.R.; Tattersall, G.J.; Harris, M.B.; McEvoy, S.D.; Richerson, D.N.; Deneris, E.S.; Johnson, R.L.; Chen, Z.-F.; Richerson, G.B. Defects in breathing and thermoregulation in mice with near-complete absence of central serotonin neurons. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nattie, E.E.; Li, A.; Richerson, G.; Lappi, D.A. Medullary serotonergic neurones and adjacent neurones that express neurokinin-1 receptors are both involved in chemoreception in vivo. J. Physiol. 2004, 556, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brust, R.D.; Corcoran, A.E.; Richerson, G.B.; Nattie, E.; Dymecki, S.M. Functional and developmental identification of a molecular subtype of brain serotonergic neuron specialized to regulate breathing dynamics. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 2152–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateika, J.H.; Komnenov, D.; Pop, A.; Kuhn, D.M. Genetic depletion of 5-HT increases central apnea frequency and duration and dampens arousal but does not impact the circadian modulation of these variables. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubin, L.; Mann, G.L. Hypoglossal motoneurons are endogenously activated by serotonin during the active period of circadian cycle. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2018, 248, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baille, G.; De Jesus, A.M.; Perez, T.; Devos, D.; Dujardin, K.; Charley, C.M.; Defebvre, L.; Moreau, C. Ventilatory Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2016, 6, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, E.M.; Moreira, R.D.F.C.; De Oliveira, A.; Ferro, A.M.; DILorenzo, V.A.P.; Gianlorenço, A.C.L. Respiratory Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2021, 11, 993–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczyńska, K.; Orłowska, M.E.; Andrzejewski, K. Respiratory Abnormalities in Parkinson’s Disease: What Do We Know from Studies in Humans and Animal Models? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquino, Y.C.; Cabral, L.M.; Miranda, N.C.; Naccarato, M.C.; Falquetto, B.; Moreira, T.S.; Takakura, A.C. Respiratory disorders of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurophysiol. 2022, 127, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrzejewski, K.; Jampolska, M.; Zaremba, M.; Joniec-Maciejak, I.; Boguszewski, P.M.; Kaczyńska, K. Respiratory pattern and phrenic and hypoglossal nerve activity during normoxia and hypoxia in 6-OHDA-induced bilateral model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Physiol. Sci. 2020, 70, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tintner, R.; Manian, P.; Gauthier, P.; Jankovic, J. Pleuropulmonary fibrosis after long-term treatment with the dopamine agonist pergolide for Parkinson Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2005, 62, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrzejewski, K.; Kaczyńska, K.; Zaremba, M. Serotonergic system in hypoxic ventilatory response in unilateral rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuppy, M.; Barna, B.F.; Alves-dos-Santos, L.; Britto, L.R.G.; Chiavegatto, S.; Moreira, T.S.; Takakura, A. Respiratory deficits in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2015, 297, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.C.; Li, A.; Nattie, E.E. Medullary serotonergic neurones modulate the ventilatory response to hypercapnia, but not hypoxia in conscious rats. J. Physiol. 2005, 566, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, A.E.; Richerson, G.B.; Harris, M.B. Serotonergic mechanisms are necessary for central respiratory chemoresponsiveness in situ. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 186, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Salloum, A.; Rowley, J.A.; Mateika, J.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Omran, Q.; Badr, M.S. Increased propensity for central apnea in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: Effect of nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, O.; Amorim, M.R.; Mendelowitz, D.; Polotsky, V.Y. Revisiting the Role of Serotonin in Sleep-Disordered Breathing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teran, F.A.; Massey, C.A.; Richerson, G.B. Serotonin neurons and central respiratory chemoreception: Where are we now? Prog. Brain Res. 2014, 209, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonye, E.C.; Bayliss, D.A. Criteria for central respiratory chemoreceptors: Experimental evidence supporting current candidate cell groups. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1241662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moreno, V.S.; Bícego, K.C.; Szawka, R.E.; Anselmo-Franci, J.A.; Gargaglioni, L.H. Serotonergic mechanisms on breathing modulation in the rat locus coeruleus. Pflug. Arch. 2010, 459, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, E.S.; Hunnicutt, B.J.; Knopp, S.J.; Williams, J.T.; Bissonnette, J.M. A selective 5-HT1a receptor agonist improves respiration in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, K.J. Eupnea and gasping in vivo are facilitated by the activation of 5-HT2A receptors. J. Neurophysiol. 2021, 125, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyal, K.G.; Petrucci, A.N.; Littlepage-Saunders, M.V.; Boodhoo, N.A.; Wendt, L.H.; Buchanan, G.F. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and 5-HT2 Receptor Agonists Have Distinct, Sleep-state Dependent Effects on Postictal Breathing in Amygdala Kindled Mice. Neuroscience 2023, 513, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szereda-Przestaszewska, M.; Kaczyńska, K. Peripheral 5-HT1A receptors are not essential for increased ventilation evoked by systemic 8-OH-DPAT challenge in anaesthetized rats. Exp. Physiol. 2007, 92, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radocaj, T.; Mustapic, S.; Prkic, I.; Stucke, A.G.; Hopp, F.A.; Stuth, E.A.E.; Zuperku, E.J. Activation of 5-HT1A receptors in the preBötzinger region has little impact on the respiratory pattern. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2015, 212–214, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Xu, F. Systemic 8-OH-DPAT challenge causes hyperventilation largely via activating pre-botzinger complex 5-HT1A receptors. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2022, 296, 103810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xu, F. 8-OH-DPAT abolishes the pulmonary C-fiber-mediated apneic response to fentanyl largely via acting on 5HT1A receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarius. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 303, R449–R458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, A.E.; Wagner, A.K.; Westergom, B.P.; Malena, R.R.; Zafonte, R.D.; Olsen, A.S.; Sozda, C.N.; Luthra, P.; Panda, M.; Cheng, J.P.; et al. Acute treatment with the 5-HT(1A) receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT and chronic environmental enrichment confer neurobehavioral benefit after experimental brain trauma. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 177, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.P.; Leary, J.B.; Sembhi, A.; Edwards, C.M.; Bondi, C.O.; Kline, A.E. 5-hydroxytryptamine1A (5-HT1A) receptor agonists: A decade of empirical evidence supports their use as an efficacious therapeutic strategy for brain trauma. Brain Res. 2016, 1640, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- De Vry, J.; Schreiber, R.; Melon, C.; Dalmus, M.; Jentzsch, K.R. 5-HT1A receptors are differentially involved in the anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects of 8-OH-DPAT and fluoxetine in the rat. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004, 14, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślifirski, G.; Król, M.; Turło, J. 5-HT Receptors and the Development of New Antidepressants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, H.F.; Frederick, D.; Kim, H.; McElgin, W.; Kung, M.P.; Mu, M.; Mozley, P.D.; Vessotskie, J.M.; Stevenson, D.A.; Kushner, S.A.; et al. In Vivo SPECT Imaging of 5-HTlA Receptors With [1231]p-MPPI in Nonhuman Primates. Synapse 1996, 24, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, F.; Ramirez, J.M. Endogenous activation of serotonin-2A receptors is required for respiratory rhythm generation in vitro. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 11055–11064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, M.R.; Wehner, M.; Aungst, J.; Smith, J.C.; Richerson, G.B. Transgenic mice lacking serotonin neurons have severe apnea and high mortality during development. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 10341–10349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptak, K.; Yamanishi, T.; Aungst, J.; Milescu, L.S.; Zhang, R.; Richerson, G.B.; Smith, J.C. Raphé neurons stimulate respiratory circuit activity by multiple mechanisms via endogenously released serotonin and substance P. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3720–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, I.F.; Zuperku, E.J.; Stucke, A.G.; Jakovcevic, D.; Hopp, F.A.; Stuth, E.A.E. Serotonergic modulation of inspiratory hypoglossal motoneurons in decerebrate dogs. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 95, 3449–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Märcher Rørsted, E.; Jensen, A.A.; Kristensen, J.L. 25CN-NBOH: A Selective Agonist for in vitro and in vivo Investigations of the Serotonin 2A Receptor. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 3263–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giovanni, G.; De Deurwaerdère, P. TCB-2 [(7R)-3-bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-bicyclo[4.2.0]octa-1,3,5-trien-7-yl]methanamine]: A hallucinogenic drug, a selective 5-HT2A receptor pharmacological tool, or none of the above? Neuropharmacology 2018, 142, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes-Junior, S.A.; Carvalho, K.S.; Moreira, T.S.; Takakura, A.C. Correlation between neuroanatomical and functional respiratory changes observed in an experimental model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Physiol. 2018, 103, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, J.C.; Oliveira, L.M.; Botelho, M.T.; Moreira, T.S.; Takakura, A.C. The involvement of the pathway connecting the substantia nigra, the periaqueductal gray matter and the retrotrapezoid nucleus in breathing control in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 302, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navailles, S.; De Deurwaerdère, P. Presynaptic control of serotonin on striatal dopamine function. Psychopharmacology 2011, 213, 213–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourine, A.V.; Llaudet, E.; Dale, N.; Spyer, K.M. ATP is a mediator of chemosensory transduction in the central nervous system. Nature 2005, 436, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenker, I.C.; Kréneisz, O.; Nishiyama, A.; Mulkey, D.K. Astrocytes in the retrotrapezoid nucleus sense H+ by inhibition of a Kir4.1-Kir5.1-like current and may contribute to chemoreception by a purinergic mechanism. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 104, 3042–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, V.; Laouafa, S.; Marcouiller, F.; Roussel, D.; Pialoux, V.; Bairam, A. Progesterone decreases apnoea and reduces oxidative stress induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia in ovariectomized female rats. Exp. Physiol. 2020, 105, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrzejewski, K.; Orłowska, M.E.; Zaremba, M.; Joniec-Maciejak, I.; Kaczyńska, K. Impact of Serotonergic 5HT1A and 5HT2A Receptor Activation on the Respiratory Response to Hypercapnia in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084403
Andrzejewski K, Orłowska ME, Zaremba M, Joniec-Maciejak I, Kaczyńska K. Impact of Serotonergic 5HT1A and 5HT2A Receptor Activation on the Respiratory Response to Hypercapnia in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(8):4403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084403
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrzejewski, Kryspin, Magdalena E. Orłowska, Małgorzata Zaremba, Ilona Joniec-Maciejak, and Katarzyna Kaczyńska. 2024. "Impact of Serotonergic 5HT1A and 5HT2A Receptor Activation on the Respiratory Response to Hypercapnia in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 8: 4403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084403
APA StyleAndrzejewski, K., Orłowska, M. E., Zaremba, M., Joniec-Maciejak, I., & Kaczyńska, K. (2024). Impact of Serotonergic 5HT1A and 5HT2A Receptor Activation on the Respiratory Response to Hypercapnia in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(8), 4403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084403





