The Rise of Fentanyl: Molecular Aspects and Forensic Investigations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fentanyl Abuse
2.1. Increasing Trends: Online Markets and the Dark Web
2.2. Combination with Xylazine
2.3. Combination with Other Drugs
3. Pharmacokinetics, Metabolism, and Pharmacogenetics of Fentanyl
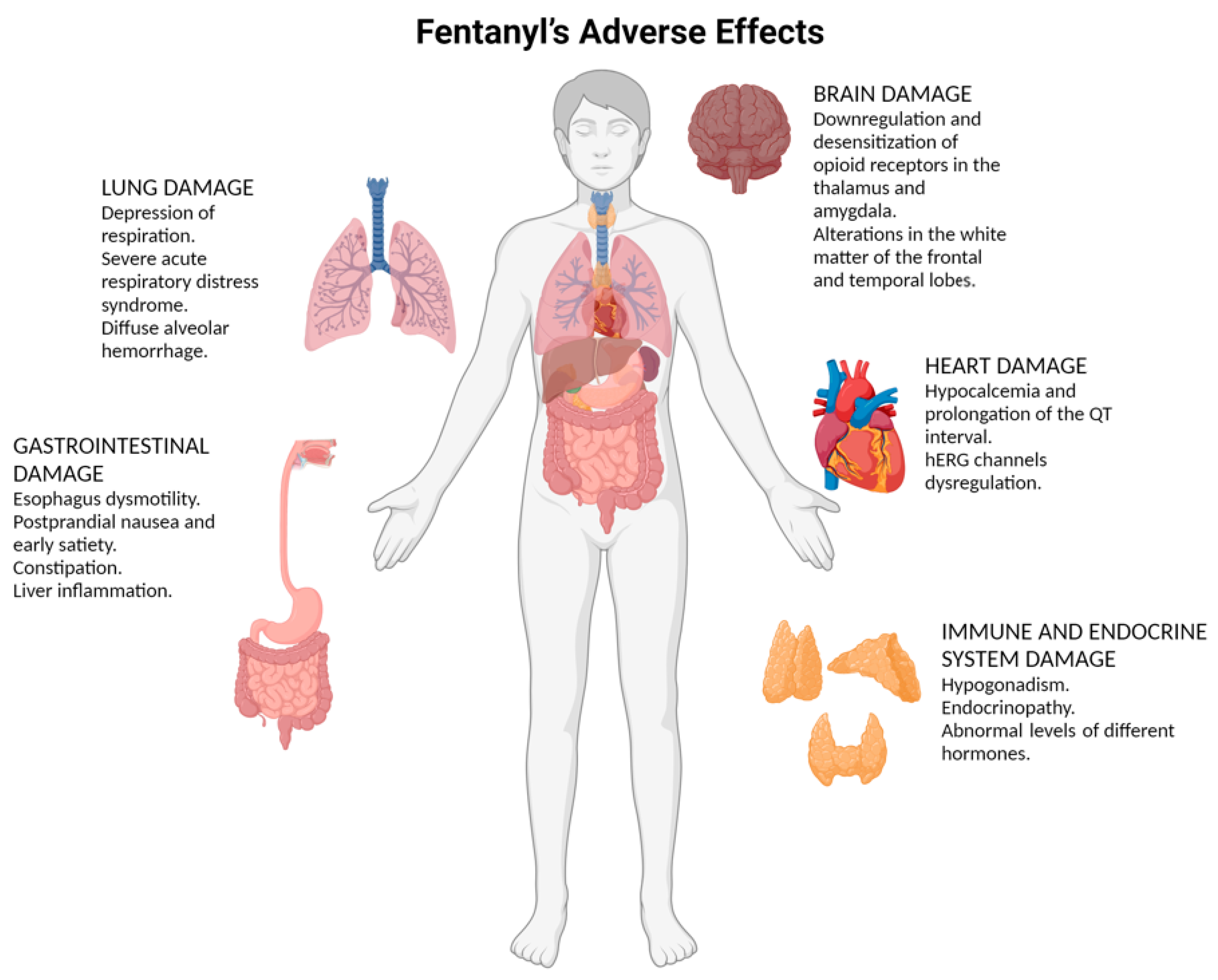
4. Fentanyl’s Adverse Effects
4.1. Brain Damage
4.2. Lung Damage
4.3. Heart Damage
4.4. Gastrointestinal Damage
4.5. Immune and Endocrine System Damage
5. Post-Mortem Investigation in Fentanyl-Related Deaths
5.1. Crime Scene Investigation
5.2. External Examination
5.3. Autopsy Investigation
- Brain: Evaluate for cerebral edema, focal hemorrhages, or signs of hypoxic-ischemic injury. Weigh and preserve the brain for histological analysis, particularly the hippocampus and cerebellum.
- Lungs: Note pulmonary edema, frothy fluid in airways, or signs of aspiration pneumonia. Weigh both lungs and assess for amorphous material within the alveoli.
- Heart: Examine for myocardial fibrosis, valvular abnormalities, or signs of arrhythmias such as focal ischemic changes. Document the weight and macroscopic findings.
- Liver: Assess for hepatomegaly, discoloration, or nodularity, indicating chronic damage. Note any portal inflammation or necrosis.
- Gastrointestinal Tract: Inspect for irritation, ulcers, or other lesions associated with opioid use.
- Gonads: In males, examine the testes for reduced size or changes in tubular structure; in females, assess the ovaries for signs of chronic endocrine disruption.
5.4. Histological Findings in Fentanyl-Related Deaths
- Brain: Chronic exposure leads to the downregulation of opioid receptors and structural changes in the white matter of the frontal and temporal lobes, resulting in cognitive and emotional impairments. Histologically, hypoxic damage is common, with loss of eosinophilic Purkinje cells in the hippocampus and cerebellum. Neuronal apoptosis, microglial activation, and cortical degeneration are also observed [138,139].
- Lungs: Pulmonary findings include edema, evidenced by a “mushroom plume” of frothy material in the airways and mouth and amorphous eosinophilic deposits in alveolar spaces. Aspiration pneumonia, intra-alveolar hemorrhage, and neutrophilic inflammation are common in cases with a prolonged interval between unconsciousness and death [140].
- Heart: Fentanyl impacts the hERG channel, disrupting potassium currents and prolonging the QT interval, increasing the risk of arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Chronic intravenous use may also result in endocarditis and myocardial fibrosis [141].
- Liver: Histopathological changes include hepatocyte necrosis, lymphocyte infiltration, and portal inflammation. Chronic use often coincides with viral hepatitis, particularly hepatitis C, in intravenous drug users [142].
5.5. Immunohistochemical Markers in Fentanyl-Related Deaths
5.6. Toxicological Investigation
- Alcohol and benzodiazepines: These central nervous system depressants exacerbate fentanyl-induced respiratory depression, increasing the likelihood of apnea and cardiac arrest [165].
- Cocaine: This stimulant can enhance cardiovascular effects, such as tachycardia and arrhythmias, which, when combined with fentanyl, can lead to sudden cardiac death [48].
5.7. Genetic Influences on Metabolism and Susceptibility
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanley, T.H. The Fentanyl Story. J. Pain. 2014, 15, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albores-García, D.; Cruz, S.L. Fentanyl and Other New Psychoactive Synthetic Opioids. Challenges to Prevention and Treatment. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2023, 75, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardanyan, R.S.; Hruby, V.J. Fentanyl-Related Compounds and Derivatives: Current Status and Future Prospects for Pharmaceutical Applications. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 385–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comer, S.D.; Cahill, C.M. Fentanyl: Receptor Pharmacology, Abuse Potential, and Implications for Treatment. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 106, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edinoff, A.N.; Kaplan, L.A.; Khan, S.; Petersen, M.; Sauce, E.; Causey, C.D.; Cornett, E.M.; Imani, F.; Moghadam, O.M.; Kaye, A.M.; et al. Full Opioid Agonists and Tramadol: Pharmacological and Clinical Considerations. Anesth. Pain. Med. 2021, 11, e119156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, H.; Nakamura, R.; Kido, H.; Narasaki, S.; Watanabe, T.; Yokota, M.; Ishii, T.; Kato, T.; Saeki, N.; Tsutsumi, Y.M. Impact of Fentanyl on Acute and Chronic Pain and Its Side Effects When Used with Epidural Analgesia after Thoracic Surgery in Multimodal Analgesia: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 5119127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, M.E. The Transdermal Delivery of Fentanyl. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christrup, L.L.; Foster, D.; Popper, L.D.; Troen, T.; Upton, R. Pharmacokinetics, Efficacy, and Tolerability of Fentanyl Following Intranasal versus Intravenous Administration in Adults Undergoing Third-Molar Extraction: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy, Two-Way, Crossover Study. Clin. Ther. 2008, 30, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, E.; Sutcliffe, K.; Cavallo, D.; Ramos-Gonzalez, N.; Alhosan, N.; Henderson, G. The Anomalous Pharmacology of Fentanyl. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 180, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötsch, J.; Walter, C.; Parnham, M.J.; Oertel, B.G.; Geisslinger, G. Pharmacokinetics of Non-Intravenous Formulations of Fentanyl. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaee, S.; Saeedi, F.; Mehrpour, O. Clinical and Pharmacokinetics Overview of Intranasal Administration of Fentanyl. Heliyon 2023, 9, e23083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, J.M. Multiple Risks for Patients Using the Transdermal Fentanyl Patch. Anesth. Prog. 2014, 61, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Han, N.; Li, N.; Gui, L.; Shi, C.; Rong, P.; Zeng, F.; Rao, H.; Chen, Y. Guidelines for Rational Clinical Use of Fentanyl Transdermal Patch. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2024, 18, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, H.; Faudzi, S.M.M. Balancing Acts: The Dual Faces of Fentanyl in Medicine and Public Health. Leg. Med. 2024, 71, 102507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Blanco, C. Substance Use Disorders: A Comprehensive Update of Classification, Epidemiology, Neurobiology, Clinical Aspects, Treatment and Prevention. World Psychiatry 2023, 22, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommerfeld-Klatta, K.; Jiers, W.; Łukasik-Głębocka, M.; Tezyk, A.; Dolińska-Kaczmarek, K.; Walter, K.; Świderski, P.; Rzepczyk, S.; Zielińska-Psuja, B.; Żaba, C. Severe and Fatal Fentanyl Poisonings from Transdermal Systems after On-Skin and Ingestion Application. Toxics 2023, 11, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, W.M.; Jones, C.M. Epidemiology of the U.S. Opioid Crisis: The Importance of the Vector. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1451, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzak, L.; Halverson, J. The Opioid Crisis in Canada: A National Perspective. Health Promot. Chronic Dis. Prev. Can. 2018, 38, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczyńska, K.; Grzonkowski, P.; Kacprzak, Ł.; Zawilska, J.B. Abuse of Fentanyl: An Emerging Problem to Face. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 289, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, J.; El-Haddad, S. A Review: Fentanyl and Non-Pharmaceutical Fentanyls. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2017, 171, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, G.; Hedden-Clayton, B.J.; Lister, J.; Lee, G.; Huynh, P.; Ray, B. Community Overdose Surveillance: Fentanyl Involvement in Overdose Deaths in Rural Michigan. Drug Alcohol Depend. Rep. 2023, 7, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccarone, D.; Ondocsin, J.; Mars, S.G. Heroin Uncertainties: Exploring Users’ Perceptions of Fentanyl-Adulterated and -Substituted ‘Heroin’. Int. J. Drug Policy 2017, 46, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.A.; Biancorosso, S.L.; Camp, J.D.; Hailu, S.H.; Johansen, A.N.; Morris, M.H.; Carlson, H.N. “Tranq-Dope” Overdose and Mortality: Lethality Induced by Fentanyl and Xylazine. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1280289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Dart, R.C.; Katz, N.P.; Paillard, F.; Adams, E.H.; Comer, S.D.; Degroot, A.; Edwards, R.R.; Haddox, J.D.; Jaffe, J.H.; et al. Classification and Definition of Misuse, Abuse, and Related Events in Clinical Trials: ACTTION Systematic Review and Recommendations. Pain 2013, 154, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintz, P.; Villain, M.; Dumestre, V.; Cirimele, V. Evidence of Addiction by Anesthesiologists as Documented by Hair Analysis. Forensic Sci. Int. 2005, 153, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarone, D. The Triple Wave Epidemic: Supply and Demand Drivers of the US Opioid Overdose Crisis. Int. J. Drug Policy 2019, 71, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, D.; King, C.R.; Galke, C. The Opioid Epidemic: A Review of the Contributing Factors, Negative Consequences, and Best Practices. Cureus 2023, 15, e41621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.M.; Havens, J.R.; Leukefeld, C.G. Route of Administration for Illicit Prescription Opioids: A Comparison of Rural and Urban Drug Users. Harm Reduct. J. 2010, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, A.; Rao, M.H. Effects of Fentanyl on Procedural Pain and Discomfort Associated with Central Venous Catheter Insertion: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 18, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schauer, C.K.M.W.; Shand, J.A.D.; Reynolds, T.M. The Fentanyl Patch Boil-Up—A Novel Method of Opioid Abuse. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 117, 358–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drug Enforcement Administration. 2019 National Drug Threat Assessment. Available online: https://www.dea.gov/sites/default/files/2020-01/2019-NDTA-final-01-14-2020_Low_Web-DIR-007-20_2019.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Drug Enforcement Administration. The Controlled Substances Act. Available online: https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/csa (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Adel, A.; Norouzifard, M. Weaponization of the Growing Cybercrimes inside the Dark Net: The Question of Detection and Application. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, J.; Islam, R.; Kabir, M.A. The Anonymity of the Dark Web: A Survey. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 33628–33660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broséus, J.; Rhumorbarbe, D.; Mireault, C.; Ouellette, V.; Crispino, F.; Décary-Hétu, D. Studying Illicit Drug Trafficking on Darknet Markets: Structure and Organisation from a Canadian Perspective. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 264, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, F.; Rice, K.; Sud, A. A Critical Content Analysis of Media Reporting on Opioids: The Social Construction of an Epidemic. Soc. Sci. Med. 2020, 244, 112642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokala, U.; Lamy, F.R.; Daniulaityte, R.; Sheth, A.; Nahhas, R.W.; Roden, J.I.; Yadav, S.; Carlson, R.G. Global Trends, Local Harms: Availability of Fentanyl-Type Drugs on the Dark Web and Accidental Overdoses in Ohio. Comput. Math. Organ. Theory 2019, 25, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanetakis, M.; Décary-Hétu, D.; Bakken, S.; Munksgaard, R.; Katzenbach, C.; Demant, J.; Paquet-Clouston, M.; Weissinger, L. Drug Markets and Anonymizing Technologies. AoIR Sel. Pap. Internet Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edinoff, A.N.; Sall, S.; Upshaw, W.C.; Spillers, N.J.; Vincik, L.A.Y.; De Witt, A.S.; Murnane, K.S.; Kaye, A.M.; Kaye, A.D. Xylazine: A Drug Adulterant of Clinical Concern. Curr. Pain. Headache Rep. 2024, 28, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, R.; Chawla, P.A. Xylazine Addiction Turning Humans to Zombies: Fact or Myth? Health Sci. Rev. 2023, 9, 100132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, J.M.; Copulsky, E.C.; Reed, M.K. Media Framing Xylazine as a “Zombie Drug” Is Amplifying Stigma onto People Who Use Drugs. Int. J. Drug Policy 2024, 125, 104338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, J.; Nelson, L.; Perrone, J.; Wightman, R.; Haroz, R. Xylazine Adulteration of the Heroin-Fentanyl Drug Supply A Narrative Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arrigo, T. Xylazine Present in Increasing Number of Fentanyl Overdose Deaths, CDC Finds. Psychiatr. News 2023, 58, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, R. Here’s What to Know about Xylazine, Aka Tranq, the Animal Tranquilizer Increasingly Found in Illicit Fentanyl Samples. JAMA 2023, 329, 1904–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, F.; Bourgois, P.; Friedman, J. Potency-Enhancing Synthetics in the Drug Overdose Epidemic: Xylazine (“Tranq”), Fentanyl, Methamphetamine, and the Displacement of Heroin in Philadelphia and Tijuana. J. Illicit Econ. Dev. 2022, 4, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, Z.; Gill, E.; Kelly, G.; Latuska, R.; Toledo, L.; Scribano, P.; Osterhoudt, K. “Tranq Dope” in Infancy: A 19- Day-Old with Life-Threatening Poisoning Due to Fentanyl/Xylazine. Clin. Toxicol. 2022, 60, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Ashique, S. Xylazine: An Abused Tranq Dope and Its Safety Concern. Curr. Drug Saf. 2024, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.D.; Fiuty, P.; Page, K.; Tracy, E.C.; Nocera, M.; Miller, C.W.; Tarhuni, L.J.; Dasgupta, N. Prevalence of Fentanyl in Methamphetamine and Cocaine Samples Collected by Community-Based Drug Checking Services. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2023, 252, 110985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarone, D. The Rise of Illicit Fentanyls, Stimulants and the Fourth Wave of the Opioid Overdose Crisis. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2021, 34, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.M.; Bekheet, F.; Park, J.N.; Alexander, G.C. The Evolving Overdose Epidemic: Synthetic Opioids and Rising Stimulant-Related Harms. Epidemiol. Rev. 2020, 42, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, F.; Salerno, M.; Cipolloni, L.; Bertozzi, G.; Messina, G.; Di Mizio, G.; Asmundo, A.; Pomara, C. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids and Brain Injury: MiRNA Evaluation in Users Compared to Cocaine Abusers and Elderly People. Aging 2020, 12, 15314–15327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, S.; Neri, M.; Mhillaj, E.; Pomara, C.; Trabace, L.; Turillazzi, E. The Role of the NADPH Oxidase Derived Brain Oxidative Stress in the Cocaine-Related Death Associated with Excited Delirium: A Literature Review. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 258, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Amsterdam, J.; Gresnigt, F.; van den Brink, W. Cardiovascular Risks of Simultaneous Use of Alcohol and Cocaine—A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Liberto, A.; Zuccarello, P.; Ministeri, F.; Licciardello, G.; Barbera, N.; Sessa, F.; Salerno, M. Heart Rupture as an Acute Complication of Cocaine Abuse: A Case Report. Leg. Med. 2022, 58, 102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessa, F.; Esposito, M.; Messina, G.; Di Mizio, G.; Di Nunno, N.; Salerno, M. Sudden Death in Adults: A Practical Flow Chart for Pathologist Guidance. Healthcare 2021, 9, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turillazzi, E.; Bello, S.; Neri, M.; Pomara, C.; Riezzo, I.; Fineschi, V. Cardiovascular Effects of Cocaine: Cellular, Ionic and Molecular Mechanisms. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 5664–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, F.; Ashraf, A.; Bhuiyan, M.R.; Bimal, T.; Iftikhar, A. A Peculiar Case of Fentanyl-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Cureus 2022, 14, e27708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, R.; Krantz, M.J. Cardiovascular Consequences of Addiction. In Textbook of Addiction Treatment; El-Guebaly, N., Carrà, G., Galanter, M., Baldacchino, A.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prekupec, M.P.; Mansky, P.A.; Baumann, M.H. Misuse of Novel Synthetic Opioids: A Deadly New Trend. J. Addict. Med. 2017, 11, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latkin, C.A.; Dayton, L.; Davey-Rothwell, M.A.; Tobin, K.E. Fentanyl and Drug Overdose: Perceptions of Fentanyl Risk, Overdose Risk Behaviors, and Opportunities for Intervention among People Who Use Opioids in Baltimore, USA. Subst. Use Misuse 2019, 54, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moallef, S.; Nosova, E.; Milloy, M.J.; DeBeck, K.; Fairbairn, N.; Wood, E.; Kerr, T.; Hayashi, K. Knowledge of Fentanyl and Perceived Risk of Overdose Among Persons Who Use Drugs in Vancouver, Canada. Public Health Rep. 2019, 134, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, H.E.; Huhn, A.S.; Dunn, K.E. Fentanyl Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion: Narrative Review and Clinical Significance Related to Illicitly Manufactured Fentanyl. J. Addict. Med. 2023, 17, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.; Kelly, E.; Henderson, G. How the Complex Pharmacology of the Fentanyls Contributes to Their Lethality. Addiction 2019, 114, 1524–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, S.R.; Haywood, A.; Hardy, J.; Lobb, M.; Tapuni, A.; Norris, R. Protein Binding of Fentanyl and Its Metabolite Nor-Fentanyl in Human Plasma, Albumin and α-1 Acid Glycoprotein. Xenobiotica 2015, 45, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.; Pizzicato, L.; Johnson, C.; Viner, K. Increasing Presence of Xylazine in Heroin and/or Fentanyl Deaths, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 2010–2019. Inj. Prev. 2021, 27, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GOV UK A Review of the Evidence on the Use and Harms of Xylazine (Accessible). Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/use-and-harms-of-xylazine-medetomidine-and-detomidine/a-review-of-the-evidence-on-the-use-and-harms-of-xylazine-accessible (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Giovannitti, J.A.; Thoms, S.M.; Crawford, J.J. Alpha-2 Adrenergic Receptor Agonists: A Review of Current Clinical Applications. Anesth. Prog. 2015, 62, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malayala, S.V.; Papudesi, B.N.; Bobb, R.; Wimbush, A. Xylazine-Induced Skin Ulcers in a Person Who Injects Drugs in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA. Cureus 2022, 14, e28160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarbeh, L.; Gorbovskaya, I.; Le Foll, B.; Jhirad, R.; Müller, D.J. Reviewing Pharmacogenetics to Advance Precision Medicine for Opioids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagos, F.T.; Horvat, C.M.; Au, A.K.; Conley, Y.P.; Li, L.; Poloyac, S.M.; Kochanek, P.M.; Clark, R.S.B.; Empey, P.E. Factors Contributing to Fentanyl Pharmacokinetic Variability Among Diagnostically Diverse Critically Ill Children. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupiec, T.C.; Raj, V.; Vu, N. Pharmacogenomics for the Forensic Toxicologist. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2006, 30, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunno, N.D.; Esposito, M.; Argo, A.; Salerno, M.; Sessa, F. Pharmacogenetics and Forensic Toxicology: A New Step towards a Multidisciplinary Approach. Toxics 2021, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmquist, G.L. Opioid Metabolism and Effects of Cytochrome P450. Pain Med. 2009, 10 (Suppl. S1), S20–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanger, U.M.; Schwab, M. Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in Drug Metabolism: Regulation of Gene Expression, Enzyme Activities, and Impact of Genetic Variation. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 103–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.; Kermanizadeh, A. A Review of Toxicological Profile of Fentanyl—A 2024 Update. Toxics 2024, 12, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Skaar, D.J.; Jacobson, P.A.; Huang, R.S. Pharmacogenomics of Medications Commonly Used in the Intensive Care Unit. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, Q.N.; Mahinthichaichan, P.; Shen, J.; Ellis, C.R. How μ-Opioid Receptor Recognizes Fentanyl. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, C.R.; Kruhlak, N.L.; Kim, M.T.; Hawkins, E.G.; Stavitskaya, L. Predicting Opioid Receptor Binding Affinity of Pharmacologically Unclassified Designer Substances Using Molecular Docking. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taqi, M.M.; Faisal, M.; Zaman, H. OPRM1 A118G Polymorphisms and Its Role in Opioid Addiction: Implication on Severity and Treatment Approaches. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2019, 12, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilic, J.; Marjanovic, V.G.; Budic, I.; Stefanovic, N.; Stokanovic, D.; Marjanovic, G.T.; Jevtovic-Stoimenov, T.; Golubovic, M.; Zecevic, M.; Velickovic-Radovanovic, R. The Impact of Opioid Receptor Gene Polymorphism on Fentanyl and Alfentanil’s Analgesic Effects in the Pediatric Perioperative Period. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2024, 17, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, C.; Remiao, F.; Cisternino, S.; Decleves, X. Opioids and the Blood-Brain Barrier: A Dynamic Interaction with Consequences on Drug Disposition in Brain. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 1156–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.S.; Bauer, B.; Hartz, A.M.S. Modulation of P-Glycoprotein at the Blood-Brain Barrier: Opportunities to Improve Central Nervous System Pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, M.; Cristofoletti, R.; Silva, C.d.M.; Mangal, N.; Turgeon, J.; Michaud, V.; Lesko, L.J.; Schmidt, S. Exploring the Impact of CYP2D6 and UGT2B7 Gene-Drug Interactions, and CYP-Mediated DDI on Oxycodone and Oxymorphone Pharmacokinetics Using Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 194, 106689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, F.; Chisari, M.; Esposito, M.; Karaboue, M.A.A.; Salerno, M.; Cocimano, G. Ethical, Legal and Social Implications (ELSI) Regarding Forensic Genetic Investigations (FGIs). J. Acad. Ethics 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandrowski, K.U.; Sharafshah, A.; Elfar, J.; Schmidt, S.L.; Blum, K.; Wetzel, F.T. A Pharmacogenomics-Based In Silico Investigation of Opioid Prescribing in Post-Operative Spine Pain Management and Personalized Therapy. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 44, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Clinical Practice Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Pain. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/rr/rr7103a1.htm?s_cid=rr7103a1.htm_w (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Al-Hasani, R.; Bruchas, M.R. Molecular Mechanisms of Opioid Receptor-Dependent Signaling and Behavior. Anesthesiology 2011, 115, 1363–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, A.A.H.; McDonald, J.; Lambert, D.G. Hot Topics in Opioid Pharmacology: Mixed and Biased Opioids. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 122, e136–e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtasik-Bakalarz, K.; Woroń, J.; Siwek, M. Adverse Effects of Opioid Analgesics from the Central Nervous System. Palliat. Med. Pract. 2021, 15, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, N.; Lima, J.D.; Spinieli, R.L.; Kaur, S. Opioids, Sleep, Analgesia and Respiratory Depression: Their Convergence on Mu (μ)-Opioid Receptors in the Parabrachial Area. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1134842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, M.; van Dorp, E.; Broens, S.; Overdyk, F. Combining Opioids and Benzodiazepines: Effects on Mortality and Severe Adverse Respiratory Events. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 9, 542–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Trana, A.; Di Giorgi, A.; Carlier, J.; Serra, F.; Busardò, F.P.; Pichini, S. “Tranq-Dope”: The First Fatal Intoxication Due to Xylazine-Adulterated Heroin in Italy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2024, 561, 119826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, K.L.; Lawson, A.J.; Duffy, J.; Mellor, A.; Treble, R.; Copeland, C.S. The First Drug-Related Death Associated with Xylazine Use in the UK and Europe. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2023, 97, 102542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wachuku, C.; Berk-Krauss, J.; Steele, K.T.; Rosenbach, M.; Messenger, E. Severe Cutaneous Ulcerations Secondary to Xylazine (Tranq): A Case Series. JAAD Case Rep. 2023, 36, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, D.L.; Walker, V.; Pai, L.; Cho, L.M. Opiates and Elderly: Use and Side Effects. Clin. Interv. Aging 2008, 3, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylliaas, H.; Idland, G.; Sandvik, L.; Forsen, L.; Bergland, A. Does Mortality of the Aged Increase with the Number of Falls? Results from a Nine-Year Follow-up Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 24, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamoun, K.; Chevillard, L.; Hajj, A.; Callebert, J.; Mégarbane, B. Mechanisms of Neurorespiratory Toxicity Induced by Fentanyl Analogs—Lessons from Animal Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yan, W.; Zheng, Y.; Khan, M.Z.; Yuan, K.; Lu, L. The Rising Crisis of Illicit Fentanyl Use, Overdose, and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuip, E.J.M.; Zandvliet, M.L.; Koolen, S.L.W.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; van der Rijt, C.C.D. A Review of Factors Explaining Variability in Fentanyl Pharmacokinetics; Focus on Implications for Cancer Patients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariano, R.E.; Duke, P.C.; Sitar, D.S. Population Pharmacokinetics of Fentanyl in Healthy Volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 41, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.T.; Friedman, J.; Bourgois, P.; Montero, F.; Tamang, S. The Emerging Fentanyl–Xylazine Syndemic in the USA: Challenges and Future Directions. Lancet 2023, 402, 1949–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xiang, H.C.; Li, H.P.; Lin, L.X.; Hu, X.F.; Zhang, H.; Meng, W.Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, C.; Shu, Y.; et al. Inhibition of GABAergic Neurons and Excitation of Glutamatergic Neurons in the Ventrolateral Periaqueductal Gray Participate in Electroacupuncture Analgesia Mediated by Cannabinoid Receptor. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, B.; Christie, M.J. Inhibition by Opioids Acting on Μ-receptors of GABAergic and Glutamatergic Postsynaptic Potentials in Single Rat Periaqueductal Gray Neurones in Vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 113, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schembri, E. Are Opioids Effective in Relieving Neuropathic Pain? SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2019, 1, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, E.T.; Lee, J.J.; Min, B.I.; Cho, Y.W. Opioid Inhibition of GABAergic Neurotransmission in Mechanically Isolated Rat Periaqueductal Gray Neurons. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 50, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, E.; Cameron-Burr, K.T.; Shaham, Y.; Kiyatkin, E.A. Fentanyl-Induced Brain Hypoxia Triggers Brain Hyperglycemia and Biphasic Changes in Brain Temperature. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montandon, G.; Horner, R.L. Electrocortical Changes Associating Sedation and Respiratory Depression by the Opioid Analgesic Fentanyl. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Mares, P.; Violante-Soria, V.; Browne, T.; Cruz, S.L. Xylazine Potentiates the Lethal but Not the Rewarding Effects of Fentanyl in Mice. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2023, 253, 110993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.; Santhakumar, R.; Dewey, W.; Kelly, E.; Henderson, G. Fentanyl Depression of Respiration: Comparison with Heroin and Morphine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansari, A.; Li, H.; Chunduru, S.; Baskaran, N. Acute Lung Injury As Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome After Fentanyl Overdose. Cureus 2024, 16, e52745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambe, V.; Desai, P.; Kondapi, D.; Shah, M.; Dogra, M. 1156: Inhaled Fentanyl Leading To Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage. Crit Care Med. 2019, 47, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaiblmair, M.; Behr, W.; Haeckel, T.; Märkl, B.; Foerg, W.; Berghaus, T. Drug Induced Interstitial Lung Disease. Open Respir. Med. J. 2012, 6, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morentin, B.; Callado, L.F.; García-Hernández, S.; Bodegas, A.; Lucena, J. The Role of Toxic Substances in Sudden Cardiac Death. Span. J. Leg. Med. 2018, 44, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltenhammer, M.H.; Marchart, K.; Paula, P.; Kordina, N.; Klupp, N.; Schneider, B.; Fitzl, C.; Risser, D.U. Micromorphological Changes in Cardiac Tissue of Drug-Related Deaths with Emphasis on Chronic Illicit Opioid Abuse. Addiction 2013, 108, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschirhart, J.N.; Li, W.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S. Blockade of the Human Ether A-Go-Go–Related Gene (HERG) Potassium Channel by Fentanyl. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 95, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.J.; Kweon, T.D.; Nam, S.B.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, C.S.; Park, C.H.; Han, D.W. Effects of Fentanyl Pretreatment on the QTc Interval during Propofol Induction. Anaesthesia 2008, 63, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M.; Lembo, A.; Katzka, D.A. Opioids in Gastroenterology: Treating Adverse Effects and Creating Therapeutic Benefits. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E. Recent Advances in the Histopathology of Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2018, 11, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verna, E.C.; Schluger, A.; Brown, R.S. Opioid Epidemic and Liver Disease. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alasmari, F.; Alasmari, M.S.; Assiri, M.A.; Alswayyed, M.; Rizwan Ahamad, S.; Alhumaydhi, A.I.; Arif, B.I.; Aljumayi, S.R.; AlAsmari, A.F.; Ali, N.; et al. Liver Metabolomics and Inflammatory Profiles in Mouse Model of Fentanyl Overdose Treated with Beta-Lactams. Metabolites 2023, 13, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Cabrerizo, R.; Cryan, J.F. A Gut (Microbiome) Feeling about Addiction: Interactions with Stress and Social Systems. Neurobiol. Stress. 2024, 30, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A.; Boland, J.W. Effects of Opioids on Immune and Endocrine Function in Patients with Cancer Pain. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2023, 24, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duca, Y.; Aversa, A.; Condorelli, R.A.; Calogero, A.E.; La Vignera, S. Substance Abuse and Male Hypogonadism. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, F.; Bruin, M.; Lobatto, D.J.; Dekkers, O.M.; Schoones, J.W.; van Furth, W.R.; Pereira, A.M.; Karavitaki, N.; Biermasz, N.R.; Zamanipoor Najafabadi, A.H. Opioids and Their Endocrine Effects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, S.; Moschetti, G.; Amodeo, G.; Sacerdote, P. Do All Opioid Drugs Share the Same Immunomodulatory Properties? A Review From Animal and Human Studies. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćupić, V.; Čolić, M.; Jandrić, D.; Milojković, B.; Varagic, V.M. Xylazine, an α 2 -Adrenergic Agonist, Induces Apoptosis of Rat Thymocytes and a Thymocyte Hybridoma Line in Vitro. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 25, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, D. Opioid Drug Death Investigations. Acad. Forensic Pathol. 2017, 7, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Sessa, F.; Cocimano, G.; Zuccarello, P.; Roccuzzo, S.; Salerno, M. Advances in Technologies in Crime Scene Investigation. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, G.; National Association of Medical Examiners. American College of Medical Toxicology Expert Panel Recommendations for the Investigation, Diagnosis, and Certification of Deaths Related to Opioid Drugs. J. Med. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- del Pozo, B.; Sightes, E.; Kang, S.; Goulka, J.; Ray, B.; Beletsky, L.A. Can Touch This: Training to Correct Police Officer Beliefs about Overdose from Incidental Contact with Fentanyl. Health Justice 2021, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A. Guidelines on Autopsy Practice; Report of a working group of The Royal College of Pathologists; London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- The Royal Collage of Pathologists. Guidelines on Autopsy Practice: Autopsy When Drugs or Poisoning May Be Involved; London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrieri, D.; Rapp, E.; Roman, M.; Druid, H.; Kronstrand, R. Postmortem and Toxicological Findings in a Series of Furanylfentanyl-Related Deaths. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2017, 41, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrico, T.; Patel, K.; Nikolov, N.; Salam, M.T.; Padhy, R.; Weinstein, D. Presence of Kratom in Opioid Overdose Deaths: Findings from Coroner Postmortem Toxicological Report. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1332999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncanson, E.R.; Mackey-Bojack, S.M. Histologic Examination of the Heart in the Forensic Autopsy. Acad. Forensic Pathol. 2018, 8, 565–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Vieira, D.N.; Magalhãaes, T. Guidelines for Collection of Biological Samples for Clinical and Forensic Toxicological Analysis. Forensic Sci. Res. 2016, 1, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milroy, C.M.; Parai, J.L. The Histopathology of Drugs of Abuse. Histopathology 2011, 59, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzu’bi, A.; Baker, W.B.; Al-Trad, B.; Zoubi, M.S.A.; AbuAlArjah, M.I.; Abu-El-Rub, E.; Tahat, L.; Helaly, A.M.; Ghorab, D.S.; El-Huneidi, W.; et al. The Impact of Chronic Fentanyl Administration on the Cerebral Cortex in Mice: Molecular and Histological Effects. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 209, 110917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaro, D.R.; Volkow, N.D.; Langleben, D.D.; Shi, Z.; Wiers, C.E. Collateral Damage: Neurological Correlates of Non-Fatal Overdose in the Era of Fentanyl-Xylazine. Neurosci. Insights 2024, 19, 26331055241247156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levasseur, A.; Knapp-Gisclon, A.; Mayer-Duverneuil, C.; Etting, I.; Lorin de la Grandmaison, G.; Alvarez, J.C. Autopsy, Histological and Toxicological Findings in Deaths Associated with New Psychoactive Substances (NPS): A Study with 12 Autopsies. Forensic Sci. Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschirhart, J.N.; Zhang, S. Fentanyl-Induced Block of HERG Channels Is Exacerbated by Hypoxia, Hypokalemia, Alkalosis, and the Presence of HERG1b. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 98, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Nagar, D.P.; Bhattacharya, R. Effect of Fentanyl and Its Three Novel Analogues on Biochemical, Oxidative, Histological, and Neuroadaptive Markers after Sub-Acute Exposure in Mice. Life Sci. 2020, 246, 117400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.G.; Aung, T.; Karavitaki, N.; Wass, J.A.H. Lesson of the Week: Opioid Induced Hypogonadism. BMJ 2010, 341, c4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneeva, N.L.; Schrott, L.M. Chronic Oxycodone Exposure Alters Translational and Signaling Pathways in the Rat Brain Stem. FASEB J. 2011, 25 (Suppl. S1), lb414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Schrott, L.M.; Arnold, T.; Snelling, S.; Rao, M.; Graham, D.; Cornelius, A.; Korneeva, N.L. Chronic Oxycodone Induces Axonal Degeneration in Rat Brain. BMC Neurosci. 2018, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacagnina, M.J.; Rivera, P.D.; Bilbo, S.D. Glial and Neuroimmune Mechanisms as Critical Modulators of Drug Use and Abuse. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 156–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammazza, A.M.; Colangeli, R.; Orban, G.; Pierucci, M.; Di Gennaro, G.; Lo Bello, M.; D’Aniello, A.; Bucchieri, F.; Pomara, C.; Valentino, M.; et al. Hsp60 Response in Experimental and Human Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riezzo, I.; Cerretani, D.; Fiore, C.; Bello, S.; Centini, F.; D’Errico, S.; Fiaschi, A.I.; Giorgi, G.; Neri, M.; Pomara, C.; et al. Enzymatic-Nonenzymatic Cellular Antioxidant Defense Systems Response and Immunohistochemical Detection of MDMA, VMAT2, HSP70, and Apoptosis as Biomarkers for MDMA (Ecstasy) Neurotoxicity. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomara, C.; Fiore, C.; D’Errico, S.; Riezzo, I.; Fineschi, V. Calcium Oxalate Crystals in Acute Ethylene Glycol Poisoning: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope Study in a Fatal Case. Clin. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uff, C.E.G.; Patel, K.; Yeung, C.; Yip, P.K. Advances in Visualizing Microglial Cells in Human Central Nervous System Tissue. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.H.; Mallampalli, R.K. The Role of Surfactant in Lung Disease and Host Defense against Pulmonary Infections. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2015, 12, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benga, G. The First Discovered Water Channel Protein, Later Called Aquaporin 1: Molecular Characteristics, Functions and Medical Implications. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 518–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.L.; Ishida, K.; Quan, L.; Fujita, M.Q.; Maeda, H. Immunohistochemistry of Pulmonary Surfactant-Associated Protein A in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Leg. Med. 2001, 3, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- deFilippi, C.R.; Tran, H.; Gattani, R.; Daniels, L.B.; Shah, P.; Ilkhanoff, L.; Christenson, R.; Lima, J.A.; Seliger, S. Association of Cardiac Troponin T and Growth Differentiation Factor 15 with Replacement and Interstitial Cardiac Fibrosis in Community Dwelling Adults: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1104715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osredkar, J.; Bajrić, A.; Možina, H.; Lipar, L.; Jerin, A. Cardiac Troponins I and T as Biomarkers of Cardiomyocyte Injury—Advantages and Disadvantages of Each. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuan, D.T.B.; Zayed, H.; Eid, A.H.; Abou-Saleh, H.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Mangoni, A.A.; Pintus, G. A Potential Link between Oxidative Stress and Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Systemic Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, S.; Rhodes, F.; Srivastava, A.; Trembling, P.M.; Rosenberg, W.M. Inflammation and Fibrosis in Chronic Liver Diseases Including Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hepatitis C. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, E.; Schwabe, R.F. Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis: Functional Links and Key Pathways. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, M.; Iwaisako, K.; Jiang, C.; Kisseleva, T. Cell Signals Influencing Hepatic Fibrosis. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 158547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmorsy, E.A.; Saber, S.; Hamad, R.S.; Abdel-Reheim, M.A.; Nadwa, E.H.; Alibrahim, A.O.E.; Alkhamiss, A.S.; AlSalloom, A.A.; Mohamed, E.A.; Nour-El-Din, M.; et al. Modulating the HSP90 Control over NFκB/NLRP3/Caspase-1 Axis Is a New Therapeutic Target in the Management of Liver Fibrosis: Insights into the Role of TAS-116 (Pimitespib). Life Sci. 2024, 354, 122966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Overland, M.; Derpinghaus, A.; Aksel, S.; Cao, M.; Ladwig, N.; Cunha, G.R.; Baskin, L.S. Development of the Human Fetal Testis: Morphology and Expression of Cellular Differentiation Markers. Differentiation 2023, 129, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argo, A.; Zerbo, S.; Buscemi, R.; Trignano, C.; Bertol, E.; Albano, G.D.; Vaiano, F. A Forensic Diagnostic Algorithm for Drug-Related Deaths: A Case Series. Toxics 2022, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, H.F.H.; Ingle, E.A.; Hunter, M.D.; Rodda, L.N. Distribution of Furanyl Fentanyl and 4-ANPP in an Accidental Acute Death: A Case Report. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 283, e13–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skolnick, P. Treatment of Overdose in the Synthetic Opioid Era. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 233, 108019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tori, M.E.; Larochelle, M.R.; Naimi, T.S. Alcohol or Benzodiazepine Co-Involvement with Opioid Overdose Deaths in the United States, 1999–2017. JAMA Netw Open 2020, 3, e202361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, T.T.; Bakr, M.H.; Nikolova, T. Case Report: Delirium Due to a Diltiazem-Fentanyl CYP3A4 Drug Interaction. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2010, 32, e9–e648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, V.; Stroh-Steiner, G.K.; Jones, P. Qualitative and Quantitative Characteristics of Xylazine-Associated Deaths Detected Using a Post-Mortem Toxicology Testing Program. Clin. Toxicol. 2023, 61, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Ali, T.; Fatima, L.; Nazir, Z.; Hafiz, A.I.; Haque, M.A. Xylazine in Illicit Drug Mixtures: A Growing Threat and Overlooked Danger. Ann. Med. Surg. 2024, 86, 3816–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, J.R.; Lin, P.T.; Nelson, L. Reliability of Postmortem Fentanyl Concentrations in Determining the Cause of Death. J. Med. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concheiro, M.; Chesser, R.; Pardi, J.; Cooper, G. Postmortem Toxicology of New Synthetic Opioids. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magarbeh, L.; Gorbovskaya, I.; Wells, R.; Jhirad, R.; Le Foll, B.; Müller, D.J. Pharmacogenetics of Lethal Opioid Overdose: Review of Current Evidence and Preliminary Results from a Pilot Study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.L.; Kannankeril, P.J.; Breeyear, J.H.; Edwards, T.L.; Van Driest, S.L.; Choi, L. Effect of CYP3A5 and CYP3A4 Genetic Variants on Fentanyl Pharmacokinetics in a Pediatric Population. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 111, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz-Rodríguez, M.; Almenara, S.; Navares-Gómez, M.; Ochoa, D.; Román, M.; Zubiaur, P.; Koller, D.; Santos, M.; Mejía, G.; Borobia, A.M.; et al. Effect of the Most Relevant CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 Polymorphisms on the Pharmacokinetic Parameters of 10 CYP3A Substrates. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, R.; Kern, C.; Columb, M.O.; Smiley, R.M.; Blouin, J.L. Genetic Variability of the μ-Opioid Receptor Influences Intrathecal Fentanyl Analgesia Requirements in Laboring Women. Pain 2008, 139, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolen, S.L.W.; Van Der Rijt, C.C.D. Is There a Role for Pharmacogenetics in the Dosing of Fentanyl? Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhard, G.S.; Kaniper, S.; Paynton, B. Fentanyl Overdoses and Pharmacogenetics. Pharmacogenet Genom. 2020, 30, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashina, Y.; Naito, T.; Mino, Y.; Yagi, T.; Ohnishi, K.; Kawakami, J. Impact of CYP3A5 and ABCB1 Gene Polymorphisms on Fentanyl Pharmacokinetics and Clinical Responses in Cancer Patients Undergoing Conversion to a Transdermal System. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 27, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Health Sciences Policy; Committee on Pain Management and Regulatory Strategies to Address Prescription Opioid Abuse; Phillips, J.K.; Ford, M.A.; Bonnie, R.J. Pain Management and the Opioid Epidemic: Balancing Societal and Individual Benefits and Risks of Prescription Opioid Use. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK458661/ (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Ghose, R.; Forati, A.M.; Mantsch, J.R. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Opioid Overdose Deaths: A Spatiotemporal Analysis. J. Urban. Health 2022, 99, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emcdda Update from the EMCDDA Expert. Network Drug-Related Deaths and Mortality in Europe RAPID Communication; EMCDDA: Lisbon, Portugal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Italian Government Fentanyl: The Global Phenomenon and the Italian Commitment. Available online: https://ambtallinn.esteri.it/en/news/dall_ambasciata/2024/05/fentanyl-the-global-phenomenon-and-the-italian-commitment/ (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Strenja, I.; Dadić-Hero, E.; Perković, M.; Šoša, I. Fentanyl and Sudden Death—A Postmortem Perspective for Diagnosing and Predicting Risk. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balyan, R.; Hahn, D.; Huang, H.; Chidambaran, V. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Considerations in Developing a Response to the Opioid Epidemic. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessa, F.; Esposito, M.; Cocimano, G.; Sablone, S.; Karaboue, M.A.A.; Chisari, M.; Albano, D.G.; Salerno, M. Artificial Intelligence and Forensic Genetics: Current Applications and Future Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Administration Method | Effect Time | Duration | Frequent Users |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intravenous | 1–2 min | 2–4 h | Surgical patients |
| Transmucosal | 10–15 min | 2–4 h | Illicit users |
| Sublingual | 5–10 min | Variable | Illicit users |
| Intranasal Spray | 5–10 min | 30 min | Chronic pain patients, illicit users |
| Transdermal Patch | Variable | 8–16 h | Chronic pain patients, illicit users |
| Organ | Toxicity | Histopathology |
|---|---|---|
| Brain | - Downregulation of opioid receptors; - Cognitive and emotional alterations (chronic); - Euphoria but also sedation (acute). | - Hypoxia in the hippocampus and cerebellum; - Neuronal apoptosis; - Microglia inflammation; - Altered distribution of microglia; - Vacuolization and gliosis of the affected regions. |
| Lung | - Hypercapnea; - Hypoxemia; - Chest wall rigidity; - Respiratory depression. | - Pulmonary edema; - Amorphous eosinophilic material in the alveolar spaces; - Intra-alveolar hemorrhage; - Inflammation of neutrophils; - Septic embolism. |
| Heart | - Hypocalcemia; - QT elongation arrhythmias; - Sudden cardiac death. | - Myocyte necrosis; - Endocarditis; - Fibrous connective tissue (myocardium). |
| Gastrointestinal system | - Nausea; - Vomit; - Constipation. | - Lymphocyte infiltration; - Portal inflammation; - Pyknosis and necrosis of hepatocytes. |
| Gonad | - Infertility; - Loss of libido and hypogonadism. | - Reduced maturation of germ cells; - Tubular diameter of the epithelium. |
| Organ | Marker | Rationale | Expected Positivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein) | Indicates astrocytic gliosis | +++ |
| NeuN | Assesses neuronal viability | ++ | |
| Cleaved Caspase-3 | Marks neuronal apoptosis | +++ | |
| Iba1 | Reflects microglial activation | +++ | |
| MBP (Myelin basic protein) | Evaluates white matter integrity | ++ | |
| Lungs | Surfactant protein A (SP-A)/SP-B | Assesses alveolar integrity | ++ |
| Aquaporin-1 | Highlights fluid balance and edema | +++ | |
| CD15 | Detects neutrophilic infiltration | +++ | |
| Myeloperoxidase (MPO) | Indicates acute inflammation | ++ | |
| CD31/VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) | Evaluates vascular endothelial damage | ++ | |
| Heart | Cardiac troponin I (cTnI) | Identifies cardiac myocyte injury | ++++ |
| Desmin | Assesses structural integrity of myocytes | +++ | |
| Collagen I/III | Indicates myocardial fibrosis | ++ | |
| CD3/CD4/CD8 | Reveals immune-mediated myocardial damage | ++ | |
| von Willebrand factor (vWF) | Highlights endothelial dysfunction | +++ | |
| Liver | Hepatocyte paraffin-1 (HepPar-1) | Identifies hepatocyte-specific cytoplasmic antigens | +++ |
| Cleaved Caspase-3 | Marks hepatocyte apoptosis | +++ | |
| Interleukin 6 (IL-6) | Reflects inflammatory response | +++ | |
| α-Smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) | Indicates stellate cell activation and fibrosis | ++ | |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen (HCcAg) | Detects hepatitis C infection | ++++ | |
| Gonads | SOX9 | Highlights Sertoli cell function | ++ |
| Inhibin-α | Marks Sertoli and Leydig cell activity | ++ | |
| Ki-67 | Indicates proliferative activity | +++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barletta, C.; Di Natale, V.; Esposito, M.; Chisari, M.; Cocimano, G.; Di Mauro, L.; Salerno, M.; Sessa, F. The Rise of Fentanyl: Molecular Aspects and Forensic Investigations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020444
Barletta C, Di Natale V, Esposito M, Chisari M, Cocimano G, Di Mauro L, Salerno M, Sessa F. The Rise of Fentanyl: Molecular Aspects and Forensic Investigations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020444
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarletta, Cecilia, Virginia Di Natale, Massimiliano Esposito, Mario Chisari, Giuseppe Cocimano, Lucio Di Mauro, Monica Salerno, and Francesco Sessa. 2025. "The Rise of Fentanyl: Molecular Aspects and Forensic Investigations" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020444
APA StyleBarletta, C., Di Natale, V., Esposito, M., Chisari, M., Cocimano, G., Di Mauro, L., Salerno, M., & Sessa, F. (2025). The Rise of Fentanyl: Molecular Aspects and Forensic Investigations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020444








