The Role of Hippo Signaling in Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: Molecular Insights into Post-Embolization Remodeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
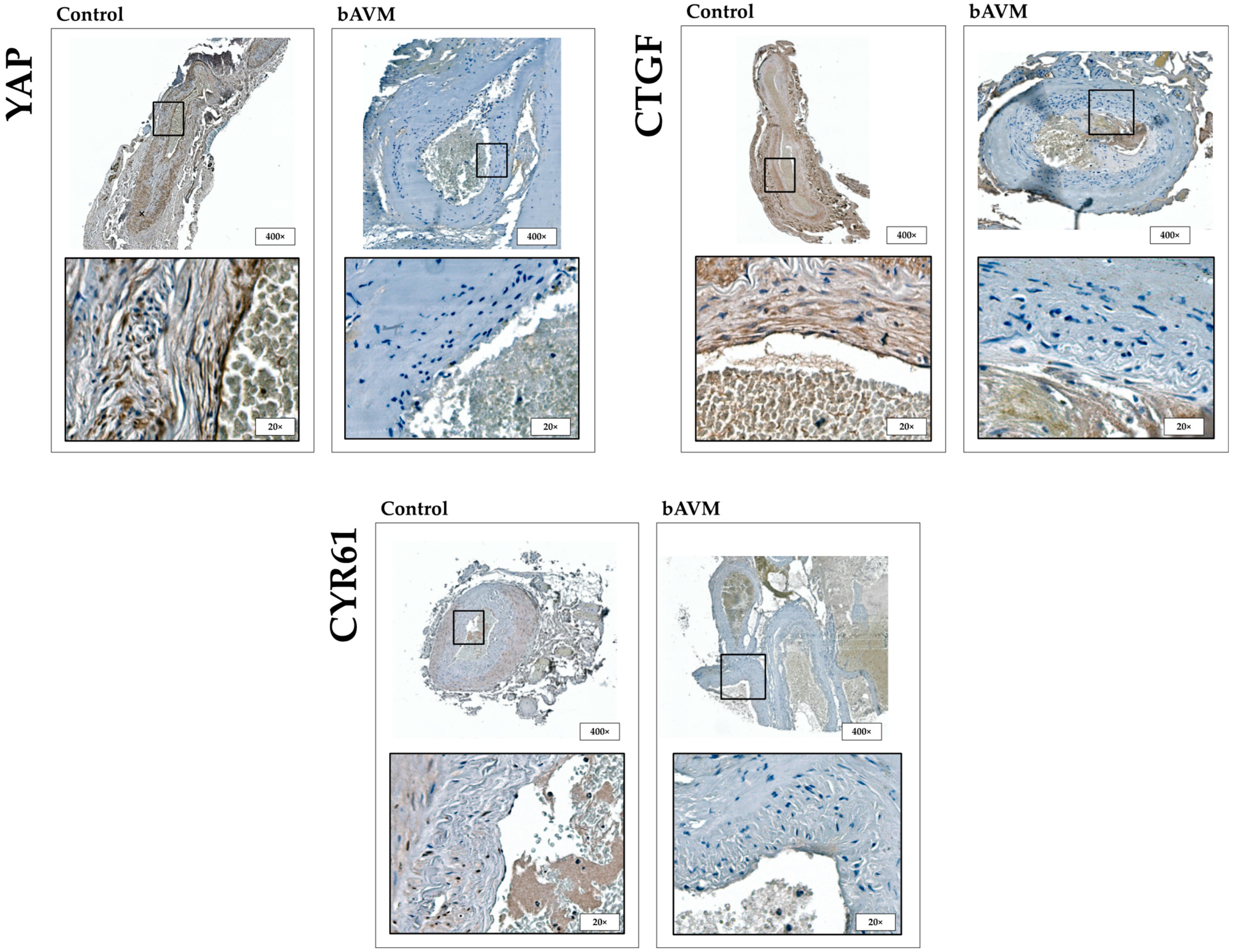
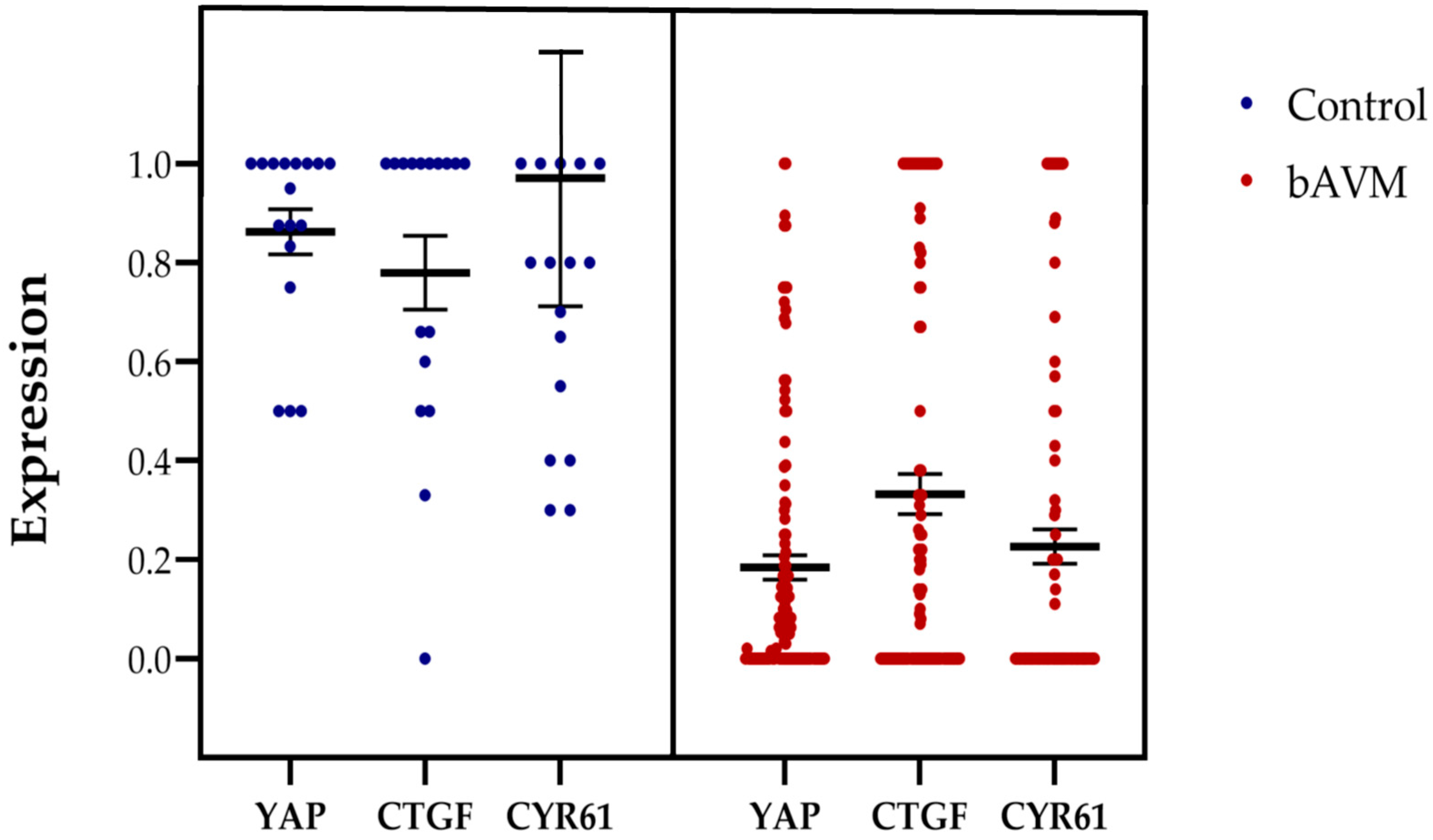
2.1. Expression Patterns of HIF-1α, FGFR1, YAP, CTGF, and CYR61 in bAVM
2.2. Correlation Between YAP, CTGF, and CYR61 Expression and Clinical Parameters
2.3. Embolization Induced Expression of YAP, CTGF and CYR61 Mediated by HIF-1α and FGFR1
3. Discussion
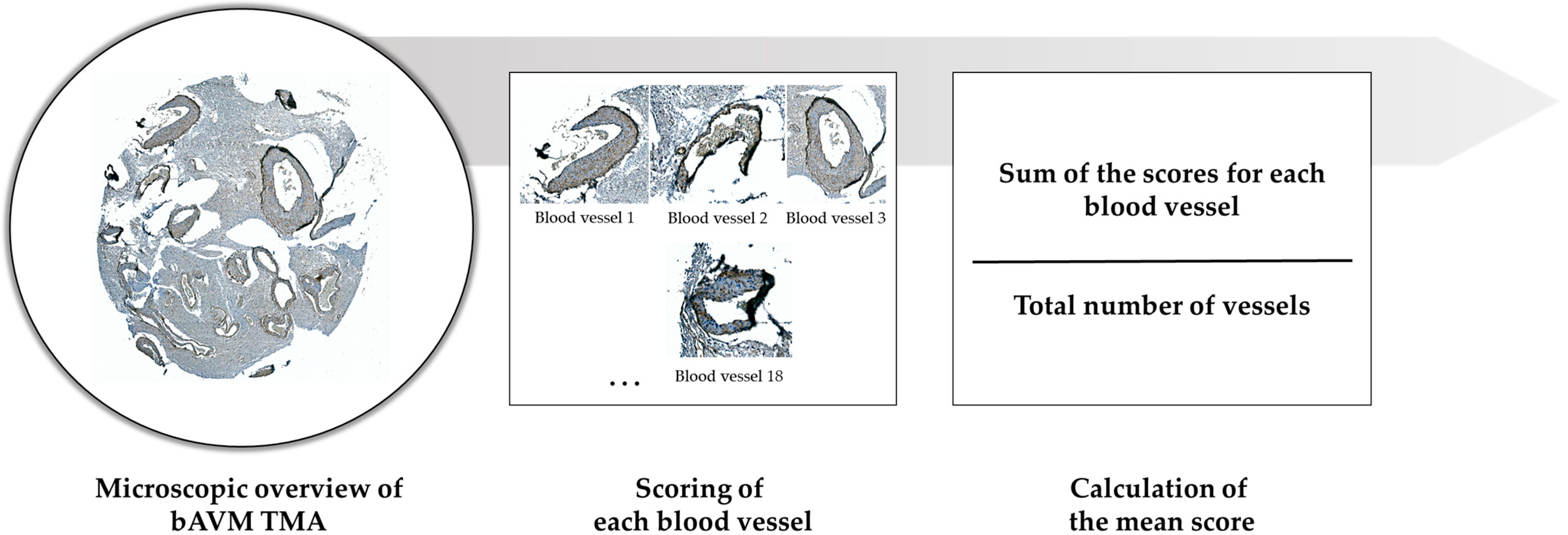
4. Materials and Methods
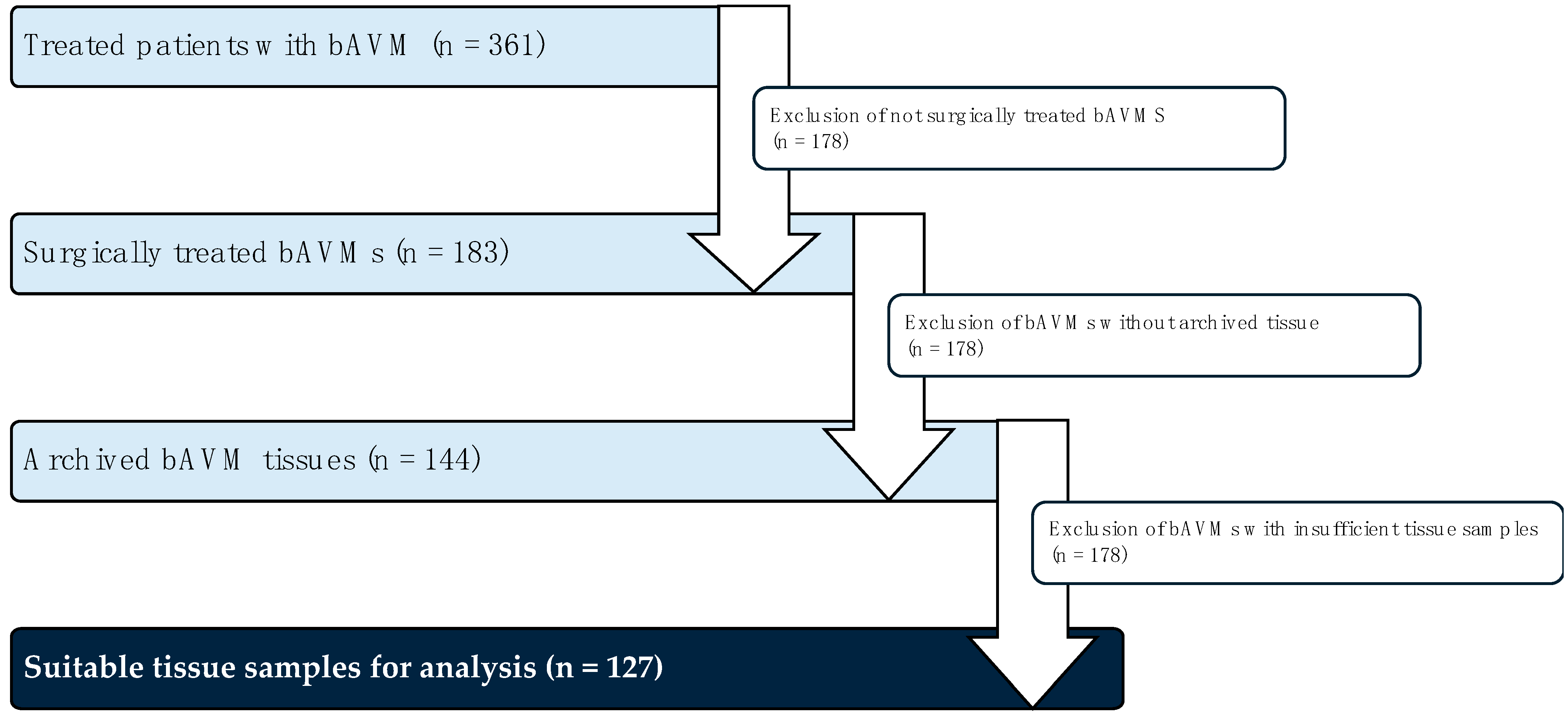
4.1. Tissue Collection and Patient Data
4.2. Immunhistochemistry
4.2.1. Control Specimen
4.2.2. TMA: Construction and Immunohistochemistry
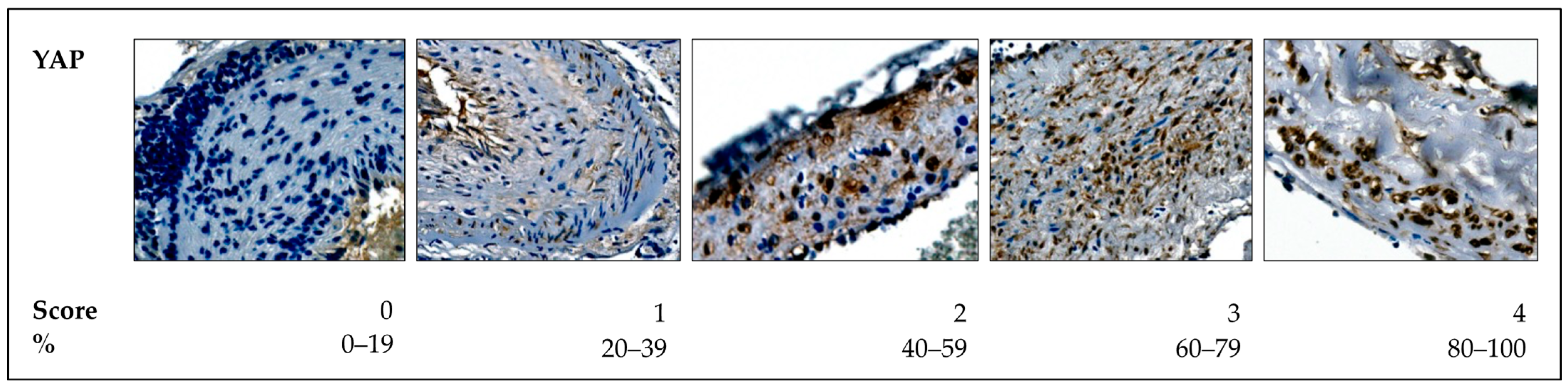
4.2.3. Histological Analysis
- Score 0: <20% positive nuclear expression.
- Score 1: 20–40% positive nuclear expression.
- Score 2: 40–60% positive nuclear expression.
- Score 3: 60–80% positive nuclear expression.
- Score 4: 80–100% positive nuclear expression.
4.2.4. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| bAVM | Brain arteriovenous malformations |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| YAP | Yes-associated protein |
| TAZ | Transcription regulator 1 |
| CTGF | connective tissue growth factor |
| CYR61 | cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61 |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| H&E | Hematoxylin–eosin |
References
- Mohr, J.P.; Parides, M.K.; Stapf, C.; Moquete, E.; Moy, C.S.; Overbey, J.R.; Al-Shahi Salman, R.; Vicaut, E.; Young, W.L.; Houdart, E.; et al. Medical Management with or without Interventional Therapy for Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations (ARUBA): A Multicentre, Non-Blinded, Randomised Trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, J.P.; Overbey, J.R.; von Kummer, R.; Stefani, M.A.; Libman, R.; Stapf, C.; Parides, M.K.; Pile-Spellman, J.; Moquete, E.; Moy, C.S.; et al. Functional Impairments for Outcomes in a Randomized Trial of Unruptured Brain AVMs. Neurology 2017, 89, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, M.T.; Rutledge, W.C.; Kim, H.; Stapf, C.; Whitehead, K.J.; Li, D.Y.; Krings, T.; terBrugge, K.; Kondziolka, D.; Morgan, M.K.; et al. Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathy, G.T.K.; Hong, W. Role of Hippo Pathway-YAP/TAZ Signaling in Angiogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.G.; Moroishi, T.; Guan, K.-L. YAP and TAZ: A Nexus for Hippo Signaling and Beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, T.; Ghahremani, M.; Yang, X. The Role of YAP and TAZ in Angiogenesis and Vascular Mimicry. Cells 2019, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; An, J.; Oh, S.W.; Lim, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.K.; Cheong, J.-H.; Kim, P. Matrix Stiffness Epigenetically Regulates the Oncogenic Activation of the Yes-Associated Protein in Gastric Cancer. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Ozasa, H.; Aoki, W.; Aburaya, S.; Yamamoto Funazo, T.; Furugaki, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Yamazoe, M.; Ajimizu, H.; Yasuda, Y.; et al. YAP1 Mediates Survival of ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer Cells Treated with Alectinib via pro-Apoptotic Protein Regulation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, S.; Morsut, L.; Aragona, M.; Enzo, E.; Giulitti, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Zanconato, F.; Le Digabel, J.; Forcato, M.; Bicciato, S.; et al. Role of YAP/TAZ in Mechanotransduction. Nature 2011, 474, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciera, T.; Azzolin, L.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. Mechanobiology of YAP and TAZ in Physiology and Disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.W.; Oh, E.J.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Huh, S.; et al. Oscillatory Shear Stress Promotes Angiogenic Effects in Arteriovenous Malformations Endothelial Cells. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-C.; Yeh, Y.-T.; Nguyen, P.; Limqueco, E.; Lopez, J.; Thorossian, S.; Guan, K.-L.; Li, Y.-S.J.; Chien, S. Flow-Dependent YAP/TAZ Activities Regulate Endothelial Phenotypes and Atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11525–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totaro, A.; Castellan, M.; Battilana, G.; Zanconato, F.; Azzolin, L.; Giulitti, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. YAP/TAZ Link Cell Mechanics to Notch Signalling to Control Epidermal Stem Cell Fate. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigstock, D.R. Regulation of Angiogenesis and Endothelial Cell Function by Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) and Cysteine-Rich 61 (CYR61). Angiogenesis 2002, 5, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponticos, M. Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CCN2) in Blood Vessels. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 58, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Ye, X.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Lin, J.D.; Wang, C.-Y.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; et al. TEAD Mediates YAP-Dependent Gene Induction and Growth Control. Genes. Dev. 2008, 22, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Hu, Y.; Lan, T.; Guan, K.-L.; Luo, T.; Luo, M. The Hippo Signalling Pathway and Its Implications in Human Health and Diseases. Sig Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Yu, J.; Guan, K.-L. Cell Detachment Activates the Hippo Pathway via Cytoskeleton Reorganization to Induce Anoikis. Genes. Dev. 2012, 26, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandalcioglu, I.E.; Wende, D.; Eggert, A.; Müller, D.; Roggenbuck, U.; Gasser, T.; Wiedemayer, H.; Stolke, D. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Plasma Levels Are Significantly Elevated in Patients with Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2006, 21, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandalcioglu, I.E.; Asgari, S.; Wende, D.; van de Nes, J.A.P.; Dumitru, C.A.; Zhu, Y.; Gizewski, E.R.; Stolke, D.; Sure, U. Proliferation Activity Is Significantly Elevated in Partially Embolized Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2010, 30, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zeng, C.; Ye, S.; Dai, X.; He, Q.; Yang, B.; Zhu, H. Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and Transcriptional Coactivator with a PDZ-Binding Motif (TAZ): A Nexus between Hypoxia and Cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.I.; Yamada, D.; Hirsova, P.; Bronk, S.F.; Werneburg, N.W.; Krishnan, A.; Salim, W.; Zhang, L.; Trushina, E.; Truty, M.J.; et al. A Hippo and Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Autocrine Pathway in Cholangiocarcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 8031–8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Furtado, J.; Poulet, M.; Chung, M.; Yun, S.; Lee, S.; Sessa, W.C.; Franco, C.A.; Schwartz, M.A.; Eichmann, A. Defective Flow-Migration Coupling Causes Arteriovenous Malformations in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. Circulation 2021, 144, 805–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Song, Q.; Yao, L.; Zhao, L.; Cai, H. YAP Overexpression in Breast Cancer Cells Promotes Angiogenesis through Activating YAP Signaling in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2022, 2022, 5942379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Qumu, S.; Nacar, O.A.; Yang, J.; Du, J.; Belen, D.; Pan, L.; Zhao, Y. Human Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Are Associated with Interruptions in Elastic Fibers and Changes in Collagen Content. Turk. Neurosurg. 2012, 23, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyazi, B.; Stein, K.-P.; Wilkens, L.; Maslehaty, H.; Dumitru, C.A.; Sandalcioglu, I.E. Age-Dependent Changes of Collagen Alpha-2(IV) Expression in the Extracellular Matrix of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 189, 105589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; He, Y.; Bai, W.; Guo, D.; Lu, T.; Duan, L.; Li, Z.; Kong, L.; Hernesniemi, J.A.; Li, T. Vascular Stability of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations after Partial Embolization. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Varshney, A.; Ma, X.; Song, B.; Riedl, M.; Avila, M.; Hof, B. Nonlinear Hydrodynamic Instability and Turbulence in Pulsatile Flow. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11233–11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Agarwala, S.; Terai, K.; Fukui, H.; Fukuhara, S.; Ando, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Yokota, Y.; Schmelzer, E.; et al. Flow-Dependent Endothelial YAP Regulation Contributes to Vessel Maintenance. Dev. Cell 2017, 40, 523–536.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ji, W.; Yu, Y.; Niu, X.; Zeng, Q.; Xia, W.; Lu, S. The Hippo/YAP1 Pathway Interacts with FGFR1 Signaling to Maintain Stemness in Lung Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 423, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, T.; Kubota, S.; Aoyama, E.; Janune, D.; Maeda, A.; Takigawa, M. Effect of CCN2 on FGF2-Induced Proliferation and MMP9 and MMP13 Productions by Chondrocytes. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 4232–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Clinical Parameter | YAP (p-Value) | CTGF (p-Value) | CYR61 (p-Value) | HIF-1α (p-Value) | FGFR1 (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.386 | 0.557 | 0.173 | 0.786 | 0.134 |
| Age | 0.144 | 0.835 | 0.729 | 0.092 | 0.051 |
| Hypertension | 0.606 | 0.760 | 0.519 | 0.489 | 0.506 |
| Nicotine abuse | 0.872 | 0.774 | 0.676 | 0.671 | 0.842 |
| Localization (supra-/infratentorial) | * 0.006 | 0.108 | * 0.046 | 0.059 | 0.106 |
| Rupture status | 0.247 | 0.130 | 0.080 | 0.133 | 0.311 |
| Spetzler–Martin grade | 0.871 | 0.954 | 0.993 | 0.677 | 0.910 |
| bAVM size | * 0.015 | * 0.019 | * 0.031 | * 0.004 | 0.087 |
| Eloquent localization | 0.348 | 0.183 | 0.285 | * 0.047 | 0.890 |
| Headache | 0.558 | 0.112 | * 0.042 | 0.919 | 0.713 |
| Epilepsy | 0.732 | 0.956 | 0.921 | 0.981 | 0.891 |
| Neurological deficits | 0.945 | 0.895 | 0.695 | 0.823 | 0.923 |
| Preoperative mRS | 0.102 | * 0.031 | * 0.011 | * 0.047 | 0.513 |
| Preoperative embolization | * 0.001 | * ≤0.001 | * 0.009 | * ≤0.001 | * 0.035 |
| Total Number (n = 127) | Percentage (100%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 68 | 53.5 |
| Female | 59 | 46.5 |
| Localization | ||
| Supratentorial | 103 | 81.1 |
| Infratentorial | 23 | 18.1 |
| Missing information | 1 | 0.8 |
| Rupture status | ||
| Unruptured | 27 | 21.3 |
| Ruptured | 99 | 78.0 |
| Missing information | 1 | 0.7 |
| Associated intranidal aneurysms | ||
| Yes | 55 | 43.3 |
| No | 16 | 12.6 |
| Missing information | 56 | 44.1 |
| bAVM size | ||
| <3 cm | 73 | 57.5 |
| 3–6 cm | 28 | 22.0 |
| >6 cm | 0 | 0 |
| Missing information | 26 | 20.5 |
| Spetzler–Martin Grading | ||
| Grade I | 29 | 22.8 |
| Grade II | 26 | 20.5 |
| Grade III | 26 | 20.5 |
| Grade IV | 4 | 3.1 |
| Missing information | 42 | 33.1 |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Hypertension | 42 | 33.1 |
| Nicotine abuse | 23 | 18.1 |
| Symptoms | ||
| Headache | 47 | 37.0 |
| Epilepsy | 40 | 31.5 |
| Neurological deficits | 87 | 68.5 |
| Preoperative mRS | ||
| 0 | 3 | 2.4 |
| 1 | 26 | 20.5 |
| 2 | 15 | 11.8 |
| 3 | 12 | 9.4 |
| 4 | 26 | 20.5 |
| 5 | 33 | 26.0 |
| Missing information | 12 | 9.4 |
| Treatment prior to surgical therapy | ||
| Embolization | 22 | 17.3 |
| Radiotherapy | 2 | 1.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neyazi, B.; Swiatek, V.M.; Karimpour, M.A.; Stassen, S.; Stein, K.-P.; Rashidi, A.; Dumitru, C.A.; Sandalcioglu, I.E. The Role of Hippo Signaling in Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: Molecular Insights into Post-Embolization Remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083791
Neyazi B, Swiatek VM, Karimpour MA, Stassen S, Stein K-P, Rashidi A, Dumitru CA, Sandalcioglu IE. The Role of Hippo Signaling in Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: Molecular Insights into Post-Embolization Remodeling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083791
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeyazi, Belal, Vanessa Magdalena Swiatek, Mohammad Ali Karimpour, Sarah Stassen, Klaus-Peter Stein, Ali Rashidi, Claudia Alexandra Dumitru, and I. Erol Sandalcioglu. 2025. "The Role of Hippo Signaling in Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: Molecular Insights into Post-Embolization Remodeling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083791
APA StyleNeyazi, B., Swiatek, V. M., Karimpour, M. A., Stassen, S., Stein, K.-P., Rashidi, A., Dumitru, C. A., & Sandalcioglu, I. E. (2025). The Role of Hippo Signaling in Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: Molecular Insights into Post-Embolization Remodeling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083791





