Identification of Risk Loci for Radiotherapy-Induced Tinnitus and Hearing Loss Through Integrated Genomic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
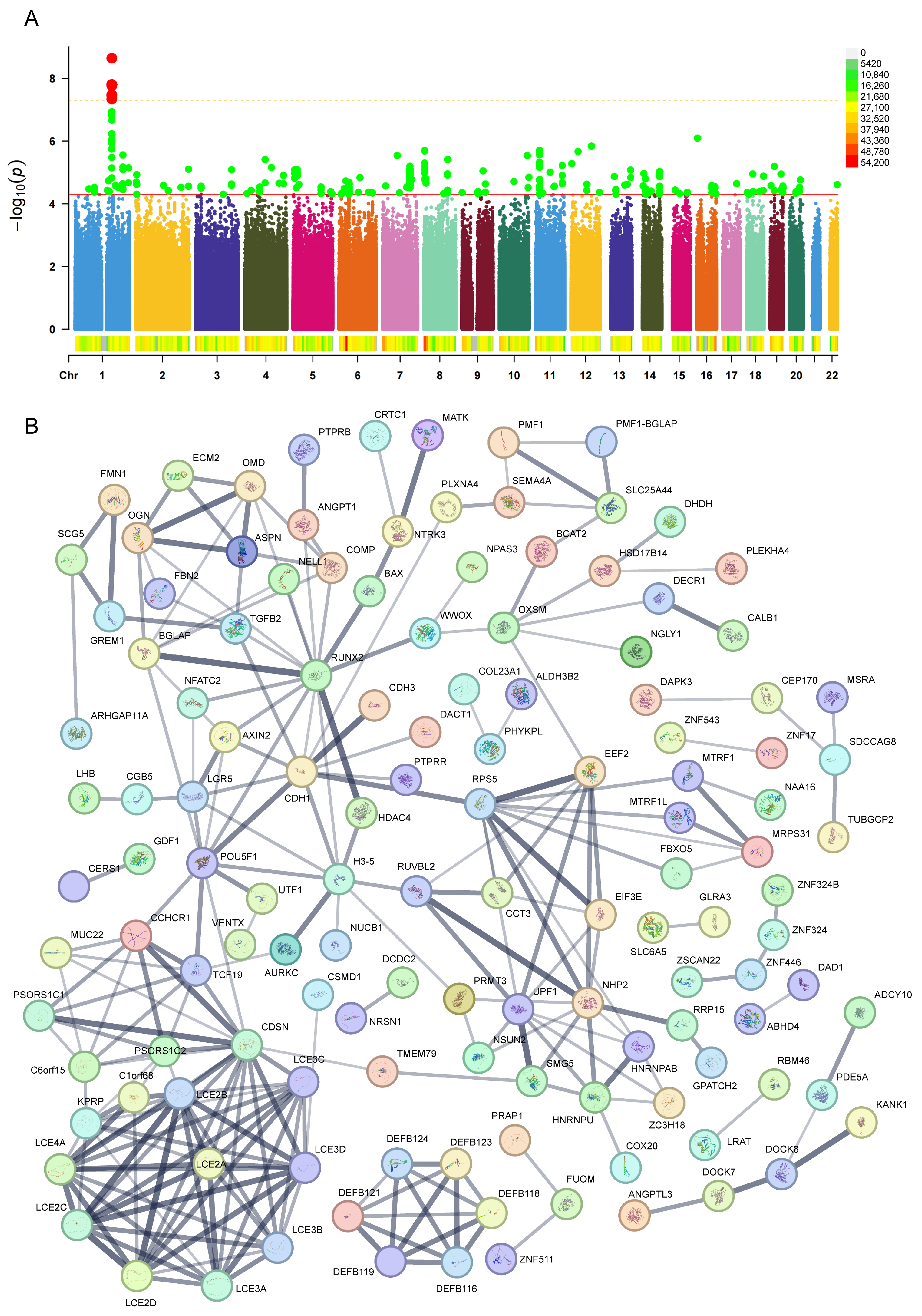
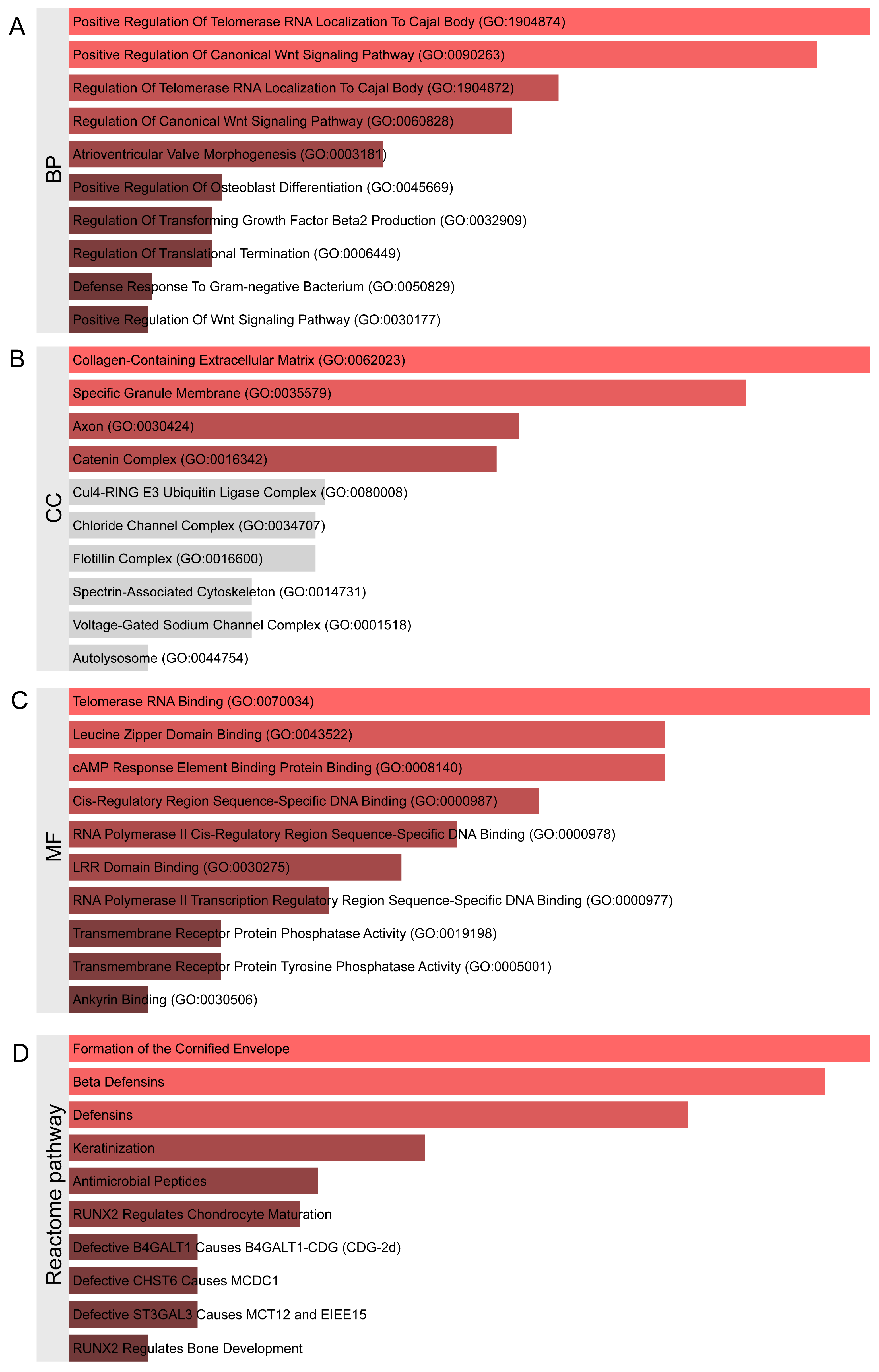
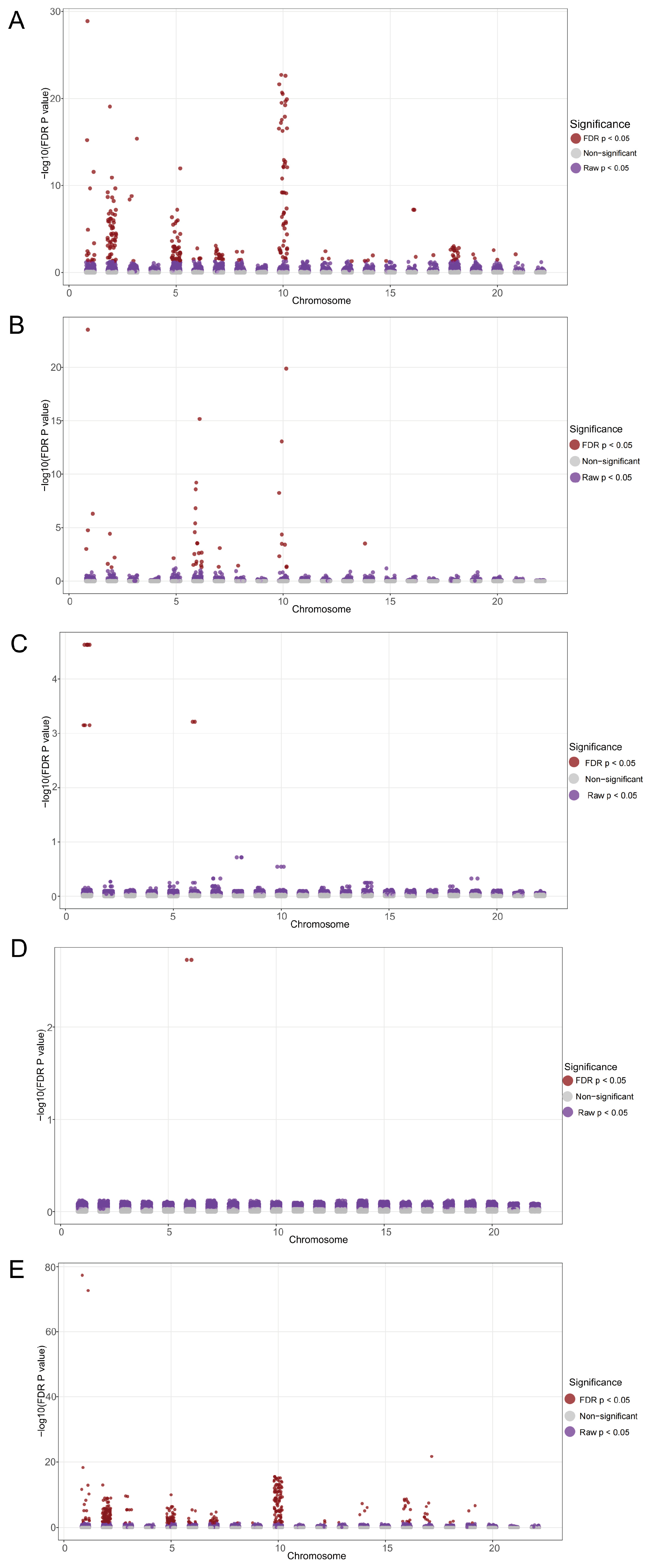
2.1. Identification of Genetic Variants and Functional Networks Associated with Radiotherapy-Induced Tinnitus Using GWAS Data
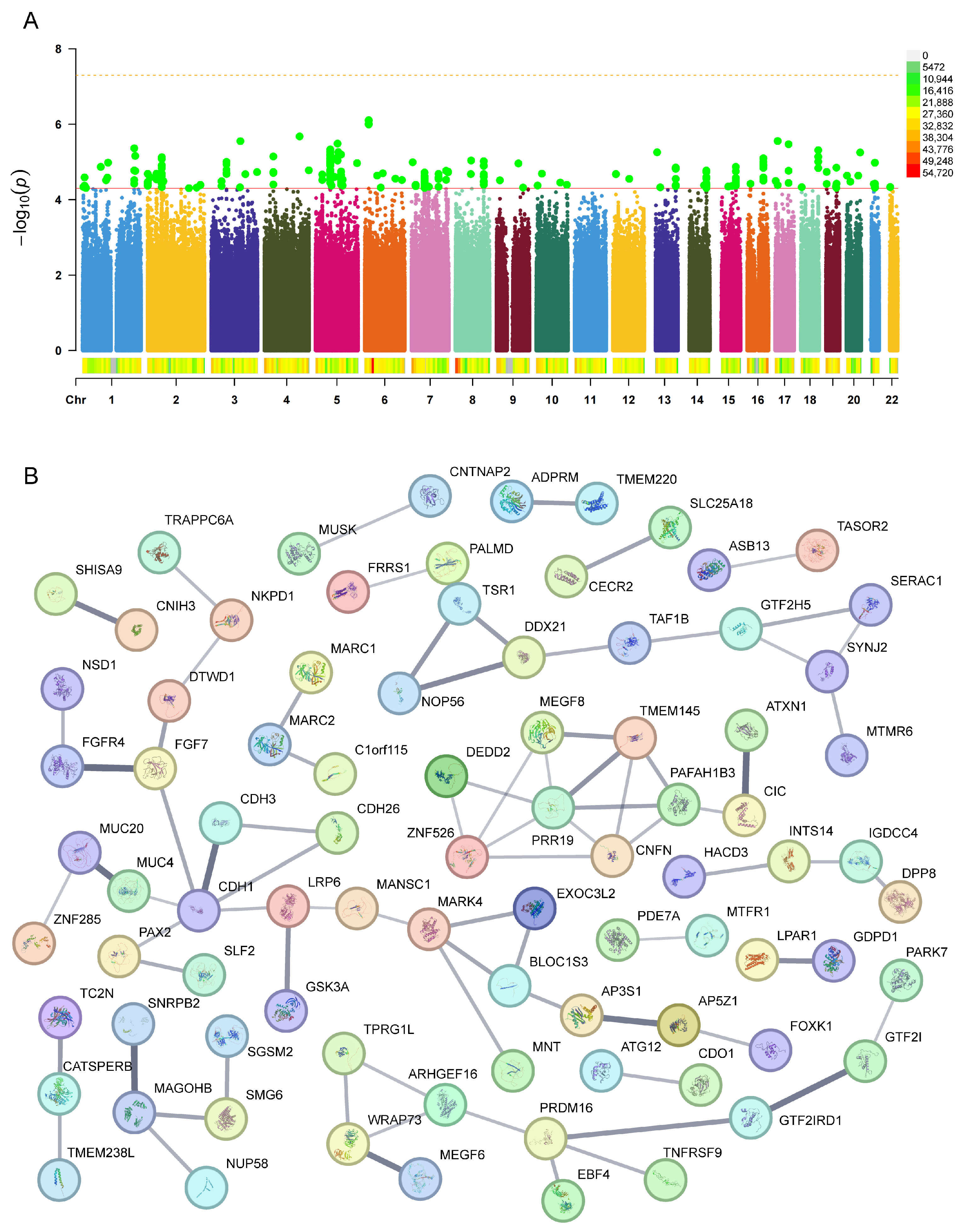
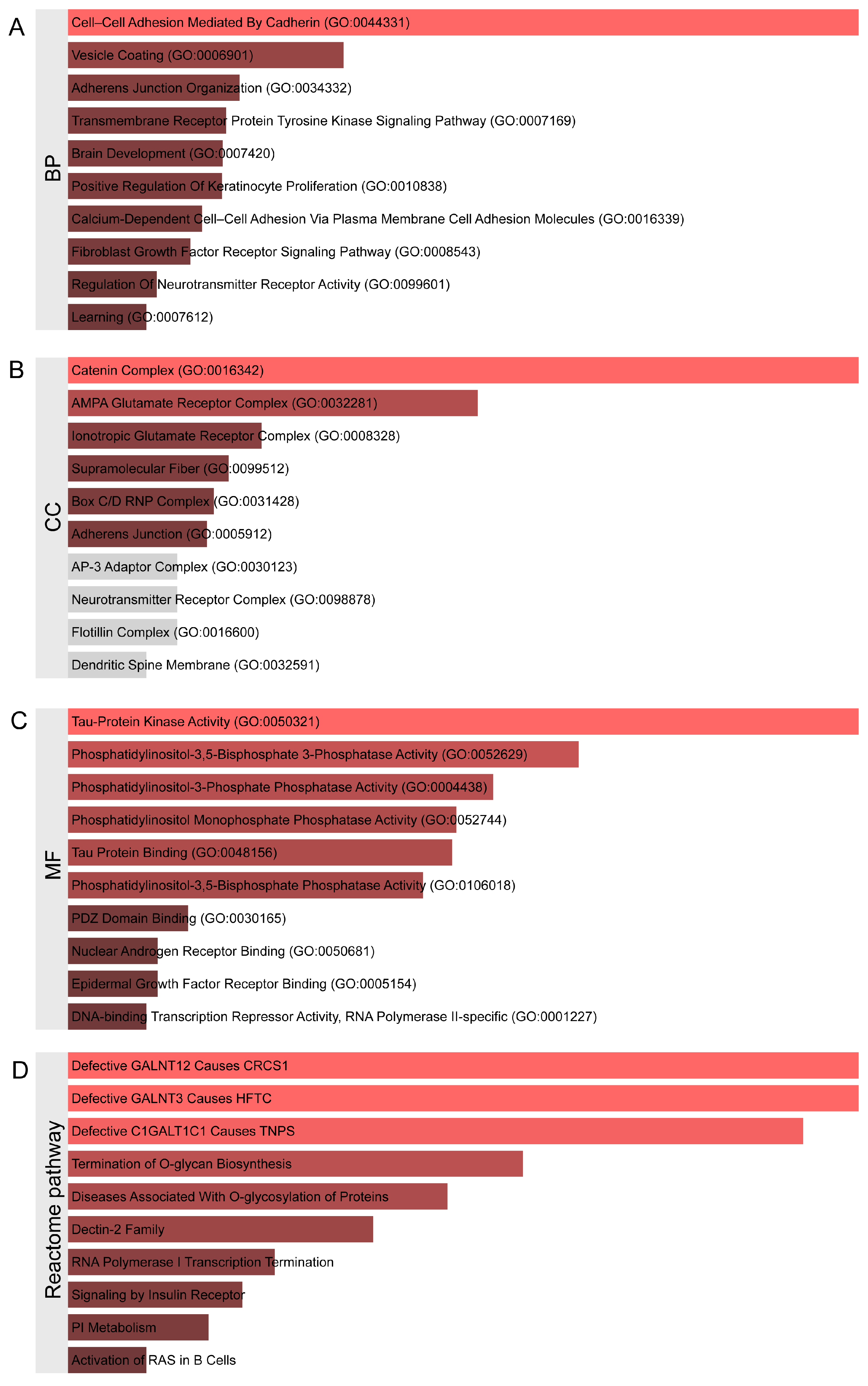
2.2. Identification of Genetic Variants and Functional Networks Associated with Radiotherapy-Induced Hearing Loss Using GWAS Data
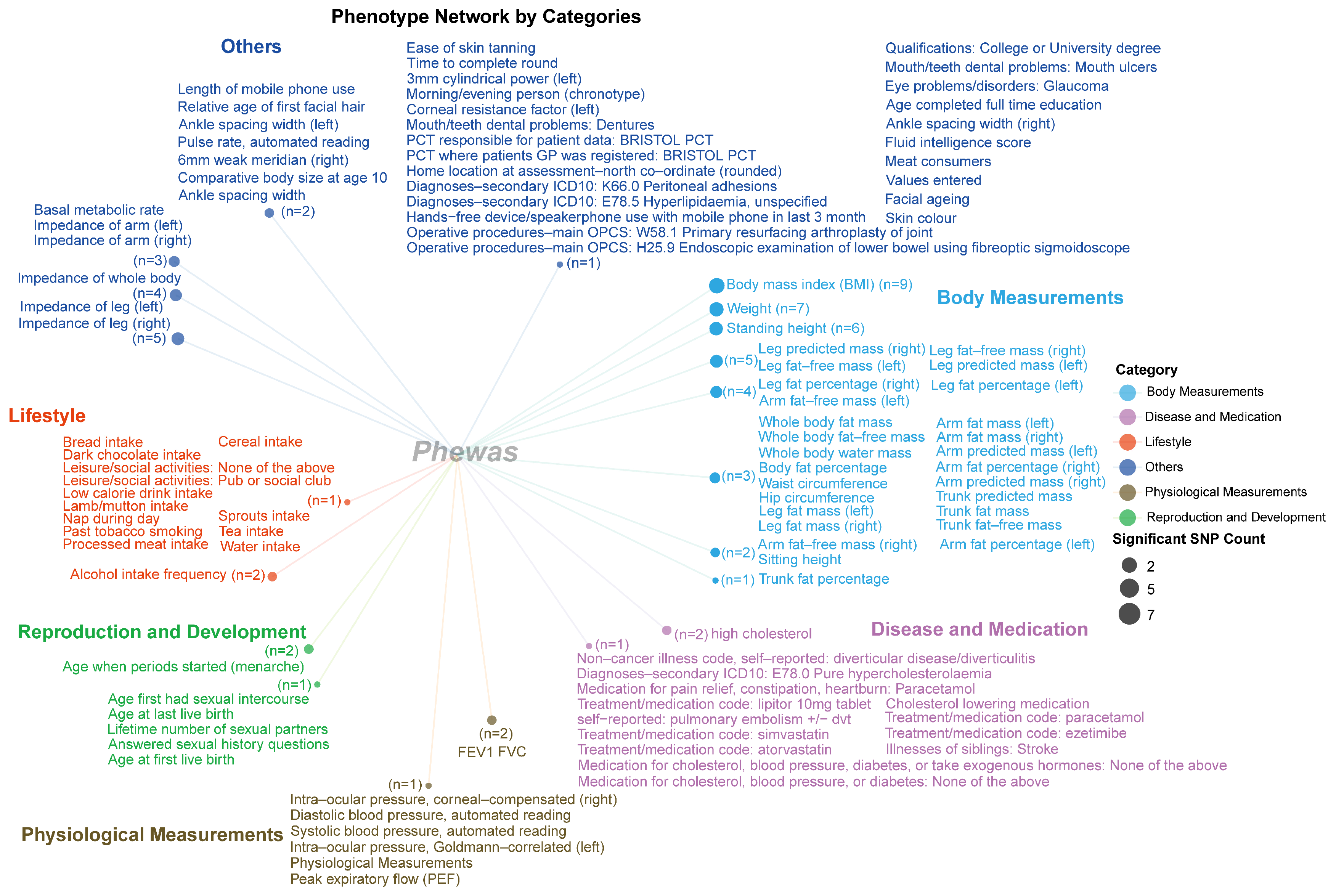
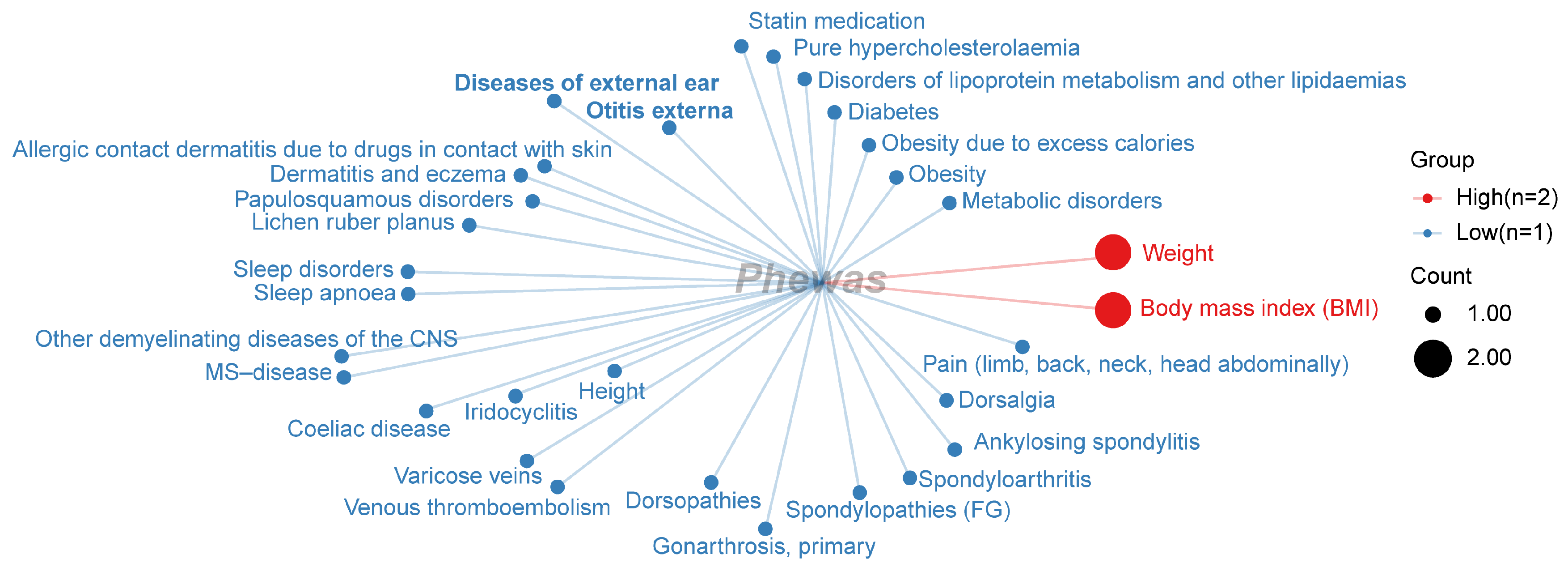
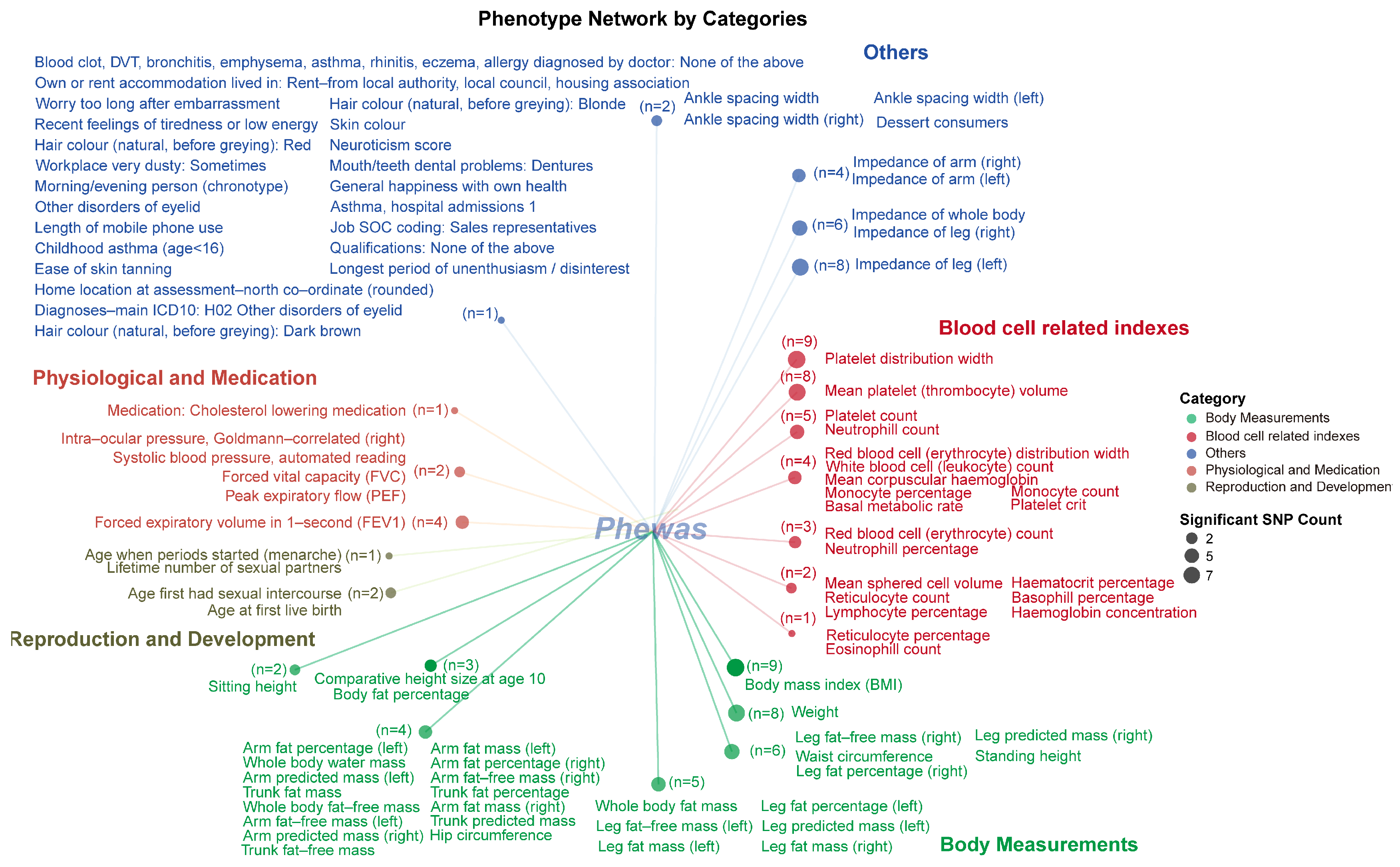
2.3. PheWAS Analysis
2.3.1. The Results of PheWAS Analysis for Phenotypes from Five Database
2.3.2. Category for Significant Phenotype Data from the IEU UK Biobank
2.3.3. Category for Significant Phenotype Data from the FinnGen Database
2.3.4. Category for Significant Phenotype Data from the UKB BOLT Database
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Sources and Study Population
3.2. Genetic Variant Selection and Processing
3.3. Gene Mapping and Functional Enrichment Analysis
3.4. Phenome-Wide Association Study (PheWAS) Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia-Moure, M.; Laspidea, V.; Gupta, S.; Gillard, A.G.; Khatua, S.; Parthasarathy, A.; He, J.; Lang, F.F.; Fueyo, J.; Alonso, M.M.; et al. The emerging field of viroimmunotherapy for pediatric brain tumors. Neuro-Oncol. 2024, 26, 1981–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNunzio, N.J.; Yock, T.I. Modern Radiotherapy for Pediatric Brain Tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.G.; Howard, S.C.; Bouffet, E.; Pritchard-Jones, K. Science and health for all children with cancer. Science 2019, 363, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Bass, J.K.; Khan, R.; Kun, L.E.; Merchant, T.E. Hearing loss after radiotherapy for pediatric brain tumors: Effect of cochlear dose. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 72, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Guo, R.; Yang, B.; Shi, L.; Sun, J.; Guo, W.; Gong, S.; Jiang, X.; Liu, K. Head and neck radiotherapy causes significant disruptions of cochlear ribbon synapses and consequent sensorineural hearing loss. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2022, 173, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, K.; Song, H.; Yin, L.; Kaijser, M.; Gurholt, T.P.; Andreassen, O.A.; Valdimarsdóttir, U.; Fang, F.; Duan, M. Depression, anxiety and brain volume after hearing loss and tinnitus: Cohort study in the UK Biobank. BJPsych Open 2024, 10, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Niu, X.; Sun, Y. The Long-Term Effect of Cochlear Implantation on Tinnitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, P.R.; Knight, K.R.; Freyer, D.R.; Campbell, K.C.; Steyger, P.S.; Blakley, B.W.; Rassekh, S.R.; Chang, K.W.; Fligor, B.J.; Rajput, K.; et al. Platinum-induced ototoxicity in children: A consensus review on mechanisms, predisposition, and protection, including a new International Society of Pediatric Oncology Boston ototoxicity scale. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmadi, A.; Abdelsamad, Y.; Al-Zuraiqi, B.; Alghamdi, S.; Hagr, A.; Saleh, E. Cochlear Implantation in Radiation-Induced Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review. Otol. Neurotol. 2023, 44, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, F.; Yin, D.; Chen, K.; Wang, S. Changes in brain gray matter volume in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients after radiotherapy in long-term follow-up. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 89, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, W.K.; Toh, S.T.; Wee, J.; Fook-Chong, S.M.; Wang, D.Y. Sensorineural hearing loss after radiotherapy and chemoradiotherapy: A single, blinded, randomized study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1904–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, C.M.; Ham, J.C.; Te Loo, M.; van Meerten, E.; van Lamoen, M.; Hakobjan, M.H.; Takes, R.P.; van der Graaf, W.T.; Kaanders, J.H.; Coenen, M.J.H.; et al. Genetic Variants as Predictive Markers for Ototoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Patients with Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Treated with Cisplatin-Containing Chemoradiotherapy (The PRONE Study). Cancers 2019, 11, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.Z.; Ong, T.C.C.; Timbadia, D.P.; Tan, H.T.A.; Kwa, E.D.; Chong, W.Q.; Goh, B.C.; Loh, W.S.; Loh, K.S.; Tan, E.C.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Influence of Genetic Variation on Ototoxicity in Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2023, 168, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, H.E.; Gamazon, E.R.; Frisina, R.D.; Perez-Cervantes, C.; El Charif, O.; Mapes, B.; Fossa, S.D.; Feldman, D.R.; Hamilton, R.J.; Vaughn, D.J.; et al. Variants in WFS1 and Other Mendelian Deafness Genes Are Associated with Cisplatin-Associated Ototoxicity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3325–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, X.; Lin, K.; Huang, R.; Bi, X.; Ming, C.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Zhao, L.; et al. Genetic screening of a Chinese cohort of children with hearing loss using a next-generation sequencing panel. Hum. Genom. 2023, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezo, M.; Sollis, E.; Ji, Y.; Lewis, E.; Abid, A.; Bircan, K.O.; Hall, P.; Hayhurst, J.; John, S.; Mosaku, A.; et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog: Standards for reusability, sustainability and diversity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 53, D998–D1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trendowski, M.R.; Baedke, J.L.; Sapkota, Y.; Travis, L.B.; Zhang, X.; El Charif, O.; Wheeler, H.E.; Leisenring, W.M.; Robison, L.L.; Hudson, M.M.; et al. Clinical and genetic risk factors for radiation-associated ototoxicity: A report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study and the St. Jude Lifetime Cohort. Cancer 2021, 127, 4091–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastarache, L.; Denny, J.C.; Roden, D.M. Phenome-Wide Association Studies. Jama 2022, 327, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Davies, N.M.; Dudbridge, F.; Gill, D.; Glymour, M.M.; Hartwig, F.P.; Kutalik, Z.; Holmes, M.V.; Minelli, C.; et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: Update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Liao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, M. Exploring the Causal Effects of Mineral Metabolism Disorders on Telomere and Mitochondrial DNA: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiji, S.; Butler-Laporte, G.; Lu, T.; Willett, J.D.S.; Su, C.Y.; Nakanishi, T.; Morrison, D.R.; Chen, Y.; Liang, K.; Hultström, M.; et al. Proteome-wide Mendelian randomization implicates nephronectin as an actionable mediator of the effect of obesity on COVID-19 severity. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Xie, H.; Gao, H.; Xie, C.; Yuan, H.; Feng, Z. Mitochondrial proteins as therapeutic targets in diabetic ketoacidosis: Evidence from Mendelian randomization analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1448505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrska-Bishop, M.; Evani, U.S.; Zhao, X.; Basile, A.O.; Abel, H.J.; Regier, A.A.; Corvelo, A.; Clarke, W.E.; Musunuri, R.; Nagulapalli, K.; et al. High-coverage whole-genome sequencing of the expanded 1000 Genomes Project cohort including 602 trios. Cell 2022, 185, 3426–3440.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, T.G.O. Expansion of the Gene Ontology knowledgebase and resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D331–D338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grentner, A.; Ragueneau, E.; Gong, C.; Prinz, A.; Gansberger, S.; Oyarzun, I.; Hermjakob, H.; Griss, J. ReactomeGSA: New features to simplify public data reuse. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, btae338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Gao, L.; Lu, Y.; He, X.; Xie, J. The potential contribution of aberrant cathepsin K expression to gastric cancer pathogenesis. Discover. Oncol. 2024, 15, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsworth, B.; Lyon, M.; Alexander, T.; Liu, Y.; Matthews, P.; Hallett, J.; Bates, P.; Palmer, T.; Haberland, V.; Smith, G.D.; et al. The MRC IEU OpenGWAS data infrastructure. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipilä, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.M.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 2023, 613, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Bi, W.; Zhao, Z.; Dey, K.K.; Jagadeesh, K.A.; Karczewski, K.J.; Daly, M.J.; Neale, B.M.; Lee, S. SAIGE-GENE+ improves the efficiency and accuracy of set-based rare variant association tests. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Selvaraj, M.S.; Van Buren, E.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, R.; McCaw, Z.R.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, M.Z.; et al. A statistical framework for multi-trait rare variant analysis in large-scale whole-genome sequencing studies. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2025, 5, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bycroft, C.; Freeman, C.; Petkova, D.; Band, G.; Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Motyer, A.; Vukcevic, D.; Delaneau, O.; O’Connell, J.; et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Labrecque, J.A. From GWAS to PheWAS: The search for causality in big data. Lancet. Digit. Health 2019, 1, e101–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Du, X.; Kuppa, A.; Feitosa, M.F.; Bielak, L.F.; O’Connell, J.R.; Musani, S.K.; Guo, X.; Kahali, B.; Chen, V.L.; et al. Genome-wide association meta-analysis identifies 17 loci associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.J.; Zhu, Y.P.; Sun, J.; Ding, X.Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.Z. PTGES2 and RNASET2 identified as novel potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for basal cell carcinoma: Insights from proteome-wide mendelian randomization, colocalization, and MR-PheWAS analyses. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1418560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; He, C.; Mei, L.; Wu, X.; Feng, Y.; Song, J. PAX3 mutation suppress otic progenitors proliferation and induce apoptosis by inhibiting WNT1/β-catenin signaling pathway in WS1 patient iPSC-derived inner ear organoids. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 698, 149510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Han, Y.; An, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Lu, J.; Meng, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Wnt signalling facilitates neuronal differentiation of cochlear Frizzled10-positive cells in mouse cochlea via glypican 6 modulation. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2025, 23, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, K.; He, S.; Yang, Z.; Song, J.; Ju, Y.; Xiong, C.; Zhang, G.; Yang, W.; Tang, C. Type XV osteogenesis imperfecta: A novel mutation in the WNT1 gene, c.620G >A (p.R207H), is associated with an inner ear deformity. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2023, 12, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Qin, J.; Bai, H.; Qin, X. Causal linkage of Graves’ disease with aging: Mendelian randomization analysis of telomere length and age-related phenotypes. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Meng, Z.; Jia, Z.; Tang, X. Exploring the Association of Leukocyte Telomere Length and Hearing Threshold Shifts of Adults in the United States. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 770159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, V.; Cheng, M.Z.; Xue, Q.L.; Simonsick, E.M.; Lane, A.P.; Agrawal, Y.; Rowan, N.R. The Association of Multiple Sensory Impairment and Telomere Length: The Health ABC Study. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 3132–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosconi, M.; Carlotto, E.; Caliogna, L.; Berni, M.; Gastaldi, G.; Conti, M.; Brancato, A.M.; Bina, V.; Minervini, D.; Malpede, S.; et al. Titanium Biohybrid Middle Ear Prostheses: A Preliminary In Vitro Study. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rämö, J.T.; Kiiskinen, T.; Seist, R.; Krebs, K.; Kanai, M.; Karjalainen, J.; Kurki, M.; Hämäläinen, E.; Häppölä, P.; Havulinna, A.S.; et al. Genome-wide screen of otosclerosis in population biobanks: 27 loci and shared associations with skeletal structure. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concas, M.P.; Morgan, A.; Serra, F.; Nagtegaal, A.P.; Oosterloo, B.C.; Seshadri, S.; Heard-Costa, N.; Van Camp, G.; Fransen, E.; Francescatto, M.; et al. Hearing Function: Identification of New Candidate Genes Further Explaining the Complexity of This Sensory Ability. Genes 2021, 12, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.W.; Christensen, J.; Chisholm, J.; Zalewski, C.; Rasooly, M.; Dempsey, C.; Magnani, A.; Frischmeyer-Guerrerio, P.; Brewer, C.C.; Kim, H.J. Audiologic and Otologic Clinical Manifestations of Loeys-Dietz Syndrome: A Heritable Connective Tissue Disorder. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2022, 166, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.Y.; Jeong, H.W.; Kim, E.; Jung, J.Y.; Lee, M.Y. Distribution and Afferent Effects of Transplanted mESCs on Cochlea in Acute and Chronic Neural Hearing Loss Models. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 4956404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merces, L.; Ferro, L.M.M.; Nawaz, A.; Sonar, P. Advanced Neuromorphic Applications Enabled by Synaptic Ion-Gating Vertical Transistors. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2305611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitko, A.A.; Goodrich, L.V. Making sense of neural development by comparing wiring strategies for seeing and hearing. Science 2021, 371, eaaz6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime Tobón, L.M.; Moser, T. Ca2+ regulation of glutamate release from inner hair cells of hearing mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2311539120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestreicher, D.; Chepurwar, S.; Kusch, K.; Rankovic, V.; Jung, S.; Strenzke, N.; Pangrsic, T. CaBP1 and 2 enable sustained Ca(V)1.3 calcium currents and synaptic transmission in inner hair cells. eLife 2024, 13, RP93646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovee, S.; Klump, G.M.; Pyott, S.J.; Sielaff, C.; Köppl, C. Cochlear Ribbon Synapses in Aged Gerbils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Mei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Che, C.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, S. Glutamate-aspartate transporter dysfunction enhances aminoglycoside-induced cochlear hair cell death via NMDA receptor activation. Neurochem. Int. 2023, 169, 105587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.L.; Yu, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Han, J.S.; Lim, J.H.; Park, S.Y.; Park, I.; Park, S.N. Tinnitus Generation and Behavioral Changes Caused by Chronic Stress: A Behavioral and Brain Study in a Rat Model. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Hogrebe, M.; Grüneberg, M.; DuChesne, I.; von der Heiden, A.L.; Reunert, J.; Schlingmann, K.P.; Boycott, K.M.; Beaulieu, C.L.; Mhanni, A.A.; et al. SLC39A8 Deficiency: A Disorder of Manganese Transport and Glycosylation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Probst, F.J.; Corrigan, R.R.; Del Gaudio, D.; Salinger, A.P.; Lorenzo, I.; Gao, S.S.; Chiu, I.; Xia, A.; Oghalai, J.S.; Justice, M.J. A point mutation in the gene for asparagine-linked glycosylation 10B (Alg10b) causes nonsyndromic hearing impairment in mice (Mus musculus). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mao, X.; Long, H.; Xiao, B.; Luo, Z.; Xiao, W.; Jin, X. Compound Heterozygous PIGS Variants Associated with Infantile Spasm, Global Developmental Delay, Hearing Loss, Visual Impairment, and Hypotonia. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, X.; Ibrahim, M.; Peltzer, N. Cell death and inflammation during obesity: “Know my methods, WAT(son)”. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, S.; Guilbaud, E.; Tait, S.W.G.; Yamazaki, T.; Galluzzi, L. Mitochondrial control of inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGettrick, A.F.; Bourner, L.A.; Dorsey, F.C.; O’Neill, L.A.J. Metabolic Messengers: Itaconate. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P.; Vijayan, V.; Liu, B.; Martinez-Delgado, B.; Matamala, N.; Nikolin, C.; Greite, R.; DeLuca, D.S.; Janciauskiene, S.; Motterlini, R.; et al. Distinct metabolic responses to heme in inflammatory human and mouse macrophages—Role of nitric oxide. Redox Biol. 2024, 73, 103191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, B.; Kong, M.; Xie, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Chai, R.; Gu, N. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle regulates microbiota-gut-inner ear axis for hearing protection. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.; Kurihara, S.; Stankovic, K.M. An In Vitro Oxidative Stress Model of the Human Inner Ear Using Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Otic Progenitor Cells. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriac, S.A.; Peineau, T.; Zuberi, A.; Lutz, C.; Géléoc, G.S.G. Loss of Pex1 in Inner Ear Hair Cells Contributes to Cochlear Synaptopathy and Hearing Loss. Cells 2022, 11, 3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Pantaleo, A.; Pontillo, V.; Barbara, F.; Murri, A.; Quaranta, N. Endothelial Dysfunction and Metabolic Disorders in Patients with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Medicina 2023, 59, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.G.; Freytag, S.; Kloos, B.; Haubner, F.; Sharaf, K.; Spiegel, J.L.; Canis, M.; Ihler, F.; Bertlich, M. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Agonism is Capable of Preventing Lipopolysaccharide Induced Decreases of Cochlear Microcirculation—A Potential Approach for Inner Ear Pathologies. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, e1396–e1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.G.; Spiegel, J.L.; Becker, S.; Strieth, S.; Olzowy, B.; Bertlich, M.; Fořt, T.; Mejzlik, J.; Lenarz, T.; Ihler, F.; et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled study on efficacy, safety and tolerability of drug-induced defibrinogenation for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: The lessons learned. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2023, 280, 4009–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.L.; Li, D.K.; Tian, Y.H.; Sun, Y. Greenness, Genetic Predisposition, and Tinnitus. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2306706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.W.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y. Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Expecting Its Application in Temporal Bone Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Med. Sci. 2023, 43, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, L.; Shi, M.; Yu, J.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Y. Ubiquitination-Related Gene Signature, Nomogram and Immune Features for Prognostic Prediction in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Genes 2024, 15, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, F.; Pang, Z.; Ji, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Bing, Z. Identification of Risk Loci for Radiotherapy-Induced Tinnitus and Hearing Loss Through Integrated Genomic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094132
Ding F, Pang Z, Ji X, Jiang Y, Wang Q, Bing Z. Identification of Risk Loci for Radiotherapy-Induced Tinnitus and Hearing Loss Through Integrated Genomic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094132
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Fan, Zehao Pang, Xiujia Ji, Yuanfang Jiang, Qiulan Wang, and Zhitong Bing. 2025. "Identification of Risk Loci for Radiotherapy-Induced Tinnitus and Hearing Loss Through Integrated Genomic Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094132
APA StyleDing, F., Pang, Z., Ji, X., Jiang, Y., Wang, Q., & Bing, Z. (2025). Identification of Risk Loci for Radiotherapy-Induced Tinnitus and Hearing Loss Through Integrated Genomic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094132






