Free-Living and Particle-Associated Microbial Communities of Lake Baikal Differ by Season and Nutrient Intake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
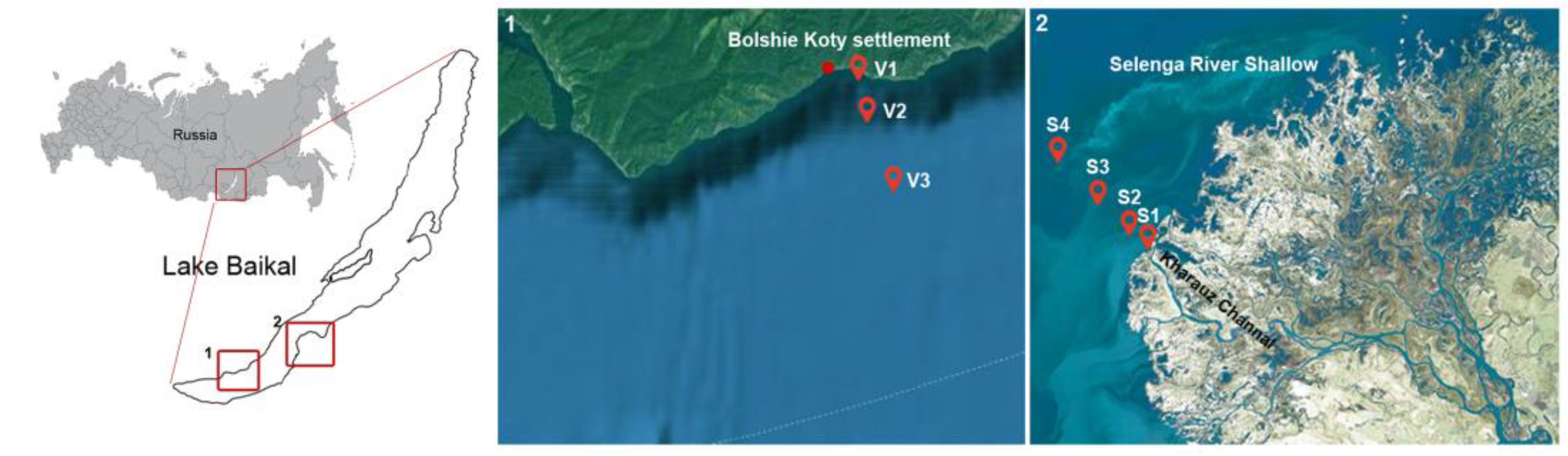
2.1. Site Description, Sampling and Environmental Parameters
2.2. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. HTS Data Analysis and Quality Control (QC)
2.4. Statistical Analyses and Data Visualization
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Parameters, Phytoplankton Abundance and Diversity, According to Microscopy
3.2. Diversity and Composition of Microeukaryotic Communities, According to Metabarcoding Data
3.3. Diversity of FL and PA Bacterial Communities
3.4. Beta-Diversity and Microbial Taxa Differing by Size Fractions and Seasons
3.5. Co-Occurrence Networks
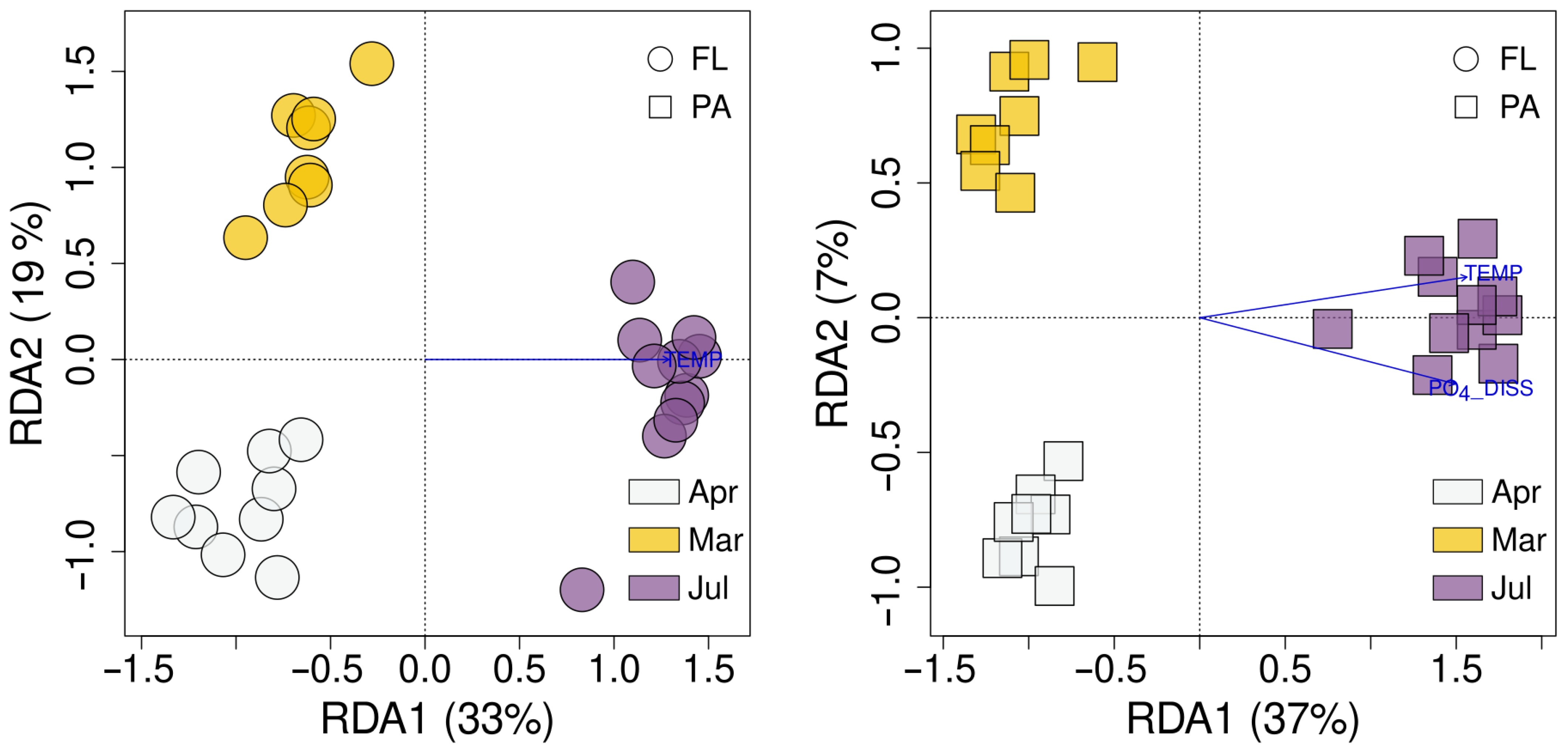
3.6. Environmental Factors Affecting FL and PA Bacterial Communities
3.7. Predicting the Metabolic Functions that Might Underlie Changes between the FL and PA Heterotrophic Community Structure
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of the River Water Inflow on the Composition of FL and PA Communities
4.2. Seasonal Changes in the Structure of FL and PA Microbial Communities
4.3. Relation of FL and PA Bacterial Communities to the Development of Microeukaryotes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azam, F.; Fenchel, T.; Field, J.G.; Gray, J.S.; Meyer-Reil, L.A.; Thingstad, F. The ecological role of water-column microbes in the sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1983, 10, 257–263. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/24814647 (accessed on 10 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Malfatti, F. Microbial structuring of marine ecosystems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.; Franks, D.; Alldredge, A. Phylogenetic diversity of aggregate-attached vs. free-living marine bacterial assemblages. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, C.T.; Deming, J.W. Comparison of free-living, suspended particle, and aggregate-associated bacterial and archaeal communities in the Laptev Sea. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Lovell, C.R. Microbial surface colonization and biofilm development in marine environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 91–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, X.; Jacob, J.; Lu, X.; Robbins, S.; Sun, S.; Ortiz, J.D. Diversity and distribution of free-living and particle-associated bacterioplankton in Sandusky Bay and adjacent waters of Lake Erie Western Basin. J. Great Lakes Res. 2013, 39, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Chao, J.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Gao, G. Spatiotemporal dynamics of bacterial community composition in large shallow eutrophic Lake Taihu: High overlap between free-living and particle-attached assemblages. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 1366–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, D.; Huang, R.; Cao, X.; Zeng, J.; Yu, Z.; Hooker, K.V.; Hambright, K.D.; Wu, Q.L. Contrasting network features between free-living and particle-attached bacterial communities in Taihu Lake. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, D.; Sinclair, L.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Parajka, J.; Reischer, G.H.; Stadler, P.; Blaschke, A.P.; Blöschl, G.; Mach, R.L.; Kirschner, A.K.T.; et al. Bacterial diversity along a 2600 km river continuum. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4994–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satinsky, B.M.; Smith, C.B.; Sharma, S.; Landa, M.; Medeiros, P.M.; Coles, V.J.; Yager, P.L.; Crump, B.C.; Moran, M.A. Expression patterns of elemental cycling genes in the Amazon River Plume. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1852–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.M.; York, J.; Biddle, J.F. Impacts of salinity and oxygen on particle-associated microbial communities in the Broadkill River, Lewes DE. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.W.; Zeigler Allen, L.; Allen, A.E.; Herfort, L.; Simon, H.M. Contrasting genomic properties of free-living and particle-attached microbial assemblages within a coastal ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bižić-Ionescu, M.; Zeder, M.; Ionescu, D.; Orlić, S.; Fuchs, B.M.; Grossart, H.P.; Amann, R. Comparison of bacterial communities on limnic versus coastal marine particles reveals profound differences in colonization. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3500–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieck, A.; Herlemann, D.P.; Jürgens, K.; Grossart, H.P. Particle-associated differ from free-living bacteria in surface waters of the Baltic Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, M.; Borrull, E.; Sala, M.M.; Gasol, J.M. Patterns of bacterial diversity in the marine planktonic particulate matter continuum. ISME J. 2017, 11, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieft, B.; Li, Z.; Bryson, S.; Crump, B.C.; Hettich, R.; Pan, C.; Mayali, X.; Mueller, R.S. Microbial community structure–function relationships in yaquina bay estuary reveal spatially distinct carbon and nitrogen cycling capacities. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Feng, J.; Yang, F.; Du, H.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Differences in metabolic potential between particle-associated and free-living bacteria along Pearl River Estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth Rosenberg, D.; Haber, M.; Goldford, J.; Lalzar, M.; Aharonovich, D.; Al-Ashhab, A.; Lehahn, Y.; Segrè, D.; Steindler, L.; Sher, D. Particle-associated and free-living bacterial communities in an oligotrophic sea are affected by different environmental factors. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 4295–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, B.; Martens, T.; Fischer, D.; Lemke, A.; Grossart, H.P.; Simon, M.; Brinkhoff, T. Short-term dynamics of bacterial communities in a tidally affected coastal ecosystem. FEMS Microb. Ecol. 2008, 66, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Joux, F.; Jeffrey, W.H.; Ghiglione, J.F. Spatial variability of particle-attached and free-living bacterial diversity in surface waters from the Mackenzie River to the Beaufort Sea (Canadian Arctic). Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 2747–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bižić-Ionescu, M.; Amann, R.; Grossart, H.P. Massive regime shifts and high activity of heterotrophic bacteria in an ice-covered lake. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allgaier, M.; Grossart, H.P. Seasonal dynamics and phylogenetic diversity of free-living and particle-associated bacterial communities in four lakes in northeastern Germany. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 45, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösel, S.; Allgaier, M.; Grossart, H.P. Long-term characterization of free-living and particle-associated bacterial communities in Lake Tiefwaren reveals distinct seasonal patterns. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeling, H.; Fuchs, B.M.; Becher, D.; Klockow, C.; Gardebrecht, A.; Bennke, C.M.; Kassabgy, M.; Huang, S.; Mann, A.J.; Waldmann, J.; et al. Substrate-controlled succession of marine bacterioplankton populations induced by a phytoplankton bloom. Science 2012, 336, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galazy, G.I. Atlas of Lake Baikal; Ruscartography: Moscow, Russia, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Shimaraev, M.N.; Verbolov, V.I.; Granin, N.G.; Sherstayankin, P.P. Physical Limnology of Lake Baikal: A Review; Baikal International Center for Ecological Research: Irkutsk, Russia, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hampton, S.E.; Izmest’eva, L.R.; Moore, M.V.; Katz, S.L.; Dennis, B.; Silow, E.A. Sixty years of environmental change in the world’s largest freshwater lake–Lake Baikal, Siberia. Global Change Biol. 2008, 14, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.V.; Hampton, S.E.; Izmest’Eva, L.R.; Silow, E.A.; Peshkova, E.V.; Pavlov, B.K. Climate change and the world’s ‘‘sacred sea”—Lake Baikal, Siberia. Bioscience 2009, 59, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimaraev, M.N.; Sizova, L.N.; Troitskaya, E.S.; Kuimova, L.N.; Yakimova, N.I. Ice-thermal regime of lake baikal under conditions of modern warming (1950–2017). Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2019, 44, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherstyankin, P.P. Dynamics of the Selenga shallow waters in early summer according to the distribution of optical characteristics and water temperature. In Hydrometeorological Regime of Lake Baikal; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1964; p. 2937. [Google Scholar]
- Bashenkhaeva, N.V.; Sinyukovich, V.N.; Sorokovikova, L.M.; Khodzher, T.V. Organic matter in the water of the Selenga river. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 2006, 1, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Tomberg, I.V.; Sorokovikova, L.M.; Popovskaya, G.I.; Bashenkhaeva, N.V.; Sinyukovich, V.N.; Ivanov, V.G. Concentration dynamics of biogenic elements and phytoplankton at Selenga R. Mouth and in Selenga shallows (Lake Baikal). Water Resour. 2014, 41, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebykin, E.P.; Sorokovikova, L.M.; Tomberg, I.V.; Rasskazov, S.V.; Khodzher, T.V.; Grachev, M.A. Current State of the Selenga River Waters in the RussianTerritory Concerning Major Components and Trace Elements. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 20, 561–580. [Google Scholar]
- Popovskaya, G.I.; Tashlykova, N.A. Phytoplankton of the Selenga River. In The Selenga River Delta: A Natural Biofilter and Indicator of the State of Lake Baikal; Izd-vo. SO RAN: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2008; pp. 167–182. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimenko, S.Y.; Zemskaya, T.I.; Pavlova, O.N.; Ivanov, V.G.; Buryukhaev, S.P. Microbial community of the water column of the Selenga River-Lake Baikal biogeochemical barrier. Microbiology 2008, 77, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, I.S.; Zakharova, Y.R.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Usoltseva, M.V.; Petrova, D.P.; Sakirko, M.V.; Likhoshway, Y.V.; Grachev, M.A. Similarity of structure of taxonomic bacterial communities in the photic layer of Lake Baikal’s three basins differing in spring phytoplankton composition and abundance. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 465, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailov, I.S.; Zakharova, Y.R.; Bukin, Y.S.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Petrova, D.P.; Sakirko, M.V.; Likhoshway, Y.V. Co-occurrence networks among bacteria and microbial eukaryotes of Lake Baikal during a spring phytoplankton bloom. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakharova, Y.R.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Kurilkina, M.I.; Likhoshvay, A.V.; Petrova, D.P.; Shishlyannikov, S.M.; Ravin, N.V.; Mardanov, A.V.; Beletsky, A.V.; Likhoshway, Y.V. The structure of microbial community and degradation of diatoms in the deep near-bottom layer of Lake Baikal. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemskaya, T.I.; Lomakina, A.V.; Mamaeva, E.V.; Zakharenko, A.S.; Pogodaeva, T.V.; Petrova, D.P.; Galachyants, Y.P. Bacterial communities in sediments of Lake Baikal from areas with oil and gas discharge. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 76, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, Y.R.; Petrova, D.P.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Bashenkhaeva, M.V.; Kurilkina, M.I.; Likhoshway, Y.V. Bacterial and archaeal community structure in the surface diatom sediments of deep freshwater Lake Baikal (eastern Siberia). Geomicrobiol. J. 2018, 35, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemskaya, T.I.; Bukin, S.V.; Lomakina, A.V.; Pavlova, O.N. Microorganisms in the Sediments of Lake Baikal, the Deepest and Oldest Lake in the World. Microbiology 2021, 90, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashenkhaeva, M.V.; Zakharova, Y.R.; Petrova, D.P.; Khanaev, I.V.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Likhoshway, Y.V. Sub-ice microalgal and bacterial communities in freshwater Lake Baikal. Russia. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashenkhaeva, M.V.; Zakharova, Y.R.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Khanaev, I.V.; Likhoshway, Y.V. Bacterial communities during the period of massive under-ice dinoflagellate development in Lake Baikal. Microbiology 2017, 86, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemskaya, T.I.; Bukin, S.V.; Bukin, Y.S.; Chernitsina, S.M.; Pogodaeva, T.V.; Rusanov, I.I.; Shubenkova, O.V.; Zakharenko, A.S.; Pimenov, N.V. Taxonomic diversity and metabolic activity of microbial communities in rivers and estuarine waters of Southern Baikal in summer. J. Great Lakes Res. 2022, 48, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, I.S.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Bukin, Y.S.; Petrova, D.P.; Bashenkhaeva, M.V.; Sakirko, M.V.; Blinov, V.V.; Titova, L.A.; Zakharova, Y.R.; Likhoshway, Y.V. Seasonal Succession and Coherence Among Bacteria and Microeukaryotes in Lake Baikal. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 84, 404–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, I.S.; Bukin, Y.S.; Zakharova, Y.R.; Usoltseva, M.V.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Sakirko, M.V.; Blinov, V.V.; Likhoshway, Y.V. Co-occurrence patterns between phytoplankton and bacterioplankton across the pelagic zone of Lake Baikal during spring. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashenkhaeva, M.V.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Khanaev, I.V.; Sakirko, M.V.; Petrova, D.P.; Likhoshway, Y.V.; Zakharova, Y.R. Comparative analysis of free-living and particle-associated bacterial communities of Lake Baikal during the ice-covered period. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossart, H.P.; Kiørboe, T.; Tang, K.; Ploug, H. Bacterial colonization of particles: Growth and interactions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3500–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.M.; Dobbs, F.C. Differential utilization of carbon substrates by aggregate-associated and water-associated heterotrophic bacterial communities. Hydrobiologia 2012, 686, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G.; Likens, G.E. Composition and biomass of phytoplankton. In Limnological Analyses; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 147–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeva, L. Manual for the Chemical Analysis of Surface Waters; RosHydromet: Rostov-on-Don, Russia, 2009; p. 1044. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Acinas, S.G.; Rodríguez-Valera, F.; Pedrós-Alió, C. Spatial and temporal variation in marine bacterioplankton diversity as shown by RFLP fingerprinting of PCR amplified 16S rDNA. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1997, 24, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, D.B.; Halpern, A.L.; Sutton, G.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Williamson, S.; Yooseph, S.; Wu, D.; Eisen, J.A.; Hoffman, J.M.; Remington, K.; et al. The Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling Expedition: Northwest Atlantic through Eastern Tropical Pacific. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, G.C.; Smith, J.J.; Cowan, D.A. Review and re-analysis of domain-specific 16S primers. J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 55, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, I.M.; Pinto, A.J.; Guest, J.S. Design and evaluation of Illumina MiSeq-compatible, 18S rRNA gene-specific primers for improved characterization of mixed phototrophic communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5878–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahe, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. Peer J. 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-6. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Terada, Y.; Shimodaira, H. Pvclust: Hierarchical Clustering with p-Values Via Multiscale Bootstrap Resampling. R Package Version 2.2-0. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pvclust (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Kolde, R. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R Package Version 1.0.12. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Van den Brand, T. ggh4x: Hacks for ‘ggplot2’. R Package Version 0.2.3. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggh4x (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, Z.D.; Müller, C.L.; Miraldi, E.R.; Littman, D.R.; Blaser, M.J.; Bonneau, R.A. Sparse and Compositionally Robust Inference of Microbial Ecological Networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cougoul, A.; Bailly, X.; Wit, E.C. MAGMA: Inference of sparse microbial association networks. BioRxiv 2019, 538579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prost, V.; Gazut, S.; Brüls, T. A zero inflated log-normal model for inference of sparse microbial association networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Alm, E.J. Inferring correlation networks from genomic survey data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.D.; Macklaim, J.M.; Linn, T.G.; Reid, G.; Gloor, G.B. ANOVA-Like Differential Expression (ALDEx) Analysis for Mixed Population RNA-Seq. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Steele, J.A.; Caporaso, J.; Steinbrück, L.; Reeder, J.; Temperton, B.; Huse, S.; McHardy, A.C.; Knight, R.; Joint, I.; et al. Defning seasonal marine microbial community dynamics. ISME J. 2012, 6, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunse, C.; Pinhassi, J. Marine bacterioplankton seasonal succession dynamics. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokovikova, L.M.; Popovskaya, G.I.; Sinyukovich, V.N.; Tomberg, I.V.; Bashenkhaeva, N.V.; Tashlykova, N.A. Water chemistry and phytoplankton in water bodies in the Selenga River’s delta under ice cover. Water Resour. 2006, 33, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokovikova, L.M.; Popovskaya, G.I.; Tomberg, I.V.; Bashenkhaeva, N.V. Space and time variations in concentrations of biogenic and organic matter and phytoplankton in the water of the Selenga River and its delta branches. Water Resour. 2009, 36, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, E.M.S.; Darcy, J.L.; Hell, K.; Schmidt, S.K. Structure of bacterial and eukaryote communities reflect in situ controls on community assembly in a high-alpine lake. J Microbiol. 2019, 57, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.M.; Unz, R.F. Filamentous sulfur bacteria of activated sludge: Characterization of Thiothrix, Beggiatoa, and Eikelboom type 021N strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämpfer, P. Some chemotaxonomic and physiological properties of the genus Sphaerotilus. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 21, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Rincón, F.J.; Welles, L.; Lopez-Vazquez, C.M.; Nierychlo, M.; Abbas, B.; Geleijnse, M.; Nielsen, P.H.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Brdjanovic, D. Long-term effects of sulphide on the enhanced biological removal of phosphorus: The symbiotic role of Thiothrix Caldifontis. Water Res. 2017, 116, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zeng, W.; Wang, B.; Fan, Z.; Peng, Y. New insights in the competition of polyphosphate-accumulating organisms and glycogen-accumulating organisms under glycogen accumulating metabolism with trace Poly-P using flow cytometry. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.H.; Kim, S.K. Sulfated polysaccharides as bioactive agents from marine algae. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcy, J.L.; Lynch, R.C.; King, A.J.; Robeson, M.S.; Schmidt, S.K. Global Distribution of Polaromonas Phylotypes-Evidence for a Highly Successful Dispersal Capacity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraishi, A.; Imhoff, J.F. Rhodoferax. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawor, J.; Grzesiak, J.; Sasin-Kurowska, J.; Borsuk, P.; Gromadka, R.; Górniak, D.; Świątecki, A.; Aleksandrzak-Piekarczyk, T.; Zdanowski, M.K. Evidence of adaptation, niche separation and microevolution within the genus Polaromonas on Arctic and Antarctic glacial surfaces. Extremophiles 2016, 20, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzler, B.E.; Pfannes, K.R.; Vogl, K.; Overmann, J. Molecular characterization of the nonphotosynthetic partner bacterium in the consortium “Chlorochromatium aggregatum”. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7434–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garneau, M.È.; Vincent, W.F.; Terrado, R.; Lovejoy, C. Importance of particle-associated bacterial heterotrophy in a coastal Arctic ecosystem. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 75, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, B.; Reveilliez, J.P.; Mary, I.; Ravet, V.; Bronner, G.; J-Fo, M.; Domaizon, I.; Debroas, D. Diversity and dynamics of free-living and particle-associated Betaproteobacteria and Actinobacteria in relation to phytoplankton and zooplankton communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 77, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votintsev, K.K. Hydrochemistry of Lake Baikal. Proc. Baikal Limnol. St. 1961, 20, 1–312. [Google Scholar]
- Glockner, F.O.; Zaichikov, E.; Belkova, N.; Denissova, L.; Pernthaler, J.; Pernthaler, A.; Amann, R. Comparative 16S rRNA analysis of lake bacterioplankton reveals globally distributed phylogenetic clusters including an abundant group of Actinobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5053–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcher, M.M.; Pernthaler, J.; Posch, T. Spatiotemporal distribution and activity patterns of bacteria from three phylogenetic groups in an oligomesotrophic lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, R.M.; Prášil, O.; Pechar, L.; Lawrenz, E.; Rozmarynowycz, M.J.; Bullerjahn, G.S. Freshwater ice as habitat: Partitioning of phytoplankton and bacteria between ice and water in central European reservoirs. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullerjahn, G.S.; McKay, R.M.L.; Bernát, G.; Prášil, O.; Vörös, L.; Pálffy, K.; Tugyi, N.; Somogyi, B. Community dynamics and function of algae and bacteria during winter in central European great lakes. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 46, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, N.A.; Rusanov, I.I.; Chernitsyna, S.M.; Shubenkova, O.V.; Zaharenko, A.S.; Pogodaeva, T.V.; Pimenov, N.V.; Zemskaya, T.I. Structure and Production Potential of Summer Phytoplankton of Lake Baikal in the Present Period. Water Resour. 2022, 49, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemskaya, T.I.; Pogodaeva, T.V.; Shubenkova, O.V.; Chernitsina, S.M.; Dagurova, O.P.; Buryukhaev, S.P.; Namsaraev, B.B.; Khlystov, O.M.; Egorov, A.V.; Krylov, A.A.; et al. Geochemical and microbiological characteristics of sediments near the Malenky mud volcano (Lake Baikal, Russia), with evidence of Archaea intermediate between the marine anaerobic methanotrophs ANME-2 and ANME-3. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2010, 30, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, O.N.; Bukin, S.V.; Lomakina, A.V.; Kalmychkov, G.V.; Ivanov, V.G.; Morozov, I.V.; Pogodaeva, T.V.; Pimenov, N.V.; Zemskaya, T.I. Production of gaseous hydrocarbons by microbial communities of Lake Baikal bottom sediments. Microbiology 2014, 83, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, K.; Graf, J.S.; Littmann, S.; Tienken, D.; Brand, A.; Wehrli, B.; Albertsen, M.; Daims, H.; Wagner, M.; Kuypers, M.M.M. Crenothrix are major methane consumers in stratified lakes. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2124–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrol, L.; Thalasso, F.; Gandois, L.; Sepulveda-Jauregui, A.; Martinez-Cruz, K.; Teisserenc, R.; Tananaev, N.; Tveit, A.; Svenningg, M.M.; Barret, M. Anaerobic oxidation of methane and associated microbiome in anoxic water of Northwestern Siberian lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharenko, A.S.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Morozov, I.V.; Shubenkova, O.V.; Morozov, A.A.; Ivanov, V.G.; Pimenov, N.V.; Krasnopeev, A.Y.; Zemskaya, T.I. Bacterial Communities in Areas of Oil and Methane Seeps in Pelagic of Lake Baikal. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, B.; Mary, I.; Vellet, A.; Ravet, V.; Debroas, D. Temporal dynamics and phylogenetic diversity of free-living and particle-associated Verrucomicrobia communities in relation to environmental variables in a mesotrophic lake. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardman, Z.; Arnosti, C.; Durbin, A.; Ziervogel, K.; Cox, C.; Steen, A.D.; Teske, A. Verrucomicrobia: Candidates for polysaccharide-degrading bacterioplankton in an Arctic fjord of Svalbard. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3749–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beall, B.F.N.; Twiss, M.R.; Smith, D.E.; Oyserman, B.O.; Rozmarynowycz, M.J.; Binding, C.E.; Bourbonniere, R.A.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; Palmer, M.E.; Reavie, E.D.; et al. Ice cover extent drives phytoplankton and bacterial community structure in a large north-temperate lake: Implications for a warming climate. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1704–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, M.; Blain, S.; Harmand, J.; Monchy, S.; Rapaport, A.; Obernosterer, I. Major changes in the composition of a Southern Ocean bacterial community in response to diatom-derived dissolved organic matter. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.; Ramachandran, A.; Khawasik, O.; Beisner, B.E.; Rautio, M.; Huot, Y.; Walsh, D.A. Microbial life under ice: Metagenome diversity and in situ activity of Verrucomicrobia in seasonally ice-covered Lakes. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2568–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Garcia, M.; Brazel, D.M.; Swan, B.K.; Arnosti, C.; Chain, P.S.; Reitenga, K.G.; Xie, G.; Poulton, N.J.; Gomez, M.L.; Masland, D.E.D.; et al. Capturing single cell genomes of active polysaccharide degraders: An unexpected contribution of Verrucomicrobia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, L.H.; Francis, T.B.; Ferraro, M.; Hehemann, J.H.; Fuchs, B.M.; Amann, R.I. Verrucomicrobiota are specialist consumers of sulfated methyl pentoses during diatom blooms. ISME J. 2022, 16, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Melgosa, S.; Sichert, A.; Francis, T.B.; Bartosik, D.; Niggemann, J.; Wichels, A.; Willats, W.G.T.; Fuchs, B.M.; Teeling, H.; Becher, D.; et al. Diatom fucan polysaccharide precipitates carbon during algal blooms. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhooren, P.T.; Vandamme, E.J. L-Fucose: Occurrence, physiological role, chemical, enzymatic and microbial synthesis. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1999, 74, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayali, X.; Azam, F. Algicidal bacteria in the sea and their impact on algal blooms. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, S.; Suthaus, A.; Melkonian, M. “Candidatus Finniella” (Rickettsiales, Alphaproteobacteria), novel endosymbionts of viridiraptorid amoeboflagellates (Cercozoa, Rhizaria). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.B.; Steppe, T.F.; Litaker, R.W.; Paer, H.W. N2-Fixing Microbial Consortia Associated with the Ice Cover of Lake Bonney, Antarctica. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 36, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klawonn, I.; Bonaglia, S.; Brüchert, V.; Ploug, H. Aerobic and anaerobic nitrogen transformation processes in N2-fixing cyanobacterial aggregates. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, M.M.; Øvreås, L. Planctomycetes dominate biofilms on surfaces of the kelp Laminaria hyperborea. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, C.; Thomas, T.; Lewis, M.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S. Composition, uniqueness and variability of the epiphytic bacterial community of the green alga Ulva australis. ISME J. 2011, 5, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachnit, T.; Meske, D.; Wahl, M.; Harder, T.; Schmitz, R. Epibacterial community patterns on marine macroalgae are host-specific but temporally variable. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, O.M.; Bondoso, J. Planctomycetes diversity associated with macroalgae: Planctomycetes-macroalgae diversity. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lage, O.M.; Bondoso, J. Planctomycetes and macroalgae, a striking association. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboré, O.D.; Godreuil, S.; Drancourt, M. Planctomycetes as host-associated bacteria: A perspective that holds promise for their future isolations, by mimicking their native environmental niches in clinical microbiology laboratories. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 519301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedysh, S.N.; Henke, P.; Ivanova, A.A.; Kulichevskaya, I.S.; Philippov, D.A.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M.; Huang, S.; Overmann, J. 100-year-old enigma solved: Identification, genomic characterization and biogeography of the yet uncultured Planctomyces bekefii. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, C.-E.; Richter-Heitmann, T.; Klindworth, A.; Klockow, C.; Richter, M.; Achstetter, T.; Glöckner, F.O.; Harder, J. Expression of sulfatases in Rhodopirellula baltica and the diversity of sulfatases in the genus Rhodopirellula. Mar. Genom. 2013, 9, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemskaya, T.; Egorov, A.; Khlystov, O.; Shubenkova, O.; Namsaraev, B.; Chernitsina, S.; Dagurova, O.; Kalmychkov, G.; Grachev, M. Biogeochemical cycles of methane in Lake Baikal. Geoph. Res. Abstr. 2005, 7, 03994. [Google Scholar]
- Gar’kusha, D.N.; Fedorov, Y.A.; Tambieva, N.S.; Andreev, Y.A.; Mikhailenko, O.A. Methane in water and bottom sediments of Lake Baikal. Water Resour. 2019, 46, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saud, S.; Florea, K.M.; Webb, E.A.; Thrash, J.C. Metagenome-Assembled Genome Sequence of Kapabacteriales Bacterium Strain Clear-D13, Assembled from a Harmful Algal Bloom Enrichment Culture. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e01118–e01120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, B.G.; Pommier, T.; Fernández-Gómez, B.; Pedrós-Alió, C. Taxonomic composition of the particle-attached and free-living bacterial assemblages in the Northwest Mediterranean Sea analyzed by pyrosequencing of the 16S rRNA. Microbiologyopen 2013, 2, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, M.C.; Hollibaugh, J.T.; Silver, M.W.; Wong, P.S. Bacterioplankton dynamics in northern San Francisco Bay: Role of particle association and seasonal freshwater flow. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardot, M.; Debroas, D.; Thouvenot, A.; Romagoux, J.C.; Berthon, J.L.; Devaux, J. Proteolytic and glycolytic activities in size-fractionated surface water samples from an oligotrophic reservoir in relation to plankton communities. Aquat. Sci. Res. Across Bound. 1999, 61, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mével, G.; Vernet, M.; Goutx, M.; Ghiglione, J.F. Seasonal to hour variation scales in abundance and production of total and particle-attached bacteria in the open NW Mediterranean Sea (0–1000 m). Biogeosciences 2008, 5, 1573–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, R. Marine microbes see a sea of gradients. Science 2012, 338, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernthaler, A.; Amann, R. Fate of heterotrophic microbes in pelagic habitats: Focus on populations. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 440–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchman, D. The ecology of Cytophaga-Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 39, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Kube, M.; Telling, H.; Richter, M.; Lombardot, T.; Allers, E.; Wurdemann, C.A.; Quast, C.; Kuhl, H.; Knaust, F.; et al. Whole genome analysis of the marine Bacteroidetes ‘Gramella forsetii’ reveals adaptations to degradation of polymeric organic matter. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossart, H.-P.; Berman, T.; Simon, M.; Pohlmann, K. Occurrence and microbial dynamics of macroscopic organic aggregates (lake snow) in Lake Kinneret, Israel, in fall. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 14, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, B.; Huber, I.; Amann, R.; Ludwig, W.; Simon, M. α- and β-Proteobacteria Control the Consumption and Release of Amino Acids on Lake Snow Aggregates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| IndepVar1 * | DepVar | ANOVA | Kruskal-Wallis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | padj | padj Sign | p | padj | padj Sign | ||
| month | pH | 9.04 × 105 | 1.45 × 104 | *** | 6.03 × 108 | 8.78 × 108 | *** |
| month | Temp | 5.87 × 1035 | 4.70 × 1034 | *** | 3.65 × 1011 | 1.95 × 1010 | *** |
| month | Ec | 1.84 × 104 | 2.68 × 104 | *** | 2.58 × 109 | 6.87 × 109 | *** |
| month | O2_conc | 5.02 × 104 | 6.69 × 104 | *** | 5.61 × 108 | 8.78 × 108 | *** |
| month | O2_sat | 4.46 × 105 | 8.93 × 105 | *** | 2.62 × 108 | 4.66 × 108 | *** |
| month | Si_diss | 8.62 × 104 | 1.06 × 103 | ** | 5.95 × 1012 | 4.76 × 1011 | *** |
| month | NH4+_diss | 1.75 × 103 | 1.99 × 103 | ** | 1.69 × 104 | 1.69 × 104 | *** |
| month | NO2_diss | 2.12 × 1016 | 1.13 × 1015 | *** | 1.32 × 1010 | 5.27 × 1010 | *** |
| month | NO3_diss | 2.86 × 102 | 2.86 × 102 | * | 5.03 × 107 | 6.19 × 107 | *** |
| month | PO4_diss | 1.95 × 1013 | 7.78 × 1013 | *** | 1.76 × 108 | 4.01 × 108 | *** |
| month | Ptot_diss | 6.59 × 108 | 2.11 × 107 | *** | 4.60 × 106 | 5.25 × 106 | *** |
| month | TOM | 5.27 × 105 | 9.36 × 105 | *** | 1.78 × 105 | 1.90 × 105 | *** |
| month | TMA | 4.07 × 106 | 9.31 × 106 | *** | 8.57 × 1010 | 2.74 × 109 | *** |
| month | TMB | 6.24 × 103 | 6.66 × 103 | ** | 2.60 × 107 | 3.47 × 107 | *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bashenkhaeva, M.; Yeletskaya, Y.; Tomberg, I.; Marchenkov, A.; Titova, L.; Galachyants, Y. Free-Living and Particle-Associated Microbial Communities of Lake Baikal Differ by Season and Nutrient Intake. Diversity 2023, 15, 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15040572
Bashenkhaeva M, Yeletskaya Y, Tomberg I, Marchenkov A, Titova L, Galachyants Y. Free-Living and Particle-Associated Microbial Communities of Lake Baikal Differ by Season and Nutrient Intake. Diversity. 2023; 15(4):572. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15040572
Chicago/Turabian StyleBashenkhaeva, Maria, Yelena Yeletskaya, Irina Tomberg, Artyom Marchenkov, Lubov Titova, and Yuri Galachyants. 2023. "Free-Living and Particle-Associated Microbial Communities of Lake Baikal Differ by Season and Nutrient Intake" Diversity 15, no. 4: 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15040572
APA StyleBashenkhaeva, M., Yeletskaya, Y., Tomberg, I., Marchenkov, A., Titova, L., & Galachyants, Y. (2023). Free-Living and Particle-Associated Microbial Communities of Lake Baikal Differ by Season and Nutrient Intake. Diversity, 15(4), 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15040572






