Foraging Resource Partitioning in the California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus) from the Southwestern Gulf of California
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Sample Collection
- Shared priors
- : A regularizing normal distribution centered on each isotope’s mean and standard deviation (times 10).
- : A weakly informative exponential distribution.
- Group-level priors
- : A normal distribution centered on each isotope’s global mean with the global standard deviation.
- : Regularizing Half Cauchy distribution for the standard deviations of each isotope and category.
- : A shifted exponential distribution centered around 30, spreading the credibility across heavy and light-tailed (normal-like) distributions.
- Likelihood:
- : A Student t likelihood that assigns a higher probability to extreme values, thus making it useful for robust estimations of parameters [20].
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adame, F.K.; Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Beier, E.; Acevedo-Whitehouse, K.; Pardo, M. The Demographic Decline of a Sea Lion Population Followed Multi-Decadal Sea Surface Warming. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelayo-González, L.; González-Rodríguez, E.; Ramos-Rodríguez, A.; Hernández-Camacho, C.J. California Sea Lion Population Decline at the Southern Limit of Its Distribution During Warm Regimes in the Pacific Ocean. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 48, 102040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Sierra-Rodríguez, G.E.; Rosales-Nanduca, H.; Acevedo-Whitehouse, K.; Sandoval-Sierra, J. Impact of the 2015 El Niño-Southern Oscillation on the abundance and foraging habits of Guadalupe fur seals and California sea lions from the San Benito Archipelago, México. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolnick, D.I.; Amarasekare, P.; Araújo, M.S.; Bürger, R.; Levine, J.M.; Novak, M.; Rudolf, V.H.; Schreiber, S.J.; Urban, M.C.; Vasseur, D.A. Why Intraspecific Trait Variation Matters in Community Ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernaléguen, L.; Arnould, J.P.Y.; Guinet, C.; Cazelles, B.; Richard, P.; Cherel, Y. Early-Life Sexual Segregation: Ontogeny of Isotopic Niche Differentiation in the Antarctic Fur Seal. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Vallejo, R.A.; Amador-Capitanachi, M.J.; Norris, T.; Hernández-Camacho, C.J.; Tripp-Valdez, A.; Moncayo-Estrada, R.; Herguera-García, J.C.; Godard-Codding, C.; Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R. Foraging Segregation by Sex and Age Class in the Guadalupe Fur Seal from Guadalupe Island, Mexico. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2024, 40, e13076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, A.; Cervantes-Duarte, R.; Reyes-Salinas, A.; Valdez-Holguín, J.E. Cambio Estacional de Clorofila a En La Bahía de La Paz, b.c.s., México. Hidrobiológica 2001, 11, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, M.A.; Silverberg, N.; Gendron, D.; Beier, E.; Palacios, D.M. Role of Environmental Seasonality in the Turnover of a Cetacean Community in the Southwestern Gulf of California. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 487, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, F.J. Ecología Alimentaria del lobo Marino de California, Zalophus californianus californianus, en Los Islotes, B.C.S. Mexico [Feeding Ecology of the California Sea Lion, Zalophus californianus californianus, in Los Islotes, B.C.S., Mexico]. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Sur (UABCS), La Paz, Mexico, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Camacho, C.J.; Pelayo-González, L.; Rosas-Hernández, M.P. California sea lion (Zalophus californianus, Lesson 1828). In Ecology and Conservation of Pinnipeds in Latin America; Hekel, G., Schramm, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 119–143. [Google Scholar]
- Porras-Peters, H.; Aurioles-Gamboa, D.; Cruz-Escalona, V.H.; Koch, P.L. Trophic Level and Overlap of Sea Lions (Zalophus Californianus) in the Gulf of California, Mexico. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2008, 24, 554–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, P.J.N. Natural Variations in δ15N in the Marine Environment. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1987, 24, 389–451. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, E.; Hattori, A. Nitrogen in the Sea: Forms, Abundances and Rate Processes; CSC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hobson, K.A.; Piatt, J.F.; Pitocchelli, J. Using Stable Isotopes to Determine Seabird Trophic Relationships. J. Anim. Ecol. 1994, 63, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, S.D.; Martinez del Rio, C.; Bearhop, S.; Phillips, D.L. A Niche for Isotopic Ecology. Front. Ecol. 2007, 5, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador-Capitanachi, M.J.; Moreno-Sánchez, X.G.; Juárez-Ruiz, A.; Ferretto, G.; Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R. Trophic Variation Between the Two Existing Guadalupe Fur Seal Colonies on Guadalupe Island and the San Benito Archipielago, México. Aquat. Mamm. 2017, 43, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinone, S.G. A Three-Dimensional Model of the Mean and Seasonal Circulation of the Gulf of California. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108, C10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBoeuf, B.J.; Aurioles-Gamboa, D.; Condit, R.; Fox, C.; Gisinner, R.; Romero, R.; Sinsel, F. Size and Distribution of the California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus) Population in México. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 1983, 43, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- DeNiro, J.M.; Epstein, S. Influence of Diet on the Distribution of Carbon Isotopes in Animals. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1978, 42, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruschke, J.K. Bayesian Estimation Supersedes the t Test. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2013, 142, 573–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Schoot, R.; Depaoli, S.; King, R.; Kramer, B.; Märtens, K.; Tadesse, M.G.; Vannucci, M.; Gelman, A.; Veen, D.; Willemsen, J.; et al. Bayesian Statistics and Modelling. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Hwang, J.; Vehtari, A. Understanding Predictive Information Criteria for Bayesian Models. Stat. Comput. 2014, 24, 997–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatier, J.; Wiecki, T.V.; Fonnesbeck, C. Probabilistic programming in Python using PyMC3. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2016, 2, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril-Pla, O.; Andreani, V.; Carroll, C.; Dong, L.; Fonnesbeck, C.J.; Kochurov, M.; Kumar, R.; Lao, J.; Luhmann, C.C.; Martin, O.A.; et al. PyMC: A Modern, and Comprehensive Probabilistic Programming Framework in Python. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rossum, G.; Drake, F.L. Python 3 Reference Manual; CreateSpace: Scotts Valley, CA, USA, 2009; ISBN 1441412697. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, M.D.; Gelman, A. The No-u-Turn Sampler: Adaptively Setting Path Lengths in Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1351–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, A.L.; Inger, R.; Parnell, A.C.; Bearhop, S. Comparing Isotopic Niche Widths Among and Within Communities: SIBER-Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 34, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Betancourt, M. A conceptual introduction to Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.02434. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Orr, A.J.; VanBlaricom, G.R.; DeLong, R.L.; Cruz-Escalona, V.H.; Newsome, S.D. Intraspecific Comparison of Diet of California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus), Assessed Using Fecal and Stable Isotope Analyses. Can. J. Zool. 2011, 89, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Aguilar, M.; Aurioles-Gamboa, D. Cuidado materno en el lobo marino de California (Zalophus californianus) de Los Islotes, Golfo de California, México. Cienc. Mar. 2003, 29, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, C.E.; Aurioles-Gamboa, D.; Costa, D.P. Habitat utilization, diving and foraging behavior of adult female California sea lions (Zalophus californianus). In Proceedings of the XXIX Reunión Internacional para el Estudio de los Mamíferos Marinos, SOMEMMA A.C., La Paz, Mexico, 2–5 May 2004; p. 78. [Google Scholar]
- Altabet, M.A.; Pilskaln, C.; Thunell, R.; Pride, C.; Sigman, D.; Chávez, F.; Francois, R. The Nitrogen Isotope Biogeochemistry of Sinking Particles from the Margin of the Eastern North Pacific. Deep Sea Res. I 1999, 46, 655–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurioles-Gamboa, D.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.Y.; Sánchez-Velasco, L.; Lavín, M.F. Habitat, Trophic Level and Residence of Marine Mammals in the Gulf of California Assessed by Stable Isotope Analysis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 488, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Sandoval-Sierra, J.; Paniagua-Mendoza, A.; Robles, R. Seasonality and potential foraging grounds of migratory California sea lions from La Paz Bay, Southern Gulf of California, Mexico. Aquat. Mamm. 2018, 44, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Aurioles-Gamboa, D.; Newsome, S.D.; Díaz, S. δ15N and δ13C Values in Dental Collagen as a Proxy for Sex and Age Variation in Foraging Strategies of California Sea Lions. Mar. Biol. 2013, 160, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, M.J.; Costa, D.P. Total Body Oxygen Stores and Physiological Diving Capacity of California Sea Lions as a Function of Sex and Age. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, C.E.; Aurioles-Gamboa, D.; Weise, M.J.; Costa, D.P. Oxygen Stores of California Sea Lion Pups: Implications for Diving Ability. In Sea Lions of the World; Trites, A.W., Atkinson, S.K., DeMaster, D.P., Fritz, L.W., Gelatt, T.S., Rea, L.D., Wynne, K.M., Eds.; Alaska Sea Grant College Program AK-SG-06-01; University of Alaska: Fairbanks, AK, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R. Variación de δ15N y δ13C en Colágeno Dental de lobos Marinos del Género Zalophus: Patrones Ontogénicos y Geográficos [δ15N and δ13C Variation in Dental Collagen of Zalophus Sea Lions: Ontogenetic and Geographic Patterns]. Master’s Thesis, Centro Interdisciplinario de Ciencias Marinas (CICIMAR-IPN), La Paz, Mexico, 2009; p. 163. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista, V.A. Alimentación del Lobo Marino de California (Zalophus californianus californianus, Lesson 1828) y su Relación con los Pelágicos Menores en Bahía Magdalena, B.C.S., México. [Diet of the California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus californianus, Lesson 1828) and Its Relationship with Small Pelagics in Magdalena Bay, B.C.S., Mexico]. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM), Mexico City, Mexico, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kurle, C.M.; Worthy, G.A.J. Stable Isotope Assessment of Temporal and Geographic Differences in Feeding Ecology of Northern Fur Seals (Callorhinus Ursinus) and Their Prey. Oecologia 2001, 126, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Juárez-Ruiz, A.; Aquino-Baleyto, M.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Aguíñiga-García, S. Isotopic Variation Between Adult Female Guadalupe Fur Seals and Their Offspring: Implications for the Use of Neonates as Proxies for Maternal Foraging. Aquat. Mamm. 2016, 42, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, S.D.; Koch, P.L.; Etnier, M.A.; Aurioles-Gamboa, D. Using Carbon and Nitrogen Isotope Values to Investigate Maternal Strategies in Northeast Pacific Otariids. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2006, 22, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horning, M.; Trilmich, F. Ontogeny of Diving Behavior in the Galápagos Fur Seal. Behaviour 1997, 134, 1211–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, B.; McKenzie, J.; Sumner, M.D.; Coyne, M.; Goldsworthy, S.D. Spatial Separation of Foraging Habitats Among New Zealand Fur Seals. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 323, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppelin, T.K.; Orr, A.J. Stable Isotope Scat Analyses Indicate Diet and Habitat Partitioning in Northern Fur Seals Callorhinus Ursinus Across the Eastern Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 409, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

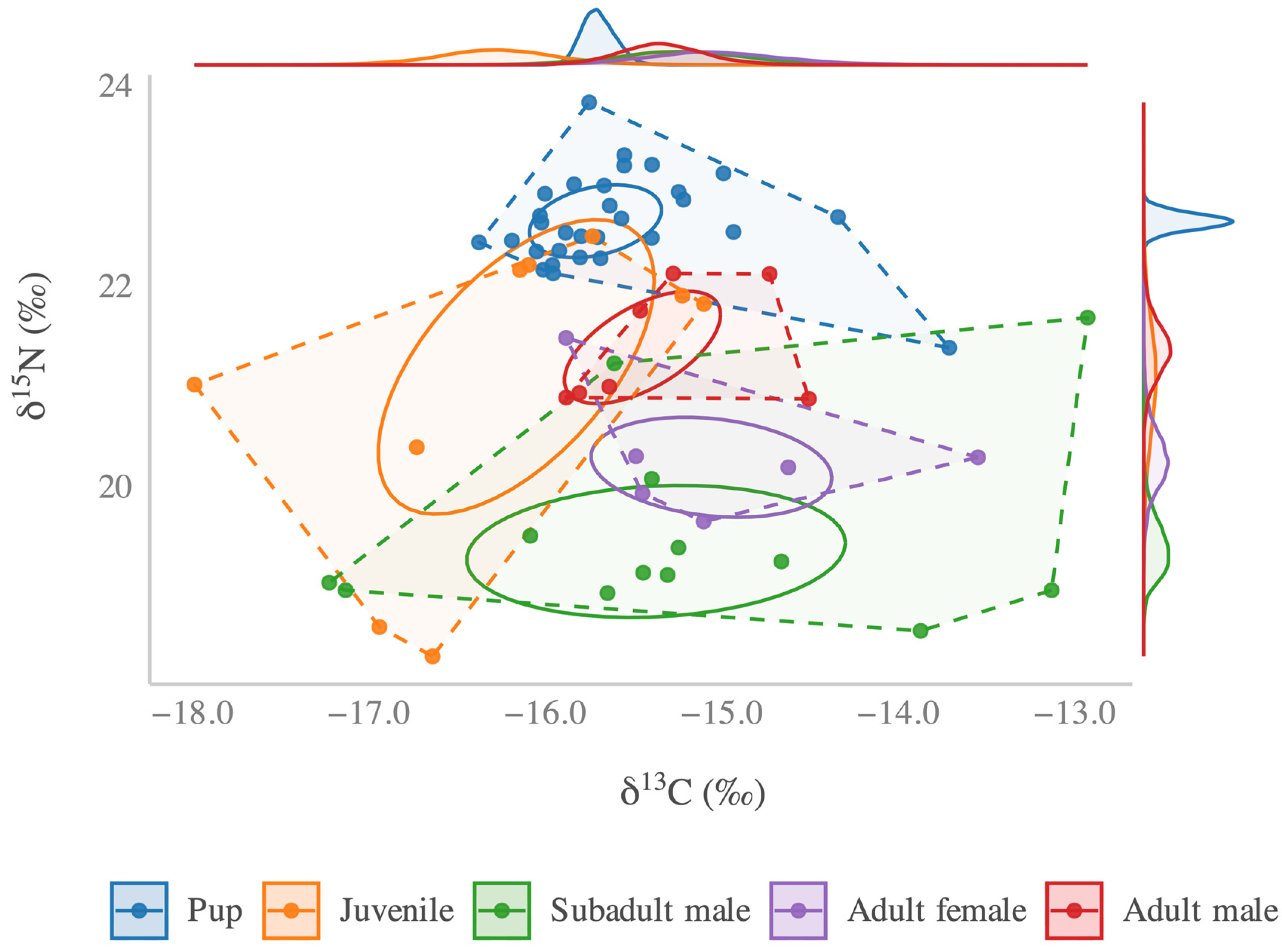

| Class | n | δ13C (‰) | δ15N (‰) | TA (‰2) | (‰2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pups | 30 | −15.7; [−15.9, −15.5] | 22.7; [22.5, 22.8] | 2.9 | 0.8; [0.5, 1.1] |
| Juveniles | 9 | −16.3; [−17.0, −15.5] | 21.1; [19.8, 22.3] | 5.9 | 4.5; [1.9, 7.8] |
| Subadult males | 13 | −15.2; [−16.1, −14.4] | 19.4; [18.9, 20.0] | 9.1 | 4.0; [2.0, 6.4] |
| Adult females | 6 | −15.1; [−16.1, −14.1] | 20.3; [19.6, 21.0] | 1.9 | 1.9; [0.6, 3.7] |
| Adult males | 7 | −14.3; [−15.9, −14.8] | 21.4; [20.8, 22.0] | 1.2 | 1.1; [0.4, 2.0] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R.; Enríquez-García, A.B.; Cruz-Vallejo, R.A. Foraging Resource Partitioning in the California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus) from the Southwestern Gulf of California. Diversity 2025, 17, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030166
Elorriaga-Verplancken FR, Enríquez-García AB, Cruz-Vallejo RA. Foraging Resource Partitioning in the California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus) from the Southwestern Gulf of California. Diversity. 2025; 17(3):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030166
Chicago/Turabian StyleElorriaga-Verplancken, Fernando R., Arturo B. Enríquez-García, and Romyna A. Cruz-Vallejo. 2025. "Foraging Resource Partitioning in the California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus) from the Southwestern Gulf of California" Diversity 17, no. 3: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030166
APA StyleElorriaga-Verplancken, F. R., Enríquez-García, A. B., & Cruz-Vallejo, R. A. (2025). Foraging Resource Partitioning in the California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus) from the Southwestern Gulf of California. Diversity, 17(3), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030166






