Allelopathic Impact of Erigeron canadensis and Erigeron annuus on Major Crop Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Test Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Aqueous Extracts of Erigeron canadensis and Erigeron annuus
2.2.2. Seed Germination and Seedling Growth Experiments
2.2.3. Measurement of Growth Indicators
number of seeds) × 100% (G3: the number of seeds germinated within
3 days)
+ [(number of germinated seeds on the final count)/(day of the final count)]
treatment value)
2.2.4. Statistics and Analysis of Data
3. Results and Analyses
3.1. Effect of Aqueous Extracts of Erigeron canadensis and Erigeron annuus on Seed Germination of Three Major Crops
3.1.1. Germination Rate
3.1.2. Germination Index
3.1.3. Germination Potential
3.2. Effect of Aqueous Extracts of Erigeron canadensis and Erigeron annuus on Seedling Growth of Three Major Grain Seeds
3.3. Index of the Chemosensory Effect of Erigeron canadensis and Erigeron annuus Extracts on Seedling Growth of Different Grain Seeds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, B.X.; Sun, Y.F.; Han, Z.H.; Huang, H.K.; Zhang, H.B.; Li, Y.K.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, W.X. Current status, problems and countermeasures of prevention and control of invasive alien species in China. J. Biosaf. 2020, 29, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.F.; Han, Y.X.; Wu, Q.M.; Wang, R.; Lin, K.J. Current Status and Control Suggestions of Alien Invasive Species in Grasslands of China. Plant Prot. 2022, 48, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kalisz, S.; Kivlin, N.S.; Bialic-Murphy, L. Allelopathy is pervasive in invasive plants. Biol. Invasions 2020, 23, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaplata, K.M.; Winter, S.; Biemelt, D.; Fischer, A. Immediate shift towards source dynamics: The pioneer species Conyza canadensis in an initial ecosystem. Flora 2011, 206, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parepa, M.; Bossdorf, O. Testing for allelopathy in invasive plants: It all depends on the substrate! Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 2975–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, W.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, H.; Ju, R.; Sun, Y.; Ding, J. Recent important research progress in plant invasion ecology in the past decade. Biodiversity 2022, 30, 276–292. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, H.; Song, X.; Fan, Z. Research progress on the distribution and invasion ability of invasive alien plants in China. Ecol. Environ. J. 2012, 21, 977–985. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Li, B. Research progress on biological invasions in China in the past decade. Biodivers. Sci. 2012, 20, 581–611. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Deng, B.; Xie, X.; Chang, N.; Ning, J.; Yang, X. Relationship between extracellular enzyme activity of thermotolerant germination fungi and seed germination of Gastrodia elata. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2022, 50, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, M. Effects of allelopathy on seed germination and seedling growth of Codonopsis tangshen. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2022, 54, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Wu, X.; Zheng, F.; Fan, Z.; Wu, R.; Xu, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, S.; Shen, S. Allelopathic effects of water extract from Spilanthes paniculata on seed germination and seedling growth of four weed species. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2023, 31, 3759–3767. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Cao, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhong, Q. Current situation and control strategies of invasive alien plants in the grasslands of Northeast China. Pratacultural Sci. 2016, 33, 2485–2493. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.S.; Li, H.R. Catalogue of Invasive Alien Plants in China; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Cheng, Z. Corrigendum: Research Progress on the Use of Plant Allelopathy in Agriculture and the Physiological and Ecological Mechanisms of Allelopathy. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Wu, H.; Qiang, S. Germination ability and seedling establishment characteristics of seeds (achenes) of some invasive Asteraceae species. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 1851–1856. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R. Reconstruction of the Invasion and Diffusion History of Seriously Threatening Invasive Alien Plants in China and Prediction of Their Potential Distribution Areas. Ph.D. Thesis, Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Botany), Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.C.; Pang, W.H.; Zhang, L.; Wen, Z.Z.; Zhao, Y.R.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yang, C. Effects of autotoxicity and allelopathy on seed germination and seedling growth in Medicago truncatula. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 908426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Wang, M.; Zhao, K.; Guo, S.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, K. Allelopathic effects of Ligularia virgaurea aqueous extracts on forage grasses. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 17, 845–850. [Google Scholar]
- Sturz, A.; Kimpinski, J. Endoroot bacteria derived from marigolds (Tagetes spp.) can decrease soil population densities of root-lesion nematodes in the potato root zone. Plant Soil 2004, 262, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, M.; Zhou, T.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Dong, Z. Allelopathic effects of Rabdosia serra (Maxim.) Hara extracts on seed germination and seedling growth of two weeds. J. Grassl. Sci. 2024, 32, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar]
- Narwal, S.; Kadian, H.S. Allelopathic potential of legumes for weed management in sustainable agriculture. Indian J. Pulses Res. 2001, 14, 90–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Liu, Z.; Fan, X.; Chen, C.; Qian, J. Allelopathic effects of fallen leaf extracts from greening trees on five herbaceous plants. J. Grassl. Sci. 2020, 28, 976–982. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z. Allelopathic effects of litter from four coniferous pure forests on three leguminous shrubs. Grassl. Sci. 2013, 30, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Yi, Y.; Zhu, X. Research Progress on Invasive Weed Erigeron annuus. J. Weed Sci. 2020, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; He, S.; Zhang, J.; Jia, W.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Y. Allelopathic effects of Erigeron canadensis aqueous extracts on seed germination and seedling growth of two ornamental plants. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2023, 43, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Boena, E.R. Methodological contribution on seed germination and seedling initial growth tests in wild plants. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca 2023, 51, 13164. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Guo, J.; Han, L.; Qiu, N.; Zhou, F. Seed Germination Indices and Their Calculation Methods. J. Triticeae Crops 2023, 43, 190–196. [Google Scholar]
- Hafez, M.; Popov, A.I.; Rashad, M. Integrated use of bio-organic fertilizers for enhancing soil fertility–plant nutrition, germination status and initial growth of corn (Zea Mays L.). Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, A.M. A Comparison of Seed Germination Calculation Formulae and the Associated Interpretation of Resulting Data. J. Proc. R. Soc. New South Wales 2005, 138, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.B.; Richardson, D. Bioassays for Allelopathy—Measuring Treatment Responses with Independent Controls. J. Chem. Ecol. 1988, 14, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, H. Extraction and GC-MS Analysis of Essential Oil from Conyza canadensis. Chin. Wild Plant Resour. 2011, 30, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, S.; Shen, G. Allelopathic Effects of the Invasive Species Erigeron philadelphicus and GC-MS Analysis of Its Crude Extracts. Acta Agric. Shanghai 2009, 25, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhong, S.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C.; Du, D. The co-phytotoxicity of two Asteraceae invasive plants Solidago canadensis L. and Bidens pilosa L. with different invasion degrees. Ecotoxicology 2023, 32, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Guo, M.; Peng, Y.Q.; Jin, C.Z.; Zhang, X.J.; Hu, Y.H.; Chen, G.; Gong, Y.H. Characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of the chloroplast genome of Erigeron annuus. Trop. Crops Res. 2023, 44, 689–698. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Han, M.; Xiao, C.P.; Yang, L.M. Study on the allelopathic potential and mechanism of the invasive species Erigeron canadensis on corn. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2011, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C. A review of bioassay methods in allelopathy research. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 1999, 10, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Balah Mohamed, A.; Al Andal, A.; Radwan Asmaa, M.; Donia Abd ElRaheim, M. Unveiling allelopathic dynamics and impacts of invasive Erigeron bonariensis and Bidens pilosa on plant communities and soil parameters. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10159. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, A.; Žlabur, J.Š.; Šurić, J.; Voća, S.; Purgar, D.D.; Pezo, L.; Voća, N. Invasive Plant Species Biomass—Evaluation of Functional Value. Molecules 2021, 26, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.B.; He, A.F.; Wu, H.F.; Wang, P.; Yu, N.J.; Xie, D.M. Allelopathic effects of invasive Xanthium species and native Xanthium in the Xanthium genus. Seeds 2018, 37, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.L.; Wu, J.W.; Yao, S.K.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhao, X.C.; He, F.M.; Zhu, Y.F.; Shi, Q.H.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y.Q. Allelopathic effects of water extracts from different parts of Iva xanthifolia on five indigenous plants. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2020, 29, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.H. Development and Application of Novel Herbicides in Wheat Fields; Shandong Binong Technology Co., Ltd.: Shandong, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Marianna, B.K.; Joanna, P.; Hanna, B. Allelopathy as a source of bioherbicides: Challenges and prospects for sustainable agriculture. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2023, 22, 471–504. [Google Scholar]
- Le, V.V.; Nguyen, A.V.; Luu, D.T.; Fritschi, F.B.; Nguyen, C.T.; Ho, T.L. Inhibitory effects of N-trans-cinnamoyltyramine on the growth of invasive weeds and weedy rice. Plant-Environ. Interact. 2024, 5, e70017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.; Tabaglio, V. Allelopathy: Mechanisms and Applications in Regenerative Agriculture. Plants 2024, 13, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Shen, K.; Jia, T.; Xia, T.Y.; Jiang, Z.L. Ecological impacts of the invasive plant Tithonia diversifolia on invaded habitats and its control strategies. J. Biosecur. 2024, 33, 7–11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Yan, S.; Huang, X.; Jin, Z.; Yan, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Yin, J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Q. Impacts of the Integrated Management of Invasive Weeds and Litter on Slope Hydrology in Eucalyptus Plantations in Central Yunnan, Southwest China. Forests 2024, 15, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.R.; Lin, J.; Li, X. Monitoring and control strategies for the invasive plants Ambrosia artemisiifolia and Ambrosia trifida in Xinjiang grasslands. Xinjiang For. 2024, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Revillini, D.; David, A.S.; Reyes, A.L.; Knecht, L.D.; Vigo, C.; Allen, P.; Searcy, C.A.; Afkhami, M.E. Allelopathy-selected microbiomes mitigate chemical inhibition of plant performance. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 2007–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anibaba, Q.A.; Dyderski, M.K.; Woźniak, G.; Jagodziński, A.M. Native plant community characteristics explain alien species success in post-industrial vegetation. NeoBiota 2023, 85, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, W.; Shen, W.; Xiong, F.; Wang, K. Allelochemicals Released from Rice Straw Inhibit Wheat Seed Germination and Seedling Growth. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
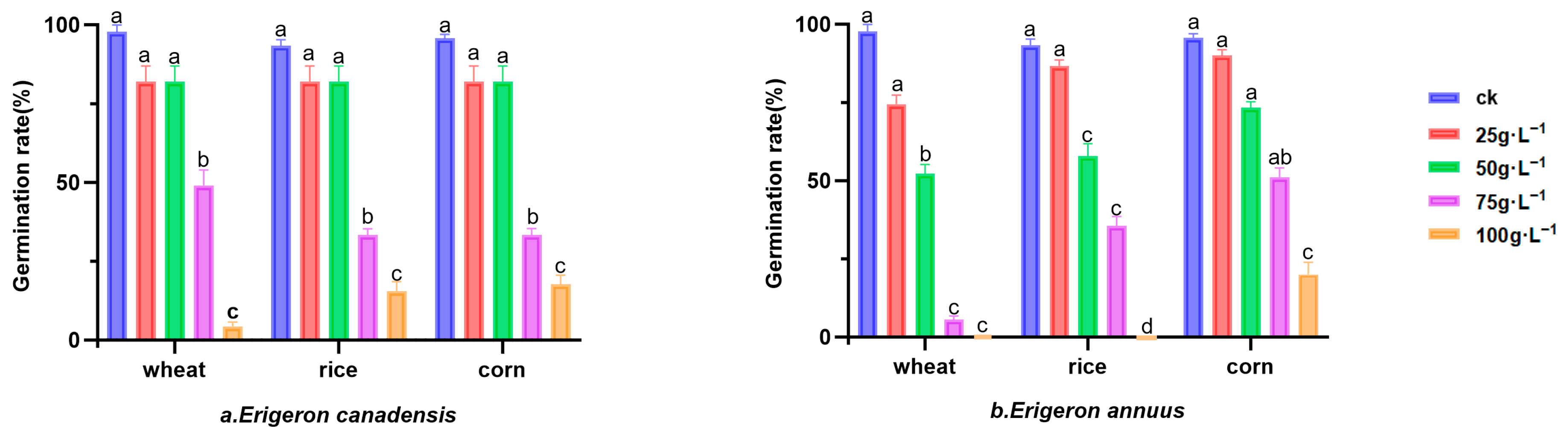
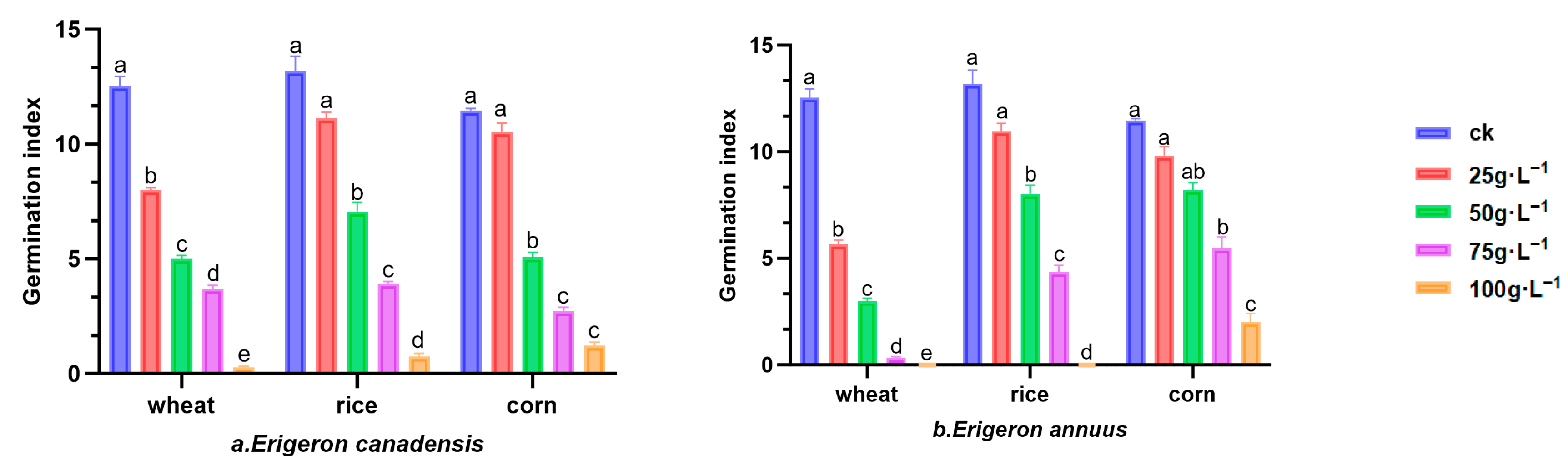


| Parametric | Species | Factor | p-Value | df | ms | f (dfn, dfd) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germination Rate | Erigeron canadensis | species | 0.5434 | 2 | 11.85 | f (1.017, 2.034) = 0.5323 | |
| concentration | 0.0050 | 4 | 11,084 | f (1.085, 2.171) = 143.5 | |||
| species×concentration | 0.0549 | 8 | 100.6 | f (1.580, 3.160) = 8.513 | |||
| Erigeron annuus | species | 0.0142 | 2 | 1512 | f (1.000, 2.000) = 68.88 | ||
| concentration | <0.0001 | 4 | 12,222 | f (1.494, 2.988) = 800.9 | |||
| species×concentration | 0.0248 | 8 | 267.9 | f (1.609, 3.218) = 14.79 |
| Parametric | Species | Factor | p-Value | df | ms | f (dfn, dfd) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germination Index | Erigeron canadensis | species | 0.0230 | 2 | 7.079 | f (1.097, 2.194) = 33.41 |
| concentration | <0.0001 | 4 | 200.8 | f (1.806, 3.612) = 684.4 | ||
| species×concentration | 0.0587 | 8 | 2.399 | f (1.131, 2.263) = 12.70 | ||
| Erigeron annuus | species | 0.0003 | 2 | 46.33 | f (1.529, 3.058) = 290.8 | |
| concentration | 0.0008 | 4 | 188.5 | f (1.302, 2.604) = 326.6 | ||
| species×concentration | 0.0149 | 8 | 7.864 | f (1.483, 2.966) = 24.74 |
| Parametric | Species | Factor | p-Value | df | ms | f (dfn, dfd) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germination Potential | Erigeron canadensis | species | 0.0260 | 2 | 81.73 | f (1.047, 2.093) = 33.09 |
| concentration | 0.0004 | 4 | 9650 | f (1.225, 2.449) = 744.1 | ||
| species×concentration | 0.2583 | 8 | 88.51 | f (1.098, 2.195) = 2.360 | ||
| Erigeron annuus | species | 0.0051 | 2 | 2042 | f (1.038, 2.077) = 166.9 | |
| concentration | 0.0032 | 4 | 7381 | f (1.134, 2.267) = 183.4 | ||
| species×concentration | 0.0387 | 8 | 461.3 | f (1.503, 3.006) = 11.90 |
| Species | Items | Concentration g·L−1 | Test Seeds | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Rice | Corn | |||
| Erigeron canadensis | Germination rate RI | 25 | −0.159 ± 0.049 | −0.128 ± 0.032 | −0.076 ± 0.054 |
| 50 | −0.364 ± 0.030 | −0.403 ± 0.032 | −0.378 ± 0.094 | ||
| 75 | −0.500 ± 0.049 | −0.642 ± 0.021 | −0.609 ± 0.063 | ||
| 100 | −0.955 ± 0.011 | −0.833 ± 0.032 | −0.769 ± 0.047 | ||
| Germination index RI | 25 | −0.36 ± 0.008 | −0.043 ± 0.023 | −0.067 ± 0.017 | |
| 50 | −0.60 ± 0.012 | −0.392 ± 0.034 | −0.464 ± 0.104 | ||
| 75 | −0.70 ± 0.012 | −0.663 ± 0.008 | −0.757 ± 0.045 | ||
| 100 | −0.98 ± 0.006 | −0.935 ± 0.011 | −0.859 ± 0.037 | ||
| Germination potential RI | 25 | −0.295 ± 0.012 | −0.273 ± 0.026 | −0.067 ± 0.026 | |
| 50 | −0.705 ± 0.012 | −0.576 ± 0.040 | −0.456 ± 0.118 | ||
| 75 | −0.897 ± 0.025 | −0.818 ± 0.026 | −0.822 ± 0.031 | ||
| 100 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −0.900 ± 0.042 | ||
| Root length RI | 25 | 0.188 ± 0.011 | −0.200 ± 0.013 | −0.431 ± 0.044 | |
| 50 | −0.436 ± 0.008 | −0.381 ± 0.009 | −0.576 ± 0.020 | ||
| 75 | −0.547 ± 0.014 | −0.445 ± 0.009 | −0.871 ± 0.006 | ||
| 100 | −0.719 ± 0.021 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −0.877 ± 0.003 | ||
| Stem length RI | 25 | −0.218 ± 0.038 | −0.414 ± 0.013 | −0.412 ± 0.006 | |
| 50 | −0.427 ± 0.022 | −0.627 ± 0.021 | −0.691 ± 0.009 | ||
| 75 | −0.542 ± 0.008 | −0.816 ± 0.010 | −0.730 ± 0.013 | ||
| 100 | −0.708 ± 0.006 | −0.963 ± 0.011 | −0.886 ± 0.010 | ||
| Synthetical allelopathic index RI | 25 | −0.160 ± 0.008 | −0.095 ± 0.016 | −0.096 ± 0.023 | |
| 50 | −0.553 ± 0.006 | −0.437 ± 0.021 | −0.378 ± 0.089 | ||
| 75 | −0.711 ± 0.004 | −0.687 ± 0.002 | −0.681 ± 0.052 | ||
| 100 | −0.920 ± 0.008 | −0.927 ± 0.009 | −0.796 ± 0.034 | ||
| Erigeron annuus | Germination rate RI | 25 | −0.239 ± 0.030 | −0.068 ± 0.021 | −0.022 ± 0.023 |
| 50 | −0.466 ± 0.030 | −0.379 ± 0.043 | −0.245 ± 0.030 | ||
| 75 | −0.943 ± 0.011 | −0.618 ± 0.032 | −0.422 ± 0.039 | ||
| 100 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −0.813 ± 0.039 | ||
| Germination index RI | 25 | −0.549 ± 0.015 | −0.057 ± 0.031 | −0.135 ± 0.037 | |
| 50 | −0.761 ± 0.011 | −0.311 ± 0.035 | −0.295 ± 0.021 | ||
| 75 | −0.973 ± 0.004 | −0.625 ± 0.026 | −0.506 ± 0.042 | ||
| 100 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −0.843 ± 0.029 | ||
| Germination potential RI | 25 | −0.590 ± 0.013 | −0.303 ± 0.066 | −0.122 ± 0.049 | |
| 50 | −0.910 ± 0.013 | −0.424 ± 0.015 | −0.267 ± 0.046 | ||
| 75 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −0.727 ± 0.045 | −0.500 ± 0.049 | ||
| 100 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −0.833 ± 0.033 | ||
| Root length RI | 25 | −0.284 ± 0.009 | −0.687 ± 0.014 | −0.439 ± 0.035 | |
| 50 | −0.558 ± 0.034 | −0.911 ± 0.014 | −0.625 ± 0.009 | ||
| 75 | −0.817 ± 0.008 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −0.853 ± 0.006 | ||
| 100 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −0.926 ± 0.004 | ||
| Stem length RI | 25 | −0.403 ± 0.027 | −0.524 ± 0.015 | −0.263 ± 0.040 | |
| 50 | −0.645 ± 0.024 | −0.634 ± 0.016 | −0.732 ± 0.006 | ||
| 75 | −0.819 ± 0.024 | −0.946 ± 0.009 | −0.796 ± 0.009 | ||
| 100 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −0.915 ± 0.017 | ||
| Synthetical allelopathic index RI | 25 | −0.398 ± 0.014 | −0.194 ± 0.024 | −0.072 ± 0.025 | |
| 50 | −0.647 ± 0.017 | −0.397 ± 0.022 | −0.359 ± 0.016 | ||
| 75 | −0.930 ± 0.002 | −0.702 ± 0.021 | −0.582 ± 0.024 | ||
| 100 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −1.000 ± 0.000 | −0.850 ± 0.018 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Fu, S.; Wang, H.; Mu, L. Allelopathic Impact of Erigeron canadensis and Erigeron annuus on Major Crop Species. Diversity 2025, 17, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050318
Liu J, Liu X, Fu S, Wang H, Mu L. Allelopathic Impact of Erigeron canadensis and Erigeron annuus on Major Crop Species. Diversity. 2025; 17(5):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050318
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiale, Xu Liu, Shengjie Fu, Hongfeng Wang, and Liqiang Mu. 2025. "Allelopathic Impact of Erigeron canadensis and Erigeron annuus on Major Crop Species" Diversity 17, no. 5: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050318
APA StyleLiu, J., Liu, X., Fu, S., Wang, H., & Mu, L. (2025). Allelopathic Impact of Erigeron canadensis and Erigeron annuus on Major Crop Species. Diversity, 17(5), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17050318







