Drug Discovery for Histone Deacetylase Inhibition: Past, Present and Future of Zinc-Binding Groups
Abstract
1. Introduction
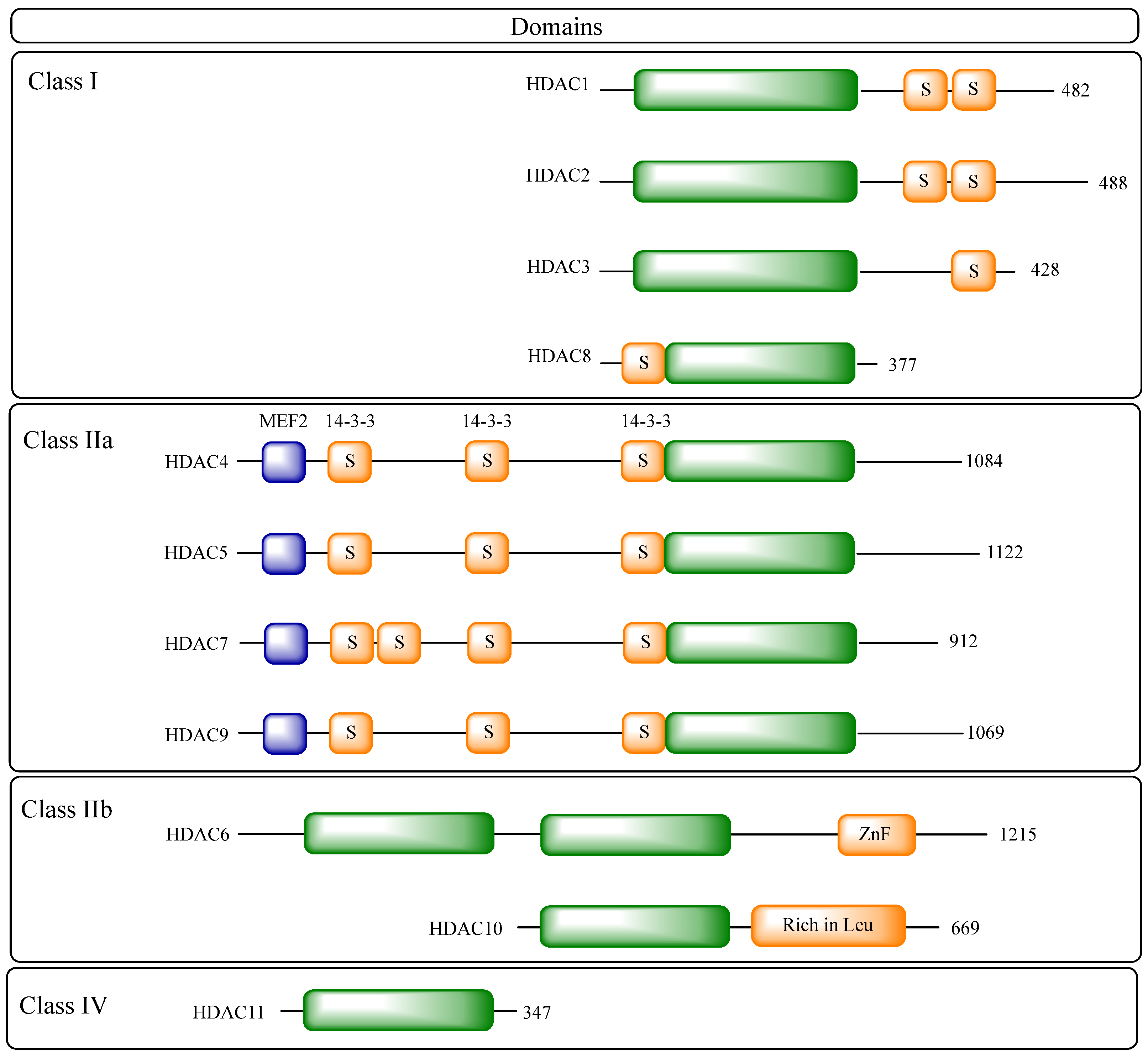
2. Histone Deacetylases
- Class I: including HDACs 1, 2, 3 and 8;
- Class IIa: including HDACs 4, 5, 7 and 9;
- Class IIb: including HDACs 6 and 10;
- Class III: including sirtuins 1–7;
2.1. HDACs as Therapeutic Targets
2.1.1. HDACs in the Context of Cancer
2.1.2. HDACs in the Context of Neurodegenerative Diseases
2.2. Structural Details of HDAC Isoforms
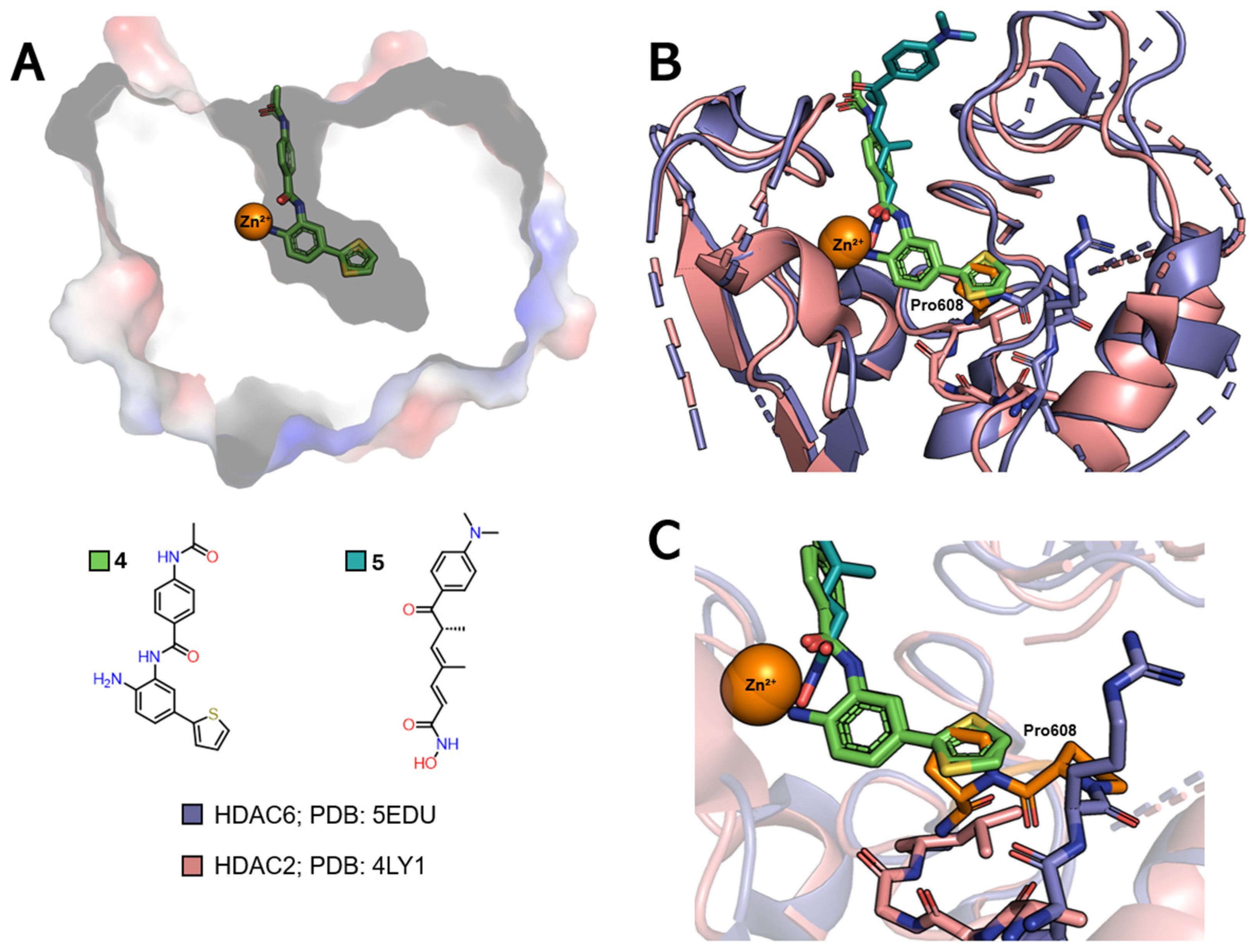
2.3. Initial Assessment of Selectivity
2.3.1. Selectivity for Class I
2.3.2. Selectivity for Class IIa
2.3.3. Selectivity for Class IIb
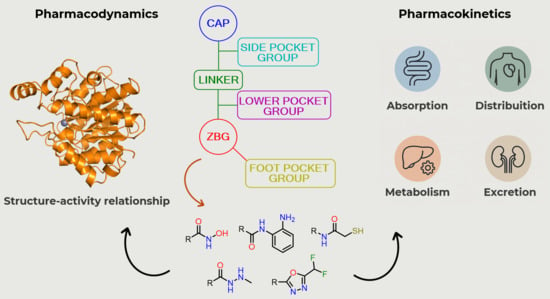
3. Structure–Activity Relationship of HDAC Inhibitors
3.1. Cap Group
3.2. Linker
3.3. Zinc-Binding Group (ZBG)
3.3.1. Hydroxamates
3.3.2. Ortho-aminoanilides
3.3.3. Mercaptoacetamides
3.3.4. Alkylhydrazides
3.3.5. 5-(Difluoromethyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole (DFMO)
4. Pharmacokinetic Profile
4.1. Hydroxamates Pharmacokinetic Profile
4.2. Non-Hydroxamates
4.2.1. Ortho-aminoanilides Pharmacokinetic Profile
4.2.2. Mercaptoacetamides Pharmacokinetic Profile
4.2.3. Alkylhydrazides Pharmacokinetic Profile
4.2.4. 5-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazole (TFMO) and 5-(Difluoromethyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole (DFMO) Pharmacokinetic Profile
5. HDACi Approved for Clinical Use
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waddington, C.H. The Epigenotype. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deans, C.; Maggert, K.A. What Do You Mean, “Epigenetic”? Genetics 2015, 199, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, P.; Cartron, P.-F.; Serandour, A.A.; Hervouet, E. From 1957 to Nowadays: A Brief History of Epigenetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, A.D.; Allis, C.D.; Bernstein, E. Epigenetics: A Landscape Takes Shape. Cell 2007, 128, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.L.; Kouzarides, T.; Shiekhattar, R.; Shilatifard, A. An Operational Definition of Epigenetics. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 781–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda Furtado, C.L.; Dos Santos Luciano, M.C.; Silva Santos, R.D.; Furtado, G.P.; Moraes, M.O.; Pessoa, C. Epidrugs: Targeting Epigenetic Marks in Cancer Treatment. Epigenetics 2019, 14, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachaiyappan, B.; Woster, P.M. Design of Small Molecule Epigenetic Modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushati, N.; Cohen, S.M. MicroRNA Functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X. The Roles of MicroRNAs in Epigenetic Regulation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 51, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, A.L.; Bailly, N.; Meissner, A. DNA Methylation: A Historical Perspective. Trends Genet. 2022, 38, 676–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA Methylation and Its Basic Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, A.M.; Bird, A. CpG Islands and the Regulation of Transcription. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornberg, R.D. Chromatin Structure: A Repeating Unit of Histones and DNA. Science 1974, 184, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luger, K.; Mäder, A.W.; Richmond, R.K.; Sargent, D.F.; Richmond, T.J. Crystal Structure of the Nucleosome Core Particle at 2.8 Å Resolution. Nature 1997, 389, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornberg, R.D.; Lorch, Y. Twenty-Five Years of the Nucleosome, Fundamental Particle of the Eukaryote Chromosome. Cell 1999, 98, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, M.; Kurumizaka, H. Structural Diversity of the Nucleosome. J. Biochem. 2018, 163, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glozak, M.A.; Seto, E. Histone Deacetylases and Cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5420–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzarides, T. Chromatin Modifications and Their Function. Cell 2007, 128, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, D.M.; Lee, S.N.; Sabat, K.A.; Baker, I.M.; Pham, T.K.; Collins, M.O.; Cowley, S.M. Rapid Degradation of Histone Deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) Reveals Essential Roles in Both Gene Repression and Active Transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, gkae1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, O.; Deubzer, H.E.; Milde, T.; Oehme, I. HDAC Family: What Are the Cancer Relevant Targets? Cancer Lett. 2009, 277, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenberg, K.J.; Johnstone, R.W. Histone Deacetylases and Their Inhibitors in Cancer, Neurological Diseases and Immune Disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melesina, J.; Simoben, C.V.; Praetorius, L.; Bülbül, E.F.; Robaa, D.; Sippl, W. Strategies To Design Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 1336–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.C.; Chan, A.H.; Ganesan, A. Thirty Years of HDAC Inhibitors: 2020 Insight and Hindsight. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12460–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, M.T.; Kozikowski, A.P.; Shen, S. Mercaptoacetamide: A Promising Zinc-Binding Group for the Discovery of Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 209, 112887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoretti, I.; Lee, Y.-M.; Goodson, H. V Molecular Evolution of the Histone Deacetylase Family: Functional Implications of Phylogenetic Analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.A.; Thota, S.; Fraga, C.A.M. Beyond the Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 6. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, P.d.S.M.; Rodrigues, D.A.; Sant’Anna, C.M.R.; Fraga, C.A.M. Modeling Zinc-oxygen Coordination in Histone Deacetylase: A Comparison of Semiempirical Methods Performance. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2018, 118, e25720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, F.; Mercurio, C. Towards Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase Isoforms: What Has Been Achieved, Where We Are and What Will Be Next. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropero, S.; Esteller, M. The Role of Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) in Human Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2007, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-J.; Seto, E. The Rpd3/Hda1 Family of Lysine Deacetylases: From Bacteria and Yeast to Mice and Men. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Kettmann, R.; Dequiedt, F. Class IIa Histone Deacetylases: Regulating the Regulators. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5450–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijter, A.J.D.; Gennip, A.H.V.; Caron, H.N.; Kemp, S.; Kuilenburg, A.B.V. Histone Deacetylases (HDACs): Characterization of the Classical HDAC Family. Biochem. J. 2003, 370, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbert, C.; Guardiola, A.; Shao, R.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Ito, A.; Nixon, A.; Yoshida, M.; Wang, X.-F.; Yao, T.-P. HDAC6 Is a Microtubule-Associated Deacetylase. Nature 2002, 417, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, J.J.; Murphy, P.J.M.; Gaillard, S.; Zhao, X.; Wu, J.-T.; Nicchitta, C.V.; Yoshida, M.; Toft, D.O.; Pratt, W.B.; Yao, T.-P. HDAC6 Regulates Hsp90 Acetylation and Chaperone-Dependent Activation of Glucocorticoid Receptor. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiech, H.; Buchner, J.; Zimmermann, R.; Jakob, U. Hsp90 Chaperones Protein Folding In Vitro. Nature 1992, 358, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.U.; Roe, S.M.; Vaughan, C.K.; Meyer, P.; Panaretou, B.; Piper, P.W.; Prodromou, C.; Pearl, L.H. Crystal Structure of an Hsp90–Nucleotide–P23/Sba1 Closed Chaperone Complex. Nature 2006, 440, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandinger, S.K.; Richter, K.; Buchner, J. The Hsp90 Chaperone Machinery. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 18473–18477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Soroka, J.; Buchner, J. The Hsp90 Chaperone Machinery: Conformational Dynamics and Regulation by Co-Chaperones. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Res. 2012, 1823, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyault, C.; Sadoul, K.; Pabion, M.; Khochbin, S. HDAC6, at the Crossroads between Cytoskeleton and Cell Signaling by Acetylation and Ubiquitination. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5468–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.J. Identification of HDAC10, a Novel Class II Human Histone Deacetylase Containing a Leucine-Rich Domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Cueto, M.A.; Asselbergs, F.; Atadja, P. Cloning and Functional Characterization of HDAC11, a Novel Member of the Human Histone Deacetylase Family. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25748–25755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, N.J.; Christianson, D.W. Structure, Mechanism, and Inhibition of the Zinc-Dependent Histone Deacetylases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 59, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutil, Z.; Novakova, Z.; Meleshin, M.; Mikesova, J.; Schutkowski, M.; Barinka, C. Histone Deacetylase 11 Is a Fatty-Acid Deacylase. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, V.D.; Kennedy, B.K. Sirtuins in Aging and Age-Related Disease. Cell 2006, 126, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniot, S.; Forgione, M.; Lucidi, A.; Hailu, G.S.; Nebbioso, A.; Carafa, V.; Baratta, F.; Altucci, L.; Giacché, N.; Passeri, D.; et al. Development of 1,2,4-Oxadiazoles as Potent and Selective Inhibitors of the Human Deacetylase Sirtuin 2: Structure–Activity Relationship, X-Ray Crystal Structure, and Anticancer Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2344–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwer, B.; Verdin, E. Conserved Metabolic Regulatory Functions of Sirtuins. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenkel, B.; Valente, S.; Zwergel, C.; Weiss, S.; Di Bello, E.; Fioravanti, R.; Aventaggiato, M.; Amorim, J.A.; Garg, N.; Kumar, S.; et al. Potent and Specific Activators for Mitochondrial Sirtuins Sirt3 and Sirt5. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 14015–14031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagunas-Rangel, F.A. SIRT7 in the Aging Process. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.A.; Denu, J.M. Biological and Catalytic Functions of Sirtuin 6 as Targets for Small-Molecule Modulators. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 11021–11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.; Olzscha, H.; La Thangue, N.B. HDAC Inhibitor-based Therapies: Can We Interpret the Code? Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Kuljaca, S.; Tee, A.; Marshall, G.M. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Multifunctional Anticancer Agents. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2006, 32, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epping, M.T.; Bernards, R. Molecular Basis of the Anti-Cancer Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botrugno, O.A.; Santoro, F.; Minucci, S. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as a New Weapon in the Arsenal of Differentiation Therapies of Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2009, 280, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarev, A.D.; Attwood, M.M.; Jonsson, J.; Chubarev, V.N.; Tarasov, V.V.; Schiöth, H.B. Recent Developments of HDAC Inhibitors: Emerging Indications and Novel Molecules. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 4577–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokmanovic, M.; Clarke, C.; Marks, P.A. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Overview and Perspectives. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolden, J.E.; Peart, M.J.; Johnstone, R.W. Anticancer Activities of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. The Development Prospection of HDAC Inhibitors as a Potential Therapeutic Direction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2017, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.G. Targeting Huntington’s Disease through Histone Deacetylases. Clin. Epigenet. 2011, 2, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Taliyan, R. Targeting Histone Deacetylases: A Novel Approach in Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Dis. 2015, 2015, 303294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraco, G.; Cavone, L.; Chiarugi, A. The Therapeutic Potential of HDAC Inhibitors in the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.A.; Pinheiro, P.d.S.M.; Sagrillo, F.S.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Fraga, C.A.M. Histone Deacetylases as Targets for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders: Challenges and Future Opportunities. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 2177–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenson, J.M.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Brown, K.D.; Trinh, M.A.; Molfese, D.L.; Sweatt, J.D. Regulation of Histone Acetylation during Memory Formation in the Hippocampus. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40545–40559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, S.; Sananbenesi, F.; Zovoilis, A.; Burkhardt, S.; Bahari-Javan, S.; Agis-Balboa, R.C.; Cota, P.; Wittnam, J.L.; Gogol-Doering, A.; Opitz, L.; et al. Altered Histone Acetylation Is Associated with Age-Dependent Memory Impairment in Mice. Science 2010, 328, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Sananbenesi, F.; Wang, X.; Dobbin, M.; Tsai, L.-H. Recovery of Learning and Memory Is Associated with Chromatin Remodelling. Nature 2007, 447, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelucchi, S.; Stringhi, R.; Marcello, E. Dendritic Spines in Alzheimer’s Disease: How the Actin Cytoskeleton Contributes to Synaptic Failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.-S.; Haggarty, S.J.; Giacometti, E.; Dannenberg, J.-H.; Joseph, N.; Gao, J.; Nieland, T.J.F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Mazitschek, R.; et al. HDAC2 Negatively Regulates Memory Formation and Synaptic Plasticity. Nature 2009, 459, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecsey, C.G.; Hawk, J.D.; Lattal, K.M.; Stein, J.M.; Fabian, S.A.; Attner, M.A.; Cabrera, S.M.; McDonough, C.B.; Brindle, P.K.; Abel, T.; et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Enhance Memory and Synaptic Plasticity via CREB: CBP-Dependent Transcriptional Activation. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 6128–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fass, D.M.; Butler, J.E.F.; Goodman, R.H. Deacetylase Activity Is Required for CAMP Activation of a Subset of CREB Target Genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 43014–43019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, C.; Gendron, T.F.; Scheffel, K.; Carlomagno, Y.; Dunmore, J.; DeTure, M.; Petrucelli, L. Loss of HDAC6, a Novel CHIP Substrate, Alleviates Abnormal Tau Accumulation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 2936–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlomagno, Y.; Chung, D.C.; Yue, M.; Castanedes-Casey, M.; Madden, B.J.; Dunmore, J.; Tong, J.; DeTure, M.; Dickson, D.W.; Petrucelli, L.; et al. An Acetylation–Phosphorylation Switch That Regulates Tau Aggregation Propensity and Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15277–15286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Tao, J.; Sui, X.; Yao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhu, H.; Sheng, S.; et al. Tubastatin A/ACY-1215 Improves Cognition in Alzheimer’s Disease Transgenic Mice. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 41, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões-Pires, C.; Zwick, V.; Nurisso, A.; Schenker, E.; Carrupt, P.-A.; Cuendet, M. HDAC6 as a Target for Neurodegenerative Diseases: What Makes It Different from the Other HDACs? Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, P.; Pranpat, M.; Bradner, J.; Balasis, M.; Fiskus, W.; Guo, F.; Rocha, K.; Kumaraswamy, S.; Boyapalle, S.; Atadja, P.; et al. Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 6 Acetylates and Disrupts the Chaperone Function of Heat Shock Protein 90. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26729–26734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, M. Structural Biology of Human Metal-Dependent Histone Deacetylases. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Studium Press (India) Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2011; pp. 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, P.M.; Cole, K.E.; Dowling, D.P.; Christianson, D.W. Structure, Mechanism, and Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases and Related Metalloenzymes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2011, 21, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, D.P.; Gattis, S.G.; Fierke, C.A.; Christianson, D.W. Structures of Metal-Substituted Human Histone Deacetylase 8 Provide Mechanistic Inferences on Biological Function. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 5048–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberland, M.; Montgomery, R.L.; Olson, E.N. The Many Roles of Histone Deacetylases in Development and Physiology: Implications for Disease and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, K.V.; Kalin, J.; Brochier, C.; Vistoli, G.; Langley, B.; Kozikowski, A.P. Rational Design and Simple Chemistry Yield a Superior, Neuroprotective HDAC6 Inhibitor, Tubastatin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10842–10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.A.; Witter, D.J.; Belvedere, S. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 5097–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckhurst, C.A.; Breccia, P.; Stott, A.J.; Aziz, O.; Birch, H.L.; Bürli, R.W.; Hughes, S.J.; Jarvis, R.E.; Lamers, M.; Leonard, P.M.; et al. Potent, Selective, and CNS-Penetrant Tetrasubstituted Cyclopropane Class IIa Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauffer, B.E.L.; Mintzer, R.; Fong, R.; Mukund, S.; Tam, C.; Zilberleyb, I.; Flicke, B.; Ritscher, A.; Fedorowicz, G.; Vallero, R.; et al. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitor Kinetic Rate Constants Correlate with Cellular Histone Acetylation but Not Transcription and Cell Viability. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26926–26943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimburg, T.; Chakrabarti, A.; Lancelot, J.; Marek, M.; Melesina, J.; Hauser, A.-T.; Shaik, T.B.; Duclaud, S.; Robaa, D.; Erdmann, F.; et al. Structure-Based Design and Synthesis of Novel Inhibitors Targeting HDAC8 from Schistosoma mansoni for the Treatment of Schistosomiasis. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2423–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoben, C.; Robaa, D.; Chakrabarti, A.; Schmidtkunz, K.; Marek, M.; Lancelot, J.; Kannan, S.; Melesina, J.; Shaik, T.; Pierce, R.; et al. A Novel Class of Schistosoma mansoni Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) Inhibitors Identified by Structure-Based Virtual Screening and In Vitro Testing. Molecules 2018, 23, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melesina, J.; Robaa, D.; Pierce, R.J.; Romier, C.; Sippl, W. Homology Modeling of Parasite Histone Deacetylases to Guide the Structure-Based Design of Selective Inhibitors. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2015, 62, 342–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhao, N.; Ge, D.; Chen, Y. Next-Generation of Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19571–19583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, N.O.; Pirone, A.; Lynch, B.A.; Hewitt, M.C.; Quinton, M.S.; McKee, T.D.; Ivarsson, M. CoREST Complex-Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Show Prosynaptic Effects and an Improved Safety Profile to Enable Treatment of Synaptopathies. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Reid, C.R.; Iyer, A.; Sweet, J.M.; Fairlie, P.D. Towards Isozyme-Selective HDAC Inhibitors for Interrogating Disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1479–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, J.C.; Jennings, A.J.; Skene, R.; Wu, Y.; Melkus, R.; De Jong, R.; O’Connell, S.; Grimshaw, C.E.; Navre, M.; Gangloff, A.R. Exploration of the HDAC2 Foot Pocket: Synthesis and SAR of Substituted N-(2-Aminophenyl)benzamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3142–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürli, R.W.; Luckhurst, C.A.; Aziz, O.; Matthews, K.L.; Yates, D.; Lyons, K.A.; Beconi, M.; McAllister, G.; Breccia, P.; Stott, A.J.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Potent and Selective Class IIa Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors as a Potential Therapy for Huntington’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9934–9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, P.; Smil, D.V.; Wahhab, A.; Leit, S.; Rahil, J.; Li, Z.; Déziel, R.; Besterman, J.M. Diphenylmethylene Hydroxamic Acids as Selective Class IIa Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5684–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, N.J.; Mahendran, A.; Breslow, R.; Christianson, D.W. Unusual Zinc-Binding Mode of HDAC6-Selective Hydroxamate Inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13459–13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D.E.; Wagner, F.F.; Kaya, T.; Gale, J.P.; Aidoud, N.; Davoine, E.L.; Lazzaro, F.; Weïwer, M.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Holson, E.B. Discovery of the First Histone Deacetylase 6/8 Dual Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 4816–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, F.F.; Olson, D.E.; Gale, J.P.; Kaya, T.; Weïwer, M.; Aidoud, N.; Thomas, M.; Davoine, E.L.; Lemercier, B.C.; Zhang, Y.-L.; et al. Potent and Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) Does Not Require a Surface-Binding Motif. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1772–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zhao, N.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, H. The Development Process: From SAHA to Hydroxamate HDAC Inhibitors with Branched CAP Region and Linear Linker. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e1900427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osko, J.D.; Christianson, D.W. Structural Determinants of Affinity and Selectivity in the Binding of Inhibitors to Histone Deacetylase 6. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sena Murteira Pinheiro, P.; Franco, L.S.; Montagnoli, T.L.; Fraga, C.A.M. Molecular Hybridization: A Powerful Tool for Multitarget Drug Discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2024, 19, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senger, J.; Melesina, J.; Marek, M.; Romier, C.; Oehme, I.; Witt, O.; Sippl, W.; Jung, M. Synthesis and Biological Investigation of Oxazole Hydroxamates as Highly Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, H. Structure-Based Inhibitor Discovery of Class I Histone Deacetylases (HDACs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnin, M.S.; Donigian, J.R.; Cohen, A.; Richon, V.M.; Rifkind, R.A.; Marks, P.A.; Breslow, R.; Pavletich, N.P. Structures of a Histone Deacetylase Homologue Bound to the TSA and SAHA Inhibitors. Nature 1999, 401, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-H.; Ma, Q.; Wu, H.-P.; Khamis, M.Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Ma, L.-Y.; Liu, H.-M. A Review of Progress in Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitors Research: Structural Specificity and Functional Diversity. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1362–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, N.J.; Wagner, F.F.; Christianson, D.W. Entropy as a Driver of Selectivity for Inhibitor Binding to Histone Deacetylase 6. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 3916–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, R.; Rajan, R.; Mandal, P.K. HDAC as Onco Target: Reviewing the Synthetic Approaches with SAR Study of Their Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 620–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, N.; Suzuki, T.; Ota, Y.; Nakano, T.; Kurihara, M.; Okuda, H.; Yamori, T.; Tsumoto, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Miyata, N. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity of Boronic Acid-Based Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2909–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurs, S.; Clarisse, D.; De Bosscher, K.; D’hooghe, M. The Zinc-Binding Group Effect: Lessons from Non-Hydroxamic Acid Vorinostat Analogs. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 7698–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Song, W. Zinc Binding Groups for Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsel, C.; Plitzko, B.; Froriep, D.; Stolfa, D.A.; Jung, M.; Kubitza, C.; Scheidig, A.J.; Havemeyer, A.; Clement, B. The Involvement of the Mitochondrial Amidoxime Reducing Component (MARC) in the Reductive Metabolism of Hydroxamic Acids. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, A.; Assmann, A.S.; Schumacher, L.; Stuijvenberg, J.V.; Kassack, M.U.; Schulz, W.A.; Roos, W.P.; Hansen, F.K.; Pflieger, M.; Kurz, T.; et al. In Vitro Assessment of the Genotoxic Hazard of Novel Hydroxamic Acid- and Benzamide-Type Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citarella, A.; Moi, D.; Pinzi, L.; Bonanni, D.; Rastelli, G. Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives: From Synthetic Strategies to Medicinal Chemistry Applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 21843–21849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Yamashita, T.; Mariko, Y.; Nosaka, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Ando, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tsuruo, T.; Nakanishi, O. A Synthetic Inhibitor of Histone Deacetylase, MS-27-275, with Marked In Vivo Antitumor Activity against Human Tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4592–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühauf, A.; Meyer-Almes, F.-J. Non-Hydroxamate Zinc-Binding Groups as Warheads for Histone Deacetylases. Molecules 2021, 26, 5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozikowski, A.P.; Chen, Y.; Gaysin, A.; Chen, B.; D’Annibale, M.A.; Suto, C.M.; Langley, B.C. Functional Differences in Epigenetic Modulators—Superiority of Mercaptoacetamide-Based Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Relative to Hydroxamates in Cortical Neuron Neuroprotection Studies. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, N.J.; Shen, S.; Barinka, C.; Kozikowski, A.P.; Christianson, D.W. Molecular Basis for the Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 6 by a Mercaptoacetamide Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Petukhov, P.A.; Jung, M.; Velena, A.; Eliseeva, E.; Dritschilo, A.; Kozikowski, A.P. Chemistry and Biology of Mercaptoacetamides as Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 1389–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Matsuura, A.; Kouketsu, A.; Nakagawa, H.; Miyata, N. Identification of a Potent Non-Hydroxamate Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor by Mechanism-Based Drug Design. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolfa, D.A.; Marek, M.; Lancelot, J.; Hauser, A.-T.; Walter, A.; Leproult, E.; Melesina, J.; Rumpf, T.; Wurtz, J.-M.; Cavarelli, J.; et al. Molecular Basis for the Antiparasitic Activity of a Mercaptoacetamide Derivative That Inhibits Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) from the Human Pathogen Schistosoma mansoni. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 3442–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sanea, M.M.; Gotina, L.; Mohamed, M.F.; Grace Thomas Parambi, D.; Gomaa, H.A.; Mathew, B.; Youssif, B.G.; Alharbi, K.S.; Elsayed, Z.M.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New HDAC1 and HDAC2 Inhibitors Endowed with Ligustrazine as a Novel Cap Moiety. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.I.; Cao, J.; Zhu, C.-L.; Miller, S.P.; Lin, H. Activity-Guided Design of HDAC11-Specific Inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Sun, S.; Jia, G.; Qin, M.; Hou, X.; Chou, C.J.; Huang, C.; Li, X. First-in-Class Hydrazide-Based HDAC6 Selective Inhibitor with Potent Oral Anti-Inflammatory Activity by Attenuating NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 12140–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, J.; Yue, K.; Huang, C.; Qin, M.; Chi, D.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, X.; Xu, T.; et al. Potent Hydrazide-Based HDAC Inhibitors with a Superior Pharmacokinetic Profile for Efficient Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia In Vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Peterson, Y.K.; Xu, T.; Himes, R.A.; Luo, X.; Yin, G.; Inks, E.S.; Dolloff, N.; Halene, S.; et al. Design of Hydrazide-Bearing HDACIs Based on Panobinostat and Their P53 and FLT3-ITD Dependency in Antileukemia Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 5501–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peterson, Y.K.; Inks, E.S.; Himes, R.A.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.; Chou, C.J. Class I HDAC Inhibitors Display Different Antitumor Mechanism in Leukemia and Prostatic Cancer Cells Depending on Their P53 Status. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2589–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, J.J.; Zhang, C.; Inks, E.S.; Peterson, Y.K.; Li, J.; Chou, C.J. Development of Allosteric Hydrazide-Containing Class I Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors for Use in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 9942–9959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goracci, L.; Deschamps, N.; Randazzo, G.M.; Petit, C.; Dos Santos Passos, C.; Carrupt, P.-A.; Simões-Pires, C.; Nurisso, A. A Rational Approach for the Identification of Non-Hydroxamate HDAC6-Selective Inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Stowe, R.L.; Pinello, C.E.; Tian, G.; Madoux, F.; Li, D.; Zhao, L.Y.; Li, J.-L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Identification of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors with Benzoylhydrazide Scaffold That Selectively Inhibit Class I Histone Deacetylases. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, L. Discovery of Indole-3-Butyric Acid Derivatives as Potent Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wang, J.; Khan, K.S.; Yang, W.; Ng, B.W.-L.; Ilment, N.; Zessin, M.; Bülbül, E.F.; Robaa, D.; Erdmann, F.; et al. Development of Alkylated Hydrazides as Highly Potent and Selective Class I Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors with T Cell Modulatory Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 16313–16337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, C.S.; Oh, J.T.; Song, H.; Choi, J.; Lee, J. Oxadiazole Amine Derivative Compounds as Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor, and the Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising the Same. WO 2017/065473 A1, 20 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Han, Y.; Kim, Y.; Min, J.; Bae, M.; Kim, D.; Jin, S.; Kyung, J. 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Sulfamide Derivative Compounds as Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor, and the Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising the Same. WO 2017/018805 A1, 2 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Kubo, O.; Kikuchi, F.; Yasu, T.; Kakegawa, K.; Ikeda, Z.; Miyazaki, T.; Arikawa, Y.; Okawa, T.; et al. Heterocyclic Compound. WO 2019/027054 A1, 7 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.K.; Ko, M.S.; Yun, S.H.; Kim, H.M. 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Derivative Compounds as Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor, and the Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising the Same. WO 2021/210857 A1, 21 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mandegar, M.A.; Patel, S.; Ding, P.; Bhatt, U.; Holan, M.; Lee, J.; Li, Y.; Medina, J.; Nerurkar, A.; Seidl, F.; et al. Fluoroalkyl-Oxadiazoles and Uses Thereof. WO 2021/127643 A1, 24 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cellupica, E.; Gaiassi, A.; Rocchio, I.; Rovelli, G.; Pomarico, R.; Sandrone, G.; Caprini, G.; Cordella, P.; Cukier, C.; Fossati, G.; et al. Mechanistic and Structural Insights on Difluoromethyl-1,3,4-Oxadiazole Inhibitors of HDAC6. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakır, I.; Hadley, C.K.; Pan, P.L.; Bagchi, R.A.; Ghamari-Langroudi, M.; Porter, D.T.; Wang, Q.; Litt, M.J.; Jana, S.; Hagen, S.; et al. Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibition Restores Leptin Sensitivity and Reduces Obesity. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keuler, T.; König, B.; Bückreiß, N.; Kraft, F.B.; König, P.; Schäker-Hübner, L.; Steinebach, C.; Bendas, G.; Gütschow, M.; Hansen, F.K. Development of the First Non-Hydroxamate Selective HDAC6 Degraders. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 11087–11090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaha, Y.; Bollmann, L.M.; Skerhut, A.J.; Fischer, F.; Horstick, N.; Roth, D.; Wecker, M.; Mammen, C.; Smits, S.H.J.; Fluegen, G.; et al. 5-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazole (TFMO)-Based Highly Selective Class IIa HDAC Inhibitors Exhibit Synergistic Anticancer Activity in Combination with Bortezomib. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 263, 115907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobera, M.; Madauss, K.P.; Pohlhaus, D.T.; Wright, Q.G.; Trocha, M.; Schmidt, D.R.; Baloglu, E.; Trump, R.P.; Head, M.S.; Hofmann, G.A.; et al. Selective Class IIa Histone Deacetylase Inhibition via a Nonchelating Zinc-Binding Group. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragin, A.; Watson, P.R.; König, B.; Hansen, F.K.; Christianson, D.W. A Novel Zinc Binding Group for HDAC6 Inhibition. FASEB J. 2022, 36, R3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptacek, J.; Snajdr, I.; Schimer, J.; Kutil, Z.; Mikesova, J.; Baranova, P.; Havlinova, B.; Tueckmantel, W.; Majer, P.; Kozikowski, A.; et al. Selectivity of Hydroxamate- and Difluoromethyloxadiazole-Based Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase 6 In Vitro and in Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, C.M. Metalloenzyme Inhibitor Compounds. U.S. Patent 2018/0256572 A1, 23 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cellupica, E.; Caprini, G.; Cordella, P.; Cukier, C.; Fossati, G.; Marchini, M.; Rocchio, I.; Sandrone, G.; Vanoni, M.A.; Vergani, B.; et al. Difluoromethyl-1,3,4-Oxadiazoles Are Slow-Binding Substrate Analog Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase 6 with Unprecedented Isotype Selectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, B.; Watson, P.R.; Reßing, N.; Cragin, A.D.; Schäker-Hübner, L.; Christianson, D.W.; Hansen, F.K. Difluoromethyl-1,3,4-Oxadiazoles Are Selective, Mechanism-Based, and Essentially Irreversible Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 13821–13837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Chu, X.; Di, L.; Gao, W.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, C.; Mao, J.; Shen, H.; Tang, H.; et al. Recent Advances in the Translation of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics Science for Drug Discovery and Development. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2751–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillpe-Meza, R.M.; Gouveia, W.L.; Barbosa, G.; Fraga, C.A.M.; Barreiro, E.J.; Lima, L.M. Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Activity of LASSBio-2208 and the Attempts to Determine Its Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics In Vitro Profile. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, R.M. Belinostat: First Global Approval. Drugs 2014, 74, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesel, B.F.; Parise, R.A.; Tjørnelund, J.; Christensen, M.K.; Loza, E.; Tawbi, H.; Chu, E.; Kummar, S.; Beumer, J.H. LC–MS/MS Assay for the Quantitation of the HDAC Inhibitor Belinostat and Five Major Metabolites in Human Plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 81, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, E.; Reddy, G.; Boni, V.; García-Cañamaque, L.; Song, T.; Tjornelund, J.; Choi, M.R.; Allen, L.F. Pharmacokinetics, Metabolism, and Excretion of 14C-Labeled Belinostat in Patients with Recurrent or Progressive Malignancies. Investig. New Drugs 2016, 34, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, H.; McPherson, J.P.; Bailey, E.B.; Werner, T.L.; Gupta, S.; Batten, J.; Reddy, G.; Bhat, G.; Sharma, S.; Agarwal, N. A Phase I Study to Determine the Pharmacokinetics and Urinary Excretion of Belinostat and Metabolites in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, N.L.; Plumb, J.A.; Vidal, L.; Tjørnelund, J.; Knoblauch, P.; Rasmussen, A.; Ooi, C.E.; Buhl-Jensen, P.; Brown, R.; Evans, T.R.J.; et al. A Phase 1 Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Study of the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Belinostat in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, N.L.; Plumb, J.A.; Vidal, L.; Tjørnelund, J.; Knoblauch, P.; Buhl-Jensen, P.; Molife, R.; Brown, R.; de Bono, J.S.; Evans, T.R.J. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Properties of an Oral Formulation of the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Belinostat (PXD101). Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-Z.; RamÃrez, J.; Yeo, W.; Chan, M.-Y.M.; Thuya, W.-L.; Lau, J.-Y.A.; Wan, S.-C.; Wong, A.L.-A.; Zee, Y.-K.; Lim, R.; et al. Correction: Glucuronidation by UGT1A1 Is the Dominant Pathway of the Metabolic Disposition of Belinostat in Liver Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e54522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, S.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Hossain, A.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G. Metabolism and Pharmacokinetic Study of the Boron-Containing Prodrug of Belinostat (ZL277), a Pan HDAC Inhibitor with Enhanced Bioavailability. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Hou, B.; Hou, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Discovery of Benzamide-Based PI3K/HDAC Dual Inhibitors with Marked Pro-Apoptosis Activity in Lymphoma Cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 262, 115915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, Q.C.; Headlee, D.; Acharya, M.; Sparreboom, A.; Trepel, J.B.; Ye, J.; Figg, W.D.; Hwang, K.; Chung, E.J.; Murgo, A.; et al. Phase I and Pharmacokinetic Study of MS-275, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced and Refractory Solid Tumors or Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3912–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A.M.; Dehnhardt, C.M.; Delos Santos, E.; Chen, Z.; Dos Santos, O.; Ayral-Kaloustian, S.; Khafizova, G.; Brooijmans, N.; Mallon, R.; Hollander, I.; et al. Bis(morpholino-1,3,5-triazine) Derivatives: Potent Adenosine 5′-Triphosphate Competitive Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitors: Discovery of Compound 26 (PKI-587), a Highly Efficacious Dual Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2636–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, P.; Andrews, P.; Baker, M.; Koeplinger, K.; Soli, E.; Miller, T.; Baillie, T. Disposition of Vorinostat, A Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor and Anticancer Agent, in Preclinical Species. Drug Metab. Lett. 2007, 1, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, A.J.; Maillard, M.C.; Beaumont, V.; Allcock, D.; Aziz, O.; Borchers, A.H.; Blackaby, W.; Breccia, P.; Creighton-Gutteridge, G.; Haughan, A.F.; et al. Evaluation of 5-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazole-Based Class IIa HDAC Inhibitors for Huntington’s Disease. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R.; Harihar, D.; Chatterji, B.P. Recent Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Cancer 2023, 129, 3372–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hong, J.H.; Ning, Z.; Pan, D.; Fu, X.; Lu, X.; Tan, J. Therapeutic Potential of Tucidinostat, a Subtype-Selective HDAC Inhibitor, in Cancer Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 932914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, E.; Vilchez, J.J.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O.; Zaidman, C.M.; Mah, J.K.; Goemans, N.; Müller-Felber, W.; Niks, E.H.; Schara-Schmidt, U.; Bertini, E.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Givinostat in Boys with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (EPIDYS): A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, D.; Goemans, N.; Takeda, S.; Mercuri, E.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



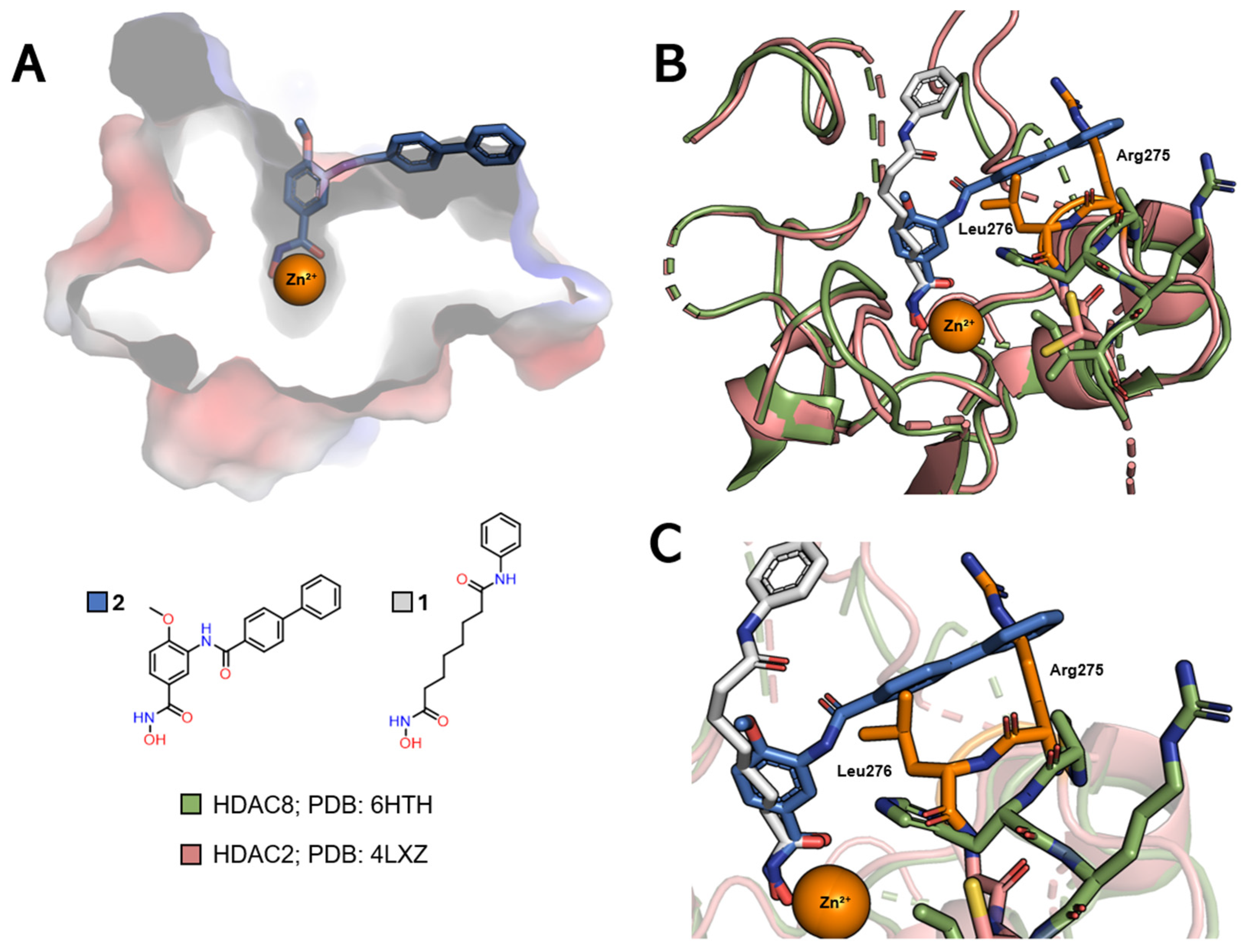
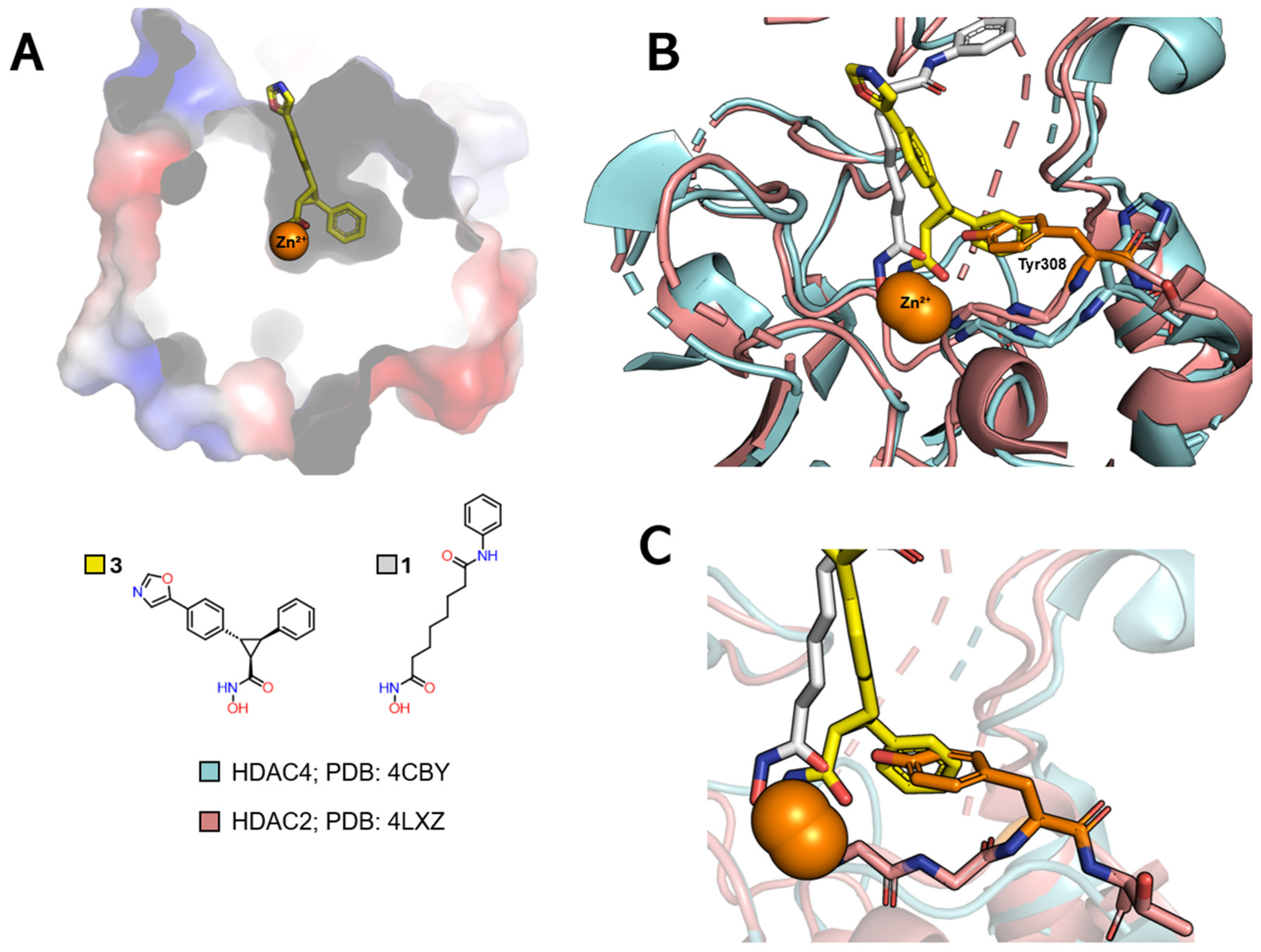

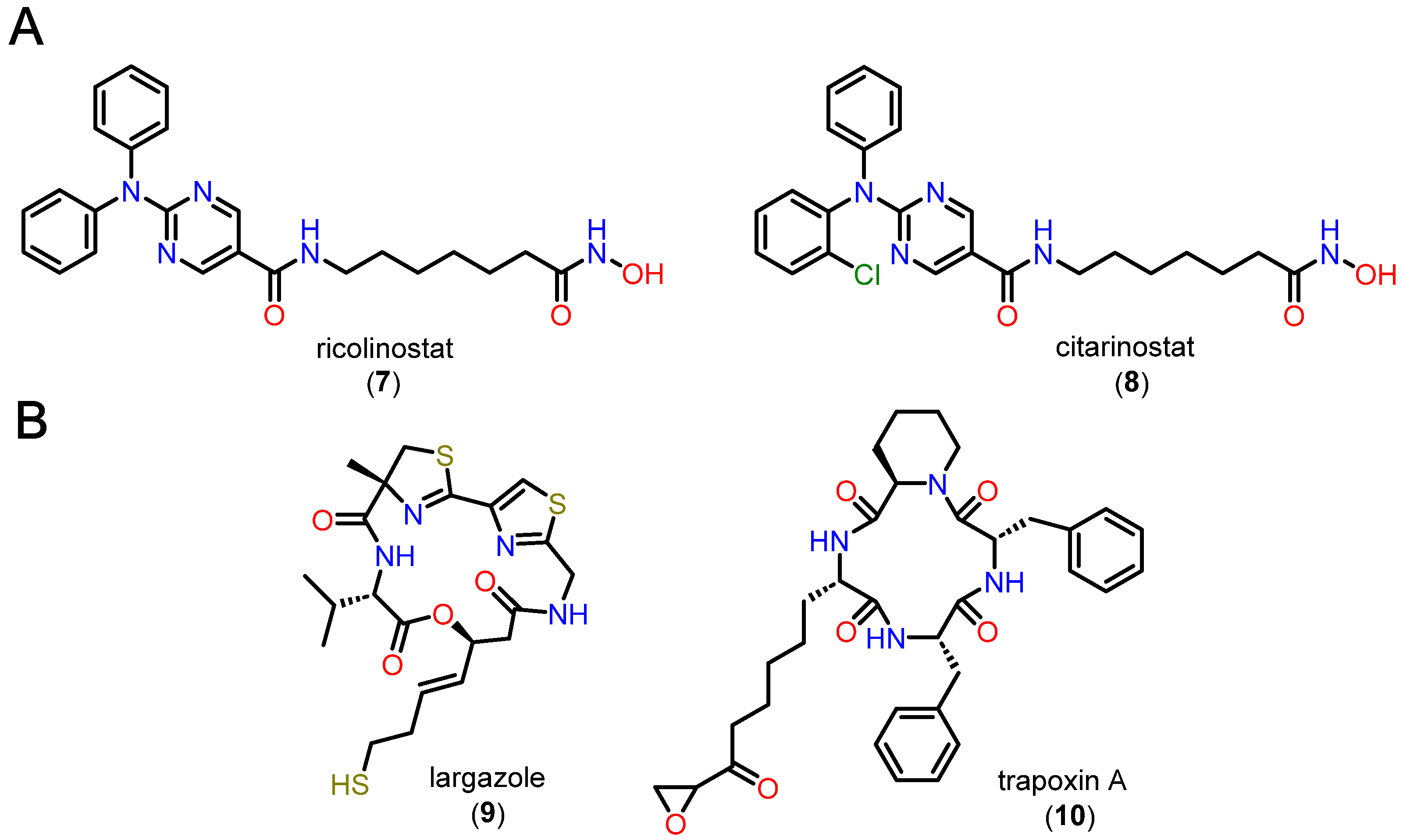
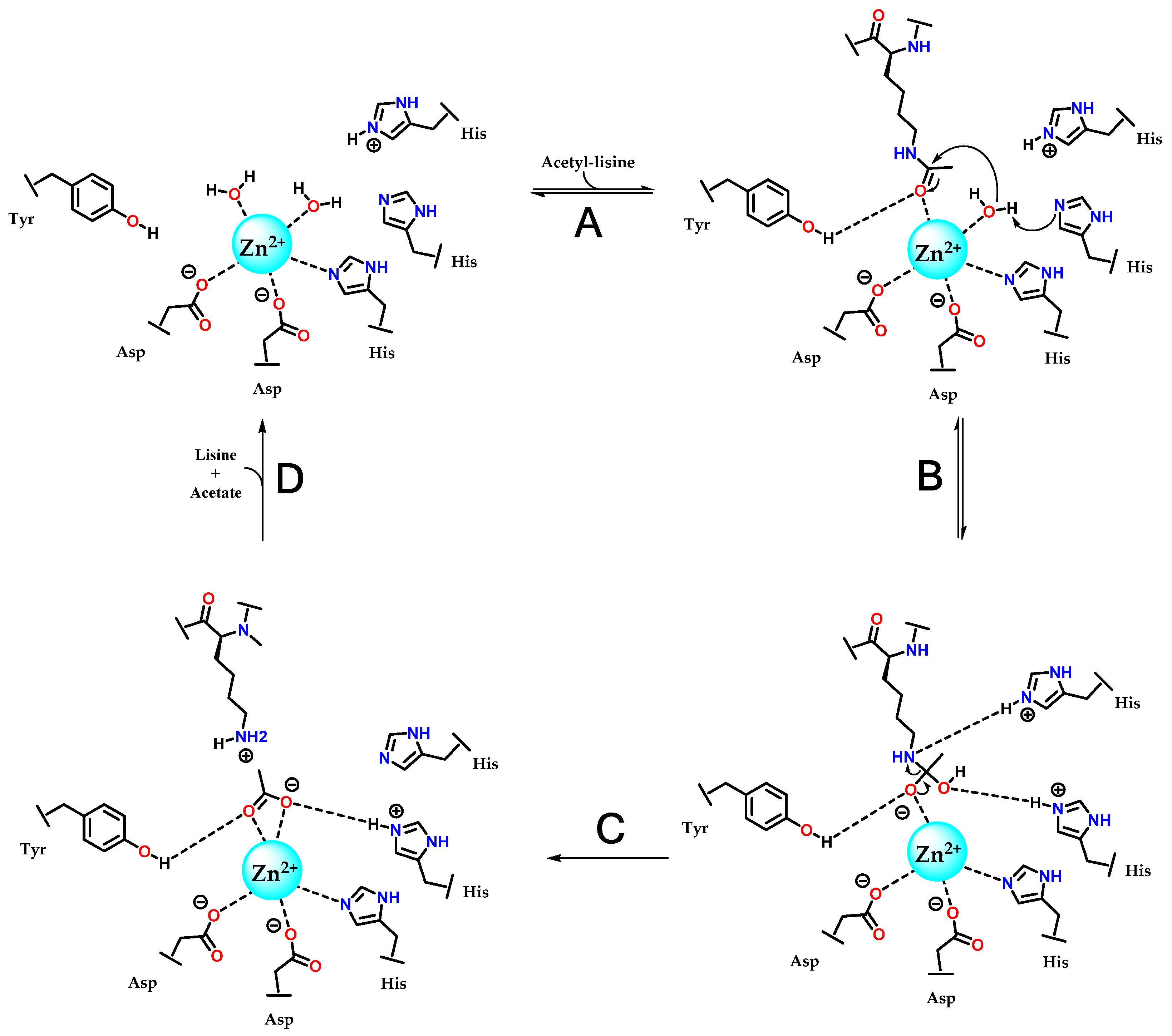
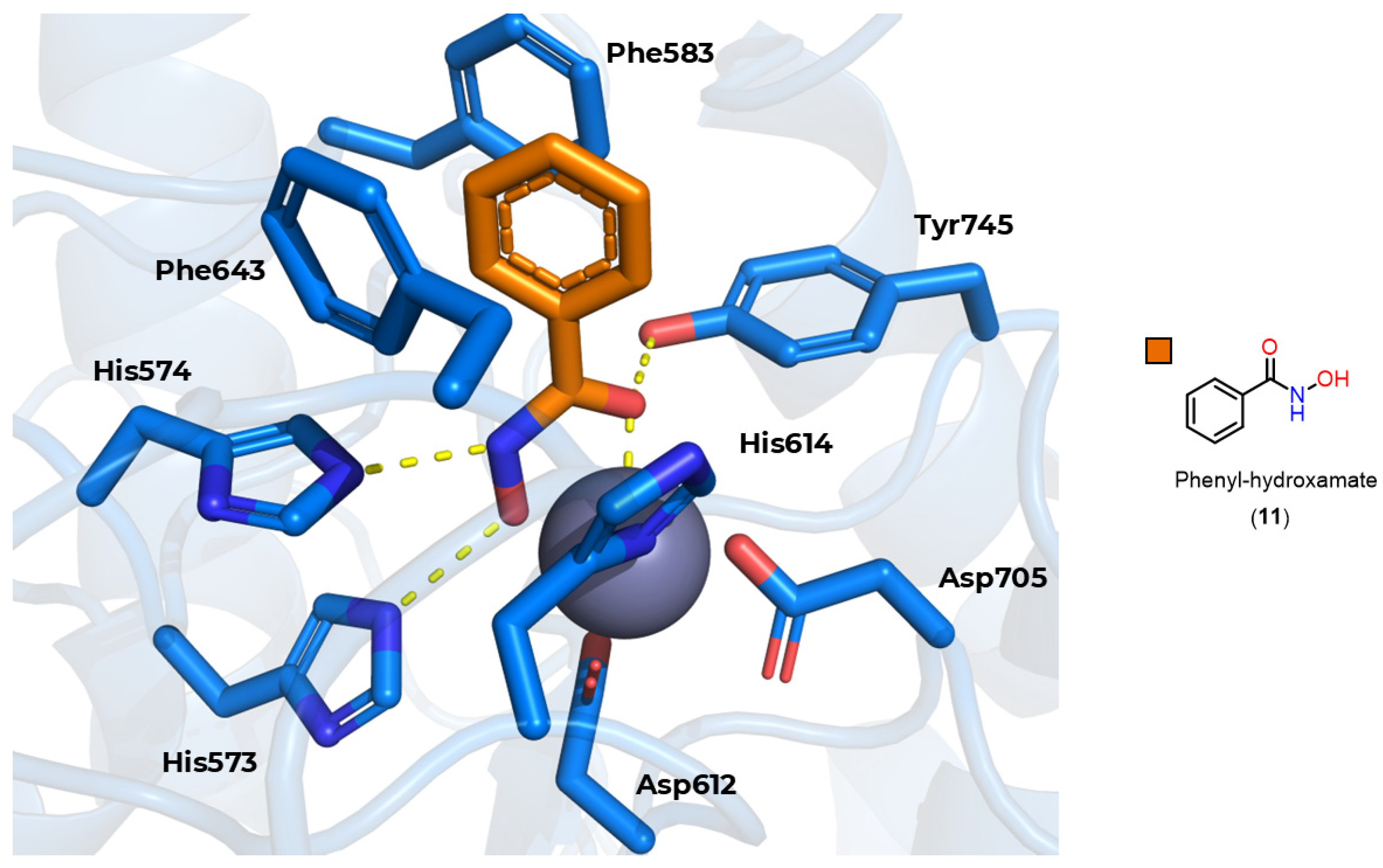
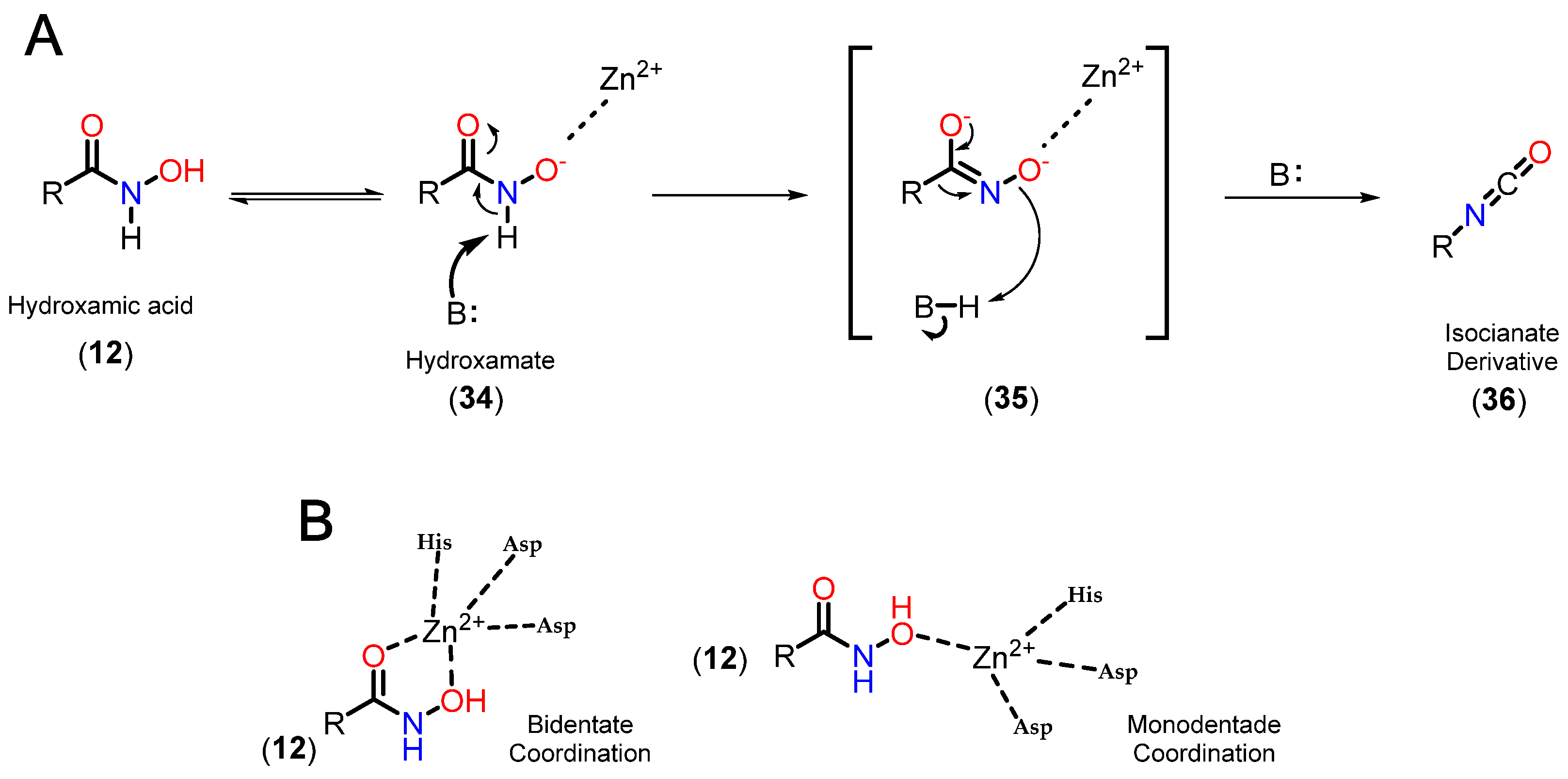

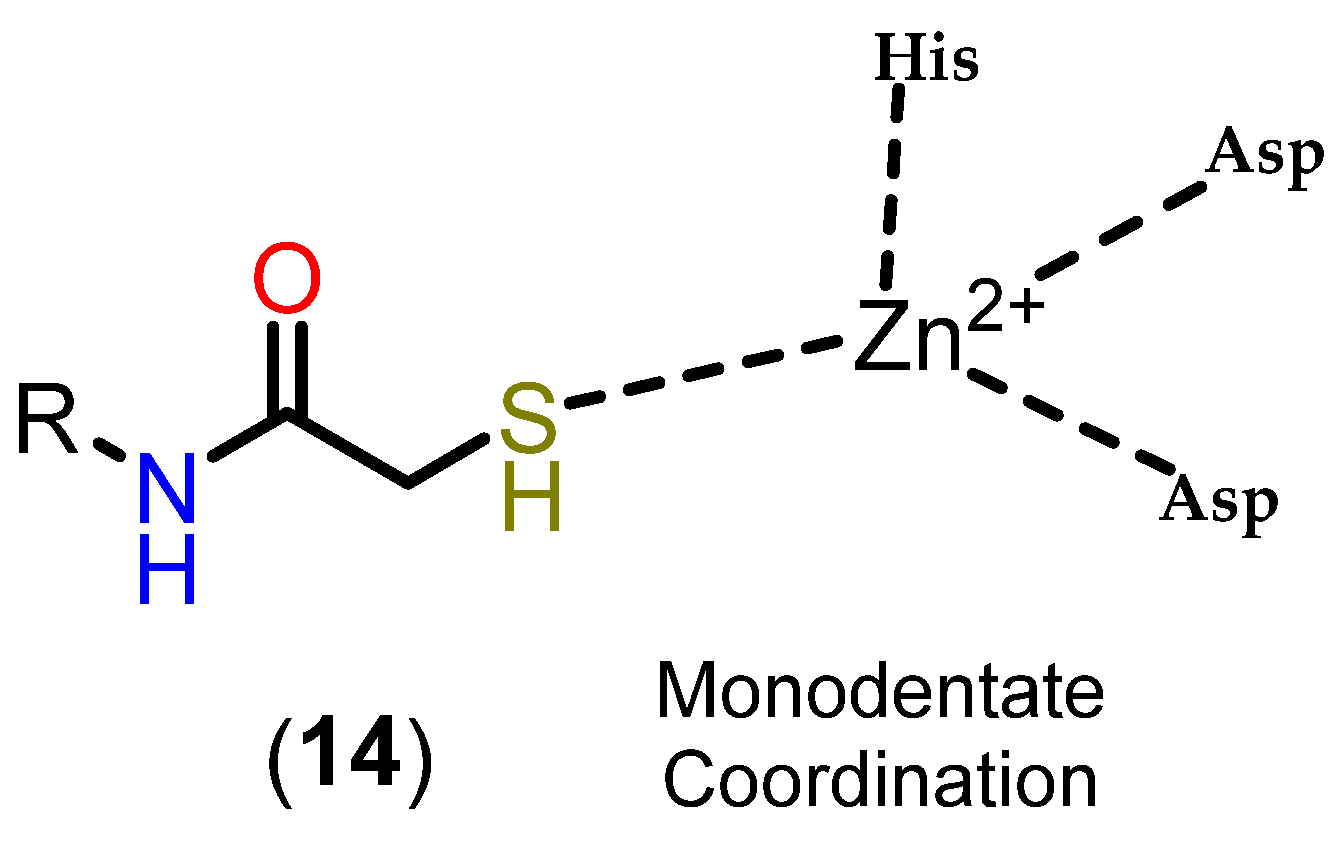
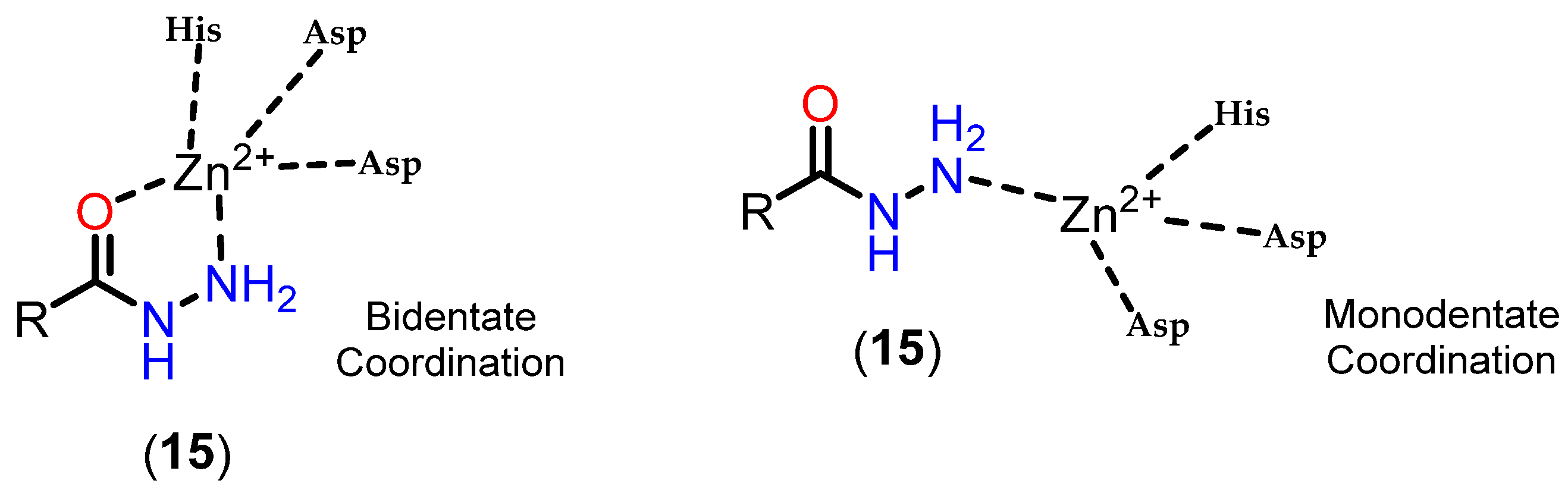
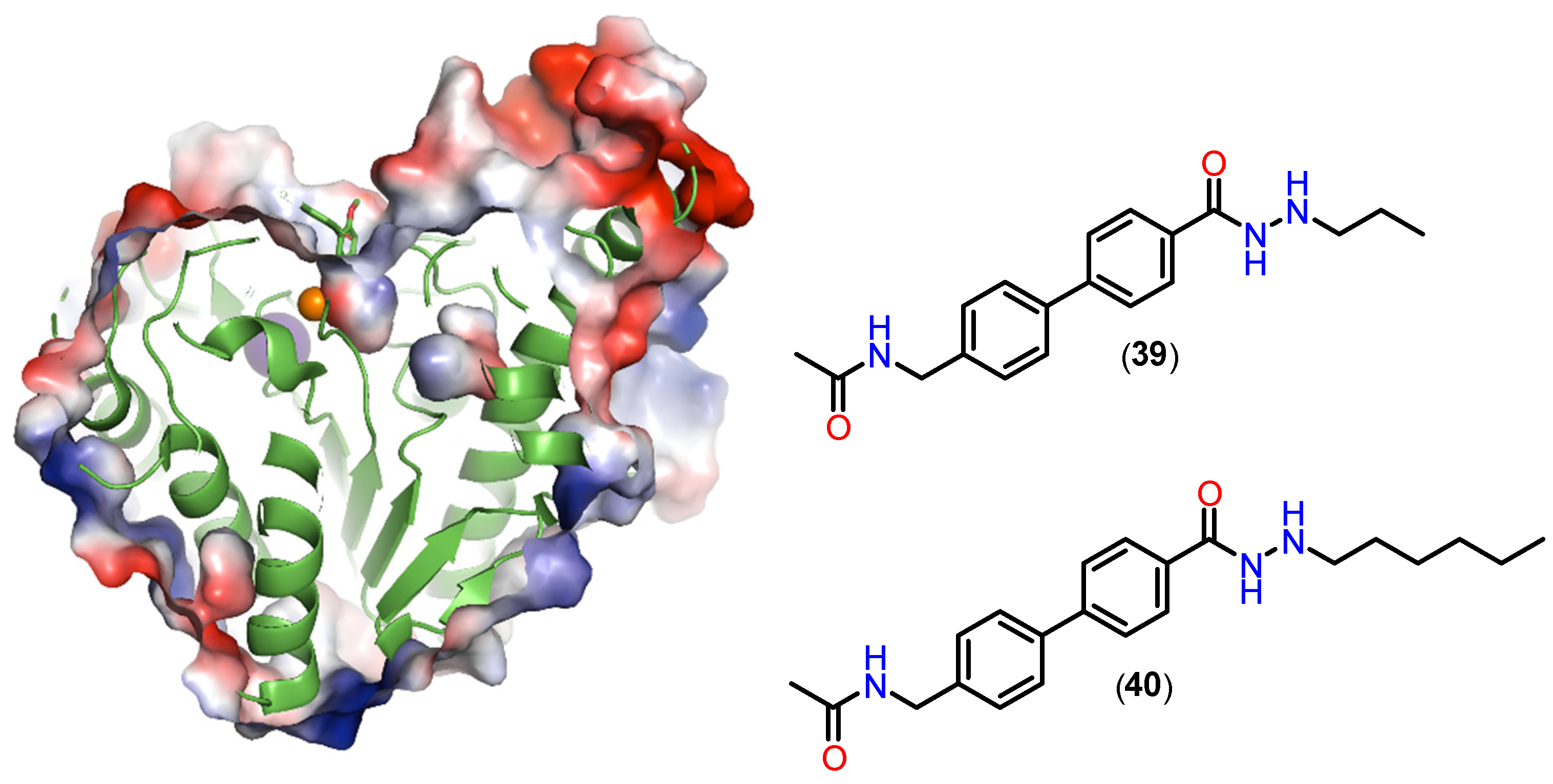

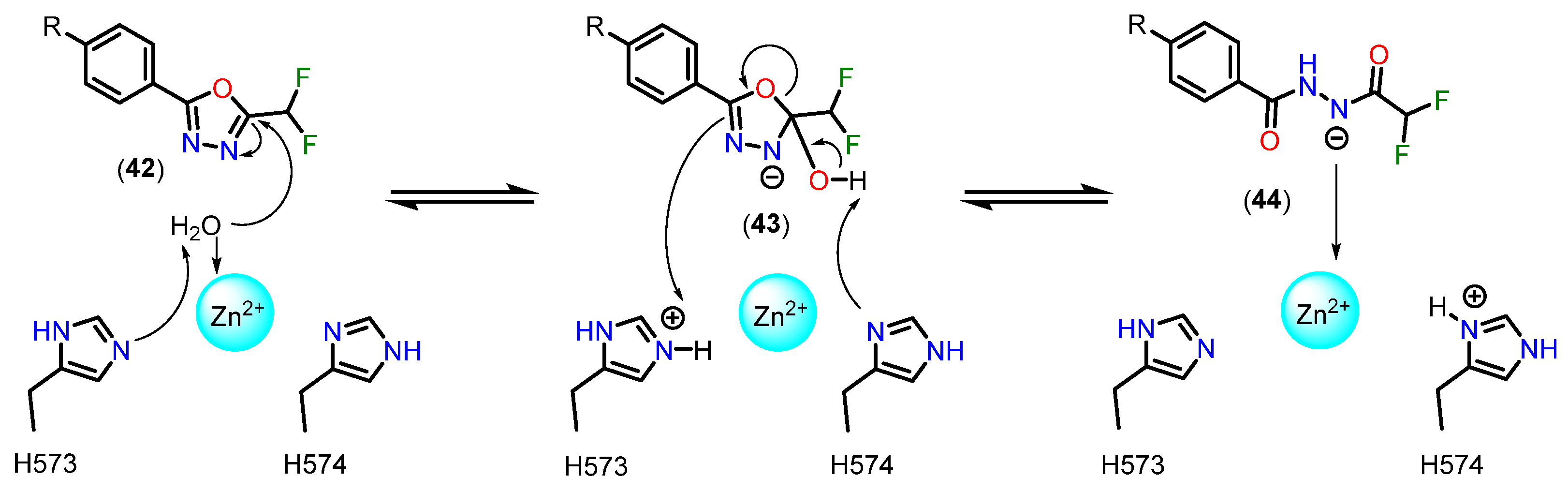

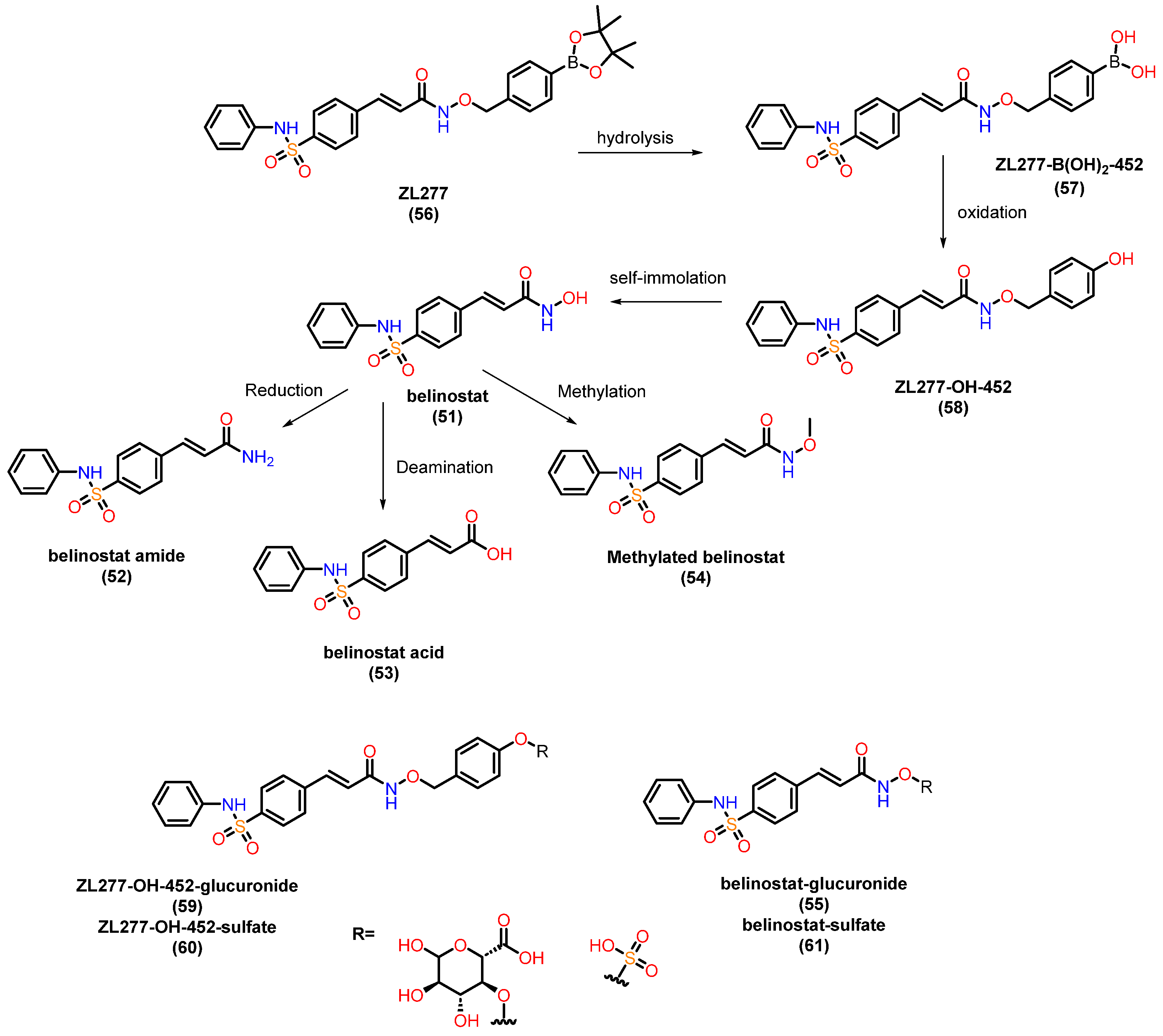
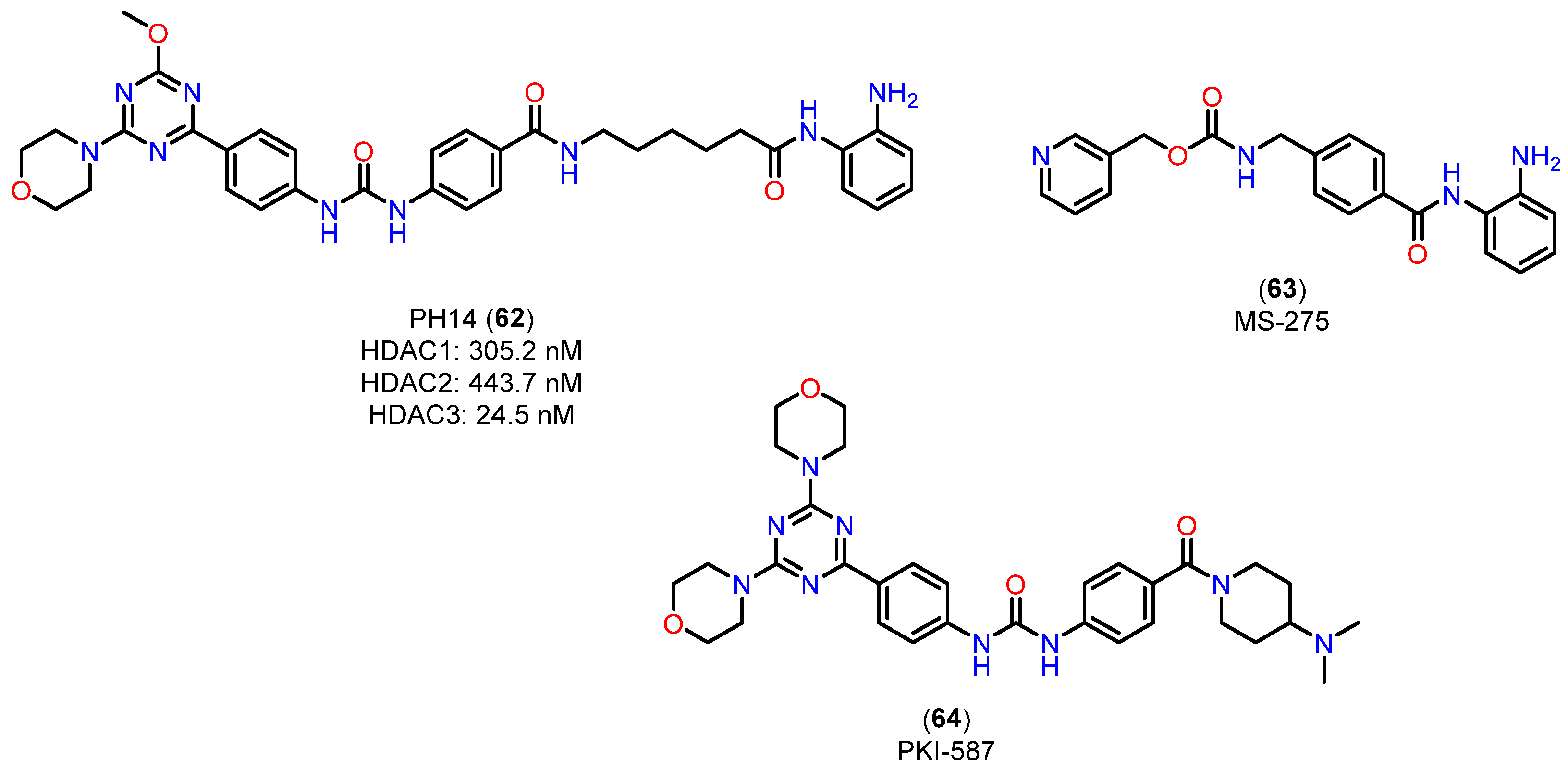
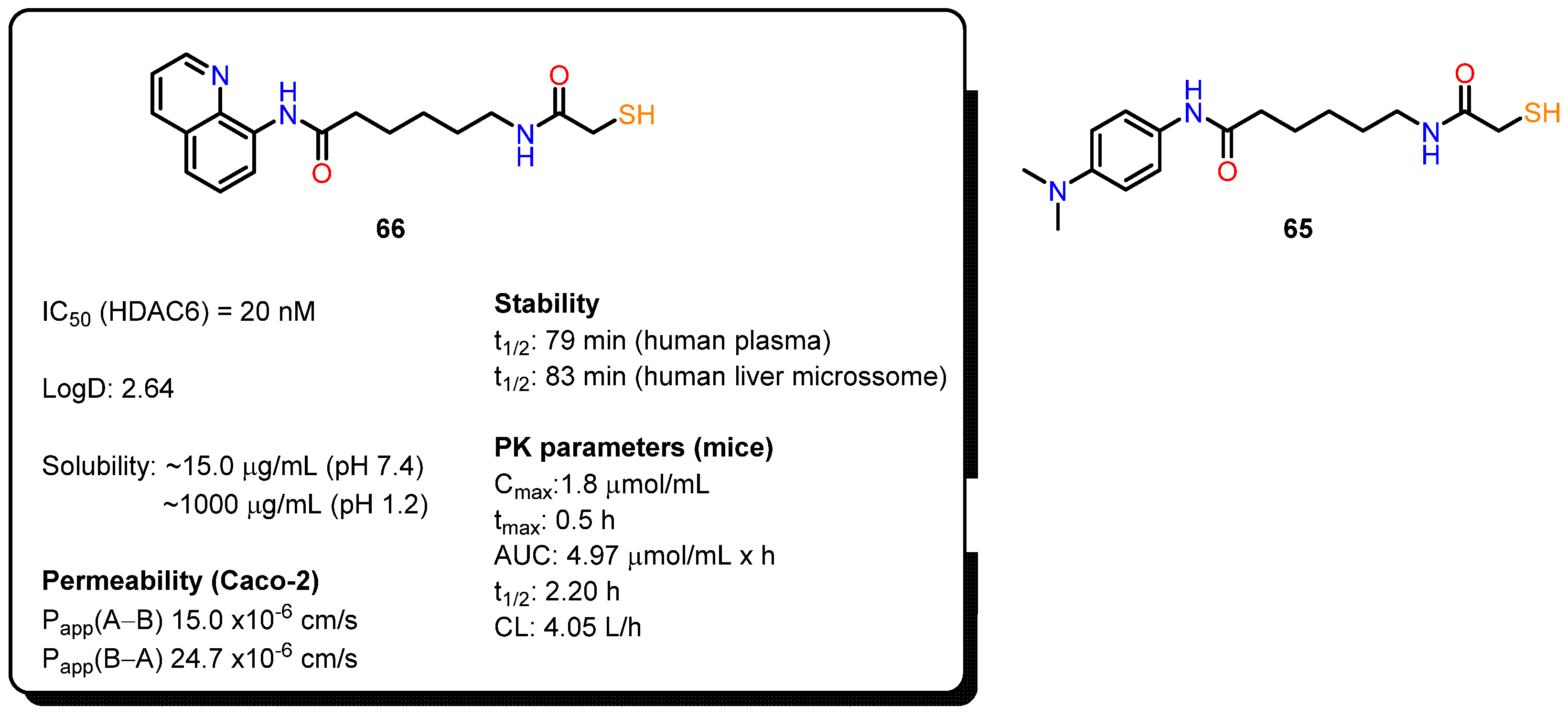
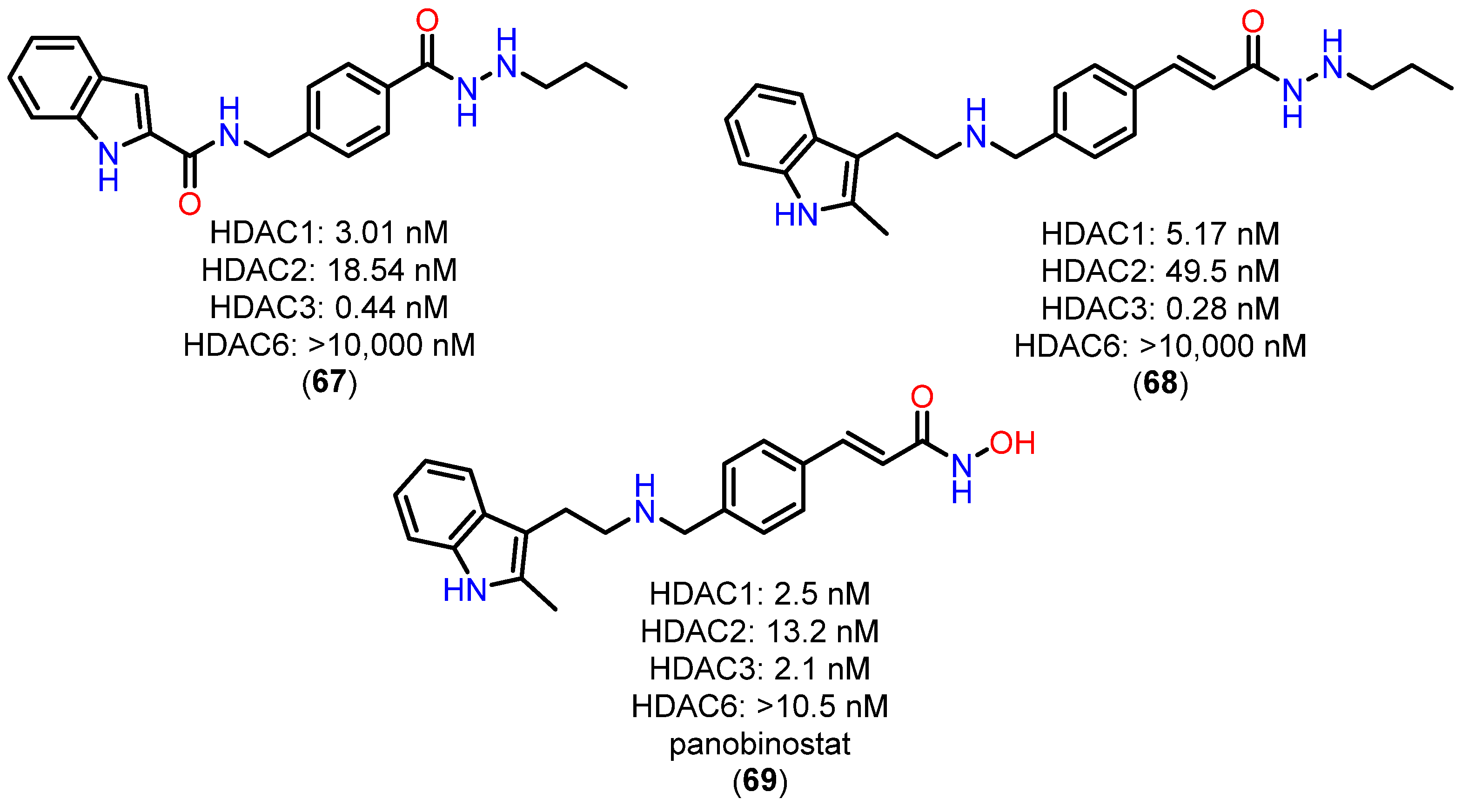
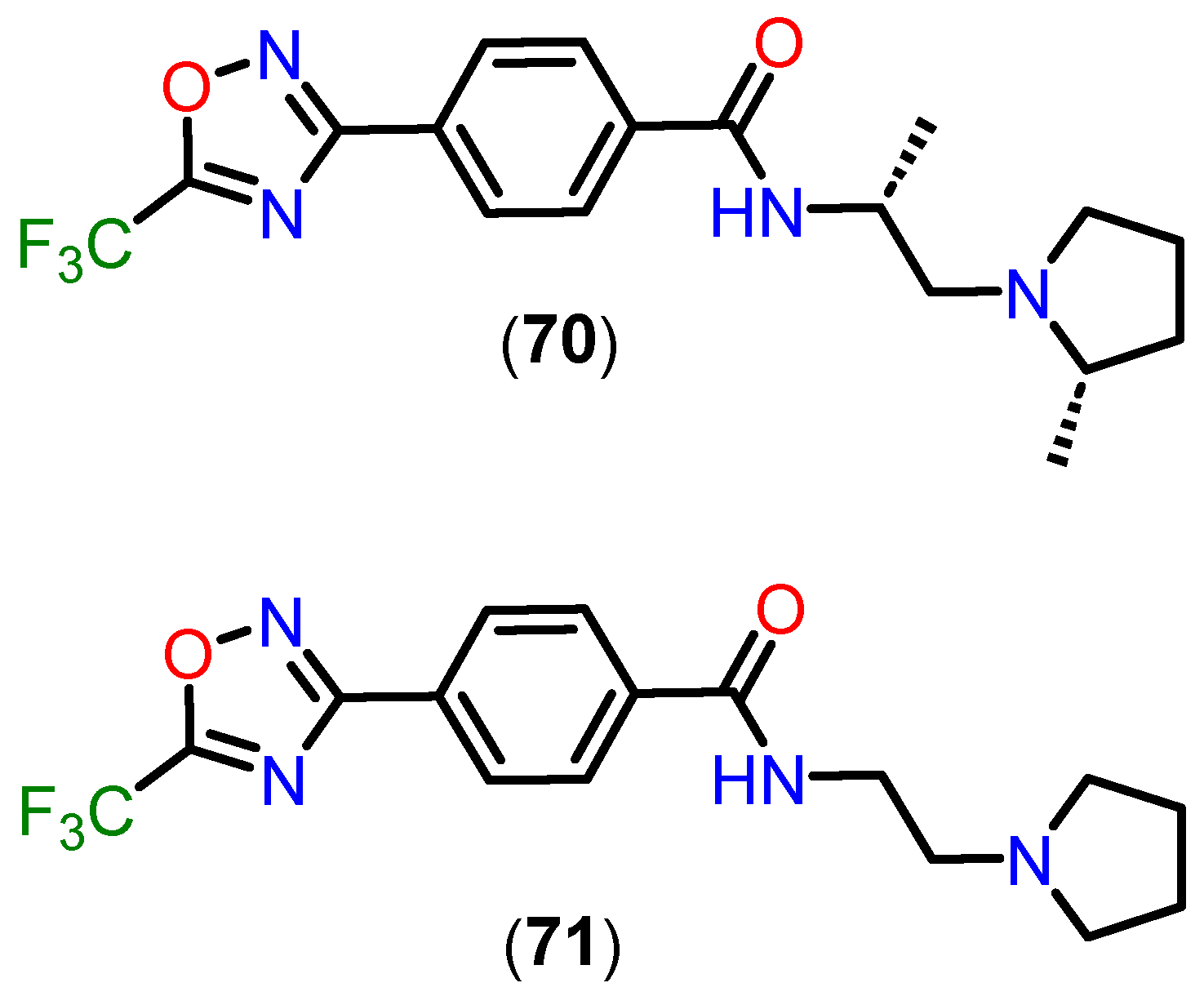
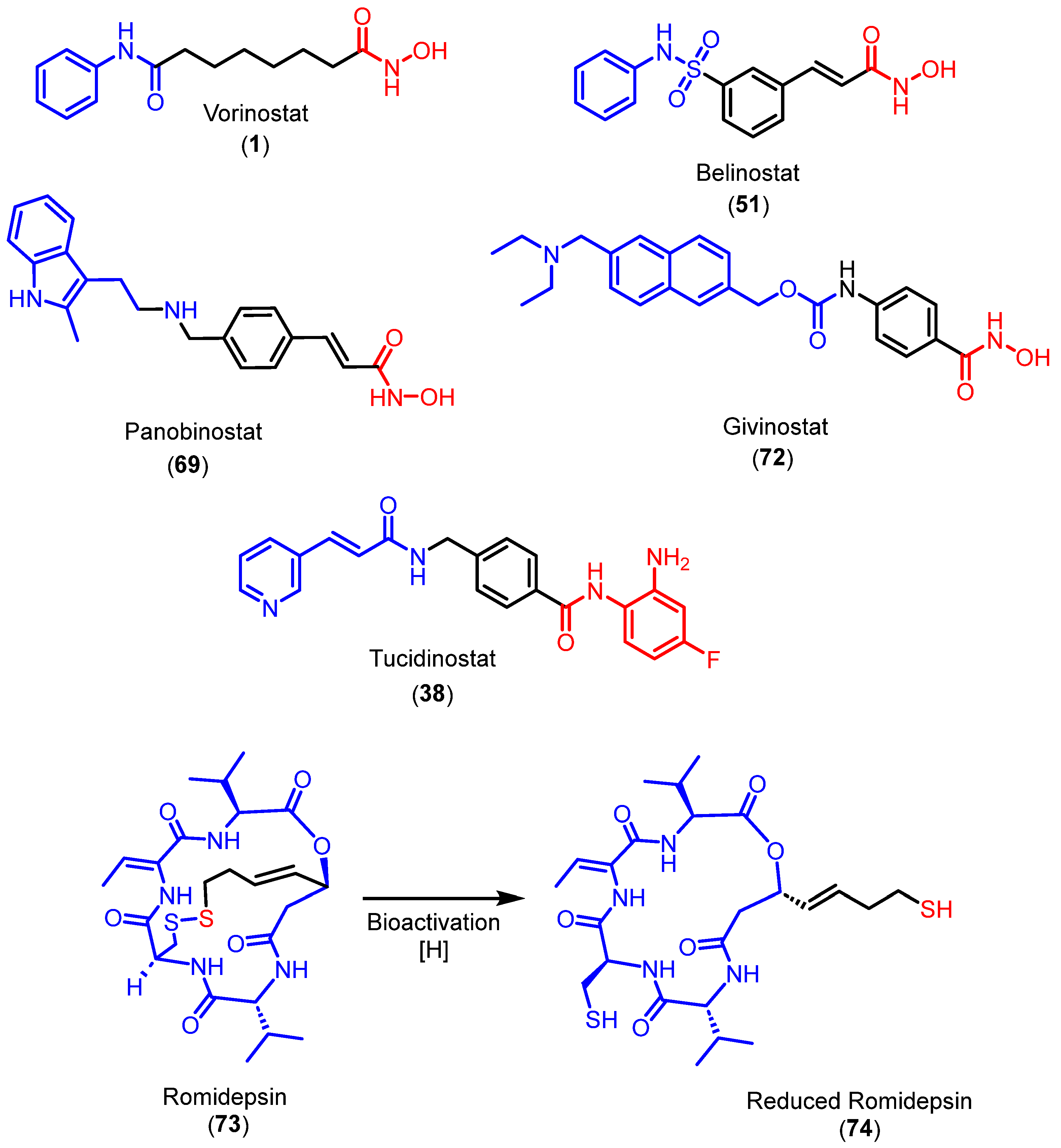
| Class | Acetate-Binding Cavity | Main Channel | Surface | Side Pocket | Lower Pocket | Foot Pocket |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDAC class I | Present | Present | Present | Present only in HDAC8 | Absent | Present only in HDACs 1–3 |
| HDAC class IIa | Present | Present | Present | Absent | Present | Absent |
| HDAC class IIb | Present | Present | Present | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| HDAC class IV | Present | Present | Present | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| ZBG | Metabolic Stability | Bioavailability | Additional Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxamate | Accelerated glucuronidation | Low | - |
| Ortho-aminoanilides | Moderate | High | Weak CYP450 inhibitor and low hERG risks |
| Mercaptoacetamides | - | - | Favorable for brain penetration |
| Alkylhidrazides | Moderate | High | Reduced metabolic loss and pre-systemic clearance |
| TFMO and DFMO | - | High | High brain penetration and minimal CYP450 inhibition and hERG interactions |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pires, G.S.; Tolomeu, H.V.; Rodrigues, D.A.; Lima, L.M.; Fraga, C.A.M.; Pinheiro, P.d.S.M. Drug Discovery for Histone Deacetylase Inhibition: Past, Present and Future of Zinc-Binding Groups. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040577
Pires GS, Tolomeu HV, Rodrigues DA, Lima LM, Fraga CAM, Pinheiro PdSM. Drug Discovery for Histone Deacetylase Inhibition: Past, Present and Future of Zinc-Binding Groups. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040577
Chicago/Turabian StylePires, Gustavo Salgado, Heber Victor Tolomeu, Daniel Alencar Rodrigues, Lídia Moreira Lima, Carlos Alberto Manssour Fraga, and Pedro de Sena Murteira Pinheiro. 2025. "Drug Discovery for Histone Deacetylase Inhibition: Past, Present and Future of Zinc-Binding Groups" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040577
APA StylePires, G. S., Tolomeu, H. V., Rodrigues, D. A., Lima, L. M., Fraga, C. A. M., & Pinheiro, P. d. S. M. (2025). Drug Discovery for Histone Deacetylase Inhibition: Past, Present and Future of Zinc-Binding Groups. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040577