Association between Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and Histological and Immunohistochemical Features in Periapical Lesions Correlated with Thickened Maxillary Sinus Mucosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Group
2.3. Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Examination
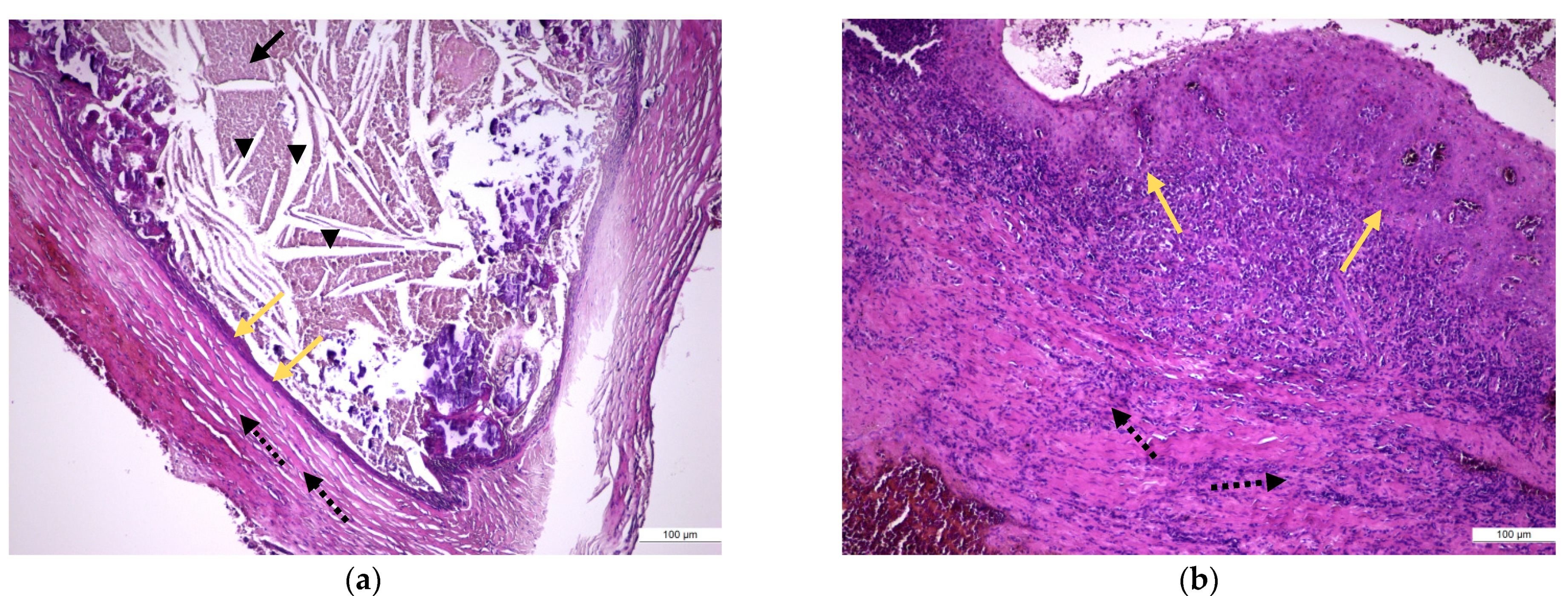
2.4. Surgical, Histological, and Immunohistochemical Examination
2.5. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van den Bergh, J.P.; Ten Bruggenkate, C.M.; Disch, F.J.; Tuinzing, D.B. Anatomical aspects of sinus floor elevations. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2000, 11, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.C.; Schulze, R.K. Detection accuracy of maxillary sinus floor septa in panoramic radiographs using CBCT as gold standard: A multi-observer receiver operating characteristic (ROC) study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedeoğlu, N.; Altun, O. Evaluation of maxillary sinus anatomical variations and pathologies in elderly, young, posterior dentate and edentulous patient groups with cone-beam computed tomography. Folia Morphol. 2019, 78, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantine, S.; Clark, B.; Kiermeier, A.; Anderson, P. Panoramic radiography is of limited value in the evaluation of maxillary sinus disease. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2019, 127, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsufyani, N.; El-Hakim, H.; Major, P. Prevalence of maxillary sinus hypoplasia and association with variations in the sinonasal complex: A cone beam CT study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 5463–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, F.; Coutinho, T.M.; Carvalho Ferreira, D.; Souza, R.C.; Gonçalves, L.S. Odontogenic sinusitis: A comprehensive review. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2017, 75, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsesis, I.; Rosen, E.; Beitlitum, I.; Dicker-Levy, E.; Matalon, S. Influence of the Periapical Status of the Posterior Maxillary Teeth on the Width of the Schneiderian Membrane of the Maxillary Sinus Mucosa. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Yagi, M.; Sakagami, T.; Sawada, S.; Kojima, Y.; Nakatani, T.; Kawachi, R.; Suzuki, K.; Murata, H.; Kanda, A.; et al. Odontogenic Maxillary Sinusitis: Therapeutic Management of Cases with Oroantral Fistulae. Sinusitis 2021, 5, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürhan, C.; Şener, E.L.; Mert, A.; Şen, G.B. Evaluation of factors affecting the association between thickening of sinus mucosa and the presence of periapical lesions using cone beam CT. Int. Endod. J. 2020, 53, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestin Fredriksson, M.; Öhman, A.; Flygare, L.; Tano, K. When maxillary sinusitis does not heal: Findings on CBCT scans of the sinuses with a particular focus on the occurrence of odontogenic causes of maxillary sinusitis. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2017, 2, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galler, K.M.; Weber, M.; Korkmaz, Y.; Widbiller, M.; Feuerer, M. Inflammatory Response Mechanisms of the Dentine–Pulp Complex and the Periapical Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, O.; Alswayyed, S.; Alshagroud, R.; AlSheddi, M. Evaluation of concordance between clinical and histopathological diagnoses in periapical lesions of endodontic origin. J. Dent. Sci. 2020, 15, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikhi, M.; Pozve, N.J.; Khorrami, L. Using cone beam computed tomography to detect the relationship between the periodontal bone loss and mucosal thickening of the maxillary sinus. Dent. Res. J. 2014, 11, 495–501. [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi, S.; Privitera, S.; Maiolino, L.; Serra, A.; Garotta, M.; Blandino, G.; Speciale, A. Bacteriological findings and antimicrobial resistance in odontogenic and non-odontogenic chronic maxillary sinusitis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Yokoi, H.; Kohno, N. Association between odontogenic infections and unilateral sinus opacification. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2015, 42, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, C.; Bueno, M.R.; Azevedo, B.C.; Azevedo, J.R.; Pécora, J.D. A new periapical index based on cone beam computed tomography. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Q.; Duan, X.; Zheng, G.; Wang, H.; Huang, D. Associations between maxillary sinus mucosal thickening and apical periodontitis using cone-beam computed tomography scanning: A retrospective study. J. Endod 2012, 38, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.K. Manual of Histological Techniques, 1st ed.; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2017; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.atlasantibodies.com/globalassets/protocols/ihc_ventana_protocol.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2017).
- Michaud, W.A.; Nichols, A.C.; Mroz, E.A.; Faquin, W.C.; Clark, J.R.; Begum, S.; Westra, W.H.; Wada, H.; Busse, P.M.; Ellisen, L.W.; et al. Bcl-2 blocks cisplatin-induced apoptosis and predicts poor outcome following chemoradiation treatment in advanced oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capelli, M.; Gatti, P. Radiological study of maxillary sinus using CBCT: Relationship between mucosal thickening and common anatomic variants in chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Clin. Diagn Res. 2016, 10, MC07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, M.; Bowles, W.R.; McClanahan, S.L. Cone-Beam computed tomography evaluation of maxillary sinusitis. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallo, J.; Suominen-Taipale, L.; Huumonen, S.; Soikkonen, K.; Norblad, A. Prevalence of mucosal abnormalities of the maxillary sinus and their relationship to dental disease in panoramic radiography: Results from the health 2000 health examination survey. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 109, E80–E87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, J.J.; Glassberg, R.M. Dental disease: A frequently unrecognized cause of maxillary sinus abnormalities? AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1996, 166, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachatryan, L.; Khachatryan, G.; Hakobyan, G.; Khachatryan, A. Simultaneous endoscopic endonasal sinus surgery and sinus augmentation with immediate implant placement: A retrospective clinical study of 23 patients. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surgery. 2019, 47, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, R.E.; Long, C.M.; Loehrl, T.A.; Poetker, D.M. Odontogenic sinusitis: A review of the current literature. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2018, 3, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goller-Bulut, D.; Sekerci, A.E.; Köse, E.; Sisman, Y. Cone beam computed tomographic analysis of maxillary premolars and molars to detect the relationship between periapical and marginal bone loss and mucosal thickness of maxillary sinus. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2015, 20, e572–e579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, D.; Fănută, B.; Stepan, A.E.; Fronie, A.I.; Dumitrescu, C.I.; Martu, M.C.; Şurlin, P.; Şurlin, V.; Popescu, M. Silent sinus syndrome—Report of a case. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2015, 56, 229–237. [Google Scholar]
- Maspero, C.; Farronato, M.; Bellincioni, F.; Annibale, A.; Machetti, J.; Abate, A.; Cavagnetto, D. Three-Dimensional Evaluation of Maxillary Sinus Changes in Growing Subjects: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Materials 2020, 13, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simuntis, R.; Tušas, P.; Kubilius, R.; Leketas, M.; Šiupšinskienė, N.; Vaitkus, S. Association between Maxillary Posterior Teeth Periapical Odontogenic Lesions and Maxillary Sinus Mucosal Thickening: A 3D Volumetric Computed Tomography Analysis. Sinusitis 2020, 4, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, S.; Karnik, P.; Shirke, P.; Shanbhag, V. Association between periapical lesions and maxillary sinus mucosal thickening: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomographic study. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, U.; Orhan, K. Association between odontogenic conditions and maxillary sinus mucosal thickening: A retrospective CBCT study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Lin, T.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Yang, L.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, J. Radiographic features of anatomic relationship between impacted third molar and inferior alveolar canal on coronal CBCT images: Risk factors for nerve injury after tooth extraction. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khorramdel, A.; Shirmohammadi, A.; Sadighi, A.; Faramarzi, M.; Babaloo, A.R.; Sadighi Shamami, M.; Mousavi, A.; Ebrahim Adhami, Z. Association between demographic and radiographic characteristics of the schneiderian membrane and periapical and periodontal diseases using cone-beam computed tomography scanning: A retrospective study. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospects 2017, 11, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.P.; Chen, H.M.; Yu, C.H.; Kuo, R.C.; Kuo, Y.S.; Wang, Y.P. Clinicopathological study of 252 jaw bone periapical lesions from a private pathology laboratory. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2010, 109, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marçal, J.R.; Samuel, R.O.; Fernandes, D.; de Araujo, M.S.; Napimoga, M.H.; Sanivia, A.; Clemente-Napimoga, J.T.; Alves, P.M.; Mattar, R.; Rodrigues, V.; et al. T-helper cell type 17/regulatory T-cell immunoregulatory balance in human radicular cysts and periapical granulomas. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liapatas, S.; Nakou, M.; Rontogianni, D. Inflammatory infiltrate of chronic periradicular lesions: An immunohistochemical study. Int. Endod. J. 2003, 36, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.C.S.; Vilas Bôas, D.S.; Oliveira, G.Q.V.; Ramos, E.A.G.; Gurgel, C.A.S.; Santos, J.N. Histopathological study of radicular cysts diagnosed in a Brazilian population. Braz. Dent. J. 2011, 22, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Çalışkan, M.K.; Kaval, M.E.; Tekin, U.Ğ.; Ünal, T. Radiographic and histological evaluation of persistent periapical lesions associated with endodontic failures after apical microsurgery. Int. Endod. J. 2016, 49, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.N.R. On the causes of persistent apical periodontitis: A review. Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 249–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plengwitthaya, C.; Dhanuthai, K.; Chantarangsu, S.; Ratisoontorn, C. Cholesterol crystals in periapical lesions of root filled teeth. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lan, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Formation of papillary mucosa folds and enhancement of epithelial barrier in odontogenic sinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeredo, S.V.; Brasil, S.C.; Antunes, H.; Marques, F.V.; Pires, F.R.; Armada, L. Distribution of macrophages and plasma cells in apical periodontitis and their relationship with clinical and image data. J Clin. Exp. Dent. 2017, 9, e1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Philippi, C.K.; Rados, P.V.; Sant’ana Filho, M.; Barbachan, J.J.; Quadros, O.F. Distribution of CD8 and CD20 lymphocytes in chronic periapical inflammatory lesions. Braz. Dent. J. 2003, 14, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, F.; Reich, K.M.; Lettner, S.; Heimel, P.; Tangl, S.; Redl, H.; Ulm, C. The vertical course of bone regeneration in maxillary sinus floor augmentations: A histomorphometric analysis of human biopsies. J. Periodontol. 2021, 92, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, V.; Chenchev, I.; Zlatev, S.; Mijiritsky, E. Comparison Study of the Histomorphometric Results after Socket Preservation with PRF and Allograft Used for Socket Preservation—Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Antibodies | Clone | Dilution | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD4 | Clone 4B12, code NCL-L-CD4-368, Novocastra, Leica Microsystem, UK | 1:40 | membranous |
| CD8 | Clone 1A5, code NCL-L-CD8-295, Novocastra, Leica Microsystem, UK | 1:80 | membranous |
| CD20 | Clone 1A5, code NCL-L-CD8-295, Novocastra, Leica Microsystem, UK | 1:80 | membranous |
| CD68 | Clone 1A5, code NCL-L-CD8-295, Novocastra, Leica Microsystem, UK | 1:80 | membranous |
| CD79α | Clone 1A5, code NCL-L-CD8-295, Novocastra, Leica Microsystem, UK | 1:80 | membranous |
| Demographical Variables | |
|---|---|
| All Patients, n | 50 |
| Male, n (%) | 29 (58) |
| Female, n (%) | 21 (42) |
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 39.8 ± 12.1 |
| Localization | Periapical Status Index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Total | |
| left PM1, n (%) | 23 (46.9) | 9 (18.4) | 7 (14.3) | 2 (4.1) | 8 (16.3) | 49 |
| left PM2, n (%) | 19 (43.2) | 10 (22.7) | 6 (13.6) | 4 (9.1) | 5 (11.4) | 44 |
| left M1, n (%) | 10 (27) | 15 (40.5) | 5 (13.5)) | 3 (8.1) | 4 (10.8) | 37 |
| left M2, n (%) | 7 (18.4) | 19 (50) | 4 (10.5) | 5 (13.2) | 3 (7.9) | 38 |
| right PM1, n (%) | 18 (46.2) | 5 (12.8) | 7 (17.9) | 3 (7.7) | 6 (15.4) | 39 |
| right PM2, n (%) | 17 (45.9) | 3 (8.1) | 7 (18.9) | 7 (18.9) | 3 (8.1) | 37 |
| right M1, n (%) | 9 (18.8) | 19 (39.6) | 10 (20.8) | 1 (2.1) | 9 (18.8) | 48 |
| right M2, n (%) | 8 (22.2) | 2 (5.6) | 7 (19.4) | 10 (27.8) | 9 (25) | 36 |
| Localization | Maxillary Sinus Mucosal Thickness (Class) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 4 | Class 5 | Total | |
| left maxillary sinus mucosa, n (%) | 6 (12) | 4 (8) | 8 (16) | 14 (28) | 18 (36) | 50 |
| right maxillary sinus mucosa, n (%) | 2 (4) | 5 (10) | 4 (8%) | 18 (36) | 21 (42) | 50 |
| Pearson’s chi-square test: χ2 = 12.34, p = 0.0041 | ||||||
| Histological Lesions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periapical Granuloma | Periapical Granuloma with Cystic Potential | Periapical Cyst | p-Value | |
| Cases, n (%) | 15 (50) | 3 (10) | 12 (40) | |
| Periapical Status Index, 5/4/<3, n (%) | 3/4/8(20/26.7/53.3) | 1/1/1(33.3/33.3/33.3) | 9/2/1(75/16.7/8.3) | 0.013 |
| MSMT, mm, (mean ± SD) | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 3.7 ± 0.8 | 0.002 |
| Treatment | ||||
| dental extraction, n (%) | 9 (60) | 1 (33.3) | 7 (58.3) | 0.051 |
| apical resection, n (%) | 6 (40) | 2 (66.7) | 5 (41.7) | 0.062 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dumitrescu, A.; Martu, M.-A.; Nemtoi, A.; Sirghe, A.; Chelaru, L.; Tatarciuc, D.; Dumitrescu, A.-M.; Haba, D. Association between Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and Histological and Immunohistochemical Features in Periapical Lesions Correlated with Thickened Maxillary Sinus Mucosa. Medicina 2021, 57, 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080840
Dumitrescu A, Martu M-A, Nemtoi A, Sirghe A, Chelaru L, Tatarciuc D, Dumitrescu A-M, Haba D. Association between Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and Histological and Immunohistochemical Features in Periapical Lesions Correlated with Thickened Maxillary Sinus Mucosa. Medicina. 2021; 57(8):840. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080840
Chicago/Turabian StyleDumitrescu, Alexandra, Maria-Alexandra Martu, Alexandru Nemtoi, Ana Sirghe, Liliana Chelaru, Diana Tatarciuc, Ana-Maria Dumitrescu, and Danisia Haba. 2021. "Association between Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and Histological and Immunohistochemical Features in Periapical Lesions Correlated with Thickened Maxillary Sinus Mucosa" Medicina 57, no. 8: 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080840
APA StyleDumitrescu, A., Martu, M.-A., Nemtoi, A., Sirghe, A., Chelaru, L., Tatarciuc, D., Dumitrescu, A.-M., & Haba, D. (2021). Association between Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and Histological and Immunohistochemical Features in Periapical Lesions Correlated with Thickened Maxillary Sinus Mucosa. Medicina, 57(8), 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080840







