Novel Animal Model of Spontaneous Cerebral Petechial Hemorrhage Using Focused Ultrasound in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects and Institutional Review Board Statement
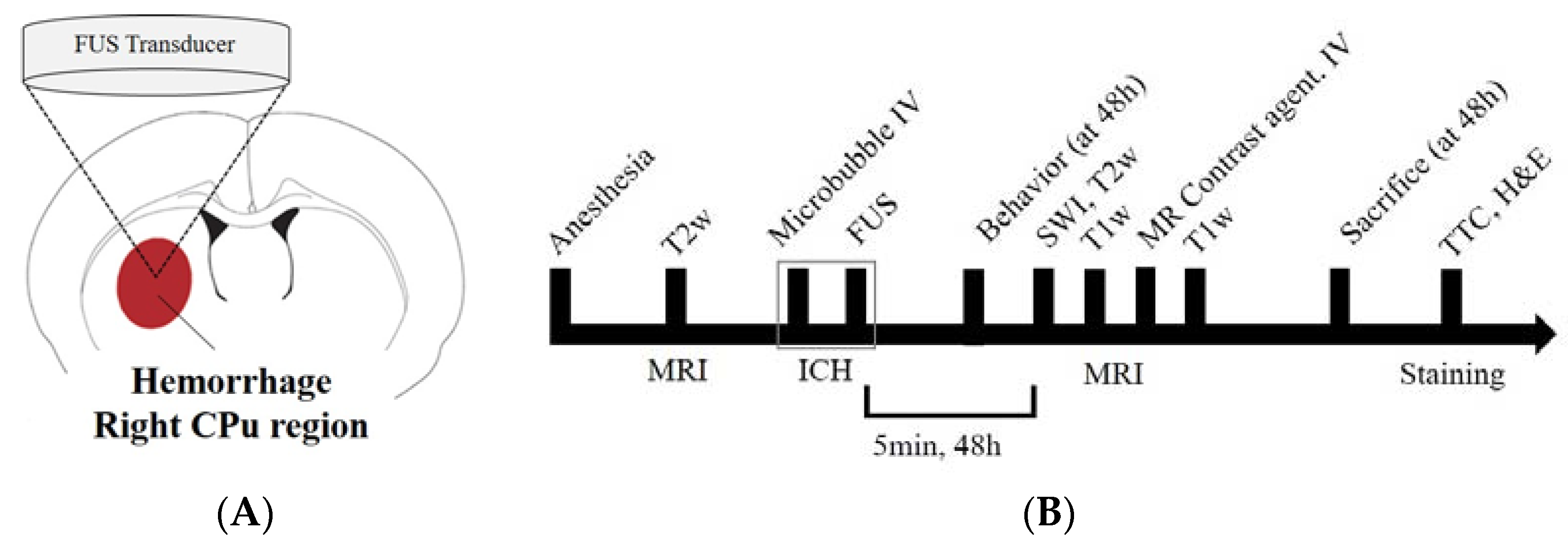
2.2. Focused Ultrasound Sonication
2.3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.4. Behavioral Assessment
2.5. Histology
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. MRgFUS System Induces Petechial Cerebral Hemorrhage with Perilesional Edema
3.2. Petechial Hemorrhage Lesion Volume
3.3. Behavioral Assessment
3.4. Histology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fanou, E.M.; Coutinho, J.M.; Shannon, P.; Kiehl, T.R.; Levi, M.M.; Wilcox, M.E.; Aviv, R.I.; Mandell, D.M. Critical Illness-Associated Cerebral Microbleeds. Stroke 2017, 48, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, F.A. Petechial Hemorrhages. A Review of Pathogenesis. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 1994, 15, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Q.; Sheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yong, V.W.; Xue, M. Intracerebral Haemorrhage: From Clinical Settings to Animal Models. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2020, 5, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Aravind, A.; Pfister, B.J.; Chandra, N.; Haorah, J. Animal Models of Traumatic Brain Injury and Assessment of Injury Severity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5332–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Animal Models of Stroke. Anim. Models Exp. Med. 2021, 4, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaenko, A.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.H.; Tang, J. Comparison of Different Preclinical Models of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2011, 111, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fredman, P.; Blennow, K.; Wikkelsø, C.; Tisell, M.; Tullberg, M.; Ma, J. Differences in cerebrospinal fluid dynamics do not affect the levels of biochemical markers in ventricular CSF from patients with aqueductal stenosis and idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Eur. J. Neurol. 2004, 11, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Siedek, F.; Yeo, S.Y.; Heijman, E.; Grinstein, O.; Bratke, G.; Heneweer, C.; Puesken, M.; Persigehl, T.; Maintz, D.; Grüll, H. Magnetic Resonance-Guided High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (MR-HIFU): Technical Background and Overview of Current Clinical Applications (Part 1). RoFo 2019, 191, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palumbo, P.; Daffinà, J.; Bruno, F.; Arrigoni, F.; Splendiani, A.; Di Cesare, E.; Barile, A.; Masciocchi, C. Basics in Magnetic Resonance Guided Focused Ultrasound: Technical Basis and Clinical Application. A Brief Overview. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Harvey, B.K.; Borden, M.A. State-of-the-Art of Microbubble-Assisted Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4393–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, H.; Park, T.Y.; Seo, H.; Han, M.; Jung, B.; Choi, H.J. A Local Difference in Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability in the Caudate Putamen and Thalamus of a Rat Brain Induced by Focused Ultrasound. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Seo, H.; Choi, H.; Lee, E.H.; Park, J. Localized Modification of Water Molecule Transport After Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption in Rat Brain. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 685977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, G.A.; Whishaw, I.Q. The Ladder Rung Walking Task: A Scoring System and Its Practical Application. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 28, e1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, Y.B.; Bae, S.K.; Oh, S.S.; Choi, J.R. Development of a Photochemical Thrombosis Investigation System to Obtain a Rabbit Ischemic Stroke Model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abumiya, T.; Sasaguri, T.; Taba, Y.; Miwa, Y.; Miyagi, M. Shear Stress Induces Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Flk-1/KDR Through the CT-Rich Sp1 Binding Site. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, M.E.; Grumbach, I.M.; Fukai, T.; Cutchins, A.; Harrison, D.G. Shear Stress Regulates Endothelial Nitric-Oxide Synthase Promoter Activity Through Nuclear Factor Kappa B Binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korenaga, R.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohura, N.; Sokabe, T.; Kamiya, A.; Ando, J. Sp1-Mediated Downregulation of P2X4 Receptor Gene Transcription in Endothelial Cells Exposed to Shear Stress. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 280, H2214–H2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, S.V.; Mackenzie, G.G.; Oteiza, P.I. The Plasma Membrane Plays a Central Role in Cells Response to Mechanical Stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, S.; Dardik, A.; Haga, M.; Yamashita, A.; Yamaguchi, S.; Koh, Y.; Madri, J.A.; Sumpio, B.E. Transcription Factor Sp1 Phosphorylation Induced by Shear Stress Inhibits Membrane type 1-Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression in Endothelium. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 34808–34814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishii, T.; Asai, T.; Urakami, T.; Oku, N. Accumulation of Macromolecules in Brain Parenchyma in Acute Phase of Cerebral Infarction/Reperfusion. Brain Res. 2010, 1321, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, J.; Leung, W.; Murphy, S.; Butler, W.; Noviski, N.; Lo, E.H. Intracranial Hemorrhage: Mechanisms of Secondary Brain Injury. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2011, 111, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, S.-Y.; Han, M.; Lee, C.; Lee, E.-H.; Kim, M.; Kim, K.-T.; Hwang, J.-H.; Na, S.; Park, J.; Park, K.-S. Novel Animal Model of Spontaneous Cerebral Petechial Hemorrhage Using Focused Ultrasound in Rats. Medicina 2022, 58, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58070881
Yoon S-Y, Han M, Lee C, Lee E-H, Kim M, Kim K-T, Hwang J-H, Na S, Park J, Park K-S. Novel Animal Model of Spontaneous Cerebral Petechial Hemorrhage Using Focused Ultrasound in Rats. Medicina. 2022; 58(7):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58070881
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Sang-Youl, Mun Han, Chaejin Lee, Eun-Hee Lee, Moonsik Kim, Kyoung-Tae Kim, Jeong-Hyun Hwang, Sungdae Na, Juyoung Park, and Ki-Su Park. 2022. "Novel Animal Model of Spontaneous Cerebral Petechial Hemorrhage Using Focused Ultrasound in Rats" Medicina 58, no. 7: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58070881
APA StyleYoon, S.-Y., Han, M., Lee, C., Lee, E.-H., Kim, M., Kim, K.-T., Hwang, J.-H., Na, S., Park, J., & Park, K.-S. (2022). Novel Animal Model of Spontaneous Cerebral Petechial Hemorrhage Using Focused Ultrasound in Rats. Medicina, 58(7), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58070881






