Accuracy of Personalized Computed Tomographic 3D Templating for Acetabular Cup Placement in Revision Arthroplasty
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preoperative Imaging
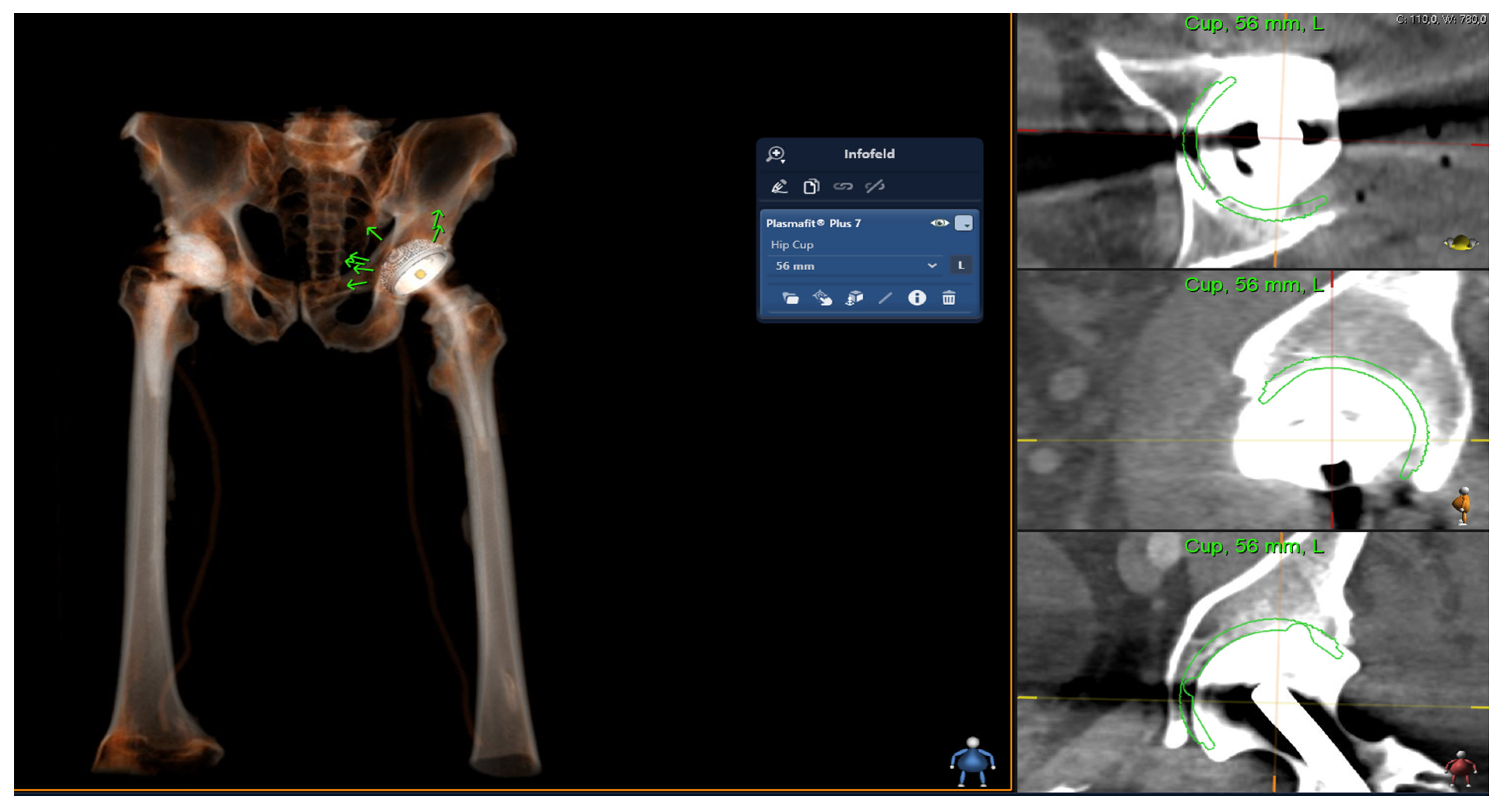
2.2. Digital Templating
2.3. Surgical Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gender and Planning Accuracy
3.2. BMI and Planning Accuracy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Computed tomographic | (CT) |
| Three-dimensional | (3D) |
| Two-dimensional | (2D) |
| Leg length discrepancy | (LLD) |
| World Health Organization | (WHO) |
| Body mass index | (BMI) |
References
- Kurtz, S.M.; Ong, K.L.; Schmier, J.; Mowat, F.; Saleh, K.; Dybvik, E.; Kärrholm, J.; Garellick, G.; Havelin, L.I.; Furnes, O.; et al. Future Clinical and Economic Impact of Revision Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2007, 89 (Suppl. S3), 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.M.; Farley, K.X.; Guild, G.N.; Bradbury, T.L. Projections and Epidemiology of Revision Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in the United States to 2030. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, S79–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammarullah, M.I.; Afif, I.Y.; Maula, M.I.; Winarni, T.I.; Tauviqirrahman, M.; Akbar, I.; Basri, H.; van der Heide, E.; Jamari, J. Tresca Stress Simulation of Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty during Normal Walking Activity. Materials 2021, 14, 7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, S.D.; Seyler, T.M.; Bennett, D.; Delanois, R.E.; Saleh, K.J.; Thongtrangan, I.; Kuskowski, M.; Cheng, E.Y.; Sharkey, P.F.; Parvizi, J.; et al. Total Hip Arthroplasties: What Are the Reasons for Revision? Int. Orthop. 2008, 32, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, D.; Hoch, A.; Rahm, S.; Stern, C.; Sutter, R.; Zingg, P.O. Combining the Advantages of 3-D and 2-D Templating of Total Hip Arthroplasty Using a New Tin-Filtered Ultra-Low-Dose CT of the Hip with Comparable Radiation Dose to Conventional Radiographs. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2022, 143, 5345–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, C.; Shaikh, N.; Shenoy, B.S.; Shaymasunder Bhat, N.; Keni, L.G.; Chethan, K.N. Wear Estimation of Hip Implants with Varying Chamfer Geometry at the Trunnion Junction: A Finite Element Analysis. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2023, 9, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, N.; Shenoy, B.S.; Bhat, N.S.; Shetty, S.; Chethan, K.N. Wear Estimation at the Contact Surfaces of Oval Shaped Hip Implants Using Finite Element Analysis. Cogent Eng. 2023, 10, 2222985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chethan, K.N.; Bhat, N.S.; Zuber, M.; Shenoy, B.S. Evolution of Different Designs and Wear Studies in Total Hip Prosthesis Using Finite Element Analysis: A Review. Cogent Eng. 2022, 9, 2027081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Static Structural Analysis of the Effect of Change in Femoral Head Sizes Used in Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Finite Element Method. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/epdf/10.1080/23311916.2022.2027080?needAccess=true&role=button (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Eggli, S.; Pisan, M.; Müller, M.E. The Value of Preoperative Planning for Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1998, 80, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motomura, G.; Hamai, S.; Ikemura, S.; Fujii, M.; Kawahara, S.; Yoshino, S.; Nakashima, Y. Contemporary Indications for First-Time Revision Surgery after Primary Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty with Emphasis on Early Failures. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrack, R.L. Preoperative Planning for Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2004, 420, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, F.S.; Masri, B.A.; Garbuz, D.S.; Duncan, C.P. The Prevention of Periprosthetic Fractures in Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 1999, 30, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, V.E. Uncemented Porous-Coated Anatomic Total Hip Replacement. Results at Six Years in a Consecutive Series. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1993, 75, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoikka, V.; Paavilainen, T.; Lindholm, T.S.; Turula, K.B.; Ylikoski, M. Measurement and Restoration of Equality in Length of the Lower Limbs in Total Hip Replacement. Skelet. Radiol. 1987, 16, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Valle, A.G.; Padgett, D.E.; Salvati, E.A. Preoperative Planning for Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2005, 13, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosashvili, Y.; Shasha, N.; Olschewski, E.; Safir, O.; White, L.; Gross, A.; Backstein, D. Digital versus Conventional Templating Techniques in Preoperative Planning for Total Hip Arthroplasty. Can. J. Surg. 2009, 52, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Desai, A.S.; Dramis, A.; Board, T.N. Leg Length Discrepancy after Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Review of Literature. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet Med. 2013, 6, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, A.; Hill, J.; Orr, J.; Humphreys, P.; Rooney, A.; Morrow, E.; Beverland, D. Patients’ Perception of Leg Length Discrepancy Post Total Hip Arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2015, 25, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaass, C.; Clauss, M.; Ochsner, P.E.; Ilchmann, T. Influence of Leg Length Discrepancy on Clinical Results after Total Hip Arthroplasty—A Prospective Clinical Trial. Hip Int. 2011, 21, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konyves, A.; Bannister, G.C. The Importance of Leg Length Discrepancy after Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2005, 87, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.D. Preoperative Planning for Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. Am. J. Orthop. 2002, 31, 179–181. [Google Scholar]
- Barrack, R.L.; Burnett, R.S.J. Preoperative Planning for Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. Instr. Course Lect. 2006, 55, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schiffner, E.; Latz, D.; Jungbluth, P.; Grassmann, J.P.; Tanner, S.; Karbowski, A.; Windolf, J.; Schneppendahl, J. Is Computerised 3D Templating More Accurate than 2D Templating to Predict Size of Components in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty? Hip Int. 2019, 29, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishi, H.; Smith, J.B.V.; Asopa, V.; Field, R.E.; Wang, C.; Sochart, D.H. Comparison of the Accuracy of 2D and 3D Templating Methods for Planning Primary Total Hip Replacement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. EFORT Open Rev. 2022, 7, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sariali, E.; Mauprivez, R.; Khiami, F.; Pascal-Mousselard, H.; Catonné, Y. Accuracy of the Preoperative Planning for Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty. A Randomised Comparison between Three-Dimensional Computerised Planning and Conventional Templating. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2012, 98, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiddon, D.R.; Bono, J.V. Digital Templating in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Instr. Course Lect. 2008, 57, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Gamble, P.; de Beer, J.; Petruccelli, D.; Winemaker, M. The Accuracy of Digital Templating in Uncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.J.; DeBuitleir, C.; Soden, P.; O’Donnchadha, B.; Tansey, A.; Abdulkarim, A.; McMahon, C.; Hurson, C.J. 3D Printing Aids Acetabular Reconstruction in Complex Revision Hip Arthroplasty. Adv. Orthop. 2017, 2017, 8925050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryada, V.R.; Mulpur, P.; Eachempati, K.K.; Annapareddy, A.; Badri Narayana Prasad, V.; Gurava Reddy, A.V. Pre-Operative Planning and Templating with 3-D Printed Models for Complex Primary and Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Orthop. 2022, 34, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [CrossRef]
- Lewinnek, G.E.; Lewis, J.L.; Tarr, R.; Compere, C.L.; Zimmerman, J.R. Dislocations after Total Hip-Replacement Arthroplasties. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1978, 60, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 18 June 2023).
- Alexander, C.; Loeb, A.E.; Fotouhi, J.; Navab, N.; Armand, M.; Khanuja, H.S. Augmented Reality for Acetabular Component Placement in Direct Anterior Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 1636–1641.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logishetty, K.; Western, L.; Morgan, R.; Iranpour, F.; Cobb, J.P.; Auvinet, E. Can an Augmented Reality Headset Improve Accuracy of Acetabular Cup Orientation in Simulated THA? A Randomized Trial. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2019, 477, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakoso, A.T.; Basri, H.; Adanta, D.; Yani, I.; Ammarullah, M.I.; Akbar, I.; Ghazali, F.A.; Syahrom, A.; Kamarul, T. The Effect of Tortuosity on Permeability of Porous Scaffold. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaha, Z.F.M.; Ammarullah, M.I.; Abdullah, N.N.A.A.; Aziz, A.U.A.; Gan, H.-S.; Abdullah, A.H.; Abdul Kadir, M.R.; Ramlee, M.H. Biomechanical Effects of the Porous Structure of Gyroid and Voronoi Hip Implants: A Finite Element Analysis Using an Experimentally Validated Model. Materials 2023, 16, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, R.; Shaikh, A.H.; O’Byrne, J.M. The Accuracy and Inter-Observer Reliability of Acetate Templating in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 182, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariali, E.; Mouttet, A.; Pasquier, G.; Durante, E.; Catone, Y. Accuracy of Reconstruction of the Hip Using Computerised Three-Dimensional Pre-Operative Planning and a Cementless Modular Neck. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2009, 91, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, A.; Radmer, S.; Asbach, P.; Juran, R.; Schwenke, C.; Diederichs, G.; Hamm, B.; Sparmann, M. Computed Tomography for Preoperative Planning in Minimal-Invasive Total Hip Arthroplasty: Radiation Exposure and Cost Analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 78, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, L.A.; Scholler, G.; Wagner, S.; Friesenbichler, J.; Maurer-Ertl, W.; Leithner, A. The Accuracy of Digital Templating in Uncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2019, 139, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Acetabular cup Revision | 30 |
Aesculap Plasmafit
| 10 2 4 4 |
| Aesculap Plasmafit Revision Avantage Acetabular System | 14 4 |
| EcoFit 2M | 1 |
| Tritanium Revision | 1 |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 71 ± 9.6 |
| Female | 14 |
| Male | 16 |
| BMI (WHO classification in kg/m2) | |
| underweight (<18.5) | 0 |
| normal weight (18.5–24.9) | 5 |
| overweight (≥25.0) | 15 |
| obese (≥30.0) | 10 |
| Accuracy of Templating | 2D Templating | 3D Templating | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precise determination of acetabular cup (2D vs. 3D) | 26.7% (8/30) | 66.7% (20/30) | p < 0.002 | |
| Gender (2D vs. 3D) | Female Male | 21.4% (3/14) 31.3% (5/16) | 50% (7/14) 81.3% (13/16) | 2D: p = 0.689 3D: p = 0.122 |
| BMI (2D vs. 3D) | Normal weight Overweight Obese | 0% (0/5) 46.7% (7/15) 10% (1/10) | 60% (3/5) 73.3% (11/15) 60% (6/10) | 2D: p = 0.765 3D: p = 0.812 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Winter, P.; Fritsch, E.; Tschernig, T.; Goebel, L.; Wolf, M.; Müller, M.; Weise, J.J.; Orth, P.; Landgraeber, S. Accuracy of Personalized Computed Tomographic 3D Templating for Acetabular Cup Placement in Revision Arthroplasty. Medicina 2023, 59, 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091608
Winter P, Fritsch E, Tschernig T, Goebel L, Wolf M, Müller M, Weise JJ, Orth P, Landgraeber S. Accuracy of Personalized Computed Tomographic 3D Templating for Acetabular Cup Placement in Revision Arthroplasty. Medicina. 2023; 59(9):1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091608
Chicago/Turabian StyleWinter, Philipp, Ekkehard Fritsch, Thomas Tschernig, Lars Goebel, Milan Wolf, Manuel Müller, Julius J. Weise, Patrick Orth, and Stefan Landgraeber. 2023. "Accuracy of Personalized Computed Tomographic 3D Templating for Acetabular Cup Placement in Revision Arthroplasty" Medicina 59, no. 9: 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091608
APA StyleWinter, P., Fritsch, E., Tschernig, T., Goebel, L., Wolf, M., Müller, M., Weise, J. J., Orth, P., & Landgraeber, S. (2023). Accuracy of Personalized Computed Tomographic 3D Templating for Acetabular Cup Placement in Revision Arthroplasty. Medicina, 59(9), 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091608






