Alterations in von Willebrand Factor Levels in Patients with Malaria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Disease Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Definitions
2.3. Systematic Review Question
2.4. Database Searches
2.5. Eligibility Criteria
2.6. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.7. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.8. Data Synthesis
3. Results
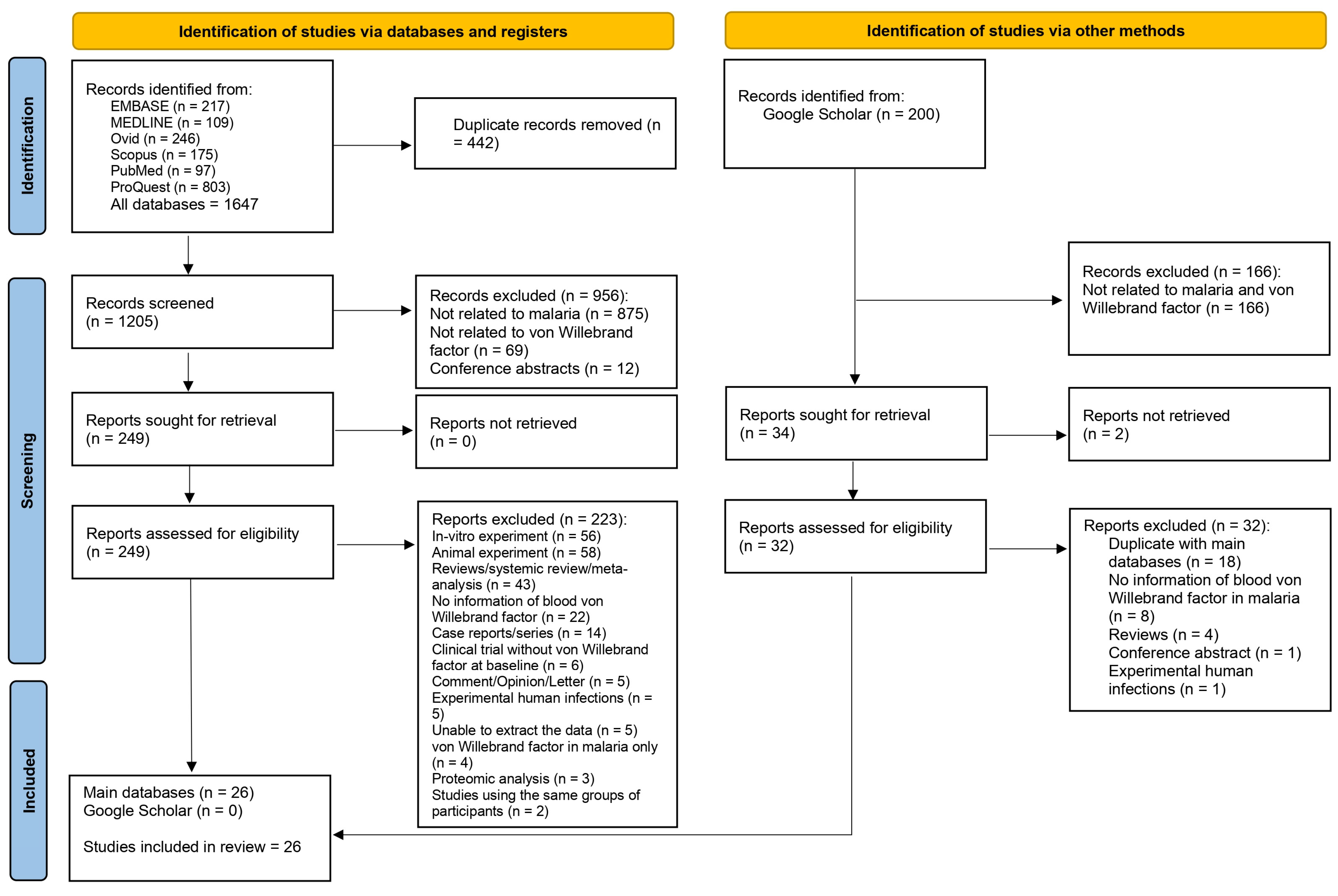
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Key Characteristics of Included Studies
3.3. Risk of Bias
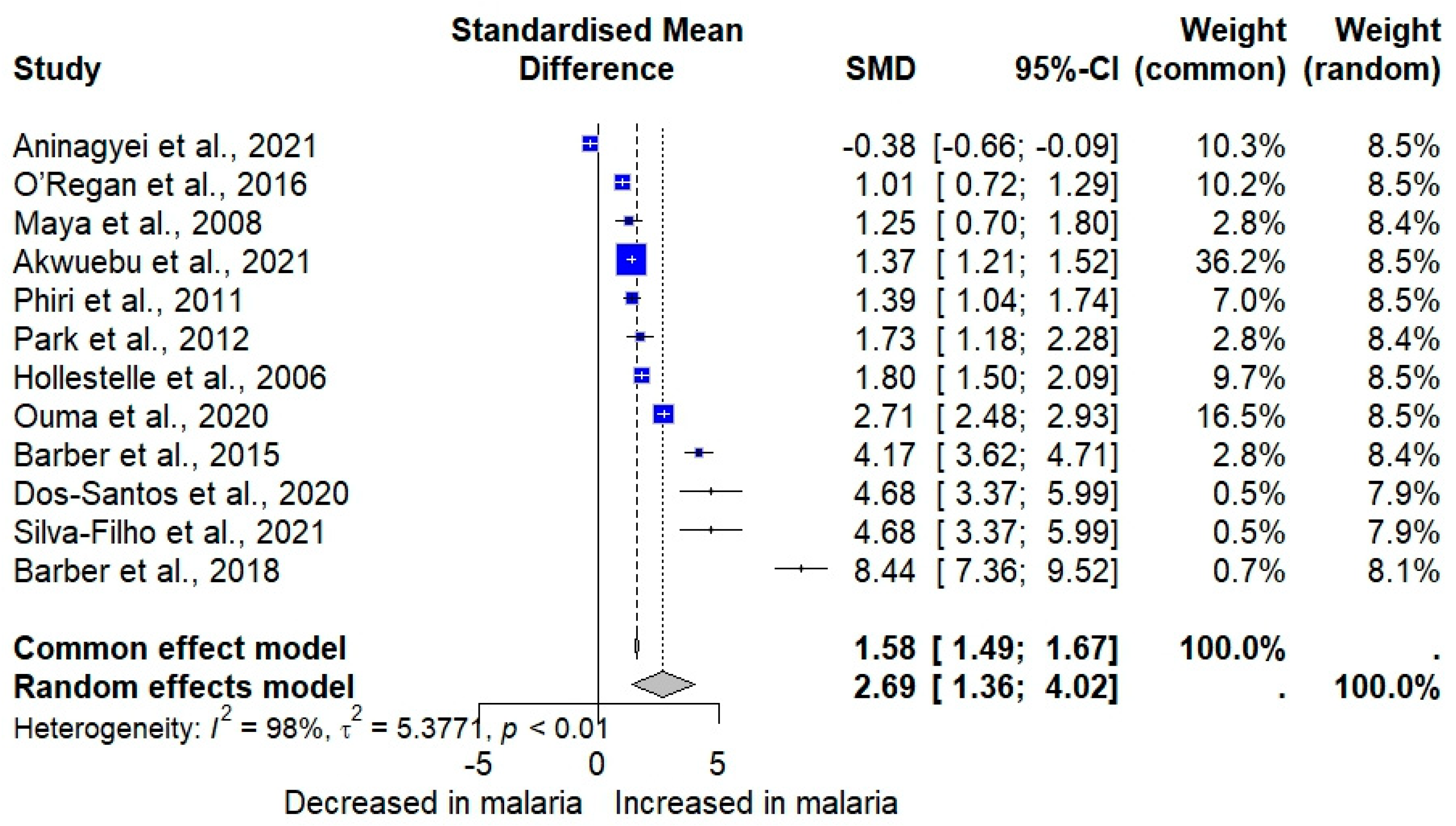
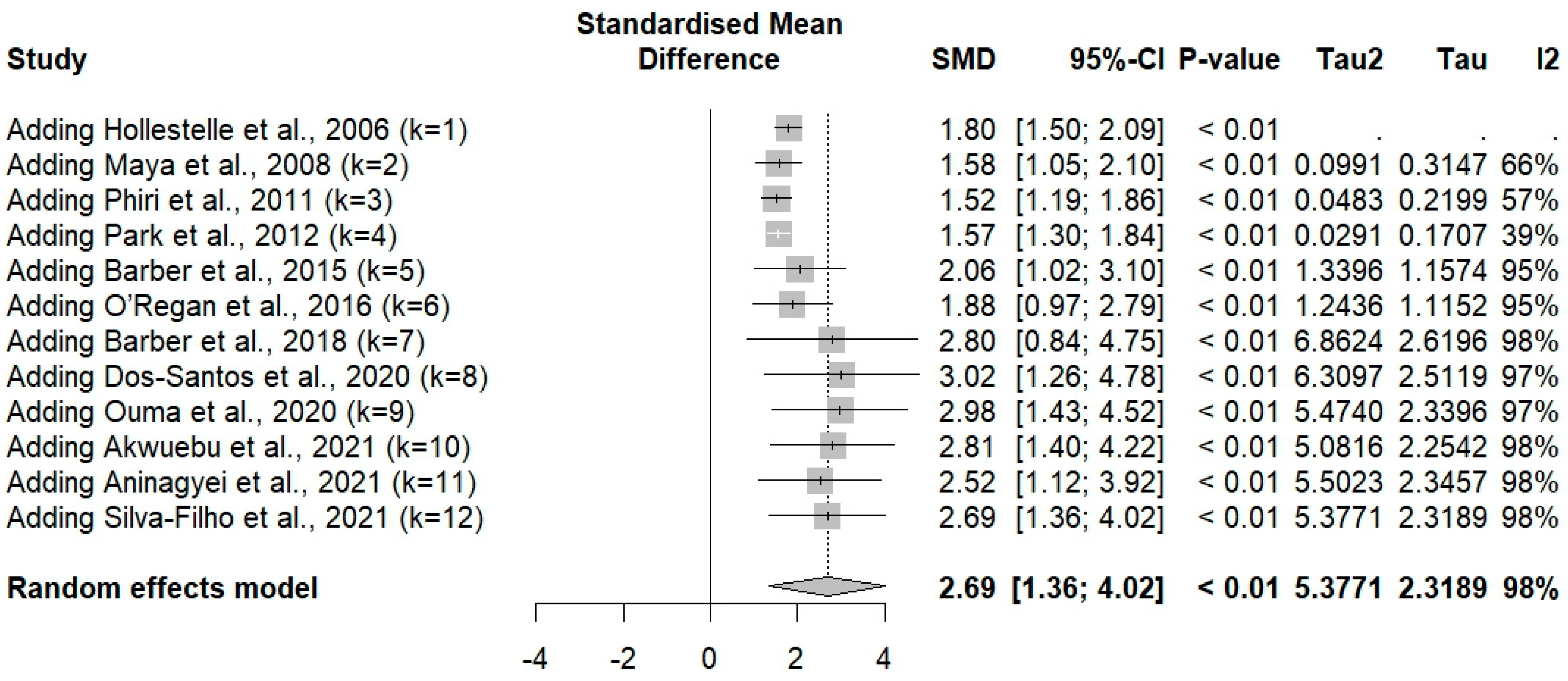
3.4. vWF Levels Between Plasmodium-Infected and -Uninfected Controls
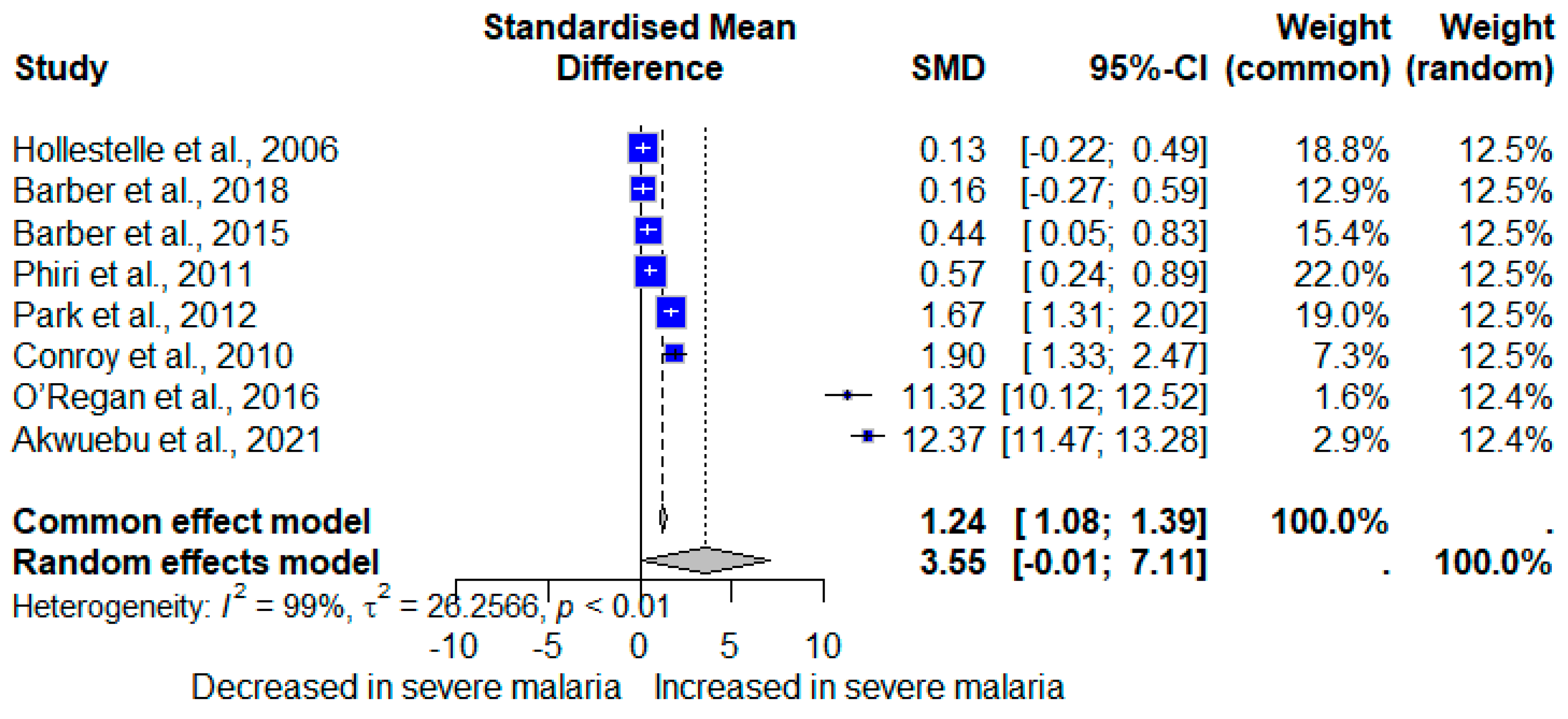
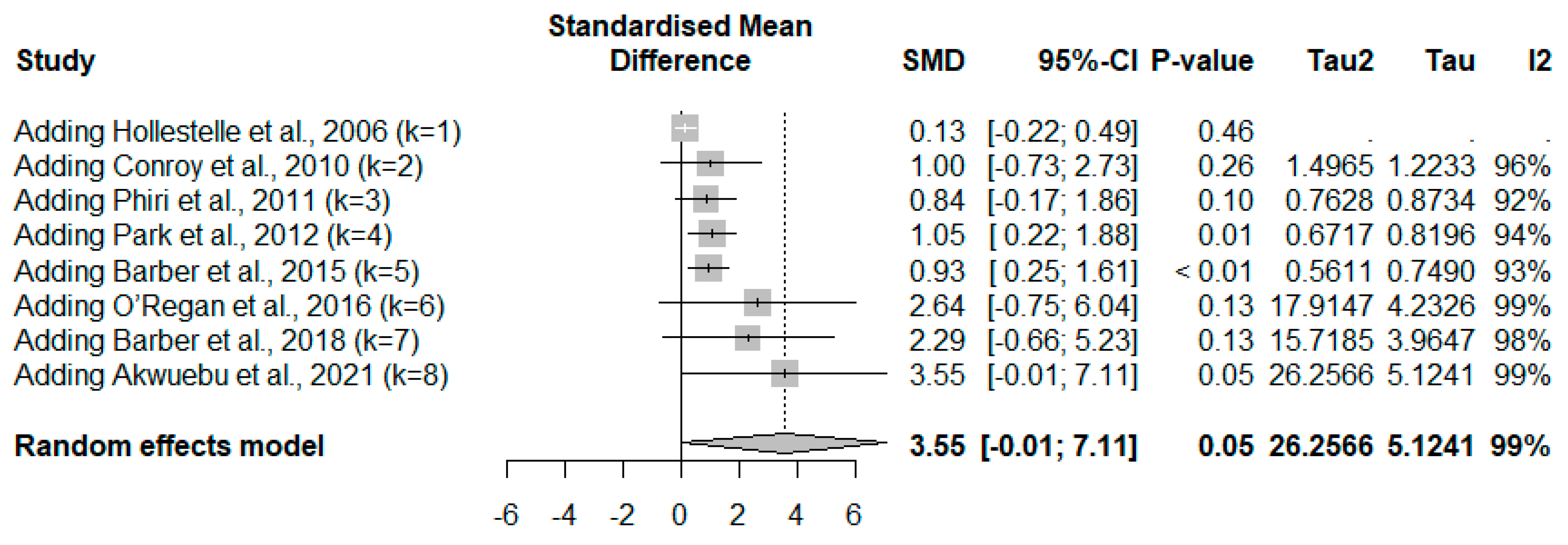
3.5. vWF in Severe and Non-Severe Plasmodium Infections
3.6. vWF in Mortality, Complications, Plasmodium Species, and Parasite Density
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fletcher, T.E.; Beeching, N.J. Malaria. J. R. Army Med. Corps 2013, 159, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meibalan, E.; Marti, M. Biology of malaria transmission. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a025452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, A.M.; Kappe, S.H.I. Malaria parasite liver infection and exoerythrocytic biology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a025486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, P. The 2023 WHO World malaria report. Lancet Microbe. 2024, 5, e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoloni, A.; Zammarchi, L. Clinical aspects of uncomplicated and severe malaria. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 4, e2012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.; Lavstsen, T.; Berger, S.S.; Wang, C.W.; Petersen, J.E.; Avril, M.; Brazier, A.J.; Freeth, J.; Jespersen, J.S.; Nielsen, M.A.; et al. Severe malaria is associated with parasite binding to endothelial protein C receptor. Nature 2013, 498, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, M.A.; Anstey, N.M.; Yeo, T.W.; Florence, S.M.; Granger, D.L.; Mwaikambo, E.D.; Weinberg, J.B. Vascular dysfunction in malaria: Understanding the role of the endothelial glycocalyx. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 751251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukati, S.; Wannatung, T.; Duangchan, T.; Kotepui, K.U.; Masangkay, F.R.; Tseng, C.P.; Kotepui, M. Alteration of prothrombin time in Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax infections with different levels of severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francischetti, I.M.; Seydel, K.B.; Monteiro, R.Q. Blood coagulation, inflammation, and malaria. Microcirculation 2008, 15, 81–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.; McConkey, S. The role of platelets in the pathogenesis of cerebral malaria. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangchan, T.; Kotepui, M.; Sukati, S.; Rattanapan, Y.; Wangdi, K. A Systematic review and meta-analysis of the proportion estimates of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) in malaria. Trop. Med. Infect Dis. 2023, 8, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.I.; Saxena, A.; Ahmad, F. Structure and function of von Willebrand factor. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2012, 23, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggeri, Z.M. Von Willebrand factor, platelets and endothelial cell interactions. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skipwith, C.G.; Cao, W.; Zheng, X.L. Factor VIII and platelets synergistically accelerate cleavage of von Willebrand factor by ADAMTS13 under fluid shear stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 28596–28603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, W.L.; Hultin, M.B.; James, A.H.; Manco-Johnson, M.J.; Montgomery, R.R.; Ortel, T.L.; Rick, M.E.; Sadler, J.E.; Weinstein, M.; Yawn, B.P. von Willebrand disease (VWD): Evidence-based diagnosis and management guidelines, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel report (USA). Haemophilia 2008, 14, 171–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patmore, S.; Dhami, S.P.S.; O’Sullivan, J.M. Von Willebrand factor and cancer; metastasis and coagulopathies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2444–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawecki, C.; Lenting, P.J.; Denis, C.V. von Willebrand factor and inflammation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhota, S.; Melnikov, I.; Avtaeva, Y.; Kozlov, S.; Gabbasov, Z. Shear stress-induced activation of von Willebrand Factor and cardiovascular pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvardsen, M.S.; Hindberg, K.; Hansen, E.S.; Morelli, V.M.; Ueland, T.; Aukrust, P.; Braekkan, S.K.; Evensen, L.H.; Hansen, J.B. Plasma levels of von Willebrand factor and future risk of incident venous thromboembolism. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, D.; de Laat, B.; Jenkins, P.V.; Bunn, J.; Craig, A.G.; Terraube, V.; Preston, R.J.; Donkor, C.; Grau, G.E.; van Mourik, J.A.; et al. Severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria is associated with circulating ultra-large von Willebrand multimers and ADAMTS13 inhibition. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, D.; Segura, C.; Arman, M.; McGill, S.; Burchmore, R.; Lopera-Mesa, T. Uncomplicated Plasmodium vivax malaria: Mapping the proteome from circulating platelets. Clin. Proteom. 2022, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, S.M.; Chen, J.; Chung, D.W.; Barker, K.R.; Conroy, A.L.; Hawkes, M.T.; Namasopo, S.; Kain, K.C.; López, J.A.; Liles, W.C. Endothelial activation, haemostasis and thrombosis biomarkers in Ugandan children with severe malaria participating in a clinical trial. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollestelle, M.J.; Donkor, C.; Mantey, E.A.; Chakravorty, S.J.; Craig, A.; Akoto, A.O.; O’Donnell, J.; van Mourik, J.A.; Bunn, J. von Willebrand factor propeptide in malaria: Evidence of acute endothelial cell activation. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 133, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Guidelines for Malaria; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kotepui, K.U.; Masangkay, F.R.; Wangdi, K.; Mahittikorn, A.; Majima, H.J.; Kotepui, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of cortisol levels in Plasmodium infections. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotepui, K.U.; Mahittikorn, A.; Wilairatana, P.; Masangkay, F.R.; Kotepui, M. Association between Plasmodium infection and nitric oxide levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.L.; Whaley, P.; Thayer, K.A.; Schunemann, H.J. Identifying the PECO: A framework for formulating good questions to explore the association of environmental and other exposures with health outcomes. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraeiad, S.; Kotepui, K.U.; Mahittikorn, A.; Masangkay, F.R.; Wilairatana, P.; Suwannatrai, A.T.; Thinkhamrop, K.; Wangdi, K.; Kotepui, M. Albumin levels in malaria patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of their association with disease severity. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moola, S.M.Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; Lisy, K.; Mu, P.-F. Chapter 7: Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. Joanna Briggs Inst. Rev. Man. 2017, 5, 217–269. [Google Scholar]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials revisited. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 45, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S. Psychosocial models of the role of social support in the etiology of physical disease. Health Psychol. 1988, 7, 269–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, A.; Abrams, K.; Jones, D.; Sheldon, T.; Song, F. Methods for Meta-analysis in Medical Research; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rolling, C.C.; Phillips, R.O.; Abass, K.M.; Poku, J.K.A.; Osei-Mireku, S.; Osei-Wusu, B.; Thompson, W.; Vinnemeier, C.D.; Huebl, L.; Langer, F.; et al. Absence of malaria-associated coagulopathy in asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum infection: Results from a cross-sectional study in the Ashanti region, Ghana. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, B.E.; William, T.; Grigg, M.J.; Parameswaran, U.; Piera, K.A.; Price, R.N.; Yeo, T.W.; Anstey, N.M. Parasite biomass-related inflammation, endothelial activation, microvascular dysfunction and disease severity in vivax malaria. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mast, Q.; Brouwers, J.; Syafruddin, D.; Bousema, T.; Baidjoe, A.Y.; de Groot, P.G.; van der Ven, A.J.; Fijnheer, R. Is asymptomatic malaria really asymptomatic? Hematological, vascular and inflammatory effects of asymptomatic malaria parasitemia. J. Infect. 2015, 71, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aninagyei, E.; Adu, P.; Rufai, T.; Ampomah, P.; Kwakye-Nuako, G.; Egyir-Yawson, A.; Acheampong, D.O. Effect of asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum parasitaemia on platelets thrombogenicity in blood donors. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. Off. J. Indian Soc. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2021, 37, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, J.; Burté, F.; Pramana, S.; Conte, I.; Brown, B.J.; Orimadegun, A.E.; Ajetunmobi, W.A.; Afolabi, N.K.; Akinkunmi, F.; Omokhodion, S.; et al. Affinity proteomics reveals elevated muscle proteins in plasma of children with cerebral malaria. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, B.E.; Grigg, M.J.; Piera, K.A.; Timothy, W.; Cooper, D.J.; Plewes, K.; Dondorp, A.M.; Yeo, T.W.; Anstey, N.M. Intravascular haemolysis in severe Plasmodium knowlesi malaria: Association with endothelial activation, microvascular dysfunction, and acute kidney injury. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mast, Q.; Groot, E.; Asih, P.B.; Syafruddin, D.; Oosting, M.; Sebastian, S.; Ferwerda, B.; Netea, M.G.; de Groot, P.G.; van der Ven, A.J.; et al. ADAMTS13 deficiency with elevated levels of ultra-large and active von Willebrand factor in P. falciparum and P. vivax malaria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos-Santos, J.C.K.; Silva-Filho, J.L.; Judice, C.C.; Kayano, A.C.A.V.; Aliberti, J.; Khouri, R.; de Lima, D.S.; Nakaya, H.; Lacerda, M.V.G.; De Paula, E.V.; et al. Platelet disturbances correlate with endothelial cell activation in uncomplicated Plasmodium vivax malaria. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huson, M.A.; Kalkman, R.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; Alabi, A.S.; van’t Veer, C.; Grobusch, M.P.; Meijers, J.C.; van der Poll, T. Impact of HIV infection on the haemostatic response during sepsis and malaria. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortz, T.B.; Nyirenda, J.; Tembo, D.; Elfving, K.; Baltzell, K.; Bandawe, G.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Macfarlane, S.B.; Mandala, W.; Nyirenda, T.S. Distinct biomarker profiles distinguish Malawian children with malarial and non-malarial sepsis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 101, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenberg, E.C.; Charunwatthana, P.; Cohen, S.; Van Den Born, B.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Yunus, E.B.; Hassan, M.U.; Hoque, G.; Maude, R.J.; Nuchsongsin, F.; et al. Severe malaria is associated with a deficiency of von Willebrand factor cleaving protease, ADAMTS13. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, D.W.M.; Mewono, L.; Nkoma, A.M.; Issifou, S.; Mavoungou, E. Markers of vascular endothelial cell damage and P. falciparum malaria: Association between levels of both sE-selectin and thrombomodulin, and cytokines, hemoglobin and clinical presentation. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2008, 19, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Regan, N.; Moxon, C.; Gegenbauer, K.; O’Sullivan, J.; Chion, A.; Smith, O.; Preston, R.; Brophy, T.; Craig, A.; O’Donnell, J. Marked elevation in plasma osteoprotegerin constitutes an early and consistent feature of cerebral malaria. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otterdal, K.; Berg, A.; Michelsen, A.E.; Patel, S.; Gregersen, I.; Sagen, E.L.; Halvorsen, B.; Yndestad, A.; Ueland, T.; Langeland, N.; et al. Plasma levels of interleukin 27 in falciparum malaria is increased independently of co-infection with HIV: Potential immune-regulatory role during malaria. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouma, B.J.; Ssenkusu, J.M.; Shabani, E.; Datta, D.; Opoka, R.O.; Idro, R.; Bangirana, P.; Park, G.; Joloba, M.L.; Kain, K.C.; et al. Endothelial activation, acute kidney injury, and cognitive impairment in pediatric severe malaria. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, e734–e743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.S.; Ireland, K.F.; Opoka, R.O.; John, C.C. Evidence of endothelial activation in asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum parasitemia and effect of blood group on levels of von Willebrand factor in malaria. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2012, 1, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, H.; Bridges, D.; Mbaya, B.; Glover, S.; De Laat, B.; Van Mourik, J.; Seydel, K.; Taylor, T.; Molyneux, M.; Craig, A.; et al. Elevated plasma von Willebrand factor and propeptide levels in Malawian children with malaria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 85, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reutersward, P.; Bergstrom, S.; Orikiiriza, J.; Lindquist, E.; Bergstrom, S.; Andersson Svahn, H.; Ayoglu, B.; Uhlen, M.; Wahlgren, M.; Normark, J.; et al. Levels of human proteins in plasma associated with acute paediatric malaria. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Filho, J.L.; Dos-Santos, J.C.K.; Judice, C.; Beraldi, D.; Kannan, V.; Lima, D.; Nakaya, H.I.; De Paula Erich, V.; Lopes, S.C.P.; Lacerda Marcus, V.G.; et al. Total parasite biomass but not peripheral parasitaemia is associated with endothelial and haematological perturbations in Plasmodium vivax patients. eLife 2021, 10, e71351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akwuebu, S.O.; Mbeera, B.S.; Ibeh, N.C.; Eze, E.M.; Jeremiah, Z.A. Influence of age category and malaria type on some haematological, vWF, ADAMTS13, L-arg, D2D, FBG, FVIII and coagulatory parameters of malaria infected paediatric subjects in Rivers State, Nigeria. Int. J. Res. Rep. Hematol. 2021, 4, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Conroy, A.L.; Phiri, H.; Hawkes, M.; Glover, S.; Mallewa, M.; Seydel, K.B.; Taylor, T.E.; Molyneux, M.E.; Kain, K.C. Endothelium-based biomarkers are associated with cerebral malaria in Malawian children: A retrospective case-control study. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdman, L.K.; Aggrey, D.; Musoke, C.; Conroy, A.L.; Hawkes, M.; Higgins, S.; Rajwans, N.; Wolofsky, K.T.; Streiner, D.L.; Liles, W.C.; et al. Combinations of host biomarkers predict mortality among Ugandan children with severe malaria: A retrospective case-control study. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gowda, N.M.; Gowda, D.C. Phagosomal acidification prevents macrophage inflammatory cytokine production to malaria, and dendritic cells are the major source at the early stages of infection: Implication for malaria protective immunity development. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 23135–23147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunst, J.; Kamena, F.; Matuschewski, K. Cytokines and chemokines in cerebral malaria pathogenesis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pober, J.S.; Sessa, W.C. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, G.D.; Ly, V.C.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tran, T.H.; Nguyen, H.P.; Bethell, D.; Wyllie, S.; Louwrier, K.; Fox, S.B.; Gatter, K.C.; et al. Systemic endothelial activation occurs in both mild and severe malaria. Correlating dermal microvascular endothelial cell phenotype and soluble cell adhesion molecules with disease severity. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar]
- Kotepui, M.; Phunphuech, B.; Phiwklam, N.; Chupeerach, C.; Duangmano, S. Effect of malarial infection on haematological parameters in population near Thailand-Myanmar border. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahittikorn, A.; Masangkay, F.R.; Kotepui, K.U.; Mala, W.; Milanez, G.J.; Wilairatana, P.; Kotepui, M. Alteration of platelet count in patients with severe non-Plasmodium falciparum malaria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biology 2021, 10, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mast, Q.; Groot, E.; Lenting, P.J.; de Groot, P.G.; McCall, M.; Sauerwein, R.W.; Fijnheer, R.; van der Ven, A. Thrombocytopenia and release of activated von Willebrand factor during early Plasmodium falciparum malaria. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, A.; Ball, C.; Nolasco, L.; Moake, J.F.; Dong, J.F. Effects of inflammatory cytokines on the release and cleavage of the endothelial cell-derived ultralarge von Willebrand factor multimers under flow. Blood 2004, 104, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Cheong, F.W.; Amir, A.; Lai, M.Y.; Tan, J.H.; Phang, W.K.; Shahari, S.; Lau, Y.L. Plasmodium knowlesi: The game changer for malaria eradication. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menkin-Smith, L.; Winders, W.T. Plasmodium vivax malaria [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Snow, R.W.; Sartorius, B.; Kyalo, D.; Maina, J.; Amratia, P.; Mundia, C.W.; Bejon, P.; Noor, A.M. The prevalence of Plasmodium falciparum in sub-Saharan Africa since 1900. Nature 2017, 550, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotepui, M.; Kotepui, K.U.; Milanez, G.D.; Masangkay, F.R. Prevalence of severe Plasmodium knowlesi infection and risk factors related to severe complications compared with non-severe P. knowlesi and severe P. falciparum malaria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakeford, C.; Aguila, S.; Roche, F.; Hokamp, K.; Fazavana, J.; Cervantes, M.P.; Curtis, A.M.; Hawerkamp, H.C.; Dhami, S.P.S.; Charles-Messance, H.; et al. Willebrand factor links primary hemostasis to innate immunity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Mansouritorghabeh, H.; Parsa-Kondelaji, M. High levels of von Willebrand factor markers in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 22, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, A.; Pranata, R.; Lim, M.A.; Akbara, M.R.; Martha, J.W. Endotheliopathy marked by high von Willebrand factor (vWF) antigen in COVID-19 is associated with poor outcome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 117, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianto Al-Farabi, M.J.; Nugraha, R.A.; Marsudi, B.A.; Azmi, Y. Biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microvasc. Res. 2021, 138, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Feng, S.; Zhao, J.; Liao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Liu, J. Prognostic value of plasma von Willebrand factor levels in major adverse cardiovascular events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, M.; Zhao, J.; Lin, L.; Liu, J. Plasma levels of von Willebrand factor in type 2 diabetes patients with and without cardiovascular diseases: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, C.; Xin, M.; He, L.; Sun, G.; Shen, F. Prognostic value of von Willebrand factor in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Key Characteristics | Number of Studies (N) | % |
|---|---|---|
| Publication year | ||
| 2000–2009 | 5 | 19.23 |
| 2010–2019 | 13 | 50.00 |
| 2020–2024 | 8 | 30.77 |
| Study designs | ||
| Cross-sectional study | 12 | 46.15 |
| Cohort study | 10 | 38.46 |
| Case-control study | 4 | 15.38 |
| Study areas | ||
| Asia | 5 | 19.23 |
| Indonesia | 2 | 7.69 |
| Malaysia | 2 | 7.69 |
| Bangladesh | 1 | 3.85 |
| Africa | 18 | 69.23 |
| Ghana | 4 | 15.38 |
| Malawi | 4 | 15.38 |
| Uganda | 4 | 15.38 |
| Gabon | 2 | 7.69 |
| Nigeria | 2 | 7.69 |
| Rwanda | 1 | 3.85 |
| Mozambique | 1 | 3.85 |
| South America | 3 | 11.54 |
| Brazil | 2 | 7.69 |
| Colombia | 1 | 3.85 |
| Plasmodium species | ||
| P. falciparum | 19 | 73.08 |
| P. vivax | 3 | 11.54 |
| P. falciparum, P. vivax | 2 | 7.69 |
| P. knowlesi | 1 | 3.85 |
| P. falciparum, P. vivax, mixed infections, unclassified species | 1 | 3.85 |
| Participants | ||
| Children | 13 | 50.00 |
| Adults | 6 | 23.08 |
| Children and adults | 5 | 19.23 |
| Not specified | 2 | 7.69 |
| Methods for detecting Plasmodium | ||
| Microscopic method | 11 | 42.31 |
| Microscopic method/RDT | 8 | 30.77 |
| Microscopic method/RDT | 4 | 15.38 |
| Microscopic method/RDT/PCR | 2 | 7.69 |
| RDT/PCR | 1 | 3.85 |
| Assays for von Willebrand factor | ||
| ELISA | 19 | 73.08 |
| Bead assays | 4 | 15.38 |
| EIA | 1 | 3.85 |
| Immunoturbidimetry | 1 | 3.85 |
| Not specified | 1 | 3.85 |
| Blood samples | ||
| Plasma | 23 | 88.46 |
| Serum | 3 | 11.54 |
| Subgroup | Test for Subgroup Differences (Random-Effects Model) | SMD (95% CI) | I2 (%) | Number of Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Publication years | 0.3088 | |||
| 2.5376 [0.6354; 4.4398] | 98.8 | 5 | |
| 3.3182 [0.6293; 6.0071] | 98.4 | 5 | |
| 1.5756 [1.0488; 2.1024] | 66.1 | 2 | |
| Study design | 0.0602 | |||
| 3.8231 [1.7725; 5.8737] | 97.8 | 6 | |
| 1.5275 [0.2926; 2.7625] | 96.6 | 6 | |
| Continent | <0.0001 | |||
| 1.3580 [0.7442; 1.9719] | 97.6 | 8 | |
| 6.2783 [2.0879; 10.4686] | 97.9 | 2 | |
| 4.6809 [3.7558; 5.6060] | 0.0 | 2 | |
| Country | <0.0001 | |||
| 2.2526 [1.2978; 3.2074] | 90.5 | 2 | |
| 1.1840 [0.8093; 1.5588] | 64.0 | 2 | |
| 0.7092 [−1.4239; 2.8422] | 99.1 | 2 | |
| 1.3662 [1.2137; 1.5187] | N/A | 1 | |
| 1.2505 [0.7000; 1.8009] | N/A | 1 | |
| 6.2783 [2.0879; 10.4686] | 97.9 | 2 | |
| 4.6809 [3.7558; 5.6060] | 0.0 | 2 | |
| Age ranges | 0.0002 | |||
| 2.1086 [−2.8482; 7.0654] | 98.2 | 2 | |
| 1.6678 [1.1845; 2.1511] | 95.8 | 6 | |
| 4.5980 [0.5205; 8.6755] | 98.7 | 3 | |
| 4.6819 [3.3734; 5.9903] | 97.9 | 1 | |
| Plasmodium species | 0.0002 | |||
| 1.3580 [0.7442; 1.9719] | 97.6 | 8 | |
| 4.6809 [3.7558; 5.6060] | 0.0 | 2 | |
| 8.4427 [7.3633; 9.5221] | N/A | 1 | |
| 4.1665 [3.6180; 4.7149] | N/A | 1 | |
| Diagnostic method for malaria | 0.0030 | |||
| 1.4942 [1.1735; 1.8150] | 71.5 | 3 | |
| 0.6690 [−0.3838; 1.7217] | 97.2 | 3 | |
| 4.3629 [2.5153; 6.2104] | 96.8 | 6 | |
| Methods for vWF | 0.0269 | |||
| 2.5200 [1.1217; 3.9184] | 98.2 | 11 | |
| 4.6819 [3.3734; 5.9903] | N/A | 1 | |
| Blood samples for vWF | 0.0583 | |||
| 3.0990 [1.6563; 4.5416] | 97.7 | 10 | |
| 0.6629 [−1.4049; 2.7306] | 97.8 | 2 |
| Subgroup | Test for Subgroup Differences (Random-Effects Model) | SMD (95% CI) | I2 (%) | Number of Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Publication years | <0.0001 | |||
| 12.3712 [11.4657; 13.2767] | N/A | 1 | |
| 2.6492 [−0.7446; 6.0429] | 98.5 | 6 | |
| 0.1348 [−0.2207; 0.4903] | N/A | 1 | |
| Study design | 0.0268 | |||
| 0.3398 [0.1195; 0.5601] | 25.5 | 4 | |
| 6.7968 [1.0861; 12.5075 | 99.5 | 4 | |
| Continent | 0.0591 | |||
| 4.6404 [0.1582; 9.1227] | 99.4 | 6 | |
| 0.3143 [0.0251; 0.6035] | 0.0 | 2 | |
| Country | <0.0001 | |||
| 4.5730 [−2.0400; 11.1859] | 99. | 3 | |
| 0.3143 [ 0.0251; 0.6035] | 0.0 | 2 | |
| 0.1348 [−0.2207; 0.4903] | N/A | 1 | |
| 12.3712 [11.4657; 13.2767] | N/A | 1 | |
| 1.6668 [ 1.3136; 2.0201] | N/A | 1 | |
| Age ranges | 0.0591 | |||
| 4.6404 [0.1582; 9.1227] | 99.4 | 6 | |
| 0.3143 [0.0251; 0.6035] | 0.0 | 2 | |
| Plasmodium species | 0.1072 | |||
| 4.6404 [ 0.1582; 9.1227] | 99.4 | 6 | |
| 0.1612 [−0.2671; 0.5895] | N/A | 1 | |
| 0.4426 [ 0.0505; 0.8347] | N/A | 1 | |
| Diagnostic method for malaria | 0.3689 | |||
| 4.7922 [−2.6849; 12.2694] | 99.7 | 3 | |
| 5.9259 [−4.6111; 16.4630] | 99.7 | 2 | |
| 0.7628 [−0.1470; 1.6726] | 94.2 | 3 | |
| Methods for vWF | N/A | |||
| 3.5506 [−0.0074; 7.1085] | 99.3 | 8 | |
| Blood samples for vWF | 0.3005 | |||
| 3.8232 [−0.2439; 7.8903] | 99.4 | 7 | |
| 1.6668 [ 1.3136; 2.0201] | N/A | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sukati, S.; Rattanatham, R.; Masangkay, F.R.; Tseng, C.-P.; Kotepui, M. Alterations in von Willebrand Factor Levels in Patients with Malaria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Disease Severity. Medicina 2025, 61, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040767
Sukati S, Rattanatham R, Masangkay FR, Tseng C-P, Kotepui M. Alterations in von Willebrand Factor Levels in Patients with Malaria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Disease Severity. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040767
Chicago/Turabian StyleSukati, Suriyan, Rujikorn Rattanatham, Frederick Ramirez Masangkay, Ching-Ping Tseng, and Manas Kotepui. 2025. "Alterations in von Willebrand Factor Levels in Patients with Malaria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Disease Severity" Medicina 61, no. 4: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040767
APA StyleSukati, S., Rattanatham, R., Masangkay, F. R., Tseng, C.-P., & Kotepui, M. (2025). Alterations in von Willebrand Factor Levels in Patients with Malaria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Disease Severity. Medicina, 61(4), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040767







