Abstract
Ambient air pollution is a growing public health concern in major African cities, including Addis Ababa (Ethiopia), where little information is available on fine particulate matter (PM2.5, with aerodynamic diameter <2.5 µm) pollution. This paper aims to characterize annual PM2.5, including bulk composition and seasonal patterns, in Addis Ababa. We collected 24-h PM2.5 samples in the central city every 6 days from November 2015 to November 2016. The mean (±SD) daily PM2.5 concentration was 53.8 (±25.0) µg/m3, with 90% of sampled days exceeding the World Health Organization’s guidelines. Principal components were organic matter (OM, 44.5%), elemental carbon (EC, 25.4%), soil dust (13.5%), and SNA (sulfate, nitrate, and ammonium ions, 8.2%). Higher PM2.5 concentrations were observed during the heavy rain season, while crustal dust concentrations ranged from 2.9 to 37.6%, with higher levels during dry months. Meteorological variables, vehicle emissions, biomass fuels, unpaved roads, and construction activity contribute to poor air quality. Compared to the Air Quality Index (AQI), 31% and 36% of observed days were unhealthy for everyone and unhealthy for sensitive groups, respectively. We recommend adopting effective prevention strategies and pursuing research on vehicle emissions, biomass burning, and dust control to curb air pollution in the city.
1. Introduction
The Global Burden of Disease estimates for 2017 show that more than 4.9 million people die prematurely every year due to the adverse health impacts of air pollution from all causes, while ambient particulate matter pollution exposure alone accounts for 4.6 million deaths [1]. Airborne particulate matter, size-fractionated as PM10 and PM2.5, with aerodynamic diameter less than 10 µm and 2.5 µm, respectively, is a widely used indicator of ambient air pollution [2]. Particles in the PM2.5 size range reach the deepest portions of the respiratory system, including the small airways and alveoli [3,4,5].
The effects of PM10 and PM2.5 on human health have been extensively studied with regard to increased morbidity and excess mortality [6,7]. The adverse health effects are both acute and chronic and reflect various underlying mechanisms, including inflammation and carcinogenesis. Particles are diverse in their characteristics, including chemical composition. The chemical composition of PM2.5 has been linked to the biological impacts of PM2.5 inhalation, such as oxidative potential [8,9]. Therefore, investigating the components of PM2.5 in polluted urban air is necessary to understand the links between the health risks posed by PM2.5 and the potential toxic components. Characterization of PM2.5 is also needed for source apportionment, which leads to the design of more efficient control strategies and air pollution abatement policy actions [10].
Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), in general, and the Eastern Africa region in particular, where Ethiopia is located, lack urban air quality monitors for PM2.5 and other pollutants. Hence, there is a paucity of evidence on fine particulate air pollution [11,12]. Addis Ababa is one of the largest metropolitan cities in SSA, characterized by a rapidly growing population with a high rate of urbanization. The number of motorized vehicles per capita is still fairly low, at 3 vehicles per 1000 persons [13]; however, the majority of the vehicles are quite old, with most operating in the absence of an emission standard, modern emission control technology, or an effective smog controlling enforcement system. Moreover, narrow roads coupled with lax annual vehicle safety inspections result in a substantial number of high-emitting trucks, buses, and automobiles. In addition, the open burning of solid waste, combustion of diesel for power generation, and particulate matter emissions from industries and construction activities also contribute to poor air quality in the city. Given these many air pollution sources, this study examines the levels and sources of ambient air pollution, particularly PM2.5, to help design appropriate policy interventions and control mechanisms in order to reduce the impact on population health and the environment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting
Addis Ababa, a city with a population of about 4.7 million [14], is located at an average altitude of 2355 m above sea level. Geographically, Addis Ababa is surrounded by mountain chains extending from the northeast to the western part of the city, with plains in the east and south. Consequently, the winds drive emissions towards the western and northwestern areas of the city. Temperature inversions are common during the seasons with low temperatures, especially during early morning and evening [12].
The weather in Addis Ababa is categorized into three main seasons based on precipitation: the Dry season (from October to January, and also May); the light to moderate rain season—Wet 1 (from February–April); and the main rain season—Wet 2 (from June–September) [15]. According to the National Meteorological Agency, the temperature in Addis Ababa ranges from a monthly average minimum of 8 degrees C to a maximum of 25 degrees C. The prevailing wind direction from the annual Wind-rose diagram shows that the sampling location has an easterly wind direction, whereas a station located near the Bole area has a prevailing southeasterly wind direction. The monthly mean rainfall in Addis Ababa ranges from a minimum of 7 mm (Nov./Dec.) to 280/290 mm (July/August). The Relative Humidity (%) monthly mean ranges from a minimum of 45.5% in December to a maximum of 79.5% in July. The monthly average daylight ranges from 11.6 to 12.6 h; monthly average sunshine ranges from 3 h (July/August–Wet 2 season) to 9 h (December–Dry season) [16]. Supplementary Figure S1a–c) depict line plots of daily minimum temperature, maximum temperature, and precipitation during 2015–2016 at the study site.
2.2. Sampling Approach
Integrated 24-h PM2.5 samples were collected at a central city meteorological station (“Met Station”) (9.019046° N, 38.747360° E), once every 6 days from November 2015 to November 2016. The sampling station was located near the meteorological measuring instruments above the ground at a height of 2 m. The Met Station is the oldest meteorological station in Ethiopia, also serving as the site for ambient air quality monitoring in Addis Ababa city; it continuously records measurements of pollutant gases (NOx, CO, and O3). The HOBO® data logger (Model Part # H08-032-08; Onset Computer Co., Bourne, MA, USA) was installed near the sampling hood under the shed of the PM2.5 monitor to measure relative humidity (RH) and temperature over the 24-h sampling period. The station is located in a typical downtown urban area surrounded by residential houses as well as public institutions and private businesses. The area is situated near one of the city’s major traffic networks, and includes an adjacent busy road (at about one-half km distance from the site) leading to the city’s largest open market area (‘Merkato’), located over a steep hill. There is an adjoining road (minimum of 25 m from the monitor). According to the near-road monitoring guidance of the US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA), a monitoring station should be at a minimum distance of 10–20 m from traffic [17] Supplemental Figure S2 depicts the map of monitoring stations in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Samples were collected on quartz fiber (37 mm diameter, GE Whatman, USA., and Teflon filters (37 mm diameter, PTFE TefloTM Pall Corporation, Port Washington, New York USA, concurrently using two 5-stage Harvard Cascade Impactor samplers (Harvard University Chan School of Public Health, Boston, MA 02115, USA), which were provided by the Southern California Environmental Health Sciences Center (SCEHSC), University of Southern California (USC, Los Angeles, CA, USA) [18]. The samplers were operated at a flow rate of 5 LPM. The flow rates were measured before and after each sample using an Omega Rotameter (Omega Engineering Inc., Norwalk, CT 06854, USA), which was calibrated using a Gilibrator ‘Bubble meter’ (Gilibrator-2 Calibrator, MPN 800271 (120 V), Sensidyne Industrial Hygiene and Safety Instrumentation, St. Petersburg, FL 33716, USA). The mean flow rate over the sampling period was used to calculate the sampled air volume. Quartz filters were baked for at least 12 h at 550 °C before sampling and stored in prebaked foil both before and after sampling. Field blanks were also collected for every 10 set of samples. To prevent evaporation of volatile components, all collected samples were sealed in polystyrene Petri dishes and then stored frozen, below −20.0 °C before analysis.
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
The PM samples were shipped for mass and chemical components analysis to the Water Science and Engineering Laboratory and Wisconsin State Laboratory for Hygiene at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. The collected particle mass concentrations were determined by weighing the Teflon filters before and after sampling on a microbalance (MT 5, Mettler-Toledo Inc., Highstown, NJ, USA) in a controlled room with the temperature kept at 20.0 °C ± 2.0 °C, and relative humidity at 40.0% ± 2.0%. A static neutralizer (500uCi Po210, NRD LLC, Grand Island, NY, USA) was used to eliminate electrostatic charges. To equilibrate the filters with humidity levels, the filters stayed in the weighing room for at least 12 h before weighing. An ion chromatography (IC, Dionex ICS 2100 for anions and Dionex 1100 for cations; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) method was used for analyzing inorganic ions after one-quarter of each Teflon filter was extracted in high-purity water. Inorganic ions, including chloride, nitrate, sulfate, sodium, ammonium, calcium, and potassium, were analyzed by ion chromatography (ICS 1100 and 2100, Dionex, Imperial, PA 15126, USA) [19]. The extracts were also used to measure the water-soluble organic carbon (WSOC) content of the samples using a Total Organic Carbon (TOC) analyzer (Siever M9, GE Analytical Instruments, Boulder, CO, USA). To determine the elemental and organic carbon levels [20,21], a 1.0 cm2 punch from the quartz fiber filters was analyzed using thermal-optical transmittance technique (Sunset laboratory, Forest Grove, OR, USA). The subtraction of the WSOC concentration from the organic carbon (OC) concentrations in the sample yielded the water-insoluble OC (WIOC) [22,23]. Total trace element concentrations were analyzed using one-quarter of each Teflon filter, and quantified after digestion and subsequent analysis by high resolution sector field inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (SF-ICP-MS) [24]. Three elements—gallium, indium, and bismuth—were used as internal standards for the HR-ICP-MS analysis along with authentic standards for each quantified element.
2.4. Data QA/QC
The samples were collected using quartz and Teflon filters and Harvard Cascade Impactor samplers at a flow rate of 5.0 LPM based on a standard protocol (adopted from University of Southern California (USC) Children’s Health Study). Field and laboratory blanks, check standards, spikes, and duplicate samples were run to ensure and control the quality of data for each chemical analysis. Spike and standard recoveries were 88.7% on average for all ions measured by IC (ranging from 69.4% to 99.7% for individual ions) and 78.4% on average for WSOC. ECOC sucrose spike recoveries were 90.9% to 105.0%, depending on the analysis batch (using standard reference materials by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology with certified reference values for given elements). A total of 18 field blank filters were used for QA/QC. On average among all analyses, field blank concentrations were less than 10% of sample concentrations. Duplicate precision agreement (relative standard deviation of duplicate measurements) was better than 5% on average for all analyses. Average field blank values were used to blank-correct all reported sample concentrations, and uncertainties were calculated based on standard deviation of field blanks and estimated instrument precision. Filter data were considered as valid if the flow rate did not vary by more than 5% of 5 LPM.
2.5. Chemical Mass Closure
We used chemical mass closure to assess major mass constituents of the collected particles in Addis Ababa. The calculated chemical constituents are ammonium, nitrate, sulfate, dust oxides, elemental carbon (EC), particulate organic matter (POM), and other elements [25,26]. The soil dust oxide concentrations were determined by converting trace element data to the most common form of oxides presented in the crustal soil composition (i.e., Al2O3, SiO2, CaO, K2O, FeO, Fe2O3, MnO2, MgO, and TiO2) using corresponding molecular weight conversion factors [27]. POM was estimated from the measured OC values multiplied by a conversion factor of 1.4 [28,29,30]. The concentrations of the other elements were calculated from the sum of all the trace elements (except major soil), which mostly represent the anthropogenic and heavy metal content of aerosols.
2.6. Data Analysis
The final PM2.5 mass concentration was obtained by subtracting the average concentration of field blanks from the measured mass concentration. The particulate OM was derived as a product of OC by a factor of 1.4. For descriptive analysis, we used mean, standard deviations, minimum and maximum. Graphical presentation of the data employed Microsoft Excel (2011, Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA 98052, USA) and R-project tools (R version 3.5.2, https://www.r-project.org/about.html) to depict graphs using line graphs, bar charts, and box plots.
3. Results
3.1. PM2.5 Concentration
Sixty-one sampling sets (days) of valid data for PM2.5 concentration and composition were available from a total of 69 sets collected and then evaluated through the QA/QC procedure. The annual average (±SD) PM2.5 mass concentration in central Addis Ababa during November 2015 to November 2016 was 53.8 (±25.0) µg/m3 and the mean (±SD) of monthly average concentrations during the same period was 55.1 (±17.7). The PM2.5 daily concentration observed in this study ranges from 19.1 to 127.0 µg/m3.
3.2. PM2.5 Bulk Composition
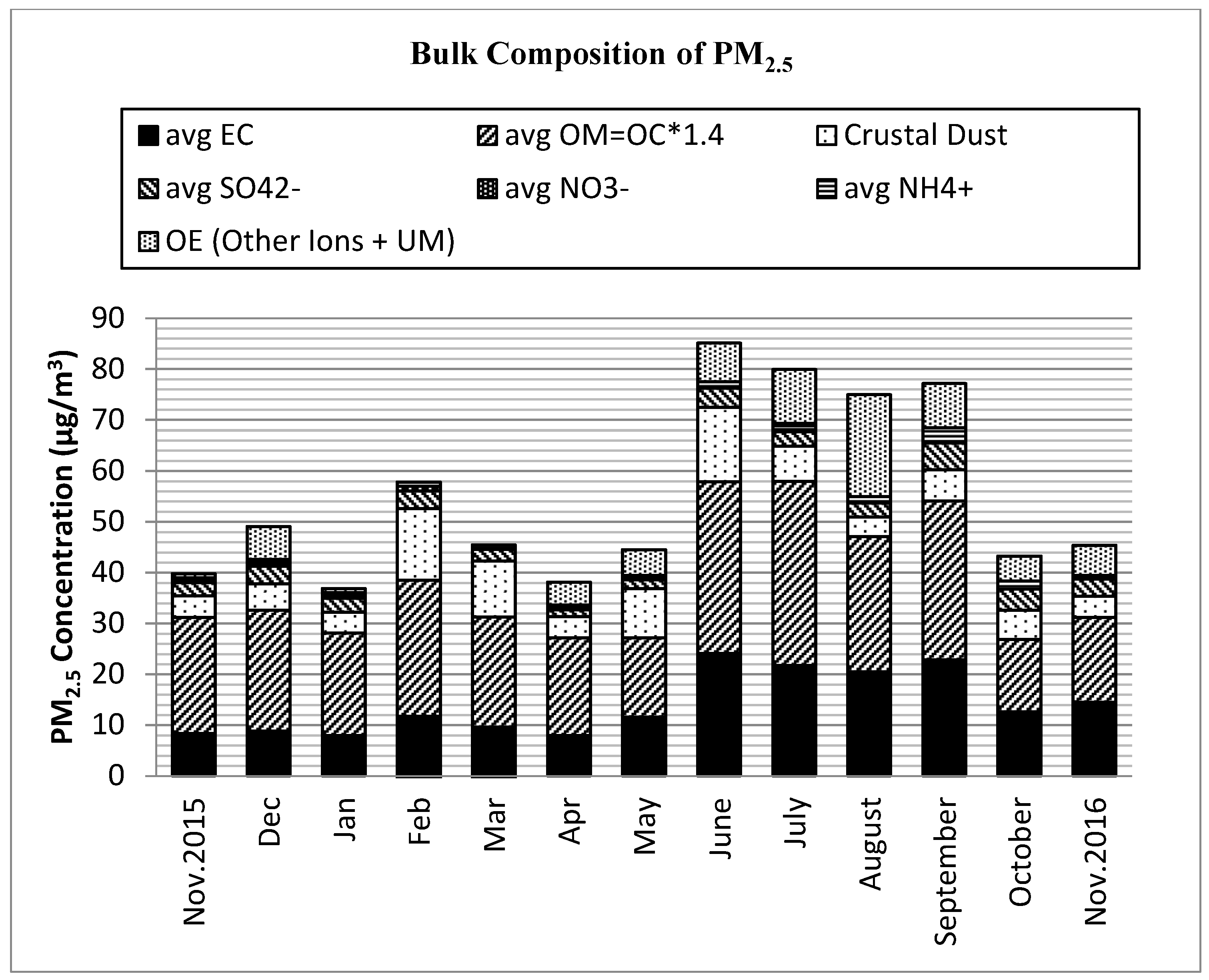
Table 1 and Figure 1 summarize the monthly and mean annual levels of PM2.5 and the elemental mass concentrations, respectively. On average, the dominant components of fine particles by proportion were OM (43.0%), EC (25.5%), dust (13.0%), sulfate (5.7%), ammonium (1.9%), nitrate (0.6%), and other ions (1.0%), including Na+, Cl−, ws K+, and Ca2+. These components accounted for an average of 88.0% of the PM2.5 mass.

Table 1.
Monthly average concentration of PM2.5 and bulk composition in Addis Ababa (µg/m3), Nov. 2015–Nov. 2016. (n is the number of observations per month).
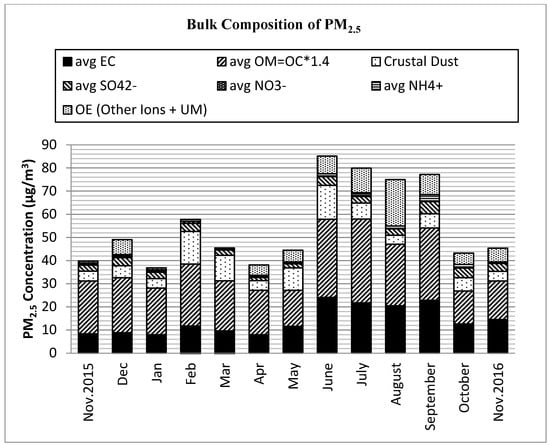
Figure 1.
Particulate matter (PM2.5) chemical species by concentration (µg/m3) of major components in Addis Ababa; EC = Elemental carbon. OM = Organic matter. OE = Other elements. Other Ions = ws Na+, ws Cl−, ws K+, ws Ca2+. Other = Unidentified matter.
The particulate OM, formed from compounds of hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur in addition to OC, was the dominant component of PM2.5 with contributions of 26.0–63.0% for most days of the year. The monthly average PM2.5 concentration shows that OM ranged from 32.9% to 57.3% (Supplementary Figure S3). The carbonaceous components, including EC, OC, WSOC, and WIOC, and dust contributions, which were found abundantly in PM2.5 are addressed in the following sections.
Other abundant forms of PM2.5 components were the secondary inorganic ions of sulfate, nitrate, and ammonium, which are formed in the atmosphere through a natural process of photochemical oxidation or condensation of the precursor gases of SO2, NH3, and NOx [31]. The annual average sulfate contribution was 5.7%. Whereas the daily SO4 components were less than 3.0% of PM2.5 mass in the majority of samples (70%), higher proportions, from 4–10%, were observed mostly during September, October, and November 2016, with monthly averages of about 6%, 7%, and 4%, respectively.
Nitrates in the urban atmosphere are formed from NOx emissions from motor vehicle exhausts and are often in the form of ammoniated nitrate (NH4-NO3). The PM2.5 in Addis Ababa had an overall daily mean NO3 concentration of 0.7% (with daily contribution to PM2.5 varying from 0 to 5% and a monthly average of 0.1–2.3%). Ammonium ions also comprised 1.7% of the annual mean PM2.5 levels. Total secondary ion concentrations were slightly higher during the dry season than at other times of the year. Other ions, such as Cl−, Na+, Ca2+, and K+ made small contributions in total, from very low to ~3% in monthly mean values.
3.3. Organic and Elemental Carbon
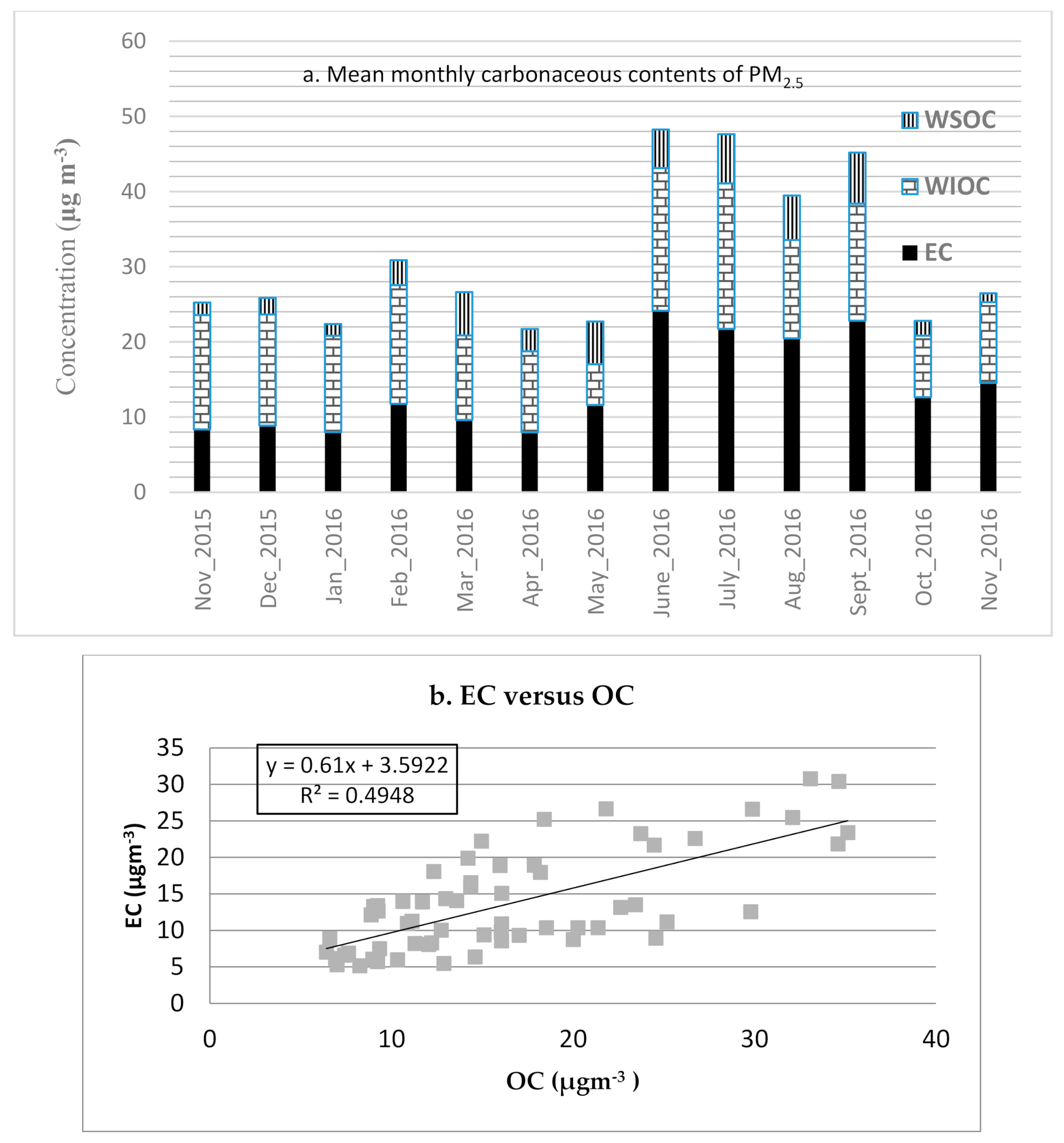
The carbonaceous component made up a major fraction of the PM2.5 in Addis Ababa. Organic matter (OM) was the most abundant species of PM2.5. Together, OM and EC comprised 69.8 ± 9.3% of the daily levels of PM2.5, ranging from 46 to 94%. The daily mean (SD) concentrations of OM (OC*1.4) and EC were 23.2 ± 11.0 µg/m3 and 13.7 ± 6.8 µg/m3, respectively. The lowest monthly mean of OM proportion was observed during October 2016, at 25.5%, followed by May and August 2016, accounting for ~27% of PM2.5 mass (Figure S3).
Generally, the proportion of OM in PM2.5 varied seasonally, with the lowest occurring from August through November 2016. Conversely, in contrast to OM, the proportion of EC reached the maximum level (27–30%) during the heavy rain season (Wet 2), while comprising a consistently lower proportion during the other seasons (18–22%).
The findings from this study revealed that the mean ratio of OC/EC is 1.3 (±0.5) and it ranges from 0.7 to 2.7. Water-soluble OC (WSOC) contributes with mean WSOC/OC of 0.22 (±0.18), ranging from negligible to 0.84.
Water soluble and insoluble components of OC (WSOC/WIOC) and EC levels, along with the seasonal trend, are presented in Figure 2a. The majority of OC was formed from WIOC, comprising 78% of the daily mean of OC (i.e., daily mean concentration of WIOC, 12.9 ± 6.7 µg/m3). The monthly mean (SD) level of WSOC was 3.6 ± 3.1 µg/m3, ranging from undetectable levels to 10.9 µg/m3 in August 2016, which had the highest daily WSOC observation, after one extreme measurement in May and another two measurements in September 2016 were excluded. A spike in the concentrations of water soluble OC (WSOC) was observed during three observation days (10 May, 19 September and 25 2016) compared to concentrations of the respective OC levels, and the spike coincided with a religious ceremony which uses the burning of biomass, particularly tree branches and leaves, as part of the celebration. As it appears that these levels overestimated the concentration of WSOC, they were excluded from the analysis. Figure 2b shows moderate correlation between OC and EC, suggesting primary source particle pollutants dominate.
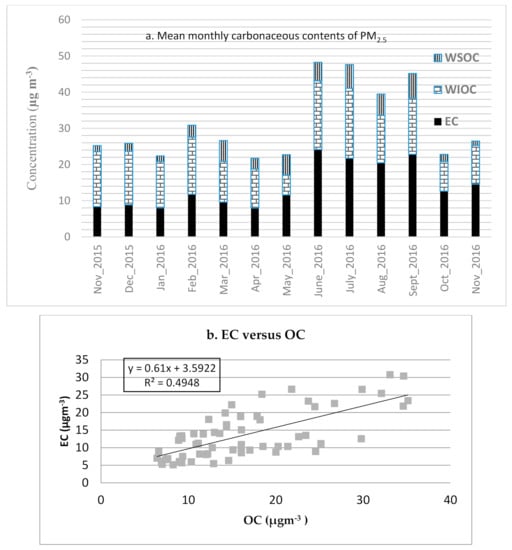
Figure 2.
(a) Carbonaceous contents of PM2.5 in central Addis Ababa, October 2015–December 2016. (b) Scatter plot of OC versus EC concentrations of PM2.5 in central Addis Ababa, October 2015–December 2016. N.B.: 24-December 2015; 16-May; 9-June, 15-June; and 3-July 2016 were missing data due to various reasons (including power outages), not days with zero values. Extreme values during 10-May, 19-September, and 25-September 2016 were excluded (not shown on Figure 2a as data aggregation to monthly).
There was relatively large seasonal variation in PM2.5 mass concentration, which was significantly higher during the heavy rain (Wet 2) season (June–September (78.6 ± 8.2 µg/m3) than during the light to moderate (Wet 1) season (February–April), and May (dry) (46.3 ± 5.4 µg/m3), as well as the main dry season (Dry) (October to January), which had the lowest observation.
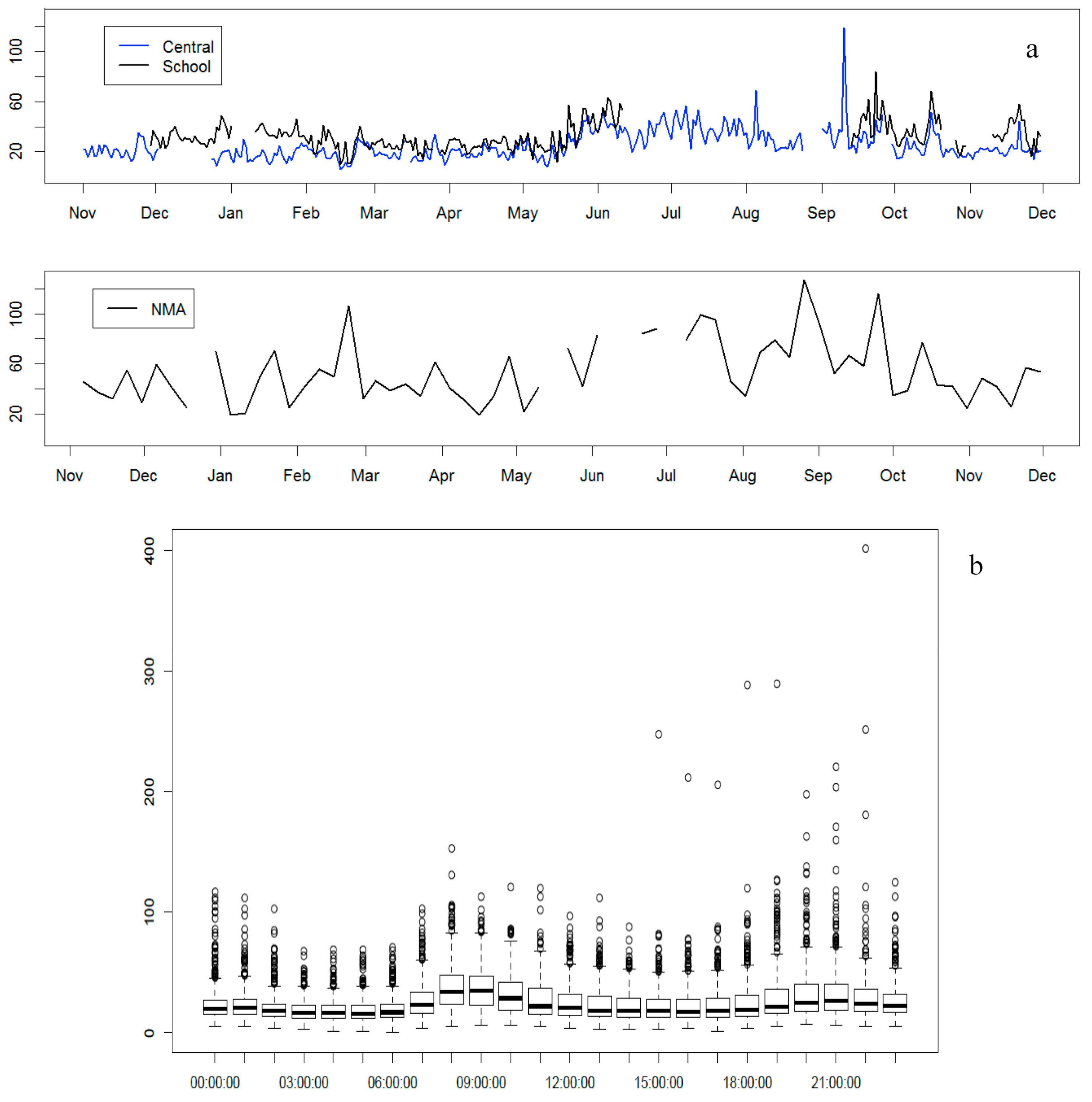
Daily mean PM2.5 mass concentrations were available from two monitors maintained by the US Department of State using US EPA equivalent reference methods. The “Central” monitor was located in the northern part of the city (background area) while the “School” monitor was located in an inner-city site in southwestern Addis Ababa. PM2.5 was measured with Beta Attenuation Monitors (BAMs), beginning in August 2016 at the two sites and present study site (Figure 3a). Our results were compared with these BAM data, as shown in Figure 3a. The figure shows a similar seasonal pattern of PM2.5 concentrations at all three sites with higher levels during the wet seasons compared to the remainder of the year.
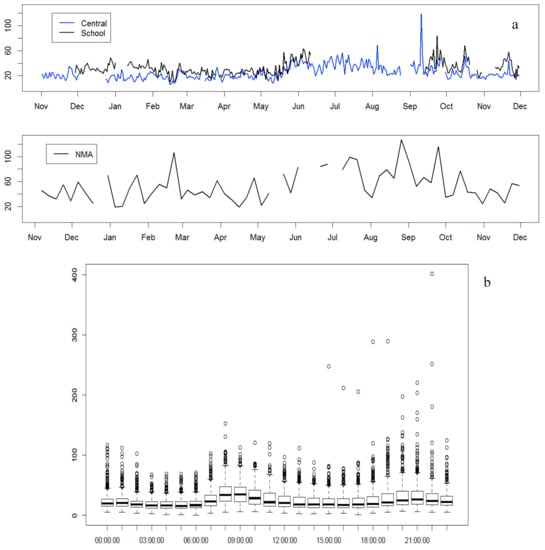
Figure 3.
(a) Line graph of PM2.5 concentration (µg/m3) trend during all seasonality (i) during August 2016 through December 2017 (US Embassy sites: Blue line—Central and Black line—School) and (ii) during November. 2015–November 2016 (NMA—Met Office) site) in Addis Ababa. (b) Diurnal pattern of the concentration of PM2.5 (given in µg/m3) for two US Embassy sites, from August 2016–December 2017, in Addis Ababa.
Figure 3b, from an aggregated data of the two BAM monitors, shows the diurnal pattern of PM2.5, with two peaks: during the morning rush (8:00–9:00 GMT+3) and late afternoon (extended from 19:00–22:00 GMT+3).
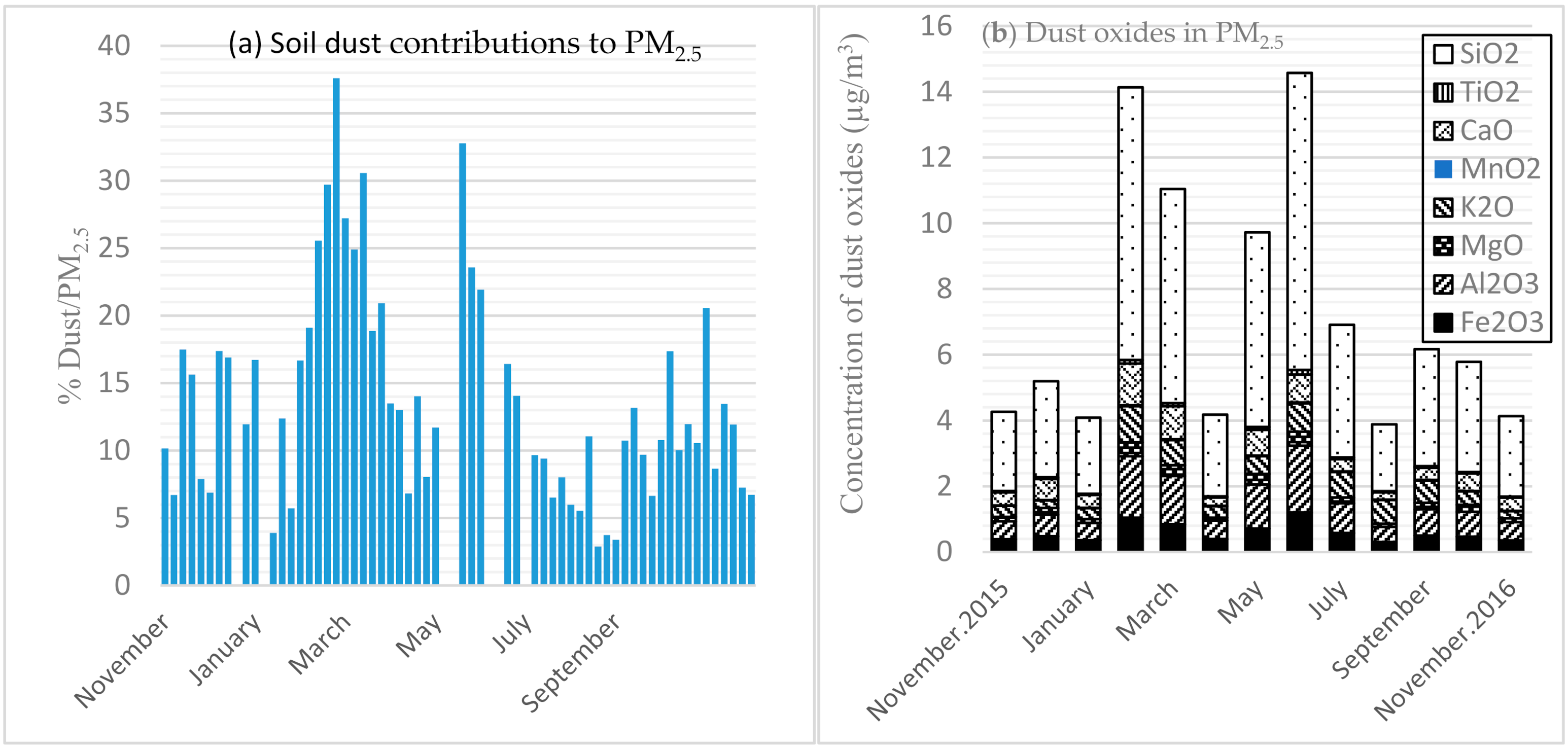
3.4. Dust Contributions and Components
Oxides in dust (Al2O3, Fe2O3, TiO2, MgO, CaO, K2O, MnO2, and SiO2) contributed a daily average of 13.5% of PM2.5, with the highest contribution in February (37.6%), followed by two more peak days during March (30.6%) and May (32.8%), which are in the light rain (Wet 1) and dry seasons (a transitional period between the two wet seasons), respectively (Figure 4a). The monthly mean contributions of dust were 25.0%, 24.0% and 22.0% during February, March, and May, respectively. The lowest proportion of dust was observed during the heavy rain season (Wet 2), with mean daily (2.9%) and monthly (5.0%) dust contributions to PM were observed during August. The daily variation of the dust oxides over the study period is depicted in Figure 4a,b, as a percentage contribution to—and dust oxides of—PM2.5, respectively.
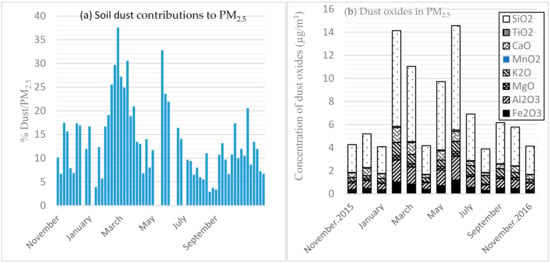
Figure 4.
Dust oxides of fine particulate matter: (a) 1-in-6 days concentration of dust contribution to PM2.5 (Left) and (b) Monthly variation of dust oxides (Right) in Addis Ababa. N.B. openings in between daily dust oxide bars in Figure 4a were missing data: 24-December 2015, 16-May, 9-June, 15-June, and 3-July 2016 due to various reasons (including power outages), not days with zero values.
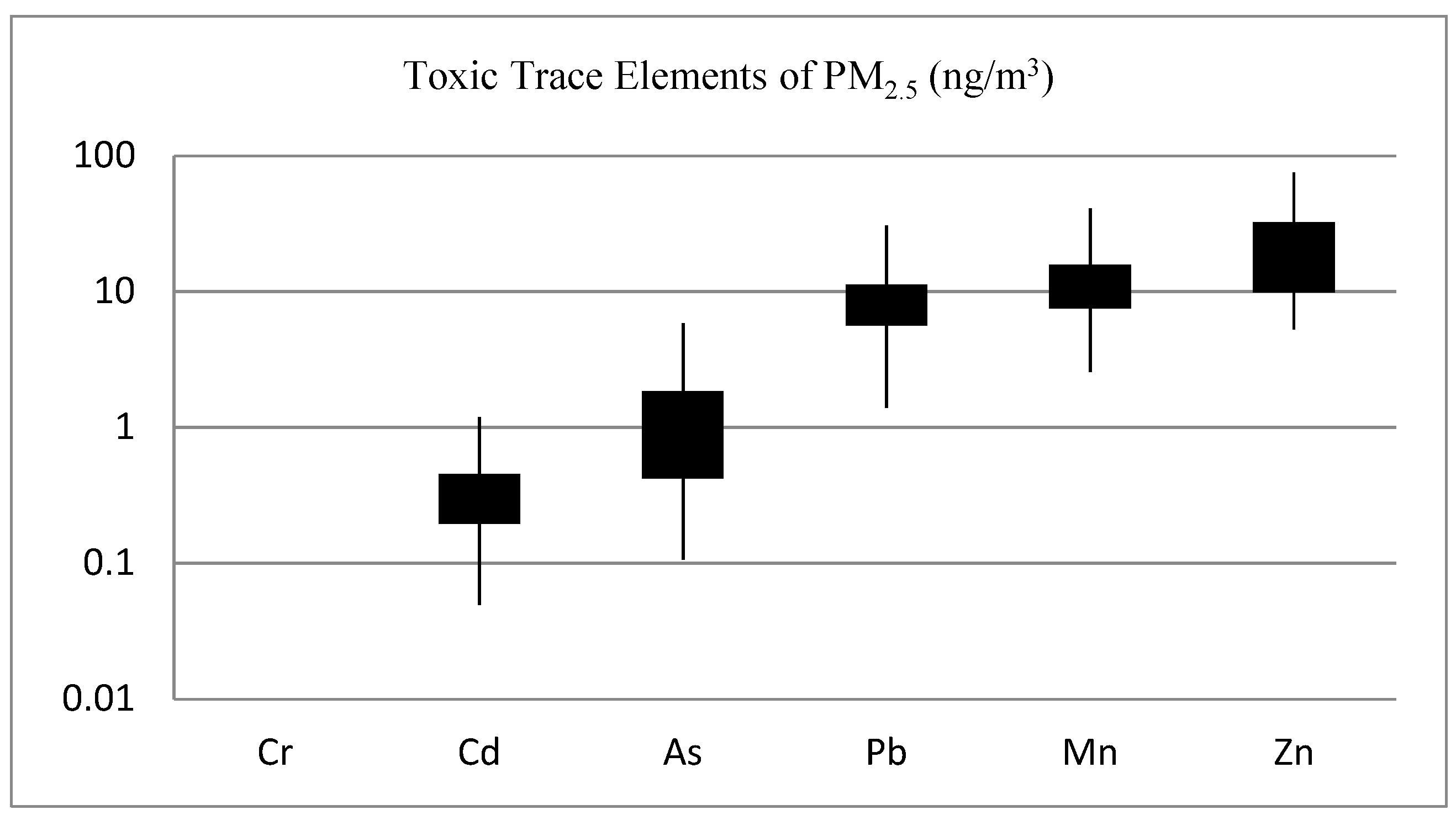
3.5. Trace Elements and Heavy Metals
As shown in Figure 5, Cd, As, Pb, Mn, and Zn are among the toxic metals of public health importance analyzed in this study. Pb, Mn, and Zn have notable concentrations, with Zn having the highest mean levels. The mean (SD) Pb level was 8.4 ± 5.3 ng/m3; ranging from 1.7 to 68.0 ng/m3. Most of the toxic elements of health significance in crustal materials, including Se, Sb, Ag, S, Sn, Pb, As, and Cu, found in PM2.5 were found to be significantly enriched, beyond what is naturally occurring in geological materials [32], by anthropogenic sources in Addis Ababa. Supplemental Table S1, listed the crustal enrichment factor (CEF) of trace elements—with CEF>100 shown in bold.
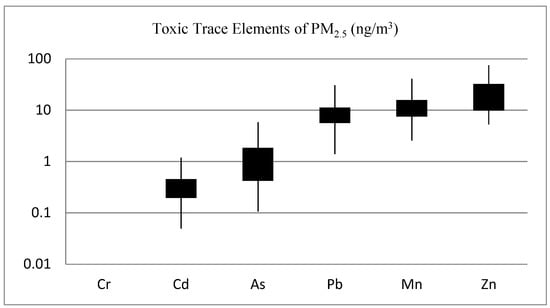
Figure 5.
Concentration of toxic trace elements of PM2.5 in central Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
4. Discussion
In this study, 61 24-h PM2.5 filter samples were collected successfully over one year at a central location in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. We estimated that the annual PM2.5 concentration was about 5-fold higher than the WHO annual mean Air Quality Guideline (AQG) value of 10.0 µg/m3 [33]. The annual mean PM2.5 air quality standard of the Ethiopian EPA (15.0 µg/m3) was also exceeded by over 3-fold [34]. The highest particulate matter concentrations were during the heavy rain season (Wet 2), suggesting the importance of increased fuel burning for heating during this period. Compared to the daily mean AQG value of the WHO (25.0 µg/m3) and that of the US EPA standard for PM2.5 (35.0 µg/m3), the PM2.5 levels in Addis Ababa exceeded these values by over 90.0% and 76.0% on the sampling days, respectively. The levels of PM2.5 measured in the city center of Addis Ababa were higher than at the two more peripheral sites maintained by the US Department of State. However, day-to-day variation was quite similar across the three sites.
In Ethiopia, there have been few studies to date on PM10; we did not identify any studies on ambient PM2.5 [11,12,35]. The health effects of air pollution have not yet been well studied in Ethiopia. However, a recent literature review by Tarekegn and Gulilat [36] discussed air pollution and health using secondary data sources in Addis Ababa. The disease burden trend in the city from 2003 to 2017 showed that acute upper respiratory infection and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease both increased by an annual rate of one-half and pneumonia grew by nearly a quarter every year. This increase could largely be attributed to the increasing traffic-related air pollution.
Moreover, despite the limited sample size, a calculated air quality index (AQI) from the observed data based on the US EPA classification (AQI: Good = 0–50; Moderate = 51–100; Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups—USG = 101–150; Unhealthy = 151–200; Very Unhealthy = 201–300; Hazardous = 301–500) shows that 36% and 31% of the observed days fell under USG and Unhealthy categories, respectively, while only a third of the observed days were Moderate.
Previous studies elsewhere show that WSOC is highly correlated with reactive oxygen species (ROS) activity [9,22]. Hence, the dominance of carbonaceous matter in PM2.5 composition, which is likely emitted from motor vehicles and biomass burning sources, could be linked to the respiratory health of the population in the city [36].
The WHO global estimate based on satellite-driven data indicated that the median level of PM2.5 in urban areas of Ethiopia was 36.0 µg/m3, ranging from 10.0 to 132.0 µg/m3. The range is in good agreement with this study. However, the annual average in urban Ethiopia is, obviously, lower compared to the PM2.5 mass concentration in this study, 53.8 µg/m3, which is largely comprised of organic and elemental carbonaceous materials indicating the importance of primary emissions from vehicles and burning of biomass fuel. The total number of vehicles in Ethiopia for 2015 was 587,400, based on data from Deloitte Africa Automotive Insights Report 2016 [37]. While the overall quantity of vehicles in the country is very small (3 per 1000 people) compared to other countries, particulate matter pollution in the metropolitan city of Addis Ababa was found to be high, possibly reflecting a contribution from motor vehicles that are mostly likely old and poorly maintained.
Brown et al. discussed the variability of the OM/OC ratio from the measurement of concentrations and concluded that using constant ratios for determining seasonal or daily concentration may over or underestimate the concentration of OM—hence, the health impact of exposure from PM2.5, of which OM is a major component [38]. For this study, we used OM/OC ratio of 1.4 [30].
Snyder et al. [39] argued that estimates of secondary OC using EC-tracer method could be potentially flawed due to presence of non-biomass sources of WSOC. In this study, we did not estimate the secondary organic aerosols. Further analysis on carbonaceous contents of PM2.5 is needed to accurately determine the temporal variability between primary and secondary OC [23].
Additionally, the contribution of biomass burning is also substantial. A large proportion of homes in urban areas nationally use biomass fuel (70.5%), including charcoal (30.0%) [40]. Although only 3.3% of the households in Ethiopia’s urban areas have a car or truck [41], the majority of these motor vehicles are found in or near the city of Addis Ababa [41].
Compared to studies in the northern and sub-Saharan regions of Africa (SSA), this study shows a mass concentration PM2.5 at least two times higher than those in studies conducted from 2008 to 2010 in Nairobi (Kenya), at both urban and industrial background sites [42], as well as in a semirural site in Accra (Ghana) [43]. Nonetheless, similar findings were reported from a study conducted in the urban center of Cairo (Egypt) during 2012 [44].
A seasonal 2-weeks sampling campaign conducted during the summer of 2011 in 7 locations of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, reported an overall average of PM2.5 mass concentration of 28.4 ± 25.4 μg/m3, with the highest mass concentration recorded in a suburban site (73.2 ± 65.1 μg/m3) and the highest PM2.5/PM10 ratio (0.52) compared to other sites in the city; the residential and urban sites had considerably lower mass concentration during the same season. The suburban site PM2.5 mass concentration in Jeddah (Saudi Arabia) [45] was comparable to the our results in Addis Ababa, with similar seasonal average mass concentrations. This shows that, despite variation in pollutant sources, PM2.5 mass concentration in this study is as high as those metropolitan cities in developing countries with large vehicle numbers and population size.
For comparison, Sharma and Mandal reported that the average mass concentration of fine PM was 125.5 ± 77.2 μg/m3 (range: 31.1–429.5 μg/m3) in Delhi (India), which is one of the most polluted cities in Asia. In Delhi, particulate organic matter (OM) is the highest contributor to PM2.5 mass, with 27.5%, followed by soli/crustal matter (16.1%), ammonium sulfate, and ammonium nitrate contributing 16.1% and 13.1%, respectively, while sea salt and light-absorbing carbon account for 17.1% and 10.2%, respectively [46]. The present study reported a higher OM and soil dust contribution to PM2.5 but a lower proportion of ammoniated compounds (ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate) compared to the Delhi study [46].
A similar finding was also reported in Beijing (China) during 2010 [47]; though it is one of the Asian cities, traditionally known for having relatively high pollution levels in the region. The daily levels of PM2.5 in this study are also higher than a recent study in Tehran (Iran) at 33.0 ± 11.0 µg/m3. However, the proportion of non-attainment days in this study, compared to the WHO guideline values, is similar to that in Tehran, with over 91.0% of the days exceeding WHO guidelines. Higher levels of PM in African cities, however, have been reported. Studies on the city center in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso [48], and on two low income neighborhoods in Nairobi (Kenya) in 2013 — Korogocho, 166.0 µg/m3 and Viwandani, 67.0 µg/m3 [42]—show that the annual mean PM2.5 concentration was much higher than the levels observed in this study.
Summer (June–Sept) in central Ethiopia is a season characterized by high rainfall, which might be expected to reduce the PM2.5 levels, especially in July and August. We suggest that the higher levels during this season could result from motor vehicle exhaust and increased biomass burning activity for cooking as well as space heating, accentuated by frequent temperature inversions during days when mornings are cold. Yet the level of crustal dust is higher during the dry season of the year compared with the wet season: in fact, the lowest level of crustal dust was observed in August. This may be due to rainfall that washes the atmosphere of suspended dust and the clearing of dust from the unpaved roads and asphalt streets. Moreover, construction activities, especially excavation of ground soil, are significantly reduced during this time of the year. The regional contribution of pollutants, particularly desert dust driven into the city of Addis Ababa by its prevailing eastward winds, needs to be further investigated in atmospheric modeling studies.
An earlier study in Addis Ababa [35] reported that 34.0% to 66.0% of PM10 mass concentrations were sourced from geological materials, while EC and OC in urban locations contributed, 31.0% and 60.0% of PM10 mass, respectively. In this study, we found an equivalent proportion of EC and OC contributions to PM10 mass compared to the prior study [35], while both Ethiopian studies seemed to have much higher levels of OC and EC compared to studies in the US and Europe, as well as in far east Asian cities such as Tehran [49,50,51,52]. This is largely due to the very low contribution of secondary inorganic aerosol, including sulfate, nitrate, and ammonium (SNA), and sea salts, compared to other regions of the world. The results emphasize the importance of direct primary emissions of particulate matter from carbon-containing fuels and that secondary inorganic components are less of a contributor to PM2.5 in Addis Ababa.
A review of PM2.5 composition by Zhang et al. [53] showed that for many of the megacities in Asia, the US, and Europe, sulfate, nitrate, and ammonium contribute more than 50%. This includes cities with high pollution levels such as Beijing; there are some exceptions, however, such as Mexico City, where the contribution represents about a third. Yet the contribution of SNA to PM2.5 is higher during winter compared to summer [53]. The present study, however, found that SNA contributes less than 10% to PM2.5 composition. In a globally and spatially diversified study [54], ammoniated sulfate in Kanpur (India), was the highest contributor in the range and more than double the sulfate observed in our study. While the combination of ammoniated sulfate and ammonium nitrate generally contribute about a quarter of PM2.5 composition, SNA only added up to 8.1% in the current study.
The two dominant sources of water-soluble organic carbon (WSOC) are secondary organic aerosols (SOA) and the burning of biomass fuels [25]. The peak WSOC levels that occurred during September and May 2016 might be due to events related to public holidays that take place across the city, involving massive burning of biomass fuel, including eucalyptus woods. Nonetheless, the WSOC seems higher during the wet seasons than the dry season.
Secondary sulfate is a major component of urban fine particulate matter in countries where coal or other high-sulfur fuels are used [49,55]. The sources of particulate matter sulfate in this study are likely high sulfur diesel vehicle fuel and diesel power generators used as alternative power sources during frequent grid power outages.
The World Health Organization reported that lead (Pb) exposure from environmental sources, including the air we breathe, accounted for an estimated 0.6% of the global burden of disease, with the highest burden occurring in the developing world [56]. The total concentration of lead (Pb) found in this study is similar to the results of a study in the city center of Ouagadougou (Burkina Faso) [47]. Compared to the levels in the urban center of Cairo (Egypt) [44], where leaded gasoline was sold on the market, our study shows a 10-fold lesser concentration. This might be attributable to the ban on leaded gasoline in Ethiopia since 2004 and to other industrial sources of lead in Cairo. However, the concentration of lead (Pb) in a semirural area of Accra (Ghana) [43], reported from measurements during 2006 and 2007, indicated much lower levels by a factor of 3 than those in this study. None of the airborne PM2.5 lead concentrations observed in this study exceeded the World Health Organization guideline values of 0.5 µg/m3 (annual average) or approached 0.1 µg/m3. Etyemezian et al. [12] reported that lead levels never exceeded 0.1 µg/m3 in PM10, which was observed 6 months after the phase-out of leaded gasoline in Addis Ababa. However, Teju et al. [57] reported a very high lead concentration from roadside soil samples compared to a control site soil samples in Addis Ababa, which might be due to past deposition of leaded gasoline and other anthropogenic sources.
5. Conclusions
This study is one of the few studies to use ground monitor data to determine the levels and chemical species composition of PM2.5 in Addis Ababa. The findings of this study will shed light on an ongoing effort to improve air quality in the region by providing critical evidence on ambient urban air pollution, particularly on levels, bulk composition, and seasonal variations of the components of PM2.5. The results from this study also serve as input to apportion resources for ongoing research to identify the problems and to take measured action based on the evidence. The PM2.5 mass concentration levels in the urban center of Addis Ababa exceeded both the WHO guidelines (10 µg/m3) and the Ethiopian EPA air quality standards (15 µg/m3) for the annual mean. These findings have a public health implication, as two-thirds of the days observed in this study were either unhealthy for the general population or unhealthy for sensitive groups (children, asthmatics, pregnant women and people with pre-existing conditions) based on the US EPA air quality index (AQI). The measurements taken at the urban center site in Addis Ababa show that PM2.5 mass concentration varies by seasonality and meteorological events, and are highest during the heavy rain season (Wet 2). Organic matter (OM), elemental carbon (EC), and dust make up more than three-quarters of the annual average PM2.5 concentration, with carbonaceous matters contributing the largest portion, followed by soil dust, with the wet season having a clear edge in increased concentration. Primary organic carbon (OC) dominates the carbonaceous contribution during the wet season. Therefore, we can conclude that anthropogenic sources, including the use of unclean fuel for vehicles, biofuels for cooking food at home, and uncontrolled dust in the urban environment could have human health consequences and are causes of concern for public health.
To guide policy for reducing ambient particulate air pollution in Addis Ababa, we recommend adopting effective prevention strategies and promoting research on vehicle emissions, biomass burning, including waste, and dust control to curb air pollution in the city.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/17/19/6998/s1, Figure S1: Mean daily Minimum Temperature (℃). (a) Maximum Temperature (℃); (b) and Precipitation (mm); (C) in Central Addis Ababa during 2015–2016. Figure S2: Fine PM Monitoring stations in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. NMA PM2.5 Sampler (Met Station site—this study); US Diplomatic Post BAM Monitors (Central and School sites) are shown in figure with blue pin. Figure S3: The percentage contribution of major mass constituents of PM2.5 in Central Addis Ababa. Table S1: Crustal Enrichment Factor (CEF > 10) of 15 trace elements identified from PM2.5 samples in central Addis Ababa.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.T., A.K., K.B., F.G., J.S., J.P. and J.J.S.; Data curation, W.T., A.L., P.S. and J.J.S.; Formal analysis, W.T., A.L., P.S. and J.J.S.; Funding acquisition, W.T., A.K., K.B., F.G., J.P. and J.J.S.; Investigation, W.T., A.K., K.B., A.L., P.S., J.S., J.P. and J.J.S.; Methodology, W.T., A.K., K.B., F.G., A.L., P.S., J.S., J.P., and J.J.S.; Project administration, W.T., A.K., K.B., J.S., J.P., and J.J.S.; Resources, A.K., K.B., J.S., J.P., and J.J.S.; Software, W.T., A.L., P.S., and J.J.S.; Supervision, W.T., A.K., K.B., F.G., J.S., J.P., and J.J.S.; Validation, W.T., A.K., K.B., F.G., A.L., P.S., and J.J.S.; Visualization, W.T., A.K., K.B., F.G., A.L., P.S., J.S., and J.J.S.; Writing—original draft, W.T.; Writing—review & editing, A.K., K.B., F.G., A.L., P.S., J.S., J.P., and J.J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by NIH Fogarty International Center, NIEHS, CDC/NIOSH, Canada’s IDRC, GACC, Grant # 5R24 TW009552; 5R24 TW009548; 1U01TW010094; 1U2RTW010125.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the following institutions: USC for providing instruments and training. AAU, USC, and the University of Wisconsin-Madison (UW-M) and State Hygiene Lab (WI) for training, preparation, sample analysis, and technical support. Individuals including Kristin (Almaz) Zakarias for facilitation of training and logistics (USC); Scott Fruin for technical support, Bethlehem Tefera—Lab personnel at Core Lab (AAU), and Agere Yegezu at Pharmacology Lab, College of Health Sciences-AAU; Robel Kebede (BSc) at Wisconsin State Hygiene Lab.; Alemayehu Worku and Zelalem Tazu (AAU) for their statistical advice. We thank Charlotte Gerczak for editing the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Forouzanfar, M.H.; Afshin, A.; Alexander, L.T.; Anderson, H.R.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Biryukov, S.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Cercy, K.; Charlson, F.J.; et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 388, 1990–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. NAAQS Table. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/criteria-air-pollutants/naaqs-table (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Londahl, J.; Massling, A.; Pagels, J.; Swietlicki, E.; Vaclavik, E.; Loft, S. Size-Resolved Respiratory-Tract Deposition of Fine and Ultrafine Hydrophobic and Hygroscopic Aerosol Particles During Rest and Exercise. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löndahl, J.; Pagels, J.; Swietlicki, E.; Zhou, J.; Ketzel, M.; Massling, A.; Bohgard, M. A set-up for field studies of respiratory tract deposition of fine and ultrafine particles in humans. Aerosol Sci. 2006, 37, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, M.; Zheng, F.; Xu, X.; Nui, L. Advances of study on monitoring and evaluation of PM2.5 pollution. Meteorol. Disaster Reduc. Res 2011, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Kabir, S. A review on the human health impact of airborne particulate matter. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the Air: A Review of the Effects of Particulate Matter Air Pollution on Human Health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.S.; Schauer, J.J.; Lee, T.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Ro, C.U.; Song, S.-K.; Shon, Z.-H. Relationship between reactive oxygen species and water-soluble organic compounds: Time-resolved benzene carboxylic acids measurement in the coastal area during the KORUS-AQ campaign. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Velali, E.; Papachristou, E.; Pantazaki, A.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T.; Planou, S.; Kouras, A.; Manoli, E.; Besis, A.; Voutsa, D.; Samara, C. Redox activity and in vitro bioactivity of the water-soluble fraction of urban particulate matter in relation to particle size and chemical composition. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Urban Ambient Air Pollution Database (updated 2016b). World Health Organization. 2014 [cited 2003 Aug 20]. Available online: http://www.who.int/entity/phe/health_topics/outdoorair/databases/who-aap-database-may2016.xlsx (accessed on 8 July 2019).
- Tefera, W.; Asfaw, A.; Gilliland, F.; Worku, A.; Wondimagegn, M.; Kumie, A.; Samet, J.; Berhane, K.; Ababa, A.; Change, C. Indoor and Outdoor Air Pollution- related Health Problem in Ethiopia: Review of Related Literature. Ethiop. J. Heal. Dev. 2016, 30, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Etyemezian, V.; Tesfaye, M.; Yimer, A.; Chow, J.C.; Mesfin, D.; Nega, T.; Nikolich, G.; Watson, J.G.; Wondmagegn, M. Results from a pilot-scale air quality study in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7849–7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Group. Worldwide Total Motor Vehicles (per 1000 People); ChartsBin Statistics Collector Team, 2011. Available online: http://chartsbin.com/view/1114 (accessed on 23 June 2019).
- UN. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia—Population 1950–2020. World Population Prospects 2019; Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Available online: https://population.un.org/wpp/ (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- NMA. Climate of City: Addis Ababa. National Meteorological Agency of Ethiopia; National Meteorological Agency: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- NMA. Long-Term Weather Forecast Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Ethiopia National Meteorological Agency (Weather Atlas). 2020. Available online: https://www.weather-atlas.com/en/ethiopia/addis-ababa-long-term-weather-forecast (accessed on 16 August 2020).
- Baldauf, R.; Watkins, N.; Heist, D.; Bailey, C.; Rowley, P.; Shores, R. Near-road air quality monitoring: Factors affecting network design and interpretation of data. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2009, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yanosky, J.; Maclntosh, D. A Comparison of Four Gravimetric Fine Particle Sampling Methods. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2001, 51, 878–884. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Tang, A.; Yuan, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Zheng, A. The ion chemistry and the source of PM2.5 aerosol in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3771–3784. [Google Scholar]
- Schauer, J.J. Evaluation of elemental carbon as a marker for diesel particulate matter. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2003, 13, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Birch, M.E.; Cary, C.R.A. Elemental carbon-based method for monitoring occupational exposures to particulate diesel exhaust. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1996, 25, 221–241. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, M.; Schauer, J.J.; Turner, J.R. Estimation of the Monthly Average Ratios of Organic Mass to Organic Carbon for Fine Particulate Matter at an Urban Site. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Villalobos, A.M.; Barraza, F.; Jorquera, H.; Schauer, J.J. Chemical speciation and source apportionment of fine particulate matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Brehmer, C.; Norris, C.; Barkjohn, K.K.; Bergin, M.H.; Zhang, J.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Black, M.; Li, Z.; Shafer, M.; et al. The impact of household air cleaners on the chemical composition and children’s exposure to PM2.5 metal sources in suburban Shanghai. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 190–198. [Google Scholar]
- Mkoma, S.L.; Chi, X.; Maenhaut, W. Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosols in ambient PM10 and PM2.5 particles in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Arhami, M.; Sillanpää, M.; Hu, S.; Olson, M.R.; Schauer, J.J.; Sioutas, C. Size-segregated inorganic and organic components of PM in the communities of the Los Angeles Harbor. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 145–160. [Google Scholar]
- Brook, J.; Dann, T.; Burnett, R. The relationship among TSP, PM10, PM2.5, and inorganic constituents of atmospheric participate matter at multiple Canadian locations. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1997, 47, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, L.M. Aerosol Organic-Mass-to-Organic-Carbon Ratio Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, S.B.; Fine, P.M.; Mayo, P.R.; Sioutas, C. Size-Fractionated Measurements of Ambient Ultrafine Particle Chemical Composition in Los Angeles Using the NanoMOUDI. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, B.J.; Lim, H. Species Contributions to PM2.5 Mass Concentrations: Revisiting Common Assumptions for Estimating Organic Mass. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arhami, M.; Kamali, N.; Rajabi, M.M. Predicting hourly air pollutant levels using artificial neural networks coupled with uncertainty analysis by Monte Carlo simulations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4777–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.C.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Chen, L.A.; Wang, X.; Watson, J.G. Mass reconstruction methods for PM 2.5: A review. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2015, 8, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Air Quality Guidelines—Global Update 2005. Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide; WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Ethiopia Guidelines Ambient Environment Standards for Ethiopia 2003, The Environmental Protection Agency and The United Nations Industrial Development Organization prepared under the Ecologically Sustainable Industrial Development (ESID) Project, August, Addis Aba; EPA: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gebre, G.; Feleke, Z.; Sahle-Demissie, E. Mass concentrations and elemental composition of urban. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2010, 24, 361–373. [Google Scholar]
- Tarekegn, M.M.; Gulilat, T.Y. Trends of Ambient Air Pollution and the Corresponding Respiratory Diseases in Addis Ababa. Res. Rep. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. J. 2018, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- OICA. Deloitte Africa Automotive Insights Navigating the African Automotive Sector: Ethiopia, Kenya and Nigeria; OICA: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.G.; Lee, T.; Roberts, P.T.; Collett, J.L., Jr. Variations in the OM/OC ratio of urban organic aerosol next to a major roadway Variations in the OM/OC ratio of urban organic aerosol next to a major roadway. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2013, 63, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.C.; Rutter, A.P.; Collins, R.; Worley, C.; Schauer, J.J. Insights into the Origin of Water Soluble Organic Carbon in Atmospheric Fine Particulate Matter Insights into the Origin of Water Soluble Organic Carbon in Atmospheric Fine Particulate Matter. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EDHS. Ethiopian Demographic and Health Survey; EDHS: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Roychowdhury, A.; Chandola, P.; Chattopadhyaya, V. Urban Air Quality Management in Ethiopia: A Guidance Framework; Center for Science and Environment (CSE): Delhi, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Egondi, T.; Muindi, K.; Kyobutungi, C.; Gatari, M.; Rocklöv, J. Measuring exposure levels of inhalable airborne particles (PM2.5) in two socially deprived areas of Nairobi, Kenya. Environ. Res. 2016, 148, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboh, I.J.K.; Henriksson, D.; Laursen, J.; Lundin, M.; Ofosu, F.G.; Pind, N.; Al, E. Identification of aerosol particle sources in semi-rural area of Kwabenya, near Accra, Ghana, by EDXRFtechniques. X-Ray Spectrom. 2009, 38, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boman, J.; Shaltout, A.A.; Abozied, A.M.; Hassan, S.K. On the elemental composition of PM2.5 in central Cairo, Egypt. X-Ray Spectrom. 2013, 42, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodeir, M.; Shamy, M.; Alghamdi, M.; Zhong, M.; Sun, H.; Costa, M.; Chen, L.Ͳ.C.; Maciejczyk, P.; Chen, L.T.C. Atmospheric Pollution Research Source apportionment and elemental composition of PM2.5 and PM 10 in Jeddah City, Saudi Arabia. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2012, 3, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Mandal, T. Chemical composition of fine mode particulate matter (PM2.5) in an urban area of Delhi, India and its source apportionment. Urban Clim. 2017, 21, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Song, Y.; Wu, B.; Li, X.; An, K.; Chu, J. Characterization and Source Apportionment of PM 2.5 in an Urban Environment in Beijing. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boman, J.; Lindén, J.; Thorsson, S.; Holmer, B.E. A tentative study of urban and suburban fine particles (PM2.5) collected in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. X-Ray Spectrom. 2009, 38, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arhami, M.; Hosseini, V.; Shahne, M.Z.; Bigdeli, M.; Lai, A.; Schauer, J.J. Seasonal trends, chemical speciation and source apportionment of fine PM in Tehran. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 153, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowlat, M.H.; Hasheminassab, S.; Sioutas, C. Source apportionment of ambient particle number concentrations in central Los Angeles using positive matrix factorization (PMF). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4849–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Xu, D. Characteristics and seasonal variations of PM2.5, PM10, and TSP aerosol in Beijing. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2006, 19, 461–468. [Google Scholar]
- Putaud, J.-P.; Raes, F.; Van Dingenen, R.; Brüggemann, E.; Facchini, M.-C.; Decesari, S.; Fuzzi, S.; Gehrig, R.; Hüglin, C.; Laj, P.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology e 2: Chemical characteristics of particulate matter at kerbside, urban, rural and background sites in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2579–2595. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Allan, J.D.; Coe, H.; Ulbrich, I.; Alfarra, M.R.; Takami, A.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Sun, Y.L.; et al. Ubiquity and dominance of oxygenated species in organic aerosols in anthropogenically-influenced Northern Hemisphere midlatitudes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Snider, G.; Weagle, C.L.; Murdymootoo, K.K.; Ring, A.; Ritchie, Y.; Stone, E.; Walsh, A.; Akoshile, C.; Anh, N.X.; Balasubramanian, R.; et al. Variation in global chemical composition of PM2.5: Emerging results from SPARTAN. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9629–9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, E.A.; Kundu, S. Composition and sources of fine particulate matter across urban and rural sites in the Midwestern United States. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 16, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Exposure to Lead: A Major Public Health Concern. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.who.int/ipcs/features/lead..pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Teju, E.; Megersa, N.; Chandravanshi, B.S.; Zewge, F. Determination of the levels of lead in the roadside soils of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Sci. 2012, 35, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).