Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to assess back pain and its relation to physical activity as well as Internet addiction among Polish university students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Methods: The research was conducted via the Internet in student groups of three universities in Poland (141 people). Back pain was examined by ODI—The Oswestry Disability Index and NDI—Neck Disability Index. The Polish-language International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) was used to assess physical activity and the level of Internet addiction was tested using the Kimberly Young Questionnaire. Results: The respondents mostly suffered from pain originating in the cervical spine. In the study group, only every fifth person had a high level of physical activity. Sex differentiates the level of the measures considered. Sitting in front of the computer affects the pain in the spine. Conclusions: Research results suggest that the pandemic is negatively affecting students. Frequent occurrence of back pain is observed with a simultaneous low level of physical activity. Maintaining regular activity during a pandemic, at least at home, is an indispensable preventive measure for physical health.
1. Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused numerous changes worldwide in many areas of socio-economic life. Several restrictions changing the lifestyle of Polish students were introduced as a result of the announcement of the epidemic in Poland. The introduced restrictions forced a change in the nature of science; the form of full time classes were replaced with online study. Considering this type of education, it is difficult to imagine functioning without access to the Internet. The period of the pandemic contributed even more to regular online presence, primarily for teaching and educational purposes. Excessive use of the Internet is associated with several health problems, such as the possibility of developing musculoskeletal pain or a decrease in the level of physical activity [1,2].
The lockdown fostered progressive change of lifestyle from being physically active to passive and sedentary, leading to a reduction in the spine resistance to static-dynamic loads, which in turn may lead to pain in the spine [3,4].
Spinal pain in the contemporary world is a growing problem that threatens physical health, as well as reduces the quality of work and everyday life [5,6].
Collective isolation lasting for several months may lead to a limitation of the current physical activity among students [7]. Daily physical activity at a low or moderate level may be treated as one of the factors which positively influence physical and mental health. Physical benefits include, for example, maintaining body weight at an appropriate level or lowering blood pressure [8]. Considering mental health, physical activity improves the functioning of the brain and helps to achieve better results in learning [9].
The aim of the study was to assess back pain and its relation to physical activity as well as Internet addiction among Polish university students during the COVID-19 pandemic.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
A cross-sectional survey was sent to physiotherapy students of four universities in Poland (Lomza State University of Applied Sciences, Medical University of Bialystok, School of Medical Science in Bialystok, Medical University of Warsaw) during the second COVID-19 lockdown in November 2020 (after 9 months of online education due to the pandemic). The survey was conducted on an official educational platform. Students were given a link to the Google form with the survey, as well as information about the survey, its purpose and the anonymity of participants. They also had to sign an informed consent for participation in a survey. This method was chosen because of epidemiological safety reasons and in order to obtain a prompt response. 141 people (104 women and 37 men) aged 18–25 took part in the study. This population was considered homogeneous in terms of age and this factor was not taken into account in further analyses. The study group is a representative sample for the population of physiotherapy students in Poland aged 18–25.
The following inclusion criteria were used: (a) age >18, (b) the status of a physiotherapy student, (c) correct completion of the questionnaire, (d) informed consent for participation in the research.
The research was approved by the Senate Commission for Ethics in Scientific Research of the School of Medical Science in Bialystok KB/18/2020.2021 and the informed consent of the participants was obtained. Participation in the study was voluntary, and its course was based on the Personal Data Protection Act of May 10, 2018 (Journal of Laws of 2018, item 1000) in accordance with the Regulation of the European Parliament and the Council (European Union) 2016/679 as of 27 April 2016, on the protection of individuals concerning the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data, and the repeal of Directive 95/46/WE (General Data Protection Regulation). Written consent was obtained from the participants.
On the basis of the standards created for the IPAQ questionnaire, the respondents were categorized into three groups of low (40.4%), medium (39.7%) and high (19.9%) physical activity. Due to the high influence of gender on the analyzed measures (especially activity measures), the analyses were performed with the subdivision into the groups of women and men.
2.2. Methods for Assessing Physical Activity, Spinal Pain, Internet Addiction
The studies presented were self-managed cross-sectional studies. The questionnaires were distributed by the authors of the article via the Internet in student groups of three universities in Poland.
Spinal pain was assessed by the Oswestry Disability Index/NDI—Neck Disability Index (ODI). The Oswestry Questionnaire is a reliable, widely used worldwide criterion for assessing the disability of people with back pain syndrome. It includes 10 questions concerning important activities of everyday life, such as pain intensity, self-service, lifting, walking, sitting, standing, sleeping, social life, traveling and work. Each answer is scored a: answer A—0 points, answer B—1 point, answer C—2 points, answer D—3 points, answer E—4 points and answer F—5 points. The points are then added up; the maximum number of points is 50.
Disability rating scale:
- 0–4: none
- 5–14: small
- 15–24: mediocre
- 25–34: serious
- over 35: total
The short version of the Polish-language International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQon), intended for people aged 15–69, was used to assess physical activity. The survey consists of 7 questions concerning all types of physical activity related to everyday life. The questionnaire takes into account activities that last continuously for at least 10 min. The different types of physical activity are expressed in units of MET—min/week, by multiplying the coefficient assigned to a given activity by the number of days it is performed per week and the duration in minutes per day. Intensity coefficients, corresponding to the multiple of the basic transformation (Metabolic Equivalent of Work—MET), are used to assess specific types of activity.
The level of Internet addiction was examined with the use of the Kimberly Young Questionnaire, which consists of 20 questions on various aspects of the frequency of Internet use. The respondents are to provide answers on a 5-point scale (1—rarely, to 5—always). The summary measure ranges from 20 to 100 points, with higher values indicating greater dependence on the Internet. This measure is categorized into three groups of low, medium and high Internet addiction (for point ranges: 20–49, 50–79 and 80–100, respectively).
2.3. Statistical Methods
The distribution of both the values of psychometric measures and measures of activity was characterized by selected descriptive statistics: the mean with the 95% confidence interval, the median, the standard deviation, and the skewness coefficient. The latter measure was significantly different from the zero value, meaning a symmetric distribution, and for several measures its value was significantly above 1, which means a clear right-hand asymmetry. This fact forced the choice of non-parametric statistical inference methods, such as the Mann–Whitney test, Kruskal–Wallis test or the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient.
3. Results
It was more often and more severe for the respondents to suffer from pain in the area of cervical spine (Table 1). All descriptive parameters related to this segment were higher than those of the lumbosacral area.

Table 1.
Back pain—descriptive parameters.
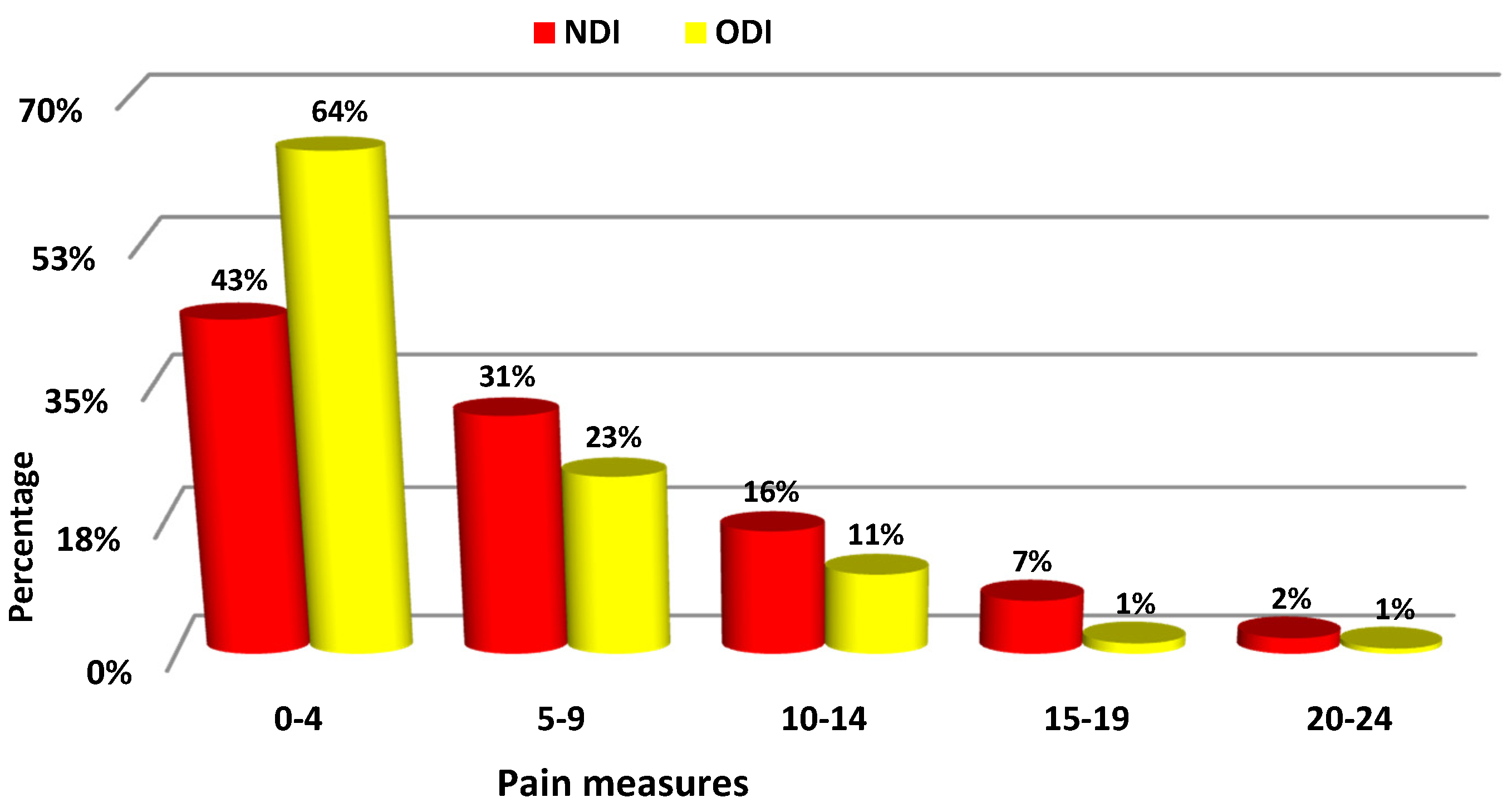
The chart (Figure 1) shows the percentage distribution of the values of both measures in intervals of 5 points. The asymmetry in the distribution of ODI (The Oswestry Disability Index) and NDI (Neck Disability Index) measures is related the fact that young people having no or very little back pain problems were assessed in the study.
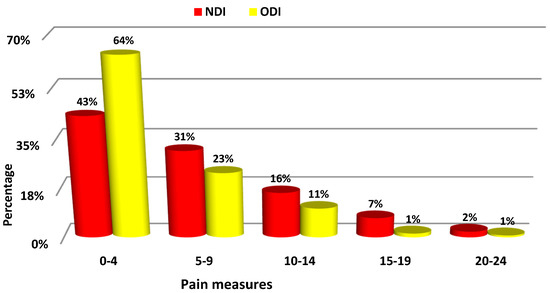
Figure 1.
Percentage distribution of NDI and ODI measures.
On the basis of the information obtained with the use of the short version of the IPAQ questionnaire physical activity (IPAQ-International Physical Activity Questionnaire) was measured in the sphere of high-intensity, moderate and light activity (Table 2). Measurements of activity are usually very asymmetric, which results from the presence of a relatively small group of people with a very high level of activity, as well as a fairly large group of people characterized with 0 activity. Therefore, a better measure of the average level is the median than the mean, which is overestimated by the above-described positive outliers: The measure of vigorous activity is slightly higher than that of walking (median values of 320 and 297 MET-min/week, respectively), while the measure of moderate intensity activity has a much lower value (median of 160 MET-min/week). week).

Table 2.
Type of activity (IPAQ)—descriptive parameters.
In the studied group, the situation was not good, because less than every fifth person could be distinguished by a high level of physical activity.
Gender differentiates the level of the measures considered, with the exception of low-intensity activity (walking) (Table 3). Men are likely to present with significantly lower levels of pain (especially ODI), are more addicted to the Internet and show a much higher level of physical activity.

Table 3.
Gender and measures of pain, Internet addiction and activity.
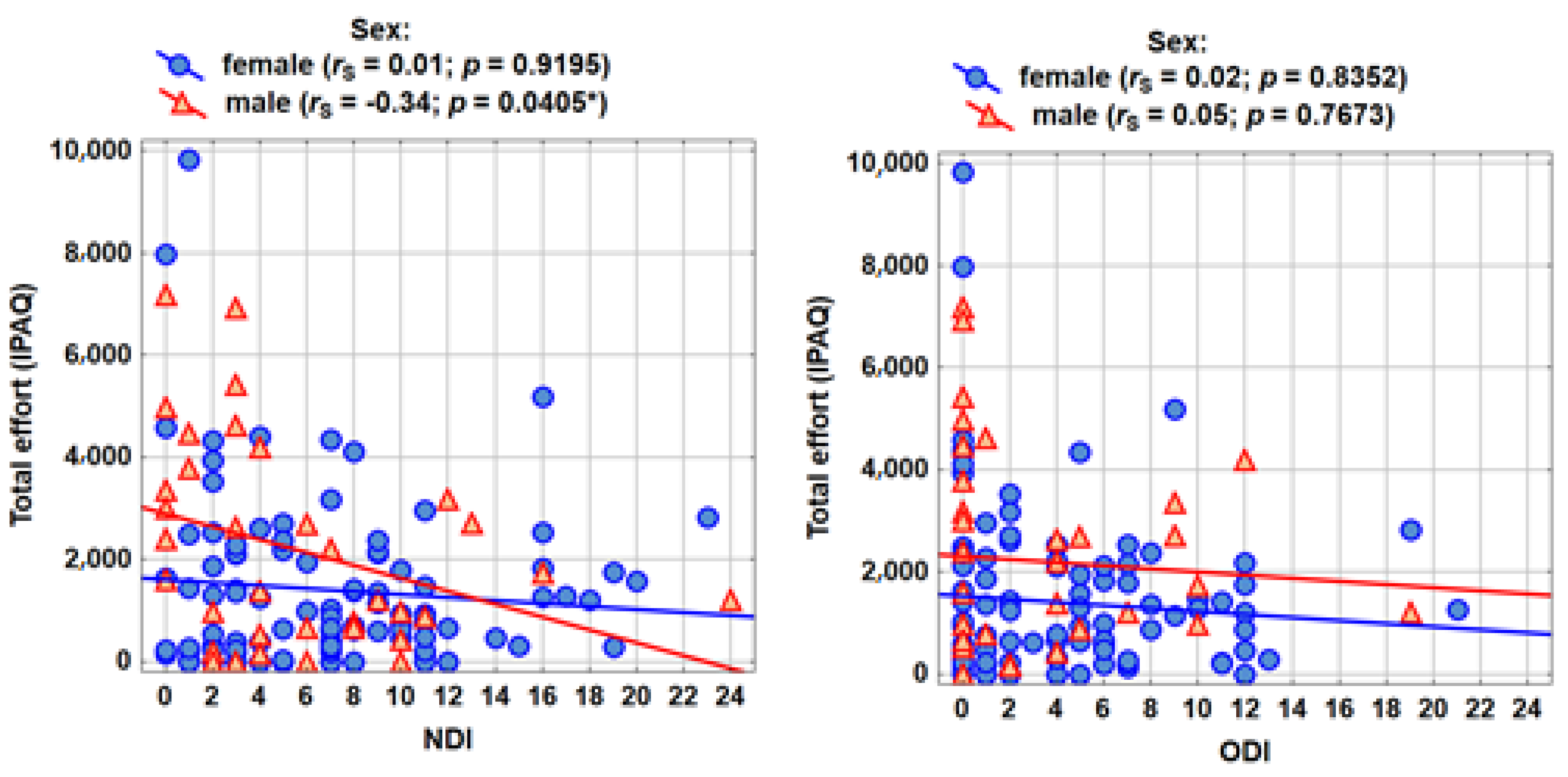
The correlation analysis was carried out according to the formulated research problems (Table 4). The Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient with the assessment of statistical significance (p < 0.05) was shown in the tables. The table shows the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients between the severity of pain and physical activity (IPAQ measures). No significant correlations were observed in the group of women, while among men there is a statistically significant (for the measure of total activity) and close to statistically significant (for the partial measures of activity) relationship with NDI. The higher the pain in the cervical area, the slightly lower the physical activity (the correlations are not strong; the absolute value of rS is approximately 0.30).

Table 4.
Correlations between back pain (ODI and NDI) and the level of physical activity (IPAQ).
The graphs (Figure 2) show the results of the analyses concerning the measure of total activity as well as NDI and ODI pain.
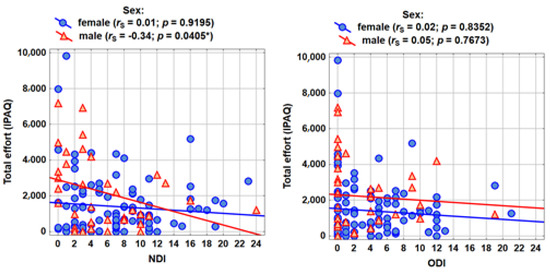
Figure 2.
Measurements of total activity of pain NDI and ODI.
Sitting in front of a computer or smartphone influences back pain (Table 5). Such a relationship occurs mainly as for cervical pain (correlations are statistically significant (p < 0.05) for both sexes, but the correlation strength is greater for men: rS = 0.37 vs. rS = 0.20), and in the case of female students, on the border of statistical significance there is the relationship between the Internet addiction and pain in the lumbosacral region (rS = 0.19; p = 0.0589).

Table 5.
Correlations between the level of Internet addiction and back pain.
4. Discussion
Online electronic questionnaires are an easy to implement and safe (especially during an epidemic) method of collecting information [10]. The period of the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as the associated isolation and online learning, had a negative impact on many areas of life.
In response to the spreading pandemic, the government significantly limited all motor behavior and enforced social distancing from citizens. Restrictions were placed on the activities of fitness industry and swimming pools. Forests, boulevards and parks were closed during a certain period of the pandemic. People could not leave their places of residence, and so learning at universities was conducted online.
Pain in the cervical and lumbar area of the spine may occur due to certain factors such as stress and psychosocial factors [11]. The high risk of developing musculoskeletal pain [12,13,14] appears more among students of medical professions than in other populations.
Our research assessed young people learning online amid realities of the pandemic. A statistically significant relationship was found between Internet addiction and lumbosacral pain. Similar relationships have been shown in previous studies in which the excessive use of electronic devices was a risk factor for the development of cervical and lumbar spine pain [12,15,16].
Interestingly enough, in the authors’ own research, the respondents mostly suffered from pain originating in the cervical spine. During the pandemic and contact restrictions, social life and science moved online. Even before this phenomenon, a positive correlation was observed between the time of using a mobile phone and the duration and intensity of neck pain [17]. These ailments could be reduced by introducing ergonomic measures [18].
Our research also shows that more intense pain in the cervical spine was positively correlated with lower physical activity, which is confirmed by the results of studies conducted among students before the pandemic [19]. Other authors also refer to the relationship between back pain and lack of physical activity [20,21].
In terms of physical activity, the situation is not good in the studied group of physiotherapy students. Almost in every fifth person the level of physical activity was estimated as high. Similar results regarding the limitation and low level of physical activity were noticed among students during the pandemic in England [22], Scotland [23], Italy [24], Spain [25], Switzerland [26], Hungary [27], USA [28], Mexico [29] and China [30]. A decrease in the level of physical activity among students of physiotherapy was observed in India, where its level was defined as medium [31]. The authors’ own research, conducted among Polish students, shows a very disturbing level of activity—low in 40.4% of the respondents. Similar results were obtained among Italian students—39.62% of them showed a low level of physical activity during the epidemic [32]. These results are alarming in the context of global studies conducted before the pandemic, which already estimated that 27.5% of the population had insufficient levels of physical activity [33].
A decrease in physical activity was more frequently observed in women. Other results were obtained in Great Britain [22], Spain [34] and Italy [35]. Savage et al. and Maugeri et al. suggest that such a situation may be caused by the preference for sports among men for social and competitive reasons as well as in public places such as gyms and fitness clubs (which was prevented by the development of the pandemic), while women (who are more likely to exercise at home) practice sports for reasons related to maintaining an adequate body weight [22,32]. The discrepancy in the results may be related to a small study group of men.
Prolonged periods of limitation in physical activity, sedentary lifestyle and isolation have a negative impact on depression and the feeling of anxiety and fear [36]. It may also be associated with the decrease in immunity [37] and undertaking risky behaviors [37]. One should notice that regular physical activity strengthens the immune functions of the body, which can contribute to reducing the risk of infection. The negative effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, prolonged lockdown and restricted social contact may have consequences for years.
The limitations of our study were the small size of the group and the significant predominance of female students among respondents, as well as the subjectivity of respondents in the online self-report survey. Subsequent research should cover students of other faculties, as well as individual age or professional groups. Future research should be oriented towards a larger sample and use more objective methods to evaluate the parameters tested.
5. Conclusions
Research results suggest that the pandemic is negatively affecting students. Frequent occurrence of back pain is observed with a simultaneous low level of physical activity. Maintaining regular activity during a pandemic, at least at home, is an indispensable preventive measure for physical health. Research results should be taken into account by university authorities in order to organize long-term support for their students. Activities aimed at promoting physical activity can improve students’ physical health and help them to cope better in uncertain times. This study supplements the literature on back pain and physical activity during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G. and A.Z.; methodology, M.G. and A.Z.; formal analysis, M.G., A.Z. and M.S.; investigation, M.G and A.Z.; data curation, M.G., A.Z. and M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G. and A.Z.; writing—review and editing, M.G., A.Z and M.S.; visualization, M.G and A.Z.; supervision, I.B.-K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the the Senate Commission for Ethics in Scientific Research of the School of Medical Science in Bialystok KB/18/2020.2021.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Garrett, L. COVID-19: The medium is the message. Lancet 2020, 395, 942–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siste, K.; Hanafi, E.; Sen, T.T.; Christian, H.; Adrian; Siswidiani, L.P.; Limawan, A.P.; Murtani, B.J.; Suwartono, C. The Impact of Physical Distancing and Associated Factors Towards Internet Addiction Among Adults in Indonesia During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Nationwide Web-Based Study. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 580977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Nogueira, Ó.; Leirós-Rodríguez, R.; Benítez-Andrades, J.; Álvarez-Álvarez, M.; Marqués-Sánchez, P.; Pinto-Carral, A. Musculoskeletal Pain and Teleworking in Times of the COVID-19: Analysis of the Impact on the Workers at Two Spanish Universities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Pitti, J.; Casajús-Mallén, J.A.; Leis-Trabazo, R.; Lucía, A.; de Lara, D.L.; Moreno-Aznar, L.A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, G. Exercise as medicine in chronic diseases during childhood and adolescence. Anales de Pediatría 2020, 92, 173.e1–173.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-M.; Alexander, R.; Lo, S.K.; Cook, J. Effects of Functional Fascial Taping on pain and function in patients with non-specific low back pain: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabilitation 2012, 26, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadi, S.; Ansari, N.N.; Naghdi, S.; Fallah, E.; Barzi, D.M.; Jalaei, S.; Bagheri, H. A study of therapeutic ultrasound and exercise treatment for muscle fatigue in patients with chronic non specific low back pain: A preliminary report. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2013, 26, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Mao, L.; Nassis, G.P.; Harmer, P.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Li, F. Returning Chinese school-aged children and adolescents to physical activity in the wake of COVID-19: Actions and precautions. J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidadi, A.; Taheri, H.; Jalili, A. Relationship between physical fitness, body composition and blood pressure in active and passive students. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. Arch. 2019, 7, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, J.E.; Hillman, C.H.; Castelli, D.; Etnier, J.L.; Lee, S.; Tomporowski, P.; Lambourne, K.; Szabo-Reed, A.N. Physical Activity, Fitness, Cognitive Function, and Academic Achievement in Children: A Systematic Review. MedSci Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 1197–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.E.; Hendrick, P.; Bateman, M.; Moffatt, F.; Rathleff, M.S.; Selfe, J.; Smith, T.O.; Logan, P. Current management strategies for patellofemoral pain: An online survey of 99 practising UK physiotherapists. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaya-Contreras, P.; Styf, J. Biopsychosocial function analyses changes the assessment of the ability to work in patients on long-term sick-leave due to chronic musculoskeletal pain: The role of undiagnosed mental health comorbidity. Scand. J. Public Health 2013, 41, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, H.; Mehmood, S.; Imtiaz, F.; Ali, S.A.; Sarfraz, M. Musculoskeletal pain and its associated risk factors among medical students of a public sector University in Karachi, Pakistan. J. Pak Med. Assoc. 2018, 68, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samoladas, E.; Barmpagianni, C.; Papadopoulos, D.V.; Gelalis, I.D. Lower back and neck pain among dentistry students: A cross-sectional study in dentistry students in Northern Greece. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2018, 28, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, R.J.; Volken, T.; Schaffert, R.; Bucher, T. Higher low back and neck pain in final year Swiss health professions’ students: Worrying susceptibilities identified in a multi-centre comparison to the national population. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.R.R.; Pitangui, A.C.R.; Xavier, M.K.A.; Junior, M.C.; De Araújo, R.C. Prevalence of musculoskeletal pain in adolescents and association with computer and videogame use. J. Pediatr. 2016, 92, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.G.; Sa-Couto, P.; Queirós, A.; Neto, M.; Rocha, N.P. Pain, pain intensity and pain disability in high school students are differently associated with physical activity, screening hours and sleep. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, F.; Bsisu, I.; AlRyalat, S.A.; Al-Zu’Bi, B.; Bsisu, R.; Hamdan, M.; Kanaan, T.; Yasin, M.; Samarah, O. Association between mobile phone use and neck pain in university students: A cross-sectional study using numeric rating scale for evaluation of neck pain. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowatt, L.; Gordon, C.; Santosh, A.B.R.; Jones, T. Computer vision syndrome and ergonomic practices among undergraduate university students. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2017, 72, e13035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarabottolo, C.; Pinto, R.Z.; Oliveira, C.B.; Zanuto, E.F.; Cardoso, J.; Christofaro, D.G.D. Back and neck pain prevalence and their association with physical inactivity domains in adolescents. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, A.; Froboese, I. Movement coaching: Study protocol of a randomized controlled trial evaluating effects on physical activity and participation in low back pain patients. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottermund, J.; Knapik, A.; Saulicz, E.; Myśliwiec, A.; Saulicz, M.; Rygiel, K.; Linek, P. Back and neck pain among school teachers in Poland and its correlations with physical activity. Med. Pr. 2015, 66, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Savage, M.J.; James, R.; Magistro, D.; Donaldson, J.; Healy, L.C.; Nevill, M.; Hennis, P.J. Mental health and movement behaviour during the COVID-19 pandemic in UK university students: Prospective cohort study. Ment. Health Phys. Act. 2020, 19, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, J.; Maciejewski, G.; Hand, C.J. Changes in Diet, Sleep, and Physical Activity Are Associated With Differences in Negative Mood During COVID-19 Lockdown. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, F.; Cenacchi, V.; Vegro, V.; Pavei, G. COVID-19 lockdown: Physical activity, sedentary behaviour and sleep in Italian medicine students. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Blanco, C.; Rodríguez-Almagro, J.; Onieva-Zafra, M.D.; Parra-Fernández, M.L.; Prado-Laguna, M.D.C.; Hernández-Martínez, A. Physical Activity and Sedentary Lifestyle in University Students: Changes during Confinement Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogan, S.; Luijckx, E.; Taeymans, J.; Haas, K.; Baur, H. Physical Activity, Nutritional Habits, and Sleep Behavior Among Health Profession Students and Employees of a Swiss University During and After COVID-19 Confinement: Protocol for a Longitudinal Observational Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2020, 9, e25051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ács, P.; Prémusz, V.; Morvay-Sey, K.; Pálvölgyi, Á.; Trpkovici, M.; Elbert, G.; Melczer, C.; Makai, A. Effects of Covid-19 on physical activity behavior among university students: Results of a hungarian online survey. Health Probl. Civiliz. 2020, 14, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughenour, C.; Gakh, M.; Pharr, J.R.; Bungum, T.; Jalene, S. Changes in Depression and Physical Activity Among College Students on a Diverse Campus After a COVID-19 Stay-at-Home Order. J. Community Health 2020, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, E.I.A.; Hall-López, J.A. Physical activity in university student athletes, prior and in confinement due to pandemic associated with COVID-19 (Actividad física en estudiantes deportistas universitarios, previo y en el confinamiento por pandemia asociada al COVID-19). Retos 2020, 39, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.-Q.; Tan, X.-M.; Sun, J.; Yang, H.-Y.; Zhao, X.-P.; Liu, L.; Hou, X.-H.; Hu, M. Relationship of Physical Activity With Anxiety and Depression Symptoms in Chinese College Students During the COVID-19 Outbreak. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 582436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastav, A.K.; Sharma, N.; Samuel, A.J. Impact of Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) lockdown on physical activity and energy expenditure among physiotherapy professionals and students using web-based open E-survey sent through WhatsApp, Facebook and Instagram messengers. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 9, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, G.; Castrogiovanni, P.; Battaglia, G.; Pippi, R.; D’Agata, V.; Palma, A.; Di Rosa, M.; Musumeci, G. The impact of physical activity on psychological health during Covid-19 pandemic in Italy. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Bull, F.C. Worldwide trends in insufficient physical activity from 2001 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 358 population-based surveys with 1·9 million participants. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e1077–e1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Larrad, A.; Mañas, A.; Labayen, I.; González-Gross, M.; Espin, A.; Aznar, S.; Serrano-Sánchez, J.A.; Vera-Garcia, F.J.; González-Lamuño, D.; Ara, I.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 Confinement on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour in Spanish University Students: Role of Gender. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giustino, V.; Parroco, A.M.; Gennaro, A.; Musumeci, G.; Palma, A.; Battaglia, G. Physical Activity Levels and Related Energy Expenditure during COVID-19 Quarantine among the Sicilian Active Population: A Cross-Sectional Online Survey Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallgren, M.; Nguyen, T.-T.-D.; Owen, N.; Vancampfort, D.; Smith, L.; Dunstan, D.W.; Andersson, G.; Wallin, P.; Ekblom-Bak, E. Associations of interruptions to leisure-time sedentary behaviour with symptoms of depression and anxiety. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkley, L.C.; Thisted, R.A.; Cacioppo, J.T. Loneliness predicts reduced physical activity: Cross-sectional & longitudinal analyses. Health Psychol. 2009, 28, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).