Abstract
Using whey, a by-product of the cheese-making process, is important for maximizing resource efficiency and promoting sustainable practices in the food industry. Reusing whey can help minimize environmental impact and produce bio-preservatives for foods with high bacterial loads, such as Mexican-style fresh cheeses. This research aims to evaluate the antimicrobial and physicochemical effect of CFS from Lactobacillus casei 21/1 produced in a conventional culture medium (MRS broth) and another medium using whey (WB medium) when applied in Mexican-style fresh cheese inoculated with several indicator bacteria (Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus, and Listeria monocytogenes). The CFSs (MRS or WB) were characterized for organic acids concentration, pH, and titratable acidity. By surface spreading, CFSs were tested on indicator bacteria inoculated in fresh cheese. Microbial counts were performed on inoculated cheeses during and after seven days of storage at 4 ± 1.0 °C. Moreover, pH and color were determined in cheeses with CFS treatment. Lactic and acetic acid were identified as the primary antimicrobial metabolites produced by the Lb. casei 21/1 fermentation in the food application. A longer storage time (7 days) led to significant reductions (p < 0.05) in the microbial population of the indicator bacteria inoculated in the cheese when it was treated with the CFSs (MRS or WB). S. enterica serovar Typhimurium was the most sensitive bacteria, decreasing 1.60 ± 0.04 log10 CFU/g with MRS-CFS, whereas WB-CFS reduced the microbial population of L. monocytogenes to 1.67 log10 CFU/g. E. coli and S. aureus were the most resistant at the end of storage. The cheese’s pH with CFSs (MRS or WB) showed a significant reduction (p < 0.05) after CFS treatment, while the application of WB-CFS did not show greater differences in color (ΔE) compared with MRS-CFS. This study highlights the potential of CFS from Lb. casei 21/1 in the WB medium as an ecological bio-preservative for Mexican-style fresh cheese, aligning with the objectives of sustainable food production and guaranteeing food safety.
1. Introduction
Most traditional Mexican fresh cheeses are artisanal products made from whole or low-fat cow’s milk, frequently without the milk’s thermal treatment, through casein coagulation with rennet (or other proteinase substitutes) [1]. Their processing is not commonly standardized; producers handle low production volumes and often utilize unpasteurized milk [2], which represents a health risk [3]. In the production of fresh Mexican-style cheese, no bacteria are inoculated because it is not a fermented product; due to its short shelf life, it is usually consumed soon after it is made [2]. It is common for this variety of cheese to be a vehicle for pathogenic microorganisms, which can be attributed to unpasteurized milk or handling techniques during its production [4]. Unfortunately, there have been multiple cases of illness linked to the consumption of this cheese, as it may contain harmful microorganisms such as Salmonella [5,6,7], Listeria monocytogenes [8,9,10], Escherichia coli [11,12], and Staphylococcus aureus [6,13,14].
Bio-preservation involves using microorganisms or their metabolites to increase the shelf life and safety of food. Among of the most promising natural biological antagonists are lactic acid bacteria (LAB), which have several potential applications. Numerous studies have reported that LAB strains produce antimicrobial substances (organic acids, short-chain fatty acids, hydrogen peroxide, and proteinaceous compounds) [15,16]. LAB are commonly used as starter cultures in the food industry, particularly in cultured dairy products [17]. Nonetheless, non-starter LAB have also been assessed for their ability to prolong the shelf life of various foods, including bread, dairy products, fresh fruits, vegetables, and animal feed [18,19,20]. Several studies have investigated the potential use of non-traditional starter LAB to increase cheese safety and shelf life. Dal Bello et al. [21] successfully controlled the growth of L. monocytogenes in cottage cheese using LAB. Settanni et al. [22] were able to extend the safety and shelf life of Tosela cheese by controlling the growth of L. monocytogenes, Salmonella spp., and coliforms using Lactobacillus paracasei NdP78 and Streptococcus macedonicus NdP1.
LAB are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) with qualified presumption of safety (QPS) [23]; many of them have been studied as bio-preservatives due to the secretion of antimicrobial compounds, either organic acids or bacteriocins [20]. Ensuring the safety of cheeses while maintaining their organoleptic characteristics is a challenge for the food industry. Therefore, the use of LAB cell-free supernatants (CFSs) can be an alternative since they have interesting antimicrobial properties [19], especially in the bio-preservation of raw foods such as beef [24], chicken [25,26,27], shrimp [28], and vegetables [29], among many others [20].
To produce these CFSs and enable their possible use in the food industry, it is essential to have a culture medium for the optimal growth of microorganisms and the production of antimicrobial metabolites. It is important to consider the economic viability and safety for consumption of the medium used to produce CFS. In most studies [19] addressing the antimicrobial activity of CFS from LAB, the culture medium used is de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) broth, which is excellent for the growth of Lactobacillus. However, due to its high cost, MRS broth is unsuitable for industrial use. Zandona et al. [30] have mentioned that whey is a sustainable food ingredient since it has been employed in the elaboration of food products such as infant formula, meat products, beverages, soups, sauces, toppings, creamers, nut coatings, pressed nuts, cheese-based sauces, potato chips, savory flavors, savory puff pastries, and special bakery products such as pizza, biscuits, macaroni, soufflés, and cakes. Hence, whey may be a potential ingredient for food-grade culture medium since its nutrient profile includes sugar (lactose 46–52 g L−1), proteins (6.5–6.6 g L−1), and minerals (5.0–5.2 g L−1) [31]. Recently, fermented whey by LAB has been investigated as an antimicrobial. For instance, Yousefi et al. [32] optimized the fermentation conditions of L. plantarum PTCC 1896 in whey to improve the antibacterial metabolites production, whereas Izzo et al. [33] analyzed the antifungal activity from fermented goat’s sweet whey utilizing four L. plantarum strains. However, they did not evaluate the antimicrobial activity in any food matrix, and thus, further research is necessary. Also, whey has been demonstrated to be suitable for LAB growth and fermented probiotic beverages [31,34]. Whey derived from the cheese industry is relatively cheap and readily available. This approach would help improve food safety and the environment since the cheese industry produces approximately 115 million tons, wasting around 47% [35]. Discharging untreated whey into the environment can cause several problems such as water contamination, dissolved oxygen depletion, and eutrophication [36]. Whey dissolved in water has a high level of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) ranging from 40 to 60 g L−1 and chemical oxygen demand (COD) ranging from 50 to 80 g L−1 [30].
Therefore, this research aims to evaluate the antimicrobial and physicochemical effect of CFS from Lactobacillus casei 21/1 produced in a conventional culture medium (MRS broth) and another medium using whey (WB) when applied in Mexican-style fresh cheese inoculated with several indicator bacteria (Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus, and Listeria monocytogenes).
2. Materials and Methods
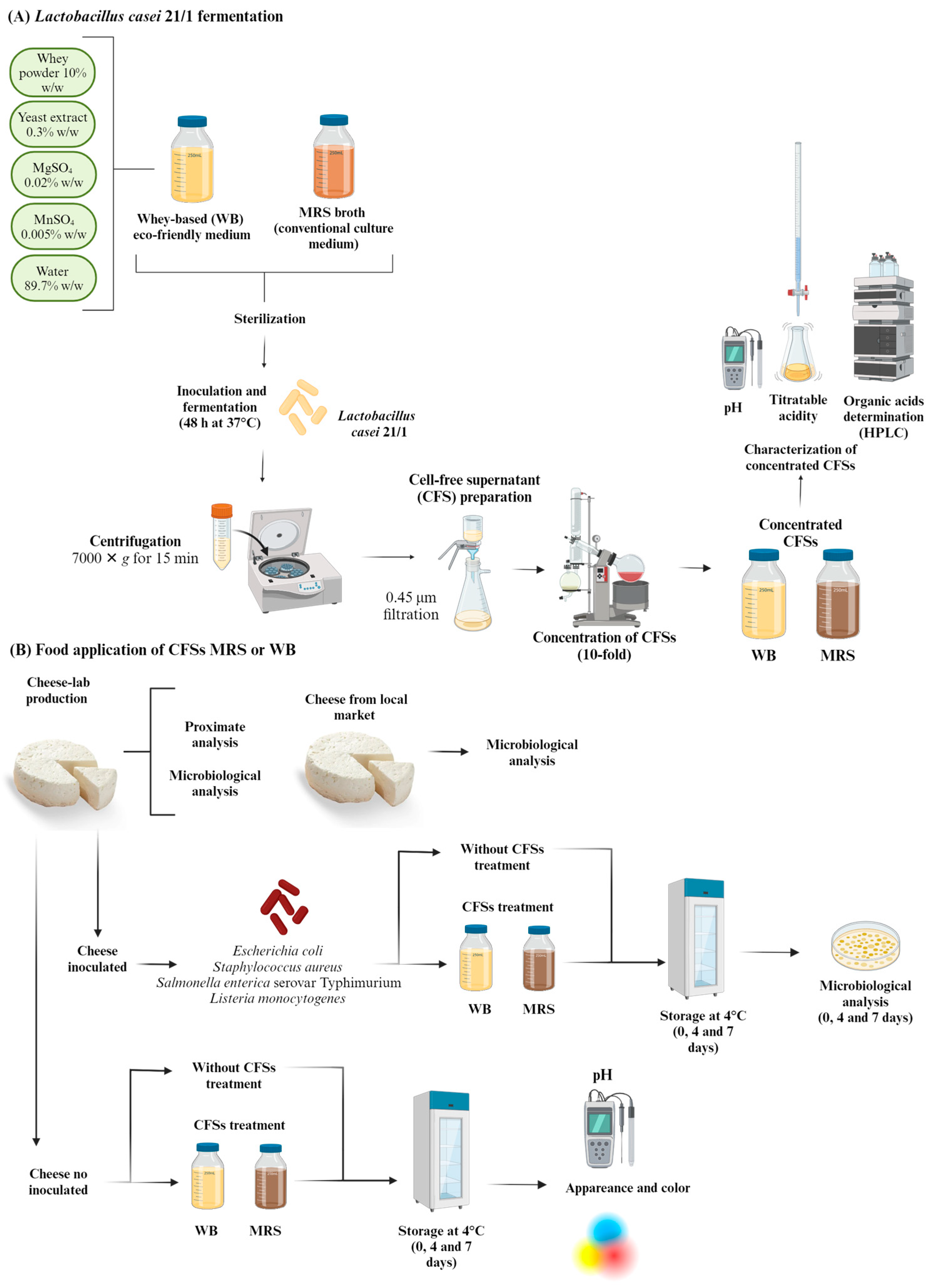
Figure 1 shows the flow diagram of the experiments performed in the present study.
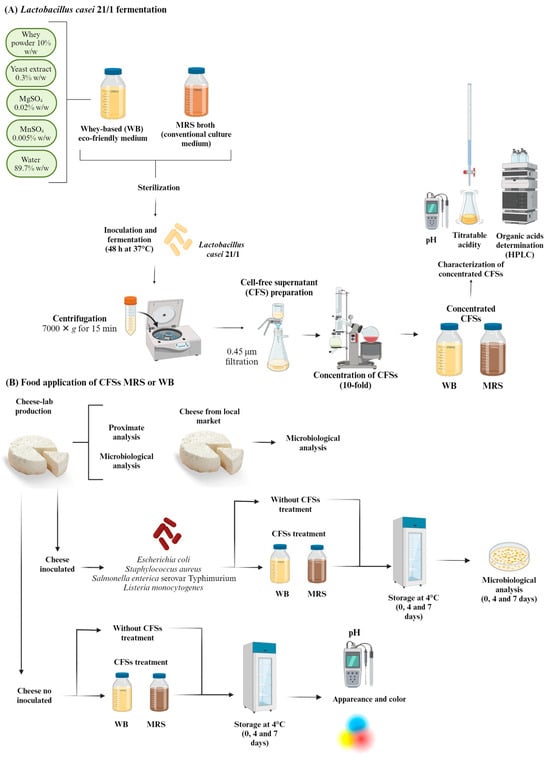
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the experiments, materials, and methods used for the present study.
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Culture Mediums Preparation and Growth Conditions
Lactobacillus casei 21/1 as well as indicator strains (Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213, and Listeria monocytogenes Scott A) were obtained from the Food Microbiology Laboratory of the Universidad de las Americas Puebla (San Andres Cholula, Puebla, Mexico). Lb. casei 21/1 was reactivated and sub-cultivated in de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) broth (Difco™ BD, Sparks, MD, USA) at 35 °C. Indicator strains were reactivated and incubated in trypticase soy broth (TSB, Bioxon BD, Mexico City, Mexico) at 35 ± 1.0 °C for 24 h.
The whey-based (WB) medium was prepared using 10.0% w/w whey powder (10% protein, 1.5% fat, 75% carbohydrates, and 1.1% sodium chloride; Food Technologies Trading, Mexico City, Mexico), yeast extract 0.3% w/w (Difco™, BD, Sparks, MD, USA), magnesium sulfate 0.02% (MgSO4•7H2O) (Merck, Burlington, MA, USA), manganese sulfate 0.005% w/w (MnSO4•H2O) (Merck, Burlington, MA, USA), and water. In a previous study [37], MRS broth (Difco™ BD, Sparks, MD, USA) was used as a conventional culture medium. Fresh cultures of Lb. casei 21/1 were used to inoculate the culture media, adding the necessary amount to obtain an initial population of 106 CFU mL−1. For the growth conditions in culture media, Lb. casei 21/1 was incubated at 35 ± 1.0 °C for 48 h.
2.2. Preparation of Cell-Free Supernatant (CFS)
After fermentation with Lb. casei 21/1, the MRS broth and WB medium were centrifugated at 7000× g for 15 min at 5 °C (Sorvall ST 8R, Thermo Fischer Scientific, Schwerte, Germany). Later, the supernatants were filtered through a 0.45 μm Millipore membrane filter (Advantec, MFS, Dublin, CA, USA). The CFSs from MRS or WB were concentrated 10-fold via vacuum evaporation on a Buchi R-210/215 rotary evaporator (Buchi, Flawil, Switzerland) at 70 ± 1.0 °C and 25 cm Hg following the methodology described by Arrioja-Bretón et al. [37]. Concentrated CFSs were refrigerated at 4 ± 1.0 °C until their use.
2.3. Characterization of CFSs
2.3.1. pH and Titratable Acidity
The pH of MRS and WB CFSs was determined by immersion electrode using a pH meter (HI 2210 Hanna Instruments, Woonsocket, RI, USA). The percentage of titratable acidity (TA%) of CFSs was determined following method 22.061 from AOAC [38] and was expressed as a percentage of lactic acid (%w/v). The measurements were performed in triplicate.
2.3.2. Organic Acid Determination in CFSs
The organic acids concentration from MRS and WB CFSs (lactic and acetic acid) was determined via high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) following the methodology reported by Hernández-Figueroa et al. [39]. The chromatograph employed was an Agilent 1260 (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) coupled with a diode array detector (DAD) at a wavelength of 210 nm. CFSs (MRS or WB) were injected (20 µL) using an Agilent G1329 autosampler (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). A C-18 column (250 × 4.6 mm) (Restek, Centre Country, PA, USA) was used with a mobile isocratic phase of 20 mM monobasic potassium phosphate buffer solution (adjusted to pH 2.4) at 0.6 mL min−1 at room temperature. For the quantification of lactic and acetic acid, the concentration of acids was linearly correlated with their respective peak areas, obtaining correlation coefficients R2 > 0.99 employing standard solutions.
2.4. Laboratory-Scale Cheese Production
For the food application of CFSs, Mexican-style fresh cheese was manufactured with commercial pasteurized brand Lala™ (Gomez Palacio, Durango, Mexico) whole milk (fat: 3.3%, protein: 3.1%, carbohydrates: 4.7%, 5 g of vitamin D/L, and 666 mg retinol equivalents/L) following the methodology of Parra-Ocampo et al. [40] with slight modifications. The milk was heated until reaching a temperature of 39 ± 1.0 °C, then 0.02% of 50% calcium chloride (Reactivos Química Meyer, Mexico City, Mexico) and 0.03% of commercial chymosin (Cuamex®, Chr. Hansen, Mexico City, Mexico) per liter of milk were added and stirred. Then, the milk was left to rest for 20 min until it curdled. The curd was cut into cubes of approximately 2 cm3 and left to rest for another 20 min. Cubes were subsequently placed on a mesh and squeezed to remove the whey. To the resulting paste, 1% salt was added to the total cheese mass. Finally, the cheese mass was molded in a cylindrical mold and pressed at 4 ± 1.0 °C for 24 h. Different batches of cheese (≈10 pieces each) were prepared for all the treatments and analyses that were carried out.
2.5. Physicochemical Analyses
2.5.1. Proximate Analysis
For characterization of manufactured Mexican-style fresh cheese, AOAC [41] methods were taken as references to determine moisture (method 33.7.03), fat (method 933.05), ash (method 33.7.07), and protein (method 33.7.12 via the Kjeldahl method using a conversion factor of 6.38). These determinations were performed in triplicate.
2.5.2. pH and Color
The cheese pH was measured according to NMX-F-317-S-1978 [42]; 10.0 ± 1.0 g of non-inoculated cheese (non-CFS) and CFS treated (MRS and WB) were mixed with 50 mL distilled water. An electrode connected to a digital pH meter (HI 2210 Hanna Instruments, Woonsocket, RI, USA) was employed. A Konica Minolta CR-400 colorimeter (Konica Minolta, Tokio, Japan) was used in reflectance mode and CIELAB scale to determine the color of the samples. Color differences () were assessed using Equation (1) where and are the initial luminosity of the sample and at the time it was analyzed, and are the initial red–green contribution, and and are the initial blue–yellow contribution of the initial sample and the analyzed sample at each time point, respectively. The pH and color measurements were taken in triplicate at 0, 4, and 7 days of storage at 4 ± 1.0 °C.
2.6. Cheese Inoculation and CFS Treatment
The indicator bacteria (E. coli, S. aureus, S. enterica serovar Typhimurium, and L. monocytogenes) were cultivated according to the conditions described in Section 2.1. Adequate 10-fold dilutions were performed to obtain a cell suspension of 105 CFU mL−1. Each side of a piece of Mexican-style fresh cheese manufactured in the laboratory (~10 g) was inoculated with 250 μL of the inoculum of each indicator microorganism and drained for 20 min. Subsequently, cheese pieces were put in individual plastic bags (Whirl-Pak1, Nasco, Fort Atkinson, WI, USA) with 1 mL of CFS from Lb. casei 21/1 (from MRS or WB) for surface spread. Then, the samples were stored at 4 ± 1.0 °C for 7 days. Inoculated indicator bacteria without CFSs cheese pieces were used as a negative control. These determinations were performed in triplicate.
2.7. Microbiological Analysis of Laboratory-Scale and Locally Marketed Cheeses
After the application of CFSs in cheese, microbial counts were performed for each indicator microorganism on days 0, 4, and 7; one piece (~10 g) of cheese inoculated with each bacterium was put in a sterile plastic bag (Whirl-Pak1, Nasco, Fort Atkinson, WI, USA), and homogenized for 2 min in a Stomacher 80 lab blender (Seward Ltd., West Sussex, UK) with 90 mL of sterile peptone water (1 g L−1). Adequate decimal dilutions were prepared into peptone water and plated in trypticase soy agar. Plates were incubated during 18–24 h at 37 ± 1.0 °C.
Mexican-style fresh cheeses are commonly consumed, and it is well known that they are associated with foodborne diseases [6]. For this reason, this study investigated the ability of the CFSs to help reduce the risk associated with these products. For comparison purposes, two cheeses were purchased in local markets (San Andres Cholula, Puebla, Mexico), and the following methodology was used to verify the sanitary quality of the lab-scale-manufactured cheeses. Counts of total mesophilic aerobic bacteria were completed using standard agar (Bioxon, BD, Edo. de Mexico, Mexico) following the method NOM-092-SSA1-1994 [43]; inoculated plates were incubated for 24 h at 37 ± 1.0 °C. For total coliform counts, violet-red bile agar (Bioxon, BD, Edo. de Mexico, Mexico) was used according to method NOM-111-SSA1-1994 [44], Baird–Parker agar (Bioxon, BD, Edo. de Mexico, Mexico) for S. aureus following the method NOM-115-SSA1-1994 [45], XLD agar (Bioxon, BD, Edo. de Mexico, Mexico) for Salmonella, Oxford agar (Difco, BD, Sparks, MD, USA) for L. monocytogenes, and MacConkey agar (Bioxon, BD, Edo. de Mexico, Mexico) for E. coli; plates were incubated at 37 ± 1.0 °C for 18–24 h. These determinations were performed in triplicate.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The data of each experiment were assessed with analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s mean comparison test p < 0.05. Minitab 20 software (Minitab LLC, State College, PA, USA) was utilized for the analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Lb. casei 21/1 CFS
Characterizing CFSs is essential in order to know the metabolites responsible for their antimicrobial activity. As shown in Table 1, the CFSs from MRS or WB had low pH values with significant differences (p < 0.05). The TA% values were high in comparison with conventional fermentations (1–2%) [46]. The values for the concentration of organic acids were high, with 1608.21 ± 11.62 and 866.42 ± 15.12 mM lactic acid for MRS and WB, respectively. In contrast, acetic acid values of 750.86 ± 17.80 mM for MRS and 146.83 ± 2.79 mM for WB were obtained. It must be considered that these values are high since the CFSs were concentrated, so the quantity of metabolites, such as organic acids, was increased. With this characterization, it is notable that the type of culture medium had a significant effect (p < 0.05), with the lab-culture medium (MRS) demonstrating a greater production of organic acids due to its excellent nutrient profile. In similar studies, lower concentrations (6.16 g L−1) of lactic acid than used in this study were reported in MRS fermentations with different strains of Lacticaseibacillus casei [47]. It is well known that acetic acid is a component that is produced in lesser quantities than lactic acid; acetic acid concentrations of 0.0128–0.0141 mmol mL−1 were reported in MRS broth fermented with Lacticaseibacillus casei BD 1415 [47].

Table 1.
pH, titratable acidity, and acids of concentrated Lb. casei 21/1 cell-free supernatants (CFSs) from de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) broth and whey-based (WB) medium.
Although the obtained values in the CFS from WB were significantly (p < 0.05) lower than those for MRS, Lb. casei produced enough organic acids in WB to exert antimicrobial activity. Whey fermentation media offers a sustainable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly approach to producing lactic and acetic acid with LAB, making it a favorable choice for industrial applications. Whey fermentation by LAB is highly scalable and can be used for commercial production of lactic and acetic acid or as a fermentate for various applications as an antimicrobial agent [32,33]. For the food industry, whey is preferably used in powder form rather than liquid as this extends its shelf life and ease of handling. The whey powdering process consists of clarifying, separating cream, pasteurization, concentrating total solids by evaporation, lactose crystallization, and whey drying (commonly by spray drying) [30]. Most research related to whey focuses on its protein isolates and concentrates, which mainly contain β-lactoglobulin, α-lactalbumin, and bovine serum albumin, among others, and are used in industry for their high protein content and bioactive properties [48].
However, obtaining whey proteins substantially increases the price and involves high energy consumption. [48]. Therefore, all the components of whey have been used to design a sustainable, eco-friendly, and economically viable culture medium. This is an advantage compared with MRS broth, which has a high cost, and it has been reported that its use as a postbiotic or CFS in food products negatively affects organoleptic properties [19].
3.2. Physicochemical Analysis and Microbial Load of Cheese
The composition of the manufactured Mexican-style fresh cheese was moisture 63.42 ± 1.77%, protein 11.48 ± 1.49%, fat 5.40 ± 0.13%, ash 1.85 ± 0.03%, and 17.85% carbohydrates (by difference), while cheese yield was approximately 10%. Caro et al. [49] previously obtained different compositions for Panela cheese with lower moisture and lactose content (54.2% and 2.23%) and higher fat, protein, and ash content (18.8%, 18.4%, and 2.57%, respectively). The differences are attributed to the manufacturing process, in which the pressing force was probably insufficient to drain the whey.
Counts of the indicator microorganisms E. coli, S. enterica serovar Typhimurium, S. aureus, and L. monocytogenes on the uninoculated Mexican-style fresh cheese were under detection level (<10 CFU/g) (Table 2). The initial counts of total mesophilic aerobic bacteria were 2.54 ± 0.09 log10 CFU/g, and total coliforms were <10 CFU/g, indicating that these bacterial counts were acceptable for the aim of the study. However, microbiological analyses of commercially available Mexican-style fresh cheese samples obtained from local markets (Table 2) indicate that these cheeses presented results outside the established microbiological quality standards. These cheeses were not suitable for consumption and represent a risk to consumer health due to high bacterial counts and pathogenic microorganisms, including L. monocytogenes. The Mexican official standard NOM-243-SSA1-2010 [50] establishes a maximum allowed level for total coliform bacteria in milk derivatives of 2 log10 CFU g−1 or mL−1, aerobic mesophilic 5 log10 CFU g−1 or mL−1, and in the case of S. aureus, 2 log10 CFU g−1 or mL−1; the microbial counts of these commercially Mexican-style fresh cheeses were above the established maximum limits and may be associated with low hygiene in their food production and/or handling processes. Silva-Paz et al. [51] reported similar counts of aerobic mesophilic bacteria (≤5 to 6.5 ≥ log10 CFU g−1) and coliforms ranging from <100 to 5 ≥ log10 CFU g−1 in artisanal cheese.

Table 2.
Microbial counts (log10 CFU/g) of Mexican-style fresh cheeses.
Raw milk used in cheese production may contain pathogens such as E. coli, Listeria, Salmonella, and S. aureus [6,9,12]. These pathogens can survive and spread during cheese production if the milk is not pasteurized correctly or becomes contaminated during handling [52]. Cross-contamination can also occur if equipment, utensils, or surfaces are not properly sanitized. Proper hygiene practices during packaging, storage, and distribution of fresh cheese are essential to prevent pathogen contamination and ensure consumer safety.
3.3. Antimicrobial Effect of CFS in Mexican-Style Fresh Cheese
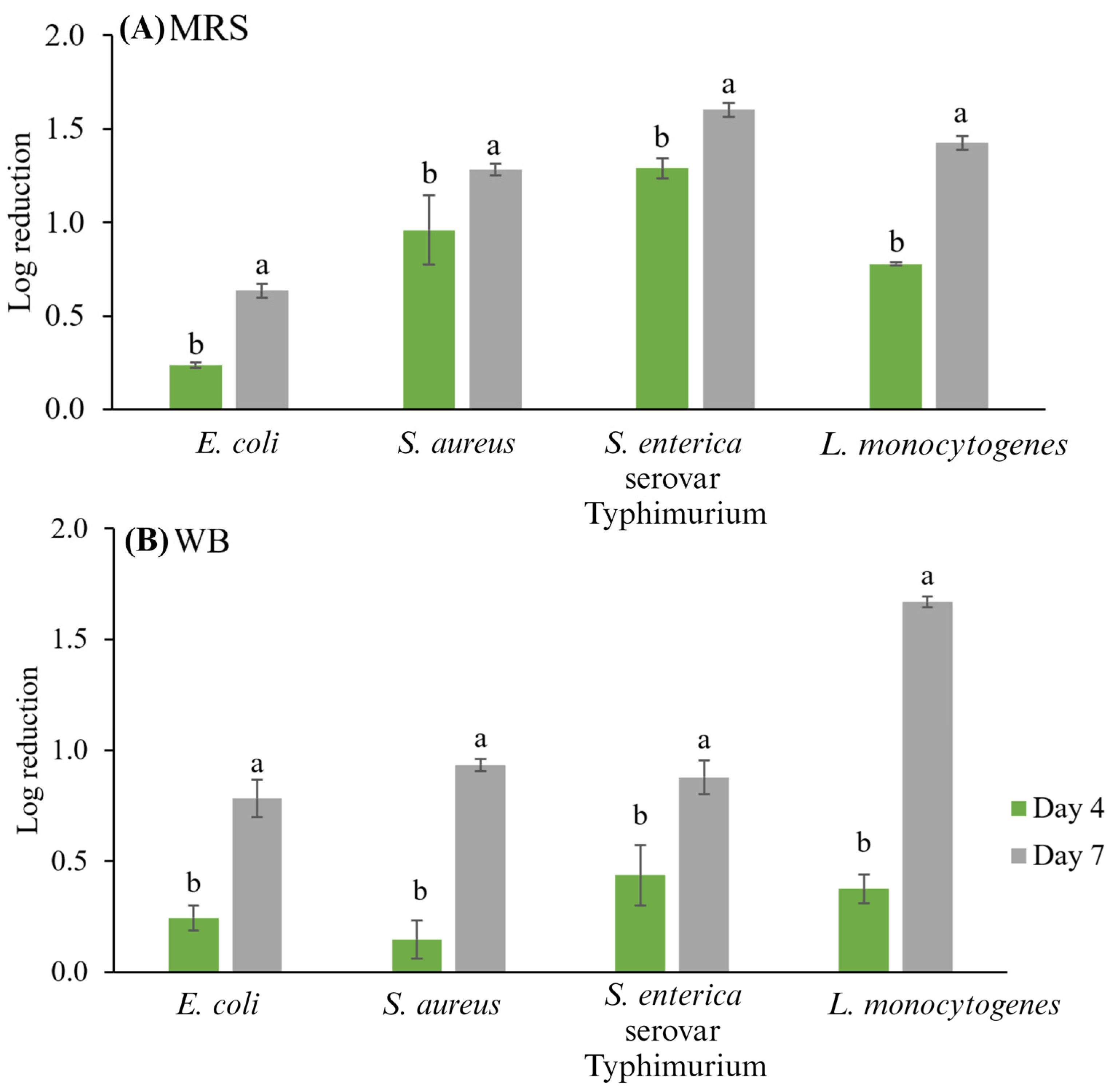
As can be observed in Figure 2, the storage time with the CFSs either from MRS or WB had a significant effect (p < 0.05) since a longer storage time (7 days) led to greater reductions in the microbial populations of indicator bacteria. The CFS from MRS broth decreased S. enterica serovar Typhimurium to 1.29 ± 0.05 log10 CFU g−1 after four days and 1.60 ± 0.04 log10 CFU g−1 after seven days of storage at 4 °C, while with CFS from WB, the microbial population decreased to 0.88 ± 0.08 log10 CFU g−1 after seven days. In the case of L. monocytogenes, applying the CFSs from MRS broth and WB medium decreased the counts by 1.43 ± 0.04 and 1.67 ± 0.03 log10 CFU g−1 after seven days of storage at 4 °C, respectively. Moreover, in vivo antimicrobial activity results showed that the type of culture medium affected the antimicrobial activity. The S. enterica serovar Typhimurium was the most sensitive microorganism to CFS from MRS broth, while L. monocytogenes was the most sensitive to the WB medium. E. coli and S. aureus were the most resistant to Lb. casei CFS (MRS and WB) activity in the studied Mexican-style fresh cheese. In a previous study, Arrioja-Bretón et al. [37] reported an in vitro assay for the antimicrobial activity of studied Lb. casei 21/1 CFS (from MRS) against the four tested indicator bacteria; L. monocytogenes was the most sensitive microorganism with inhibition zones higher than 22 mm, followed by S. enterica serovar Typhimurium, while the most resistant tested microorganisms were S. aureus and E. coli with lower inhibition halos.
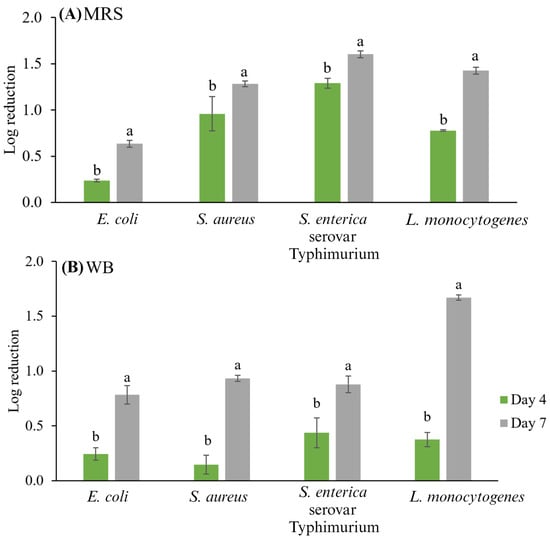
Figure 2.
Logarithmic reductions (N/N0) of tested indicator microorganisms (E. coli ATCC 25922, S. aureus ATCC 29213, S. enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028, and L. monocytogenes Scott A) in studied Mexican-style fresh cheese treated with Lb. casei 21/1 CFS from (A) de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) broth and (B) whey-based medium (WB). Different letters show a significant difference (p < 0.05) between the samples.
The reductions in log10 cycles were similar to those reported in similar studies. For instance, Dal Bello et al. [21] successfully controlled the growth of L. monocytogenes using bacteriocins produced by Lactococcus lactis while manufacturing cottage cheese. In addition, Kousta et al. [53] studied the effect of adding ferulic acid or nisin (4 mg/g) to fresh cheese to inhibit L. monocytogenes growth; they observed reductions of 2.0 or 1.5 logarithmic cycles after 21 days of storage, respectively. Major inhibition rates were reported from Lb. rhamnosus in semi-hard goat cheese against S. aureus (21.66%), L. monocytogenes (10.23%), and Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis (5.52%) after 21 days of storage at 4 °C. [54]. Sometimes, LAB can only have a bacteriostatic effect, such as in the study reported by Settanni et al. [22], who controlled the growth of L. monocytogenes and Salmonella spp. in Tosèla cheese employing Lactobacillus paracasei NdP78 or Streptococcus macedonicus NdP1. They achieved reductions of 1.79 and 2.22 log10 CFU g−1 in coliforms and S. aureus, respectively.
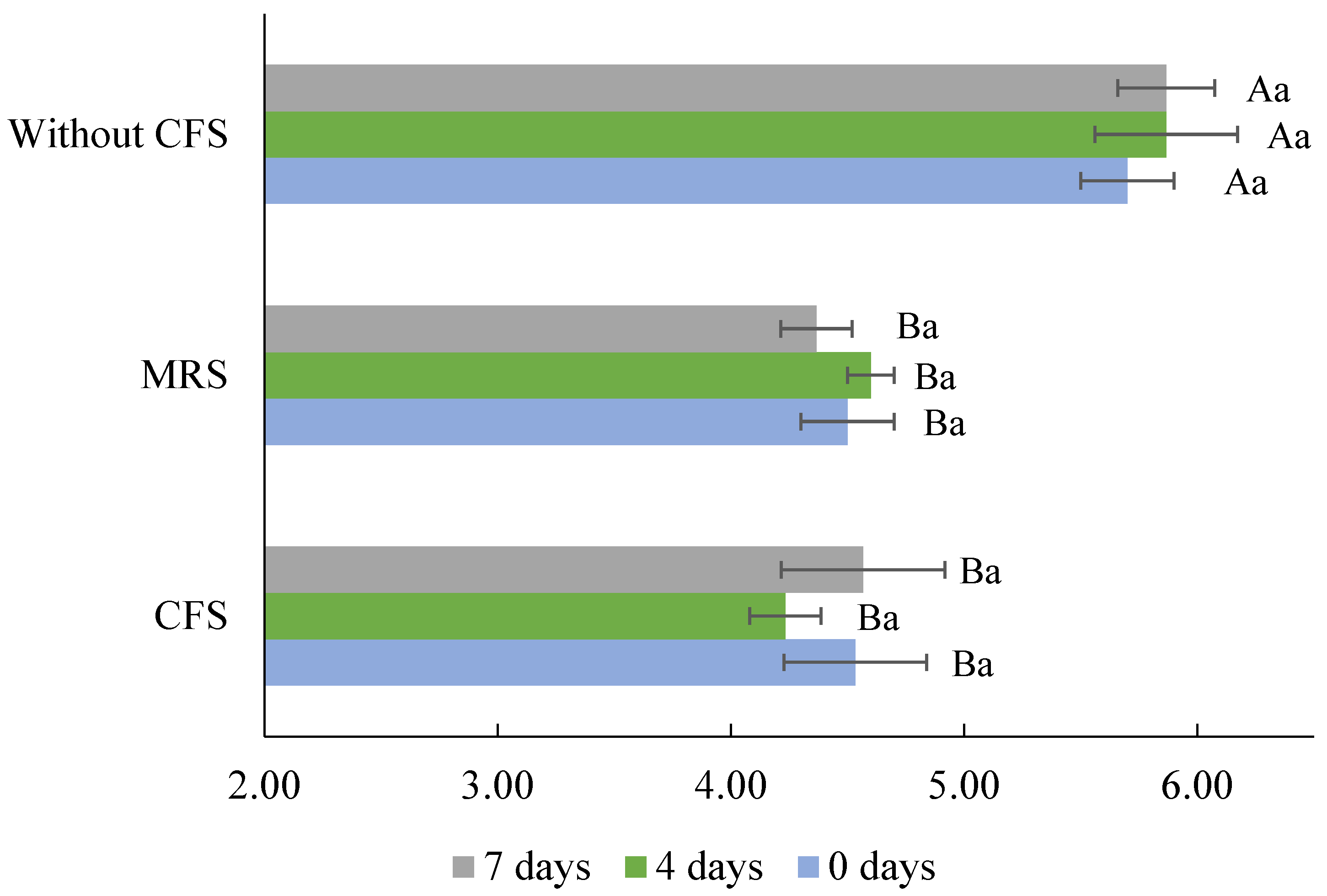
The bacterial inhibition can be attributed to the high concentration of organic acids (lactic and acetic acid) in the CFSs, which act as antimicrobial compounds; their efficacy is well known since, in the food industry, organic acids are widely used as disinfectants or natural preservatives [16,46]. Organic acids reduce the pH of foods, and if this is <pKa of the organic acid, cell acidification occurs and interferes with the maintenance of the cell wall integrity of microorganisms, affecting the transport of metabolites and altering essential functions [46]. According to our previous reports, Lb. casei’s 21/1 antimicrobial activity is primarily due to organic acids, since neutralized CFS (pH 6.5) from MRS or flour–water mixture lost inhibitory activity entirely [37,55]. In the disinfection of the meat products, lactic acid has been widely used, with concentrations close to that of this study (1342.15 mM or ≈10% v/w) applied at 55 °C on bovine skin reducing Salmonella population to 3.4 log10 cycles [56]. Meanwhile, acetic acid was used to disinfect meat at concentrations of 268.43 mM or ≈2% v/w, reducing the microbial population of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium and E. coli [46]. As observed in Figure 3, the pH of the cheeses decreased significantly (p < 0.05) with the addition of CFSs (4.23–4.60). The pH of the control cheese was in the range reported for queso blanco or queso fresco (5.2–6.8) [57]. Previous studies also observed a descending pH value of foods when CFS from Lactobacillus was applied. For instance, fresh beef surfaces treated with CFS from Lb. plantarum reached a pH of 3.80 [37]. In contrast, ground beef’s pH decreased by 0.5 or 1.0 after 3 or 6 days of storage at 4 °C (pH = 4.9) wrapped in bacterial nanocellulose films impregnated with 20% CFS from Lb. plantarum [58]. Lactic and acetic acids are impregnated and incorporated into the food matrix, leading to a lower pH after CFS treatment. Regarding storage, the pH remained stable and no significant differences were observed (p > 0.05). With these results, it can be argued that CFS from WB medium fermented with Lb. casei 21/1 is a source of antimicrobial compounds that are sustainable, eco-friendly, and economically viable. Furthermore, applying them as bio-preservatives to Mexican-style fresh cheeses would help avoid foodborne diseases and improve food safety, given that it has been demonstrated that commercial cheeses present a risk for human consumption.
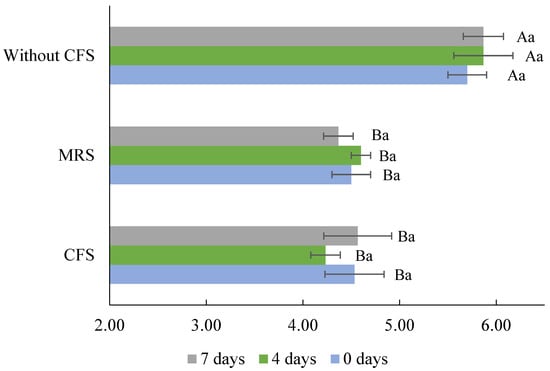
Figure 3.
Evolution of pH during storage of fresh Mexican-style cheeses without cell-free supernatant (Without CFS) and with Lb. casei 21/1 CFS from de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe broth (MRS) or whey medium (CFS). Different capital letters indicate significant differences between the different cheeses at the same storage time at 4 °C (p < 0.05). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between storage time at 4 °C in the same sample.
3.4. Appearance of Cheese with CFSs of Lb. casei 21/1
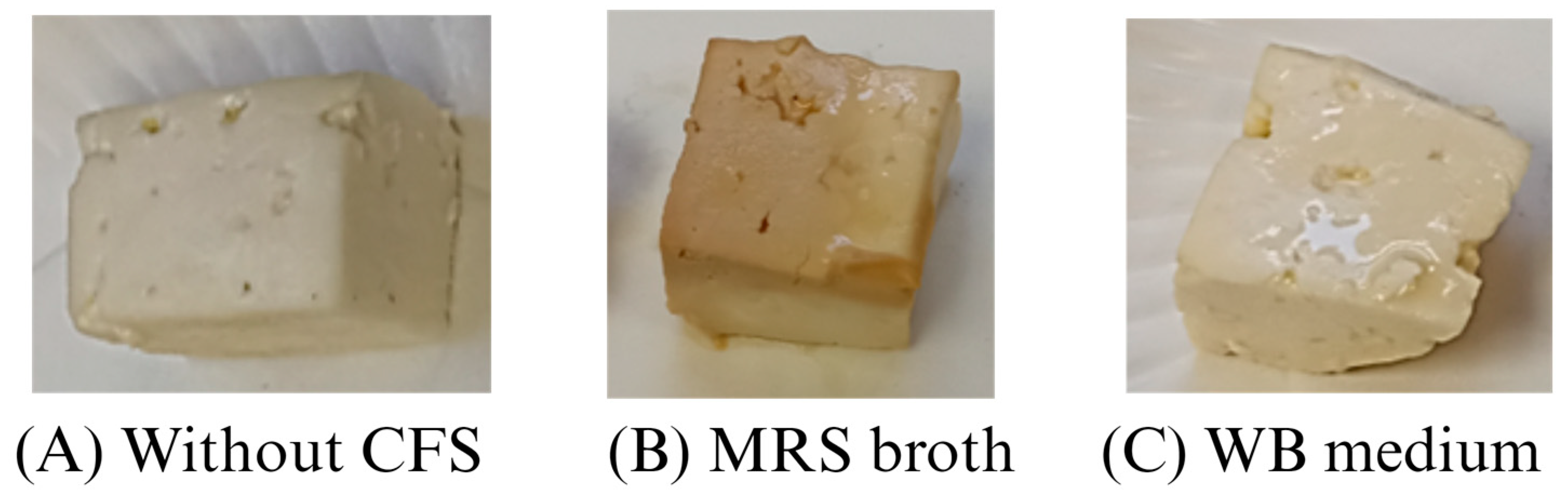
The appearance and color of a product are important aspects to consider since they influence consumers’ acceptability. As can be seen (Figure 4), the addition of CFS from MRS affected the appearance of the cheese; a slight brown color developed, while CFS from WB media did not exert a notable change. This agrees with the color parameters (Table 3), because the differences in color to MRS samples were more distinctive than in the WB-treated cheeses, according to the scale categorization proposed by Francis and Clydesdale [59]. Furthermore, the contribution of a* in MRS cheeses increased significantly (p < 0.05), and L* values decreased significantly (p < 0.05), giving brownish colors characteristic of the culture medium. On the other hand, the parameters of color in cheeses treated with CFS from WB presented an increase in yellowish color due to the a* and b* values, which significantly (p < 0.05) increased and decreased, respectively. The brown color of CFS from MRS broth directly impacted the food color, whereas WB medium slightly modified it. In previous studies, CFS from MRS stained beef cubes (wrapped in whey isolate film with added CFS from L. sakei or immersed in a marinade containing CFS from L. plantarum) to brown colors [55,60].
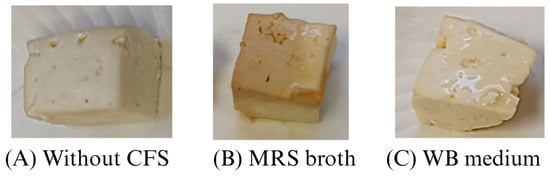
Figure 4.
Comparison of cheeses after 7 days of storage at 4 °C treated (A) without cell-free supernatant (CFS), (B) MRS broth, and (C) WB medium obtained from Lb. casei 21/1.

Table 3.
Color properties and color difference of Mexican-style fresh cheeses with Lb. casei 21/1 CFS.
4. Conclusions
The studied cell-free supernatants from Lb. casei 21/1 from MRS broth and WB medium were effective against microorganisms causing foodborne illness, mainly S. enterica serovar Typhimurium and L. monocytogenes. The CFS from WB medium can be a suitable alternative as a bio-preservative in foods at risk of contamination, such as Mexican-style fresh cheeses, due to its economic viability and as a safe consumption ingredient. The incorporation of CFS from WB medium slightly affected the color and appearance of cheeses compared with MRS broth. Further studies could examine the best way to incorporate supernatants into cheeses or other foods, evaluating the contact time and changes in sensory properties. Although Lb. casei 21/1 is a LAB commonly recognized as GRAS, it will be important to consider toxicological studies of CFS obtained from the WB culture medium. In addition, exploration of other bioactive properties that benefit consumers’ health could be sought, as occurs with postbiotics. Whey, a by-product of cheese production, can be utilized as a fermentation substrate, which can help reduce production costs compared with conventional culture medium. Not only is this cost effective, but it also aids in managing dairy waste sustainably. Whey contains valuable nutrients that promote the growth of lactic acid bacteria, thus enhancing acid production efficiency. Whey fermentation aligns with sustainability and regulatory guidelines by reducing waste and promoting efficient resource use, helping companies comply with environmental regulations and meet their social responsibility objectives.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.E.V.-S., R.H.H.-F., D.A.-B., M.T.J.-M., E.M.-L. and A.L.-M.; visualization, V.E.V.-S. and D.A.-B.; validation, V.E.V.-S., R.H.H.-F., D.A.-B., M.T.J.-M., E.M.-L. and A.L.-M.; investigation, V.E.V.-S., R.H.H.-F. and D.A.-B.; resources, M.T.J.-M. and A.L.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, V.E.V.-S. and D.A.-B.; writing—review and editing, V.E.V.-S., R.H.H.-F., D.A.-B., M.T.J.-M., E.M.-L. and A.L.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request.
Acknowledgments
Authors Vera-Santander and Hernández-Figueroa acknowledge the financial support for their Ph.D. studies in Food Science from the National Council for Humanities, Sciences, and Technologies (CONAHCyT) and Universidad de las Américas Puebla (UDLAP).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Centeno-Rodríguez, M.A.C.; Gutiérrez-Cárdenas, M.G.; Jaime-Patlán, M.; Meza-Plaza, E.F.; Montecillos-Ramírez, K.E.; Rojas-Salinas, W.B.; Ozuna, C. Genuine Mexican cheeses: Technological processes and manufacturing parameters. Agro Product. 2020, 13, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas de Gante, A.; Santos Moreno, A.; Cervantes Escoto, F. Los Quesos Mexicanos Tradicionales; Universidad Autónoma Chapingo: Chapingo, Mexico, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Verraes, C.; Vlaemynck, G.; Van Weyenberg, S.; De Zutter, L.; Daube, G.; Sindic, M.; Uyttendaele, M.; Herman, L. A Review of the Microbiological Hazards of Dairy Products Made from Raw Milk. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 50, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaridis, I.; Psomas, E.; Karatzia, M.-A.; Samouris, G. Hygiene and Safety of Hard Cheese Made from Raw Cows’ Milk. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godínez-Oviedo, A.; Sampedro, F.; Bowman, J.P.; Garcés-Vega, F.J.; Hernández-Iturriaga, M. Risk Ranking of Food Categories Associated with Salmonella enterica Contamination in the Central Region of Mexico. Risk Anal. 2023, 43, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olea-Rodríguez, M.; de los, Á.; Chombo-Morales, P.; Nuño, K.; Vázquez-Paulino, O.; Villagrán-de la Mora, Z.; Garay-Martínez, L.E.; Castro-Rosas, J.; Villarruel-López, A.; Torres-Vitela, M.R. Microbiological Characteristics and Behavior of Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella Spp., Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcal Toxin during Making and Maturing Cotija Cheese. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elafify, M.; Darwish, W.S.; El-Toukhy, M.; Badawy, B.M.; Mohamed, R.E.; Shata, R.R. Prevalence of Multidrug Resistant Salmonella spp. in Dairy Products with the Evaluation of the Inhibitory Effects of Ascorbic Acid, Pomegranate Peel Extract, and D-Tryptophan against Salmonella Growth in Cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 364, 109534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.A.; Gould, L.H.; Hunter, J.C.; Kucerova, Z.; Jackson, B. Listeriosis Outbreaks Associated with Soft Cheeses, United States, 1998–20141. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1116–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria-Herrera, R.J.; Dominguez-Gonzalez, K.G.; Rumbo-Pino, R.; Piña-Lazaro, A.; Alvarez-Perez, J.J.; Rivera-Gutierrez, S.; Ponce-Saavedra, J.; Ortiz-Alvarado, R.; Gonzalez-Y-Merchand, J.A.; Yahuaca-Juarez, B.; et al. Occurrence of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria, Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, and Staphylococcus aureus in Artisanal Unpasteurized Cheeses in the State of Michoacan, Mexico. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falardeau, J.; Trmčić, A.; Wang, S. The Occurrence, Growth, and Biocontrol of Listeria monocytogenes in Fresh and Surface-ripened Soft and Semisoft Cheeses. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4019–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imre, K.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Herman, V.; Sallam, K.I.; Cristina, R.T.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Morar, D.; Popa, S.A.; Imre, M.; Morar, A. Occurrence, Pathogenic Potential and Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli Isolated from Raw Milk Cheese Commercialized in Banat Region, Romania. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeza-Lara, P.D.; Medina-Estrada, R.I.; Bravo-Monzón, Á.E.; Jiménez-Mejía, R. Frequency and Characteristics of ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Mexican Fresh Cheese. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, e108222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Kou, X.; Ji, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S.; Li, B.; Dong, J.; Wang, Q.; et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Kazak Cheese in Xinjiang, China. Food Control 2021, 123, 107759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Muñiz, D.; Cerna-Cortes, J.F.; Lopez-Saucedo, C.; Angeles-Morales, E.; Bobadilla-Del Valle, M.; Ponce-De Leon, A.; Estrada-Garcia, T. Isolation of Staphylococcus aureus, Uropathogenic Escherichia coli, and Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Strains from Pasteurized Cheeses and Unpasteurized Cream Sold at Traditional Open Markets in Mexico City. J. Food Prot. 2022, 85, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Figueroa, R.H.; Morales-Camacho, J.I.; Mani-López, E.; López-Malo, A. Assessment of Antifungal Activity of Aqueous Extracts and Protein Fractions from Sourdough Fermented by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. Future Foods 2024, 9, 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Figueroa, R.H.; López-Malo, A.; Mani-López, E. Antimicrobial Activity and Applications of Fermentates from Lactic Acid Bacteria—A Review. Sustain. Food Technol. 2024, 2, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; De Vuyst, L. Lactic Acid Bacteria as Functional Starter Cultures for the Food Fermentation Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Figueroa, R.H.; Mani-López, E.; Palou, E.; López-Malo, A. Sourdoughs as Natural Enhancers of Bread Quality and Shelf Life: A Review. Fermentation 2023, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Kousheh, S.A.; Almasi, H.; Alizadeh, A.; Guimarães, J.T.; Yılmaz, N.; Lotfi, A. Postbiotics Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria: The next Frontier in Food Safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3390–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani-López, E.; Arrioja-Bretón, D.; López-Malo, A. The Impacts of Antimicrobial and Antifungal Activity of Cell-free Supernatants from Lactic Acid Bacteria in Vitro and Foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 604–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bello, B.; Cocolin, L.; Zeppa, G.; Field, D.; Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C. Technological Characterization of Bacteriocin Producing Lactococcus lactis Strains Employed to Control Listeria monocytogenes in Cottage Cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 153, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settanni, L.; Franciosi, E.; Cavazza, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Poznanski, E. Extension of Tosèla Cheese Shelf-Life Using Non-Starter Lactic Acid Bacteria. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Sieiro, P.; Montalbán-López, M.; Mu, D.; Kuipers, O.P. Bacteriocins of Lactic Acid Bacteria: Extending the Family. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2939–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoades, J.; Kargiotou, C.; Katsanidis, E.; Koutsoumanis, K.P. Use of Marination for Controlling Salmonella enterica and Listeria monocytogenes in Raw Beef. Food Microbiol. 2013, 36, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, C.; McKee, S. Marination to Improve Functional Properties and Safety of Poultry Meat. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2007, 16, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İncili, G.K.; Karatepe, P.; Akgöl, M.; Güngören, A.; Koluman, A.; İlhak, O.İ.; Kanmaz, H.; Kaya, B.; Hayaloğlu, A.A. Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Postbiotics, Evaluation in-Vitro Antibacterial Effect, Microbial and Chemical Quality on Chicken Drumsticks. Food Microbiol. 2022, 104, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- İncili, G.K.; Karatepe, P.; Akgöl, M.; Kaya, B.; Kanmaz, H.; Hayaloğlu, A.A. Characterization of Pediococcus acidilactici Postbiotic and Impact of Postbiotic-Fortified Chitosan Coating on the Microbial and Chemical Quality of Chicken Breast Fillets. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, X.; Shi, G.; Chang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, M. Cooperation of Lactic Acid Bacteria Regulated by the AI-2/LuxS System Involve in the Biopreservation of Refrigerated Shrimp. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Park, H.W.; Choi, E.J.; Chun, H.H. Effects of CFSs Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria in Combination with Grape Seed Extract on the Microbial Quality of Ready-to-Eat Baby Leaf Vegetables. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1268742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandona, E.; Blažić, M.; Režek Jambrak, A. Whey Utilization: Sustainable Uses and Environmental Approach. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 59, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papademas, P.; Kotsaki, P. Technological Utilization of Whey towards Sustainable Exploitation. J. Adv. Dairy Res. 2019, 7, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi, H.; Moosavi-Nasab, M.; Soleimanian-Zad, S.; Golmakani, M.-T.; Majdinasab, M. Antibacterial Metabolites Production by Lactobacillus plantarum PTCC 1896 in Fermented Whey and Optimization of Fermentation Conditions for Maximum Production Using RSM. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 152, 105882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, L.; Luz, C.; Ritieni, A.; Quiles Beses, J.; Mañes, J.; Meca, G. Inhibitory Effect of Sweet Whey Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum Strains against Fungal Growth: A Potential Application as an Antifungal Agent. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3920–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, P.; Vinderola, G.; Molinari, F.; Reinheimer, J. Suitability of Whey and Buttermilk for the Growth and Frozen Storage of Probiotic Lactobacilli. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2008, 61, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareb, O.; Aïder, M. Whey and Its Derivatives for Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Functional Foods: A Critical Review. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 348–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, S.; Rezazadeh-Bari, M.; Alizadeh-Khaledabad, M.; Rezaei-Mokarram, R.; Sowti-Khiabani, M. Fermentation Optimization for Co-Production of Postbiotics by Bifidobacterium lactis BB12 in Cheese Whey. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 5869–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrioja-Bretón, D.; Mani-López, E.; Palou, E.; López-Malo, A. Antimicrobial Activity and Storage Stability of Cell-Free Supernatants from Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Applications with Fresh Beef. Food Control 2020, 115, 107286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, W.; Latimer, G.W. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 21st ed.; Latimer, G.W., AOAC International, Eds.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2019; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Figueroa, R.H.; Mani-López, E.; López-Malo, A. Antifungal Capacity of Poolish-Type Sourdough Supplemented with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Its Aqueous Extracts In Vitro and Bread. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Ocampo, K.A.; Martín-del-Campo, S.T.; Montejano-Gaitán, J.G.; Zárraga-Alcántar, R.; Cardador-Martínez, A. Evaluation of Biological, Textural, and Physicochemical Parameters of Panela Cheese Added with Probiotics. Foods 2020, 9, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International|Wageningen University and Research Library Catalog. Available online: https://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/titel/585790 (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Norma Mexicana NMX-F-317-S-1978; Determinación de pH en Alimentos. Diario Oficial de la Federación. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?title=Determinaci%C3%B3n+de+pH+en+alimentos&author=NMX-F-317-S-1978&publication_year=1978 (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-092-SSA1-1994; Bienes y Servicios. Método Para La Cuenta de Bacterias Aerobias En Placa. Diario Oficial de la Federación. Secretaría de Salud: Mexico City, Mexico, 1994; Volume 12, pp. 1–20.
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-111-SSA1-1994; Bienes y Servicios. Método Para La Cuenta de Mohos y Levaduras En Alimentos. Secretaría de Salud: Mexico City, Mexico, 1994; Volume 6, pp. 1–10.
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-115-SSA1–1994; Bienes y Servicios. Método Para La Determinacioń de Staphylococcus Aureus En Alimentos. Secretaría de Salud: Mexico City, Mexico, 1995; Volume 5, pp. 1–14.
- Mani-López, E.; García, H.S.; López-Malo, A. Organic 12- 1-16Acids as Antimicrobials to Control Salmonella in Meat and Poultry Products. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia Bangar, S.; Suri, S.; Trif, M.; Ozogul, F. Organic Acids Production from Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Preservation Approach. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandelli, A.; Daroit, D.J.; Corrêa, A.P.F. Whey as a Source of Peptides with Remarkable Biological Activities. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, I.; Soto, S.; Fuentes, L.; Gutiérrez-Méndez, N.; García-Islas, B.; Monroy-Gayosso, K.E.; Mateo, J. Compositional, Functional and Sensory Characteristics of Selected Mexican Cheeses. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 05, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-243-SSA1-2010; Productos y Servicios. Leche Fórmula Láctea Prod. Lácteo Comb. Deriv. Lácteos Disposiciones Especificaciones Sanit. Métod. Prueba México DF. Secretaría de Salud: Mexico City, Mexico, 2010; Volume 27, pp. 1–15.
- Silva-Paz, L.E.; Medina-Basulto, G.E.; López-Valencia, G.; Montaño-Gómez, M.F.; Villa-Angulo, R.; Herrera Ramírez, J.C.; González-Silva, A.L.; Monge-Navarro, F.; Cueto-González, S.A.; Felipe-García, G. Caracterización de La Leche y Queso Artesanal de La Región de Ojos Negros Baja California, México. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2020, 11, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Martínez, A.; Paredes-Montoya, P.; Rentería-Monterrubio, A.-L.; Corral-Luna, A.; Lechuga-Valles, R.; Dominguez-Viveros, J.; Sánchez-Vega, R.; Santellano-Estrada, E. Microbial Quality and Prevalence of Foodborne Pathogens of Cheeses Commercialized at Different Retail Points in Mexico. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 39 (Suppl. S2), 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousta, M.; Mataragas, M.; Skandamis, P.; Drosinos, E.H. Prevalence and Sources of Cheese Contamination with Pathogens at Farm and Processing Levels. Food Control 2010, 21, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolim, F.R.L.; dos Santos, K.M.O.; de Barcelos, S.C.; do Egito, A.S.; Ribeiro, T.S.; da Conceição, M.L.; Magnani, M.; de Oliveira, M.E.G.; Queiroga, R.d.C.R.d.E. Survival of Lactobacillus rhamnosus EM1107 in Simulated Gastrointestinal Conditions and Its Inhibitory Effect against Pathogenic Bacteria in Semi-Hard Goat Cheese. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Figueroa, R.H.; Mani-López, E.; López-Malo, A. Antifungal Activity of Wheat-Flour Sourdough (Type II) from Two Different Lactobacillus in Vitro and Bread. Appl. Food Res. 2023, 3, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B.A.; Ruby, J.; Smith, G.C.; Sofos, J.N.; Bellinger, G.R.; Warren-Serna, W.; Centrella, B.; Bowling, R.A.; Belk, K.E. Comparison of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Multiple Beef Hide Decontamination Strategies To Reduce Levels of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 2223–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra-Sánchez, L.A.; Van Tassell, M.L.; Miller, M.J. Invited Review: Hispanic-Style Cheeses and Their Association with Listeria monocytogenes. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafipour Yordshahi, A.; Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Molaei, R. Design and Preparation of Antimicrobial Meat Wrapping Nanopaper with Bacterial Cellulose and Postbiotics of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 321, 108561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, F.J.; Clydesdale, F.M. Food Colorimetry: Theory and Applications; Avi Pub. Co.: Westport, CT, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Beristain-Bauza, S.C.; Mani-López, E.; Palou, E.; López-Malo, A. Antimicrobial Activity and Physical Properties of Protein Films Added with Cell-Free Supernatant of Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Food Control 2016, 62, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).