Optimal Energy Efficiency Tracking in the Energy-Stored Quasi-Z-Source Inverter
Abstract
1. Introduction
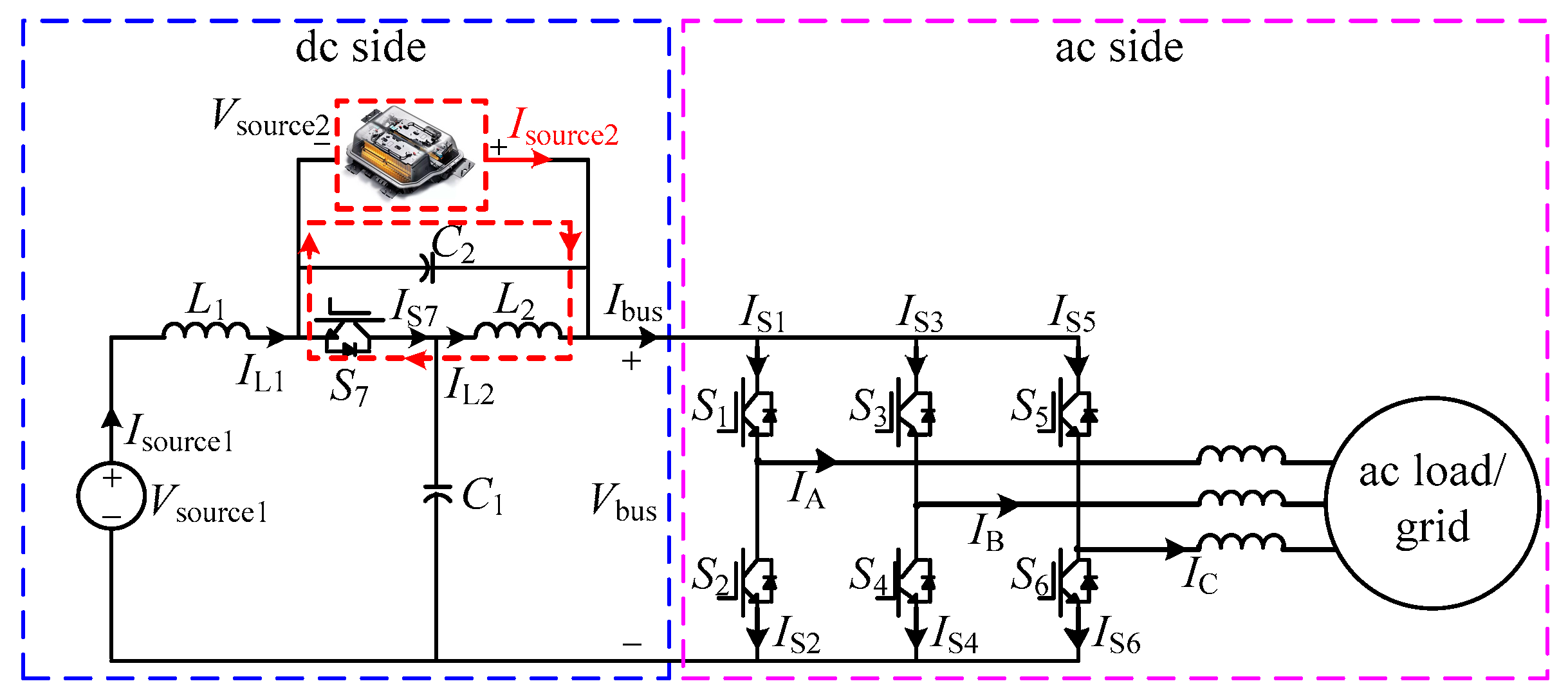
2. Principle of Current Counteraction in ES-qZSI
3. Stress Reduction and Power Loss Profile in ES-qZSI
3.1. Device Stress Analysis for ES-qZSI
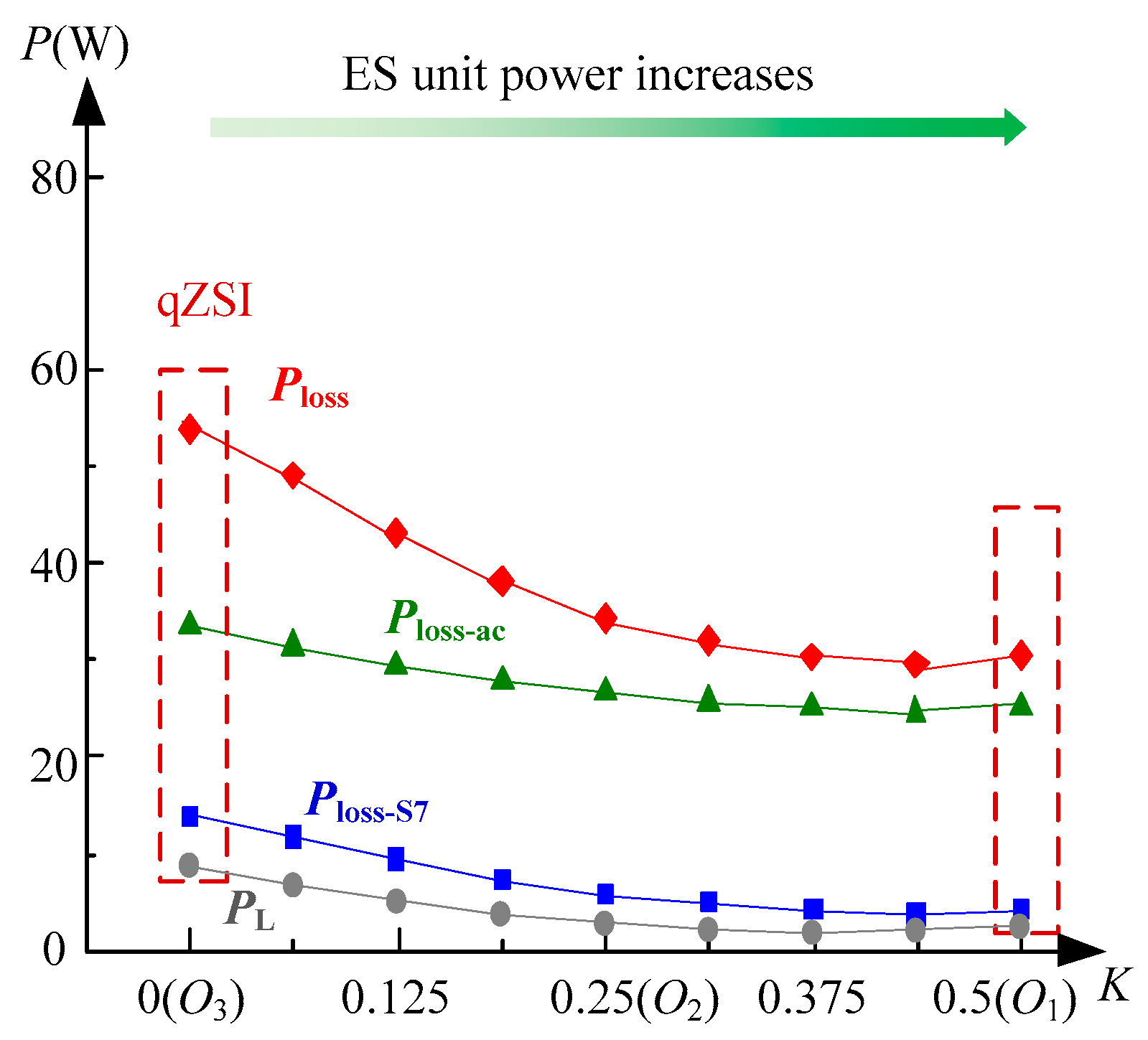
3.2. Power Loss Profile Derivation for ES-qZSI
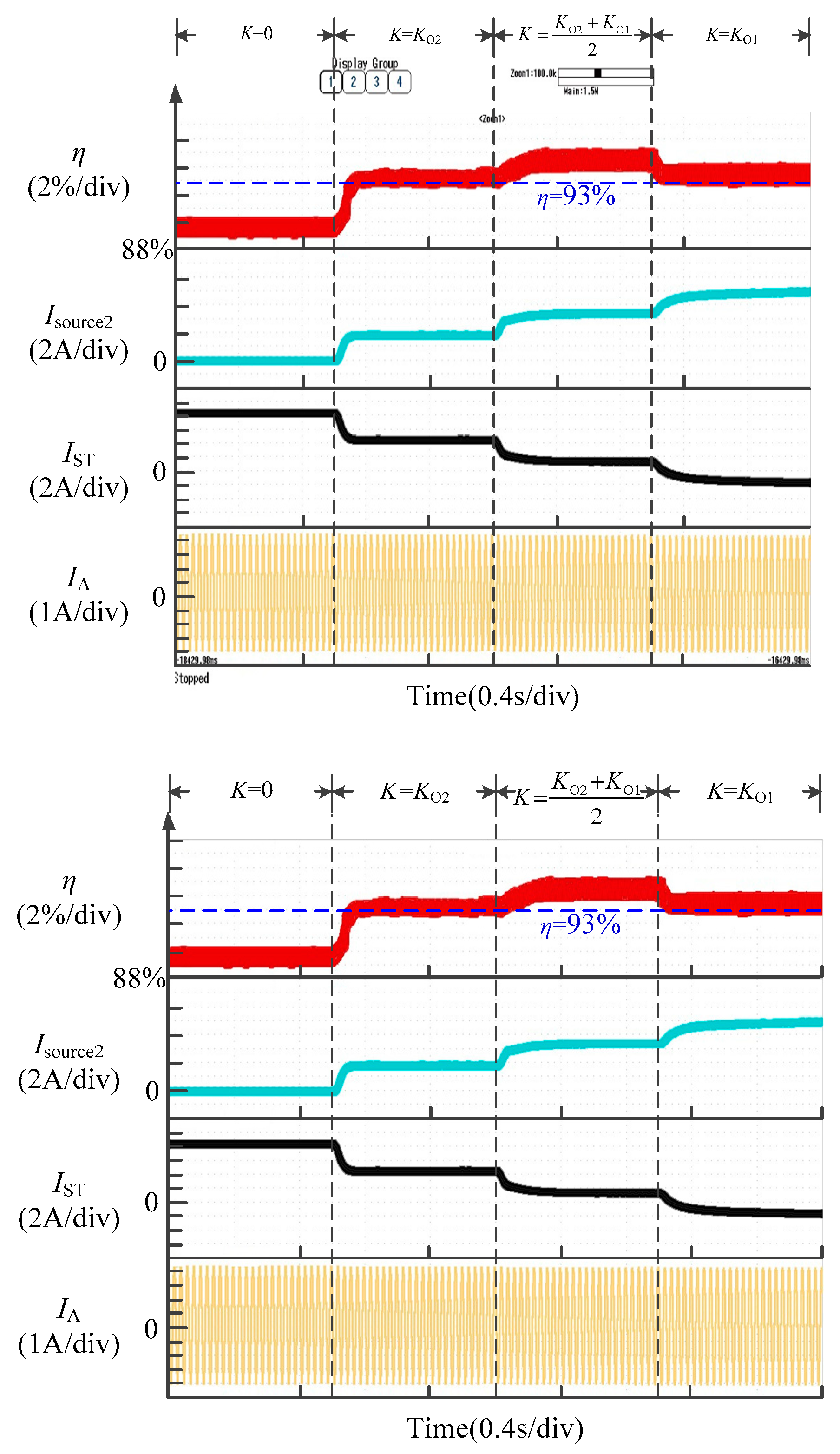
4. Optimal Energy Efficiency Tracking and Practical Implementation
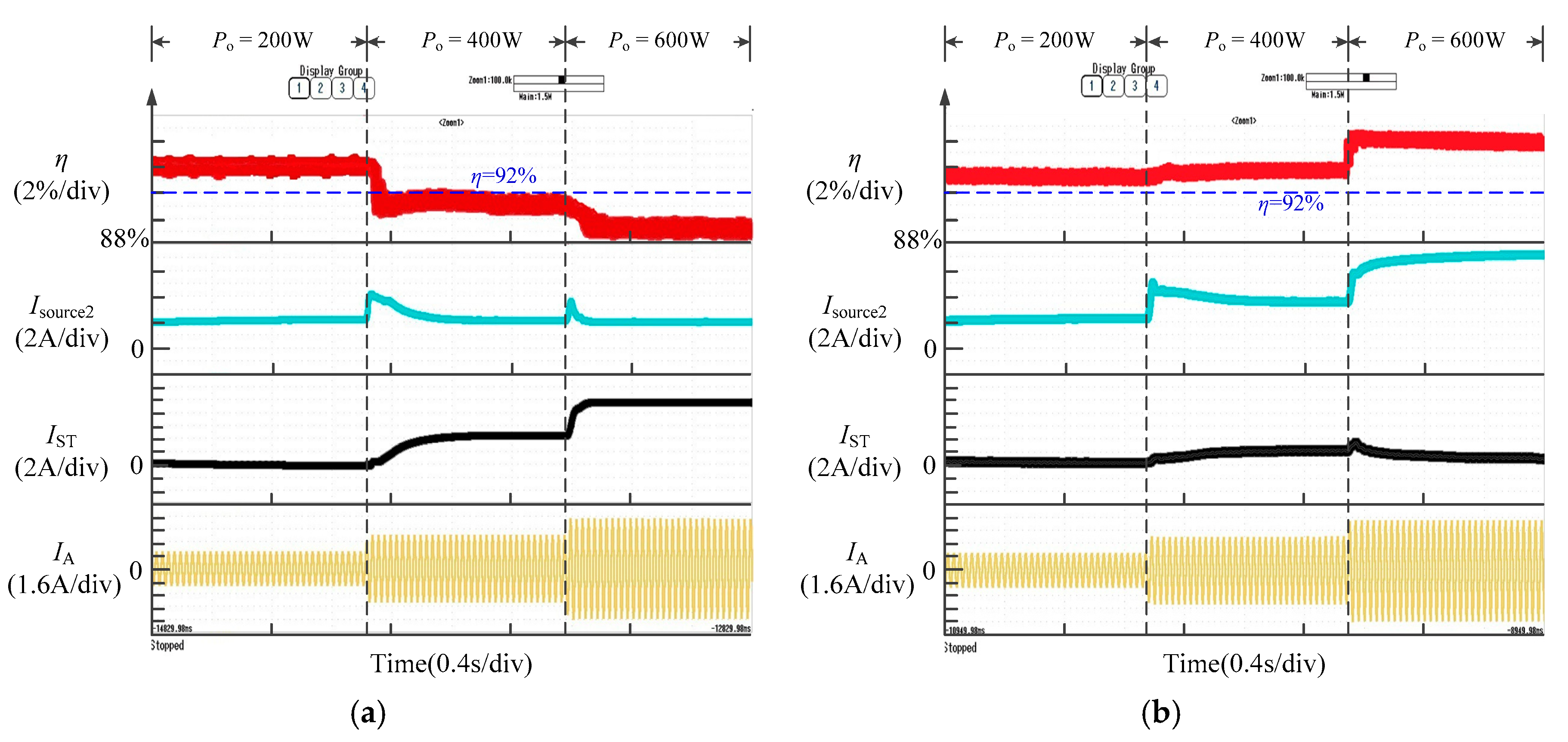
5. Simulation and Experimental Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Vbus | Voltage of the DC link |
| Vsource1 | Voltage of source 1 |
| Vsource2 | Voltage of source 2 |
| Idc_link | DC-link current |
| Ibus | Average value of DC-link current |
| Isource1 | Current of source 1 |
| Isource2 | Current of source 2 |
| D | Shoot-through duty ratio |
| IST | Shoot-through current |
| Po | Output power |
| Psource1 | Power of source 1 |
| Psource2 | Power of source 2 |
| η | Efficiency of the system |
| K | Power distribution ratio for source 2 |
| IL1, IL2 | Current of inductors L1 and L2 |
| B | Boost ratio, Vbus/Vsource1 |
| M | Modulation index |
| Iph | Peak value of the phase current |
| ISn | Current of switching device Sn |
| IA, IB, IC | Phase currents |
| EDiode, EIGBT | Switching energy loss of diode and IGBT (insulated gate bipolar transistor) per unit voltage and per unit current |
| fs | Switching frequency |
| , | Energy loss during turn-on and turn-off processes from the datasheet |
| Vref, Iref | Turn-off voltage and turn-on current in the test condition from the datasheet |
| Peak value of the reverse recovery current of the diode | |
| Reverse recovery time of the diode | |
| Psw-S7, Pcon-S7 | Switching and conduction loss of DC side |
| Psw-ac, Pcon-ac | Switching and conduction loss of AC side |
| fg | Frequency of the grid |
| Ts | Switching period |
| T1, T2 | Operation time for the active vectors |
| VCE0 | Forward voltage drop of IGBT or diode |
| ron | On resistance of IGBT or diode |
| rL | Parasitic resistance of inductors L1 and L2 |
Appendix A
Appendix A1. Switching Loss Derivation
Appendix A2. Conduction Loss Derivation
Appendix A3. Inductor Conduction Loss Derivation
References
- Xiao, J.; Wang, P.; Setyawan, L. Hierarchical control of hybrid energy storage system in DC microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 4915–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Emadi, A. A new battery/ultracapacitor hybrid energy storage system for electric, hybrid, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 22–132. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal, M.; Hannan, M.A.; Ker, P.J.; Hussain, A.; Mansor, M.B.; Blaabjerg, F. Review of energy storage system technologies in microgrid applications: Issues and challenges. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 35143–35164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Konstantinou, G.; Townsend, C.D.; Pou, J.; Vazquez, S.; Demetriades, G.D.; Agelidis, V.G. A review of power electronics for grid connection of utility-scale battery energy storage systems. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 7, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Choi, I.-S.; Ahn, G.-H.; Wong, D.-J. Advanced power sharing method to improve the energy efficiency of multiple battery energy storages system. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Khambadkone, A.M. Energy management for lifetime extension of energy storage system in micro-grid applications. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusmez, S.; Khaligh, A. A supervisory power splitting approach for a new ultracapacitor-battery vehicle deploying two propulsion machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 2014, 10, 1960–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobeidli, K.; Khadkikar, V. A new ultracapacitor state of charge control concept to enhance battery lifespan of dual storage electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 10470–10481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbao, E.; Barrade, P.; Etxeberria-Otadui, I.; Rufer, A.; Luri, S.; Gil, I. Optimal energy management strategy of an improved elevator with energy storage capacity based on dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liang, Z.; He, X. Ultracapacitor-battery hybrid energy storage system based on the asymmetric bidirectional Z-source topology for EV. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 7489–7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ge, B.; Abu-Rub, H.; Peng, F.Z. Control system design of battery-assisted quasi-Z-source inverter for grid-tie photovoltaic power generation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rub, H.; Iqbal, A.; Ahmed, S.M.; Li, Y.; Ge, B. Quasi-Z-source inverter-based photovoltaic generation system with maximum power tracking control using ANFIS. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Liu, Y.; Abu-Rub, H.; Peng, F.Z. State-of-charge balancing control for a battery-energy-stored quasi-Z-source cascaded-multilevel-inverter-based photovoltaic power system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 2268–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashab, A.; Sera, D.; Martins, J.; Guerrero, J.M. Dual-input quasi-z-source PV inverter: Dynamic modeling, design, and control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 6483–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhakim, A.; Davari, P.; Blaabjerg, F.; Mattavelli, P. Switching loss reduction in the three-phase quasi-Z-source inverters utilizing modified space vector modulation strategies. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 4045–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ge, B.; Abu-Rub, H.; Peng, F.Z. Overview of space vector modulations for three-phase Z-source/quasi-Z-source inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2098–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolski, K.; Majtczak, P.; Rabkowski, J. Minimum-hard-switching-number modulation method for high-frequency SiC-based impedance-source inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 8351–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liang, Z.; Fan, D.; He, X. Hybrid ultracapacitor-battery energy storage system based on quasi-Z-source topology and enhanced frequency dividing coordinated control for EV. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 7598–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, M.; Hu, S.; He, X. power allocation for energy stored quasi-z-source inverter based on the power loss modelling. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 September–3 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Z.; Hong, F. Research on a time-variant shoot-through modulation strategy for quasi-Z-source inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 9104–9109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battiston, A.; Martin, J.; Miliani, E.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Pierfederici, S.; Meibody-Tabar, F. Comparison criteria for electric traction system using Z-source/quasi Z-source inverter and conventional architectures. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 2, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Item | Expression | Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Switching loss | DC side | ||
| AC side | |||
| Conduction loss | DC side | ||
| AC side | |||
| Inductor loss | |||
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Frequency of the grid fg | 50 Hz |
| Switching frequency fs | 10 kHz |
| Voltage of source 2 Vsource2 | 50 V |
| Voltage of source 1 Vsource1 | 100 V |
| Inductors L1, L2 | 4 mH |
| Capacitors C1, C2 | 820 μF |
| Inductor parasitic resistance rL | 80 mΩ |
| Switching Device S1–S7 | IKW40N120T2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yu, X. Optimal Energy Efficiency Tracking in the Energy-Stored Quasi-Z-Source Inverter. Energies 2020, 13, 5902. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13225902
Hu S, Liang Z, Zhou J, Yu X. Optimal Energy Efficiency Tracking in the Energy-Stored Quasi-Z-Source Inverter. Energies. 2020; 13(22):5902. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13225902
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Sideng, Zipeng Liang, Jing Zhou, and Xiaoli Yu. 2020. "Optimal Energy Efficiency Tracking in the Energy-Stored Quasi-Z-Source Inverter" Energies 13, no. 22: 5902. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13225902
APA StyleHu, S., Liang, Z., Zhou, J., & Yu, X. (2020). Optimal Energy Efficiency Tracking in the Energy-Stored Quasi-Z-Source Inverter. Energies, 13(22), 5902. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13225902







