Abstract
Research to date has mainly focused on the properties and efficiency of the production of selected, individual types of biofuels from microalgae biomass. There are not enough studies investigating the efficiency of the production of all energy sources synthesised by these microorganisms in a single technological cycle. The aim of this research was to determine the possibilities and efficiency of the production of hydrogen, bio-oil, and methane in the continuous cycle of processing T. subcordiformis microalgae biomass. This study showed it was feasible to produce these three energy carriers, but the production protocol adopted was not necessarily valuable from the energy gain standpoint. The production of bio-oil was found to be the least viable process, as bio-oil energy value was only 1.3 kWh/MgTS. The most valuable single process for microalgae biomass conversion turned out to be methane fermentation. The highest specific gross energy gain was found after applying a protocol combining biomass production, hydrogen biosynthesis, and subsequent methane production from T. subcordiformis biomass, which yielded a total value of 1891.4 kWh/MgTS. The direct methane fermentation of T. subcordiformis biomass enabled energy production at 1769.8 kWh/MgTS.
Keywords:
biofuels; microalgae; T. subcordiformis; biomass; hydrogen; bio-oil; anaerobic digestion; methane; bioenergy production 1. Introduction
Bioenergy technologies based on the production and utilisation of microalgae biomass are seen as very universal, promising solutions with great potential for implementation [1]. This conviction is based, among other things, on the proven possibility of utilising this substrate for the production of many types of biofuels, including biogas from methane fermentation [2] or the hydrogen fermentation process [3], hydrogen in direct biophotolysis [4], ethanol from alcohol fermentation [5], or biodiesel through transesterification of storage lipids [6]. The suitability of microalgae biomass for typical thermochemical energy processes has also been demonstrated, including gasification [7], pyrolysis [8], plasma processes [9], torrefaction [10], and simple combustion [11].
Energy carriers produced from microalgae biomass are categorised as third-generation biofuels [12]. Their use is in line with the assumptions of the circular economy [13], directly meets the requirements related to the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect the climate [14], and also supports the policy of developing renewable energy sources [15]. Therefore, interest in these solutions is continuously growing, leading to the development of technologies and a systematic increase in their technological readiness level. The European Union (EU) has adopted a very ambitious strategy for the development of the bioeconomy, in which microalgae biomass is a resource of great importance that can be widely utilised for environmental protection technologies, bioenergy production, and as a source of valuable nutrients for humans and animals [16].
This results in the need to develop concepts for new solutions and to improve existing methods for producing this type of biomass and converting it into energy carriers [17]. One possibility for a major breakthrough and the basis for the development of innovative yet profitable and sustainable protocols for the production of biofuels is the use of saltwater green algae of the Tetraselmis subcordiformis species. These are unicellular, naturally photoautotrophic microorganisms that can also develop through mixotrophic growth, which significantly increases the universality of their use [18]. This species has been shown to be capable of efficiently producing a variety of biofuels, including bio-oil [19], biogas [20], bioethanol [21], and hydrogen [22]. It is characterised by dynamic growth [23], achieves high biomass concentrations in photobioreactors [24], and is resistant to harsh environmental conditions [25]. Its important advantage is the fact that it sediments easily, which is important to reduce the cost of techniques used for its thickening, separation, and final recovery of the biomass from the culture medium [26].
Previous research has mainly addressed the production characteristics of selected individual species of energy carriers produced by T. subcordiformis [27]. The main focus has been on hydrogen production based on direct biophotolysis, which occurs thanks to hydrogenase catalysing the reversible H2 oxidation reaction and releasing hydrogen gas by reducing protons [28]. There are also numerous works on the possibility of using this species to synthesise significant amounts of fatty substances for the production of biodiesel [29]. This process may be intensifying by modifying technological parameters of the cultivation process which determine the conditions under which the microalgae biomass stores reserve substances in the form of lipids [25]. Research has also been carried out to develop and optimise the methane fermentation process of Tetraselmis sp. biomass [30]. Anaerobic digestion has been carried out directly on the grown biomass [31] or on the residues after bio-oil extraction [32]. Co-digestion with other organic substrates has also been used to increase the technological efficiency [20,33].
To the best of authors’ knowledge, there have been no studies so far that would demonstrate the feasibility of utilising all energy carriers synthesised by the biomass of T. subcordiformis in a single, continuous production cycle. By carrying out laboratory experiments and continuing them on a pilot scale, data can be collected that will enable ecological, economic, and energy analyses, and form grounds for assessing the competitiveness of this solution. The in-house experiments presented in this work are pioneering research that may be extended to further, more advanced, and large-scale research.
The aim of this study was to determine the possibilities and assess the effectiveness of the cultivation of T. subcordiformis microalgae using dairy wastewater, and then to analyse the potential for recovery of energy carriers synthesised from the biomass produced, including hydrogen and bio-oil, for the production of biodiesel and methane in a single, continuous production cycle. A preliminary comparative gross energy balance was established for different protocols aimed at producing biofuels from the T. subcordiformis biomass.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Organisation of the Experiment
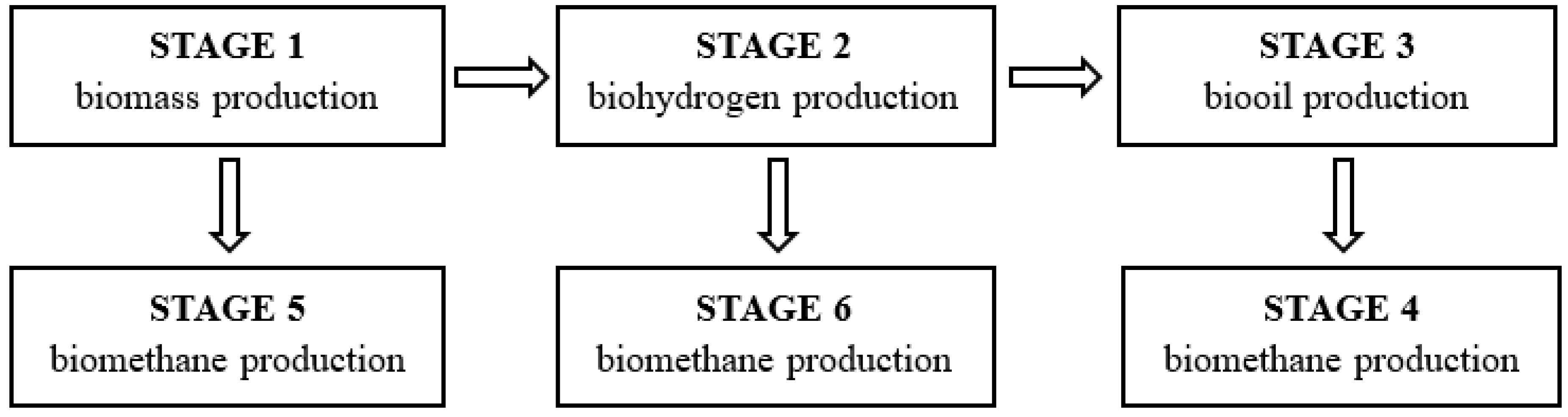
The experiments were carried out in 6 stages (S), the separation criteria of which were the individual technological processes. Initially, the research focused on the production of microalgae biomass (S1), followed by work on biomass conversion into energy carriers (S2–6). The cultivation of T. subcordiformis biomass was carried out in S1. In S2, the microalgal biomass separated from the original culture medium was stimulated to produce hydrogen by modifying the environmental conditions. In S3, the concentrated and then dried T. subcordiformis biomass was subjected to a chemical oil extraction process. In S4, after processing, the microalgae biomass residues were subjected to anaerobic digestion to produce biomethane. In addition, alternative protocols were used to compare energy production efficiency. S5 involved methane fermentation of biomass obtained directly after cultivation in a photobioreactor (S1), while in S6 the biomass was anaerobically fermented after the process of hydrogen production (S2). Figure 1 depicts the course of the experiments and the protocols used.
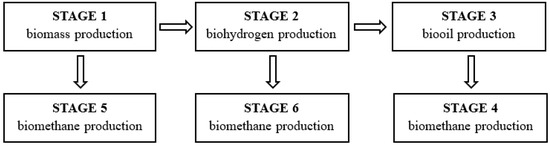
Figure 1.
Organisational diagram of the experimental works.
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Microalgae Biomass
The microalgae T. subcordiformis (Wille) Butcher (Chlorophyta) (UTEX B171 culture collection of algae, University of Texas, Austin, TX, USA) were used for the experiments. In the initial phase, the biomass was propagated in sterilised (15 min, 121 °C, 2840 EL-D autoclave (Tuttnauer, Breda, The Netherlands)) falcon vials (50 mL). Then, it was used for the exact experiments.
2.2.2. Medium Used in S1 (Biomass Production)
The medium contained deionised water, chemical compounds and trace elements [34], and dairy wastewater pretreated in an anaerobic labyrinth flow hybrid reactor [35]. Prior to use, the fermented dairy wastewater was pasteurised (90 °C for 30 min) using a 2840 EL-D autoclave (Tuttnauer, Breda, The Netherlands) to ensure the purity of the culture during microalgae cultivation. Based on the results of the authors’ previous research, the proportion of dairy wastewater in the culture medium was 50% by volume [22]. The values of the basic indicators of the culture medium tested were as follows: COD—621 ± 37 mgO2/L, TN—127 ± 12 mgN/L, TP—24 ± 3.7 mgP/L, P-PO4—21 ± 3.2 mgP/L, N-NH4—112 ± 11 mgN/L, and pH—7.66 ± 0.12.
2.2.3. Medium Used in S2 (Hydrogen Production)
The medium consisted of deionised water supplemented with chemical compounds according to the protocol described by Ran et al. (2009) [36] and Guan et al. (2004) [34]: 0.667 mg/L KCl, 27.23 mg/L NaCl, 5.079 mg/L MgCl2, 1.123 mg/L CaCl2, 0.002 mg/L CuCl2, 0.024 mg/L SrCl2, 0.003 mg/L NaF, 0.098 mg/L KBr, 0.196 mg/L NaHCO3, and 0.098 mg/L H3BO3. The pH was in the range of 7.90–8.00.
2.2.4. Anaerobic Sludge Used in S4–S6 (Methane Production)
The anaerobic sludge used in Stages 4 to 6 was obtained directly from the closed digesters of the municipal sewage treatment plant in Olsztyn (Poland), which are used to stabilise the sewage sludge. These are fully mixed contact reactors operating at a temperature of 35 °C, with an organic loading rate of 2.5 kgVS/m3·d and a hydraulic retention time of the substrates in the technological system of 20 days. The properties of the anaerobic sludge are as follows: VS—74.3 ± 2.7% TS, TC—761 ± 68 mg/gTS, TOC—601 ± 37 mg/gTS, TN—40.3 ± 6.4 mg/gTS, TP—3.4 ± 0.9 mg/gTS, C:N—14.9 ± 1.2, and pH—7.13 ± 0.11.
2.3. Research Stations
2.3.1. Photobioreactor Used in S1 (Biomass Production)
The biomass of T. subcrodiformis was cultivated in a BioFlo 115 bioreactor (New Brunswick, Edison, NJ, USA) with an active volume of 2.0 L. The experiments were carried out at a temperature of 25 ± 1 °C. White light illumination with an intensity of 5 klux (5000 lm, 67.5 µmol/m2·s) was used, including a 14 h light/10 h dark cycle (Philips Lighting MASTER TL-D Super 80)—(Philips Lighting, Eindhoven, The Netherlands). The colour temperature was 6500 K, which corresponds to daylight, and the power was 58 W. The photobioreactor was aerated (200 L/h) and continuously stirred with vertical stirrers (150 rpm). The initial biomass concentration of T. subcrodiformis was 150 mgVS/L. A mixed cellulose ester vacuum filter with a porosity of 8.0 μm (MBS 1 filtration kit, Whatman, Maidstone, UK) functionally coupled with a Mobil 20 vacuum pump (DILO Company, Inc., Odessa, FL, USA) was used to separate and concentrate the T. subcrodiformis biomass.
2.3.2. Photobioreactor Used in S2 (Hydrogen Production)
In S2, the biomass of T. subcrodiformis was incubated at a temperature of 25 ± 1 °C in respirometric bioreactors with an active volume of 0.5 L, permanently connected to a pressure change recorder (WTW, Weilheim, Germany). The initial biomass concentration of T. subcordiformis was 4.0 gVS/L. The respirometer set was used to measure and record every 10 h the changes in partial pressure caused by the production of gaseous products (hydrogen) of the T. subcrodiformis biomass metabolism. The contents of the respirometers were mixed at a speed of 100 rpm using VMS—C4 magnetic stirrers (Advanced, VWR, Lutterworth, UK). The incubation time was 150 h, including 30 h in the absence of light and 120 h in white light with an intensity of 5 klux (Philips Lighting MASTER TL-D Super 80)—(Philips Lighting, Eindhoven, The Netherlands).
2.3.3. Bioreactor Used in S4 to S6 (Methane Production)
Methane was produced by volumetric gas production in batch respirometric reactors (AMPTS II, BPC Instruments AB, Lund, Sweden). Fermentation was carried out at a temperature of 37 ± 1 °C. The bioreactors were equipped with a vertical agitator operating at a capacity of 100 rpm every 10 min for 30 s. The active volume of the respirometers was 500 mL. The initial organic load rate (OLR) was 5.0 gVS/L. A detailed description of the operation of the AMPTS II bioreactors was presented in previous works by the authors [37,38].
2.4. Analytical Methods
The composition of the biomass was analysed in all stages. The concentrations of total solids (TS), volatile solids (VS), and mineral solids (MS) were determined using the gravimetric method. The TS content in the biomass was determined by drying to a constant mass at a temperature of 105 °C. The MS/VS content was determined by burning the biomass at a temperature of 550 °C. The loss after combustion was VS according to the PN-EN 15935:23022-01 standard [39]. In S1, the gravimetric method was used at the end of each selected growth phase of T. subscordiformis biomass. The TSS Portable probe (Hach Lange GmbH, Germany) was used for daily measurements of the biomass content in the reactor. In S2 and S3 the gravimetric method was used at the end of the experiment. TN, TC, and TOC were determined in biomass samples dried at 105 °C using a Thermo Flash 2000 organic molecule analyser (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). TP was determined colourimetrically in ammonium metavanadate (V) and ammonium molybdate after prior mineralisation in a mixture of sulphuric (VI) and chloric acid (VII) at 390 nm using a DR 2800 spectrophotometer (Hach-Lange, Düsseldorf, Germany). The total protein content was estimated by multiplying the TN value by the protein conversion factor of 6.25. The lipid concentration was determined using the Soxhlet method with a Büchi extraction device (B-811, Büchi AG, Flawil, Switzerland). The reducing sugars were determined colourimetrically with an anthrone reagent at 600 nm using a DR 2800 spectrophotometer (Hach-Lange, Düsseldorf, Germany). The pH value was determined by weighing 10 g of the homogenised, air-dry sample into a 100 mL beaker, adding 50 mL of distilled water and mixing, and then measuring the pH value in the sample after calibrating the device.
2.5. Procedures Used in Individual Stages
2.5.1. S1 (Biomass Production)
Taxonomic analysis of algal biomass was performed using an MF 346 biological microscope with an Optech 3MP camera (Delta Optical, Warsaw, Poland). The content of the monitored indicators in the culture medium was determined using a UV/VIS DR 5000 spectrophotometer (Hach Lange, Düsseldorf, Germany). The salinity of the medium was tested using a marine control digital instrument (Aqua Medic, Bissendorf, Germany). The light intensity was measured with an HI 97500 luxmeter (Hanna Instruments, Woonsocket, RI, USA).
2.5.2. S2 (Hydrogen Production)
Gaseous metabolic products of T. subcordiformis (5 mL) were collected from the respirometers using a gas-tight syringe (Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany). Their composition and percentage were analysed using a GC 7890 A gas chromatograph (Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The percentages of the following biogas components were determined: carbon dioxide CO2, oxygen O2, and hydrogen H2.
2.5.3. S3 (Bio-Oil Production)
The biomass was separated from the medium with a flow centrifuge (CEPA LEA Lab, Ingersheim, Germany) at 40,000 rpm, and the flow of the liquid was about 35 L/h. The harvested biomass was dried at 105 °C for 24 h. Next, it was crushed using a grinder (IKA Multidrive, IKA ® -Werke GmbH, Staufen, Germany) at 20,000 rpm for 60 s (every 100 g). Hexane was added to the crushed biomass in a dose of 300 mL per 100 g of biomass. Next, the mixture was sonicated for 60 s, which resulted in energy production at 18,635.57 Ws and an amplitude of 100%. The separation of hexane with oil from the biomass was performed in a centrifuge (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) at 11,000 rpm for 3 min. Next, the hexane was evaporated from the oil, and the oil was subjected to transesterification (following the S Van Wychen protocol [40]).
The properties of bio-oils were analysed in accordance with the following standards: viscosity at 40 °C—ISO 3104 [41], density at 15 °C—ISO 3675 [42], flash point—ISO 15267 [43], total contamination—EN 12662 [44], calorific value—DIN 51900 [45], carbon residue—ISO 10370 [46], oxidation stability at 110 °C—EN 14112 [47], water content—ISO 12937 [48], acid value—EN 14104 [49], phosphorus content—ISO 10540 [50], sulphur content—ISO 3987 [51], and iodine value—EN 14111 [52]. The degree of reaction of triglycerides contained in the bio-oils tested in the transesterification process was determined using the HPLC technique (LC-10AT chromatograph, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The chromatograph was equipped with two detectors—DAD (wavelength λ = 205 nm) and a C-18 column. The temperature of the column was 25 °C, the injection volume was 1.0 µL, and the flow rate was 0.9 mL/min. The mobile phase was a mixture of solvent A—isopropanol-hexane (4/5) and solvent B—methanol, and was applied according to the following gradient: 0 min—100% solvent A, 20 min—100% solvent A, 45 min—100% solvent B, 70 min—100% solvent B, 71 min—100% solvent A, and 75 min—100% solvent A.
The reaction products of algal oil transesterification were analysed using a GC chromatograph (GC-15A Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) equipped with an Rt-2560 column (110 m × 0.20 µm I.D., 0.25 mm film thickness). The quantitative and qualitative analyses were performed using the following analytical standards: Food Industry FAME Mix with 37 methyl esters (C4:0—C24:1) and FAME Mix C18:0—C20:0 (certified reference material): methyl oleate 20% (w/w), methyl laidate 20% (w/w), methyl linoleate 20% (w/w), methyl linoleate 20 % (w/w), methyl arachidate 10% (w/w), and methyl stearate 10% (w/w). The parameters of the GC analysis were as follows: initial column temperature—100 °C, temperature gradient: 4.0 °C/min—185 °C, 0.5 °C/min—220 °C, 5.0 °C/min—240 °C, split ratio—10:1, make-up gas flow rate—40 mL/min, and column flow rate—0.80 mL/min.
2.5.4. S4 to S6 (Methane Production)
The composition of biogas produced at each section of the reactor was measured every 24 h using a gas-tight syringe (20 mL injection volume) and a gas chromatograph (GC, 7890A Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA) equipped with a thermal conductivity detector (TCD). The GC was fitted with two molecular sieve columns (60/80 mesh), two Hayesep Q columns (80/100 mesh), and a Porapak Q column (80/100) operating at a temperature of 70 °C. The temperature of the injection was 150 °C, and that of detector ports was 250 °C. Argon and helium were used as the carrier gases at a flow rate of 15 mL/min.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis of the results obtained was performed using the STATISTICA 13.3 PL package. The significance of differences between the groups was determined using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The significance of differences between the analysed variables was determined using Tukey’s test. A significance level of p = 0.05 was assumed in the tests.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Stage 1 (Biomass Production)
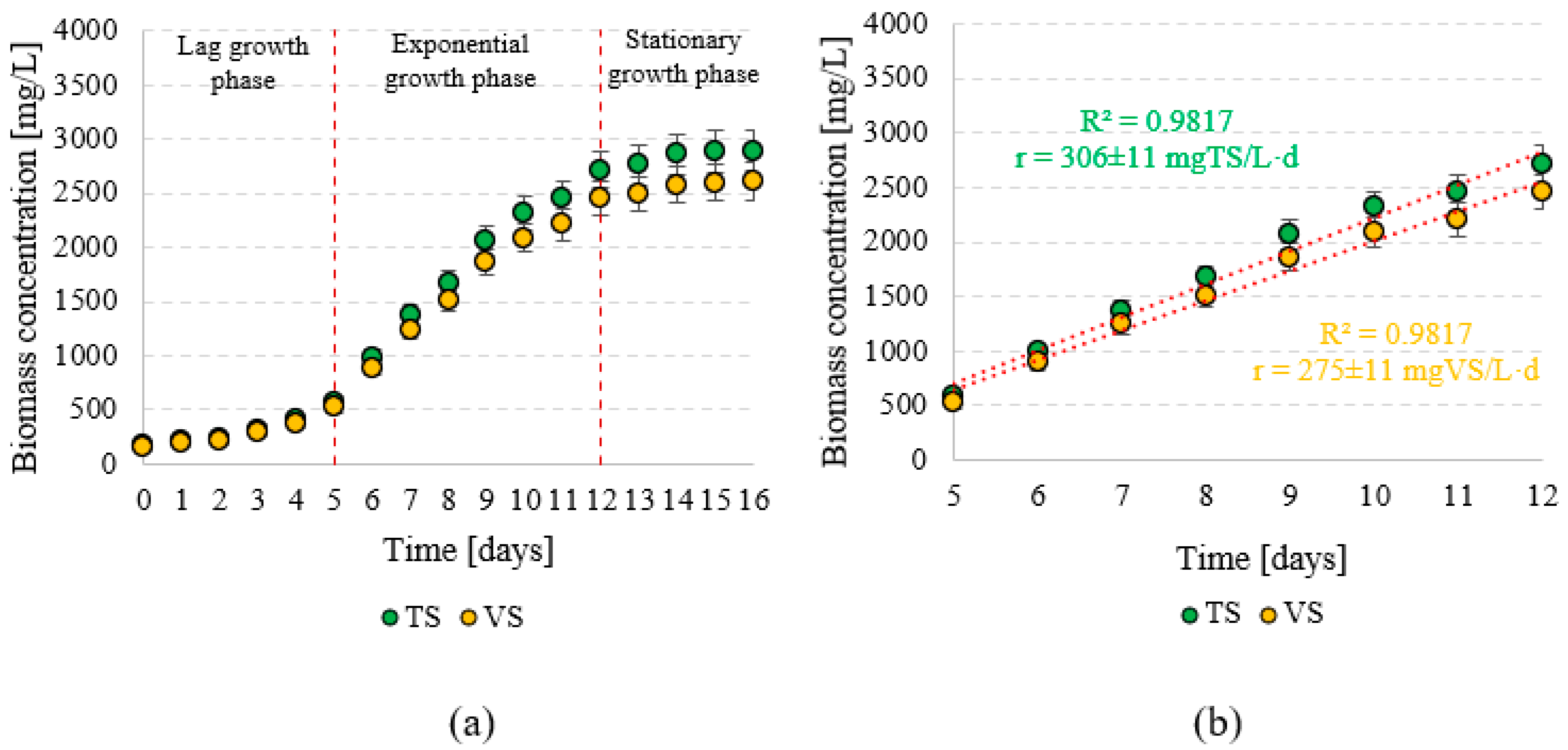
T. subcordiformis biomass growth was observed until the 14th day of incubation in the photobioreactor (Figure 2a). At the end of the culture cycle, the biomass reached concentrations of 2610 ± 170 mgVS/L and 2893 ± 192 mgTS/L. The multiplication rate of the microalgae biomass in the exponential growth phase (from day 5 to day 12 of the culture) reached 275 ± 11 mgVS/L·d and 306 ± 11 mgTS/L·d (Figure 2b). During this time, an increase from 520 ± 51 gVS/L to 2450 ± 155 gVS/L was recorded in biomass concentration (Figure 2b). In the following days of the cultivation process, the biomass growth rate did not exceed 90 gVS/L·d. The lag growth phase lasted until day 5, and the observed biomass growth rate was 74 ± 7 gVS/L·d (82 ± 9 gTS/L·d). During this time, the biomass concentration increased from 150 ± 25 mgVS/L (166 ± 28 mgTS/L) to 520 ± 51 gVS/L (576 ± 57 gTS/L) (Figure 2a). After 12 days of incubation, the T. subcordiformis population reached the stationary growth phase, in which the biomass increased by only 40 ± 3 mgVS/L·d (44 ± 4 mgTS/L·d) (Figure 2a).
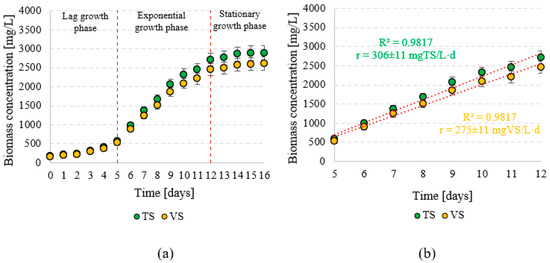
Figure 2.
Production of T. subcordiformis biomass during incubation in a photobioreactor (a) and biomass production rate in the exponential growth phase (b).
Researchers most frequently describe the feasibility of producing T. subcordiformis biomass using culture media prepared based on distilled water and chemical reagents [53,54]. Their use provides the microalgae with optimal growth conditions. Ji et al. (2010) [53], for example, achieved T. subcordiformis biomass production of 3200 mgVS/L under such conditions. Xie et al. (2001) [54], in turn, were able to increase the biomass concentration of these microalgae to 3680 mgVS/L. A comparable value, namely 3493.33 ± 465.44 mgVS/L, was achieved by using water from natural reservoirs, i.e., from the Gulf of Gdansk, as an environment for the intensive production of T. subcordiformis biomass [55]. However, the culture medium had to be supplemented with nitrogen and phosphorus compounds from external sources, as the content of biogenic compounds in the waters from the coastal zone of the Baltic Sea was too low to ensure intensive development of the T. subcordiformis biomass [55]. The usefulness of various urban and industrial wastewater or post-production water from aquaculture and fermentation residues for the propagation of microalgae of the genus Tetraselmis sp. has also been demonstrated [56]. Heo et al. (2015) [57] used pretreated wastewater from the food sector and obtained a Tetraselmis suecica biomass concentration of 2000 mg/L. In turn, Schulze et al. (2017) [58] analysed the feasibility of using urban wastewater before and after the nitrification process for the production of T. subcordiformis biomass. To this end, they evaluated the influence of the mineral form of nitrogen (ammonium nitrogen and nitrates) on the production of microalgae biomass. In both variants, about 1900 mgVS/L of biomass was produced at the growth rate of about 343 ± 53 mg/L·d [58]. Dudek et al. (2022) [59] achieved T. subcordiformis biomass production of 2240 ± 206 mgVS/L using dairy wastewater and deionised water as a culture medium (at 50%:50% ratio, v:v). However, increasing the proportion of wastewater in the culture medium to 100% led to a decrease in microalgal biomass production to 2110 ± 273 mgVS/L [59]. The lower efficiency of microalgal biomass growth in the culture media with wastewater could be due to its complex nature and the presence of substances that inhibit microalgal growth [60]. Researchers emphasise that urban and industrial wastewater has high loads of toxic compounds, including heavy metals and antibiotics [61].
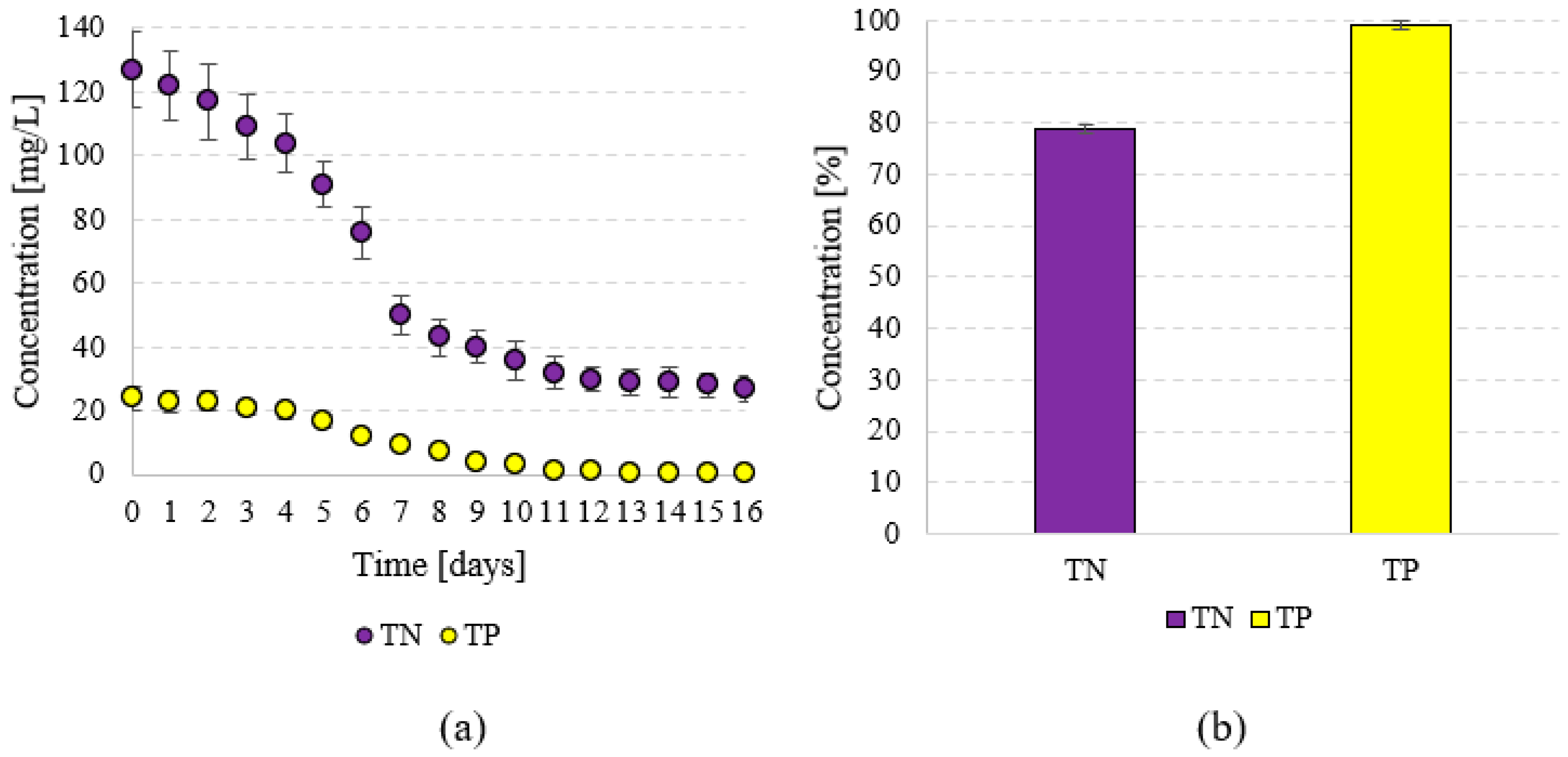
Efficient utilisation of nutrients from the culture medium was observed during T. subcordiformis biomass production. The initial concentration of nitrogen compounds, indicated by the TN concentration, was 127 ± 12 mgN/L. At the end of the cultivation cycle, less than 30 mgN/L was determined (Figure 3a). In the logarithmic growth phase, the N compounds were utilised with an efficiency of 0.26 mgN/mgVS, while in the lag phase it was 0.30 mgN/gVS. The final TN removal efficiency at the end of S1 was 78.7 ± 1.2% (Figure 3b). The TP concentration in the culture medium at the beginning of the photobioreactor operation was 24 ± 3.7 mgP/L. The growing population of T. subcordiformis consumed this nutrient almost completely, with 0.2 ± 0.1 mgTP/L measured at the end (Figure 3a). The efficiency of TP utilisation was 99.1 ± 0.8% (Figure 3b). In the logarithmic growth phase, the specific TP binding efficiency was 0.07 mgP/mgVS, while in the lag phase it was 0.05 mgP/mgVS. The biomass of T. subcordiformis obtained in S1 had a VS content of 90.21 ± 3.4%TS and a TOC content of 459.8 ± 22.7 mg/gTS. The concentration of proteins was at 29.37 ± 3.5%TS, lipids at 9.91 ± 1.6%TS, and saccharides at 37.56 ± 5.2%TS (Table 1).
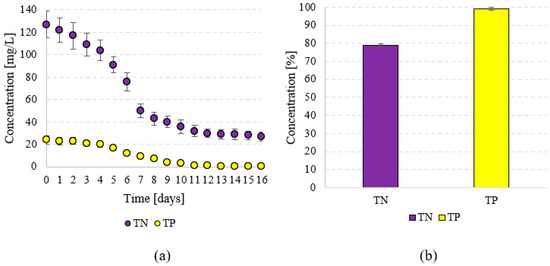
Figure 3.
Changes in TN and TP concentration in the culture medium (a) and the efficiency of TN and TP removal (b).

Table 1.
Characteristics of the biomass of T. subcordiformis in the subsequent stages of the technological protocol used.
The benefits of Tetraselmis sp. strains have been repeatedly demonstrated in wastewater treatment technology, especially in the removal of biogenic compounds [62]. Xiang et al. (2021) [25], who used synthetic industrial wastewater with a nitrogen concentration of 3500 mg/L for the cultivation of T. subcordiformis, demonstrated the possibility of complete removal of this nutrient in the technological system. A similar high efficiency of nitrogen removal was reported by Heo et al. (2015) [57] who used pretreated wastewater from the food sector for Tetraselmis sp. cultivation. The wastewater had contents of nitrogen and phosphorus compounds of about 390 ± 14 mg/L and 438.3 ± 54.4 mg/L, respectively. The biogenes were removed from the medium with an efficiency of 99% and 52.3%, respectively [57]. Amit et al. (2017) [63], who used the Tetraselmis indica Arora & Anil strain in the treatment of social wastewater, recorded a removal efficiency of the monitored N and P indicators at 72.94% and 60.93%, respectively [63]. Another study [64] also confirmed the high efficiency of nutrient utilisation by T. subcordiformis from aquaculture wastewater, namely 87.0–95.0% for nitrogen and 98.0–99.0% for phosphorus [64]. As Chew et al. (2018) [65] show, the efficiency of biogenic compound removal is closely related to the type of culture medium used [65]. The phosphorus removal efficiency achieved in the present study was very high (99.1 ± 0.8%), whereas the nitrogen removal efficiency (78.7 ± 1.2%) was lower compared to literature data. The lower efficiency of the removal of biogenic compounds from wastewater is often explained by the presence of factors that inhibit the development of microalgal biomass [66]. These include the presence of organic compounds that influence the development of competing groups of microorganisms, like, e.g., bacteria [67]. Together with the naturally increased turbidity of the wastewater, this phenomenon restricts light transmission, which directly reduces the rate of photosynthesis and thus biomass growth [68]. This has an immediate effect on the efficiency of nutrient consumption from the culture medium [69].
3.2. Stage 2 (Hydrogen Production)
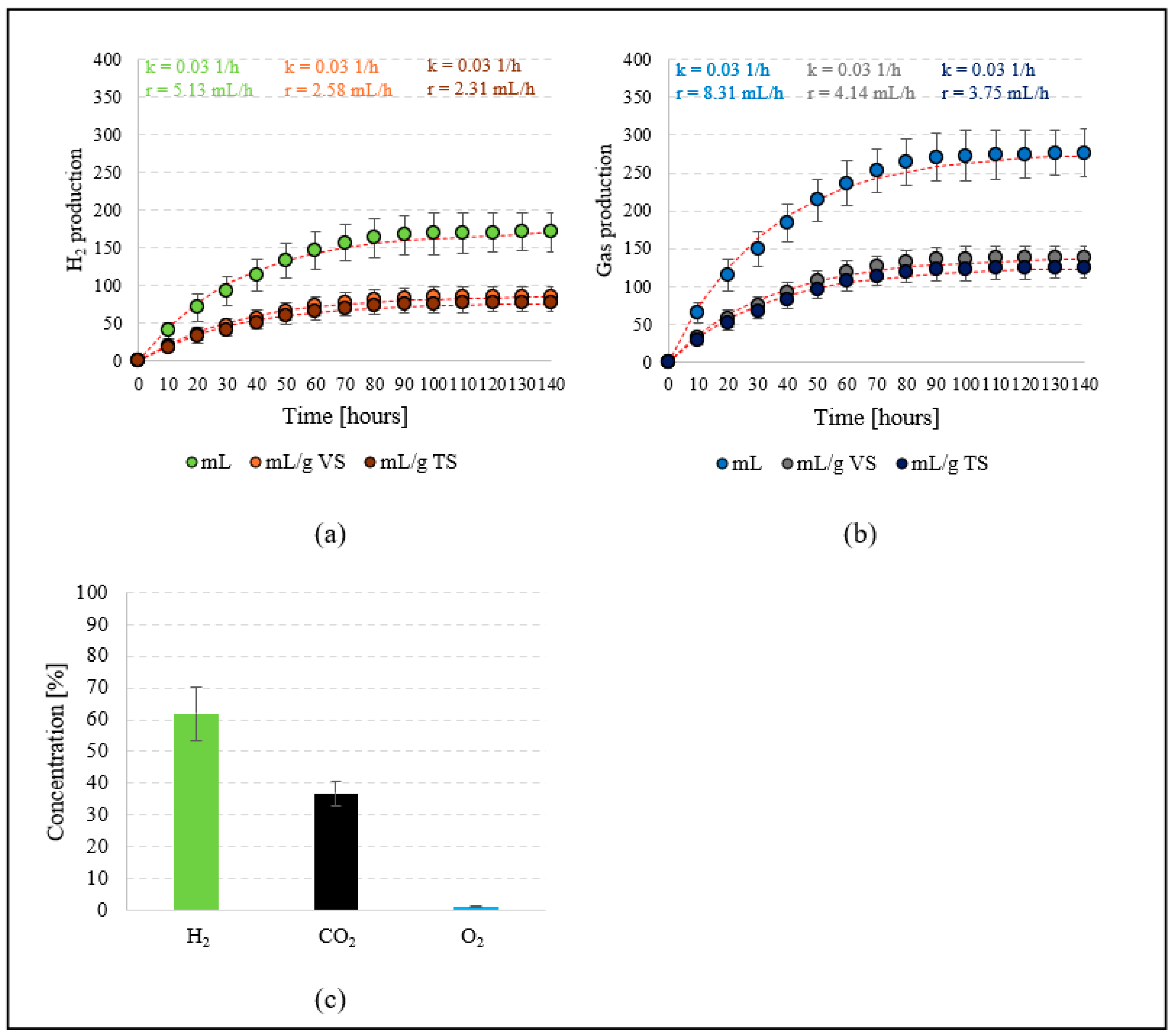
The total volume of hydrogen produced in S2 was 171 ± 26 mL. The production rate of this component of the gaseous metabolites of T. subcordiformis was 5.13 mL/h, and the rate constant (k) reached 0.031/h (Figure 4a). The efficiency of hydrogen synthesis reached 85.6 ± 13 mL/gVS and 77.2 ± 11.7 mL/gTS. The production rates were 2.58 mL/gVS·h and 2.31 mL/gTS·h, respectively (Figure 4a). The total volume of gaseous metabolites of T. subcordiformis biomass was 277 ± 31 mL, which allowed a production rate of 8.31 mL/h (k = 0.03 1/h) (Figure 4b). The gas produced in S2 contained the following components: H2—61.9 ± 5.3%, CO2—36.8 ± 3.7%, and O2—1.3 ± 0.2% (Figure 4c). The biomass of T. subcordiformis after the process had a VS content of 88.13 ± 2.5%TS and a TOC content of 421.8 ± 23.5 mg/gTS. The concentration of proteins was 31.2 ± 2.9%TS, that of lipids was 8.41 ± 1.1%TS, and that of saccharides was 23.5 ± 4.1%TS (Table 1).
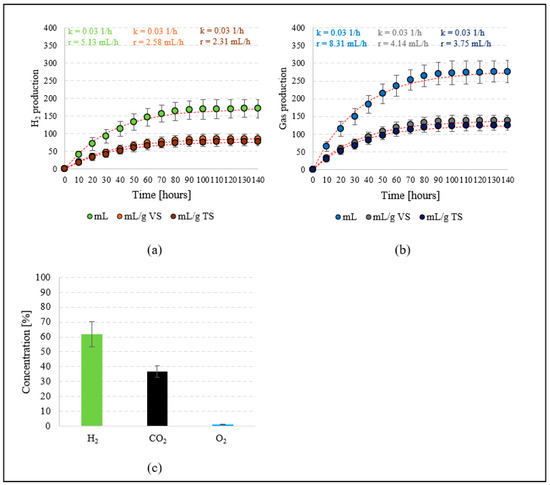
Figure 4.
H2 production (a), production of gaseous metabolites of the biomass of T. subcordiformis (b) and gas components in S2 (c).
Some researchers are of the opinion that the process of biomass production should be continued until the middle of the exponential growth phase [70]. However, others prove that a higher density of algal cells has a direct impact on improving efficiency and prolonging hydrogen production time [71]. Ji et al. (2010) [53] demonstrated that with a T. subcordiformis cell density of 0.5 g/L, a hydrogen production of 16 mL/g biomass could be achieved, and that increasing the cell concentration to 3.2 g/L led to a hydrogen production of over 49 mL/g biomass. An almost 10-fold increase in the gas production rate with increasing substrate density was also observed [53]. Other studies [72] have not confirmed this phenomenon. Hydrogen production was investigated at initial concentrations of T. subcordiformis cells in the bioreactor of 3.0 gVS/L and 5.0 gVS/L. The amounts of hydrogen produced were similar in both variants and reached 63.98 ± 6.35 mL and 64.74 ± 4.11 mL, respectively. The percentage concentration of hydrogen in the biogas was 59.9 ± 1.6% and 63.2 ± 1.4%, respectively. The technological parameters tested resulted in statistically significant differences in the efficiency of gaseous metabolite production by microalgae biomass per unit biomass growth, which reached 35.44 ± 3.52 mL/gVS and 27.14 ± 0.43 mL/gVS, respectively. The efficiency of biohydrogen production was similar, amounting to 21.33 ± 2.12 mL/gVS and 16.87 ± 0.27 mL/gVS, respectively [72]. Ji et al. (2011) [73] investigated the production of T. subcordiformis biomass in substrates depleted in nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulphur. At the same cell density of 6 × 106 cells/mL, the efficiency of hydrogen production was found to be the highest when the T. subcordiformis cells were maintained in a nitrogen-free medium for 6 days. A total of 55.8 mL H2/L of the culture was then achieved in the presence of carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP). It was also found that the lack of nitrogen in the medium reduced the protein content in the cells of T. subcordiformis, but increased the carbohydrate content by more than fourfold, resulting in a 5.5-fold increase in hydrogen production [73]. Guo et al. (2016) [27] used a photobioreactor with an integrated alkaline fuel cell (AFC) to increase the hydrogen yield. After 40 h of continuous irradiation, hydrogen production from T. subcordiformis reached 78 ± 5 mL/L. This was a 1.5-fold higher value compared to an algae culture without AFC, which yielded hydrogen production at 50 ± 3 mL H2/L [27]. Guo et al. (2017) [74] also attempted to improve hydrogen photoproduction using a system based on T. subcordiformis. They found that a high H2 efficiency of 126 ± 10 mL/L could be obtained under a 9/6 h light/dark regime, which was 1.6-fold higher than that achieved under continuous illumination. They also observed that hydrogen production was accompanied by physiological and morphological changes in the cells [74].
3.3. Stage 3 (Bio-Oil Production)
The bio-oil content was 8.41 ± 1.1%TS. Characterisation of the FAMEs in the bio-oil produced showed octadecatrienoic acid C18:3 (all-cis-9,12,15) to be the major FAME, which accounted for 48.63 ± 3.44% m/m (Table 1). Other major FAMEs were oleic acid C18:1 (cis-9) and octadecadienoic acid C18:2 (all-cis-9.12), whose concentrations were 27.09 ± 2.36% m/m and 13.08 ± 1.17% m/m, respectively. The concentration of palmitic acid and stearic acid was below 5% m/m. The remaining FAMEs of the analysed bio-oils were detected in traces (Table 2). The bio-oil produced had a calorific value of 40.2 ± 4.2 MJ/kg, a density (measured at 15 °C) of 823 ± 23 kg/m3, and a viscosity of 3.7 ± 0.9 Mm2/s. Its acid value was 0.2 ± 0.1 mg·KOH/g, and the iodine value was 53.8 ± 3.4 mg·KOH/g. Other physical and chemical properties of the bio-oil are listed in Table 3. The biomass of T. subcordiformis after the bio-oil extraction had a VS content of 82.67 ± 3.3%TS and a TOC content of 372.2 ± 21.4 mg/gTS. The concentration of proteins was 30.7 ± 3.3%TS and that of saccharides was 23.5 ± 4.1%TS (Table 1).

Table 2.
Characteristics of fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) in bio-oil.

Table 3.
Properties and characteristics of the bio-oil produced.
Other authors have also attempted to investigate the potential conversion of the biomass of various microalgae species following hydrogen production. In the study by Torri et al. (2011) [75], the biomass of the alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii P.A.Dangeard was processed into nitrogen-rich biochar, biodiesel, and pyrolysis oil (bio-oil) after hydrogen fermentation. The lipid content (algal oil) obtained by solvent extraction was 15±2% w/w TS [75]. In addition, methods to increase the lipid content in T. subcordiformis microalgae are still being sought. Attempts have been made to optimise the technological conditions for their cultivation. Wei et al. (2015) [76] cultured T. subcordiformis at different temperatures and then analysed the biomass properties. They found that T. subcordiformis grew best at 20 °C and produced the highest total lipids of 22.25%. The major fatty acid methyl esters were C16:0, C16:3n3, C18:3n3, and C20:0, and their proportions were, respectively, 14.93–18.49%, 6.77–12.30%, 15.99–23.65%, and 9.04–10.09%. With increasing temperature, the proportions of saturated fatty acids C16:0 and C18:1 and monounsaturated fatty acids increased significantly. However, the proportions of C16:3n3, C18:3n3, C20:5n3, and polyunsaturated fatty acids decreased significantly. Their study also demonstrated that the predicted cetane number of fatty acid methyl esters increased from 45.3 to 47.6 [76]. Huang et al. (2014) [29], in turn, investigated the effect of iron ions on the lipid content and fatty acid profiles of T. subcordiformis. The microalgae were grown at the following iron ion concentrations: 1.2 × 10−2, 1.2 × 10−1, 1.2, and 12 mmol/L. The lipid content was 17.41 ± 0.38% when the biomass was cultured in the medium with 1.2 × 10−2 mmol/L iron ions. As the iron ion concentration increased, the total lipid content increased and then decreased. When treated with 1.2 mmol/L iron ions, the biomass of T. subcordiformis had a significantly higher total lipid content of 33.72 ± 0.22%. The major fatty acids were C16:0 (14.28–39.06%), C16:3 (0–12.91%), C18:2n6 (11.32–13.88%), C18:3n3 (1.65–19.56%), and C20:0 (6.82–11.52%). Fatty acids 18-C and 16-C accounted for over 80% of all fatty acids [29]. Different methods of extracting bio-oil from Tetraselmis sp. have also been tested. For example, Grierson et al. (2012) [77] compared the use of an organic solvent, supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2), and pyrolysis to evaluate their relative ability to extract oil from the marine microalgae Tetraselmis chui Butcher. The SC-CO2 technique was found to be the least effective in the natural extraction of bio-oil from T. chui. Solvent extraction alone ensured the most complete extraction of bio-oil at a content slightly below 15% by weight. In turn, the subsequent pyrolysis of the residue from solvent extraction increased the total amount of bio-oil produced by more than 11% [77].
3.4. Stages 4–6 (Methane Production)
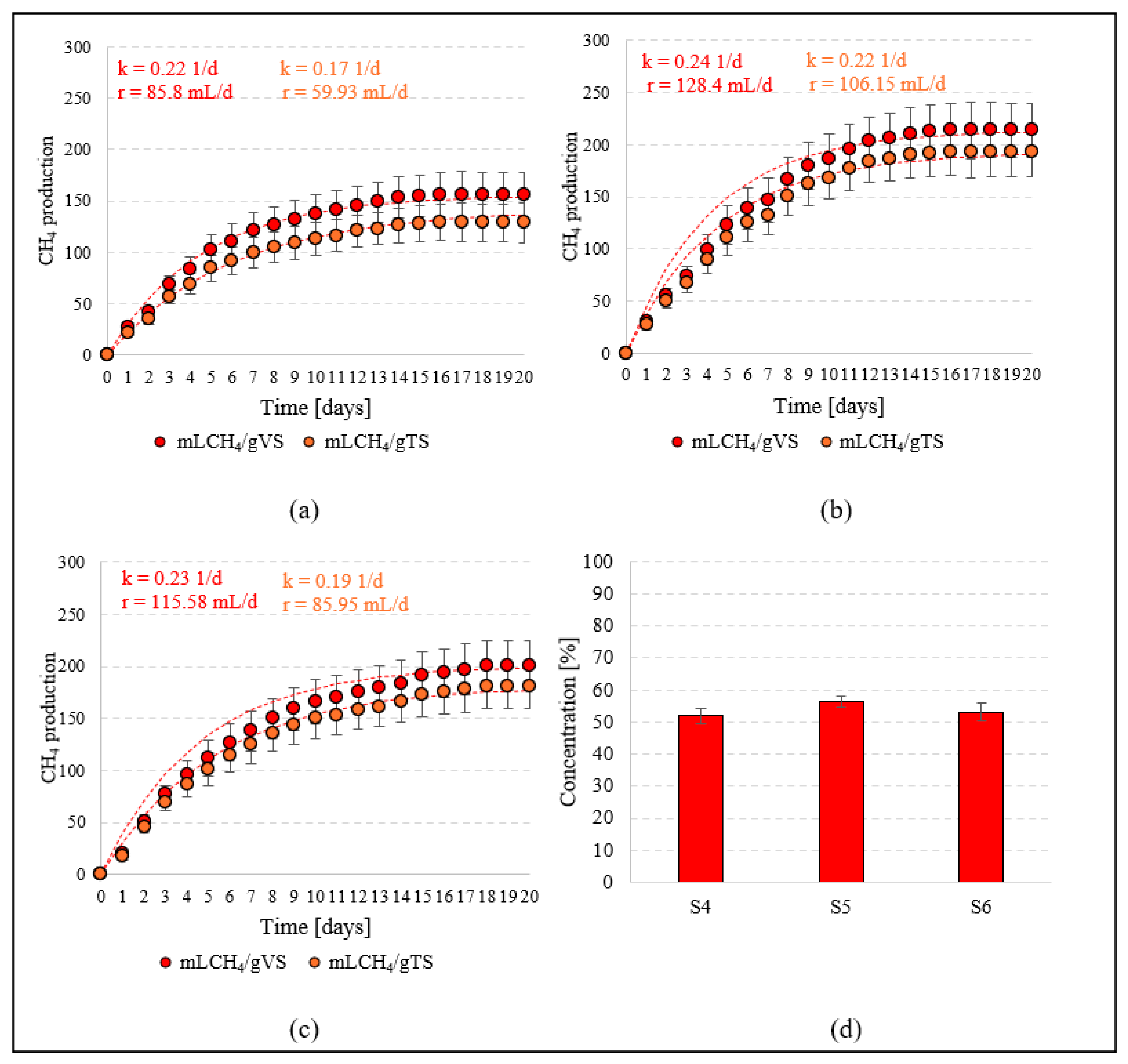
The CH4 production efficiency of T. subcordiformis biomass remaining after chemical extraction of the bio-oil (S4) was 156 ± 21.6 mL/gVS. The anaerobic digestion rate characterised by methane synthesis was 85.8 mL/gVS·d, with a constant k = 0.22 1/d (Figure 5a). In terms of total solids, the specific biomethane production rate was 129 ± 19.5 mL/gTS. The qualitative analysis of the biogas produced showed that the CH4 content was 52.1 ± 2.4% (Figure 5d). Methane fermentation of T. subcordiformis biomass obtained immediately after cultivation in the photobioreactor (S1) was carried out in S5. In this case, CH4 production efficiency reached 214 ± 25.9 mL/gVS and 193 ± 23.4 mL/g TS (Figure 5b), and production rate was 128.4 mL/gVS·d. The content of this fermentation gas component was 56.4 ± 1.7% (Figure 5d). The post-processed biomass from S2 was used in S6. In this variant, the biogas production efficiency was 201 ± 23.8 mL/gVS and 181 ± 21.4 mL/gTS (Figure 5c). The methane production rate was 115.58 mL/gVS·d, and the methane content was 53.2 ± 2.6% (Figure 5d).
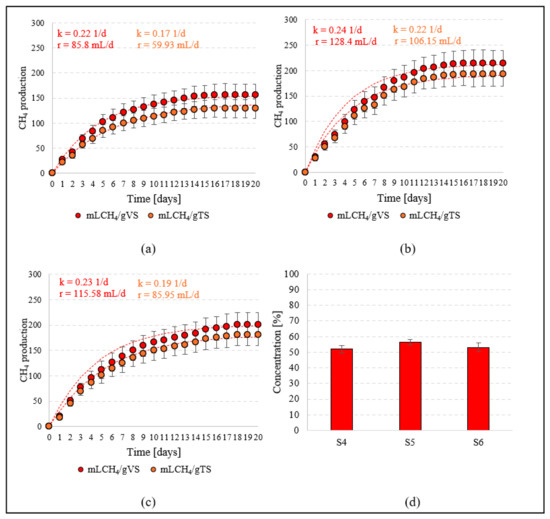
Figure 5.
Biomethane production in S4 (a), S5 (b), and S6 (c), and CH4 concentration in S4–S6 series (d).
Other researchers also subjected the Tetraselmis sp. microalgae to methane fermentation and obtained satisfactory results. Bohutskyi et al. (2014) [31] performed methane fermentation of Tetraselmis sp. collected by centrifugation and recorded a higher methane yield than in this present study, which was 0.42 ± 0.01 L/gVS. The methane concentration of the biogas was 79% [31]. In turn, Hernandez et al. (2014) [32] achieved a methane production of 236 mL/gVS from the biomass of the Tetraselmis sp. alga after lipid extraction. Santos-Ballardo et al. (2015) [33] also investigated the feasibility of recovering methane from the solid biomass residue of Tetraselmis suecica (Kylin) Butcher microalgae after oil extraction. The influence of different types of inoculum on the efficiency of methane production was determined, and the co-fermentation of microalgae biomass with glycerol was investigated. The highest biogas production of 173.78 ± 9.57 mL/gVS was detected when mesophilic inoculum was used, with almost double the methane production than under thermophilic conditions. In addition, an increase in methane production was found when co-fermentation with glycerol was applied, reaching 438.46 ± 40.50 mL/gVS [33]. Feki et al. (2024) [30] investigated the co-digestion of Tetraselmis sp. microalgae biomass with frying oil residues using ultrasonic pretreatment. They found that correcting the C/N ratio with frying oil waste coupled with the sonication of Tetraselmis sp. biomass resulted in the highest methane yield of 443.7 ± 6.4 mL/gVS [30].
3.5. Gross Energy Production
On the basis of the results obtained, an estimated energy balance was drawn up to compare which protocol and which technological sequence of biofuel production can produce the highest gross energy yield. The studies carried out under laboratory conditions provide a reliable basis for calculating the necessary energy input for this type of process and, therefore, do not allow even approximate estimates of the net energy effect. Taking into account the production efficiency of each type of energy carrier and its unit energy value, the total amount of energy that can be obtained was determined as a function of the technological line used. The lowest energy efficiency was found in the protocols in which the grown T. subcordiformis biomass was used only for the production of hydrogen (S1, S2) or hydrogen followed by bio-oil (S1, S2, S3). In these technological variants, the total gross energy yield was 231.6 kWh/MgTS and 232.9 kWh/MgTS (Table 4). It should be emphasised that bio-oil extraction for the subsequent biodiesel production is the least profitable from the point of view of energy yield. Taking into account the low content of fatty substances in the biomass, the unit energy value of the bio-oil was only 1.3 kWh/MgTS (Table 4). Research to date has shown that methane fermentation is the most energetically suitable process for T. subcordiformis biomass conversion. Its inclusion into the technological line significantly increases the gross energy gain, which for the protocol combining all three processes (S1, S2, S3, S4) is 1415.9 kWh/MgTS, including the biomethane fraction with 1182.9 kWh/MgTS (Table 4). The most energy-efficient protocol proved to be the combination of biomass production (S1), hydrogen biosynthesis (S2), and anaerobic digestion (S6) of the post-processed T. subcordiformis biomass. A total of 1891.4 kWh/MgTS was achieved with this variant. The direct use of microalgae biomass as an organic substrate in methane fermentation made it possible to obtain 1769.8 kWh/MgTS (Table 4).

Table 4.
Comparison of the gross energy gain per unit mass depending on the technological protocol for biofuel production.
4. Conclusions
The research results have shown that the recovery of three energy carriers from the biomass of T. subcordiformis, although possible, is not the most viable technological protocol from the standpoint of energy production. Bio-oil extraction for biodiesel production was found to be the least efficient and justified process in this respect.
Research has proven that methane fermentation of T. subcordiformis biomass is the most advisable single process from the perspective of energy conversion. Regardless of the technological protocol applied, the biomethane produced made the largest contribution to the gross energy balance. However, it should be emphasised that the upstream performance of other individual processes, such as hydrogen biosynthesis or bio-oil production, significantly reduces the efficiency of anaerobic digestion, the methane yield, and the final energy gain.
A comparative analysis of the technological protocols applied made it possible to draw up an estimated energy balance. It showed that the highest gross energy gain was obtained with the technological variant combining the processes of hydrogen biosynthesis and subsequent methane fermentation of T. subcordiformis biomass.
The experiments carried out should be considered as preliminary studies, because on a laboratory scale it is not possible to establish a complete energy balance that takes into account both the gains and the different types of outputs. The next step should be to carry out pilot-scale experiments in which the operating parameters of individual processes are close to real conditions. In this way, the necessary data will be collected to conduct a reliable and dependable analysis of technological effectiveness, economic profitability, and environmental neutrality.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski); methodology, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski), M.D. (Magda Dudek) and M.Z.; software, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski); validation, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski) and M.D. (Magda Dudek); formal analysis, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski); investigation, M.D. (Magda Dudek), P.Q., P.R., Ł.B. and A.N.; resources, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski), M.D. (Magda Dudek), J.K., P.Q., P.R., Ł.B., A.N. and M.Z.; data curation, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski) and M.D. (Magda Dudek); writing—original draft preparation, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski) and J.K.; writing—review and editing, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski) and J.K.; visualisation, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski) and J.K; supervision, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski); project administration, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski); funding acquisition, M.D. (Marcin Dębowski). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by works no. 29.610.023-110 of the University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn and WZ/WB-IIŚ/3/2022 of the Bialystok University of Technology, funded by the Minister of Science and Higher Education.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Choudhary, S.; Tripathi, S.; Poluri, K.M. Microalgal-Based Bioenergy: Strategies, Prospects, and Sustainability. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 14584–14612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabed, H.M.; Akter, S.; Yun, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, X. Biogas from Microalgae: Technologies, Challenges and Opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 117, 109503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Khoo, K.S.; Chew, K.W.; Selvarajoo, A.; Chen, W.H.; Chang, J.S.; Show, P.L. Microalgae: The Future Supply House of Biohydrogen and Biogas. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 660399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.A.; Zafar, A.M.; Aly Hassan, A.; Zaidi, A.A.; Farooq, M.; El Badawy, A.; Lundquist, T.; Mohamed, M.M.A.; Al-Zuhair, S. The Role of Oxygen Regulation and Algal Growth Parameters in Hydrogen Production via Biophotolysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condor, B.E.; de Luna, M.D.G.; Chang, Y.H.; Chen, J.H.; Leong, Y.K.; Chen, P.T.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Chang, J.S. Bioethanol Production from Microalgae Biomass at High-Solids Loadings. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 128002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, K.C.C.; Conceição, D.; Vargas, J.V.C.; Mitchell, D.A.; Mariano, A.B.; Ordonez, J.C.; Galli-Terasawa, L.V.; Kava, V.M. Enhanced Microalgae Biomass and Lipid Output for Increased Biodiesel Productivity. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.F.; Soares, R.B.; Gonçalves, R.F. Microalgae: The Challenges from Harvest to the Thermal Gasification. In Algal Biotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lin, R. Research on the Thermochemical Conversion Utilization of Nitrogen-Rich Microalgae: Two-Step Catalytic Pyrolysis of Nannochloropsis Sp over ZSM-5. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 258, 115475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.C.; Illathukandy, B.; Wu, W.; Chang, J.S. Energy, Exergy, and Environmental Analyses of Renewable Hydrogen Production through Plasma Gasification of Microalgal Biomass. Energy 2021, 223, 120025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Felix, C.B. Thermo-Kinetics Study of Microalgal Biomass in Oxidative Torrefaction Followed by Machine Learning Regression and Classification Approaches. Energy 2024, 301, 131677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Brindhadevi, K.; Xia, C.; Salah Khalifa, A.; Elfasakhany, A.; Unpaprom, Y.; Whangchai, K. Performance, Combustion and Emission Characteristics of the CI Engine Fueled with Botryococcus Braunii Microalgae with Addition of TiO2 Nanoparticle. Fuel 2022, 317, 121898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthi, V.; Raja, R.; Carvalho, I.S.; Brindhadevi, K.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Arun, A. A Realistic Scenario on Microalgae Based Biodiesel Production: Third Generation Biofuel. Fuel 2021, 284, 118965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmikandan, M.; Wang, S.; Murugesan, A.G.; Saravanakumar, M.; Selvakumar, G. Co-Cultivation of Streptomyces and Microalgal Cells as an Efficient System for Biodiesel Production and Bioflocculation Formation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olabi, A.G.; Shehata, N.; Sayed, E.T.; Rodriguez, C.; Anyanwu, R.C.; Russell, C.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Role of Microalgae in Achieving Sustainable Development Goals and Circular Economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.Y.B.; Jacob, A.; Nader, C.; Oliveira, C.D.L.; Matos, Â.P.; Araújo, E.S.; Shabnam, N.; Ashok, B.; Gálvez, A.O. An Overview on Microalgae as Renewable Resources for Meeting Sustainable Development Goals. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira de Mendonça, H.; Assemany, P.; Abreu, M.; Couto, E.; Maciel, A.M.; Duarte, R.L.; Barbosa dos Santos, M.G.; Reis, A. Microalgae in a Global World: New Solutions for Old Problems? Renew. Energy 2021, 165, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiki, S.Y.A.; Mofijur, M.; Kumar, P.S.; Ahmed, S.F.; Inayat, A.; Kusumo, F.; Badruddin, I.A.; Khan, T.M.Y.; Nghiem, L.D.; Ong, H.C.; et al. Microalgae Biomass as a Sustainable Source for Biofuel, Biochemical and Biobased Value-Added Products: An Integrated Biorefinery Concept. Fuel 2022, 307, 121782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, E.A.; Mandalà, G.; Dall’osto, L.; Bassi, R. Harnessing the Algal Chloroplast for Heterologous Protein Production. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaramakrishnan, R.; Incharoensakdi, A. Cyanobacteria as Renewable Sources of Bioenergy (Biohydrogen, Bioethanol, and Bio-Oil Production). In Ecophysiology and Biochemistry of Cyanobacteria; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 431–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dȩbowski, M.; Kisielewska, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Rudnicka, A.; Dudek, M.; Romanowska-Duda, Z.; Zielínski, M. The Effects of Microalgae Biomass Co-Substrate on Biogas Production from the Common Agricultural Biogas Plants Feedstock. Energies 2020, 13, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.D.; Martins, C.B.; Assunção, M.F.; Santos, L.M. Microalgae Biomass as an Alternative to Fossil Carbons. In Biomass, Bioproducts and Biofuels; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębowski, M.; Dudek, M.; Nowicka, A.; Quattrocelli, P.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Zieliński, M. Suitability of Pre-Digested Dairy Effluent for Mixotrophic Cultivation of the Hydrogen-Producing Microalgae Tetraselmis Subcordiformis. Environ. Technol. 2022, 45, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya Montoya, L.M.; Pérez, A.A.A.; Giraldo Calderón, N.D.; Garcés, L.A. Analysis of Cell Growth, Photosynthetic Behavior and the Fatty Acid Profile in Tetraselmis Subcordiformis under Different Lighting Scenarios. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 1679–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, W.; Xiang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, C. Enhancing Photosynthetic Starch Production by γ-Aminobutyric Acid Addition in a Marine Green Microalga Tetraselmis Subcordiformis under Nitrogen Stress. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 17103–17112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Wei, X.; Yang, Z.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Pan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Yao, C. Acclimation to a Broad Range of Nitrate Strength on a Euryhaline Marine Microalga Tetraselmis Subcordiformis for Photosynthetic Nitrate Removal and High-Quality Biomass Production. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, G.; Alam, M.A.; Mofijur, M.; Jahirul, M.I.; Lv, Y.; Xiong, W.; Ong, H.C.; Xu, J. Modern Developmental Aspects in the Field of Economical Harvesting and Biodiesel Production from Microalgae Biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, H. Characterization of H2 Photoproduction by Marine Green Alga Tetraselmis Subcordiformis Integrated with an Alkaline Fuel Cell. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, M.; Nowicka, A.; Zieliński, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Dębowski, M. The Effect of Biomass Separation Method on the Efficiency of Hydrogen Production by Platymonas Subcordiformis. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2023, 14, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wei, L.; Huang, Z.; Yan, J. Effect of High Ferric Ion Concentrations on Total Lipids and Lipid Characteristics of Tetraselmis Subcordiformis, Nannochloropsis Oculata and Pavlova Viridis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feki, F.; Cherif, M.; Masmoudi, M.A.; Chamkha, M.; Saadaoui, I.; Das, P.; Sayadi, S. Methane Production Enhancement from Tetraselmis Biomass Co-Digestion Using Frying Oil Residue as Co-Substrate and Ultrasonication as Pretreatment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 33, 103478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohutskyi, P.; Betenbaugh, M.J.; Bouwer, E.J. The Effects of Alternative Pretreatment Strategies on Anaerobic Digestion and Methane Production from Different Algal Strains. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 155, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, D.; Solana, M.; Riaño, B.; García-González, M.C.; Bertucco, A. Biofuels from Microalgae: Lipid Extraction and Methane Production from the Residual Biomass in a Biorefinery Approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 170, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Ballardo, D.U.; Font-Segura, X.; Ferrer, A.S.; Barrena, R.; Rossi, S.; Valdez-Ortiz, A. Valorisation of Biodiesel Production Wastes: Anaerobic Digestion of Residual Tetraselmis Suecica Biomass and Co-Digestion with Glycerol. Waste Manag. Res. 2015, 33, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Deng, M.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W. Two-Stage Photo-Biological Production of Hydrogen by Marine Green Alga Platymonas Subcordiformis. Biochem. Eng. J. 2004, 19, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, M.; Dębowski, M.; Kazimierowicz, J. Microwave Radiation Influence on Dairy Waste Anaerobic Digestion in a Multi-Section Hybrid Anaerobic Reactor (M-SHAR). Processes 2021, 9, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Zhang, F.; Sun, H.; Zhao, B. Effect of Culture Medium on Hydrogen Production by Sulfur-Deprived Marine Green Algae Platymonas Subcordiformis. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2009, 14, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębowski, M.; Kisielewska, M.; Zieliński, M.; Kazimierowicz, J. The Influence of the Ultrasound Disintegration of Microalgal–Bacterial Granular Sludge on Anaerobic Digestion Efficiency. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębowski, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Nowicka, A.; Dudek, M.; Zieliński, M. The Use of Hydrodynamic Cavitation to Improve the Anaerobic Digestion of Waste from Dairy Cattle Farming—From Laboratory Tests to Large-Scale Agricultural Biogas Plants. Energies 2024, 17, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN 15935:2022-01; Soil, Waste, Treated Bio-Waste and Sewage Sludge—Determination of Losses on Ignition. Health, Environment and Medicine Sector. Technical Body of Soil Chemistry: Warsaw, Poland, 2022.
- Van Wychen, S.; Ramirez, K.; Laurens, L.M.L. Determination of Total Lipids as Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (FAME) by in Situ Transesterification: Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP); National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2016. [CrossRef]
- ISO 3104; Petroleum Products—Transparent and Opaque Liquids—Determination of Kinematic Viscosity and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity. International Organization for Standardization, 2023. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:3104:ed-4:v1:en (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- ISO 3675; Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Products—Laboratory Determination of Density—Hydrometer Method. International Organization for Standardization, 1998. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/26326.html (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- ISO 15267; Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils—Flashpoint Limit Test Using Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Flash Tester. International Organization for Standardization, 1998. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/27141.html (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- EN 12662; Liquid Petroleum Products—Determination of Total Contamination. European Standard, 2024. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/8dbff4b1-811d-426a-8197-f34e172273aa/en-12662-1-2024 (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- DIN 51900; Testing of Solid and Liquid Fuels—Determination of Gross Calorific Value by the Bomb Calorimeter and Calculation of Net Calorific Value. European Standard, 2023. Available online: https://store.accuristech.com/standards/din-51900?product_id=2578000 (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- ISO 10370; Petroleum Products—Determination of Carbon Residue—Micro Method. International Organization for Standardization, 2014. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/57081.html (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- EN 14112; Fat and Oil Derivatives—Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (FAME)—Determination of Oxidation Stability (Accelerated Oxidation Test). European Standard, 2021. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/aa4b70be-e467-4a60-83ef-c2543b937f19/en-14112-2020 (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- ISO 12937; Petroleum Products—Determination of Water—Coulometric Karl Fischer Titration Method. International Organization for Standardization, 2000. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/2730.html (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- EN 14104; Fat and Oil Derivates—Fatty Acid Methyl Ester (FAME)—Determination of Acid Value. European Standard, 2021. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/7a67b9de-1b54-4a80-bd13-c5db21ec455f/en-14104-2021 (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- ISO 10540; Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils—Determination of Phosphorus Content. International Organization for Standardization, 2002. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/33121.html (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- ISO 3987; Petroleum Products—Determination of Sulfated Ash in Lubricating Oils and Additives. International Organization for Standardization, 2010. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/44979.html (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- EN 14111; Fat and Oil Derivatives—Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (FAME)—Determination of Iodine Value. European Standard, 2022. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/515ecaab-fec3-49e4-9d98-c2d20a515dda/en-14111-2022 (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Ji, C.F.; Legrand, J.; Pruvost, J.; Chen, Z.A.; Zhang, W. Characterization of Hydrogen Production by Platymonas Subcordiformis in Torus Photobioreactor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 7200–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Mixotrophic Cultivation of Platymonas Subcordiformis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2001, 13, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.; Dębowski, M.; Nowicka, A.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Zieliński, M. Applicability of Water from the Bay of Gdańsk as a Growth Medium for Mixotrophic Culture of Platymonas Subcordiformis. Front. Biosci.-Elit. 2022, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aketo, T.; Hoshikawa, Y.; Nojima, D.; Yabu, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Takano, H.; Tanaka, T. Selection and Characterization of Microalgae with Potential for Nutrient Removal from Municipal Wastewater and Simultaneous Lipid Production. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 129, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.W.; Ryu, B.G.; Nam, K.; Kim, W.; Yang, J.W. Simultaneous Treatment of Food-Waste Recycling Wastewater and Cultivation of Tetraselmis Suecica for Biodiesel Production. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, P.S.C.; Carvalho, C.F.M.; Pereira, H.; Gangadhar, K.N.; Schüler, L.M.; Santos, T.F.; Varela, J.C.S.; Barreira, L. Urban Wastewater Treatment by Tetraselmis Sp. CTP4 (Chlorophyta). Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.; Dębowski, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Zieliński, M.; Quattrocelli, P.; Nowicka, A. The cultivation of biohydrogen-producing tetraselmis subcordiformis microalgae as the third stage of dairy wastewater aerobic treatment system. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Mehariya, S.; Bhatia, R.K.; Kumar, M.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Awasthi, M.K.; Atabani, A.E.; Kumar, G.; Kim, W.; Seo, S.O.; et al. Wastewater Based Microalgal Biorefinery for Bioenergy Production: Progress and Challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.; Anbarasu, A.; Pasupuleti, R.R.; Manigandan, S.; Praveenkumar, T.R.; Aravind Kumar, J. Treatment of Heavy Metals Containing Wastewater Using Biodegradable Adsorbents: A Review of Mechanism and Future Trends. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, R.K.; Agrawal, K.; Mehariya, S.; Verma, P. Current Perspective on Wastewater Treatment Using Photobioreactor for Tetraselmis Sp.: An Emerging and Foreseeable Sustainable Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 1, 61905–61937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amit; Chandra, R.; Ghosh, U.K.; Nayak, J.K. Phycoremediation Potential of Marine Microalga Tetraselmis Indica on Secondary Treated Domestic Sewage for Nutrient Removal and Biodiesel Production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20868–20875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Yan, S.; Mu, J. Microalgae Cultivation Using an Aquaculture Wastewater as Growth Medium for Biomass and Biofuel Production. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25 (Suppl. S1), S85–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.W.; Chia, S.R.; Show, P.L.; Yap, Y.J.; Ling, T.C.; Chang, J.S. Effects of Water Culture Medium, Cultivation Systems and Growth Modes for Microalgae Cultivation: A Review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sánchez, A.; Silva-Gálvez, A.L.; Aguilar-Juárez, Ó.; Senés-Guerrero, C.; Orozco-Nunnelly, D.A.; Carrillo-Nieves, D.; Gradilla-Hernández, M.S. Microalgae-Based Livestock Wastewater Treatment (MbWT) as a Circular Bioeconomy Approach: Enhancement of Biomass Productivity, Pollutant Removal and High-Value Compound Production. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Qiu, S.; Li, M.; Yuan, W.; Ge, S. Granular Indigenous Microalgal-Bacterial Consortium for Wastewater Treatment: Establishment Strategy, Functional Microorganism, Nutrient Removal, and Influencing Factor. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 353, 127130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, K.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Yin, F.; Liang, C.; Zhang, W. A Review of Biogas Slurry Treatment Technology Based on Microalgae Cultivation. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 25, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhan, J.; Luo, G.; Hao Ngo, H.; Zhang, S. Progress on Microalgae Biomass Production from Wastewater Phycoremediation: Metabolic Mechanism, Response Behavior, Improvement Strategy and Principle. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 137187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Qiu, S.; Tremblay, D.; Viner, K.; Champagne, P.; Jessop, P.G. Centrate Wastewater Treatment with Chlorella Vulgaris: Simultaneous Enhancement of Nutrient Removal, Biomass and Lipid Production. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, D.; Di Dong, C.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Chang, J.S. Biohydrogen Production from Microalgae—Major Bottlenecks and Future Research Perspectives. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 16, 2000124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, M.; Dębowski, M.; Nowicka, A.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Zieliński, M. The Effect of Autotrophic Cultivation of Platymonas Subcordiformis in Waters from the Natural Aquatic Reservoir on Hydrogen Yield. Resources 2022, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.F.; Yu, X.J.; Chen, Z.A.; Xue, S.; Legrand, J.; Zhang, W. Effects of Nutrient Deprivation on Biochemical Compositions and Photo-Hydrogen Production of Tetraselmis Subcordiformis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 5817–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, H. Effect of Light/Dark Regimens on Hydrogen Production by Tetraselmis Subcordiformis Coupled with an Alkaline Fuel Cell System. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 183, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torri, C.; Samorì, C.; Adamiano, A.; Fabbri, D.; Faraloni, C.; Torzillo, G. Preliminary Investigation on the Production of Fuels and Bio-Char from Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii Biomass Residue after Bio-Hydrogen Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8707–8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Huang, X.; Huang, Z. Temperature Effects on Lipid Properties of Microalgae Tetraselmis Subcordiformis and Nannochloropsis Oculata as Biofuel Resources. Chinese J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grierson, S.; Strezov, V.; Bray, S.; Mummacari, R.; Danh, L.T.; Foster, N. Assessment of Bio-Oil Extraction from Tetraselmis Chui Microalgae Comparing Supercritical CO2, Solvent Extraction, and Thermal Processing. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).