A Model Predictive Control Strategy with Minimum Model Error Kalman Filter Observer for HMEV-AS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. HMEV-AS Model
2.1. Hub-Motor Model
2.2. Unbalance Magnetic Pull
2.3. Linear Air Suspension Model
2.4. Dynamic Model
2.5. Road Excitation Model
3. Experimental Validations
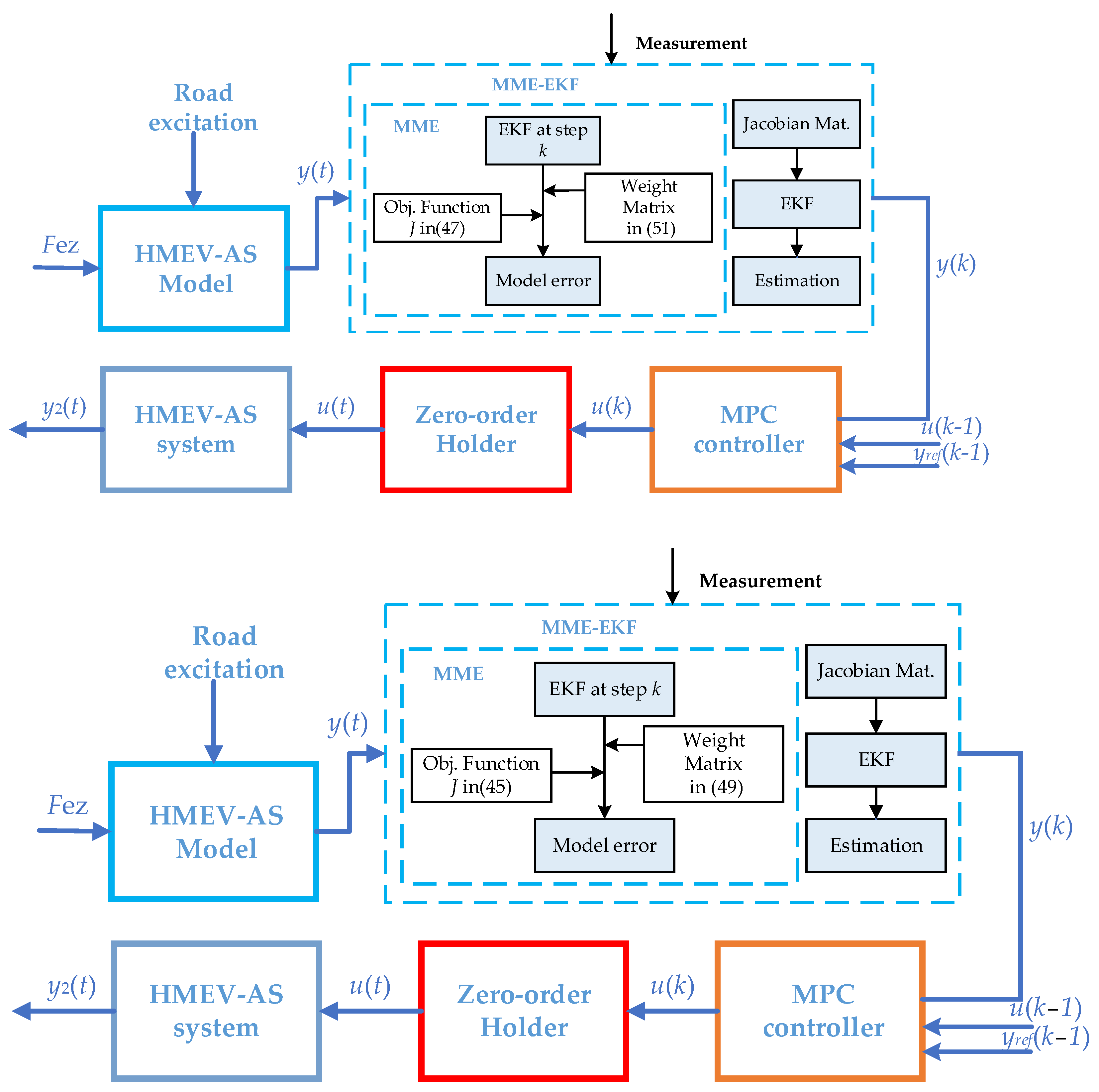
4. MPC Control Design
4.1. MPC Controller Design
4.2. Minimum Model Error Kalman Observer Design
5. Simulation Result
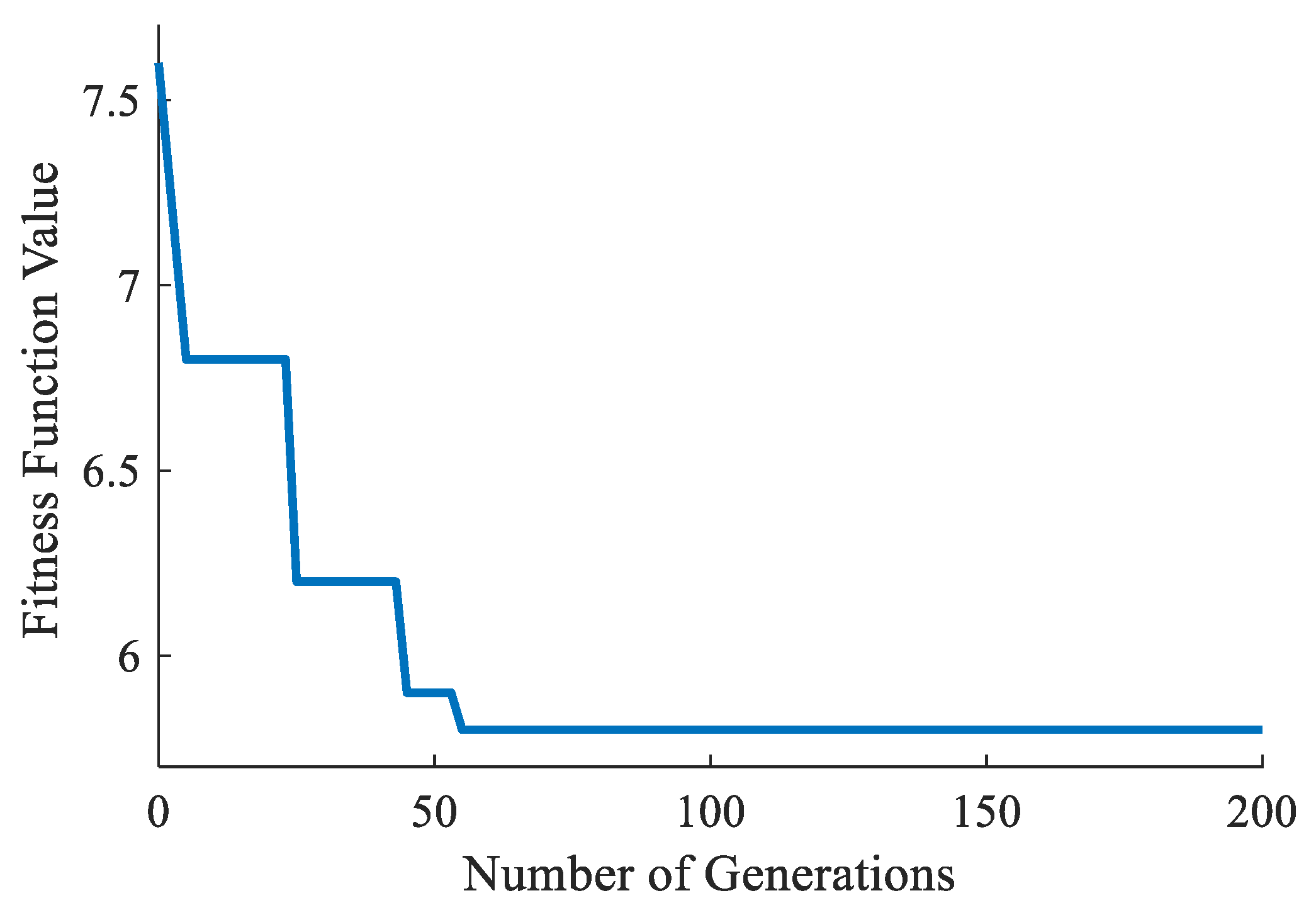
5.1. Simulation Analysis of MME-EKF Observer
5.2. Simulation Analysis of MPC Controller
6. Conclusions
- The developed MME-EKF observer effectively estimates vehicle dynamics, including tire dynamic load, vehicle body velocity, vehicle body acceleration, roll rate, and pitch rate.
- Compared with a PID-based control scheme, the MPC controller achieves further reductions in key evaluation metrics: sprung mass vertical acceleration (41.59%), front-front motor eccentricity (14.29%), front-front tire dynamic load (1.78%), roll angular acceleration (17.65%), and pitch angular acceleration (16.67%).
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sivaramanan, S. Global Warming and Climate Change, Causes, Impacts and Mitigation; Central Environmental Authority: Battaramulla, Sri Lanka, 2015; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S. Energy Crisis and Climate Change: Global Concerns and Their Solutions. In Energy: Crises, Challenges and Solutions; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Marinković, D.; Dezső, G.; Milojević, S. Application of Machine Learning During Maintenance and Exploitation of Electric Vehicles. Adv. Eng. Lett. 2024, 3, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Yan, Z.; Xu, L.; Wei, C.; Yin, G. Improving vibration performance of electric vehicles based on in-wheel motor-active suspension system via robust finite frequency control. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, C. Optimized handling stability control strategy for a four in-wheel motor independent-drive electric vehicle. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 17017–17032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Mei, K.; Ding, S. Direct yaw-moment control design for in-wheel electric vehicle with composite terminal sliding mode. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 17141–17156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, G.; Marino, R. Adaptive slip vectoring for speed and yaw-rate control in electric vehicles with four in-wheel motors. Control Eng. Pract. 2023, 135, 105511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Qin, H.; Chen, T.; Luo, X.; Wei, H. Integrated optimization of the in-wheel motor driving system considering the ride comfort of the electric vehicle under multiple operating conditions. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2023, 238, 09544070231201686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Fan, Z. Optimisation of electric vehicle with the in-wheel motor as a dynamic vibration absorber considering ride comfort and motor vibration based on particle swarm algorithm. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part K J. Multi-Body Dyn. 2023, 237, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y. Coupling effects in hub motor and optimization for active suspension system to improve the vehicle and the motor performance. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 482, 115426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingül, Ö.; Yıldız, A. Fuzzy logic and proportional integral derivative based multi-objective optimization of active suspension system of a 4×4 in-wheel motor driven electrical vehicle. J. Vib. Control 2023, 29, 1366–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, X.; Chen, X.; Xue, H. Dynamic Characteristics Analysis of the Hub Direct Drive-Air Suspension System from Vertical and Longitudinal Directions. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.-S.; Choi, S.-B. Adaptive Control for Suspension System of In-Wheel Motor Vehicle with Magnetorheological Damper. Machines 2024, 12, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyaneza, O.; Turabimana, P.; Oh, J.-S.; Choi, S.-B.; Sohn, J.W. Design and analysis of a hybrid annular radial magnetorheological damper for semi-active in-wheel motor suspension. Sensors 2022, 22, 3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Hu, Y. Comprehensive analysis for influence of complex coupling effect and controllable suspension time delay on hub-driving electric vehicle performance. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2022, 236, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Gimenez, J.; Nieto, J.; Vinolas, J. Air suspension characterisation and effectiveness of a variable area orifice. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2010, 48 (Suppl. S1), 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-Q.; Cai, Y.-F.; Yuan, C.-C.; Wang, S.-H.; Chen, L. Fuzzy sliding mode control for the vehicle height and leveling adjustment system of an electronic air suspension. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 31, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ruan, Z.; Gu, R.; Hu, G. Fuzzy sliding mode control of vehicle magnetorheological semi-active air suspension. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirgni, H.B.; Wang, J. LQR-based adaptive TSMC for nuclear reactor in load following operation. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2023, 156, 104560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Shi, W. Seismic control of adaptive variable stiffness intelligent structures using fuzzy control strategy combined with LSTM. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 78, 107549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Hu, G. Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of ceramic motorized spindle considering unbalanced magnetic pull and contact force effects. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2024, 46, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Vertical dynamics analysis and multi-objective optimization of electric vehicle considering the integrated powertrain system. Appl. Math. Model. 2024, 131, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X. A Novel Air Spring Dynamic Model with Pneumatic Thermodynamics, Effective Friction and Viscoelastic Damping. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 409, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, D.; Avila, S.; Morais, M. Parameter Identification of Bouc-Wen Model for MR Damper; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, C. Hybrid model predictive control of semi-active suspension in electric vehicle with hub-motor. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.B.; Li, Y.C.; Chang, K.C. Effect of road surface roughness on the response of a moving vehicle for identification of bridge frequencies. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2012, 5, 347–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 4970-2009; Test Method for Automobile Ride Comfort. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Liu, W.; He, H.; Sun, F. Vehicle state estimation based on minimum model error criterion combining with extended Kalman filter. J. Frankl. Inst. 2016, 353, 834–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameters | Value | Unit | Parameters | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winding turns Ns | 24 | - | Radius of permanent magnet position | Rm | 0.1008 | m |
| Slot number Qs | 51 | - | Permanent magnet thickness | hm | 0.0025 | m |
| Parallel branches of winding number a | 1 | - | Axial length of motor | L | 0.06 | m |
| Slot width b0 | 0.00214 | m | Permanent magnet remanence | Br | 1.33 | T |
| Slot angle α0 | 0.0214 | rad | Winding pitch | αy | 1 | rad |
| Outer radius of stator Rs | 0.1 | m | Polar arc coefficient | αp | 1 | - |
| Inner radius Rr | 0.1033 | m | Pole pairs | p | 23 | - |
| Relative recovery permeability μr | 1.1 | - | Initial angle of stator to rotor | θ0 | 0 | rad |
| Single-phase winding number N | 17 | - | Vacuum permeability | μ0 | 4π × 10−7 | N/A2 |
| a0 + | 4002.72 | a0 − | −2002.45 |
| a1 + | −1567.91 | a1 − | 801.58 |
| b0 + | 3.41 | b0 − | 9.48 |
| C + | 1.31 | C − | 3.38 |
| Specifications | Value |
|---|---|
| Mb (kg) | 710 |
| Mω_mri (kg) | 20 |
| Mmsi (kg) | 30.4 |
| Mti (kg) | 34.4 |
| Br (m) | 1.55 |
| r (m) | 0.245 |
| lf (m) | 0.795 |
| lr (m) | 0.975 |
| U (V) | 72 |
| Kt (kN/s) | 260 |
| Molecular Coefficient | Denominator Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 406,250 | 406,249 | ||
| 690,430 | 750,487 | ||
| 61.0354 | 102,122 | ||
| Specifications | Zotye Zhidou 1 |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Zotye Zhidou |
| Power Type | Pure Electric |
| Range | 120 km (NEDC Standard) |
| Top speed | 80 km/h |
| Battery Type | Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) Battery (10.5 kWh) |
| Charging Time | Slow Charge: 6 h (0–100%) |
| Fast Charge: 20 min (0–80%) | |
| Motor Power | Rated Power: 9 kW, Peak Power: 18 kW |
| RMSEvaluation index | Uncontrol | PID | Improvement | MPC | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.13 m/s2 | 1.05 m/s2 | 7.08% | 0.58 m/s2 | 48.67% | |
| e1 | 0.28 mm | 0.26 mm | 7.14% | 0.22 mm | 21.43% |
| Ftd1 | 845 N | 772 N | 8.63% | 757 N | 10.41% |
| 0.17 rad/s2 | 0.16 rad/s2 | 5.88% | 0.13 rad/s2 | 23.53% | |
| 0.12 rad/s2 | 0.11 rad/s2 | 8.33% | 0.85 rad/s2 | 25.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y. A Model Predictive Control Strategy with Minimum Model Error Kalman Filter Observer for HMEV-AS. Energies 2025, 18, 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061557
Zhou Y, Liu C, Li Z, Yu Y. A Model Predictive Control Strategy with Minimum Model Error Kalman Filter Observer for HMEV-AS. Energies. 2025; 18(6):1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061557
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ying, Chenlai Liu, Zhongxing Li, and Yi Yu. 2025. "A Model Predictive Control Strategy with Minimum Model Error Kalman Filter Observer for HMEV-AS" Energies 18, no. 6: 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061557
APA StyleZhou, Y., Liu, C., Li, Z., & Yu, Y. (2025). A Model Predictive Control Strategy with Minimum Model Error Kalman Filter Observer for HMEV-AS. Energies, 18(6), 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061557






