Abstract
CO is a toxic gas discharged as a byproduct in tail gases from different industrial flue gases, which needs to be taken care of urgently. In this study, a CuCl/AC adsorbent was made by a facile route of physically mixing CuCl2 and Cu(HCOO)2 powder with activated carbon (AC), followed by heating at 533 K under vacuum. The samples were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), N2 adsorption/desorption, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). It was shown that Cu(II) can be completely reduced to Cu(I), and the monolayer dispersion threshold of CuCl on AC support is 4 mmol·g−1 AC. The adsorption isotherms of CO, CO2, CH4, and N2 on CuCl/AC adsorbents were measured by the volumetric method, and the CO/CO2, CO/CH4, and CO/N2 selectivities of the adsorbents were predicted using ideal adsorbed solution theory (IAST). The obtained adsorbent displayed a high CO adsorption capacity, high CO/N2, CO/CH4, and CO/CO2 selectivities, excellent ad/desorption cycle performance, rapid adsorption rate, and appropriate isosteric heat of adsorption, which made it a promising adsorbent for CO separation and purification.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of C−1 chemistry recently in the chemical industry, carbon monoxide (CO) as a significant resource has been widely applied to prepare a large variety of chemical products, such as formic acid, acetic acid, oxalic acid ester, carbonic acid two methyl ester, anhydride, etc. [1,2]. Most of these preparations need high-purity CO. The main methods of producing CO are the steam reforming of natural gas and coal gasification [3]. In addition, a significant amount of CO is discharged as a byproduct in tail gases from different industrial flue gases including carbon black tail gas, silicon carbide furnace gas, yellow phosphorus tail gas, coke oven gas, blast furnace gas, etc. [4,5,6]. From both processes, the obtained CO is mixed with N2, H2, CH4, CO2, and vapor. CO is toxic to humans because it combines with hemoglobin in the blood to form carboxy-hemoglobin hindering the transportation and release of oxygen in the blood, which leads to death [7]. Moreover, even a trace amount of CO can poison the noble catalysts, such as the proton-exchange membrane fuel cells, which restrict the CO content below 0.2 ppm to protect the platinum electrocatalyst [8,9]. Thus, the separation and purification of CO from different gas mixtures have significance both industrially and environmentally.
Among the proven technologies for CO separation and purification, adsorption processes, such as pressure swing adsorption (PSA) and temperature swing adsorption (TSA) have the advantages of convenient operation, low energy consumption, low operating cost, etc., and have been widely used in CO separation [10,11,12,13,14]. Adsorbent plays a crucial role in the adsorption based gas separation process, it has been found that many porous materials, such as activated carbons [15,16], zeolites [17,18], and metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) [19,20], have adsorption capacities to a certain extent. However, it is difficult to separate and purify CO from gas mixtures by using these materials directly since their adsorption capacity and selectivities are low. Cu(I) adsorbents for CO separation have received extensive attention for their high CO adsorption capacity and high selectivity, since CO molecules can form a -complexation bond with Cu(I) ions on the adsorbent, which are stronger than the interaction caused by van der Waals forces [21,22,23,24,25,26]. More importantly, -complexation bonds are still weak enough to be broken by normal engineering operations, such as increasing temperature or reducing pressure, and the adsorbed CO can be easily desorbed, which makes it a suitable adsorbent in PSA and TSA systems [23]. Two approaches are used for making Cu(I) adsorbents. In the first process, Cu(I) adsorbents are prepared by impregnating Cu(II) salts into a porous support including zeolites, activated carbons (ACs) and MOFs, etc. [20,25,27], and then reducing Cu(II) to Cu(I) using reducing gases, such as H2 or CO. However, it is difficult to control the reduction degree, and Cu(II) is easily over reduced to Cu. In the second process, Cu(I) adsorbents are prepared by direct dispersion and impregnation of CuCl. Hirai et al. [28,29] and Tamon et al. [30] obtained Cu(I)/AC adsorbents by using dispersing reagents, such as concentrated hydrochloric acid or organic solvents, to disperse CuCl onto the AC surfaces, and then drying at 403 K in N2. Xie et al. [31] prepared CuCl/zeolite adsorbents by dispersing CuCl powder spontaneously onto the surfaces of zeolites at 623 K in an inert atmosphere, which displayed high adsorption capacity and selectivity for CO. When using CuCl as a starting material, the adsorbent preparation has to be carefully performed in a dry inert atmosphere, to prohibit the oxidation and hydrolysis of Cu(I). In our previous work, we successfully obtained Cu(Ι) π-complexation adsorbents with an aqueous solution of equimolar CuCl2 and Cu(HCOO)2 as starting materials by the traditional impregnation method followed by activating at the temperature of 583 K [32].
Herein, the purpose of this work is to develop CO adsorbent using a solid-state auto reduction–dispersion method with CuCl2 and Cu(HCOO)2 as the initial material. Then, X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), N2 adsorption/desorption and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were employed to characterize the samples. Pure component CO, CO2, N2, and CH4 adsorption isotherms on the adsorbents were measured in a volumetric method. The CO/CO2, CO/CH4, and CO/N2 selectivities of the adsorbents were predicted by using ideal adsorbed solution theory (IAST). The adsorption isotherms were fitted with the Langmuir–Freundlich model, and the corresponding heats of adsorption were calculated. The cyclic CO adsorption on adsorbent was performed to evaluate its repeated availability during the adsorption and desorption cycles. Furthermore, the CO adsorption rate on adsorbent was discussed and reported.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Copper formate tetrahydrate (Cu(HCOO)2·4H2O, 98%) and cupric chloride dihydrate (CuCl2·2H2O, 99%) were purchased from Alfa Aesar Chemical Co. Ltd.(Ward Hill, MA, USA). Activated carbon (AC) was purchased from Chengde Jingda Activated Carbon Manufacturing Co. Ltd. (Chengde, China).
2.2. Preparation of CuCl/AC Adsorbents
CuCl/AC adsorbents were synthesized following two steps. First, the AC was physically mixed with CuCl2 and Cu(HCOO)2 powder to obtain CuCl/AC adsorbent precursors. Then, the obtained precursors were dried at 373 K and activated in a tube furnace at 533 K for 4 h under vacuum. The obtained precursors and CuCl/AC adsorbents were marked as Cu(II)-x/AC and Cu(I)-x/AC (x = 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), in which the loading of copper is 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 mmol·g−1 AC, respectively. The as-synthesized CuCl/AC adsorbents were stored in vacuum dry storage in a desiccator.
2.3. Adsorbent Characterization
Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the samples were recorded by a Shimadzu LabX XRD-6000 system (Kyoto, Japan) in the 2θ range of 5 to 35° using CuKα1 (λ=1.54056 Å) radiation operated at 40 kV and 30 mA. The pore volume and surface area of the samples were calculated from N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms measured on a surface area and pore size analyzer (QUADRASORB SI, Quantachrome Inc., Boynton Beach, FL, USA) after activating the samples at 393 K for 4 h under vacuum. The specific surface areas (SBET) were determined using the BET (Brunauer–Emmett–Teller) method under relative pressure in the range of 0.01 to 0.20. The adsorbed amount of N2 at p/p0 = 0.98 was employed to calculate the total pore volume (VTotal). Scanning electron microscope (SEM, Hitachi S4800, Hitachi Ltd., Tokyo Japan) was used to observe the samples’ morphology. Cu contents were measured by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES, Thermo-ICAP6300, Thermo Fisher Scientific Co., Ltd., Waltham, MA, USA).
2.4. Adsorption Measurements
Before the adsorption measurements, the samples were degassed under vacuum while heating up to 393 K for 4 h. The CO, CO2, CH4, and N2 adsorption isotherms were measured at the temperature required using a static volumetric apparatus (NOVE1000e, Quantachrome Inc., Boynton Beach, FL, USA). During the adsorption measurements, the temperature was maintained by circulating ethanediol-water from a bath with setting temperature. The adsorption capacity was determined from the adsorption isotherm measured at 298 K. Ultrahigh purity grade CO (99.99%), CO2 (99.999%), CH4 (99.99%), and N2 (99.999%) were used without any purification.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Samples
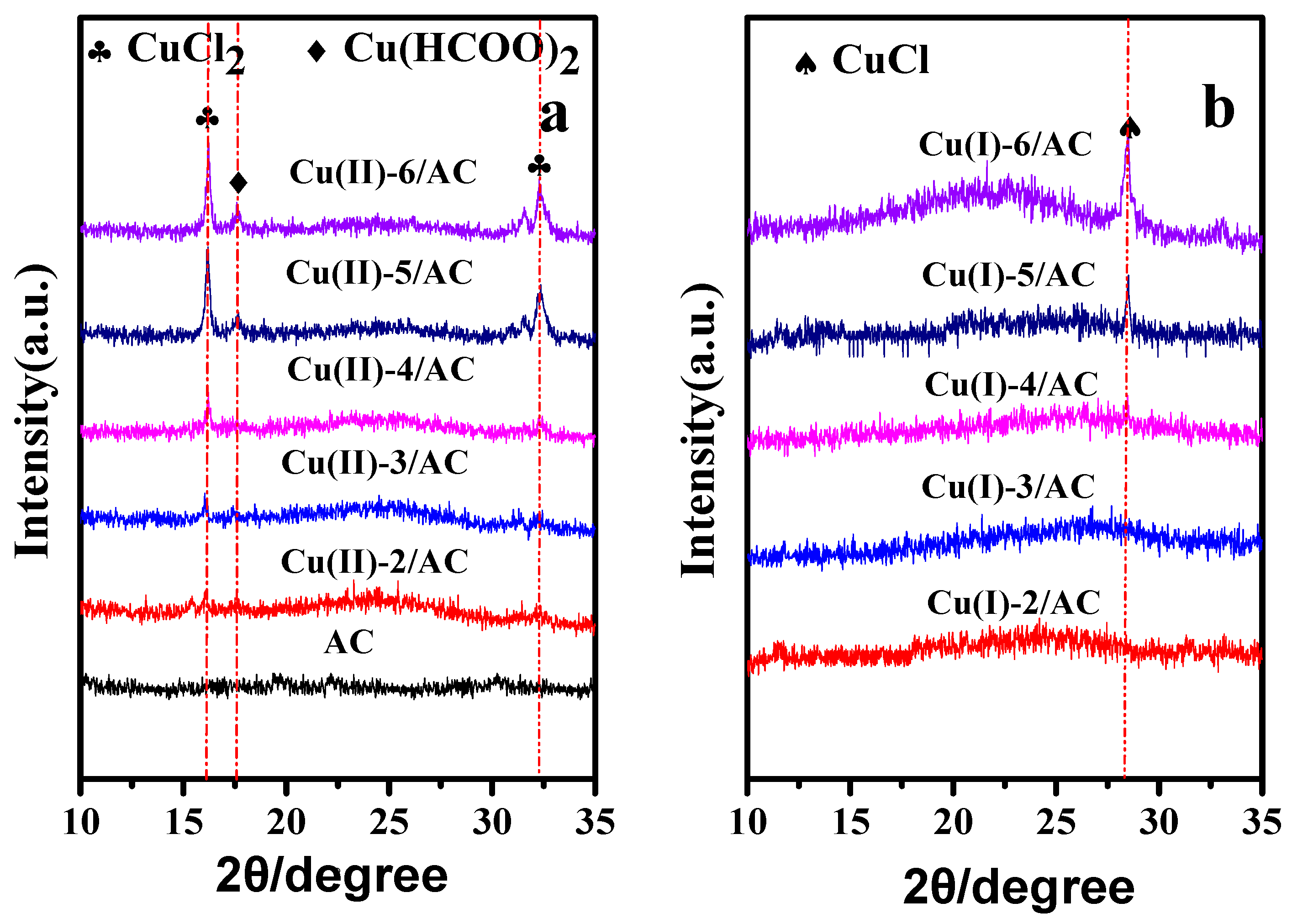
The XRD patterns of the copper loaded AC samples before and after activation are presented in Figure 1. Before activation, the diffraction peaks of Cu(HCOO)2 and CuCl2 [33,34] can be observed in the Cu(II)-x/AC samples, and the reflection intensities increased with the increase of copper loading. After activation, the diffraction peaks of CuCl2 and Cu(HCOO)2 disappeared, and the Cu(I)-5/AC sample displayed only a relatively weak peak (2θ = 28.5°) of CuCl [35], suggesting that Cu(HCOO)2 and CuCl2 were transformed into CuCl after activation. Meanwhile, the absence of CuCl diffraction peak on Cu(I)-2/AC, Cu(I)-3/AC, and Cu(I)-4/AC samples might be due to the well dispersion of CuCl on the AC surface beyond the detection limit of XRD [36]. By further increasing the copper loading to 5 and 6 mmol·g−1, the appearance of the characteristic peak of CuCl implies that the crystal size of CuCl on the AC surface increased with the increase of CuCl loading, which was able to be detected by XRD with the CuCl loading higher than 5 mmol·g−1.
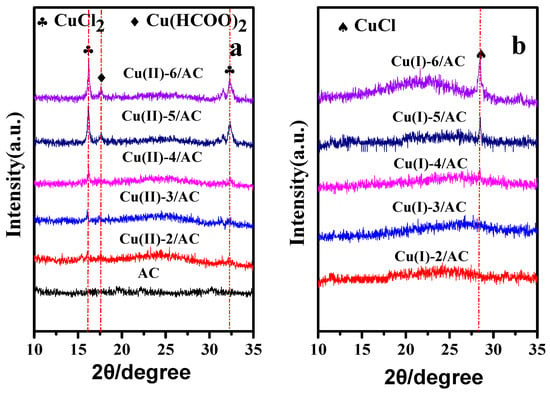
Figure 1.
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) patterns of activated carbon (AC), Cu (II)-x/AC (a) and Cu(I)-x/AC (b).
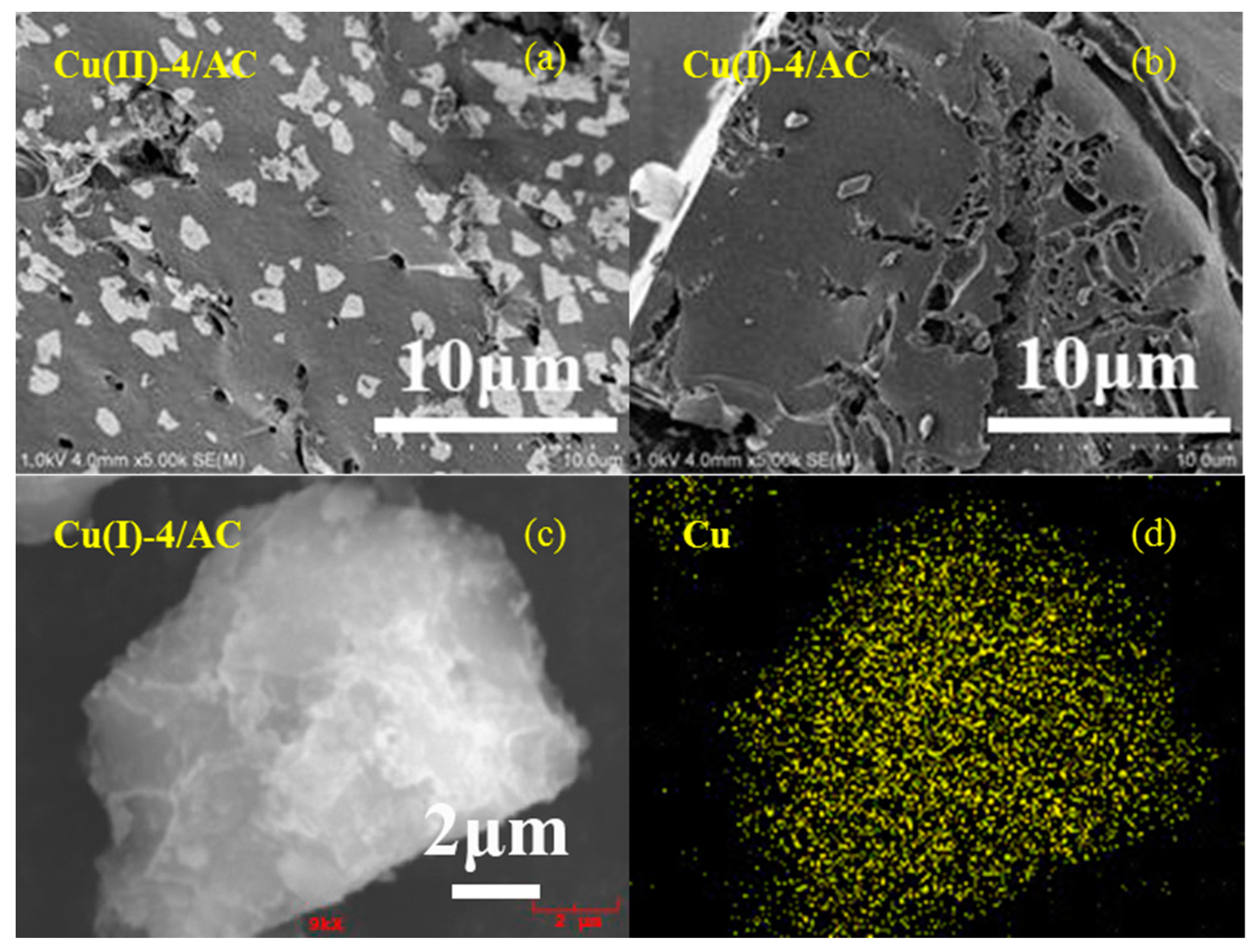
Figure 2a,b show the representative SEM images of the copper loaded AC samples before and after activation. It can be clearly observed that the particles of copper species present on the AC surface for the Cu(II)-4/AC. However, the particles on the AC surface disappeared after activation, which implies that the activation process contributes to the CuCl dispersion on the AC surface. Figure 2c,d show selected-area and the element mapping analyses of Cu(I)-4/AC. It revealed that the copper particles are uniformly dispersed on the AC surface. The good dispersion of CuCl on Cu(I)-4/AC observed by SEM agreed well with the XRD results in Figure 1.
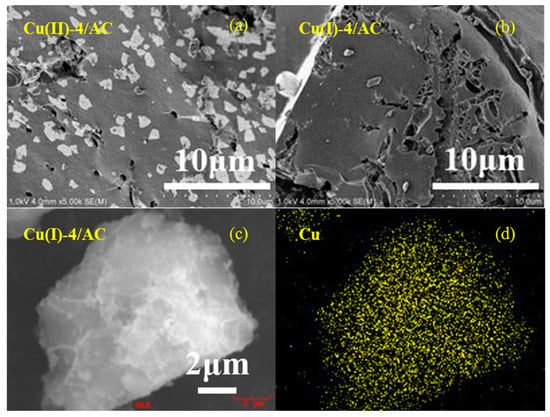
Figure 2.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of Cu(II)-4/AC (a), Cu(I)-4/AC (b), and selected-area element mapping analyses of Cu(I)-4/AC (c,d).
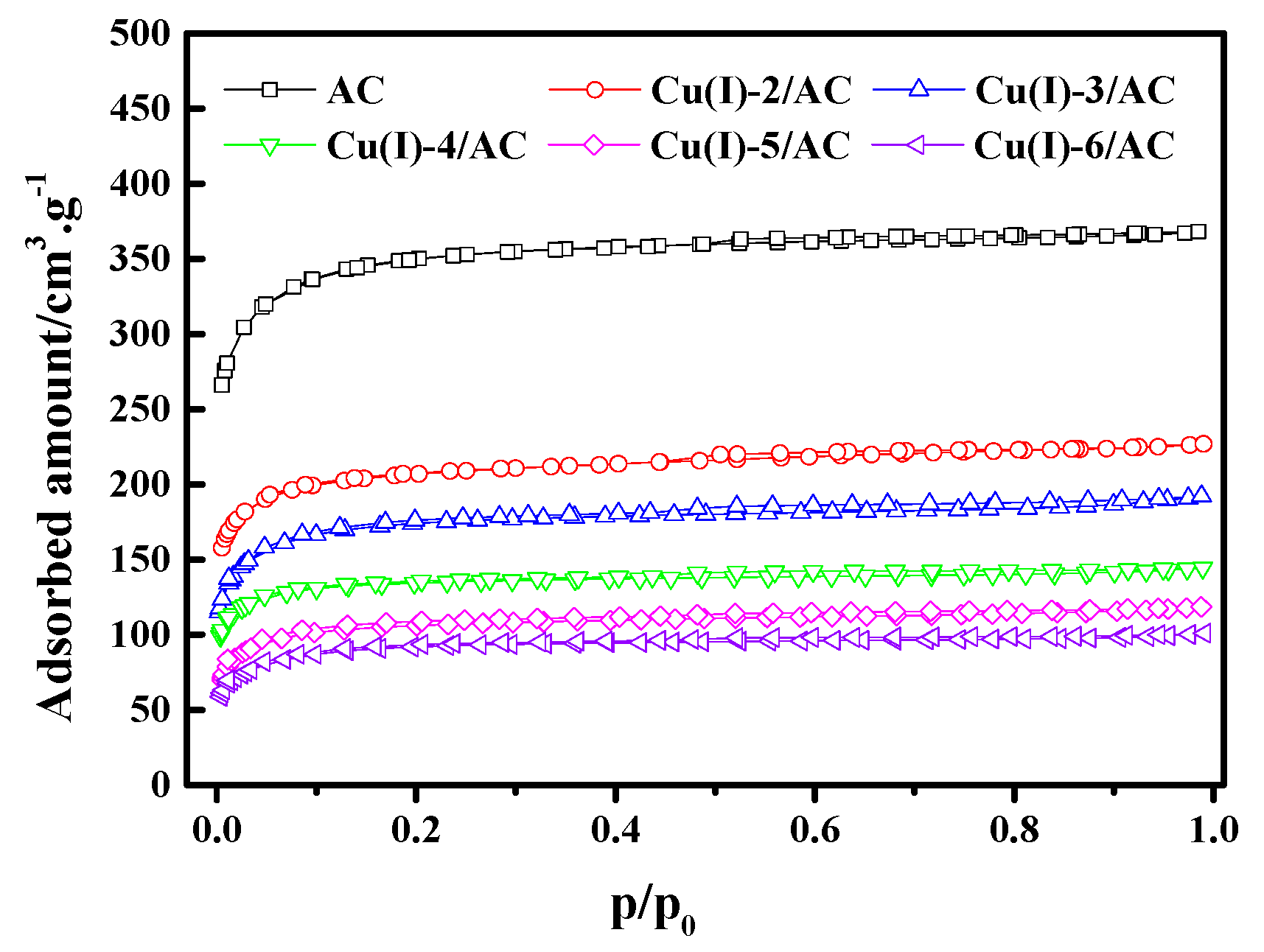
Figure 3 shows the N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms of the Cu(I)-x/AC samples at 77 K. The N2 adsorption gradually decreased with increasing CuCl loading. Table 1 lists the textural parameters of AC and Cu(I)-x/AC. It can be observed that the total pore volume (VTotal) and BET surface area (SBET) gradually decreased with the increase of CuCl loading, indicating that CuCl had been loaded into the pores of the parent AC. As the CuCl loading increased, more and more surface within the pores were occupied by CuCl, which may result in a further decrease of VTotal and SBET. As CuCl was well dispersed on the surface of AC when the CuCl loading was below 4 mmol/g, the average pore sizes decreased with the increase of CuCl loading. Smaller pores were filled with the further increase of the CuCl loading. Therefore, the increased average pore size resulted from the percentage increase of the available larger pores in AC, which is similar to the observation by Ramli et al. [37].
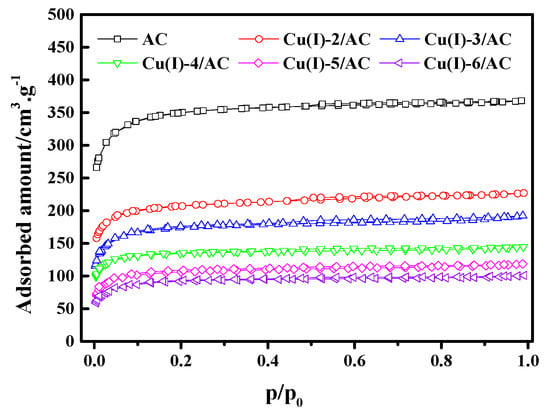
Figure 3.
N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms of Cu(I)-x/AC.

Table 1.
The parameters of pore structure, loading and utilization coefficient of CuCl for Cu(I)-x/activated carbon (AC).
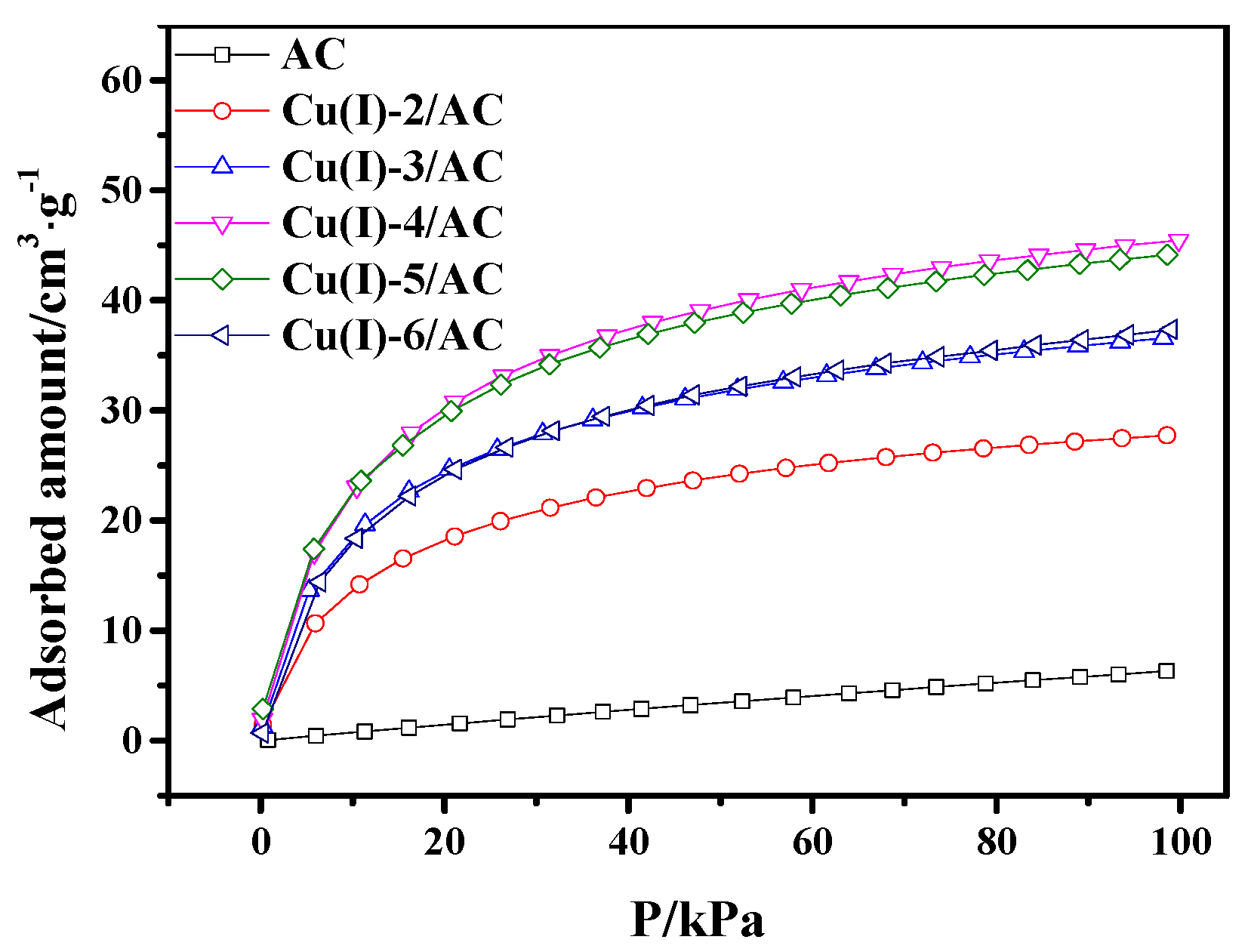
It can be observed from Figure 4 that the CO adsorption capacity of CuCl/AC increased with CuCl loading in the range of 0 to 4 mmol·g−1. The maximum value of adsorption capacity was 45.4 cm3·g−1. With the continuous increase of the CuCl loading, the CO adsorption capacity of CuCl/AC with the copper loading of 5 mmol·g−1 was almost the same as that with 4 mmol·g−1. The decrease of CO adsorption occurred with further increasing the copper loading to 6 mmol·g−1. This phenomenon can be ascribed to the following reason. The more copper loaded, the more active sites of CuCl/AC adsorbents present, which would enhance CO adsorption. However, the increase of copper loading also resulted in a decrease of surface area for CuCl/AC adsorbents, as shown in Table 1. As a result, the increase of the adsorbed amount from the increased active sites and the decrease of adsorbed amount from the decrease of surface area were in a dynamic balance in the copper loading range of 4 to 5 mmol·g−1. When the copper loading reached 6 mmol·g−1, on the one hand, the amount of adsorbed CO decreased because the decrease of surface area; on the other hand, the Cu(I) started to agglomerate on AC surface with considerable copper loading, resulting in the low utilization of active sites.
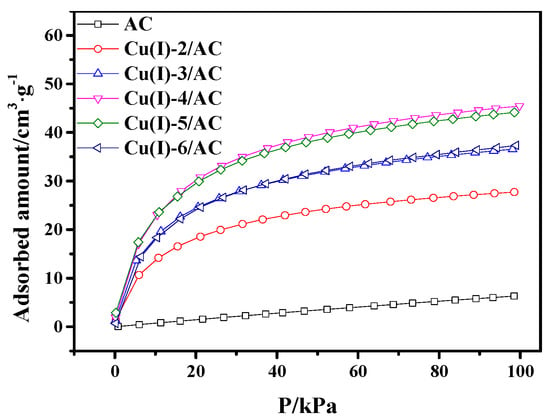
Figure 4.
CO adsorption isotherms on AC and Cu(I)-x/AC at 298 K.
In addition, Table 1 lists the measured Cu contents with ICP-OES, which are closely approximate to the values in the raw material. The utilization coefficient of surface CuCl is described from the equation:
where is the utilization coefficient of CuCl, is the actual CO adsorption capacity at 298 K and 100 kPa, is the mole of CuCl per gram CuCl/AC adsorbent. According to this equation, the utilization coefficients were calculated and presented in Table 1. It can be seen that the utilization coefficient decreased with the increasing of CuCl loading, which means that the high CuCl loading on AC could not guarantee high utilization of CuCl, since not all Cu(I) species can be utilized.
3.2. Adsorption Selectivities of CO to CO2, CH4, and N2
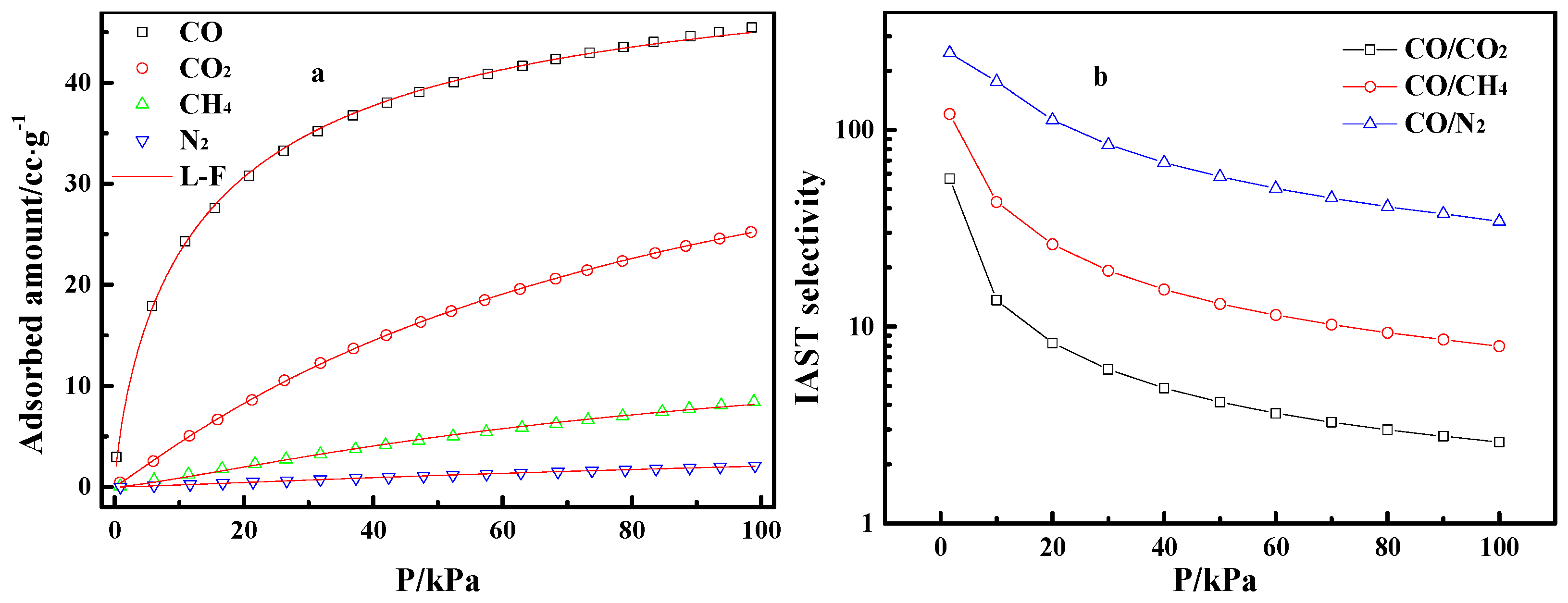
Figure 5a gives the adsorption isotherms of pure CO, CO2, CH4, and N2 on Cu(I)-4/AC in the pressure range of 0 to 100 kPa. The adsorption of CO2, CH4, and N2 on Cu(I)-4/AC increased almost linearly with pressure, while the adsorption isotherm of CO on Cu(I)-4/AC presented a type-Ι isotherm [38], that is the CO adsorption increased sharply with pressure at a low pressure range, implying the adsorption of relatively strong CO-Cu(I) π-complexation, which is propitious to separate CO from CO/CO2/CH4/N2 mixed gas.
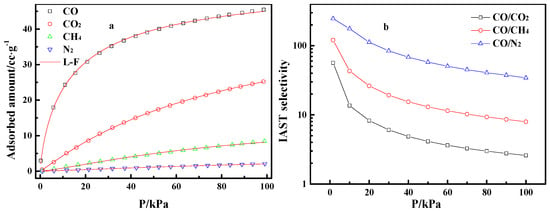
Figure 5.
Adsorption isotherms of CO, CO2, CH4, and N2 on Cu(I)-4/AC and Langmuir–Freundlich (L-F) fitting lines (a), and ideal adsorbed solution theory (IAST)-predicted adsorption selectivities (b).
The Langmuir–Freundlich (L-F) model and IAST were employed together to calculate the CO/CO2, CO/CH4, and CO/N2 selectivities with the equimolar CO/CO2, CO/CH4, and CO/N2 mixture. The L-F model can be expressed as
where is the adsorbed amount, is the pressure and is the saturation adsorbed amount, is the adsorption affinity and is the corresponding deviation from the Langmuir isotherm.
First, the adsorption isotherm of pure CO, CO2, CH4, and N2 were fitted by the L-F model [38]. After that, the CO/CO2, CO/CH4, and CO/N2 selectivities were predicted by IAST theory [39,40]. Finally, the relevant selectivities curves along with the increase of pressure were obtained. Figure 5b shows that the CO/CO2, CO/CH4, and CO/N2 selectivities decrease gradually with increasing pressure. Nevertheless, the CO/CO2, CO/CH4, and CO/N2 selectivities on Cu(I)-4/AC were still up to 2.6, 8.0, and 34.3 at 100 kPa, respectively, which suggests that it has the potential for the effective separation of CO from the gas mixtures. Table 2 lists the benchmark materials for CO adsorption. Cu(I) adsorbents have higher adsorption capacity than the conventional porous adsorbent. The Cu(I)-4/AC adsorbent prepared in this study has relatively high CO/CO2 selectivity among the selected adsorbents.

Table 2.
Comparisons with adsorbents in the literature.
3.3. Isosteric Heat of Adsorption
Isosteric heat of adsorption is a significant thermodynamic parameter to characterize the interaction between the adsorbate and the adsorbent and to design a gas adsorption separation process, which can be calculated by Clausius–Clapeyron equation [41] as
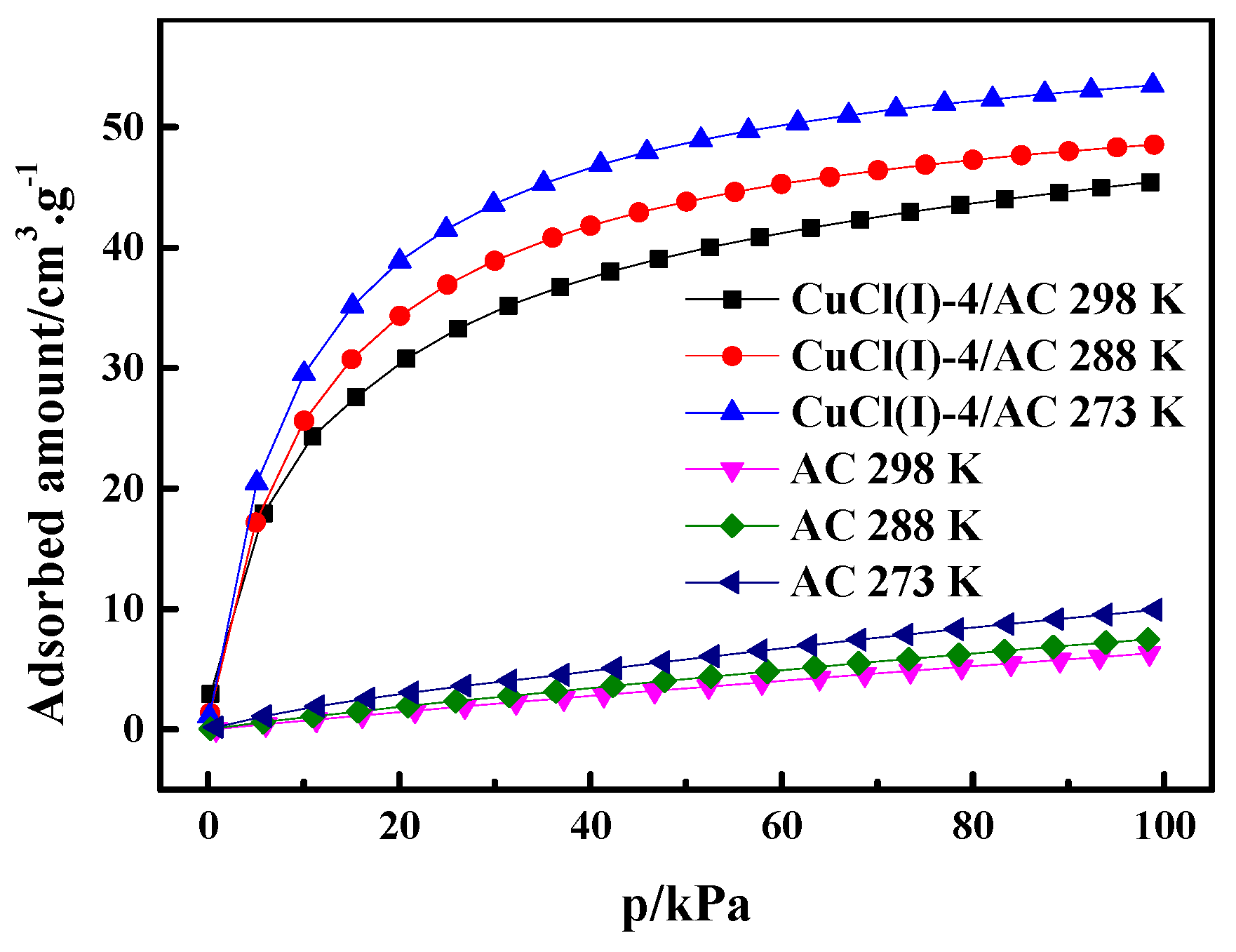
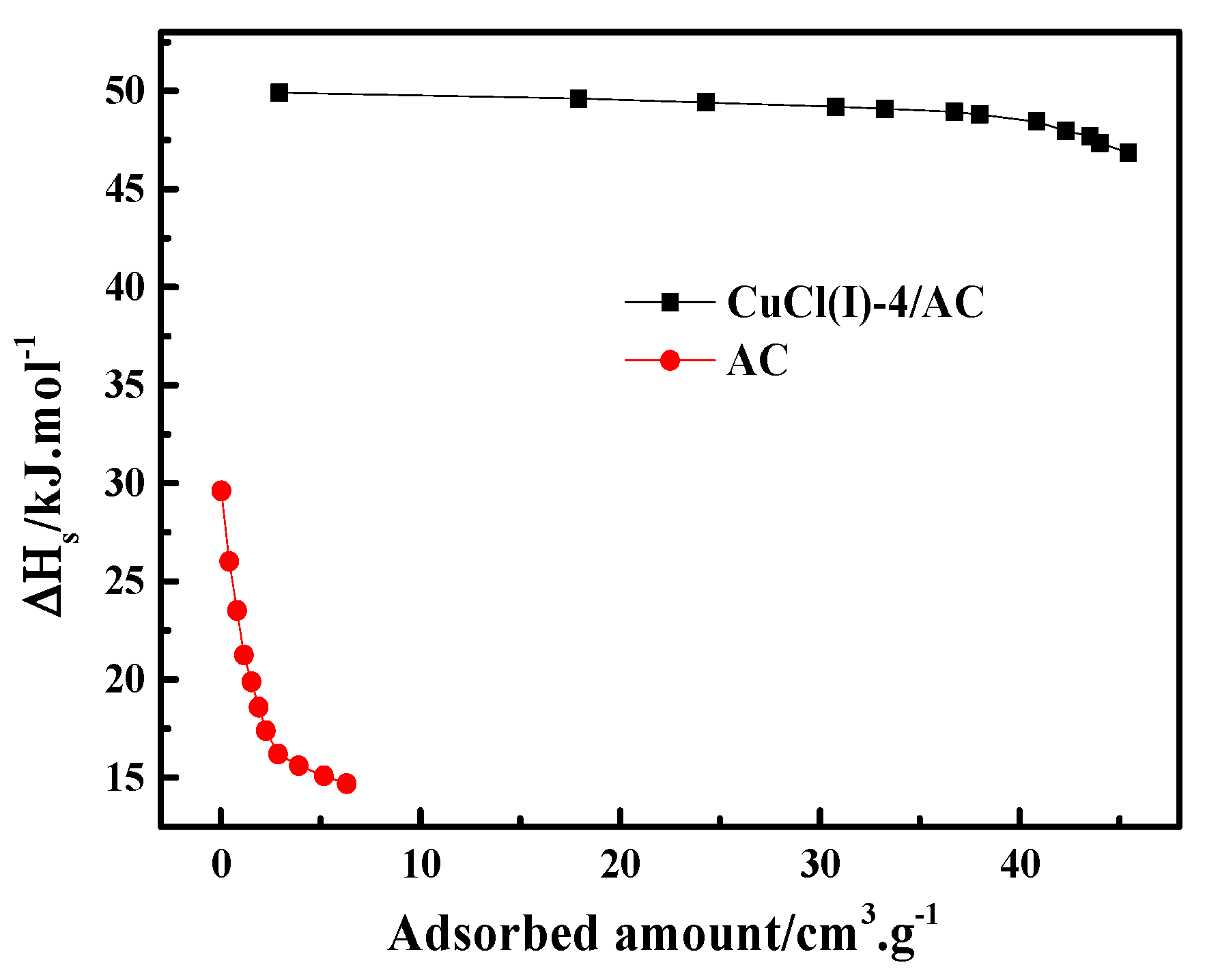
where is the pressure, is the ideal gas constant, is the experimental temperature, is the adsorption amount, and is the isosteric heat of adsorption. In this work, the experimental isotherms and the L-F model predicted isotherms of CO at different temperatures of 273 K, 293 K, and 298 K (as shown in Figure 6) were used to calculate of CO adsorption on AC and Cu(I)-4/AC. The conventional Langmuir–Freundlich (L-F) adsorption model correlated the experimental results and the fitting parameters, which are listed in Table 3. The experimental data fit well with L-F model, as can be seen by the high values of R2 (the coefficient of the experimental data and the fitting data). can be derived from the slopes of the plots of versus at given adsorption amounts, as shown in Figure 7. It was shown that the isosteric heats of CO adsorption on Cu(I)-4/AC are remarkably much higher than those on AC. The result indicates that the π-complexation interaction between CO and Cu(I) is stronger than the van der Waals interaction of CO with the parent adsorbent. Usually, is <20 kJ·mol−1 for common physical adsorption and >80 kJ·mol−1 for chemical adsorption [42]. The values of on Cu(I)-4/AC maintained around 50 kJ·mol−1 in the whole pressure range, suggesting that the strength of complex adsorption is between physisorption and chemisorption. Such isosteric heat is not only propitious to adsorb CO, but also liable to desorb CO with a normal engineering operations (evidence as shown in Figure 9).
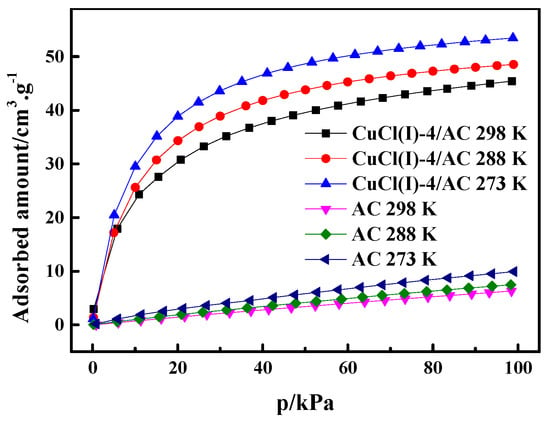
Figure 6.
CO adsorption isotherms of AC and Cu(I)-4/AC at 273 K, 288 K, and 298 K.

Table 3.
Langmuir–Freundlich (L-F) fitting parameters of CO isotherms on AC and Cu(I)-4/AC.
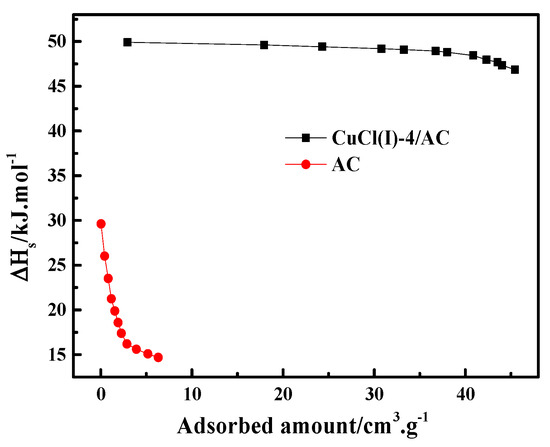
Figure 7.
Isosteric heats of AC and Cu(I)-4/AC as the function of the adsorbed amount of CO.
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics of CO
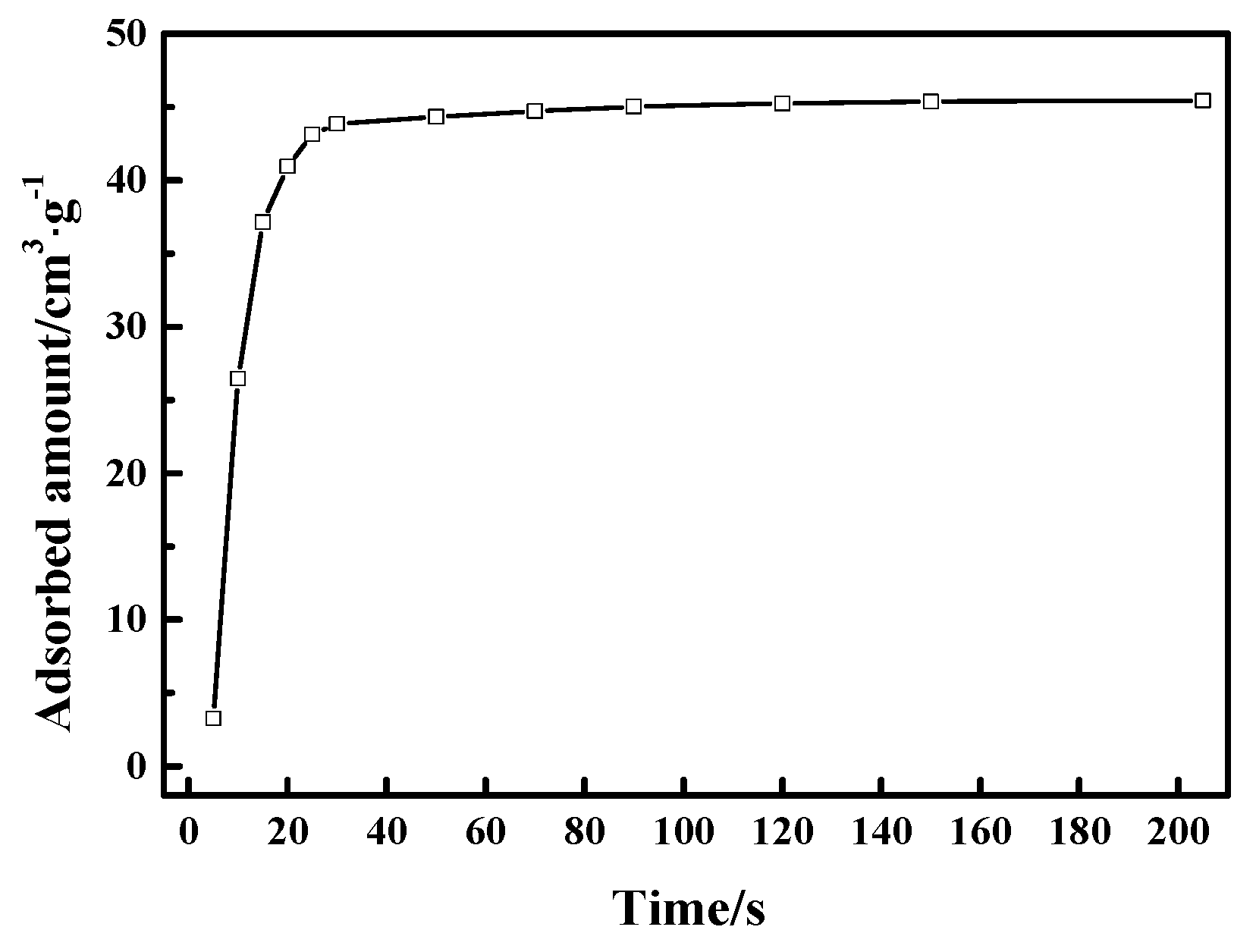
In addition, it is also crucial that the CO adsorption rate need to be quite rapid for potential applications of CuCl/AC adsorbent in the adsorption-driven separation of CO from gas mixtures containing CO, CO2, CH4, and N2. Typically, the requirement of the adsorption process in industrial applications is shorter than 1 min [43]. Here, we studied the time-dependent adsorption of CO on Cu(I)-4/AC adsorbent by releasing a small amount of CO and studying the adsorbed amount as a function of time as shown in Figure 8. Cu(I)-4/AC showed a relatively rapid adsorption rate, which reached 96% of the CO capacity within 25 s. The rapid CO adsorption rate suggests that Cu(I)-4/AC can meet the requirements for industrial application of adsorbent to separate CO from gas mixtures containing CO, CO2, CH4, and N2 in a PSA process.
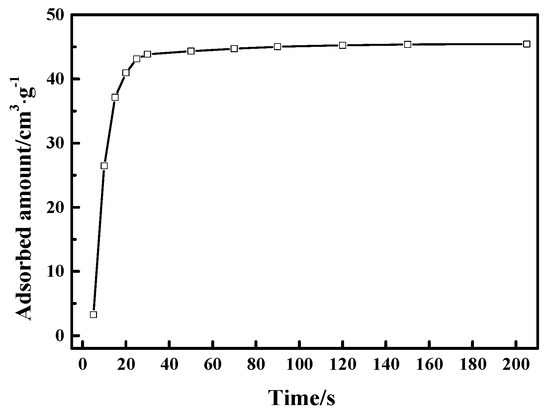
Figure 8.
Uptake kinetics for Cu(I)-4/AC at 298 K.
3.5. Cycle Adsorption of CO on Cu(Ι)/AC
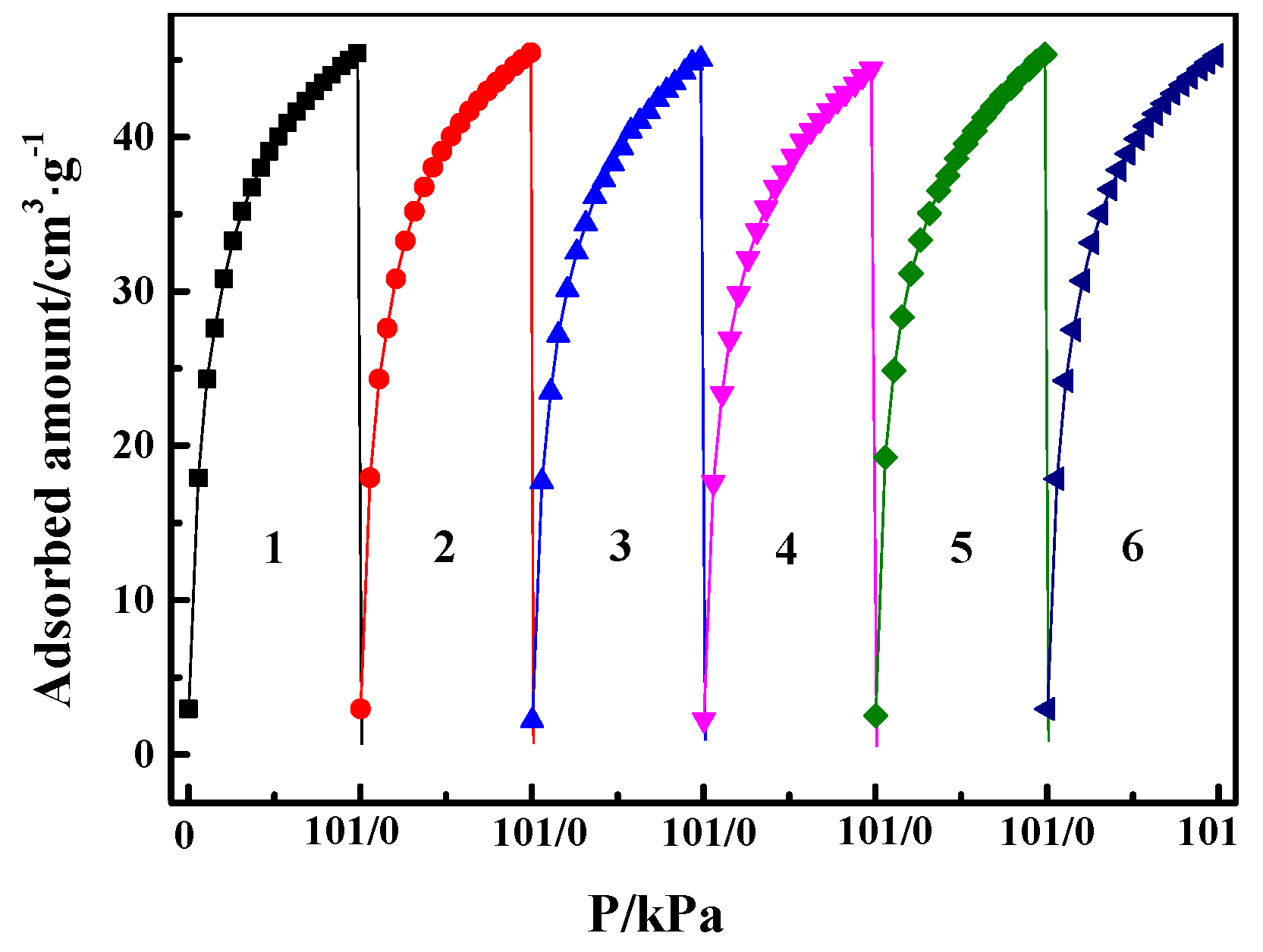
In the actual processes of gas separation, an ideal adsorbent not only needs to have high adsorption capacity and high selectivity but also needs to exhibit a stable cyclic adsorption performance in long-term adsorption/desorption cyclical operation. The pure CO cyclical adsorption/desorption isotherm at 298 K was evaluated for six times (The degassing between each cycle was carried out at 353 K under vacuum). As shown in Figure 9, the maximum amount of CO adsorption was reduced by about 1.3% after six cycles of adsorption and desorption, suggesting that the CO adsorption process using CuCl/AC adsorbent is stable under the investigated conditions. Its stable adsorption behavior indicates that the CuCl/AC has broad application prospects in selective adsorption of CO. It must be noted that the parent gases for the separation of CO must be pretreated to remove moisture in industrial processes, since the Cu(Ι) in the CuCl/AC can be oxidized to Cu(II) in the form of copper chloride once in contact with water vapor and O2 (especially under light condition [44,45]), which then cannot form complexation with CO.
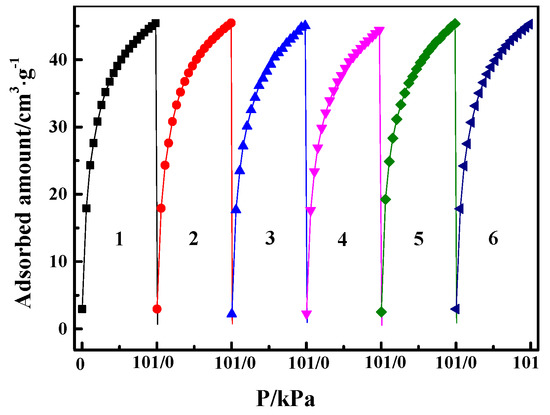
Figure 9.
Adsorption and desorption cycles for CO at 298 K on Cu(I)-4/AC (the degassing between each cycle was carried out at 353 K under vacuum).
4. Conclusions
CuCl/AC adsorbents for the separation of CO have been successfully obtained using CuCl2 and Cu(HCOO)2 as the initial material by a solid-state auto dispersion method. CuCl2 and Cu(HCOO)2 can be transformed into highly dispersed CuCl with activation at 533 K under vacuum atmosphere. The CO adsorption capacity increased with transformed CuCl loading until 4 mmol·g−1 and then decreased afterward. The CO adsorption capacity of Cu(I)-4/AC achieved 45.4 cm3·g−1, and the CO/CO2, CO/CH4, and CO/N2 selectivities were up to 2.6, 8.0, and 34.3 at 100 kPa, respectively. In addition, the isosteric heat of adsorption on Cu(I)-4/AC was about 50 kJ·mol−1. The CO adsorption capacity almost remains constant during six times cyclical adsorption and rapid adsorption kinetics at the adsorption process. Those excellent properties of Cu(I)-4/AC adsorbent would make it a promising adsorbent for CO separation and purification.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M.; methodology, C.X. and J.M.; formal analysis, C.X., W.H. and W.C.; resources, R.L.; data curation, W.C.; writing—original draft preparation, C.X.; writing—review and editing, W.H.; supervision, J.M.; funding acquisition, J.M. and R.L.
Funding
This research was funded by Key Scientific and Technological Project of coal fund of Shanxi province (No.FT201402-03) and Shanxi Provincial Key Innovative Research Team in Science and Technology (No.2014131006).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Key Scientific and Technological Project of coal fund of Shanxi province (No.FT201402-03) and Shanxi Provincial Key Innovative Research Team in Science and Technology (No.2014131006).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Saha, D.; Deng, S. Adsorption equilibria and kinetics of carbon monoxide on zeolite 5A, 13X, MOF-5, and MOF−177. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.F.; Fang, X.; Wu, L.; Jackstell, R.; Neumann, H.; Beller, M. Transition-metal-catalyzed carbonylation reactions of olefins and alkynes: A personal account. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1041–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymans, N.; Alban, B.; Moreau, S.; De Weireld, G. Experimental and theoretical study of the adsorption of pure molecules and binary systems containing methane, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and nitrogen. Application to the syngas generation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 3850–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlacher, T.; Melin, T.; Wessling, M. Techno-economic analysis of membrane-based argon recovery in a silicon carbide process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10460–10466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarca, G.; Ortiz, I.; Urtiaga, A. Kinetics of the carbon monoxide reactive uptake by an imidazolium chlorocuprate (I) ionic liquid. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Selective CO adsorbent CuCl/AC prepared using CuCl2 as a precursor by a facile method. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 34439–34446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCoste, J.B.; Peterson, G.W. Metal–organic frameworks for air purification of toxic chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5695–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, L.C.; Koski, P.; Ihonen, J.; Sousa, J.M.; Mendes, A. Effect of fuel utilization on the carbon monoxide poisoning dynamics of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2014, 258, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, E.L.; Wilhite, B.A. Composite catalytic-permselective membranes: Modeling analysis for H2 purification assisted by water–gas-shift reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 207, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Yan, T.; Sun, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.B. Titanium-decorated graphene oxide for carbon monoxide capture and separation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 21126–21131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethia, G.; Patel, H.A.; Pawar, R.R.; Bajaj, H.C. Porous synthetic hectorites for selective adsorption of carbon dioxide over nitrogen, methane, carbon monoxide and oxygen. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 91, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethia, G.; Somani, R.S.; Bajaj, H.C. Adsorption of carbon monoxide, methane and nitrogen on alkaline earth metal ion exchanged zeolite-X: Structure, cation position and adsorption relationship. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12773–12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.V.S.; Grande, C.A.; Ribeiro, A.M.; Loureiro, J.M.; Evaggelos, O.; Nikolakis, V.; Rodrigues, A.E. Adsorption of H2, CO2, CH4, CO, N2 and H2O in activated carbon and zeolite for hydrogen production. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1045–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.A.; Águeda, V.I.; Uguina, M.A.; Sotelo, J.L.; Brea, P.; Grande, C.A. Adsorption and diffusion of H2, CO, CH4, and CO2 in BPL activated carbon and 13X zeolite: Evaluation of performance in pressure swing adsorption hydrogen purification by simulation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 15414–15426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos-Neto, M.; Moeller, A.; Staudt, R.; Böhm, J.; Gläser, R. Dynamic bed measurements of CO adsorption on microporous adsorbents at high pressures for hydrogen purification processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 77, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, C.A.; Lopes, F.V.S.; Ribeiro, A.M.; Loureiro, J.M.; Rodrigues, A.E. Adsorption of off-gases from steam methane reforming (H2, CO2, CH4, CO and N2) on activated carbon. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 1338–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutaya, H.; Izumi, J. Carbon monoxide adsorption by zeolite. Zeolites 1991, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakarova, K.; Hadjiivanov, K. H-bonding of zeolite hydroxyls with weak bases: FTIR study of CO and N2 adsorption on HD-ZSM-5. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 4806–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.; Mekala, S.; Dreisbach, F.; Gumma, S. Adsorption of CO, CO2 and CH4 on Cu-BTC and MIL−101 metal organic frameworks: Effect of open metal sites and adsorbate polarity. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2012, 152, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Mekala, S.; Dreisbach, F.; Mandal, B.; Gumma, S. Adsorption of CO2, CO, CH4 and N2 on a zinc based metal organic framework. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 94, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Xian, S.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, Z. A supported Cu(I)@MIL−100 (Fe) adsorbent with high CO adsorption capacity and CO/N2 selectivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Selective adsorption of CO on CuCl/Y adsorbent prepared using CuCl2 as precursor: Equilibrium and thermodynamics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal and separation of chemicals with metal-organic frameworks: Contribution of π-complexation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Yoon, T.U.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, A.R.; Jung, T.S.; Han, S.S.; Bae, Y.S. Highly selective adsorption of CO over CO2 in a Cu(I)-chelated porous organic polymer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.J.; Yin, Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Yin, X.Q.; Shi, Y.Q.; Sun, L.B. Fabrication of supported cuprous sites at low temperatures: An efficient, controllable strategy using vapor-induced reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8137–8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Kim, J.; Beum, H.T.; Jung, T.; Han, S.S. Synthesis of CuCl/Boehmite adsorbents that exhibit high CO selectivity in CO/CO2 separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, R.T.; Heinzel, J.M. Desulfurization of jet fuel by π-complexation adsorption with metal halides supported on MCM-41 and SBA−15 mesoporous materials. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Wada, K.; Komiyama, M. Active carbon-supported copper (I) chloride as solid adsorbent for carbon monoxide. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1986, 59, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Wada, K.; Kurima, K.; Komiyama, M. Carbon monoxide adsorbent composed of copper (I) chloride and polystyrene resin having amino groups. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1986, 59, 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamon, H.; Kitamura, K.; Okazaki, M. Adsorption of carbon monoxide on activated carbon impregnated with metal halide. AIChE J. 1996, 42, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, J.; Tong, X.; Fu, J.; Yang, G.; Yan, H.; Tang, Y. Zeolites modified by CuCl for separating CO from gas mixtures containing CO2. Adsorption 1997, 3, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, L.; Ren, J.; Li, R. CO adsorption on activated carbon-supported Cu-based adsorbent prepared by a facile route. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 76, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas, D.M.; La Iglesia, V.M.; Cano, E.; Fajardo, S.; Bastidas, J.M. Kinetic study of formate compounds developed on copper in the presence of formic acid vapor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, C578–C582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powder Diffraction File (PDF) Database; International Centre for Diffraction Data: Swarthmore, PA, USA, 1988.
- Zhong, L.; Ruiyu, W.; Huayan, Z.; Kechang, X. Preparation of CuIY catalyst using CuCl2 as precursor for vapor phase oxidative carbonylation of methanol to dimethyl carbonate. Fuel 2010, 89, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, C.; Li, Y.; Song, C.; Bolin, T.B. Sulfur poisoning mechanism of steam reforming catalysts: An X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectroscopic study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 5707–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, N.A.S.; Amin, N.A.S. Fe/HY zeolite as an effective catalyst for levulinic acid production from glucose: Characterization and catalytic performance. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 163, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhou, X.; Xia, Q.; Peng, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Z. Preparation and adsorption performance of GrO@Cu-BTC for separation of CO2/CH4. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 11176–11184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnowski, N.B.K.; Avila, A.M.; Lin, C.C.H.; Shi, M.; Kuznicki, S.M. Extraction of ethane from natural gas by adsorption on modified ETS−10. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 1697–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.L.; Prausnitz, J.M. Thermodynamics of mixed-gas adsorption. AIChE J. 1965, 11, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.L. Statistical mechanics of adsorption. V. Thermodynamics and heat of adsorption. J. Chem. Phys. 1949, 17, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Schmitt, J.; Chen, Z.; Liang, L.; McCarthy, J.F. Adsorption and desorption of natural organic matter on iron oxide: Mechanisms and models. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Björkman, E.; Lilliestråle, M.; Hedin, N. Activated carbons prepared from hydrothermally carbonized waste biomass used as adsorbents for CO2. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, B.; Wettermark, G. Optical properties of metallic copper in relation to the photochromic system CuCl(s) H2O(l). J. Photochem. 1976, 5, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, B.; Wettermark, G. The photochromic properties of the system CuCl(s)H2O(l) in relation to the composition of the aqueous solution. J. Photochem. 1979, 11, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).