Application of a Bioactive/Bioresorbable Three-Dimensional Porous Uncalcined and Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/Poly-d/l-lactide Composite with Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Bone Regeneration in Maxillofacial Surgery: A Pilot Animal Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The 3D-HA/PDLLA Composite Scaffold
2.2. Preparation of Human Bone Marrow MSCs
2.3. The Critical Mandibular Defect Rat Model
2.4. Microcomputed Tomography (Micro-CT) Analysis
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Micro-CT Analysis
3.1.1. Image Description
3.1.2. Material–Host Bone Combinations and the Quantity of Newly Formed Osteoid Tissue
3.1.3. Difference in Osteogenesis between the Superior and Inferior Sides of the Critical Mandibular Defect
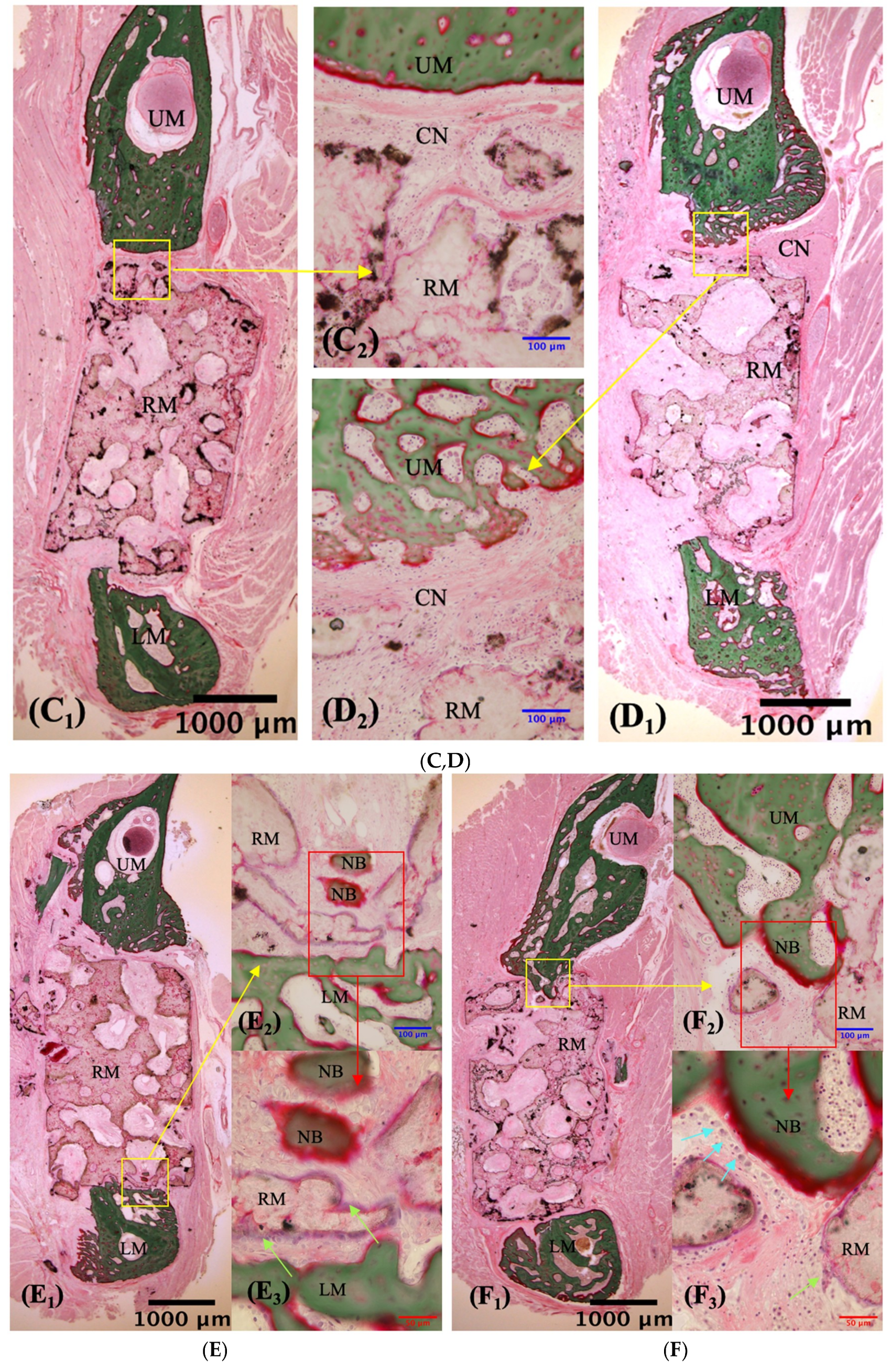
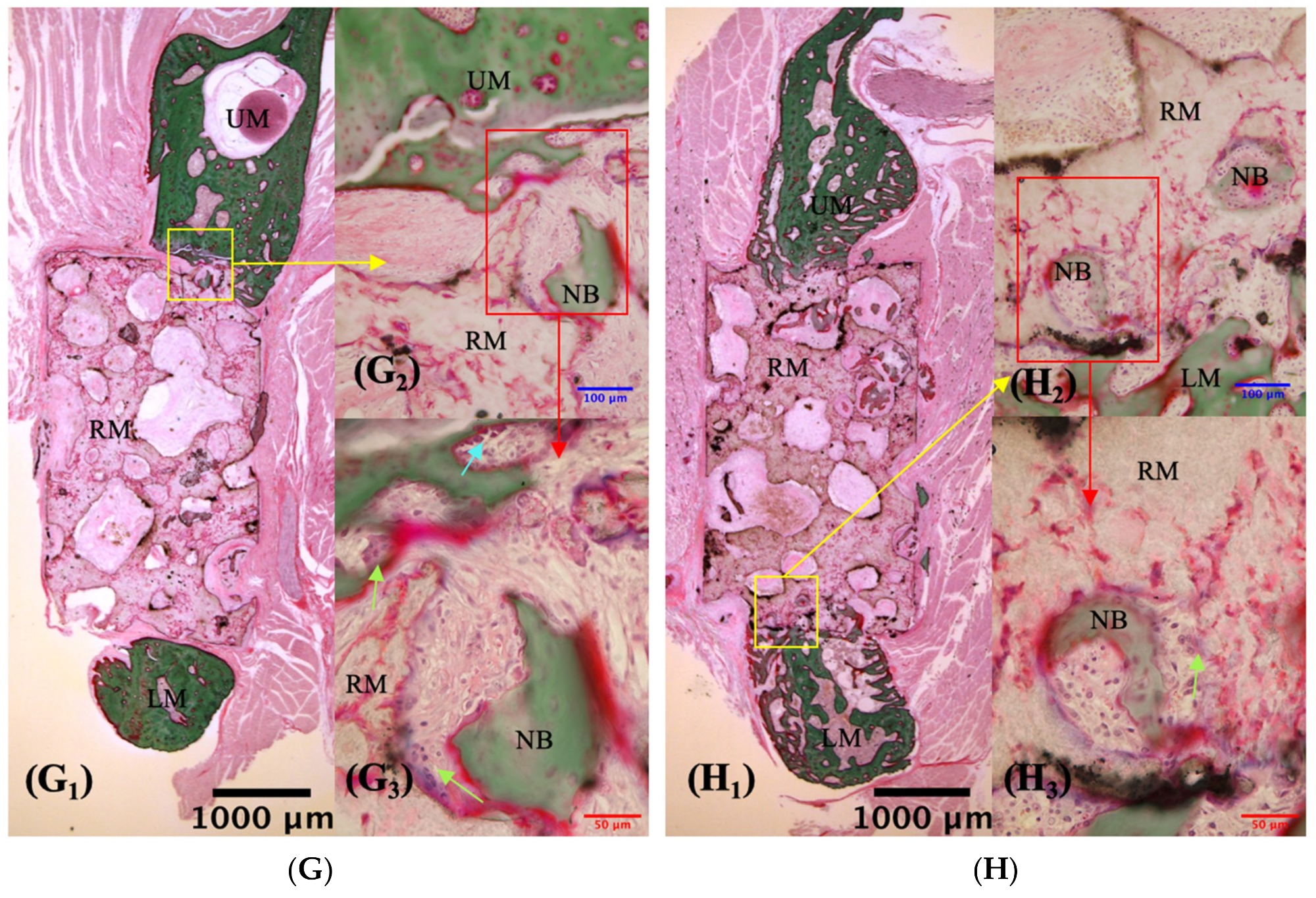
3.2. VG Staining Results
3.2.1. Description of VG Staining
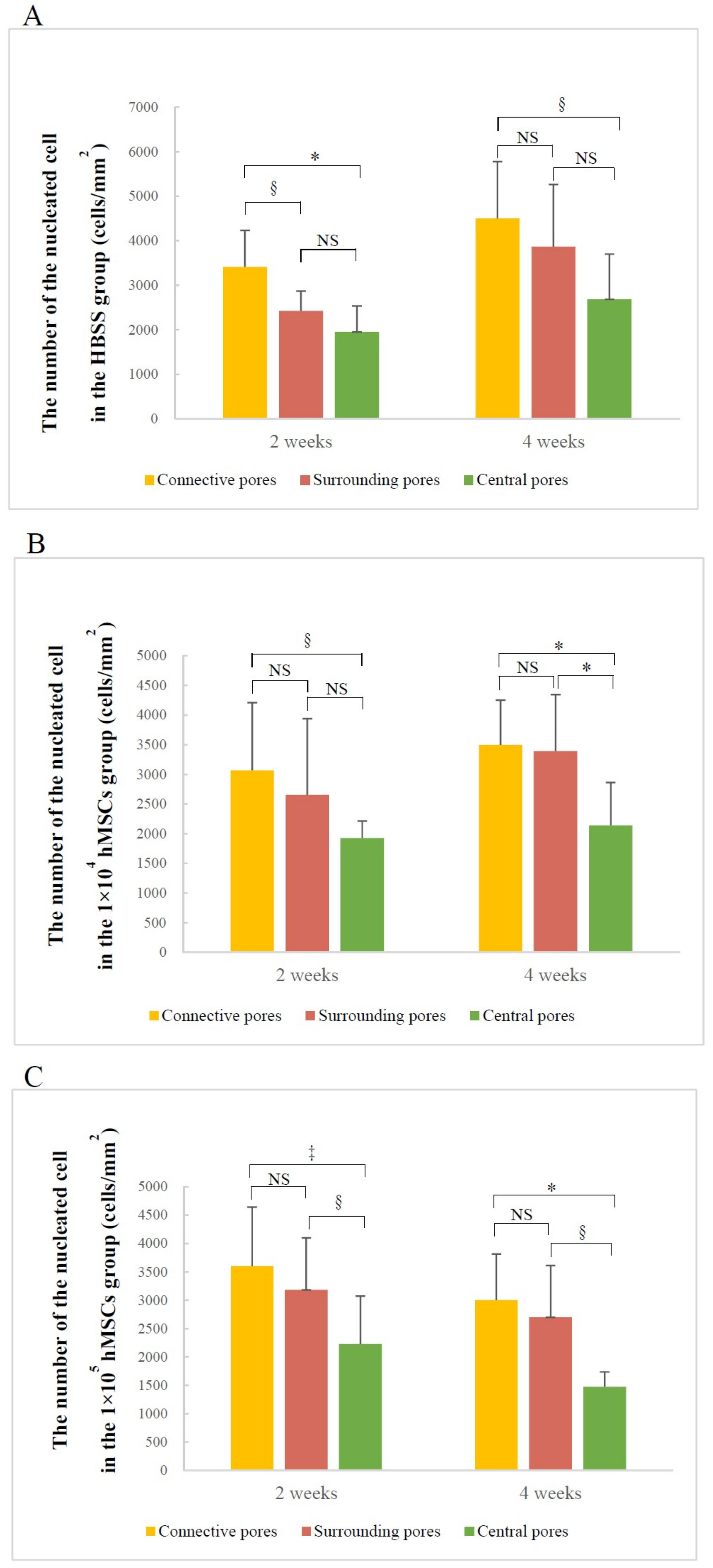
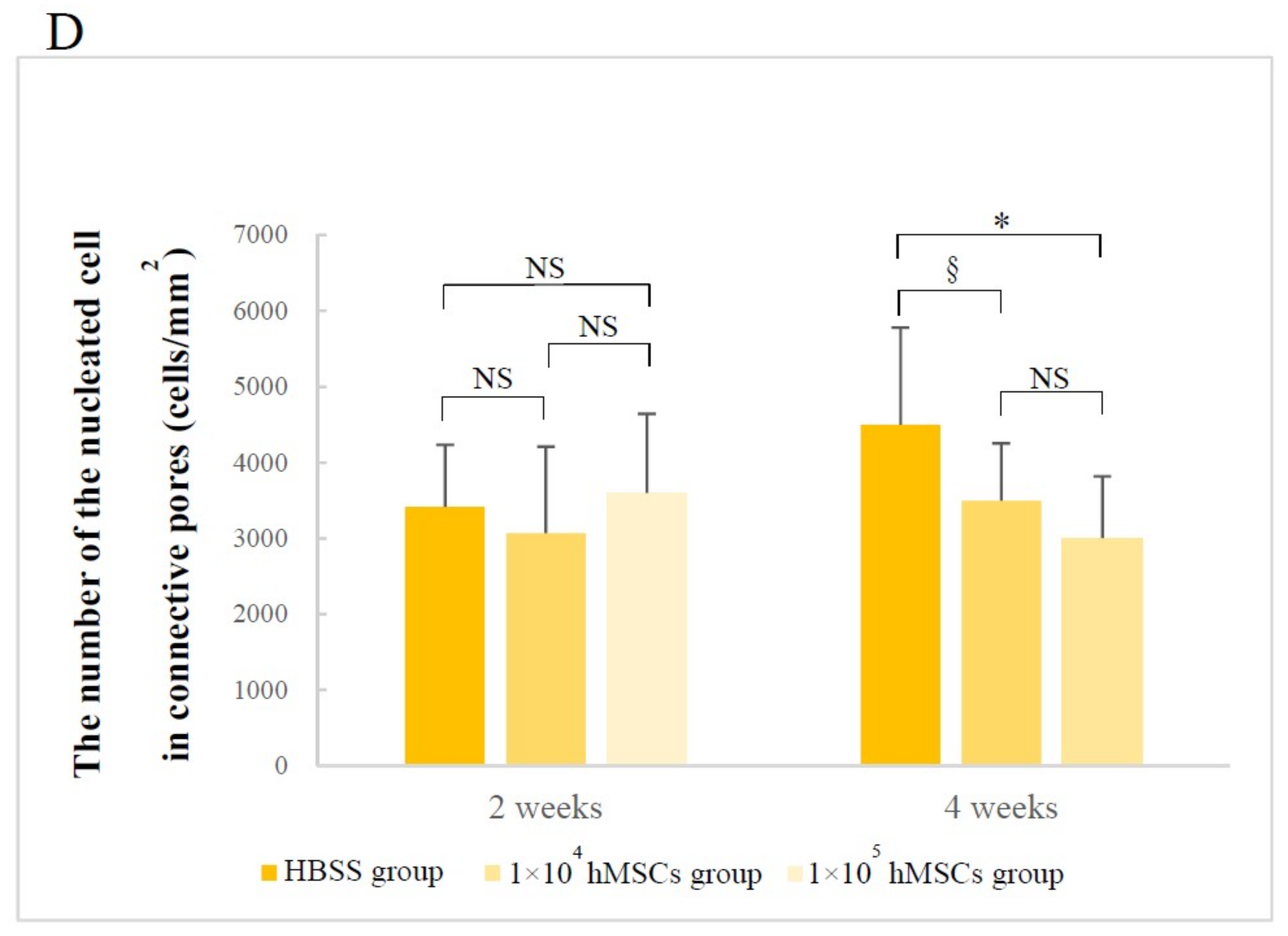
3.2.2. Number of Nucleated Cells in Different Pore Areas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | three-dimensional; |
| 3D-HA/PDLLA | three-dimensional porous uncalcined and unsintered hydroxyapatite/poly-d/l-lactide; |
| MSCs | mesenchymal stem cells; |
| hMSCs | human mesenchymal stem cells; |
| β-TCP | β-tricalcium phosphate |
| BMA | bone marrow aspirate |
| CD90 | Thy-1, cluster of differentiation 90 |
| CD271 | low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor |
| MECs | moderately expanding mesenchymal stem cell clones |
| u-HA | uncalcined and unsintered hydroxyapatite |
| PDLLA | poly-d/l-lactide |
| Mv | viscosity-average molecular weight |
| d/l | dextrorotatory-lactide acid/levorotatory-lactide acid |
| Ca/P | calcium/phosphorus |
| HBS | Hank’s balanced salt solution |
| SD | Sprague Dawley |
| Micro-CT | microcomputed tomography |
| VG staining | Villanueva Goldner staining |
| PLA | polylactic acid |
| PLLA | poly-l-lactide |
| PDLA | poly-d-lactide |
| d | dextrorotatory |
| l | levorotatory |
| HIF2A | hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha |
| Runx2 | runt-related transcription factor 2 |
References
- Zhang, B.; Li, K.Y.; Jiang, L.C.; Meng, Z.; Wang, X.M.; Cui, F.Z.; Zhu, Y.N.; Wu, Y.P. Rib Composite Flap with Intercostal Nerve and Internal Thoracic Vessels for Mandibular Reconstruction. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2016, 27, 1815–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torroni, A.; Marianetti, T.M.; Romandini, M.; Gasparini, G.; Cervelli, D.; Pelo, S. Mandibular Reconstruction with Different Techniques. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2015, 26, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felice, P.; Barausse, C.; Barone, A.; Zucchelli, G.; Piattelli, M.; Pistilli, R.; Ippolito, D.R.; Simion, M. Interpositional Augmentation Technique in the Treatment of Posterior Mandibular Atrophies: A Retrospective Study Comparing 129 Autogenous and Heterologous Bone Blocks with 2 to 7 Years Follow-Up. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2017, 37, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, R.; Vacanti, J.P. Tissue Engineering. Science 1993, 80, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampieri, A.; Sandri, M.; Landi, E.; Pressato, D.; Francioli, S.; Quarto, R.; Martin, I. Design of Graded Biomimetic Osteochondral Composite Scaffolds. Biomaterials 2008, 2, 3539–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, E.; Filardo, G.; Perdisa, F.; Venieri, G.; Marcacci, M. Clinical Results of Multilayered Biomaterials for Osteochondral Regeneration. J. Exp. Orthop. 2014, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akino, N.; Tachikawa, N.; Munakata, M.; Kasugai, S. The Use of Porous Composite Uncalcined Hydroxyapatite/Poly-DL-Lactide for Vertical Ridge Augmentation. J. Oral Tissue Eng. 2013, 10, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikinami, Y.; Okazaki, K.; Saito, M.; Okuno, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Tamura, J.; Fujibayashi, S.; Nakamura, T. Bioactive and Bioresorbable Cellular Cubic-Composite Scaffolds for Use in Bone Reconstruction. J. R. Soc. Interface 2006, 3, 805–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, S.; Tamura, J.; Neo, M.; Goto, K.; Shikinami, Y.; Saito, M.; Kita, M.; Nakamura, T. In Vivo Evaluation of a Porous Hydroxyapatite/Poly-DL-Lactide Composite for Use as a Bone Substitute. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2005, 75, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, H.; Ochi, H.; Soeta, S.; Kanno, N.; Yoshihara, M.; Okazaki, K.; Yogo, T.; Harada, Y.; Amasaki, H.; Hara, Y. A Comparison of the Process of Remodeling of Hydroxyapatite/Poly-D/L-Lactide and Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate in a Loading Site. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 730105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, S.; Tamura, J.; Neo, M.; Fujibayashi, S.; Goto, K.; Shikinami, Y.; Okazaki, K.; Nakamura, T. In Vivo Evaluation of Porous Hydroxyapatite/Poly-D/L-Lactide Composite for Bone Substitutes and Scaffolds. Key Eng. Mater. 2006, 309, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, S.; Neo, M.; Tamura, J.; Fujibayashi, S.; Takemoto, M.; Shikinami, Y.; Okazaki, K.; Nakamura, T. In Vivo Evaluation of a Porous Hydroxyapatite/Poly-DL-Lactide Composite for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 81, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Takemoto, M.; Fujibayashi, S.; Neo, M.; Shikinami, Y.; Nakamura, T. A Bioactive and Bioresorbable Porous Cubic Composite Scaffold Loaded with Bone Marrow Aspirate: A Potential Alternative to Autogenous Bone Grafting. Spine 2011, 36, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernigou, P.; Poignard, A.; Beaujean, F.; Rouard, H. Percutaneous Autologous Bone-marrow Grafting for Nonunions: Influence of the Number and Concentration of Progenitor Cells. J. Bone Joint Surg. 2005, 87, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabuchi, Y.; Morikawa, S.; Harada, S.; Niibe, K.; Suzuki, S.; Renault-Mihara, F.; Houlihan, D.D.; Akazawa, C.; Okano, H.; Matsuzaki, Y. LNGFR+THY-1+VCAM-1hi+ Cells Reveal Functionally Distinct Subpopulations in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2013, 1, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankrum, J.A.; Ong, J.F.; Karp, J.M. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Immune Evasive, not Immune Privileged. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahla, R.S. Stem Cells Applications in Regenerative Medicine and Disease Therapeutics. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabuchi, Y.; Matsuzaki, Y. Prospective Isolation of Resident Adult Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Population from Multiple Organs. Int. J. Hematol. 2016, 103, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillot, P.V.; Abass, O.; Bassett, J.H.D.; Shefelbine, S.J.; Bou-Gharios, G.; Chan, J.; Kurata, H.; Williams, G.R.; Polak, J.; Fisk, N.M. Intrauterine Transplantation of Human Fetal Mesenchymal Stem Cells from First-Trimester Blood Repairs Bone and Reduces Fractures in Osteogenesis Imperfecta Mice. Blood 2008, 111, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Guan, J.; Zhang, C. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Mechanisms and Role in Bone Regeneration. Postgrad. Med. J. 2014, 90, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.; Bauer, G.; Nolta, J.A. Concise Review: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Progress toward Safe Clinical Products. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stappenbeck, T.S.; Miyoshi, H. The Role of Stromal Stem Cells in Tissue Regeneration and Wound Repair. Science 2009, 324, 1666–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Kanno, T.; Tatsumi, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Sha, J.; Hideshima, K.; Matsuzaki, Y. Feasibility of a Three-Dimensional Porous Uncalcined and Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/poly-d/l-lactide Composite as a Regenerative Biomaterial in Maxillofacial Surgery. Materials 2018, 11, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudel, S.B.; Bhattarai, G.; Kim, J.H.; Kook, S.H.; Seo, Y.K.; Jeon, Y.M.; Lee, J.C. Local Delivery of Recombinant Human FGF7 Enhances Bone Formation in Rat Mandible Defects. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2017, 35, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, H.; Kuroda, S.; Tachikawa, N.; Okada, E.; Akatsuka, M.; Kasugai, S.; Kondo, H. Histological and Micro-computed Tomographic Observations after Maxillary Sinus Augmentation with Porous Hydroxyapatite Alloplasts: A Clinical Case Series. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karageorgiou, V.; Kaplan, D. Porosity of 3D Biomaterial Scaffolds and Osteogenesis. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5474–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.S.; Lee, C.K.; Hong, K.S.; Youn, H.J.; Ryu, H.S.; Chung, S.S.; Park, K.W. Osteoconduction at Porous Hydroxyapatite with Various Pore Configurations. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Kurashina, K.; Bruijn, J.D.; Li, Y.; Groot, K.; Zhang, X. A Preliminary Study on Osteoinduction of Two Kinds of Calcium Phosphate Ceramics. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, B.J.; Wagner, W.R.; Gaisser, D.M.; Cook, S.D.; Rust-Dawicki, A.M. In Vivo Performance of a Modified CSTi Dental Implant Coating. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1998, 13, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liverani, C.; Mercatali, L.; Cristofolini, L.; Giordano, E.; Minardi, S.; Della Porta, G.; De Vita, A.; Miserocchi, G.; Spadazzi, C.; Tasciotti, E.; et al. Investigating the Mechanobiology of Cancer Cell–ECM Interaction Through Collagen-Based 3D Scaffolds. Cell Mol. Bioeng. 2017, 10, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschler, G.F.; Nakamoto, C.; Griffith, L.G. Engineering Principles of Clinical Cell-based Tissue Engineering. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2004, 86, 1541–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukegawa, S.; Kanno, T.; Manabe, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Sukegawa-Takahashi, Y.; Masui, M.; Furuki, Y. Biomechanical Loading Evaluation of Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/Poly-L-Lactide Plate System in Bilateral Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy. Materials 2017, 10, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pina, S.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Bioresorbable Plates and Screws for Clinical Applications: A Review. J. Health Eng. 2012, 3, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Wu, L.; Shi, G.; Chen, L.I.; Dong, Q. Increased Runx2 Expression Associated with Enhanced Wnt Signaling in PDLLA Internal Fixation for Fracture Treatment. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, M.; Kugimiya, F.; Fukai, A.; Saito, T.; Yano, F.; Ikeda, T.; Nakamura, K.; Chung, U.-I.; Kawaguchi, H. 060 Molecular Network on the C/Ebp-Beta Axis Including Runx2, Mmp13, and Hif2a Controls Osteoarthritis Development. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santana Santos, T.; Flores Abuna, R.P.; Bacha Lopes, H.; Gonçalves De Almeida, A.L.; Beloti, M.M.; Luiz Rosa, A. Association of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Osteoblasts for Bone Repair. Regen. Med. 2015, 10, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, L.; Malmström, H.; Ren, Y.F. Porous Collagen-Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds with Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Bone Regeneration. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 41, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viateau, V.; Guillemin, G.; Bousson, V.; Oudina, K.; Hannouche, D.; Sedel, L.; Logeart-Avramoglou, D.; Petite, H. Long-bone Critical-size Defects Treated with Tissue-engineered Grafts: A Study on Sheep. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linero, I.; Chaparro, O. Paracrine Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Human Adipose Tissue in Bone Regeneration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, E.M.; Gordon, P.L.; Koo, W.K.K.; Marx, J.C.; Neel, M.D.; McNall, R.Y.; Muul, L.; Hofmann, T. Isolated Allogeneic Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Cells Engraft and Stimulate Growth in Children with Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Implications for Cell Therapy of Bone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8932–8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šponer, P.; Kučera, T.; Diaz-Garcia, D.; Filip, S. The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Bone Repair and Regeneration. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2014, 24, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganath, S.H.; Levy, O.; Inamdar, M.S.; Karp, J.M. Harnessing the Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osugi, M.; Katagiri, W.; Yoshimi, R.; Inukai, T.; Hibi, H.; Ueda, M. Conditioned Media from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhanced Bone Regeneration in Rat Calvarial Bone Defects. Tissue Eng. Part A 2012, 18, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inukai, T.; Katagiri, W.; Yoshimi, R.; Osugi, M.; Kawai, T.; Hibi, H.; Ueda, M. Novel Application of Stem Cell-Derived Factors for Periodontal Regeneration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polacek, M.; Bruun, J.A.; Elvenes, J.; Figenschau, Y.; Martinez, I. The Secretory Profiles of Cultured Human Articular Chondrocytes and Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Implications for Autologous Cell Transplantation Strategies. Cell Transpl. 2011, 20, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Matsubara, K.; Ishikawa, J.; Fujio, M.; Shohara, R.; Hibi, H.; Ueda, M.; Yamamoto, A. Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Accelerates Distraction Osteogenesis through Multiple Regenerative Mechanisms. Bone 2014, 61, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Lingling, E.; Liu, H. The Effects of Separating Inferior Alveolar Neurovascular Bundles on Osteogenesis of Tissue-Engineered Bone and Vascularization. Biomed. Pap. 2015, 159, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausman, M.R.; Schaffler, M.B.; Majeska, R.J. Prevention of Fracture Healing in Rats by an Inhibitor of Angiogenesis. Bone 2001, 29, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, D.; Agata, H.; Furue, H.; Kimura, A.; Narita, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Ishii, Y.; Ueda, M.; Tojo, A.; Kagami, H. Limited but Heterogeneous Osteogenic Response of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 and Serum. Growth Factors 2010, 28, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groeneveld, E.H.; van den Bergh, J.P.; Holzmann, P.; ten Bruggen-kate, C.M.; Tuinzing, D.B.; Burger, E.H. Mineralization Processes in Demineralized Bone Matrix Grafts in Human Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevations. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 48, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
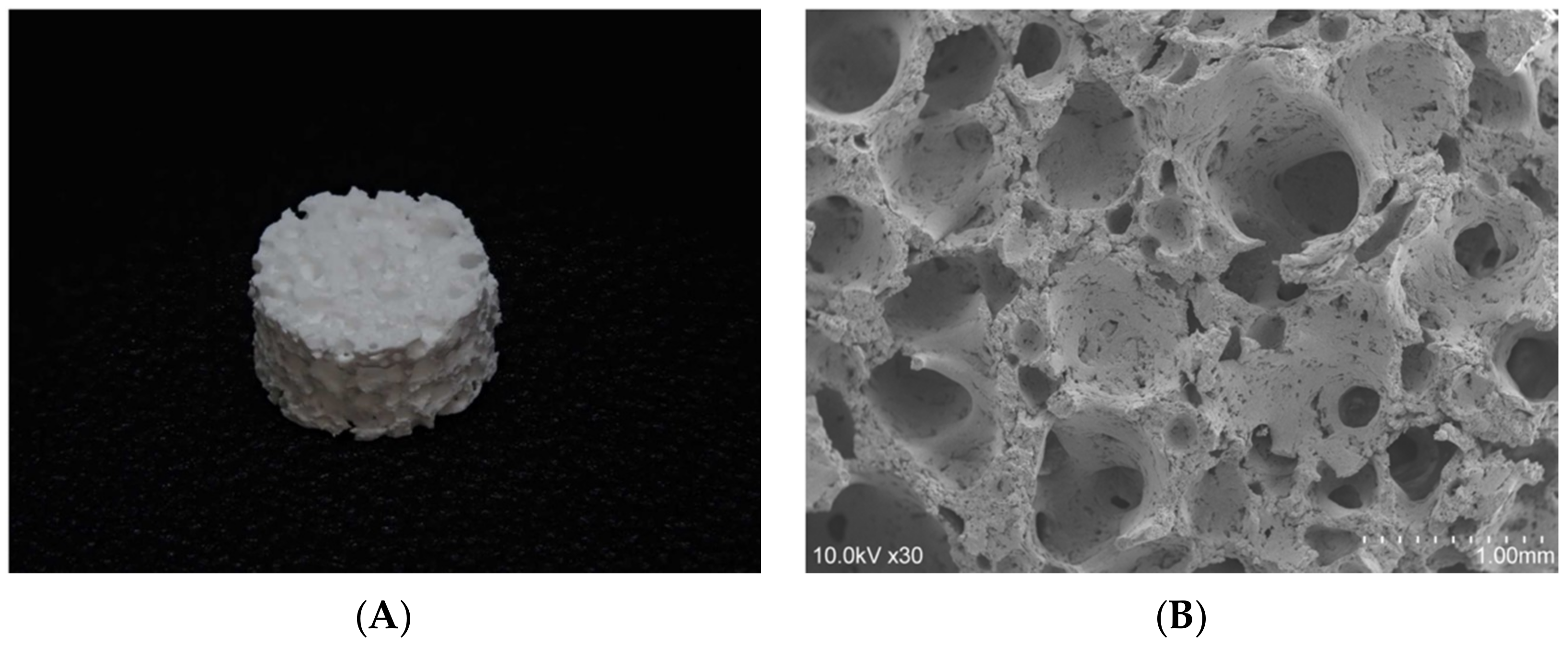


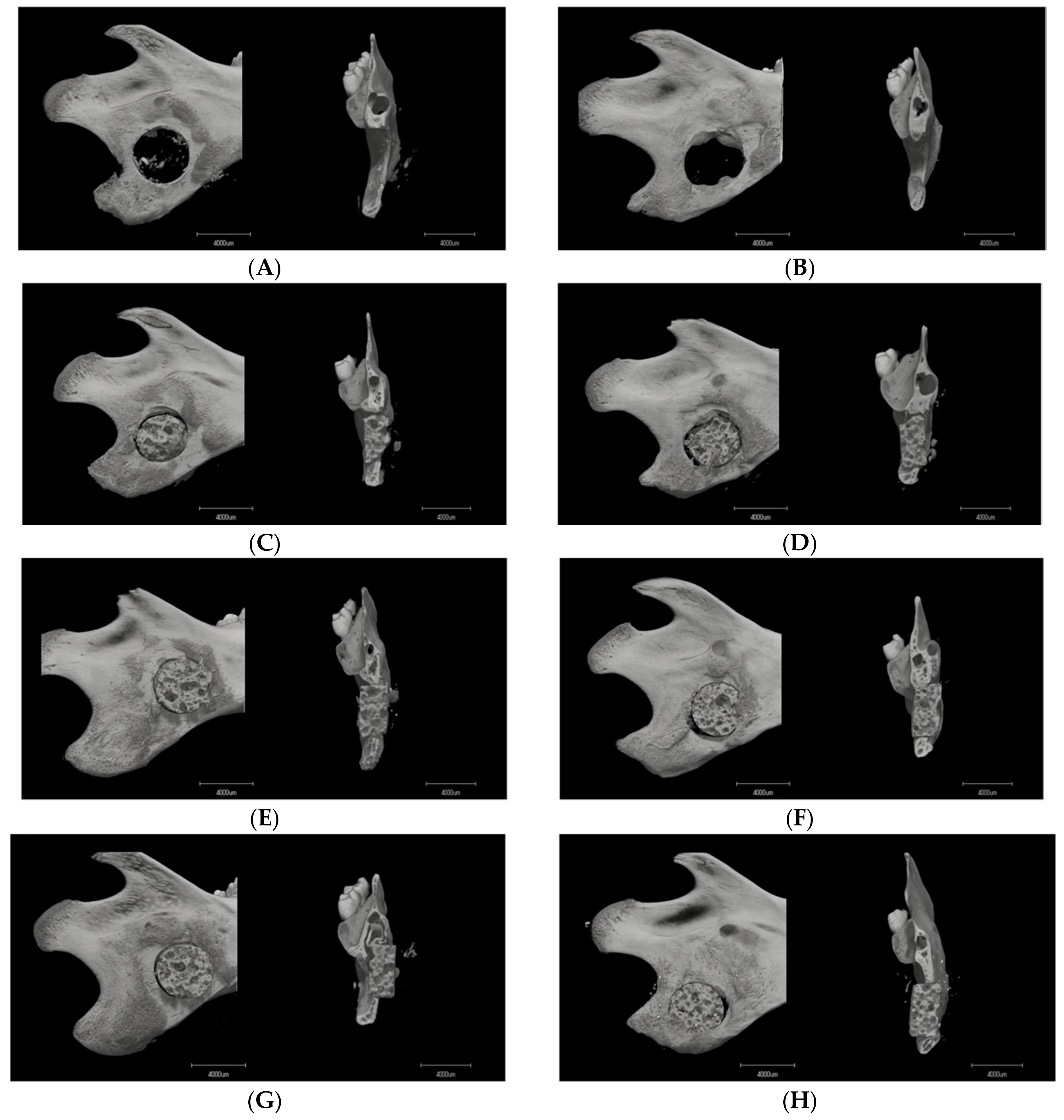
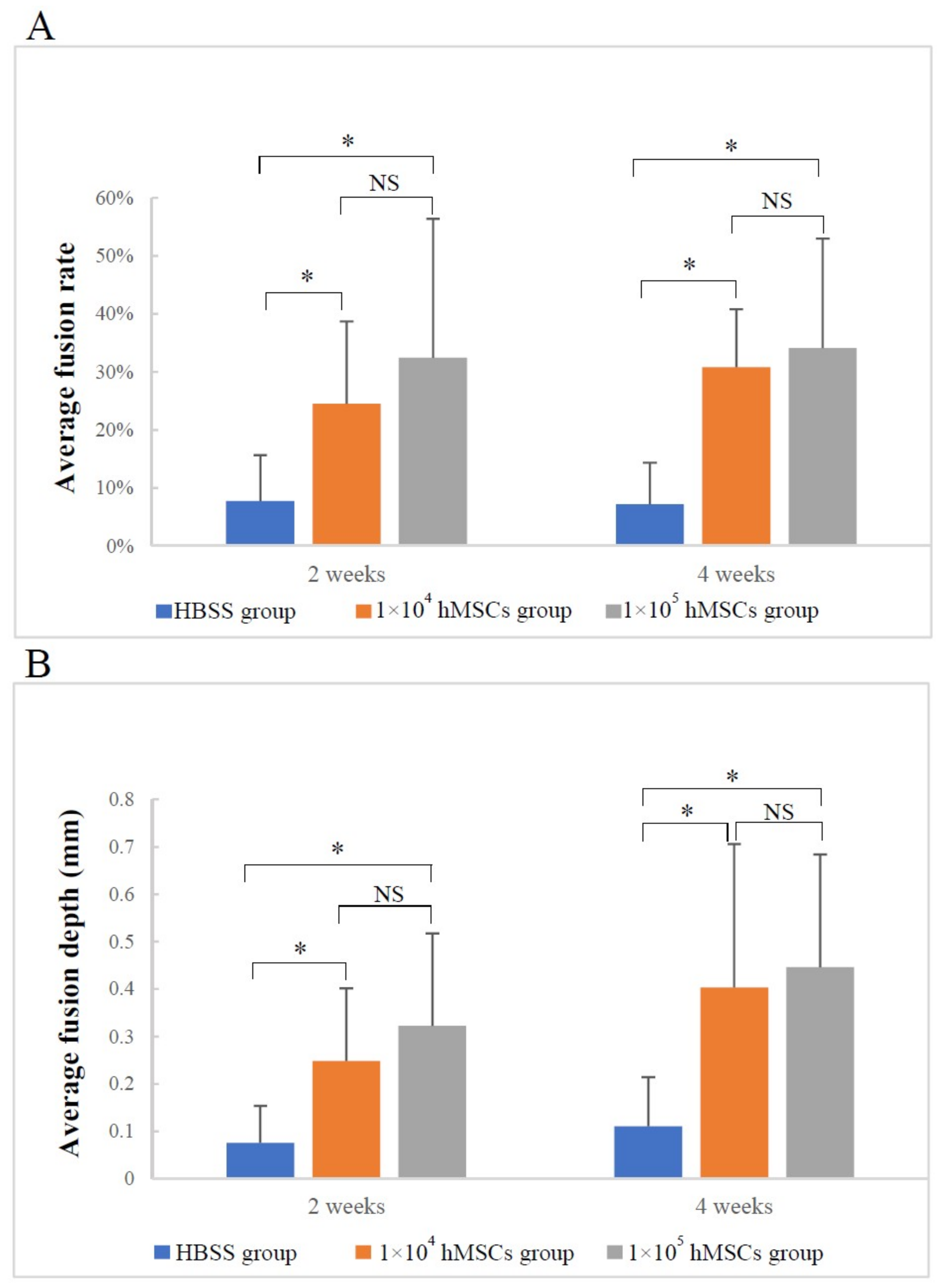
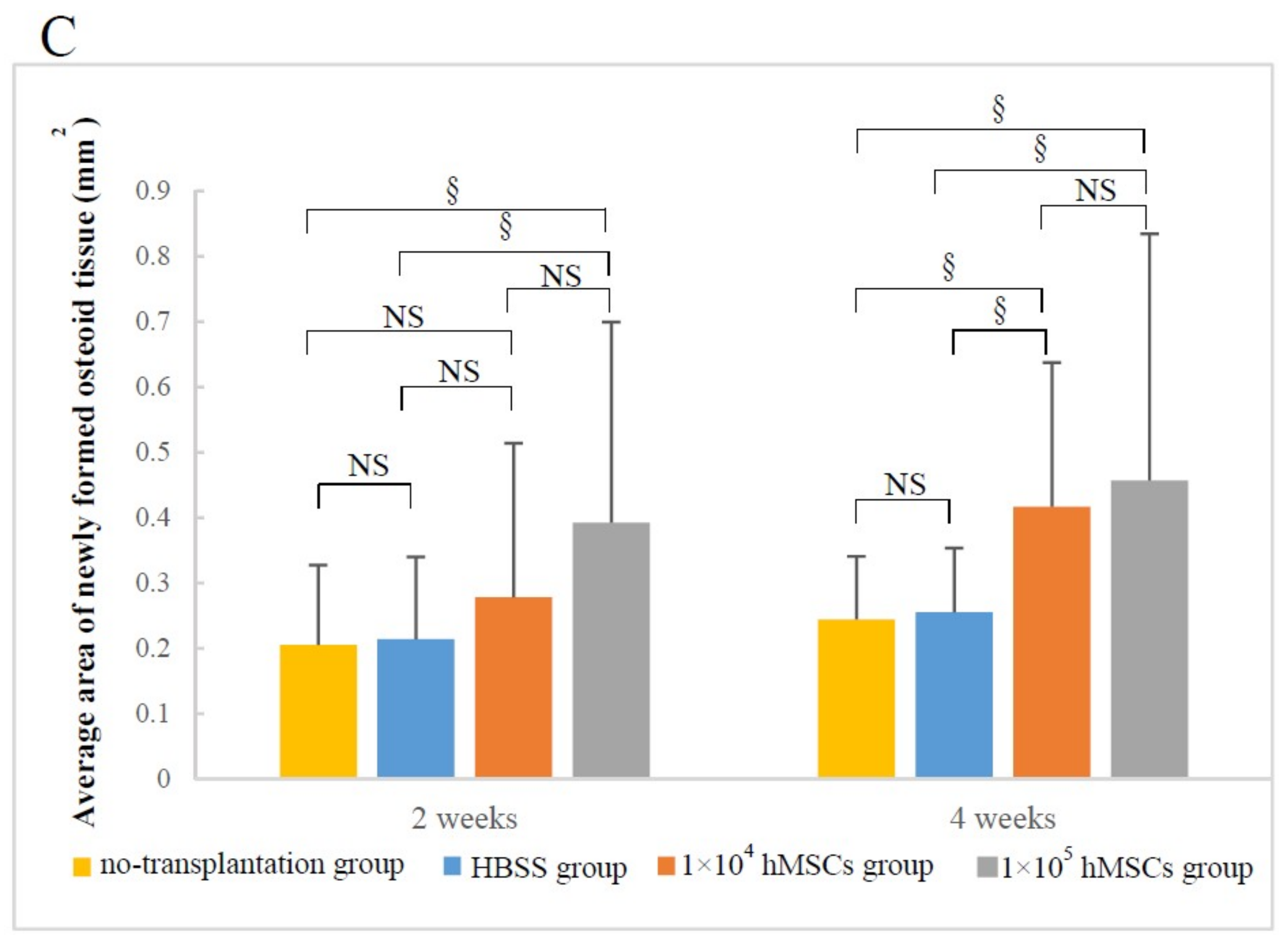

| Time | Superior Side Mean ± S.D. (%) | Inferior Side Mean ± S.D. (%) | Z Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 weeks | 23.61 ± 23.65 | 25.04 ± 24.95 | 0.370 | 0.711 |
| 4 weeks | 35.91 ± 26.61 | 15.54 ± 19.16 | 3.611 | 0.005 |
| Time | Superior Side Mean ± S.D. (mm) | Inferior Side Mean ± S.D. (mm) | Z Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 weeks | 0.256 ± 0.248 | 0.191 ± 0.225 | 1.264 | 0.206 |
| 4 weeks | 0.458 ± 0.449 | 0.265 ± 0.245 | 2.749 | 0.006 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sha, J.; Kanno, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Bai, Y.; Hideshima, K.; Matsuzaki, Y. Application of a Bioactive/Bioresorbable Three-Dimensional Porous Uncalcined and Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/Poly-d/l-lactide Composite with Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Bone Regeneration in Maxillofacial Surgery: A Pilot Animal Study. Materials 2019, 12, 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050705
Sha J, Kanno T, Miyamoto K, Bai Y, Hideshima K, Matsuzaki Y. Application of a Bioactive/Bioresorbable Three-Dimensional Porous Uncalcined and Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/Poly-d/l-lactide Composite with Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Bone Regeneration in Maxillofacial Surgery: A Pilot Animal Study. Materials. 2019; 12(5):705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050705
Chicago/Turabian StyleSha, Jingjing, Takahiro Kanno, Kenichi Miyamoto, Yunpeng Bai, Katsumi Hideshima, and Yumi Matsuzaki. 2019. "Application of a Bioactive/Bioresorbable Three-Dimensional Porous Uncalcined and Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/Poly-d/l-lactide Composite with Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Bone Regeneration in Maxillofacial Surgery: A Pilot Animal Study" Materials 12, no. 5: 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050705
APA StyleSha, J., Kanno, T., Miyamoto, K., Bai, Y., Hideshima, K., & Matsuzaki, Y. (2019). Application of a Bioactive/Bioresorbable Three-Dimensional Porous Uncalcined and Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/Poly-d/l-lactide Composite with Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Bone Regeneration in Maxillofacial Surgery: A Pilot Animal Study. Materials, 12(5), 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050705






