Influence of Accelerating Admixtures on the Reactivity of Synthetic Aluminosilicate Glasses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Synthetic Aluminosilicate Glasses
2.2. Dissolution Experiments of the Aluminosilicate Glasses
2.3. Effect of Accelerators on the Reactivity and Mineralogy of Synthetic Glass Pastes
2.3.1. Preparation of Pastes
2.3.2. Hydration Kinetics and Characterization of the Reaction Products
3. Results
3.1. Dissolution of the Aluminosilicate Glasses at Far from Equilibrium Conditions
3.2. Hydration Kinetics of the Glasses
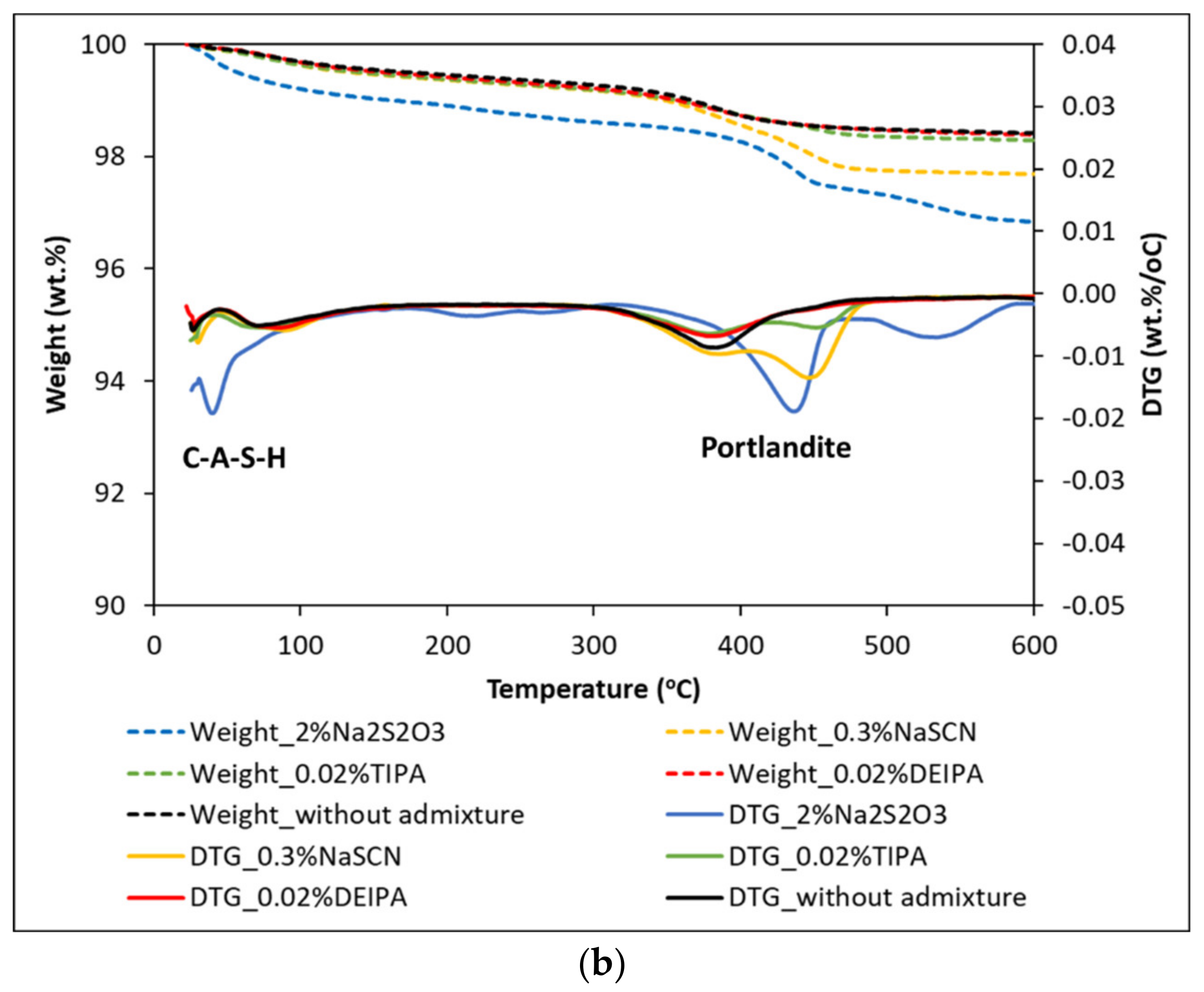
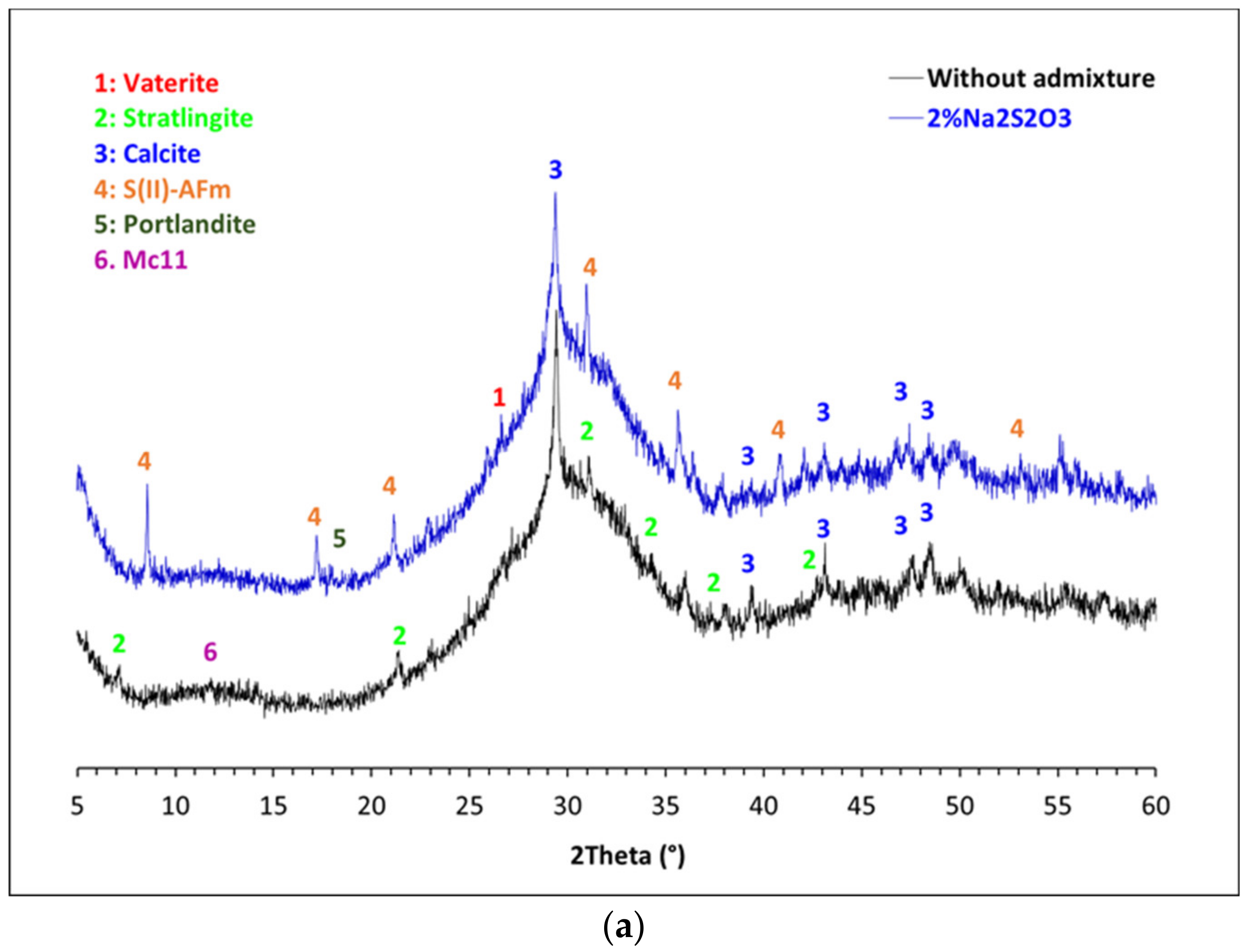
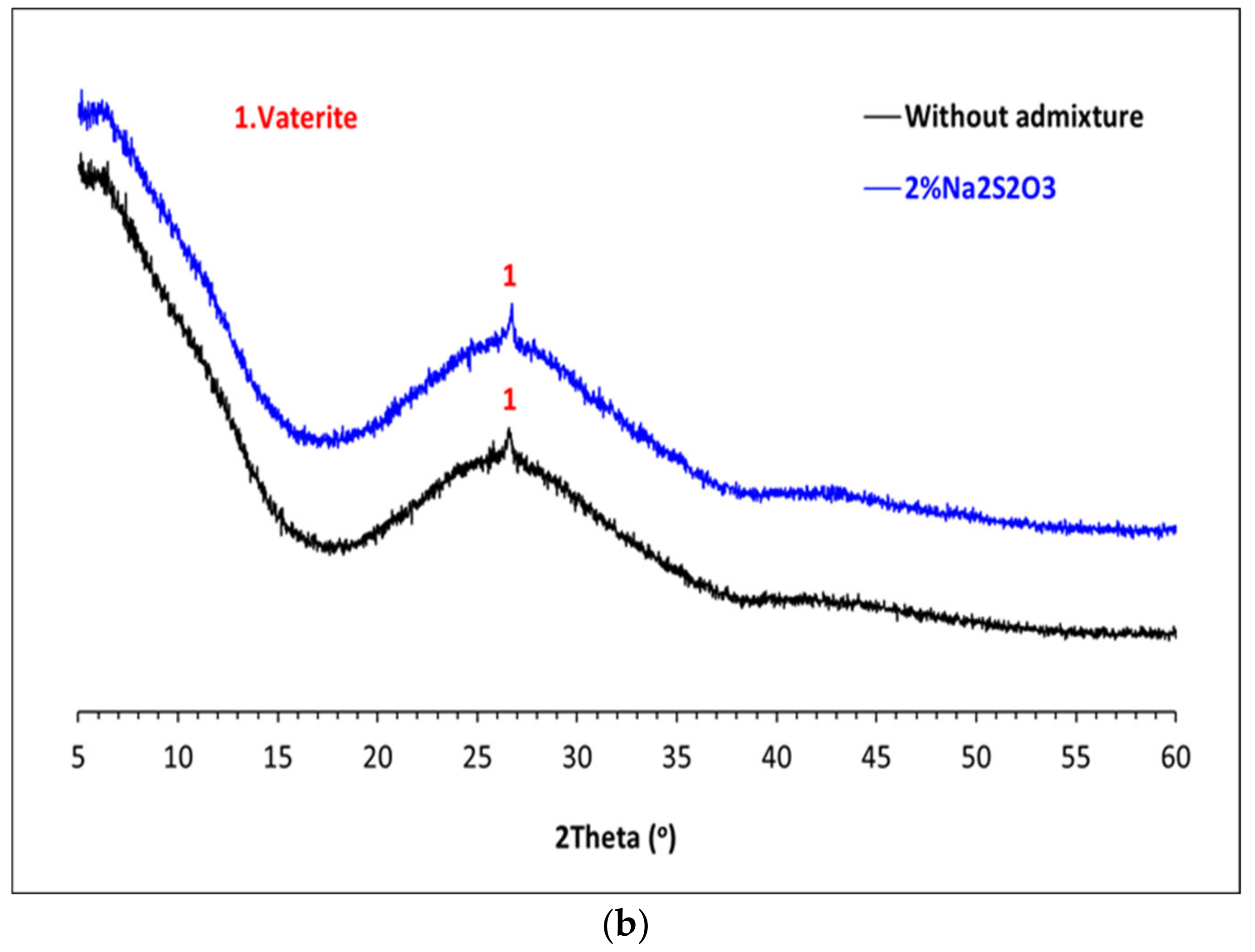
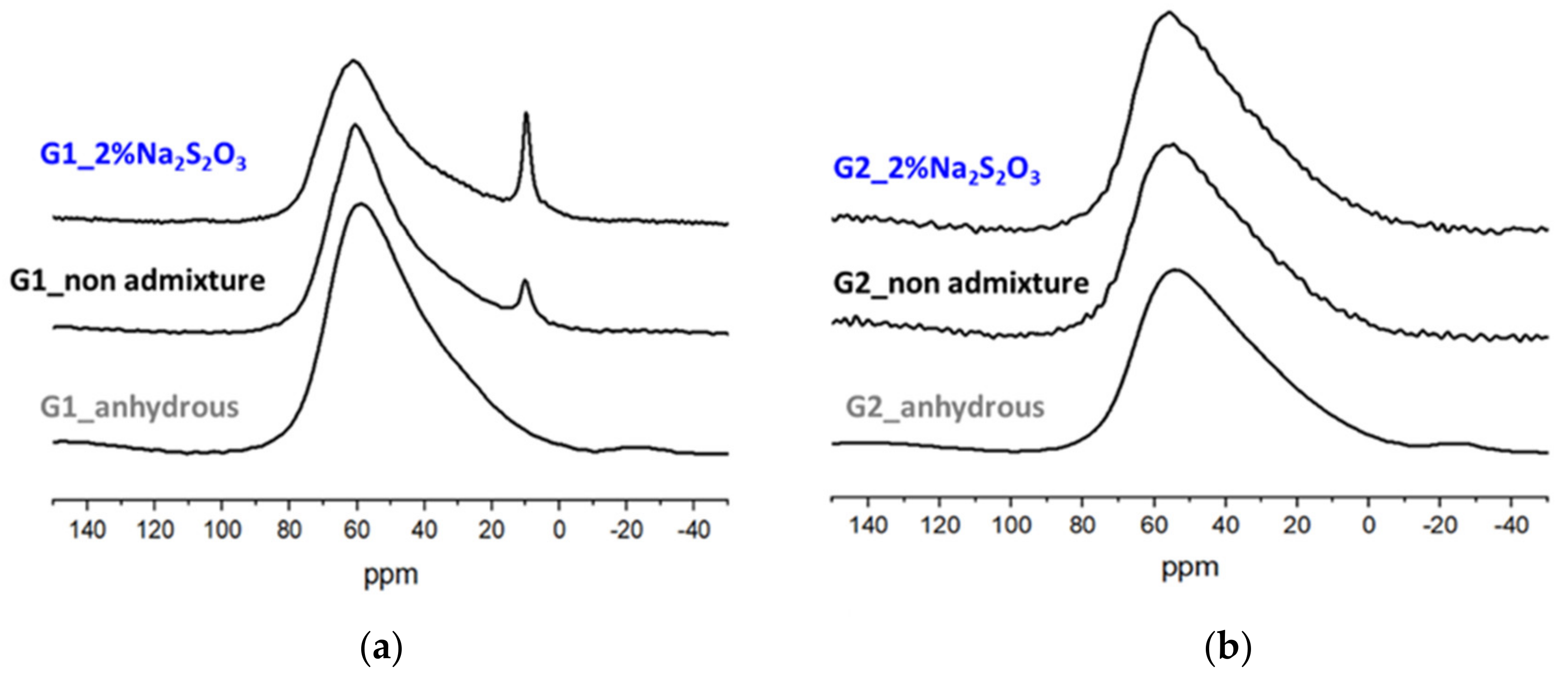
3.3. Mineralogical Characterization of the Glass Pastes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scrivener, K.L.; Vanderley, J.M.; Gartner, E.M. Eco-Efficient Cements: Potential, Economically Viable Solutions for Low CO2, Cement-Based Materials Industry; United Nations Environment Program Report; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Boscaro, F.; Palacios, M.; Flatt, R.J. Formulation of low clinker blended cements and concrete with enhanced fresh and hardened properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 150, 106605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juenger, M.; Monteiro, P.; Gartner, E.; Denbeaux, G. A soft X-ray microscope investigation into the effects of calcium chloride on tricalcium silicate hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, B.; Matschei, T.; Scrivener, K. Impact of NaOH and Na2SO4 on the kinetics and microstructural development of white cement hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 108, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, B.; Matschei, T.; Scrivener, K. The influence of sodium salts and gypsum on alite hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 75, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, V. Action of triethanolamine on the hydration of tricalcium aluminate. Cem. Concr. Res. 1973, 3, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, V. Hydration of cement—Role of triethanolamine. Cem. Concr. Res. 1976, 6, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gartner, E.; Myers, D. Influence of Tertiary Alkanolamines on Portland Cement Hydration. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993, 76, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizoń, J.; Łaźniewska-Piekarczyk, B. Microstructure of CEM II/B-S Pastes Modified with Set Accelerating Admixtures. Materials 2021, 14, 6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, B.; Matschei, T.; Scrivener, K. Impact of sodium gluconate on white cement-slag systems with Na2SO4. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 122, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Cui, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. Impact of four kinds of alkanolamines on hydration of steel slag-blended cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, K.; Justnes, H.; Geiker, M. Early age strength increase of fly ash blended cement by a ternary hardening accelerating admixture. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 81, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steger, L.; Blotevogel, S.; Frouin, L.; Patapy, C.; Cyr, M. Experimental evidence for the acceleration of slag hydration in blended cements by the addition of CaCl2. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 149, 106558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahrache, S.; Winnefeld, F.; Champenois, J.-B.; Hesselbarth, F.; Lothenbach, B. Chemical activation of hybrid binders based on siliceous fly ash and Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 66, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, D.; Göbel, M.; Hilbig, H.; Urbonas, L.; Bujauskaite, G. Effect of TEA on fly ash solubility and early age strength of mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riding, K.; Silva, D.A.; Scrivener, K. Early age strength enhancement of blended cement systems by CaCl2 and diethanol-isopropanolamine. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Li, X.; Avet, F.; Hanpongpun, W.; Scrivener, K. Strength-promoting mechanism of alkanolamines on limestone-calcined clay cement and the role of sulfate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 147, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.C. The Influence of Structure on the Physico-chemical Properties of Slags. ISIJ Int. 1993, 33, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynor, B.; Uvegi, H.; Olivetti, E.; Lothenbach, B.; Myers, R.J. Methodology for pH measurement in high alkali cementitious systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 135, 106122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newlands, K.C.; Foss, M.; Matchei, T.; Skibsted, J.; Macphee, D.E. Early stage dissolution characteristics of aluminosilicate glasses with blast furnace slag- and fly-ash-like compositions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 1941–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newlands, K.C.; Macphee, D. The reactivity of aluminosilicate glasses in cements–effects of Ca content on dissolution characteristics and surface precipitation. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2017, 116, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.; Sibbick, R.; Nicolich, J.; Detellis, J. Impact of alkanolamines on hydration of Portland and Fly Ash cements. In Proceedings of the 14th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement, Beijing, China, 13–16 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Panicello, L.; Palacios, M. Enhancemnt of the reactivity of blended cement by chemical admixtures. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Construction Research, Madrid, Spain, 21–23 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, J.; Jeknavorian, A.; Roberts, L.; Silva, D. Impact of admixtures on the hydration kinetics of Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1289–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöler, A.; Winnefeld, F.; Ben Haha, M.; Lothenbach, B. The effect of glass composition on the reactivity of synthetic glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 2553–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oey, T.; La Plante, E.C.; Falzone, G.; Yang, K.; Wada, A.; Bauchy, M.; Bullard, J.W.; Sant, G. Topological controls on aluminosilicate glass dissolution: Complexities induced in hyperalkaline aqueous environments. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 6198–6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, R.; Cotte, S.; Cadel, E.; Malladi, S.; Karlsson, L.S.; Lozano-Perez, S.; Cabié, M.; Seyeux, A. Nanometre-scale evidence for interfacial dissolution–reprecipitation control of silicate glass corrosion. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellings, R. Solution-Controlled Dissolution of Supplementary Cementitious Material Glasses at pH 13: The Effect of Solution Composition on Glass Dissolution Rates. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, D.A.; Wagner, T.; Dmytrieva, S.V.; Kosakowski, G.; Hingerl, F.F.; Chudnenko, K.; Berner, U.R. GEM-Selektor geochemical modeling package: Revised algorithm and GEMS3K numerical kernel for coupled simulation codes. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 17, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thoenen, T.; Hummel, W.; Berner, U.; Curti, E. Thermodynamic Database 12/07; PSI Report 14-04; Villigen PSI: Villigen, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lothenbach, B.; Kulik, D.A.; Matschei, T.; Balonis, M.; Baquerizo, L.; Dilnesa, B.; Miron, G.; Myers, R.J. Cemdata18: A chemical thermodynamic database for hydrated Portland cements and alkali-activated materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 115, 472–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palacios, M.; Gismera, S.; Alonso, M.; de Lacaillerie, J.D.; Lothenbach, B.; Favier, A.; Brumaud, C.; Puertas, F. Early reactivity of sodium silicate-activated slag pastes and its impact on rheological properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 140, 106302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pustovgar, E.; Mishra, R.; Palacios, M.; de Lacaillerie, J.-B.D.; Matschei, T.; Andreev, A.; Heinz, H.; Verel, R.; Flatt, R. Influence of aluminates on the hydration kinetics of tricalcium silicate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchon, D.; Juilland, P.; Gallucci, E.; Frunz, L.; Flatt, R.J. Molecular and submolecular scale effects of comb-copolymers on tri-calcium silicate reactivity: Toward molecular design. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 817–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Lodeiro, I.; Jimenez, A.M.F.; Pena, P.; Palomo, A. Alkaline activation of synthetic aluminosilicate glass. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 5547–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedyalkova, L.; Lothenbach, B.; Renaudin, G.; Mäder, U.; Tits, J. Effect of redox conditions on the structure and solubility of sulfur- and selenium-AFm phases. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 123, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Durdziński, P.T.; De Weerdt, K. Chapter 5. Thermogravimetric analysis. In A Practical Guide to Microstructural Analysis of Cementitious Materials; Scrivener, K., Snellings, R., Lothenbach, B., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquerizo, L.G.; Matschei, T.; Scrivener, K.L.; Saeidpour, M.; Wadsö, L. Hydration states of AFm cement phases. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 73, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoronkwo, M.U.; Glasser, F.P. Stability of strätlingite in the CASH system. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 4305–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacruz, I.; la Torre, Á.G.D.; Álvarez-Pinazo, G.; Cabeza, A.; Cuesta, A.; Sanz, J.; Aranda, M.A.G. Structure of stratlingite and effect of hydration methodology on microstructure. Adv. Cem. Res. 2016, 28, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwan, S.; LaRosa, J.L.; Grutzeck, M.W. 29Si and27Al MASNMR Study of Stratlingite. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1995, 78, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharczyk, S.; Zajac, M.; Stabler, C.; Thomsen, R.M.; Ben Haha, M.; Skibsted, J.; Deja, J. Structure and reactivity of synthetic CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 glasses. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 120, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappex, T.; Scrivener, K.L. The Effect of Aluminum in Solution on the Dissolution of Amorphous Silica and its Relation to Cementitious Systems. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 96, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iler, R. Effect of adsorbed alumina on the solubility of amorphous silica in water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1973, 43, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
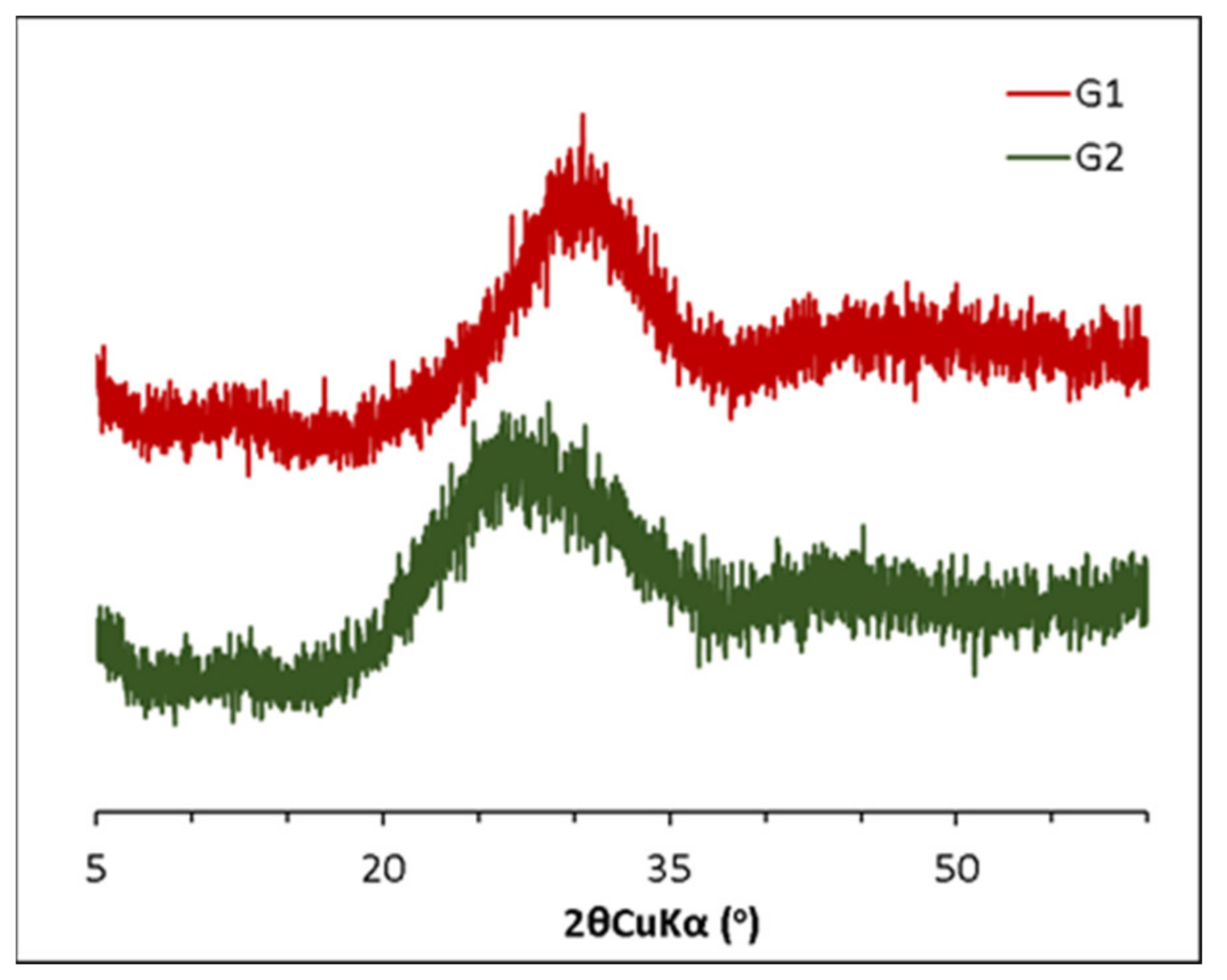
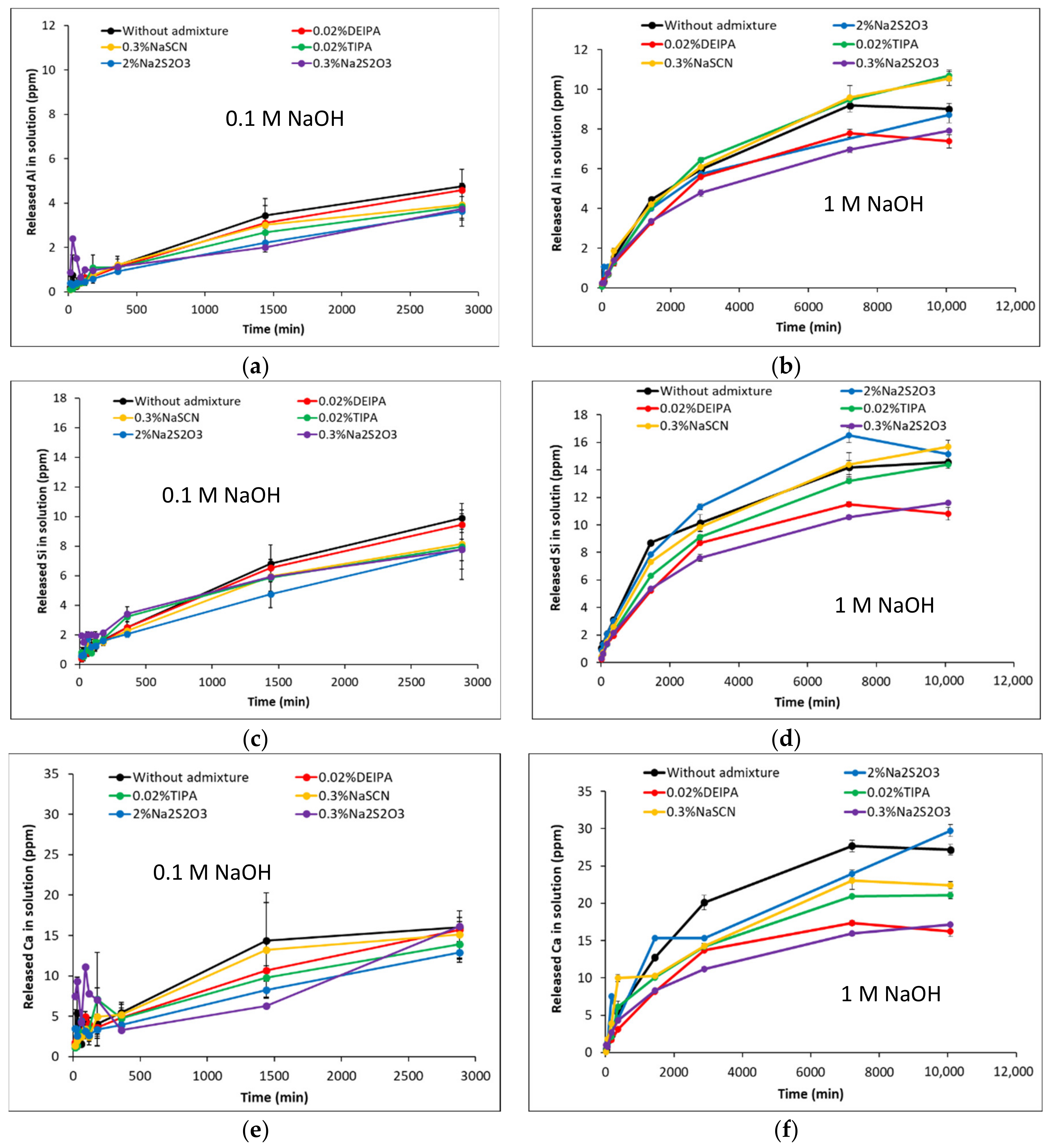

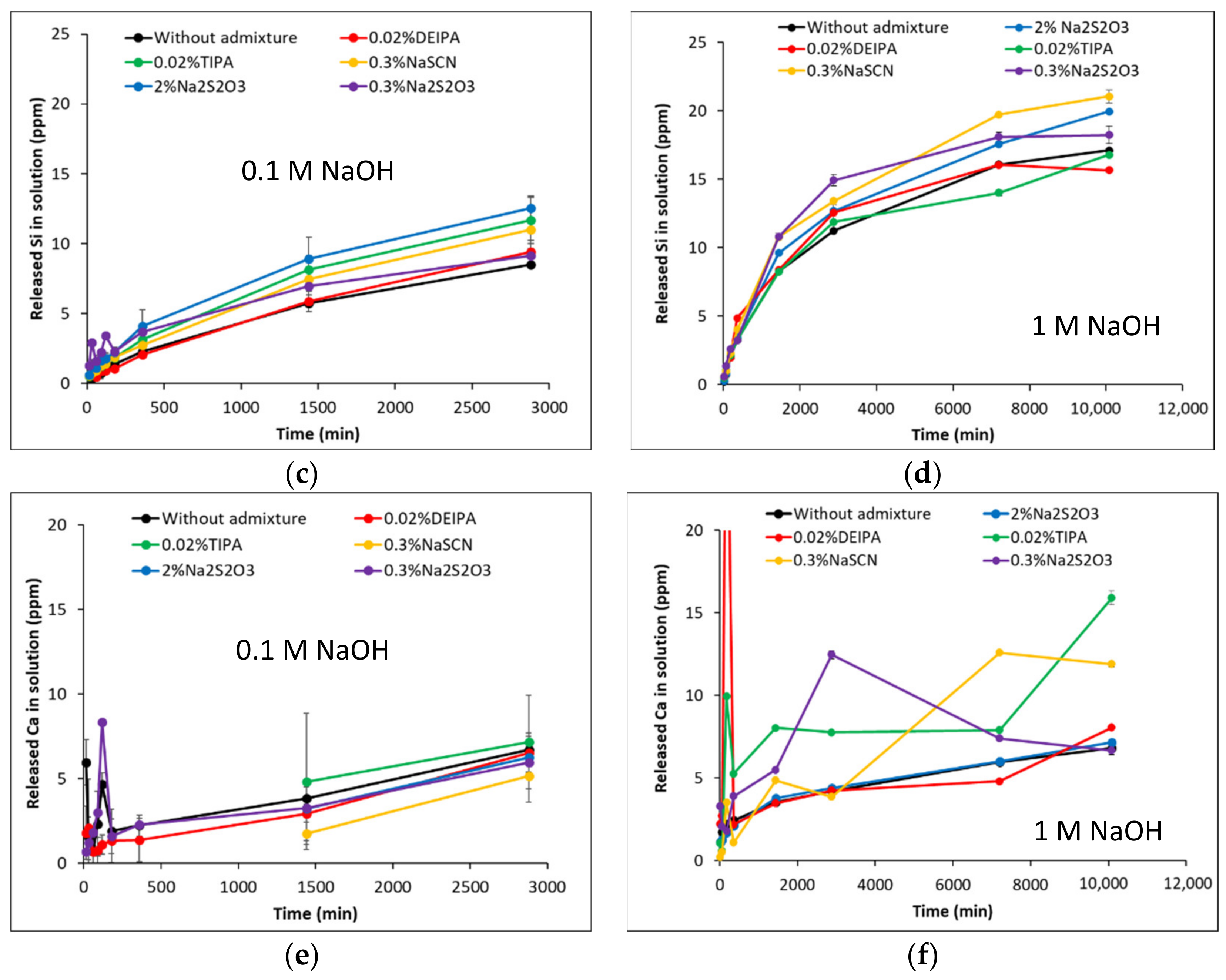
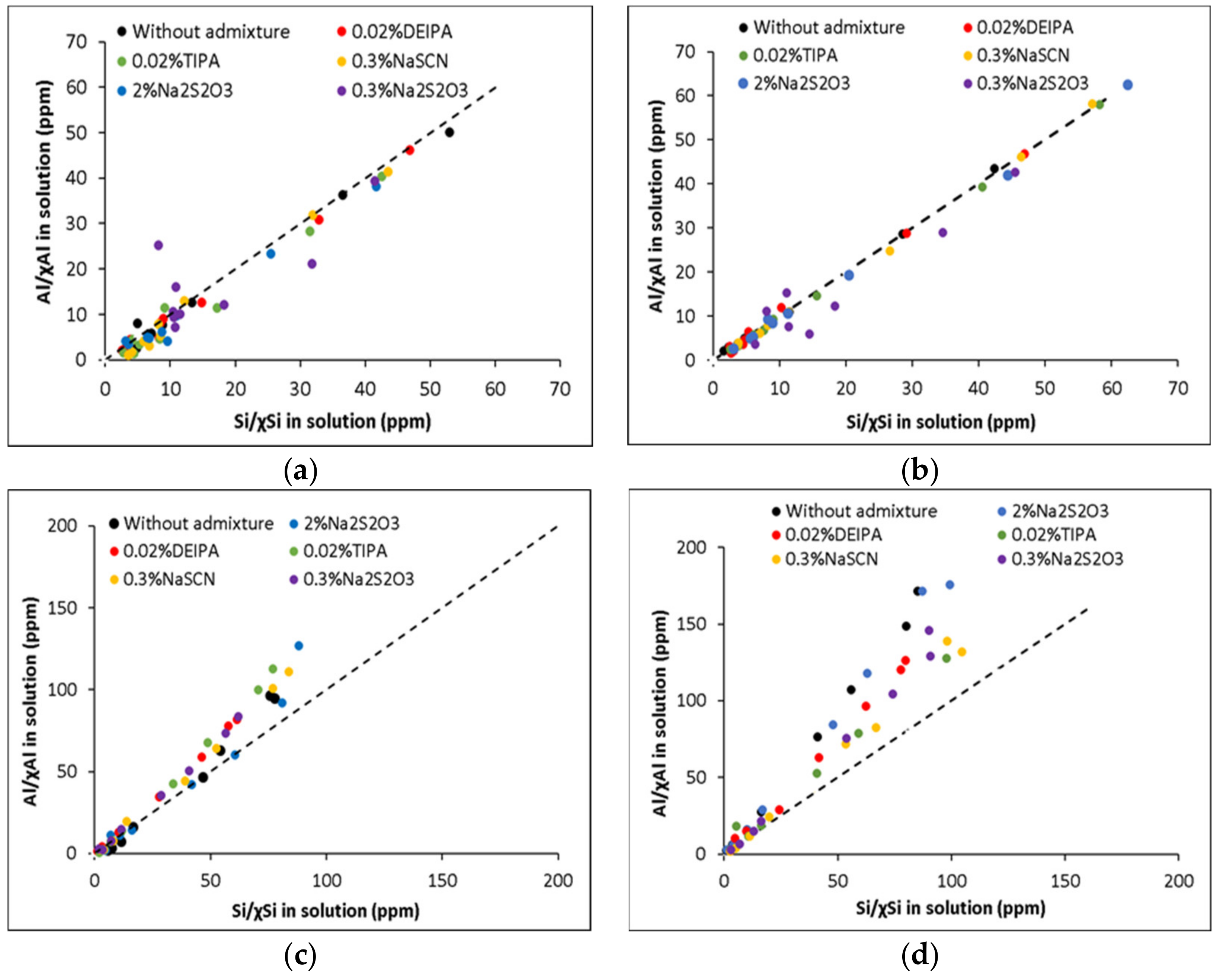

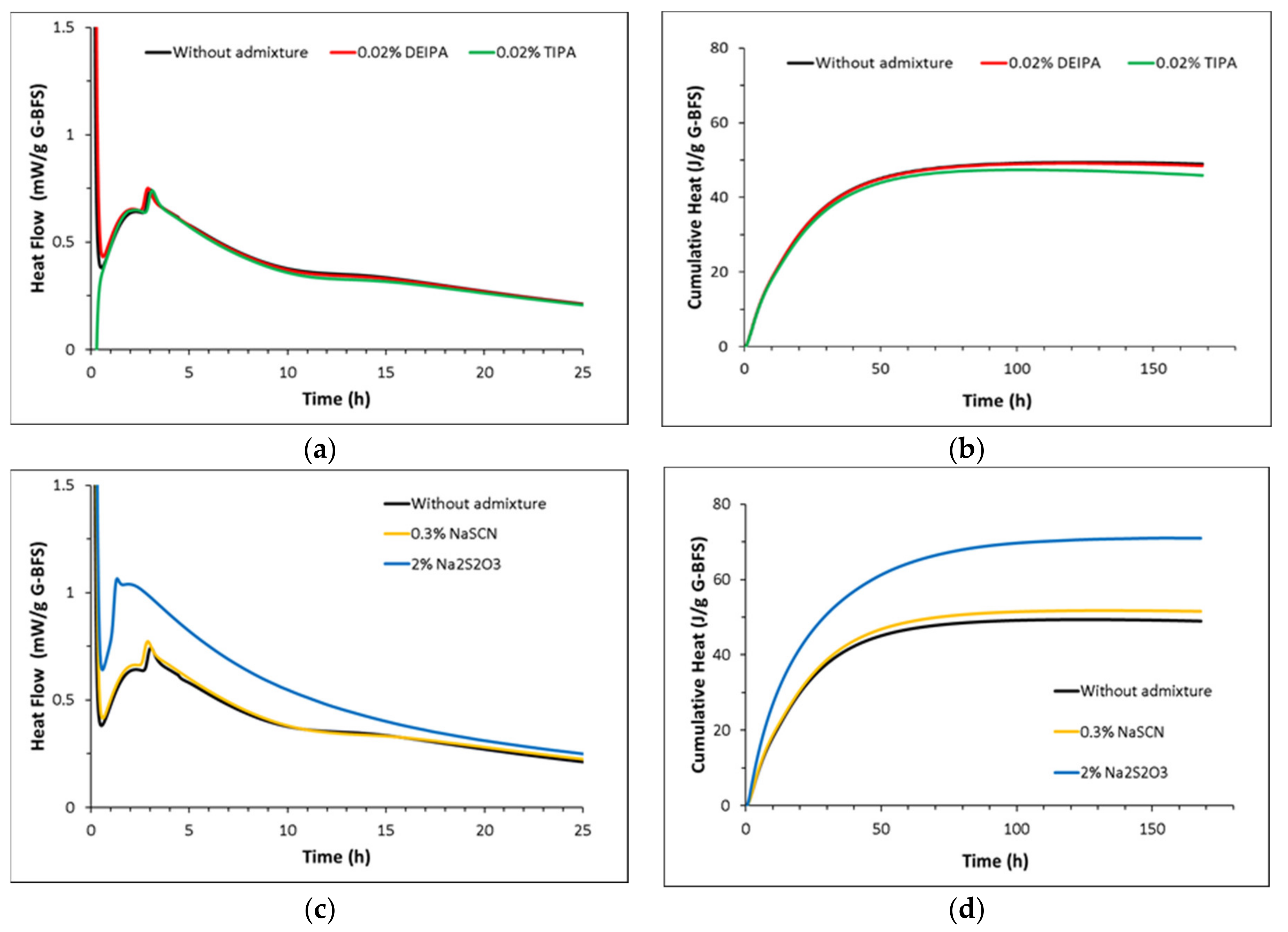
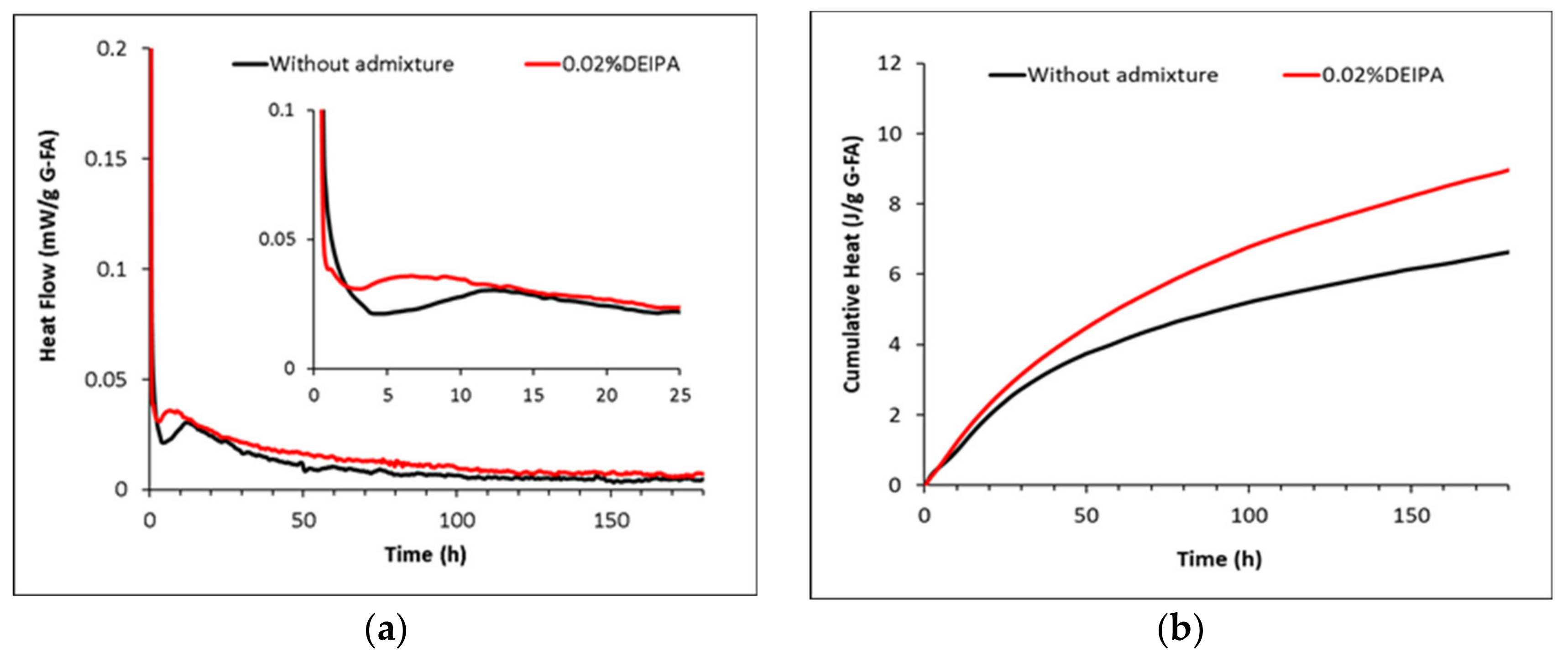
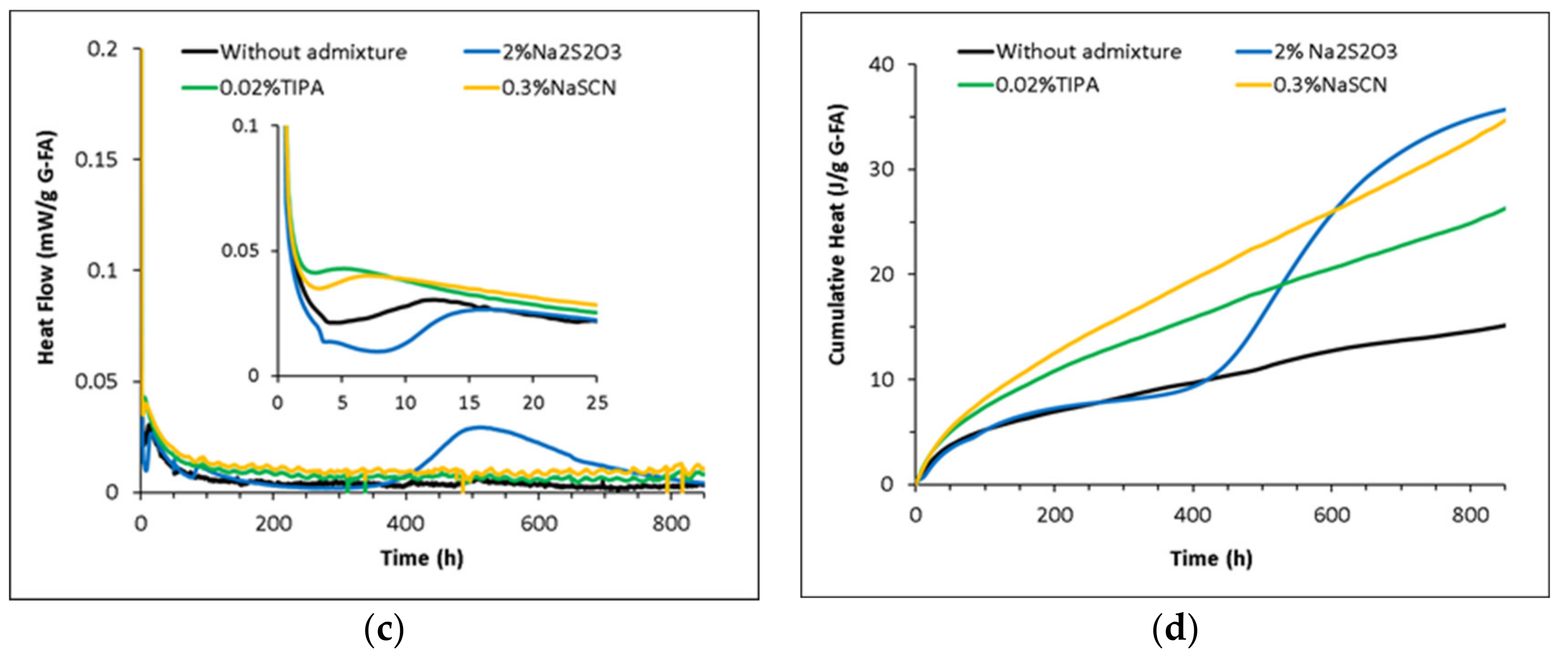
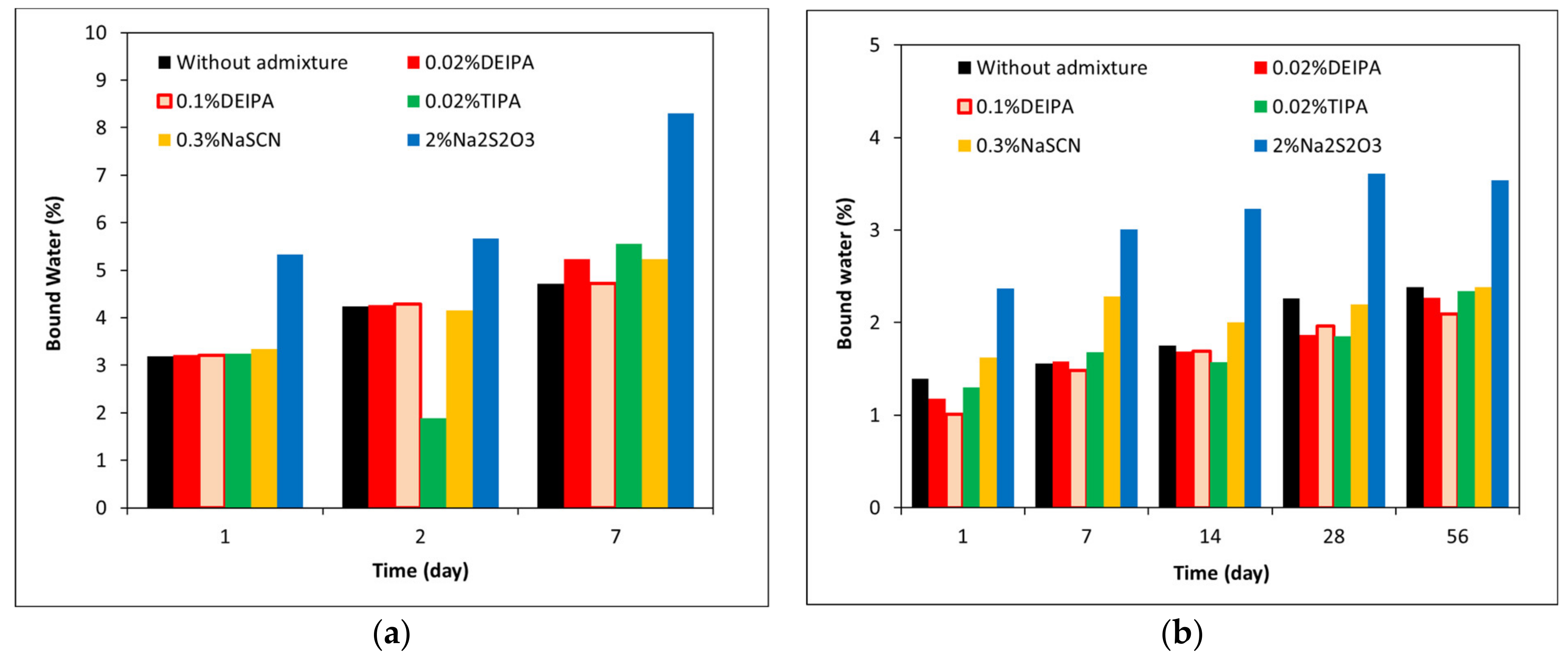


| Glass Notation | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | NBO/T |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 47.29 | 41.62 | 11.09 | 1.58 |
| G2 | 24.86 | 49.89 | 25.25 | 0.33 |
| Glass Type | SSA (m2/g) | Particle Size (µm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dv10 | Dv50 | Dv90 | ||
| G1 | 1.08 | 1.77 | 13.28 | 42.03 |
| G2 | 1.47 | 1.07 | 5.55 | 22.74 |
| Glass | NaOH Concentration | Parameter | Without Admixture | 0.02% DEIPA | 0.02% TIPA | 0.3% NaSCN | 0.3% Na2S2O3 | 2% Na2S2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 0.1 M | Log r+Si (mol/m2/s) over first 6 h | −10.64 | −10.64 | −10.54 | −10.68 | −10.51 | −10.73 |
| Glass reacted after 48 h (%) | 5.26 | 5.02 | 4.23 | 4.32 | 4.13 | 4.14 | ||
| 1 M | Log r+Si (mol/m2/s) over first 6 h | −10.56 | −10.76 | −10.71 | −10.65 | −10.73 | −10.57 | |
| Glass reacted after 7 days (%) | 7.43 | 5.55 | 7.35 | 7.97 | 5.93 | 7.73 | ||
| G2 | 0.1 M | Log r+Si (mol/m2/s) over first 6 h | −11.50 | −11.47 | −11.37 | −11.43 | −11.30 | −11.26 |
| Glass reacted after 48 h (%) | 4.23 | 4.66 | 5.78 | 5.45 | 4.53 | 6.22 | ||
| 1 M | Log r+Si (mol/m2/s) over first 6 h | −11.35 | −11.19 | −11.36 | −11.28 | −11.37 | −11.33 | |
| Glass reacted after 7 days (%) | 8.46 | 7.44 | 7.98 | 9.89 | 8.65 | 9.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzalez-Panicello, L.; Garcia-Lodeiro, I.; Puertas, F.; Palacios, M. Influence of Accelerating Admixtures on the Reactivity of Synthetic Aluminosilicate Glasses. Materials 2022, 15, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15030818
Gonzalez-Panicello L, Garcia-Lodeiro I, Puertas F, Palacios M. Influence of Accelerating Admixtures on the Reactivity of Synthetic Aluminosilicate Glasses. Materials. 2022; 15(3):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15030818
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzalez-Panicello, Laura, Ines Garcia-Lodeiro, Francisca Puertas, and Marta Palacios. 2022. "Influence of Accelerating Admixtures on the Reactivity of Synthetic Aluminosilicate Glasses" Materials 15, no. 3: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15030818
APA StyleGonzalez-Panicello, L., Garcia-Lodeiro, I., Puertas, F., & Palacios, M. (2022). Influence of Accelerating Admixtures on the Reactivity of Synthetic Aluminosilicate Glasses. Materials, 15(3), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15030818








