Alkali Activation of Milled Red Brick Waste and Calcined Illite Clay with Silica Gel Addition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Mixture Compositions
2.3. Testing Methods
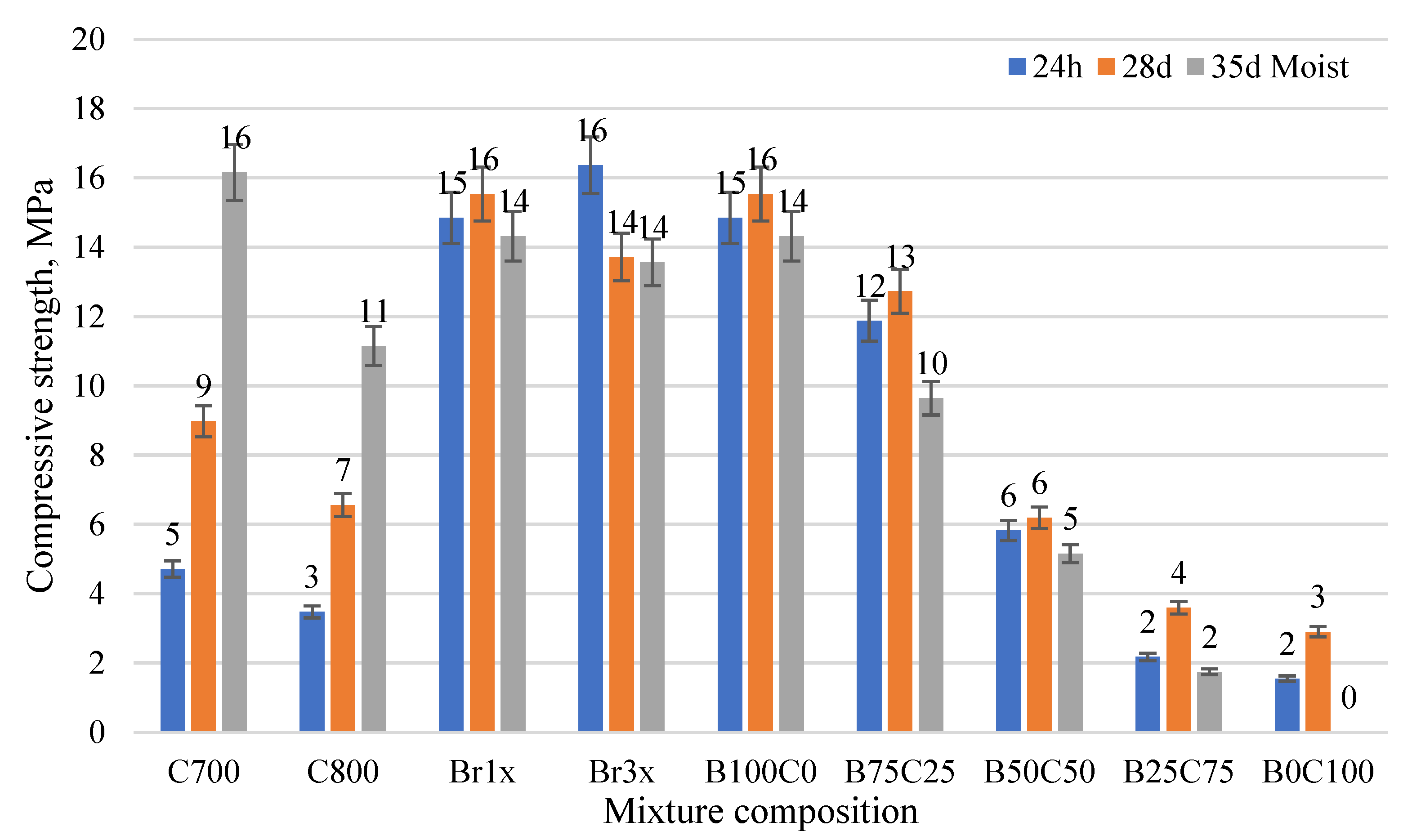
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Novais, R.M.; Ribeiro, A.; Seabra, P.; Tarelho, L. Novel Biomass Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers for Environmental Applications. Int. J. Renew. Energy Sources 2016, 1, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Novais, R.M.; Carvalheiras, J.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Pullar, R.C.; Labrincha, J.A. Synthesis of Porous Biomass Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Spheres for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue from Wastewaters. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedmale, G.; Korovkins, A.; Seglins, V.; Lindina, L. Application of Chemical Trated Illite Clay for Development of Ceramics Products. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Competitive Materials and Technological Processes (IC-CMTP2), Miskolc-Lillafüred, Hungary, 8–12 October 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalifa, A.Z.; Pontikes, Y.; Elsen, J.; Cizer, Ö. Comparing the Reactivity of Different Natural Clays under Thermal and Alkali Activation. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2019, 4, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchwald, A.; Hohmann, M.; Posern, K.; Brendler, E. The Suitability of Thermally Activated Illite/Smectite Clay as Raw Material for Geopolymer Binders. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, A.; Heath, A.; Patureau, P.; Evernden, M.; Walker, P. Alkali Activation Behaviour of Un-Calcined Montmorillonite and Illite Clay Minerals. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 166, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ounissi, C.; Mahmoudi, S.; Valentini, L.; Bennour, A.; Garbin, E.; Artioli, G.; Montacer, M. Potential Use of Kebilian Clay Reserves (Southern Tunisia) for the Production of Geopolymer Materials. Clay Miner. 2020, 55, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Palomo, A.; Deventer, J.S.J.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymer Technology: The Current State of the Art. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 42, 2917–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgarlata, C.; Formia, A.; Siligardi, C.; Ferrari, F.; Leonelli, C. Mine Clay Washing Residues as a Source for Alkali-Activated Binders. Materials 2022, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietel, J.; Warr, L.N.; Bertmer, M.; Steudel, A.; Grathoff, G.H.; Emmerich, K. The Importance of Specific Surface Area in the Geopolymerization of Heated Illitic Clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 139, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasić, M.V.; Terzić, A.; Radovanović, Ž.; Radojević, Z.; Warr, L.N. Alkali-activated geopolymerization of a low illitic raw clay and waste brick mixture. An alternative to traditional ceramics. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 218, 106410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hafid, K.; Hajjaji, M. Effects of the Experimental Factors on the Microstructure and the Properties of Cured Alkali-Activated Heated Clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 116–117, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Bernsmeier, D.; Grathoff, G.H.; Warr, L.N. The Influence of Alkali Activator Type, Curing Temperature and Gibbsite on the Geopolymerization of an Interstratified Illite-Smectite Rich Clay from Friedland. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, R.P.; Vaičiukynienė, D.; Gurskis, V.; Nizevičienė, D.; Skominas, R.; Ramukevičius, D.; Sadzevičius, R. Alkali-Activated Material Based on Red Clay and Silica Gel Waste. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 2973–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiciukyniene, D.; Vaitkevičius, V.; Kantautas, A.; Sasnauskas, V. Effect of AlF3 Production Waste on the Properties of Hardened Cement Paste. Mater. Sci. 2012, 18, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumanis, G.; Vaiciukyniene, D. Mechanical Properties of Alkali Activated Material Based on Red Clay and Silica Gel Precursor. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2021, 25, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumanis, G.; Goljandin, D.; Bajare, D. The Properties of Mineral Additives Obtained by Collision Milling in Disintegrator. KEM 2017, 721, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumanis, G.; Bajare, D. Porous Alkali Activated Materials with Slow Alkali Release Dynamic. Role of Composition. Mater. Constr. 2018, 68, e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conconi, M.S.; Morosi, M.; Maggi, J.; Zalba, P.E.; Cravero, F.; Rendtorff, N.M. Thermal Behavior (TG-DTA-TMA), Sintering and Properties of a Kaolinitic Clay from Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Ceramica 2019, 65, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumanis, G.; Bajare, D.; Korjakins, A. Influence of the Carbonate-Free Clay Calcination Temperature and Curing Conditions on the Properties of Alkali-Activated Mortar. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference. Innovative Materials, Structures and Technologies, Riga, Latvia, 8 November 2013; p. 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ntah, Z.L.E.; Sobott, R.; Fabbri, B.; Bente, K. Characterization of Some Archaeological Ceramics and Clay Samples from Zamala -Far-Northern Part of Cameroon (West Central Africa). Ceramica 2017, 63, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rattanasak, U.; Chindaprasirt, P. Influence of NaOH Solution on the Synthesis of Fly Ash Geopolymer. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Plana, P.; Rodríguez-Expósito, A.; Bueno-Rodríguez, S.; Pérez-Villarejo, L.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Labrincha, J.A.; Eliche-Quesada, D. Effect of Activating Solution Modulus on the Synthesis of Sustainable Geopolymer Binders Using Spent Oil Bleaching Earths as Precursor. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Zhao, C.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Cang, D.; Zong, Y.; Zhao, C.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Cang, D. Preparation of Hydro-Sodalite from Fly Ash Using a Hydrothermal Method with a Submolten Salt System and Study of the Phase Transition Process. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Cristelo, N.; Miranda, T.; Palomo, Á. Sustainable Alkali Activated Materials: Precursor and Activator Derived from Industrial Wastes. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albidah, A.; Alghannam, M.; Abbas, H.; Almusallam, T.; Al-Salloum, Y. Characteristics of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Concrete for Different Mix Design Parameters. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boycheva, S.V. Synthetic Zeolitic Ion-Exchangers from Coal Ash for Decontamination of Nuclear Wastewaters. BgNS Trans. 2016, 20, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Kozhukhova, N.I.; Zhernovskaya, I.V.; Teslya, A.Y.; Kozhukhova, M.I.; Yakovlev, E.A. High Temperature Effect on Structure Formation and Performance of Hybrid Geopolymers. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1353, 12066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

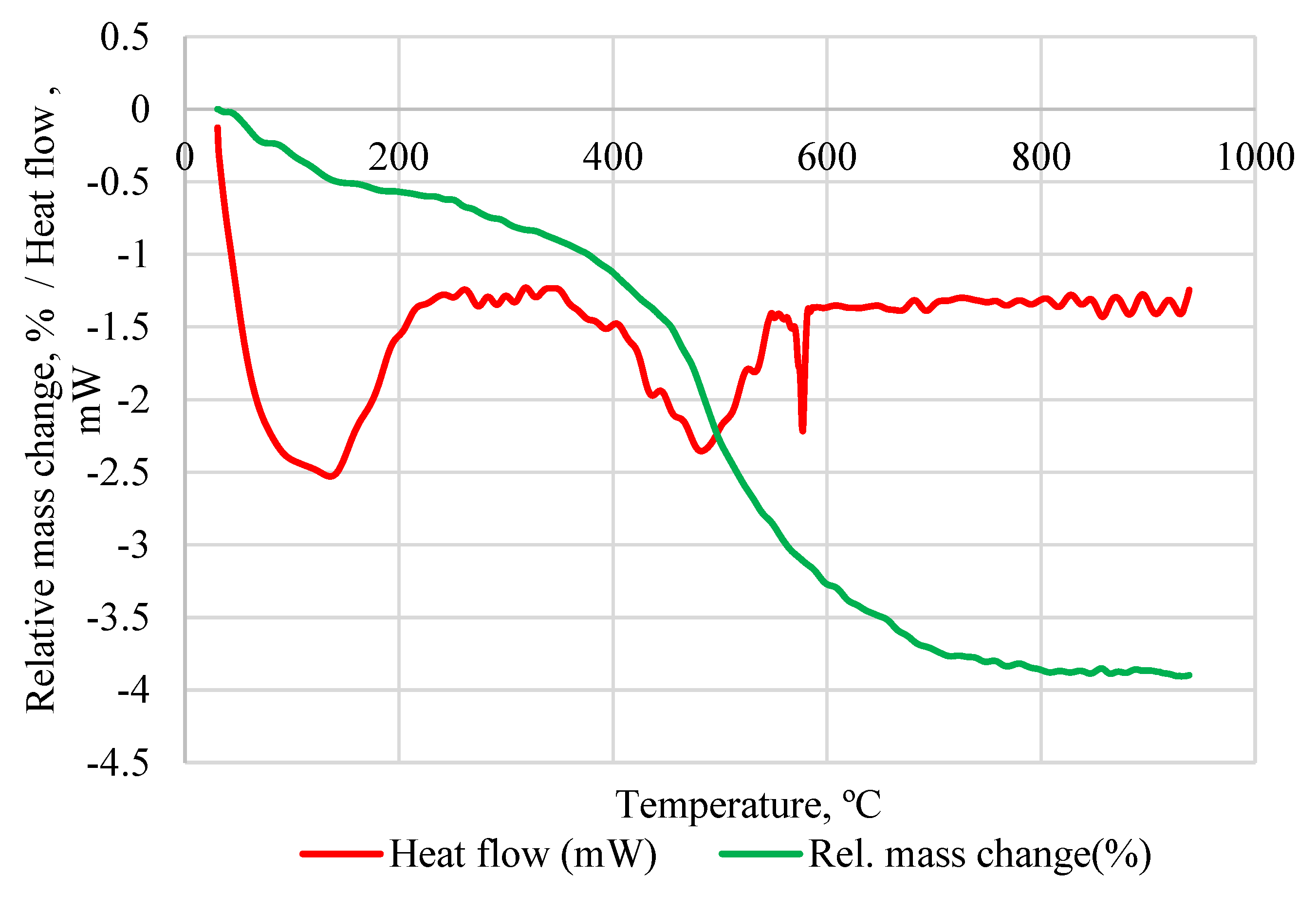
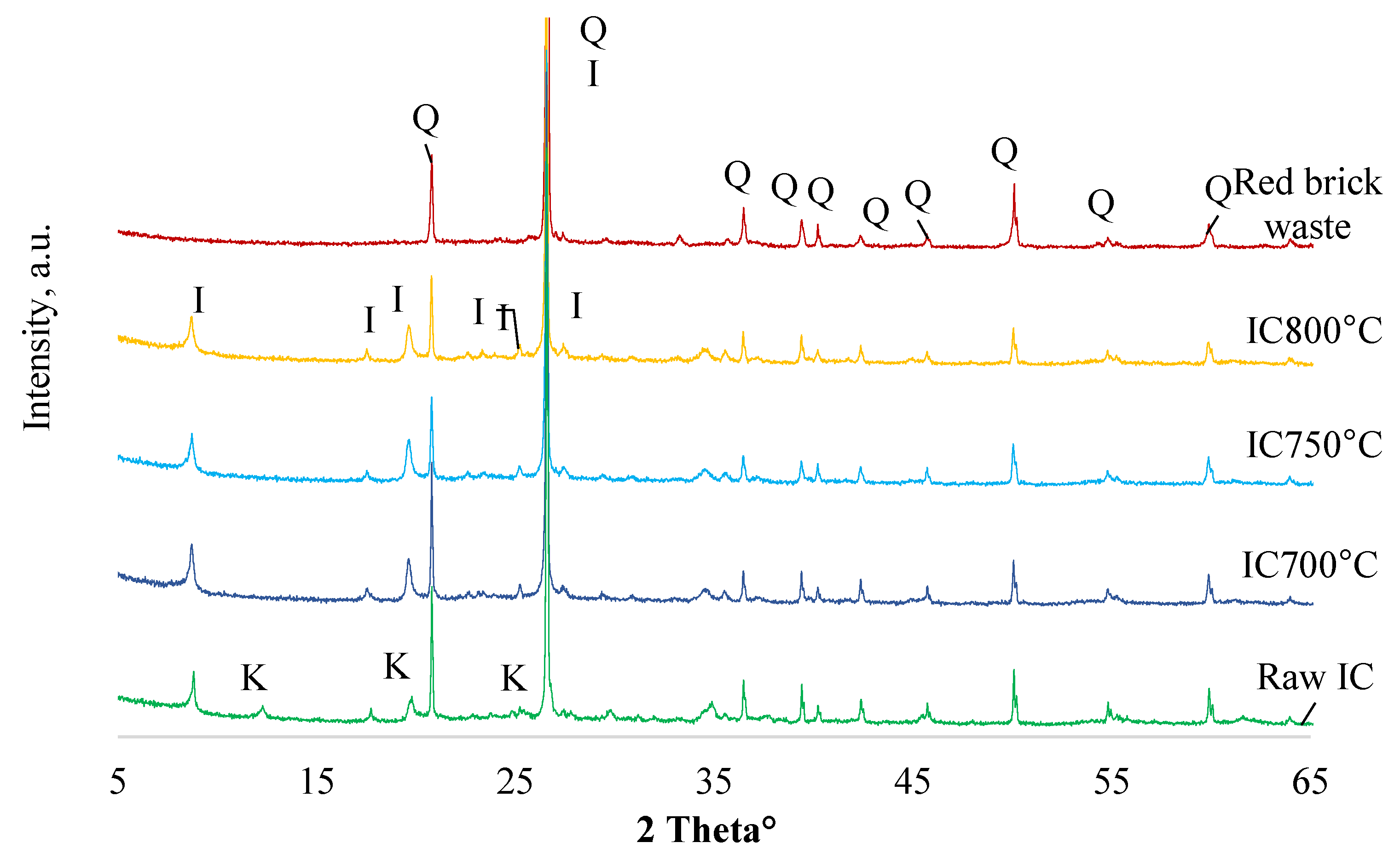

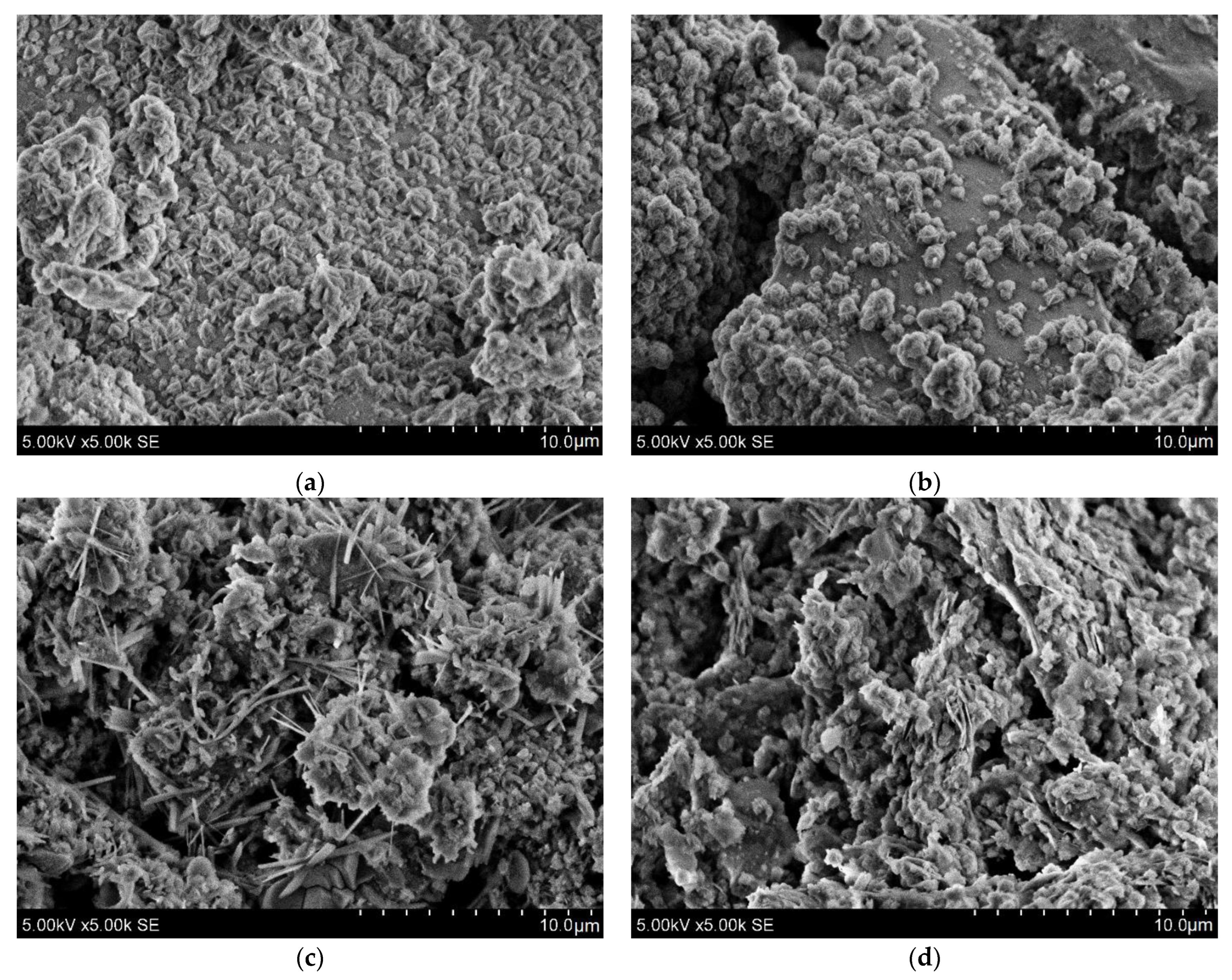
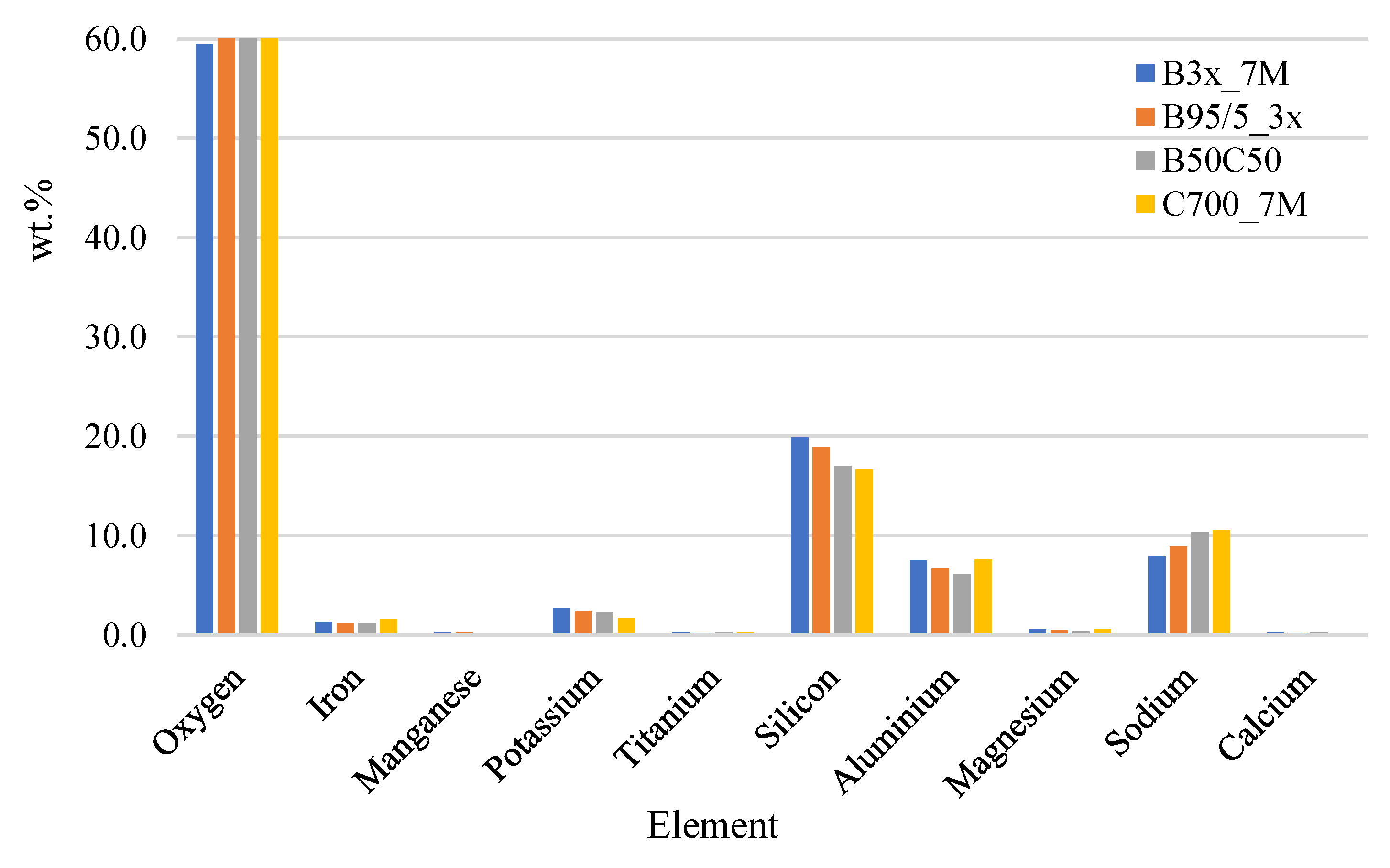

| Compound | Silica Gel | Raw IC | Red Brick Waste |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 5.7 | 14.5 | 14.5 |
| SiO2 | 72.2 | 70.3 | 68.4 |
| CaO | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.6 |
| TiO2 | - | 0.9 | 1.3 |
| Na2O | - | 0.1 | - |
| K2O | - | 4.0 | 5.7 |
| MgO | - | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.7 | 5.4 | 6.6 |
| F | 21 | - | - |
| Others | - | 1.4 | 0.4 |
| LOI, 1000 °C | - | 2.0 | - |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Composition | 6 M NaOH Solution | Red Brick Waste | Calcined IC | AAS/Solid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C700 | 60 | - | 100 | 0.60 |
| 2 | C800 | 60 | - | 100 | 0.60 |
| 3 | Br1x | 43 | 100 | - | 0.43 |
| 4 | Br3x | 43 | 100 | - | 0.43 |
| 5 | B100C0 | 43 | 100 | - | 0.43 |
| 6 | B75C25 | 47 | 25 | 75 | 0.47 |
| 7 | B50C50 | 52 | 50 | 50 | 0.52 |
| 8 | B50C50 7 M | 43 | 50 | 50 | 0.43 |
| 9 | B25C75 | 56 | 70 | 25 | 0.56 |
| 10 | B0C100 | 60 | - | 100 | 0.60 |
| Composition | AAS | Red Brick Waste 1x | Red Brick Waste 3x | Waste Silica gel | AAS/Solid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br_1x_6 M | 43 | 100 | - | - | 0.43 |
| Br_1x_7 M | 43 | 100 | - | - | 0.43 |
| Br_3x_6 M | 43 | - | 100 | - | 0.43 |
| Br_3x_7 M | 43 | - | 100 | - | 0.43 |
| B95/5_1x_6 M | 43 | 95 | - | 5 | 0.43 |
| B95/5_1x_7 M | 43 | 95 | - | 5 | 0.43 |
| B95/5_3x_6 M | 43 | - | 95 | 5 | 0.43 |
| B95/5_3x_7 M | 43 | - | 95 | 5 | 0.43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bumanis, G.; Vaičiukynienė, D. Alkali Activation of Milled Red Brick Waste and Calcined Illite Clay with Silica Gel Addition. Materials 2022, 15, 3195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093195
Bumanis G, Vaičiukynienė D. Alkali Activation of Milled Red Brick Waste and Calcined Illite Clay with Silica Gel Addition. Materials. 2022; 15(9):3195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093195
Chicago/Turabian StyleBumanis, Girts, and Danutė Vaičiukynienė. 2022. "Alkali Activation of Milled Red Brick Waste and Calcined Illite Clay with Silica Gel Addition" Materials 15, no. 9: 3195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093195
APA StyleBumanis, G., & Vaičiukynienė, D. (2022). Alkali Activation of Milled Red Brick Waste and Calcined Illite Clay with Silica Gel Addition. Materials, 15(9), 3195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093195







