Functional Characterization of Abdominal-A in the Pine Caterpillar Moth, Dendrolimus punctatus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
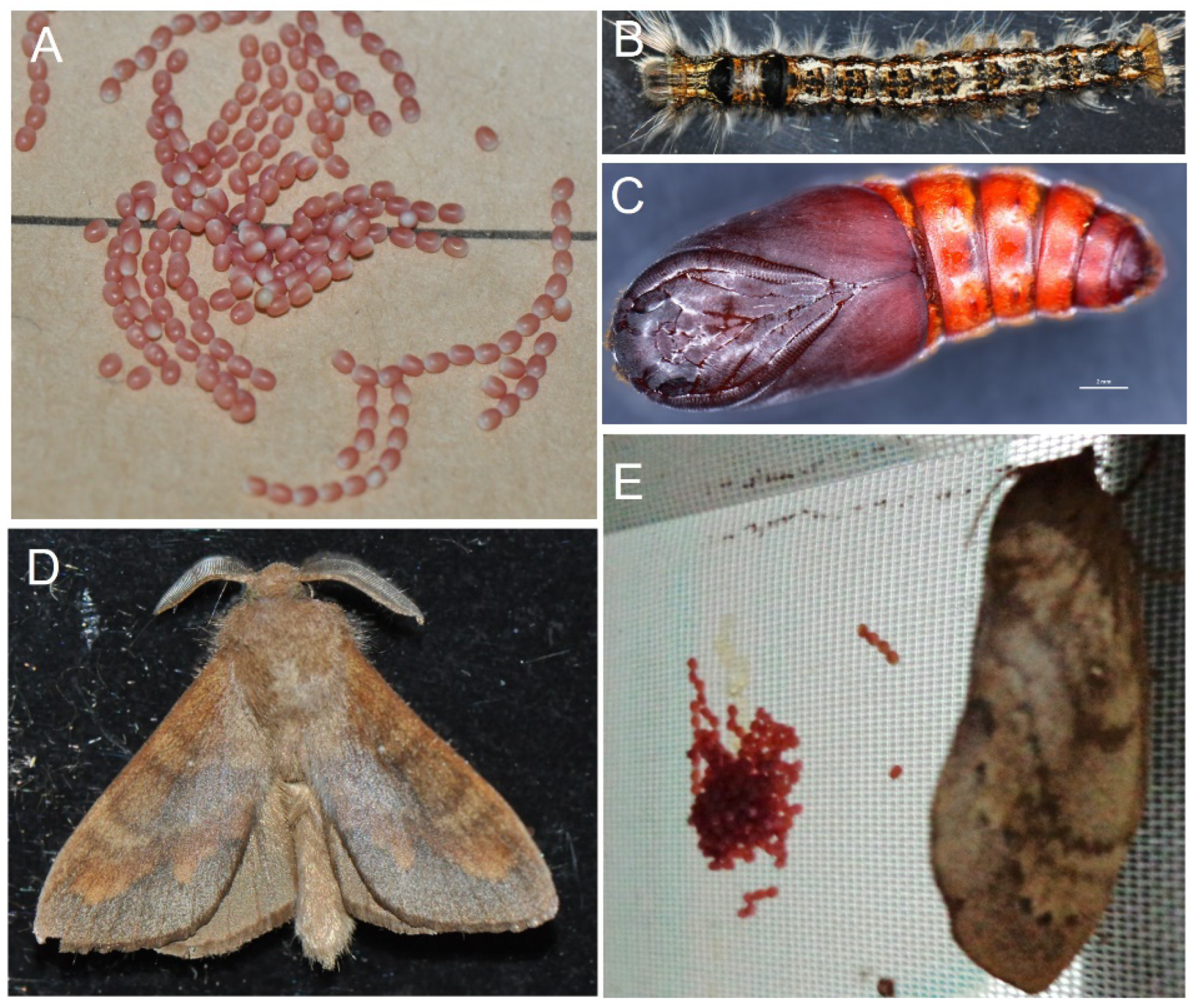
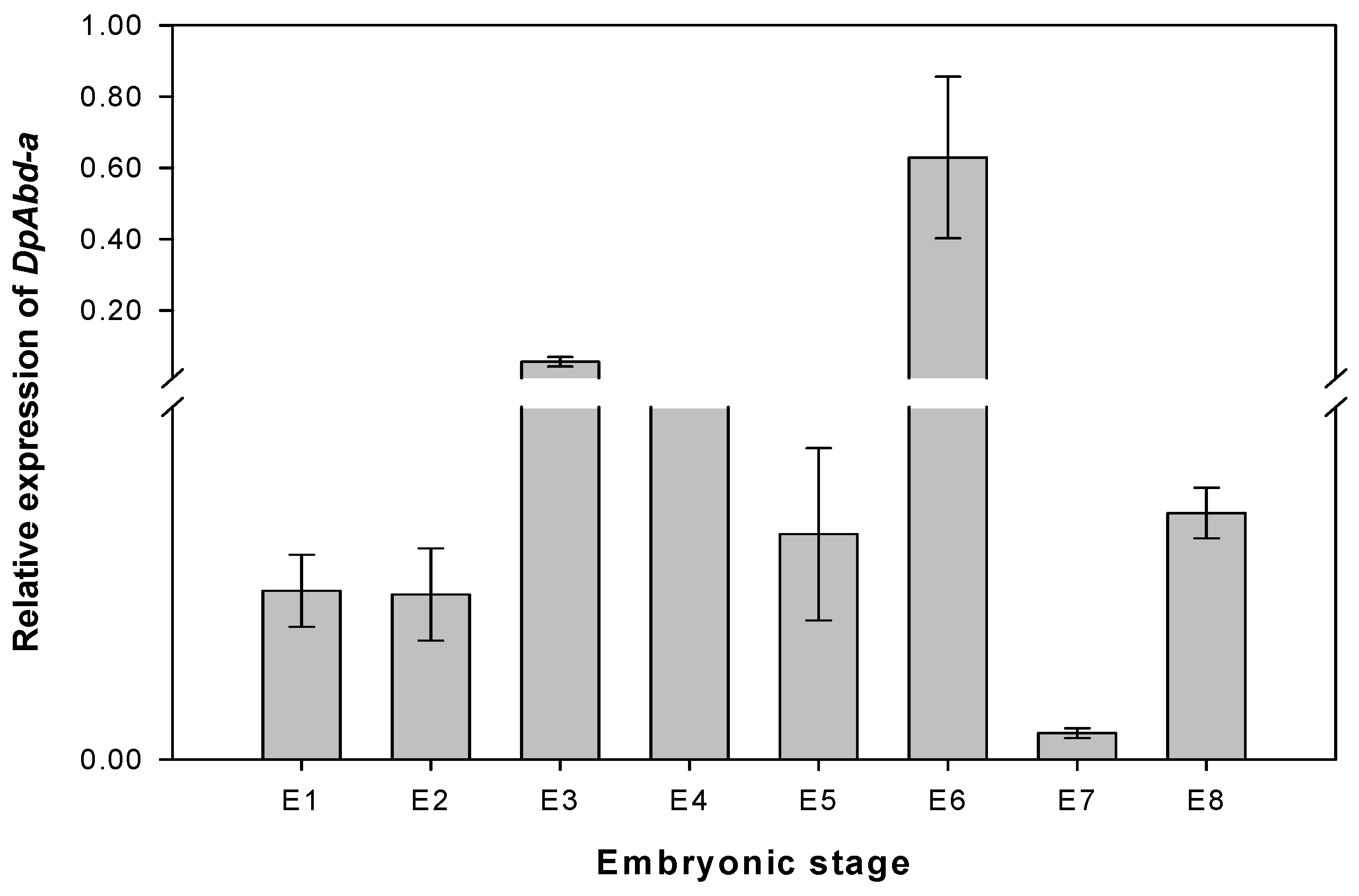
2.1. cDNA Cloning, Sequence Analysis, and Expression Pattern of the DpAbd-a Gene
2.2. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Mutations in the DpAbd-a Gene in the G0 and G1 Generation of D. punctatus
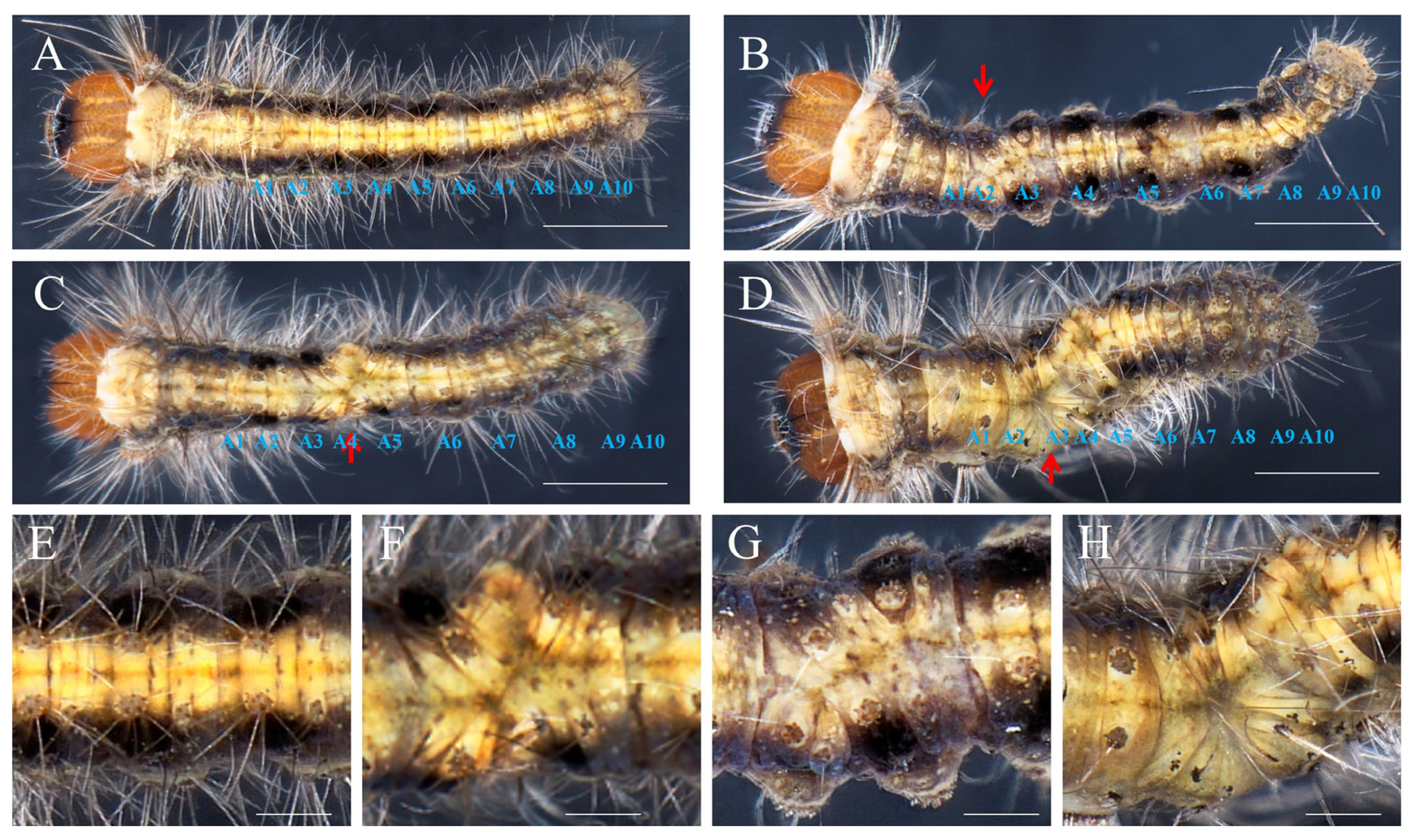
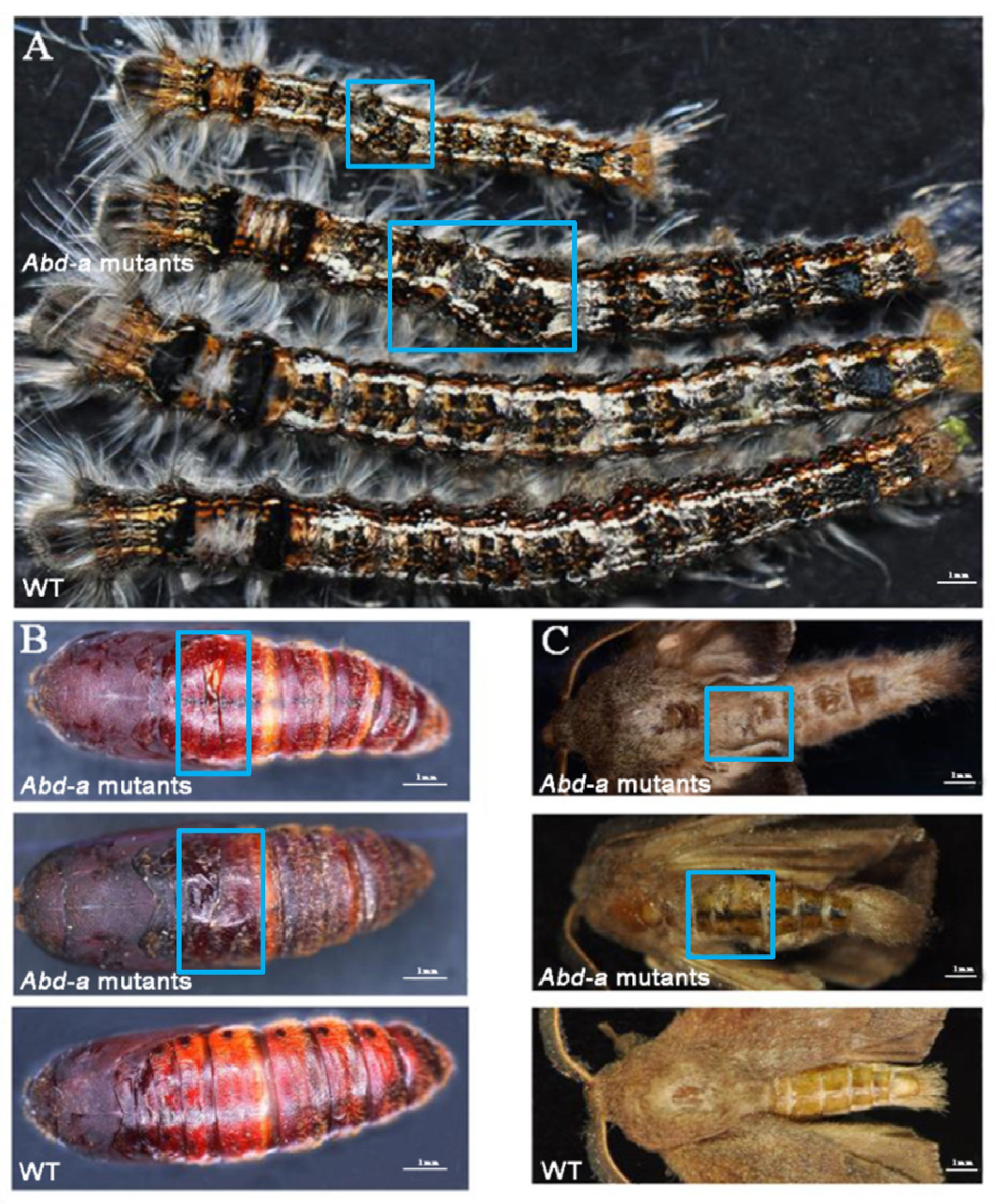
2.3. Roles of DpAbd-a in Posterior Segmentation and Appendage Development
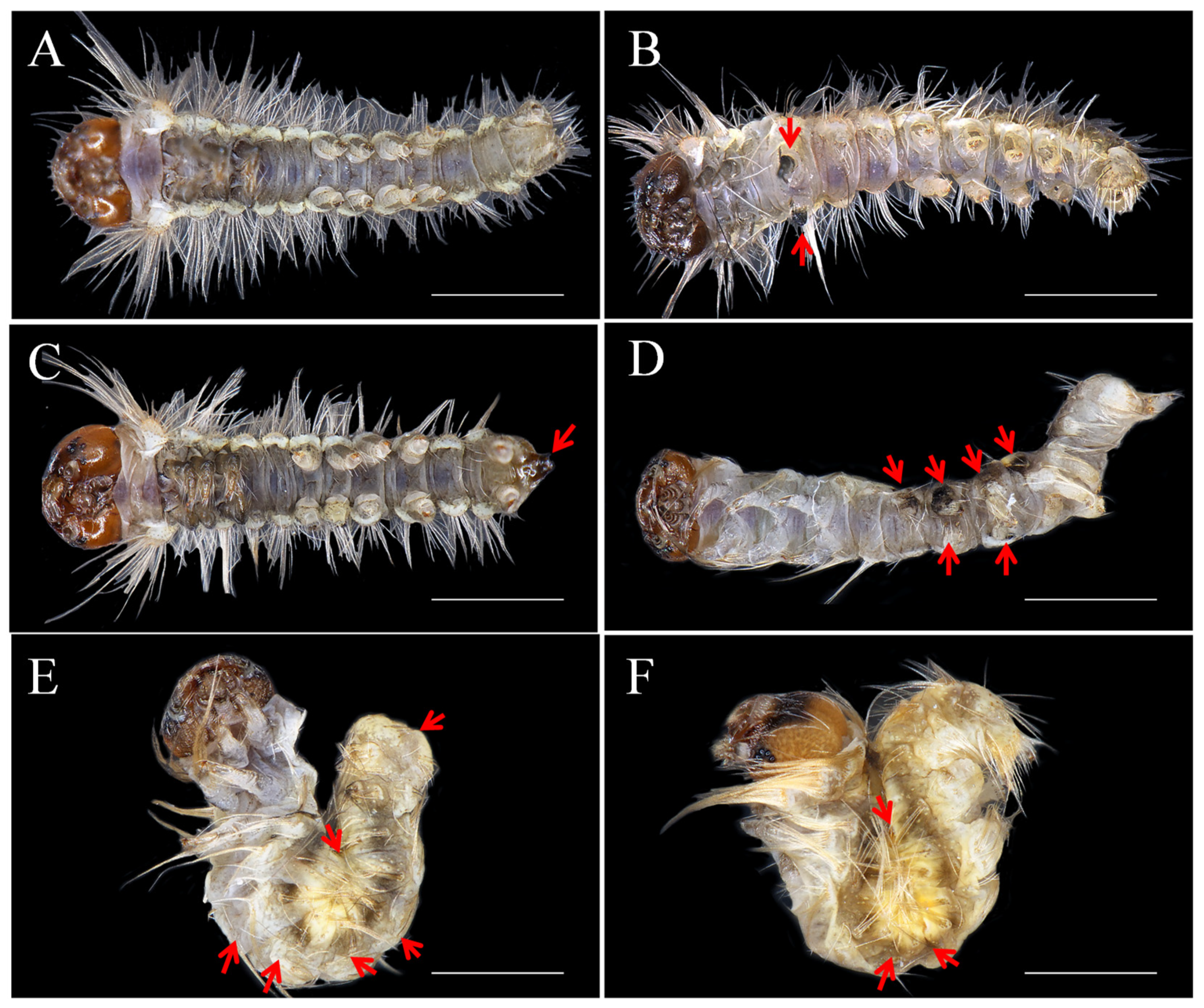
2.4. Pleiotropic Effects of DpAbd-a Knockout
3. Discussion
3.1. CRISPR/Cas9 System for Abd-a Loss of Function
3.2. Characterization of the DpAbd-a Homolog
3.3. Abd-a Is Involved in the Determination of Posterior Segments
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Rearing
4.2. Gene Identification and Phylogenetic Analyses
4.3. Real Time Quantitative PCR
4.4. In Vitro Transcription and Purification of Cas9 and sgRNA
4.5. Embryonic Microinjection
4.6. Screening and Analysis of Cas9/sgRNA-Induced Mutations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, J.; Ge, F.; Su, J.; He, Z. Researches on the occurrences of major forest insect pests of pine caterpillar Dendrolimus spp. in China. Chin. Bull. Entomol. 2010, 47, 451–459. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, S.; Peng, J.; Zhou, X.; Kong, X.; Ren, P.; Liu, F.; Han, L.; Zhan, S.; Huang, Y.; et al. Chromosome-level genome assembly of an important pine defoliator, Dendrolimus punctatus (Lepidoptera; Lasiocampidae). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horak, K.E. RNAi: Applications in Vertebrate Pest Management. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Huang, Y.N.; Tang, X.M. RNAi-based pest control: Production, application and the fate of dsRNA. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 29, 1080576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.M.; De Schutter, K. Biosafety aspects of RNAi-based pests control. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalakouras, A.; Koidou, V.; Papadopoulou, K. DsRNA-based pesticides: Considerations for efficiency and risk assessment. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Palli, S.R. Mechanisms, Applications, and Challenges of Insect RNA Interference. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiwal, A.; Natarajaswamy, K.; Rajam, M.V. RNA silencing of hormonal biosynthetic genes impairs larval growth and development in cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, M.; Fite, T. RNA interference (RNAi) applications to the management of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): Its current trends and future prospects. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 944774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swevers, L.; Liu, J.; Smagghe, G. Defense Mechanisms against Viral Infection in Drosophila: RNAi and Non-RNAi. Viruses 2018, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltshire, R.M.; Duman-Scheel, M. Advances in oral RNAi for disease vector mosquito research and control. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2020, 40, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Yin, M.Z.; Shen, J. Nanoparticle-based nontransformative RNA insecticides for sustainable pest control: Mechanisms, current status and challenges. Entomol. Generalis. 2023, 43, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, E.; Peel, A.D.; Akam, M. Arthropod segmentation. Development 2019, 146, dev170480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peel, A.D.; Chipman, A.D.; Akam, M. Arthropod segmentation: Beyond the Drosophila paradigm. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Tusscher, K.H. Mechanisms and constraints shaping the evolution of body plan segmentation. Eur. Phys. J. E Soft. Matter. 2013, 36, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, D.S.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. The origin of pattern and polarity in the drosophila embryo. Cell 1992, 68, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karch, F.; Weiffenbach, B.; Peifer, M.; Bender, W.; Duncan, I.; Celniker, S.; Crosby, M.; Lewis, E.B. The abdominal region of the bithorax complex. Cell 1985, 43, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, R.K.; Karch, F. The ABC of the BX-C: The bithorax complex explained. Development 2006, 133, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, R.M.; Grbic, M.; Nagy, L.M. Composition and genomic organization of arthropod Hox clusters. Evodevo 2016, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilder, D.; Graba, Y.; Scott, M.P. Wnt and TGFbeta signals subdivide the AbdA Hox domain during Drosophila mesoderm patterning. Development 1998, 125, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estacio-Gomez, A.; Moris-Sanz, M.; Schafer, A.K.; Perea, D.; Herrero, P.; Diaz-Benjumea, F.J. Bithorax-complex genes sculpt the pattern of leucokinergic neurons in the Drosophila central nervous system. Development 2013, 140, 2139–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foronda, D.; Estrada, B.; de Navas, L.; Sanchez-Herrero, E. Requirement of Abdominal-A and Abdominal-B in the developing genitalia of Drosophila breaks the posterior downregulation rule. Development 2006, 133, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roumengous, S.; Rousset, R.; Noselli, S. Polycomb and Hox Genes Control JNK-Induced Remodeling of the segment boundary during Drosophila morphogenesis. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinnis, W.; Krumlauf, R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell 1992, 68, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, R.; Berger, C.; Myneni, S.; Technau, G.M.; Shashidhara, L.S. Abdominal-A mediated repression of Cyclin E expression during cell-fate specification in the Drosophila central nervous system. Mech. Dev. 2010, 127, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, M.; Fanti, L.; Berloco, M.; Pimpinelli, S. Differential expression of the Drosophila BX-C in polytene chromosomes in cells of larval fat bodies: A cytological approach to identifying in vivo targets of the homeotic Ubx, Abd-A and Abd-B proteins. Development 2003, 130, 3683–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodkinson, L.J.; Smith, C.; Comstra, H.S.; Ajani, B.A.; Albanese, E.H.; Arsalan, K.; Daisson, A.P.; Forrest, K.B.; Fox, E.H.; Guerette, M.R.; et al. A bioinformatics screen reveals hox and chromatin remodeling factors at the Drosophila histone locus. BMC Genom. Data. 2023, 24, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; Mishra, R.K. Role of Abd-A and Abd-B in development of abdominal epithelia breaks posterior prevalence rule. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Merchant, A.; Gu, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Q. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis of Abdominal-A and Ultrabithorax in the Asian Corn Borer, Ostrinia furnacalis. Insects 2022, 13, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, D.L.; DeCamillis, M.; Bennett, R.L. Distinct roles of the homeotic genes Ubx and abd-A in beetle embryonic abdominal appendage development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4504–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, B.; Wang, Y.; James, A.A.; Gurr, G.M.; Yang, G.; Lin, X.; Huang, Y.; You, M. CRISPR/Cas9 mediated knockout of the abdominal-A homeotic gene in the global pest, diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 75, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Chai, C.L.; Zhang, C.D.; Lu, C.; Xiang, Z.H. Identification and function of Abdominal-A in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Mol. Biol. 2009, 18, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, H.L.; Xu, J.; Tan, A.J.; Huang, Y.P. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted gene mutagenesis in Spodoptera litura. Insect Sci. 2016, 23, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Cuadros, M.; Pourquie, O.; El-Sherif, E. Patterning with clocks and genetic cascades: Segmentation and regionalization of vertebrate versus insect body plans. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Genome Editing of Wnt-1, a Gene Associated with Segmentation, via CRISPR/Cas9 in the Pine Caterpillar Moth, Dendrolimus punctatus. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Shirk, P.D.; Taylor, C.E.; Furlong, R.B.; Shirk, B.D.; Pinheiro, D.H.; Siegfried, B.D. CRISPR/Cas9 mediated knockout of the abdominal-A homeotic gene in fall armyworm moth (Spodoptera frugiperda). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.L.; Fu, M.Y.; Chen, P.; Chen, L.; Xiang, Z.H.; Lu, C.; Dai, F.Y. Ultrabithorax and abdominal-A specify the abdominal appendage in a dosage-dependent manner in silkworm, Bombyx mori. Heredity 2017, 118, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, F.B.; Parker, E.; Krasnow, M.A. Extradenticle protein is a selective cofactor for the Drosophila homeotics Role of the homeodomain and YPWM amino acid motif in the interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karch, F.; Bender, W.; Weiffenbach, B. abdA expression in Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1990, 4, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, L.M.; Booker, R.; Riddiford, L.M. Isolation and embryonic expression of an abdominal-A-like gene from the lepidopteran, Manduca sexta. Development 1991, 112, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shippy, T.D.; Brown, S.J.; Denell, R.E. Molecular characterization of the Tribolium abdominal-A ortholog and implications for the products of the Drosophila gene. Dev. Genes. Evol. 1998, 207, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Shinmyo, Y.; Mito, T.; Miyawaki, K.; Sarashina, I.; Ohuchi, H.; Noji, S. Expression patterns of the homeotic genes Scr, Antp, Ubx, and abd-A during embryogenesis of the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. Gene Expr. Patterns. 2005, 5, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palopoli, M.F.; Patel, N.H. Evolution of the interaction between Hox genes and a downstream target. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Khoo, A.; Fambrough, D., Jr.; Garza, L.; Booker, R. Homeotic gene expression in the wild-type and a homeotic mutant of the moth Manduca sexta. Dev. Genes Evol. 1999, 209, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandvakili, A.; Uhl, J.D.; Campbell, I.; Salomone, J.; Song, Y.C.; Gebelein, B. The cis-regulatory logic underlying abdominal Hox-mediated repression versus activation of regulatory elements in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 2019, 445, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, Y.; Murugesan, S.N.; Prakash, A.; Monteiro, A. Lepidopteran prolegs are novel traits, not leg homologs. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadd9389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.P.; Hua, B.Z. Distinct roles of the Hox genes Ultrabithorax and abdominal-A in scorpionfly embryonic proleg development. Insect Mol. Biol. 2024, 33, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Liu, L.; Huang, L.; Xu, W.H.; Palli, S.R.; Feng, Q. Homeodomain POU and Abd-A proteins regulate the transcription of pupal genes during metamorphosis of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12598–12603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Deng, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zheng, S.; Song, Q.; Feng, Q. Identification of the binding domains and key amino acids for the interaction of the transcription factors BmPOUM2 and BmAbd-A in Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 81, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foronda, D.; Martin, P.; Sanchez-Herrero, E. Drosophila Hox and sex-determination genes control segment elimination through EGFR and extramacrochetae activity. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Xu, H.; Ma, S.; Guo, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zha, X.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q. Ectopic expression of the male BmDSX affects formation of the chitin plate in female Bombyx mori. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2014, 81, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Li, Z.Q.; Xu, J.; Zeng, B.S.; Ling, L.; You, L.; Chen, Y.Z.; Huang, Y.P.; Tan, A.J. The CRISPR/Cas system mediates efficient genome engineering in Bombyx mori. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 1414–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Aslam, A.F.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Huang, Y.; Tan, A. Functional analysis of Bombyx Wnt1 during embryogenesis using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 79, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Cas9/sgRNA Concentration (ng/μL) | Treatment Number (n) | G0 a | G1 a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Embryo Mortality (%) | Defective Larvae b (%) | Pupae (n) | Adults (n) | Embryo Mortality (%) | Defective Larvae b (%) | Pupae (n) | Adults (n) | ||
| Abd-a 500/500 | 480 | 70.4 | 17.5 | 3 | 2 | 32.3 | 28.6 | 0 | 0 |
| EGFP 500/500 | 120 | 35.8 | 0 | 28 | 23 | 17.6 | 0 | 37 | 28 |
| WT 0/0 | 120 | 38.8 | 0 | 32 | 27 | 19.8 | 0 | 55 | 47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Ma, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X. Functional Characterization of Abdominal-A in the Pine Caterpillar Moth, Dendrolimus punctatus. Forests 2024, 15, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15071157
Liu H, Chen L, Ma Q, Wang X, Zhang S, Zhou X. Functional Characterization of Abdominal-A in the Pine Caterpillar Moth, Dendrolimus punctatus. Forests. 2024; 15(7):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15071157
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huihui, Lin Chen, Qinghua Ma, Xinghong Wang, Sufang Zhang, and Xuguo Zhou. 2024. "Functional Characterization of Abdominal-A in the Pine Caterpillar Moth, Dendrolimus punctatus" Forests 15, no. 7: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15071157
APA StyleLiu, H., Chen, L., Ma, Q., Wang, X., Zhang, S., & Zhou, X. (2024). Functional Characterization of Abdominal-A in the Pine Caterpillar Moth, Dendrolimus punctatus. Forests, 15(7), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15071157









