Abstract
Bamboo breeding strategies are essential in realizing “Bamboo as a Substitute for Plastic (BASP)”. This review article aims to explore the crucial role of breeding strategies in achieving the substitution of plastic products with bamboo as outlined under the BASP Initiative. Firstly, we address the issue of plastic pollution, along with the background of reducing the market share and demand for plastic products. It categorizes the types of bamboo products that can fully or partially replace plastic products in various categories, such as daily necessities, building materials, and industrial products. Then, we investigate which bamboo species can replace which plastic products and propose the need for bamboo improvement. Furthermore, it presents data from positioning observation research stations for bamboo forest ecosystems in China and outlines the essential traits necessary for bamboo substitution, including characteristics like long internode length, extended fiber length, thick culm wall, and optimal cellulose-to-lignin content ratio, among others. Finally, we discuss breeding methods and genetic improvement as key strategies to achieve bamboo substitution and suggest the potential of enhancing bamboo traits to serve as a viable replacement source for plastics. This comprehensive approach aims to enhance bamboo’s growth features and physical properties to meet the criteria for substituting bamboo for plastics effectively.
1. Introduction
Bamboo, a green and environmentally friendly, high-quality biomass resource, is abundant in warm and humid climates found in tropical, sub-tropical, and temperate regions worldwide. Its distribution spans the Asia-Pacific bamboo region, the Americas bamboo region, the African bamboo region, and introduced areas [1]. Among these regions, the Asia–Pacific bamboo region stands out as the largest in the world, encompassing major bamboo-producing countries such as China, India, Myanmar, Thailand, Bangladesh, Cambodia, Vietnam, Japan, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, South Korea, and Sri Lanka.
As global demand for timber rises and forest reserves dwindle, bamboo emerges as a crucial forest resource. Its significance is underscored by its role in achieving the “carbon peaking and carbon neutrality” goals and supporting the envisioned “bamboo as a substitute for plastic (BASP)” initiative [2]. In China, bamboo resources are plentiful, covering approximately 3.31% of the forest area, with moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) occupying the largest, approximately three-quarters of the bamboo grove. Moso bamboo forests are distributed in 13 provinces nationwide, with a total area of 5.2776 million hectares [3]. Moso bamboo shoots grow rapidly in spring, and bamboo plants have very short cultivation cycle. It takes only one and a half months from bamboo shoots to bamboo plants (reaching heights of 33–66 feet and a diameter at breast height of 3–6 inches), and bamboo plants can be harvested for bamboo products after 3–5 years. Stem culms of 4-year-old bamboo have optimal mechanical properties, meeting the requirements for industrial continuous production.
With robust reproductive capabilities, moso bamboo offers sustainable utilization opportunities, excelling in harsh conditions and proving ideal for mountain afforestation, a crucial feature as suitable afforestation land diminishes in China. Notably, moso bamboo boasts exceptional mechanical properties, surpassing wood and conventional steel in specific strength and stiffness [4]. Its high cellulose content, superior fiber morphology, and remarkable pulp extensibility contribute to its strength and plasticity [5,6,7,8]. Thus, moso bamboo emerges as a prime eco-friendly high-quality biomass material for substituting plastics, aligning with the global sustainability drive [2].
Bamboo has successfully integrated into various aspects of our lives, from daily essentials to industrial products [9]. Notable examples include bamboo straws, which have gained popularity as a sustainable alternative to plastic ones. In Fujian Province, the Longzhu Technology Group has developed a thin bamboo material for making bamboo straws, preserving the natural bamboo texture and offering scalability and cost advantages [10]. Similarly, the Heiyang Xiangrui Bamboo Industry in Hunan Province produces millions of bamboo straws daily, exporting them to the European Union (EU) and exploring partnerships in Australia and Italy [11]. In agriculture, plastic mulch has significantly contributed to agricultural efficiency, the safety of food supply, and increased farmers’ incomes. However, the extensive use of plastic mulch and the lack of effective recycling and disposal have directly harmed the agricultural sector. Wang et al. developed a biodegradable paper sheet using bamboo paper sludge, poplar wood fibers, and viscose fibers through wet-laid nonwoven technology, capable of fulfilling the demand for replacing agricultural plastic sheeting for soil moisture retention and plant growth promotion [12]. Furthermore, a bamboo-based offshore photovoltaic platform (Jilin No. 1) has been developed, showcasing the potential to replace high-density polyethylene and steel structures with eco-friendly, cost-effective bamboo materials [13].
2. International and Chinese Policy Advantages
2.1. International Policy Drivers for Reducing Plastic Pollution
The issue of plastic pollution has gained global attention in recent years, with alarming statistics revealing the extent of the problem. According to the report “From Pollution to Solution: A Global Assessment of Marine Litter and Plastic Pollution”, released by the United Nations Environment Programme in October 2021, of the 9.2 billion tons of plastic produced between 1950 and 2017, approximately 7 billion tons became plastic waste, either dumped in landfills or irresponsibly disposed of [14]. About mean between 23 and 37 million metric tons of plastic waste enter the oceans each year [15]. It is evident that the pollution brought about by plastic products is escalating at an alarming rate, posing a grave threat to our environment and aquatic ecosystems.
In response to this crisis, various international societies and organizations have taken action to support the reduction and elimination of plastic products, encourage the development of alternatives, adjust industrial and trade policies, and reduce plastic pollution. Since 2018, more than forty policies have been enacted or implemented by international organizations, including the United Nations, the European Union, the International Bamboo and Rattan Organization (INBAR), and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, among others, representing over ten countries from six continents. These international policies include explicit bans on the production and sale of single-use plastic cotton swabs and disposable foam plastic tableware, as well as restrictions or bans on non-biodegradable plastic bags, non-biodegradable plastic tableware, and non-biodegradable plastic straws [16].
The proliferation of international policies restricting plastic use has stimulated efforts to explore alternative materials as substitutes for plastic [17]. Due to its natural, renewable, and fast-growing characteristics, bamboo is considered an excellent alternative material to plastic [18]. With the capacity to be transformed into various products such as bamboo fiberboards, composites, and textiles, bamboo offers superior biodegradability and environmental sustainability compared to traditional plastics [18,19]. Moreover, international policies are supporting the development and promotion of alternative plastic materials, driving the application of bamboo and other substitute materials. Businesses and consumers are gradually realizing the environmental hazards of plastic pollution and are willing to choose more eco-friendly alternative materials, providing opportunities and market demand for the development of bamboo and other substitute plastic materials. Therefore, encouraged and supported by international environmental drivers, the research and production of bamboo and other alternative plastic materials will help reduce plastic pollution, protect the environment, and promote sustainable green development.
2.2. Domestic Policy Support in China
In the wave of global efforts to govern plastic pollution, the Chinese government, in collaboration with the INBAR, launched the BASP initiative in November 2022 to promote the reduction of plastic pollution, address climate change, and accelerate the implementation of the United Nations’ 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda. Subsequently, in October 2023, the National Development and Reform Commission and other departments issued the “Three-year Action Plan to Promote the Use of Bamboo as an Alternative to Plastic Products to Curb Pollution” (Abbreviated as “Three-year Action Plan”), which sets action goals such as the preliminary establishment of the bamboo substitution for plastics industrial system by 2025. Therefore, in the coming years, we should focus on promoting the full or partial substitution of plastic products, including daily necessities, building materials, and industrial products, with bamboo products and bamboo-based composites (Figure 1). This will play a crucial role in strengthening the overall governance of plastic pollution, realizing the value of eco-friendly products, facilitating carbon peak and neutrality goals, and advancing the construction of a beautiful world through the BASP initiative.

Figure 1.
The list of BASP initiative products.
In November 2023, China and the INBAR jointly released the Global Action Plan for Bamboo Substitution for Plastics. This plan delineates six major action objectives, including accelerating support measures, enhancing scientific research, encouraging innovation, advancing market mechanisms, strengthening promotion efforts, and consolidating partnership foundations, comprising a total of 23 specific actions [20]. In December 2023, the development, production, and application of bamboo substitute products were included in the 2024 edition of China’s National Development and Reform Commission’s Guidance Catalog for Industrial Structural Adjustment under the category of encouraged industries [21]. In February 2024, bamboo substitution was further included in the 2024 edition of China’s National Development and Reform Commission’s Guidance Catalog for Green and Low-Carbon Transformation Industries [22]. Recently, on 8 April 2024, the National Development and Reform Commission of China issued a notice regarding the implementation of the “Special Management Measures for Central Budgetary Investment in Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction.” This notice emphasizes support for bamboo product production, including daily necessities, building materials, and industrial products [23].
Since 2023, provinces and municipalities in China such as Fujian, Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Hunan, Sichuan, Guizhou, and Anhui have successively implemented a series of measures to promote the inclusion of bamboo substitute products in government procurement support, establish incentive compensation mechanisms for promoting the application of bamboo substitutes, and pioneer demonstration activities for bamboo substitution. Simultaneously, since 2023, the Ministry of Commerce in China has been actively promoting the matching of supply and demand for bamboo substitutes, with relevant departments and localities actively promoting the use of bamboo substitute products in public places such as offices and meeting rooms. In the aviation sector, airlines are actively using bamboo utensils to replace disposable plastic ones. In sectors such as catering takeout, hotel accommodation, express packaging, and industrial production, a group of enterprises are accelerating the promotion of bamboo utensils, bamboo daily necessities, and bamboo-based biodegradable packaging materials, among others [24]. “Bamboo substitution for plastics” is becoming a new trend in green living. It is evident that domestic policies strongly support the development of environmentally friendly substitute products for plastics to address the global environmental issues caused by plastic pollution, which affect the livelihoods, food production capacity, and social welfare of millions of people.
3. Environmental and Cultural Advantages
Bamboo possesses an astonishing ability to regenerate and is the fastest-growing plant in the world, with a relatively short growth cycle typically ranging from 3 to 5 years, making it a sustainable long-term resource [1]. In contrast, the growth cycle of wood may take several decades or even longer. Therefore, using bamboo as a raw material can alleviate pressure on natural forest resources. Additionally, bamboo absorbs a significant amount of carbon dioxide and releases oxygen during its growth, and bamboo products, once produced, sequester large amounts of carbon dioxide from the air, aiding in mitigating the impact of global warming and climate change [25,26,27,28]. Furthermore, bamboo products typically do not require the use of harmful chemicals for processing or maintenance, thus generating no pollutants during use [29]. Moreover, when bamboo products reach the end of their lifespan, they can naturally degrade or be recycled for further use. In conclusion, the environmental advantages of bamboo products make them a sustainable and eco-friendly choice, with an increasing number of consumers and businesses opting for bamboo products to achieve sustainable consumption and reduce environmental impact.
Bamboo holds a profound cultural significance and a long history in Chinese culture, representing traditional values and cultural heritage [30]. Bamboo holds a highly symbolic status in Chinese culture, symbolizing noble virtues [31]. Its widespread use in cultural arts spans from being a material for creating artworks to serving as a symbol in various representations. The graceful and fresh lines and colors of bamboo add a unique aesthetic appeal to bamboo products, which are greatly appreciated and admired by people. Additionally, in ancient China, people relied on bamboo to create various everyday items such as brush pens, stationery, utensils, furniture, and more. The use of these bamboo products not only fulfilled people’s daily needs but also embodied the accumulation of traditional culture, enriching folk traditions.
4. Breeding Strategies for the BASP Initiative
While bamboo presents itself as a substitute for plastic products, it still faces some drawbacks, such as susceptibility to cracking, short internodes, thin culm walls, and hollow culms, which result in lower efficiency in the manufacturing process of bamboo products and a lack of superior bamboo species suitable for replacing plastics. As people’s concern for environmental issues increases, more bamboo products are entering our lives, showing great potential to replace plastic products. To meet the demands for different types of bamboo products, such as bamboo straws, chopping boards, furniture, automotive interiors, bamboo mulching film, bamboo-wrapped pipelines, etc., there is a need to optimize breeding strategies for bamboo species.
4.1. Location-Specific Cultivation and Cultivar Improvement
The Bamboo Forest Ecosystem is an important component of forest ecosystems. Researchers collected samples from 15 geographic distribution areas of moso bamboo across China, representing nearly all habitats. They discovered relatively low whole-genome diversity in the moso bamboo population but observed distinct phenotypic and material traits across different habitats [32]. For instance, culms from Anhui Jinzhai, Fujian Wuyishan, and Yongan grow thicker, with a ground diameter exceeding 13 cm, suitable for mechanized processing of large-diameter bamboo. Moso bamboo from Anhui Jinzhai and Zhejiang Longyou exhibits strong compressive strength, while that from Guizhou Chishui shows robust bending strength. These diverse phenotypic and mechanical properties play varied roles in the BASP sector.
Given the varying phenotypic and material traits of the same bamboo species across different environments, establishing Bamboo Forest Ecological Observation and Research Stations equipped with a variety of sensor technologies facilitates the systematic collection of data regarding bamboo forest ecosystems. The layout of bamboo forest ecological observation stations needs to comprehensively consider various factors such as natural geographical conditions, bamboo distribution areas, and types of bamboo species. It is necessary to establish multiple ecological observation stations, including tropical climbing bamboo ecological stations, southeastern coastal sympodial bamboo ecological stations, southwestern sympodial bamboo ecological stations, eastern mixed bamboo ecological stations, central mixed bamboo ecological stations, western mixed bamboo ecological stations, mountainous sympodial and monopodial bamboo ecological stations, and mountainous monopodial bamboo ecological stations [33].
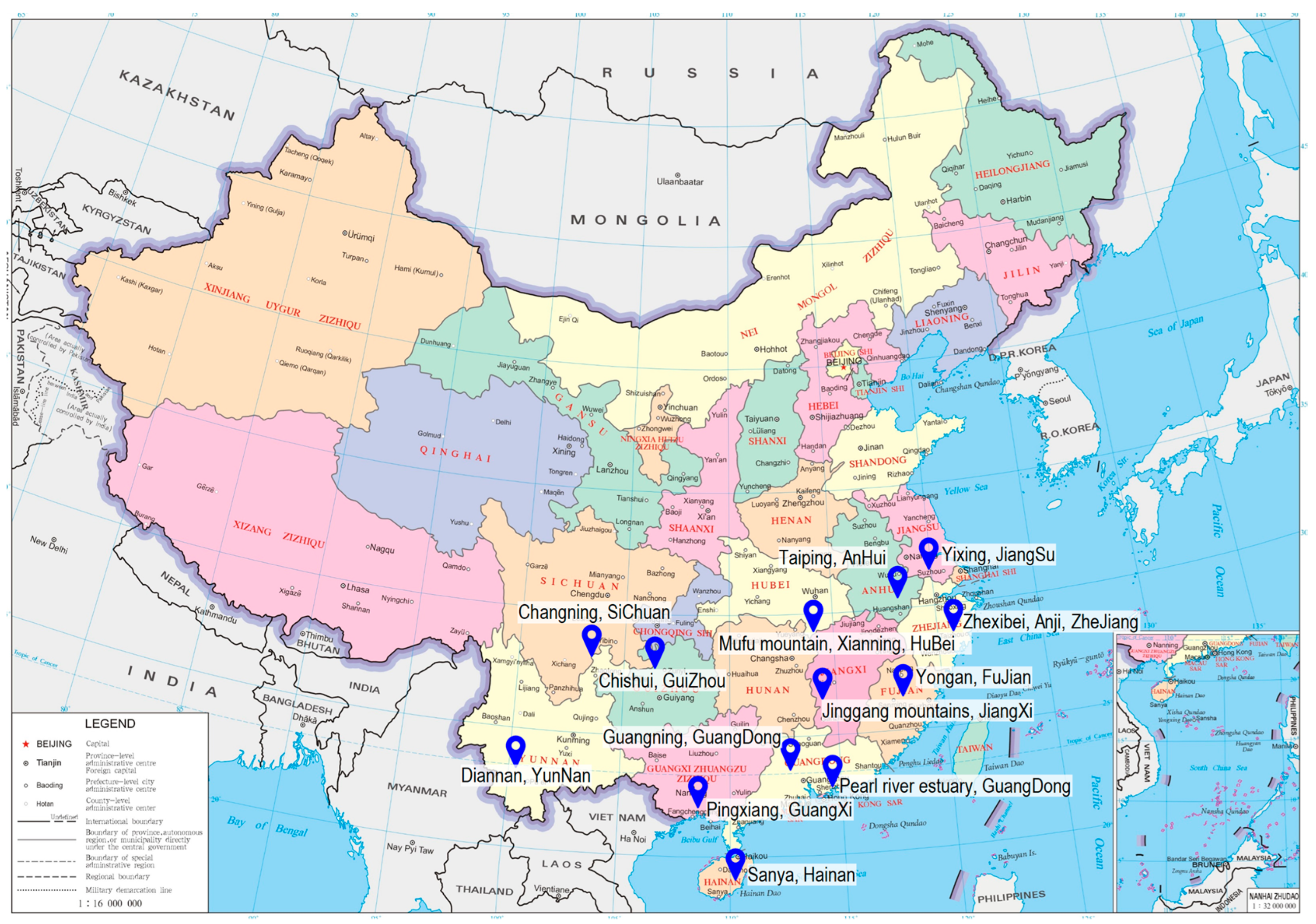
Currently, China has more than 13 bamboo forest ecological observation stations, including those in Taiping, Anhui, and Sanya, Hainan, which effectively cover the main types of bamboo forests in different climatic zones in China, forming a comprehensive bamboo forest ecological observation network (Figure 2; Table 1). These stations are capable of collecting environmental data such as climate, temperature, soil quality, water quality, and air quality. However, the existing ecological observation stations are primarily located in tropical and subtropical regions, while bamboo distribution is not limited to these regions; bamboo also grows in temperate areas. For example, in the temperate region of China, bamboo species like P. reticulata and P. glauca are found in Boai County, Henan Province, while species such as P. nigra, P. aureosulcata, Pleioblastus fortunei, and others are distributed in Beijing. Therefore, it is crucial to establish additional ecological observation stations in regions with diverse natural geographical conditions, such as temperate regions (e.g., Beijing, Henan Province in China), encompassing a broader range of climate types, altitudes, latitudes, and site conditions. This expansion will facilitate the collection of more comprehensive ecological information about bamboo forests in various environments.
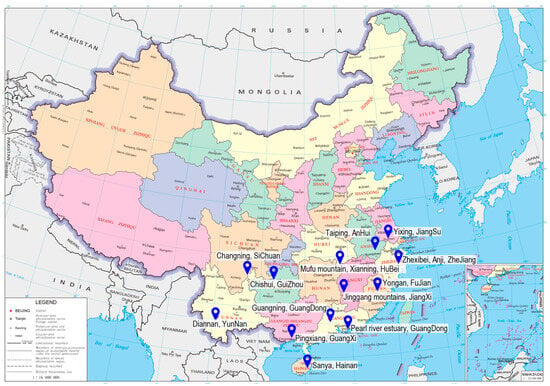
Figure 2.
Positioning observation research station for bamboo forest ecosystem in China.

Table 1.
Information of the positioning observation research stations for the bamboo forest ecosystem.
Furthermore, based on existing observation stations, by equipping them with more sensor technologies such as three-dimensional morphological information, morphological and color analysis, chlorophyll content, and photosynthetic efficiency in bamboo leaves, we can integrate bamboo phenotype data with environmental factors to comprehensively analyze which cultivars are suitable for cultivation in different locations and under which site conditions certain superior bamboo phenotypes can be cultivated. Moreover, the information from ecological observation stations can guide us in determining which breeding methods can improve the phenotypes of specific bamboo species.
4.2. Strengthening Basic Research on the Impact of Environmental Factors on Bamboo Phenotypes
Optimizing bamboo forest cultivation methods to obtain desired bamboo phenotypes requires considering multiple factors, including soil management, water supply, light control, temperature regulation, and fertilization. Bamboo typically thrives in sandy soils with good drainage, and enhancing soil structure can involve the addition of soil with appropriate pH and organic matter [34,35]. Maintaining air moisture, soil temperature, and moisture are crucial for bamboo growth, especially during dry seasons or growth periods [36,37,38,39]. The transportation and accumulation of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) are critical for the explosive growth of bamboo shoots. Existing research has shown that applying nitrogen fertilizer in bamboo forests accelerates shoot growth and alters the lignification process [40]. Research has demonstrated that the required carbon for shoots originates from attached mature bamboo via underground rhizomes, indicating the dynamic allocation and transfer of non-structural carbohydrates (NSC) [41]. The rapid growth rate of plants, including bamboo, necessitates a higher concentration of phosphorus (P) and a lower N:P ratio, which is supplied to bamboo shoots by mature bamboo via underground rhizomes [42,43]. Additionally, factors such as light intensity and temperature influence bamboo shoot germination, leaf biosynthesis, photosynthesis, and growth speed [44,45,46,47].
The development of bamboo is constrained by various environmental factors such as soil types, microbial species in the soil, nitrogen–phosphorus–potassium fertilizers, soil moisture content, altitude, latitude, wind direction, as well as climatic factors including light intensity, photoperiod, carbon dioxide concentration, temperature, and humidity. However, we have not fully understood the effects of these factors on the phenotype of bamboo. It remains unclear for bamboo farmers in bamboo forests when and where to use what means to obtain excellent phenotypes. By enhancing research on the impact of environmental factors on bamboo phenotypes, including the manipulation of single-factor variables to assess their effects on specific bamboo species, we can artificially adjust one or more environmental factors to achieve desired phenotypes.
4.3. Addressing the Bottlenecks in Hybrid Breeding
Traditional bamboo hybrid breeding lags behind common crops due to the lengthy vegetative growth stage and uncertain flowering period [48,49]. Bamboo flowering possesses distinct characteristics and remains a mystery. Therefore, inducing flowering, artificially predicting, and pollen preservation techniques will be essential in addressing the challenges associated with bamboo breeding. To induce flowering, a substantial body of research suggests that plant hormones, such as auxin–cytokinin and ABA, are the primary means of inducing flowering in vitro [50,51,52]. There is also evidence that external stress can induce flowering, as Gao et al. [53] found that an increase in Dof expression under drought stress induced MADS-box expression, subsequently promoting flowering in moso bamboo. Fire and pruning have been observed to induce flowering in Bambusa tulda, B. balcooa, Dendrocalamus hookeri, and Melocanna baccifera [54].
Bamboo flowering is the only way for sexual reproduction, and it is capable of generating genetic diversity. By predicting the flowering time of bamboo, breeders can better plan breeding projects to ensure hybrid experiments can take place when bamboo is flowering, thereby cultivating new bamboo species or improved varieties. Accurately predicting bamboo flowering time is crucial for preserving bamboo’s genetic resources, ensuring timely measures are taken, such as seed collection, to retain valuable genetic materials. Currently, it is possible to predict bamboo flowering by analyzing environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and rainfall [55], intrinsic biological rhythms of specific bamboo species [56], and the morphology of bamboo rhizomes [57]. Additionally, certain genes that exhibit specific expression patterns during bamboo flowering are also key factors for predicting flowering. For example, ectopic expression of the PpMADS1 and PpMADS2 genes from P. praecox significantly promoted early flowering in transgenic plants, suggesting the involvement of both genes in floral transition, with PpMADS2 potentially playing a more significant role than PpMADS1 in the floral development of P. praecox [48]. In B. oldhamii, a PISTILLATA homolog (BoPI) was highly expressed in the flower organs and gradually increased during flower development, indicating its crucial role in flower development [49]. In moso bamboo, the PheDof1, PheMADS14, and six miRNAs may play vital regulatory roles in flower development and floral transition [58].
Additionally, preserving bamboo pollen, as an important part of the genetic resources of bamboo species, enables the utilization of these precious genetic materials in future breeding efforts, such as hybridization or other breeding experiments, to create new bamboo species or improved varieties. Techniques such as long-distance pollen transfer, precise pollination, and pollen storage can enhance bamboo reproduction efficiency and quality. Therefore, pollen preservation is essential for cross-species hybridization and the creation of new varieties, playing a crucial role in bamboo conservation and utilization. Enhanced research on flowering induction, prediction, pollen preservation techniques, and consolidation of existing flowering data, coupled with more comprehensive transcriptomics, metabolomics, and degradationomics big data analysis, can lead to improved flower prediction and help identify factors that influence flowering, such as hormone levels, environmental factors [55], specific phenotypes [56,57], and genes [48,49], ultimately simplifying hybrid breeding and shortening the breeding cycle.
Although hybrid breeding in bamboo presents challenges, diligent efforts by researchers have yielded some valuable hybrids. For instance, hybrids like B. textilis and B. pervariabilis exhibit tall culms, strong sprouting abilities, and good wood properties, along with hybrids possessing long fibers suitable for papermaking [59,60]. Hybrids of B. pervariabilis and D. daii offer delicious bamboo shoots and long fibers suitable for papermaking [61,62,63]. These hybrid varieties are suitable for promotion in tropical and subtropical regions, providing raw materials for bamboo pulp production in BASP.
4.4. Direct Genetic Improvement through Genetic Engineering
Utilizing big data, artificial intelligence, and genetic engineering techniques can cultivate bamboo species with more desirable traits to meet market demands and promote the application of bamboo products in broader fields. It is important to note that direct genetic improvement of bamboo is still at a very preliminary stage, hindered by factors such as lengthy growth cycles and immature transgenic technologies. Consequently, successful cases are few and far between. Currently, our references primarily involve functional validation of bamboo genes in other model plants or data on gene functions in closely related species, which will serve as the foundation for future direct genetic improvement of bamboo. However, we believe that in the near future, we will be able to achieve these objectives.
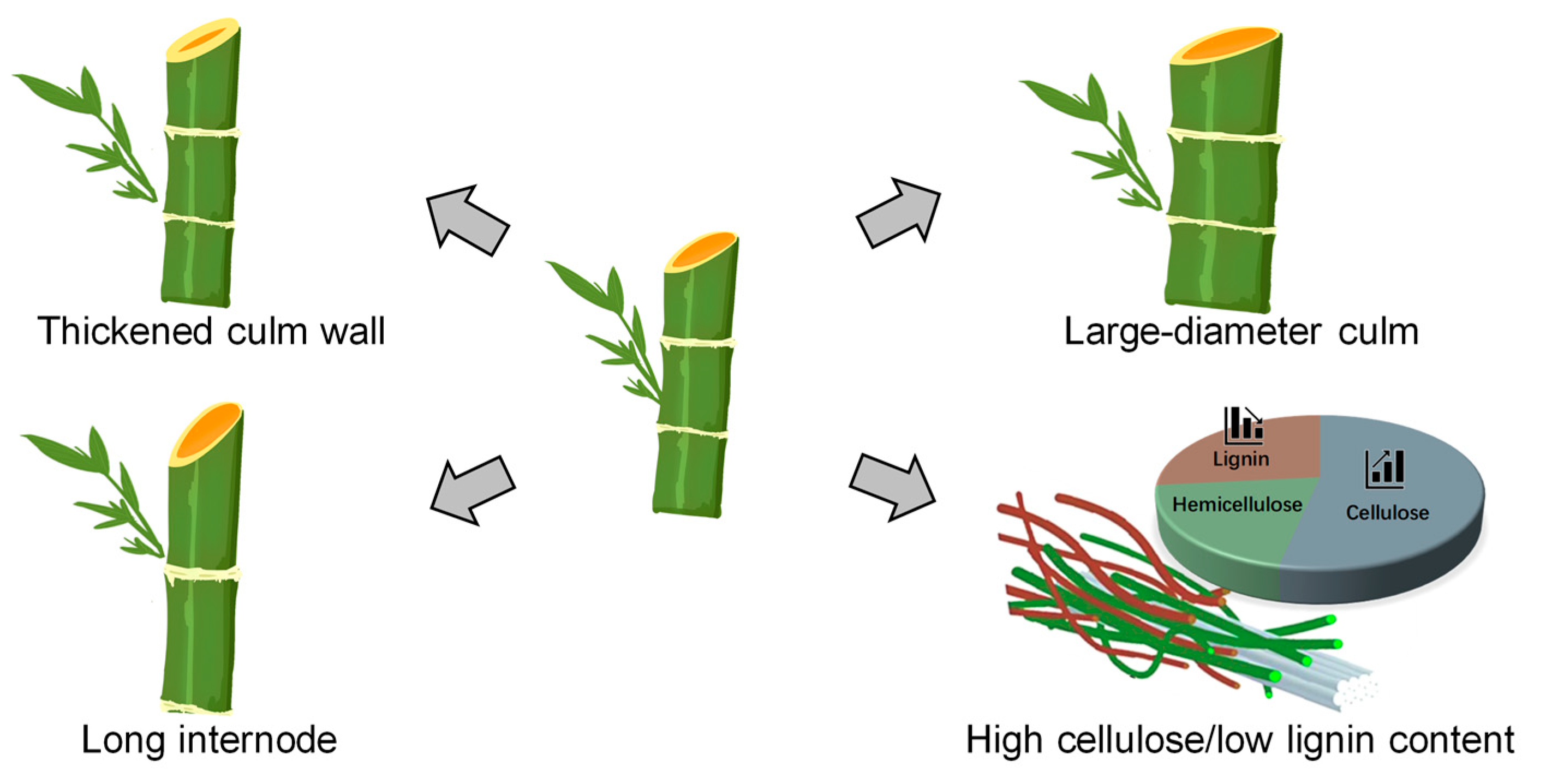
Recently, with the establishment of genetic transformation and gene editing systems in moso bamboo and ma bamboo [64,65,66], targeted genetic improvement based on gene function has become possible. Although the efficiency of genetic transformation and gene editing in bamboo is not yet high, it represents a breakthrough that allows us to carry out targeted genetic improvements on bamboo [67]. The desirable characteristics pursued for bamboo in substitution for plastics include long internode length, long fiber length, thick culm wall, and high cellulose/low lignin content (Figure 3).
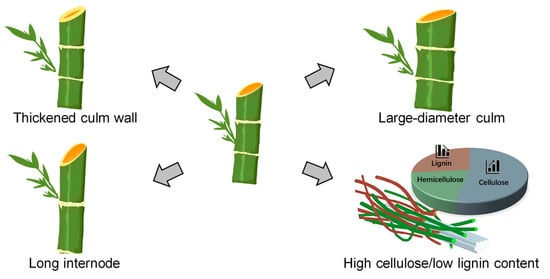
Figure 3.
The desirable characteristics pursued for bamboo breeding.
4.4.1. Thickened Culm Walls and Large-Diameter
Thickened culm walls and large-diameter bamboo culms can yield more bamboo material and also enhance the load-bearing capacity and compression strength of bamboo, thereby providing better strength and durability to a certain extent. Bamboo materials become more resistant to wear and more durable during use, prolonging the maintenance of their structure and functionality. Thickened culm walls and large-diameter bamboo stems can be utilized in a wider range of fields and applications, such as construction, furniture, and handicrafts, offering broader choices for different industries. In the process of creating thickened culm walls or large-diameter bamboo germplasm, regulatory factors such as transcription factors NAC and MYB, and related structural genes (such as SND, NST, VND, and C4H) can be employed. Additionally, genes involved in cell wall development (including cellulose synthase, expansin, fasciclin arabinogalactan protein, pectinacetylesterase, caffeoyl CoA-O-methyltransferase, etc.) and genes responsive to plant hormones (such as auxin-responsive SAUR, cytoki CoCOMT nin dehydrogenase, ethylene-responsive proteins, GRAS transcription factors, gibberellin receptors, etc.) are pivotal in this process [68,69,70,71]. Those transcription factor genes or structural genes with tissue-specific promoter expression vectors can be constructed and transformed to obtain new germplasm with increased wall thickness/stem diameter.
4.4.2. High Cellulose and Low Lignin Content
In the process of bamboo refinement, lignin must be removed to extract cellulose. By increasing the cellulose content and reducing lignin content, not only can the energy consumption in bamboo refinement be reduced, but also the efficiency of bamboo fiber production can be enhanced. To create bamboo germplasm with high cellulose/low lignin content, enzyme genes in cellulose biosynthesis (such as CesA, SUS, UGDH, etc.) and key enzyme genes in lignin biosynthesis (such as CoCOMT, 4CL, etc.) are utilized to increase cellulose content [72,73,74,75]. Overexpression of the bamboo sucrose synthase gene improves cellulose production, cell wall thickness, and fiber quality [76,77]. Alternatively, CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing [65,66,67] and RNA interference of these genes are conducted to inhibit lignin biosynthesis, indirectly increasing cellulose content to obtain bamboo germplasm with high cellulose/low lignin content.
It is worth mentioning that Wang et al. altered lignin accumulation in transgenic bamboo through the alternation of the expressions of transcription factor genes ARF3 and ARF6, and proposed that ARF3 and ARF6 directly bind to the promoter regions of the key genes 4CL or CCoAOMT genes involved in lignin biosynthesis, crucial genes for lignin biosynthesis, and activate their expressions [78]. After passing transgenic safety tests and obtaining certification, transgenic products can be widely promoted, which also provides a reference for future targeted breeding of bamboo with altered lignin content.
4.4.3. Bamboo Culms with Long Internodes
The length of bamboo fibers plays a crucial role in fiber processing and product quality. Longer fiber length typically enhances the tensile and flexural strength of fibers, resulting in more durable and sturdy bamboo products. The elongation of bamboo internodes signifies an increase in the length of fiber cells within the bamboo. This can be achieved through the modulation of relevant genes and transcription factors. For instance, in the creation of bamboo germplasm with elongated fibers, genes that promote fiber cell elongation (such as BRI1, DWF1, etc.) and transcription factor genes (such as E2F3, EFG/EF2, etc.) can be utilized to enhance fiber cell length and the ratio of fiber length to diameter [79,80,81].
For creating bamboo germplasm with longer internodes, regulatory factors controlling stem internode elongation (such as Expansin, KNOX, etc.) genes and transcription factors promoting fiber cell elongation (including WRKY78, PheAUX/IAA, etc.), and genes related to gibberellin signaling (including DlmGRG1, BvCIGR, etc.) can be obtained and utilized [65,82,83,84,85,86]. Additionally, inhibiting the expression of the florigen activation complex BmSnf1 and FD genes can promote the rapid growth of bamboo internodes [87,88]. Adjusting the expression levels of miRNAs such as miR529 and miR396a can also enhance cell elongation and cell wall thickness, thereby facilitating internode elongation [89]. Therefore, the elongation of bamboo internodes aims to increase the length of bamboo fibers, thereby enhancing the performance and quality of bamboo material for a wide range of applications.
This expedites the breeding process, enabling the rapid development of bamboo materials with increased internode growth, elevated cellulose content, decreased lignin content, high bamboo density, large fiber length-to-diameter ratio, low ash content, and robust environmental adaptability. This can effectively implement bamboo breeding strategies guided by market demands, cultivate high-quality bamboo species that are more suitable for replacing plastic products, and drive the sustainable development and innovation of the bamboo product industry.
5. Economic Viability Assessment of BASP
The economic viability assessment of BASP involves evaluating the financial feasibility and sustainability of using bamboo as a raw material for manufacturing plastic alternatives. This assessment encompasses analyzing factors such as bamboo harvesting costs, transport costs, processing costs, market acceptance, competitive positioning of the products, and environmental impacts. The objective is to determine whether BASP can compete economically with traditional plastics while positively contributing to long-term sustainability goals.
5.1. Bamboo Harvesting, Transport, and Processing Costs
It is acknowledged that bamboo incurs higher harvesting and processing costs compared to plastic, primarily due to the absence of suitable mechanization and the complex growth environment of bamboo forests. Bamboo plantations can expand biomass production into marginal lands, such as hilly or mountainous terrain with steep slopes, which complicates growth conditions and increases harvesting and transportation costs. These areas are inaccessible to machinery due to rugged terrain, necessitating manual labor, which raises labor costs and time requirements.
To address the challenges posed by bamboo’s complex growth environment, Zhou et al. developed a fleet of miniature smart aerial robots capable of navigating dense bamboo forests. These robots maneuver through spaces as narrow as 30 cm between bamboo stalks and other obstacles, facilitating harvesting and transportation [90]. The application of drones promises to streamline bamboo harvesting and transportation.
Unlike many agricultural crops benefiting from advanced machinery, bamboo harvesting has seen limited technological advancement. The reliance on manual methods drives up labor costs and limits scalability. This labor-intensive process contributes to the higher cost of bamboo products. For instance, the labor cost for harvesting one ton of bamboo is nearly RMB 450, while the market price averages less than RMB 600 [91]. Increased mechanization could significantly reduce costs. For instance, Guerra et al. developed a single-pass cut-and-shred harvester for powerful farm tractors, achieving high productivity close to theoretical limits with ongoing potential for efficiency improvements [92]. Reducing bamboo harvesting, transport, and processing costs requires technological innovation, research breakthroughs, and mechanization. Integrated industries leveraging mechanization will enhance cost efficiency and scalability, which is crucial for scaling production in the BASP sector.
Government policies and financial incentives are pivotal in cost-reduction efforts. For instance, China has included BASP under the “Special Management Measures for Central Budgetary Investment in Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction”, offering up to 15% funding support for projects, with individual projects eligible for up to RMB 100 million [23]. Anji County in Zhejiang Province has led the way by expanding the use of bamboo tableware to over 6000 sets across nearly 300 hotels, achieving a 100% adoption rate and reducing the use of disposable plastic consumables by over 3.5 million sets. Jiangxi Province aims to reach a comprehensive output value of RMB 100 billion for its bamboo industry by 2025 while maintaining a stable bamboo forest area of 16 million mu. Fujian Province targets stabilizing its bamboo forest area at 18.19 million mu by 2025, with the construction of 5000 km of bamboo mountain roads, aiming for a total output value of RMB 120 billion for the bamboo industry, with an average annual growth rate exceeding 10% [93].
5.2. Market Acceptance, Competitive Positioning, and Environmental Impacts of Bamboo Products
While bamboo products offer advantages over plastic, such as environmental friendliness, natural aesthetics, and health benefits, their market acceptance and competitive positioning lag behind plastic products. However, this should not hinder the development of bamboo products.
In terms of market acceptance, bamboo products are mostly confined to traditional uses like artwork, furniture, woven crafts, chopsticks, and skewers. Newer bamboo products such as bamboo straws, bamboo mulching film, and bamboo-wrapped pipelines are not widely recognized. Therefore, there is a need to enhance social awareness through traditional and new media channels. It is crucial to promote and educate the public about the benefits of replacing plastic with bamboo, advocating for a green lifestyle and consumption habits [94,95].
Regarding competitive positioning, we can analyze from two aspects: bamboo artworks and other bamboo products. Bamboo artworks embody bamboo’s unique aesthetic appeal, characterized by graceful lines and natural colors, blending Eastern Zen aesthetics with contemporary minimalism. Therefore, it’s crucial to establish a distinctive brand identity that reflects these bamboo characteristics. This identity positions bamboo products as symbols of simplicity, respect for nature, and noble virtues [30,31]. As for other bamboo products, traditional items often lack the diversity in shapes, sizes, and colors that plastic products offer. Hence, there is a need to intensify efforts in bamboo craftsmanship to unlock its limitless potential. This includes utilizing bamboo materials to produce various products, such as bamboo fiber or bamboo pulp, processed through techniques like hot pressing and molding. These innovations not only meet practical needs but also enrich cultural traditions.
In terms of environmental impact, bamboo offers significant advantages. Unlike plastics, which contribute to massive environmental issues, with billions of tons ending up as waste in landfills and oceans annually [14,15], bamboo is a renewable forest resource that grows rapidly. Bamboo plants can be harvested for products in just 3–5 years, making it a sustainable and endlessly renewable material. Moreover, bamboo does not pose the same environmental hazards as petroleum-based plastics do during production and disposal. The use of BASP products can mitigate the environmental problems caused by plastic waste. Additionally, bamboo naturally sequesters carbon dioxide, contributing to greenhouse gas reduction.
6. Discussions and Conclusions
Bamboo presents an abundant forest resource with rapid growth and a short cultivation cycle, making it ideal for sustainable use. In contrast to petroleum-based plastics, bamboo is renewable and environmentally friendly, mitigating resource depletion and environmental pollution from plastic products [1,2,3]. As global environmental awareness grows, demand for alternatives to traditional plastics is increasing. The concept of substituting bamboo for plastic, known as “BASP”, shows promising market prospects. Market research indicates a rising annual demand trend for bamboo substitutes [96]. It is important to note that BASP is currently in its early stages, with many aspects still in the conceptual phase. This review paper provides a prospective view on this concept, acknowledging that specifics such as breeding traits and their outcomes are yet to be fully understood. While the exact traits achievable through breeding remain uncertain at this stage, establishing breeding goals and progressing in this direction is key. We believe that in the near future, we can realize these objectives.
Compared to plastic, bamboo products offer environmental friendliness, natural aesthetics, health benefits, and heat resistance. Plastic excels in durability, versatility in shapes, sizes, and colors, waterproof properties, and ease of cleaning [97]. The choice between bamboo and plastic products hinges on specific needs, balancing ecological and economic costs. Despite the existence of various bamboo substitutes for plastics, their market penetration remains limited. Therefore, effective promotion via government and media channels is crucial to raise awareness about how bamboo products can mitigate environmental plastic pollution.
Globally, according to the International Bamboo and Rattan Organization (INBAR)‘s 2021 Global Bamboo and Rattan Goods International Trade Report, global exports of bamboo and rattan products totaled USD 4.133 billion in 2021, marking a 23.23% year-on-year increase. Asia dominates traditional bamboo product exports, while Europe and North America lead in advanced processing capabilities [98]. To address global disparities in bamboo industry development, international cooperation, industry values sharing, and technological exchanges are essential. Organizations like INBAR play a pivotal role in strategizing BASP implementation across different regions, promoting policy support, scientific research, and technological innovations to enhance industry competitiveness.
Breeding strategies are a crucial means to achieve the BASP. Through breeding methods, bamboo species with desirable traits can be selected for large-scale propagation and dissemination. Genetic improvement is another significant strategy, wherein traits of bamboo can be enhanced by studying relevant genes or pathways. Transgenic technology or gene editing can expedite trait improvements and make the process more precise. Additionally, new breeding technologies have emerged in recent years, such as those based on genomics and transcriptomics, which aid in deciphering the genetic mechanisms of bamboo traits and accelerating breeding processes. To meet the requirements for BASP, key traits need to be improved, including increased internode length, thickening of culm walls, elongation of bamboo fibers, and optimization of lignin cellulose content ratio. Through genetic improvement, transgenic technology, or gene editing, genes or pathways controlling these traits can be pinpointed and optimized for targeted enhancements.
Author Contributions
Acquired funding, H.S.; wrote the draft of the manuscript, X.L. and H.S.; contributed to revising and editing, supervision, X.L. and H.S.; conceived the study and reviewed the literature, X.L. and H.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds of ICBR of China, grant number 1632023008.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yuan, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, T.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Effects of one-Step hot oil treatment on the physical, mechanical, and surface properties of bamboo scrimber. Molecules 2020, 25, 4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ye, H.; Chen, F.; Wang, G. Bamboo as a substitute for plastic: Research on the application performance and influencing mechanism of bamboo buttons. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 446, 141297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Li, Y. China’s bamboo resources in 2021. World Bamboo Ratt. 2023, 21, 100–103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Tian, J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, H. Test and prediction of mechanical properties of moso bamboo. J. Eng. Fiber. Fabr. 2021, 16, 15589250211066802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Nie, S.; Cao, H.; Xu, Q.; Liu, H. Improving the flexibility of bamboo mechanical pulp fibers for production of high soft tissue hand-sheets. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 150, 112410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Mohammad, N.; Xu, W.; Tunc, S.; Shan, X.; Zhou, C.; Semple, K.; Dai, C.; Li, T. Large-scale industry-compatible sub-ambient radiative cooling pulp. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 101125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Lei, L.; Hou, Y.; Liu, C. Effect of balloon-like structure on properties of bamboo pulp during beating process. Cellulose 2023, 30, 7965–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, U.; Malik, S.; Rana, V.; Joshi, G. Bamboo in the pulp, paper and al-lied industries. Adv. Bamboo Sci. 2024, 7, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowski, P.F.; Patuk, I.; Bandala, E.R. Innovative industrial use of bamboo as key “Green” material. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innovating with a Bamboo Straw: Exploring the Path to Industrial Upgrading. Available online: https://www.163.com/dy/article/IOLNMBDN0519CQ3E.html (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Bamboo as a Substitute for Plastic: Exporting Bamboo Products from Yiyang Region Overseas. Available online: http://www.cbiachina.com/index.php/News/view/id/709.html (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Wang, C.-G.; Chen, M.-L.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Pei, Y.-W.; Liu, C.-Q. Biodegradable paper sheeting as agricultural covering with incorporation of bamboo pulp sludge. BioResources 2014, 9, 4128–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Li, D.; Su, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhao, B. New application of “bamboo product as a substitute for plastic” in the marine field: Bamboo-based offshore photovoltaic platform. World Bamboo Ratt. 2023, 21, 51–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, R. A brief history of plastics. In Mare Plasticum—The Plastic Sea: Combatting Plastic Pollution through Science and Art; Streit-Bianchi, M., Cimadevila, M., Trettnak, W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Plastic Pollution on Course to Double by 2030. Available online: https://news.un.org/en/story/2021/10/1103692 (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Ye, H.; Wang, G.; Cheng, H.; Chen, F.; Jiang, Z. Unlocking the potential of bamboo as a substitute for plastic to lead global sustainable development. World Bamboo Ratt. 2023, 21, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Verma, A.; Shome, A.; Sinha, R.; Sinha, S.; Jha, P.K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Shubham; Das, S.; et al. Impacts of plastic pollution on ecosystem services, sustainable development goals, and need to focus on circular economy and policy interventions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; He, S.; Leng, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z. Replacing plastic with bamboo: A review of the properties and green applications of bamboo-fiber-reinforced polymer composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, F.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, G. Replacing plastic with bamboo: Eco-friendly disposable tableware based on the separation of bamboo fibers and the reconstruction of their network structure. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 7407–7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Action Plan for Bamboo as a Substitute for Plastic (2023–2030). Available online: https://www.inbar.int/resources/inbar_publications/gap-for-basp/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Guidelines for Industrial Structure Adjustment Catalog (2024 Edition). Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/202401/content_6924187.htm (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Guidelines for Green and Low-Carbon Transformation Industries (2024 Edition). Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/202403/content_6935418.htm (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Special Management Measures for Central Budgetary Investment in Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/ghxwj/202404/t20240408_1365534.html (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Further Stimulating the Development Potential of Substituting Plastic with Bamboo. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/lianbo/2023-04/12/content_5751071.htm (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Li, M.F.; Li, X.; Bian, J.; Xu, J.K.; Yang, S.; Sun, R.C. Influence of temperature on bamboo torrefaction under carbon dioxide atmosphere. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 76, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, E.J.; Sabulal, B.; Nair, D.N.K.; Johnson, A.J.; Kumar, C.S.P. Carbon dioxide emission from bamboo culms. Plant Biol. 2016, 18, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Baredar, P.; Prakash, O. Bamboo as a complementary crop to address climate change and livelihoods–Insights from India. Forest Policy Econ. 2019, 102, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, E. Carbon Sinks of Steel: Using Bamboo to Combat Climate Change. Consilience 2021, 24. Available online: https://journals.library.columbia.edu/index.php/consilience/article/view/7644 (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Gupta, A.; Kumar, A. Potential of bamboo in sustainable development. Asia Pac. Bus. Rev. 2008, 4, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, L.C.; Fakudze, S.; Makombe, G.G.; Muse, S.; Zhu, J. Bamboo as a valuable resource and its utilization in historical and modern-day China. BioResources 2022, 17, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chongtham, N. The Healing Touch of Bamboo: Soul, Mind and Body. In Proceedings of the 11th World Bamboo Congress, Xalapa, Mexico, 14–18 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Sun, S.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yue, X.; Du, X.; Wei, Q.; Fan, G.; Sun, H.; Lou, Y.; et al. Analysis of 427 genomes reveals moso bamboo population structure and genetic basis of property traits. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Fan, S.; Guan, F.; Qi, L. Distribution of Chinese bamboo forest ecosystem research stations. For. Resour. Manag. 2009, 3, 17–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, M.; Tian, D.; Pan, J.; Chen, G.; Su, H.; Yan, Z.; Yang, Q.; Ji, C.; Tang, Z.; Fang, J. Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) invasion increases forest soil pH in subtropical China. Catena 2022, 215, 106339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, J.; Tang, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Cui, H.; Qi, L. Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) expansion enhances soil pH and alters soil nutrients and microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, L.; Yunxiang, L.; Zhangcheng, Z. Effects of moisture availability on clonal growth in bamboo Pleioblastus maculata. Plant Ecol. 2004, 173, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, Y.; Otsuki, K. Comparisons of soil-water content between a moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) forest and an evergreen broadleaved forest in western Japan. Plant Spec. Biol. 2015, 30, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qian, Z.; Zhuang, S. Effects of soil temperature, water content, species, and fertilization on soil respiration in bamboo forest in subtropical China. Forests 2020, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tang, X.; Cai, C.; Fan, S.; Sun, L.; Yang, F.; Liu, H. Air moisture and soil texture are crucial for the water dynamics of riparian bamboo in a subtropical region. Plant Soil 2020, 455, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Song, X.; Gao, Z. Nitrogen fertilization in bamboo forest accelerates the shoot growth and alters the lignification process in shoots. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 187, 115368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Peng, C.; Zhou, G.; Gu, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C. Dynamic allocation and transfer of non-structural carbohydrates, a possible mechanism for the explosive growth of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys heterocycla). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reef, R.; Ball, M.C.; Feller, I.C.; Lovelock, C.E. Relationships among RNA:DNA ratio, growth and elemental stoichiometry in mangrove trees. Funct. Ecol. 2010, 24, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, Q.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, J.; Song, X.; Song, X. Ecological stoichiometry of nitrogen and phosphorus in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) during the explosive growth period of new emergent shoots. J. Plant Res. 2019, 132, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banik, R.L. Growth response of bamboo seedlings under different light conditions at nursery stage. Bang. J. For. Sci. 1997, 26, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, T.; Shimano, K.; Muraoka, H. Effect of light availability on the carbon gain of beech (Fagus crenata) seedlings with reference to the density of dwarf bamboo (Sasa kurilensis) in an understory of Japan Sea type beech forest. Plant Spec. Biol. 2004, 19, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Goethem, D.; Van Elst, A.; De Smedt, S.; Valcke, R.; Potters, G.; Samson, R. The effect of light intensity and temperature on the chlorophyll fluorescence of Phyllostachys aureosulcata bamboo plants under controlled growth chamber conditions. Bamboo Sci. Cult. 2015, 28, 10–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Li, B.; Han, Y.; Chen, L.; He, T.; Zheng, Y.; Rong, J. Lower light intensities increase shoot germination with improved leaf biosynthesis in ma bamboo (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro). Forests 2022, 13, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.P.; Peng, H.Z.; Jin, Q.Y.; Deng, M.J.; Li, T.; Xiao, X.C.; Hua, X.Q.; Wang, K.H.; Bian, H.W.; Han, N.; et al. Identification and characterization of two bamboo (Phyllostachys praecox) AP1/SQUA-like MADS-box genes during floral transition. Planta 2009, 231, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Shi, Y.; Zang, Q.; Shi, Q.; Liu, S.; Xu, Y.; Lin, X. Functional analysis of PI-like gene in relation to flower development from bamboo (Bambusa oldhamii). J. Genet. 2016, 95, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, C.K.; Nadgauda, R.S. Review in vitro-induced flowering in bamboos. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 1999, 35, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Nadgauda, R.S. Cytokinins and in vitro induction of flowering in bamboo: Bambusa arundinacea (Retz.) Willd. Curr. Sci. 1997, 73, 523–526. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.L.; Yue, J.J.; Gu, X.P.; Lin, C.S. Flowering of woody bamboo in tissue culture systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 289700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qi, F.; Li, X.; Mu, S.; Peng, Z. Characterization of the floral transcriptome of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) at different flowering developmental stages by transcriptome sequencing and RNA-seq analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Sarkar, A.; Kharlyngdoh, E.; Somkuwar, B.G.; Biswas, P.; Dutta, S.; Guha, S.; Das, M. Evidence of stress induced flowering in bamboo and comments on probable biochemical and molecular factors. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, D.C. Synchrony and asynchrony: Observations and hypotheses for the flowering wave in a long-lived semelparous bamboo. J. Biogeogr. 2010, 31, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, C. Flowering cycles of woody bamboos native to southern south America. J. Plant Res. 2014, 127, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagle, L.; Murúa, R.; Briones, M.; Montalba, R.; Lambin, X. Determination of minimal age of five species of Chusquea bamboos through rhizome analysis as a tool to predict the flowering in southern Chile. Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 2013, 86, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Hou, D.; Li, X.; Gao, J. Main regulatory pathways, key genes and microRNAs involved in flower formation and development of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Plant Biotech. J. 2017, 15, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.C.; Chen, F.S. Excellent sexual hybrids of bamboo: Chengmaqing No.1. Sci. Silvae Sin. 1980, 16, 124–126. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.C.; Chen, F.S. Study on bamboo hybrid breeding. Guangdong For. Sci. Technol. 1986, 3, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, G.C.; Li, X.W. An evaluation on shoot quality of sympodial bamboo species and their hybirds. J. Bamboo Res. 2005, 24, 39–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mo, J.M.; Wang, S.F.; Lan, R.C.; Huang, Y.G.; Zhou, G.L. Pulping property analysis of crossbred bamboos Bamdusa pervariadilisx Grandis nin. Pap. Sci. Technol. 2005, 24, 28–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, R.H.; Chen, P.; Li, B. Analysis on characteristics and pulping performance of Dendrocalamus mutates. J. Sichuan For. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 64–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.; Cai, C.; Ren, H.; Wang, W.; Xiang, M.; Tang, X.; Zhu, C.; Yin, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Q. An efficient plant regeneration and transformation system of ma bamboo (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro) started from young shoot as explant. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Chen, G.; Kohnen, M.V.; Wang, W.; Cai, C.; Ding, W.; Wu, C.; Gu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, X.; et al. Robust CRISPR/Cas9 mediated genome editing and its application in manipulating plant height in the first generation of hexaploid ma bamboo (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1501–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhuo, R.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Jin, K.; Qiao, G. An efficient genetic transformation and CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing system for moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 822022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Tahseen, S.; Wasi, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, A.A. Application of biotechnological tool in bamboo improvement. In Biotechnological Advances in Bamboo; Ahmad, Z., Ding, Y., Shahzad, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 291–312. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Jiao, C.; Guo, L.; Ding, Y.; Cao, J.; Feng, J.; Dong, X.; Mao, L.; Sun, H.; Yu, F.; et al. Exploring key cellular processes and candidate genes regulating the primary thickening growth of moso underground shoots. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Ding, Y.; Fei, Z.; Jiao, C.; Fan, M.; Yao, B.; Xin, P.; Chu, J.; Wei, Q. Cellular and molecular characterization of a thick-walled variant reveal a pivotal role of shoot apical meristem in transverse development of bamboo culm. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 3911–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, L.; Lou, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, X.; Gao, Z. A regulatory network driving shoot lignification in rapidly growing bamboo. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 900–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiao, G.; Xu, J.; Jin, K.; Fan, M.; Ding, Y.; Wei, Q.; Zhuo, R. Anatomical characteristics and variation mechanisms on the thick-walled and dwarfed culm of shidu bamboo (Phyllostachys nidularia f. farcta). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 876658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, B.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. Biological, anatomical, and chemical characteristics of bamboo. In Secondary Xylem Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 283–306. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.Y.; Cheng, Y.S. Heterologous overexpression, purification and functional analysis of plant cellulose synthase from green bamboo. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Fang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Du, X.; Yu, L.; Meng, X.; Li, M.; Yoo, C.G.; Chen, B.; Zhai, S.; et al. Increasing the carbohydrate output of bamboo using a combinatorial pretreatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 7380–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kang, L.; Wu, R.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C. Genome-wide identification and characterization of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase family genes in moso bamboo and functional analysis of PeUGDH4 in hemicellulose synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liao, Q.; Hu, S.; Cao, Y.; Xu, G.; Long, Z.; Lu, X. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of seven sucrose synthase genes in bamboo (Bambusa emeiensis): Investigation of possible roles in the regulation of cellulose biosynthesis and response to hormones. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, S.; Luo, X.; Cao, Y. Overexpression of the bamboo sucrose synthase gene (BeSUS5) improves cellulose production, cell wall thickness and fiber quality in transgenic poplar. Tree Genet. Genomes 2020, 16, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Cai, C.; Zhu, Q. Auxin response factors fine-tune lignin biosynthesis in response to mechanical bending in bamboo. New Phytol. 2024, 241, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ge, X.; Lu, L.; Qin, W.; Qanmber, G.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, F. Brassinosteroids regulate cotton fiber elongation by modulating very-long-chain fatty acid biosynthesis. Plant Cell. 2023, 35, 2114–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Zhao, C.; Mao, J.; Song, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D.; Han, M.; An, N. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of brassinosteroid biosynthesis and metabolism genes regulating apple tree shoot and lateral root growth. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 231, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shi, Q.; Li, Z.; Gao, J. Genome-wide identification and functional characterization of the PheE2F/DP gene family in moso bamboo. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.X.; Gu, M.H.; Liu, Q.Q. The WRKY transcription factor OsWRKY78 regulates stem elongation and seed development in rice. Planta 2011, 234, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, D. Characterization and primary functional analysis of BvCIGR, a member of the GRAS gene family in Bambusa ventricosa. Bot. Rev. 2011, 77, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Guo, L.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Xiang, Y.; Jiao, C.; Jiang, J.; Vinod, K.K.; Fei, Z.; Que, F.; Ding, Y.; et al. Cellular and molecular characterizations of the irregular internode division zone formation of a slow-growing bamboo variant. Tree Physiol. 2022, 42, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Cai, M.; Mu, C.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xie, Y.; Gao, J. Integrative analysis of exogenous auxin mediated plant height regulation in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 200, 116852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Tan, J.; Guo, H.; Huang, B.; Ying, Y.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Zhang, Z. Genome-wide analysis of the KNOX gene family in moso bamboo: Insights into their role in promoting the rapid shoot growth. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Guo, L.; Jiao, C.; Fei, Z.; Chen, M.; Cao, J.; Ding, Y.; Yuan, Q. Characterization of the developmental dynamics of the elongation of a bamboo internode during the fast growth stage. Tree Physiol. 2019, 39, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Deb, A.; Biswas, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Guha, S.; Mitra, D.; Geist, B.; Schäffner, A.R.; Das, M. Identification and functional characterization of two bamboo FD gene homologs having contrasting effects on shoot growth and flowering. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Lin, X.C.; Xia, R.; Song, L.; Wu, A.M. MicroRNAs play important roles in regulating the rapid growth of the Phyllostachys edulis culm internode. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 2215–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, T.; Lu, H.; Cao, Y.; Xu, C.; et al. Swarm of micro flying robots in the wild. Sci. Robot. 2022, 7, eabm5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What Are the Advantages and Challenges of “Bamboo as a Substitute for Plastic”. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/ztzl/slwrzlzxd/202401/t20240108_1363144.html (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Guerra, S.P.S.; Oguri, G.; Junior, H.D.J.E.; de Melo, R.X.; Spinelli, R. Mechanized harvesting of bamboo plantations for energy production: Preliminary tests with a cut-and-shred harvester. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2016, 34, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Focus: China Promotes Bamboo as Eco-friendly Substitute for Plastic. Available online: http://www.china.org.cn/china/Off_the_Wire/2024-06/05/content_117236235.htm (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- International Bamboo and Rattan Center Launches Community Outreach Campaign “Bamboo as a Substitute for Plastic Initiative”. Available online: https://mp.pdnews.cn/Pc/ArtInfoApi/article?id=37643043 (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Taojiang City Introduces First Batch of Bamboo as a Substitute for Plastic Products into Schools. Available online: https://www.yiyang.gov.cn/yiyang/2/3/74/content_1945008.html (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- The Prospect of Bamboo as a Substitute for Plastic Is Promising. Available online: https://news.gmw.cn/2023-04/29/content_36532790.htm (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Moshood, T.D.; Nawanir, G.; Mahmud, F.; Mohamad, F.; Ahmad, M.H.; AbdulGhani, A.; Kumar, S. Green product innovation: A means towards achieving global sustainable product within biodegradable plastic industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, J. Global plastic ban policy and development opportunities of bamboo industry. World Bamboo Ratt. 2021, 19, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).