Testing a Benchtop Wet-Milling Method for Preparing Nanoparticles and Suspensions as Hospital Formulations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of NPs
2.3. Physicochemical Properties of NPs in Suspension
2.3.1. Observation of NPs with Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.2. Measurement of Particle Size of NPs in Suspension
2.3.3. Measurement of Zeta Potential of NPs in Suspension
2.3.4. Evaluation of Molecular Interactions in Suspension
2.3.5. Measurement of Viscosity of Suspensions
2.3.6. Evaluation of Crystallinity of NPs in Suspension
2.4. Evaluation of Dispersion Stability of the Suspension
2.5. Measurement of Solubility
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Various Grinding Conditions on the Particle Size of NPs
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of NPs in Suspension
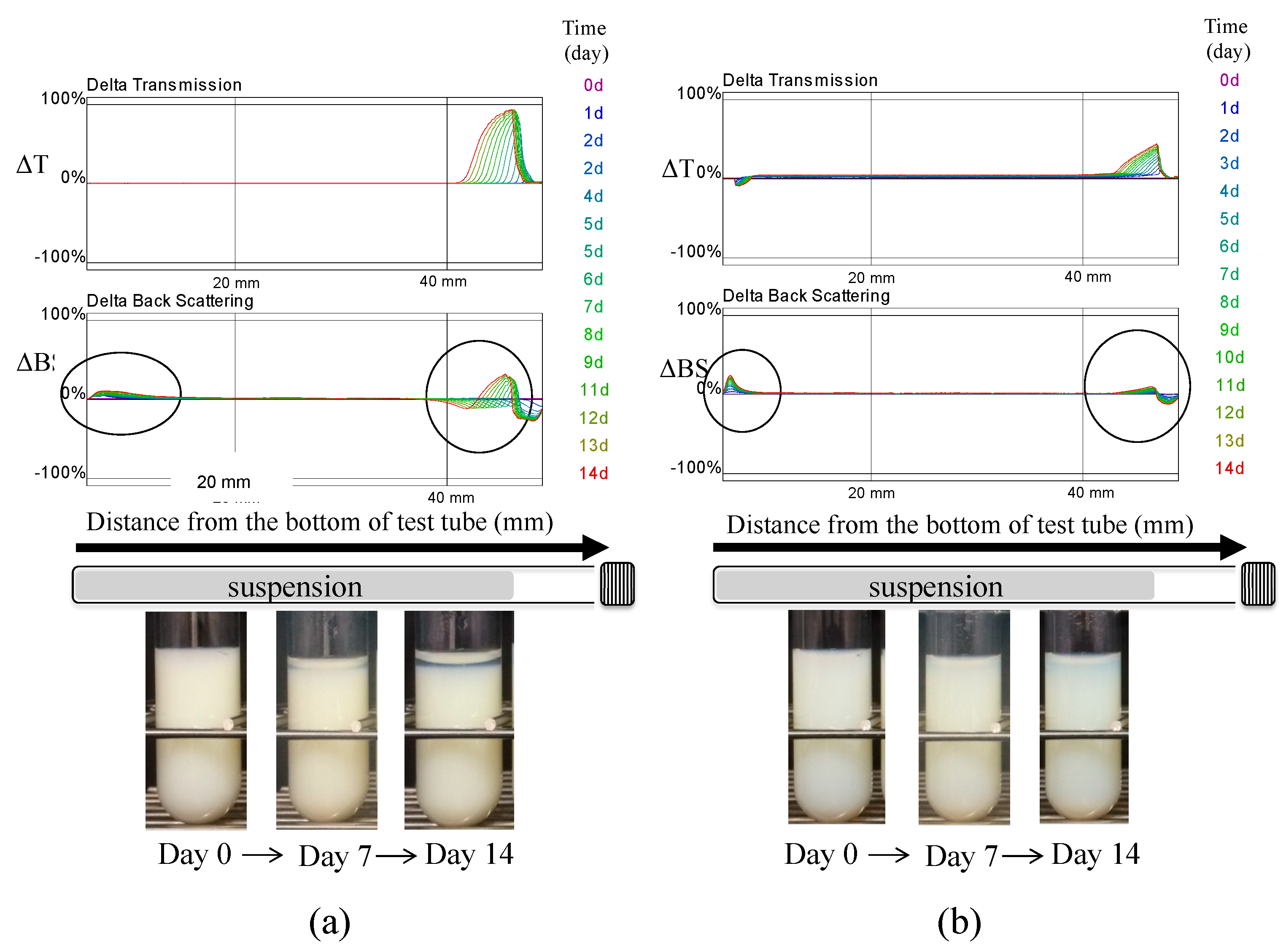
3.3. Evaluation of Dispersion Stability
3.4. Measurement of Solubility
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-Like Properties and the Causes of Poor Solubility and Poor Permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegemann, S.; Leveiller, F.; Franchi, D.; De Jong, H.; Lindén, H. When Poor Solubility Becomes an Issue: From Early Stage to Proof of Concept. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 31, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellington, K.; Curran, M.P. Spotlight on Cefditoren Pivoxil in Bacterial Infections1. Treat. Respir. Med. 2005, 4, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, A.; Miller, J.M.; Amidon, G.L. Prediction of Solubility and Permeability Class Membership: Provisional BCS Classification of the World’s Top Oral Drugs. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A Theoretical Basis for a Biopharmaceutic Drug Classification: The Correlation of in Vitro Drug Product Dissolution and in Vivo Bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otsuka, N.; Ueda, K.; Ohyagi, N.; Shimizu, K.; Katakawa, K.; Kumamoto, T.; Higashi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Moribe, K. An Insight into Different Stabilization Mechanisms of Phenytoin Derivatives Supersaturation by HPMC and PVP. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2574–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, T.; Miura, S.; Danjo, K. Universal Wet-Milling Technique to Prepare Oral Nanosuspension Focused on Discovery and Preclinical Animal Studies—Development of Particle Design Method. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 405, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merisko-Liversidge, E.; Sarpotdar, P.; Bruno, J.; Hajj, S.; Wei, L.; Peltier, N.; Rake, J.; Shaw, J.M.; Pugh, S.; Polin, L.; et al. Formulation and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Nanocrystalline Suspensions of Poorly Soluble Anticancer Drugs. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Inkyo, M.; Yumoto, R.; Nagai, J.; Takano, M.; Nagata, S. Nanoparticulation of Probucol, a Poorly Water-Soluble Drug, Using a Novel Wet-Milling Process to Improvein Vitrodissolution Andin Vivooral Absorption. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 38, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Inkyo, M.; Yumoto, R.; Nagai, J.; Takano, M.; Nagata, S. Nanoparticulation of Poorly Water Soluble Drugs Using a Wet-Mill Process and Physicochemical Properties of the Nanopowders. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Jong, W.H. Drug Delivery and Nanoparticles: Applications and Hazards. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merisko-Liversidge, E.; Liversidge, G.G. Nanosizing for Oral and Parenteral Drug Delivery: A Perspective on Formulating Poorly-Water Soluble Compounds Using Wet Media Milling Technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhnke, M.; Berghausen, J.; Timpe, C. Accelerated Formulation Development for Nanomilled Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Using a Screening Approach. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2010, 33, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Junghanns, J.-U.A.H. Nanocrystal Technology, Drug Delivery and Clinical Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, H.; Lee, S.; Jung, H.S.; Kim, J.-B. Effect of Ball Size and Powder Loading on the Milling Efficiency of a Laboratory-Scale Wet Ball Mill. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 8963–8968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Ishii, N.; Shimizu, Y.; Hanawa, T. Development and Characterization of a Suspension Containing Nanoparticu-Lated Rebamipide for Mouth Wash for Stomatitis. J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Jpn. 2017, 77, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medarević, D.; Djuriš, J.; Ibrić, S.; Mitrić, M.; Kachrimanis, K. Optimization of Formulation and Process Parameters for the Production of Carvedilol Nanosuspension by Wet Media Milling. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 540, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongpeerapat, A.; Wanawongthai, C.; Tozuka, Y.; Moribe, K.; Yamamoto, K. Formation Mechanism of Colloidal Nanoparticles Obtained from Probucol/PVP/SDS Ternary Ground Mixture. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 352, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Alvarez, P.; Orbe, P.; Bilgili, E. Multi-Faceted Characterization of Wet-Milled Griseofulvin Nanosuspensions for Elucidation of Aggregation State and Stabilization Mechanisms. Aaps Pharmscitech 2018, 19, 1789–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basa, S.; Muniyappan, T.; Karatgi, P.; Prabhu, R.; Pillai, R. Production and In Vitro Characterization of Solid Dosage form Incorporating Drug Nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2008, 34, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, E.; Afolabi, A. A Combined Microhydrodynamics–Polymer Adsorption Analysis for Elucidation of the Roles of Stabilizers in Wet Stirred Media Milling. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 439, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meruva, S.; Thool, P.; Shah, S.; Karki, S.; Bowen, W.; Ghosh, I.; Kumar, S. Formulation and Performance of Irbesartan Nanocrystalline Suspension and Granulated or Bead-Layered Dried Powders—Part I. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 568, 118189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, Y.; Yonemochi, E.; Terada, K. Changes in Surface Properties by Granulation and Physicochemical Stability of Granu-lated Amorphous Cefditoren Pivoxil with Additives. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 280, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shudo, J.; Pongpeerapat, A.; Wanawongthai, C.; Moribe, K.; Yamamoto, K. In Vivo Assessment of Oral Administration of Probucol Nanoparticles in Rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoh, K.; Pongpeerapat, A.; Tozuka, Y.; Oguchi, T.; Yamamoto, K. Nanoparticle Formation of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs from Ternary Ground Mixtures with PVP and SDS. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karavas, E.; Georgarakis, M.; Docoslis, A.; Bikiaris, D. Combining SEM, TEM, and Micro-Raman Techniques to Differentiate Between the Amorphous Molecular Level Dispersions and Nanodispersions of a Poorly Water-Soluble Drug within a Polymer Matrix. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 340, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Azad, M.; Davé, R.; Bilgili, E. Nanomilling of Drugs for Bioavailability Enhancement: A Holistic Formulation-Process Perspective. Pharmaceutics 2016, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mengual, O.; Meunier, G.; Cayre, I.; Puech, K.; Snabre, P. Characterisation of Instability of Concentrated Dispersions by a New Optical Analyser: The Turbiscan MA 1000. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 152, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff-Pérez, M.; Torcello-Gómez, A.; Gálvez-Ruíz, M.; Martín-Rodríguez, A. Stability of Emulsions for Parenteral Feeding: Preparation and Characterization of o/w Nanoemulsions with Natural Oils and Pluronic f68 as Surfactant. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Sime, F.B.; Cabot, P.J.; Maqbool, F.; Roberts, J.A.; Falconer, J.R. Solid Nanoparticles for Oral Antimicrobial Drug Delivery: A review. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopalarao, G.; Lakshmipathy, R.; Gadamsetty, G.; Sarada, N. Absorption and Bioavailability of Cefditoren Pivoxil in Hydrogels in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2015, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Dispersing Media | Particle Size | Zeta Potential (mV) ± S.D. | Viscosity (mPa·s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | Surfactant | Mean (nm) ± S.D. | D50 (nm) ± S.D. | PDI | |||
| PEO | 0.25% | SLS 0.1% | 167.6 ± 2.8 | 152.1 ± 5.5 | 0.227 | −0.7 ± 0.4 | 1.31 |
| 0.5% | 160.4 ±4.0 | 301.0 ± 22.0 | 0.171 | −1.4 ± 0.4 | 1.71 | ||
| 1.0% | 204.7 ± 3.9 | 187.7 ± 2.4 | 0.229 | 0.3 ± 0.8 | 2.91 | ||
| HPC-L | 0.25% | 142.8 ± 1.4 | 140.5 ± 4.1 | 0.188 | −7.5 ± 1.4 | 1.29 | |
| 0.5% | 133.6 ± 0.6 | 127.8 ± 2.9 | 0.172 | −11.5 ± 2.4 | 1.96 | ||
| 1.0% | 208.1 ± 1.2 | 205.9 ± 1.2 | 0.170 | −4.6 ± 0.6 | 3.76 | ||
| HPC-SL | 0.25% | 137.0 ± 0.3 | 137.8 ± 7.5 | 0.182 | −4.9 ± 1.2 | 1.18 | |
| 0.5% | 123.3 ± 1.9 | 121.5 ± 7.3 | 0.176 | −6.1 ± 1.2 | 1.50 | ||
| 1.0% | 158.8 ± 1.3 | 152.7 ± 1.4 | 0.135 | −2.4 ± 0.7 | 2.41 | ||
| HPC-SSL | 0.25% | 128.7 ± 0.4 | 128.2 ± 6.3 | 0.176 | −9.8 ± 1.1 | 1.07 | |
| 0.5% | 116.1 ± 0.4 | 111.7 ± 5.2 | 0.167 | −3.7 ± 0.4 | 1.21 | ||
| 1.0% | 135.3 ± 9.0 | 137.5 ± 14.0 | 0.221 | −4.9 ± 0.3 | 1.68 | ||
| HPMC | 0.25% | 209.6 ± 2.0 | 212.0 ± 2.9 | 0.226 | −3.5 ± 0.8 | 1.72 | |
| 0.5% | 275.1 ± 4.3 | 273.7 ± 12.1 | 0.221 | −0.8 ± 0.3 | 2.95 | ||
| 1.0% | 413.8 ± 1.0 | 386.4 ±3.8 | 0.182 | −2.9 ± 0.7 | 7.30 | ||
| PVP | 0.25% | 134.0 ± 2.2 | 134.4 ± 9.0 | 0.187 | −7.2 ± 2.6 | 1.00 | |
| 0.5% | 173.2 ± 3.0 | 175.6 ± 10.7 | 0.219 | −5.5 ± 0.5 | 1.05 | ||
| 1.0% | 127.4 ± 0.4 | 120.5 ± 6.3 | 0.158 | −4.9 ± 0.2 | 1.15 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawano, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Hanawa, T. Testing a Benchtop Wet-Milling Method for Preparing Nanoparticles and Suspensions as Hospital Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040482
Kawano Y, Shimizu Y, Hanawa T. Testing a Benchtop Wet-Milling Method for Preparing Nanoparticles and Suspensions as Hospital Formulations. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(4):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040482
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawano, Yayoi, Yuichiro Shimizu, and Takehisa Hanawa. 2021. "Testing a Benchtop Wet-Milling Method for Preparing Nanoparticles and Suspensions as Hospital Formulations" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 4: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040482
APA StyleKawano, Y., Shimizu, Y., & Hanawa, T. (2021). Testing a Benchtop Wet-Milling Method for Preparing Nanoparticles and Suspensions as Hospital Formulations. Pharmaceutics, 13(4), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040482









