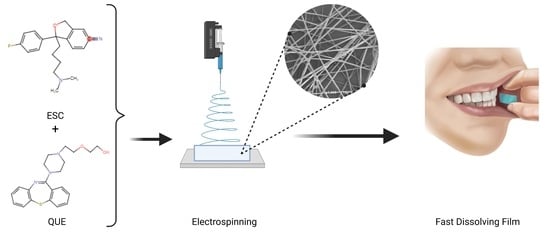
Fabrication and Characterization of Fast-Dissolving Films Containing Escitalopram/Quetiapine for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Drug-Loaded Fibers Using Electrospinning Technique
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.5. Thermal Analysis and Physical-State Characterization
2.5.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.5.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.6. Disintegration Test of the Electrospun Fibers
2.7. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) for Drugs Determination and Quantification
2.8. Determination of the Drug Loading (DL), Entrapment Efficiency (EE%), and Fiber Yield (Y) of the Drug-Loaded Fibers
2.9. Determination of the In Vitro Drug Release of the Drug-Loaded Fibers
2.10. Ex Vivo Permeation Study of the Drug-Loaded Fibers
2.11. Stability Studies
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
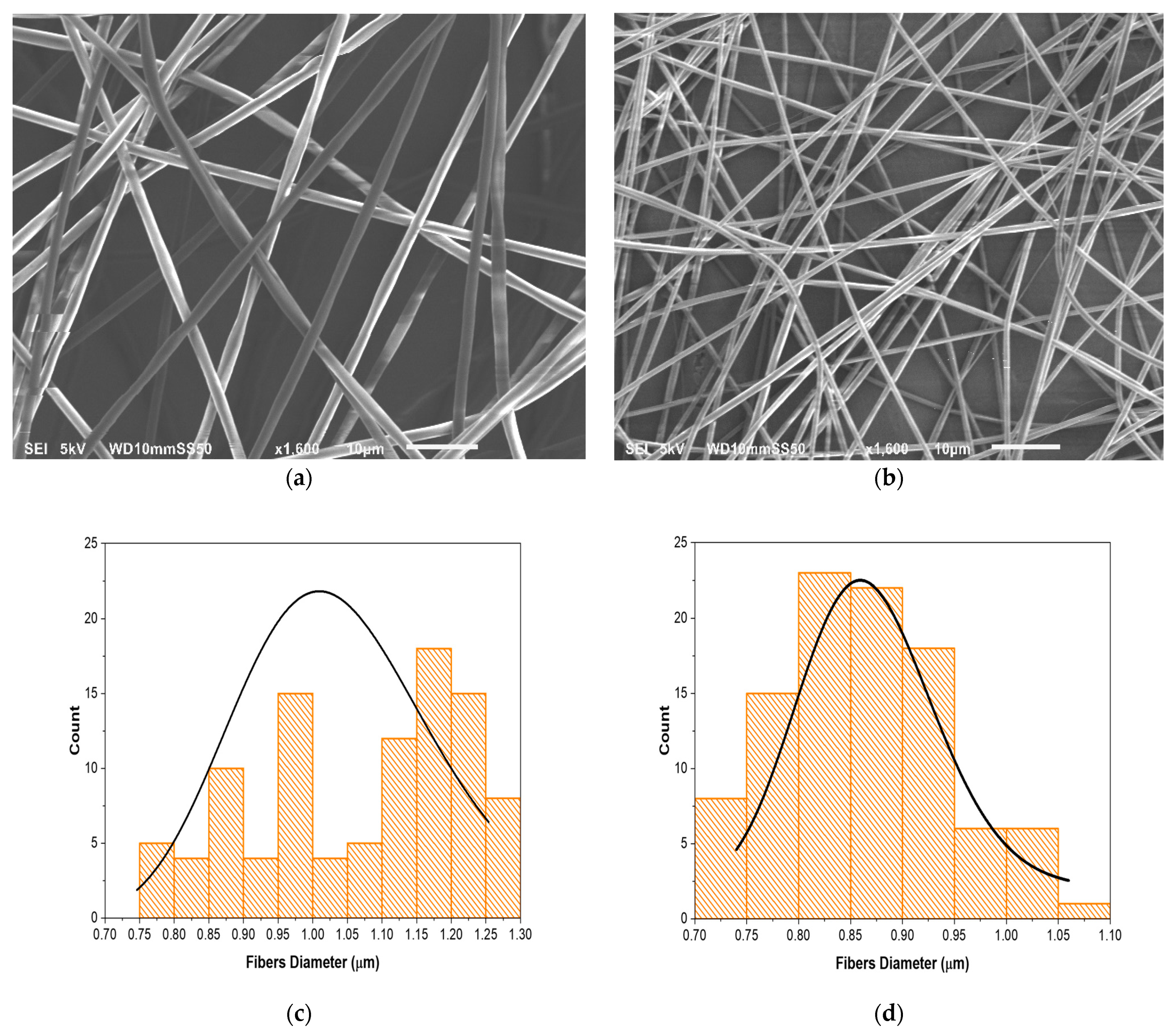
3.1. Fiber Morphology and Size Analysis
3.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.3. Physical Form Characterization by XRD
3.4. Physical Form Characterization by FTIR
3.5. Disintegration Time of the Coaxial Fibers
3.6. Drug Loading (DL), Entrapment Efficiency (EE%), and Fiber Yield (Y) of the Drug-Loaded Coaxial Fibers
3.7. In Vitro Drug Release Determination of the Drug-Loaded Coaxial Fibers
3.8. Ex Vivo Permeation Study of the Drug-Loaded Coaxial Fibers
3.9. Stability Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Depression. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression (accessed on 23 February 2021).
- Verduijn, J.; Milaneschi, Y.; A Schoevers, R.; Van Hemert, A.M.; Beekman, A.T.F.; Penninx, B.W.J.H. Pathophysiology of major depressive disorder: Mechanisms involved in etiology are not associated with clinical progression. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenberg, A.J.; Freeman, M.P.; Markowitz, J.C.; Rosenbaum, J.F.; Thase, M.E.; Trivedi, M.H.; van Rhoads, R.S.; Reus, V.I.; DePaulo, J.R., Jr.; Fawcett, J.A.; et al. Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Major Depressive Disorder, Third Edition. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Brakemeier, E.-L.; Radtke, M.; Engel, V.; Zimmermann, J.; Tuschen-Caffier, B.; Hautzinger, M.; Schramm, E.; Berger, M.; Normann, C. Overcoming Treatment Resistance in Chronic Depression: A Pilot Study on Outcome and Feasibility of the Cognitive Behavioral Analysis System of Psychotherapy as an Inpatient Treatment Program. Psychother. Psychosom. 2014, 84, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberto, V.L.; Jha, M.K.; Murrough, J.W. Pharmacological Treatments for Patients with Treatment-Resistant Depression. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moret, C. Combination/augmentation strategies for improving the treatment of depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2005, 1, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lam, R.W.; Ali, M.K. Comparative efficacy of escitalopram in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2011, 7, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirino, E. Escitalopram for the management of major depressive disorder: A review of its efficacy, safety, and patient acceptability. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2012, 6, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Approval Letter of Seroquel. 2009. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2009/022047Orig1s011.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2020).
- Fountoulakis, K.N.; Kelsoe, J.R.; Akiskal, H. Receptor targets for antidepressant therapy in bipolar disorder: An overview. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 138, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothdurfter, C.; Schmotz, C.; Sarubin, N.; Baghai, T.C.; Laenger, A.; Lieb, M.; Bondy, B.; Rupprecht, R.; Schüle, C. Effects of escitalopram/quetiapine combination therapy versus escitalopram monotherapy on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal-axis activity in relation to antidepressant effectiveness. J. Psychiatr Res. 2014, 52, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.; Khunt, D.; Misra, M.; Padh, H. Non-invasive intranasal delivery of quetiapine fumarate loaded microemulsion for brain targeting: Formulation, physicochemical and pharmacokinetic consideration. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 91, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, E.; Scarpa, M.; Abdelhakim, H.; Bukhary, H.; Craig, D.; Barker, S.; Orlu, M. A Potential Alternative Orodispersible Formulation to Prednisolone Sodium Phosphate Orally Disintegrating Tablets. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhakim, H.; Williams, G.R.; Craig, D.Q.; Orlu, M.; Tuleu, C. Human mouthfeel panel investigating the acceptability of electrospun and solvent cast orodispersible films. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Rabel, S.; Bukhtar, Q.; Qadir, M.I.; Jabeen, F.; Khan, A. Orally disintegrating films: A modern expansion in drug delivery system. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, D.R.; Patel, V.A.; Chhalotiya, U.K.; Patel, H.V.; Kundawala, A.J. Development and Characterization of Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Fast Dissolving Films Containing Levocetirizine. Sci. Pharm. 2012, 80, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldridge, K.J.; Taylor, N.F. Dysphagia is a Common and Serious Problem for Adults with Mental Illness: A Systematic Review. Dysphagia 2011, 27, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishi, H.; Sakata, O. Preparation and evaluation of fast-dissolving films of etilefrine hydrochloride for practical buccal dosing. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.S.; Kumar, T.P.; Gowda, D.V. Orodispersible Thin Film: A new patient-centered innovation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Hassan, R.; Razzaq, S.; Mahmood, A.; Amjad, M.W.; Raja, M.A.G.; Qaisar, A.A.; Majeed, A.; Hanif, M.; Tahir, R.A. Fabrication of polyvinyl alcohol based fast dissolving oral strips of sumatriptan succinate and metoclopramide HCL. Sci. Prog. 2020, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Boateng, J.S.; Mitchell, J.; Trivedi, V. Formulation, Characterisation and Stabilisation of Buccal Films for Paediatric Drug Delivery of Omeprazole. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soni, G.; Yadav, K.S. Fast-Dissolving Films of Sumatriptan Succinate: Factorial Design to Optimize In Vitro Dispersion Time. J. Pharm. Innov. 2015, 10, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, B.V.; Darkunde, S.L. Orodispersible Film: A Novel Drug Delivery System. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2014, 7, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Elbadawi, M.; McCoubrey, L.E.; Gavins, F.K.; Ong, J.J.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for the Next Generation of 3D Printed Medicines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane-Viaño, I.; Trenfield, S.J.; Basit, A.W.; Goyanes, Á. Translating 3D printed pharmaceuticals: From hype to real-world clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Orlu, M.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Scarpa, M.; Kiefer, O.; Kottke, D.; Sjöholm, E.; Öblom, H.; Sandler, N.; Hinrichs, W.L.J.; et al. Oromucosal films: From patient centricity to production by printing techniques. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vuddanda, P.R.; Alomari, M.; Dodoo, C.; Trenfield, S.J.; Velaga, S.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. Personalisation of warfarin therapy using thermal ink-jet printing. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 117, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomari, M.; Vuddanda, P.R.; Trenfield, S.J.; Dodoo, C.; Velaga, S.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. Printing T3 and T4 oral drug combinations as a novel strategy for hypothyroidism. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Chandra, A.; Praveen, G.; Snigdha, S.; Roy, S.; Agatemor, C.; Thomas, S.; Provaznik, I. Electrospinning over Solvent Casting: Tuning of Mechanical Properties of Membranes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buanz, A.; Belaunde, C.C.; Soutari, N.; Tuleu, C.; Gul, M.O.; Gaisford, S. Ink-jet printing versus solvent casting to prepare oral films: Effect on mechanical properties and physical stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Li, J.J.; Williams, G.R.; Zhao, M. Electrospun Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Poorly Water-soluble Drugs: A Review. J. Control. Release 2018, 292, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, G.R.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T.; Luo, C.J. Nanofibres in Drug Delivery; UCL Press: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, F.L.; Shearman, G.C.; Gaisford, S.; Williams, G.R. Amorphous Formulations of Indomethacin and Griseofulvin Prepared by Electrospinning. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 4327–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazbouz, M.B.; Tronci, G. Two-layer Electrospun System Enabling Wound Exudate Management and Visual Infection Response. Sensors 2019, 19, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Illangakoon, U.E.; Gill, H.; Shearman, G.C.; Parhizkar, M.; Mahalingam, S.; Chatterton, N.P.; Williams, G.R. Fast dissolving paracetamol/caffeine nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peddio, G.; Pittau, B.; Manca, I.; Salis, R.; Pani, L.; Pira, L. Validated Method to Determine Quetiapine and Norquetiapine in Microsomal Matrix by LC MS–MS: Implication in Quetiapine Metabolism. Chromatographia 2013, 77, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakde, R.B.; Satone, D.D.; Gadapayale, K.K.; Kakde, M.G. Stability-Indicating RP-HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Escitalopram Oxalate and Clonazepam. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2012, 51, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.S.; Shah, H.; Gupta, S.; Jain, M.; Sharma, K.; Thakkar, P.; Shah, R. Liquid Chromatography–electrospray Ionisation Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Escitalopram in Human Plasma and Its Application in Bioequivalence Study. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 811, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Li, K.; Xie, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, W.; Wang, F.; Zhu, R.; Li, H. Simultaneous determination of clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone and quetiapine in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 802, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rençber, S.; Karavana, S.Y.; Yılmaz, F.F.; Eraç, B.; Nenni, M.; Ozbal, S.; Pekcetin, C.; Gurer-Orhan, H.; Hosgor-Limoncu, M.; Güneri, P.; et al. Development, characterization, and in vivo assessment of mucoadhesive nanoparticles containing fluconazole for the local treatment of oral candidiasis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2641–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marques, M.R.C.; Loebenberg, R.; Almukainzi, M. Simulated Biological Fluids with Possible Application in Dissolution Testing. Dissolution Technol. 2011, 18, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. Influence of solvents on the formation of ultrathin uniform poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) nanofibers with electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. Part. B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 3721–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuangchote, S.; Sagawa, T.; Yoshikawa, S. Electrospinning of poly(vinyl pyrrolidone): Effects of solvents on electrospinnability for the fabrication of poly(p-phenylene vinylene) and TiO2 nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 2777–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, E.A.; Craig, D.Q.; Barker, S.A. Dual drug-loaded coaxial nanofibers for the treatment of corneal abrasion. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, B.V.; Ferreira, A.P.G.; Cavalheiro, E.T.G. Thermal degradation mechanism for citalopram and escitalopram. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 133, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narala, A.; Veerabrahma, K. Preparation, Characterization and Evaluation of Quetiapine Fumarate Solid Lipid Nanoparticles to Improve the Oral Bioavailability. J. Pharm. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhary, H.; Williams, G.R.; Orlu, M. Electrospun fixed dose formulations of amlodipine besylate and valsartan. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Jain, C. Preparation and characterization of solid dispersions of carvedilol with PVP K30. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 5, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Purohit, N.; Patel, J. Preparation, characterization and dissolution studies of inclusion complexes of Escitalopram oxalate. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 5, 2259–2263. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lu, M.; Wu, C. PVP VA64 as a Novel Release-modifier for Sustained-release Mini-matrices Prepared via Hot Melt Extrusion. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Quan, P.; Xiang, R.; Fang, L. Regulating the Skin Permeation Rate of Escitalopram by Ion-pair Formation with Organic Acids. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumbhar, M.S. Enhancement of Solubility and Dissolution Rate of Escitalopram Oxalate by Liquisolid Compact Technology. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Sci. 2013, 2, 2277–5005. [Google Scholar]
- Vadlamudi, H.C.; Yalavarthi, P.R.; Nagaswaram, T.; Rasheed, A.; Peesa, J.P. In-vitro and pharmacodynamic characterization of solidified self microemulsified system of quetiapine fumarate. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendar, D.; Arjun, N.; Someshwar, K.; Rao, Y.M. Quality by Design Approach for Development and Optimization of Quetiapine Fumarate Effervescent Floating Matrix Tablets for Improved Oral Bioavailability. J. Pharm. Investig. 2016, 46, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburayan, W.S.; Booq, R.Y.; Binsaleh, N.S.; Alfassam, H.A.; Bakr, A.A.; Bukhary, H.A.; Alyamani, E.J.; Tawfik, E.A. The Delivery of the Novel Drug ‘Halicin’ Using Electrospun Fibers for the Treatment of Pressure Ulcer against Pathogenic Bacteria. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chachlioutaki, K.; Tzimtzimis, E.K.; Tzetzis, D.; Chang, M.-W.; Ahmad, Z.; Karavasili, C.; Fatouros, D.G. Electrospun Orodispersible Films of Isoniazid for Pediatric Tuberculosis Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Setouhy, D.A.; Abd El-Malak, N.S. Formulation of a Novel Tianeptine Sodium Orodispersible Film. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garsuch, V.; Breitkreutz, J. Novel analytical methods for the characterization of oral wafers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 73, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Guidance for Industry Orally Disintegrating Tablets-CDER Data Standards Manual. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/70877/download (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Bukhary, H.; Williams, G.R.; Orlu, M. Fabrication of Electrospun Levodopa-Carbidopa Fixed-Dose Combinations. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2020, 2, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasekh, M.; Karavasili, C.; Soong, Y.L.; Bouropoulos, N.; Morris, M.; Armitage, D.; Li, X.; Fatouros, D.G.; Ahmad, Z. Electrospun PVP–indomethacin constituents for transdermal dressings and drug delivery devices. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutoprapat, R.; Chan, L.W.; Heng, P.W.S. Ex-vivo permeation study of chlorin e6-polyvinylpyrrolidone complexes through the chick chorioallantoic membrane model. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokate, A.; Li, X.; Williams, P.J.; Singh, P.; Jasti, B.R. In Silico Prediction of Drug Permeability Across Buccal Mucosa. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shojaei, A.H.; Khan, M.; Lim, G.; Khosravan, R. Transbuccal permeation of a nucleoside analog, dideoxycytidine: Effects of menthol as a permeation enhancer. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 192, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junginger, H.E.; Hoogstraate, J.A.; Verhoef, J. Recent advances in buccal drug delivery and absorption—In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Control. Release 1999, 62, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolazzo, J.A.; Reed, B.L.; Finnin, B.C. Buccal penetration enhancers—How do they really work? J. Control. Release 2005, 105, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhou, F.; Williams, G.R. Developing and scaling up fast-dissolving electrospun formulations based on poly(vinylpyrrolidone) and ketoprofen. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.; Samanta, S.; Kothari, K.; Mistry, P.; Suryanarayanan, R. Effect of Polymer Molecular Weight on the Crystallization Behavior of Indomethacin Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 3142–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettmann, B.K.; Myerson, A.S.; Trout, B.L. Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study of the Physical Stability of Electrospun Drug and Polymer Solid Solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 2185–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkahtani, M.E.; Aodah, A.H.; Abu Asab, O.A.; Basit, A.W.; Orlu, M.; Tawfik, E.A. Fabrication and Characterization of Fast-Dissolving Films Containing Escitalopram/Quetiapine for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060891
Alkahtani ME, Aodah AH, Abu Asab OA, Basit AW, Orlu M, Tawfik EA. Fabrication and Characterization of Fast-Dissolving Films Containing Escitalopram/Quetiapine for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(6):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060891
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkahtani, Manal E., Alhassan H. Aodah, Omar A. Abu Asab, Abdul W. Basit, Mine Orlu, and Essam A. Tawfik. 2021. "Fabrication and Characterization of Fast-Dissolving Films Containing Escitalopram/Quetiapine for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 6: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060891
APA StyleAlkahtani, M. E., Aodah, A. H., Abu Asab, O. A., Basit, A. W., Orlu, M., & Tawfik, E. A. (2021). Fabrication and Characterization of Fast-Dissolving Films Containing Escitalopram/Quetiapine for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. Pharmaceutics, 13(6), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060891