Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Enavogliflozin in Mice and Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
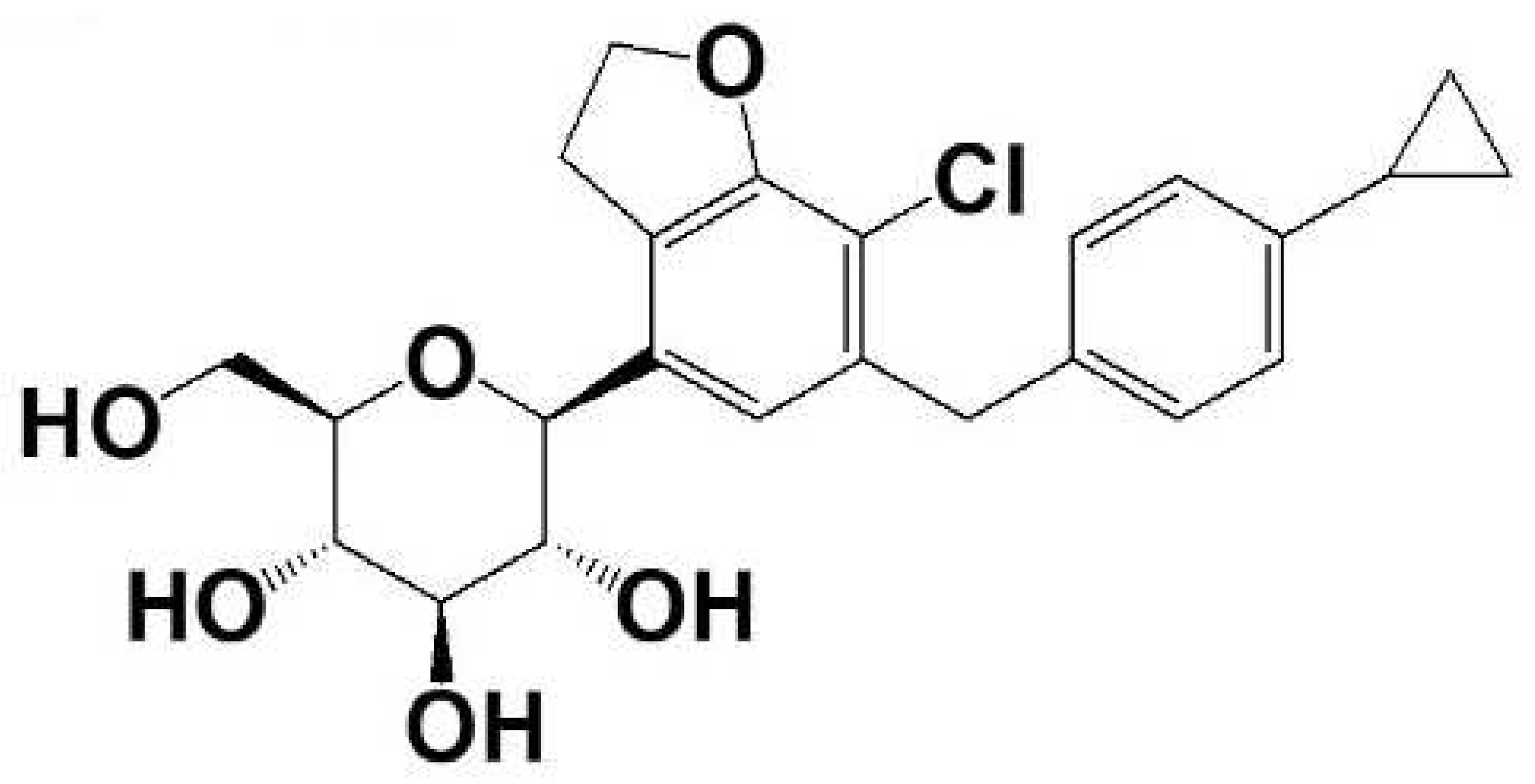
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pharmacokinetic Study
2.2.1. Pharmacokinetic Study
2.2.2. Tissue Distribution Study
2.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Enavogliflozin
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
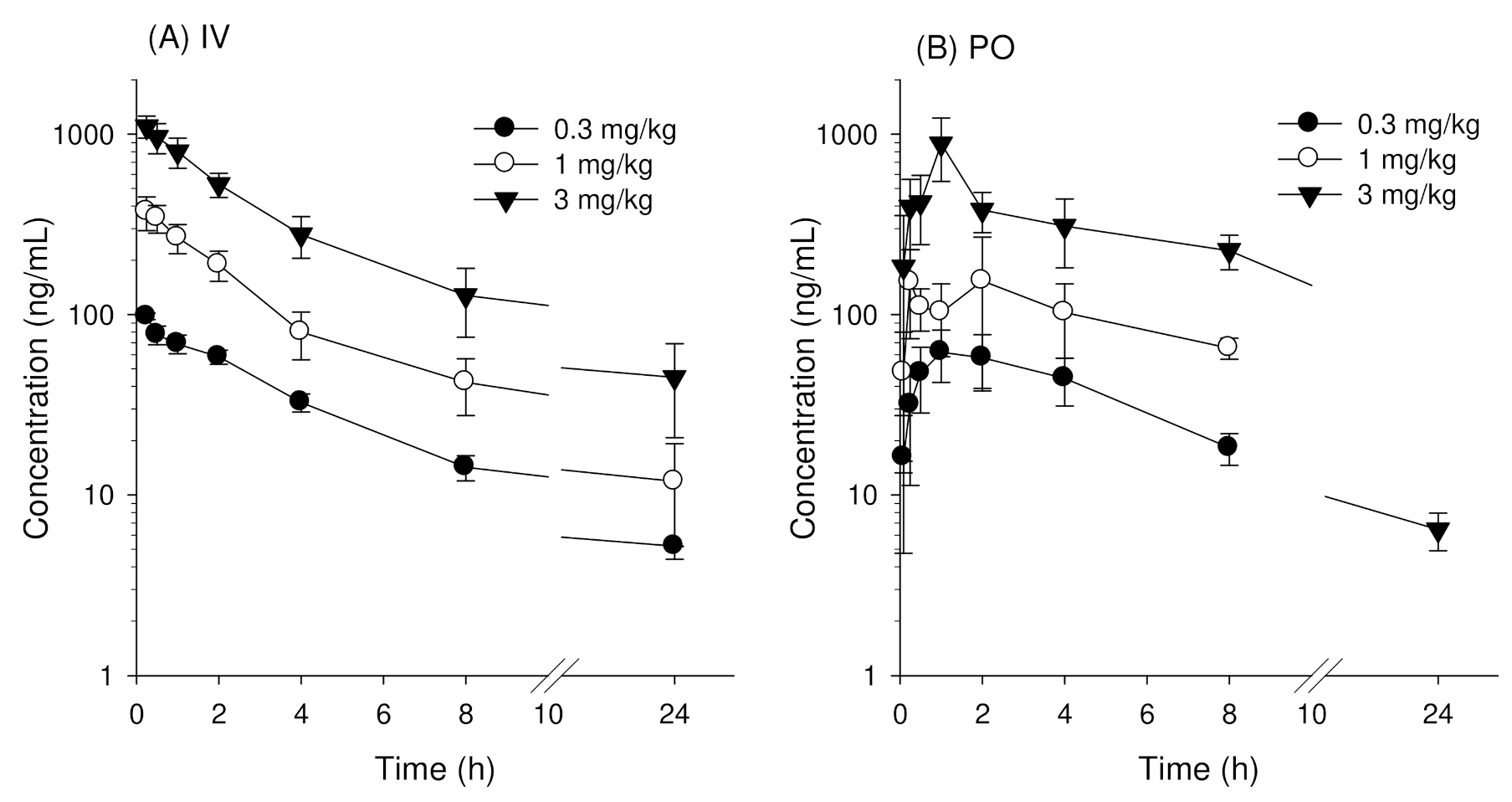
3.1. Pharmacokinetics of Enavogliflozin in Mice
3.2. Pharmacokinetics of Enavogliflozin in Rats
3.3. Recovery of Enavogliflozin in Mice and Rats
3.3.1. Recovery of Enavogliflozin in Mice
3.3.2. Recovery of Enavogliflozin in Rats
3.4. Tissue Distribution of Enavogliflozin in Mice
3.4.1. Single Oral Administration of Enavogliflozin in Mice
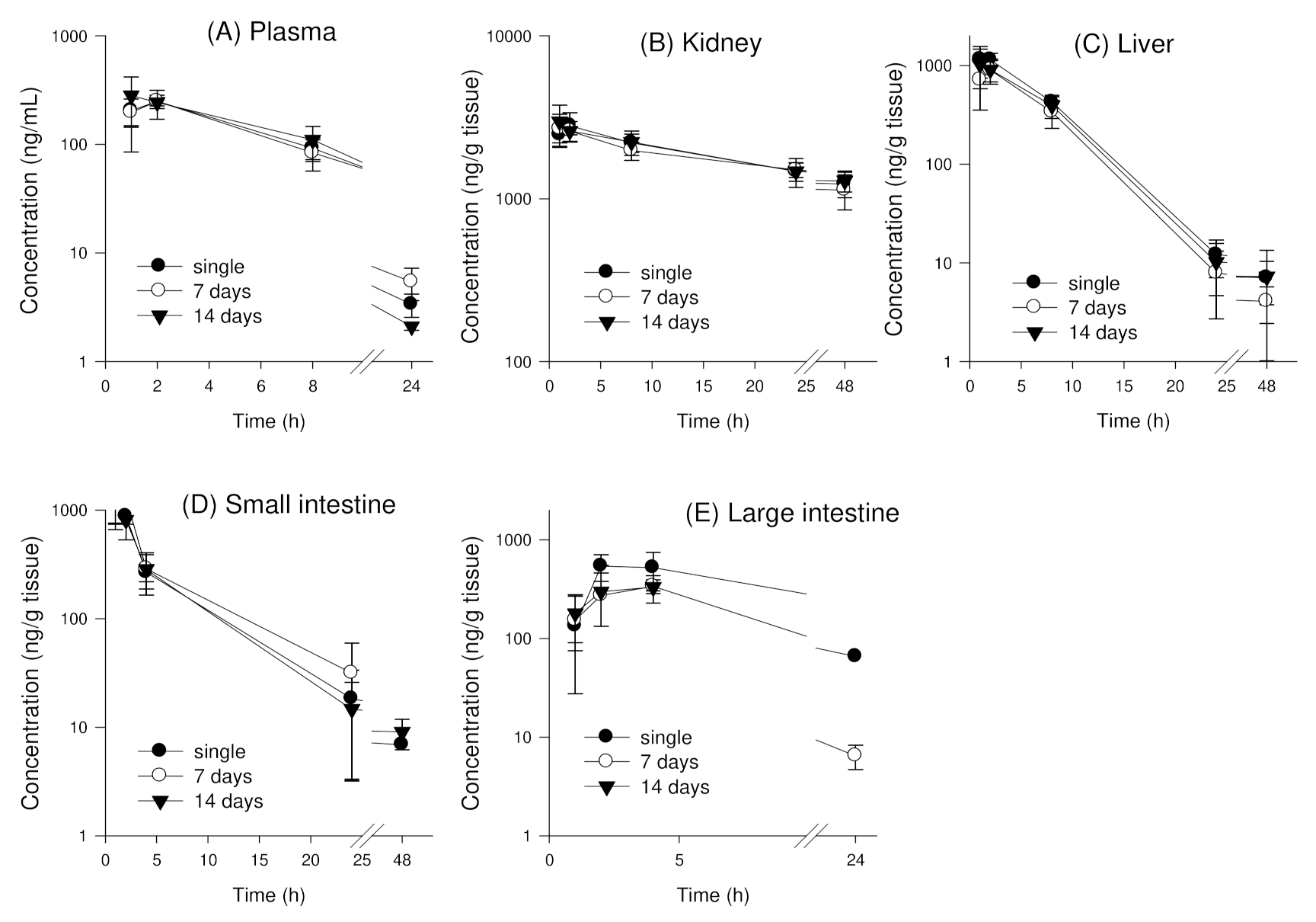
3.4.2. Tissue Distribution of Enavogliflozin following Repeated Oral Administration of Enavogliflozin in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tentolouris, A.; Vlachakis, P.; Tzeravini, E.; Eleftheriadou, I.; Tentolouris, N. SGLT2 inhibitors: A review of their antidiabetic and cardioprotective effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, E.C.; Henry, R.R. SGLT2 inhibition—A novel strategy for diabetes treatment. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, E.; Solini, A. SGLT2 inhibition in diabetes mellitus: Rationale and clinical prospects. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.N.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Che, W.S.; Leung, S.W. The efficacy of dapagliflozin combined with hypoglycaemic drugs in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus: Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in yype 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; De Zeeuw, D.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Barrett, T.D.; Weidner-Wells, M.; Deng, H.W.; Matthews, D.R.; et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: Results from the CANVAS Program randomised clinical trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, C.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Von Eynatten, M.; Mattheus, M.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Zinman, B.; et al. Empagliflozin and progression ofkidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Baar, M.J.B.; Van Ruiten, C.C.; Muskiet, M.H.A.; Van Bloemendaal, L.; RG, I.J.; Van Raalte, D.H. SGLT2 inhibitors in combination therapy: From mechanisms to clinical considerations in type 2 diabetes management. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahara, A.; Takasu, T.; Yokono, M.; Imamura, M.; Kurosaki, E. Characterization and comparison of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: Part 2. Antidiabetic effects in type 2 diabetic mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 131, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Im, K.; Goodrich, E.L.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Furtado, R.H.M.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet 2019, 393, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Harashima, S.; Maruyama, N.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Goda, M.; Iijima, H. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in combination with insulin: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenstock, J.; Chuck, L.; González-Ortiz, M.; Merton, K.; Craig, J.; Capuano, G.; Qiu, R. Initial combination therapy with canagliflozin plus metformin versus each component as monotherapy for drug-naïve type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leiter, L.A.; Yoon, K.H.; Arias, P.; Langslet, G.; Xie, J.; Balis, D.A.; Millington, D.; Vercruysse, F.; Canovatchel, W.; Meininger, G. Canagliflozin provides durable glycemic improvements and body weight reduction over 104 weeks versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes on metformin: A randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Choi, M.-K.; Song, I.-S. Pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides following repeated oral administration of red ginseng extract significantly differ between species of experimental animals. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, R.M.; Dungo, R.T. Ipragliflozin: First global approval. Drugs 2014, 74, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clar, C.; Gill, J.A.; Court, R.; Waugh, N. Systematic review of SGLT2 receptor inhibitors in dual or triple therapy in type 2 diabetes. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e001007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häring, H.U.; Merker, L.; Seewaldt-Becker, E.; Weimer, M.; Meinicke, T.; Broedl, U.C.; Woerle, H.J. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kovacs, C.S.; Seshiah, V.; Swallow, R.; Jones, R.; Rattunde, H.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C. Empagliflozin improves glycaemic and weight control as add-on therapy to pioglitazone or pioglitazone plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.K.; Nam, S.J.; Ji, H.Y.; Park, M.J.; Choi, J.S.; Song, I.S. Comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a novel sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, DWP16001, with dapagliflozin and ipragliflozin. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.G.; Lee, S.; Huh, W.; Han, J.; Oh, J.; Jang, I.J.; Yu, K.S. Dose-dependent glucosuria of DWP16001, a novel selective sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor, in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, A.; Takasu, T.; Yokono, M.; Imamura, M.; Kurosaki, E. Characterization and comparison of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacologic effects. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 130, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.K.; Choi, W.G.; Ji, H.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Song, I.S.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.S. In vitro metabolism of DWP16001, a novel sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, in human and animal hepatocytes. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamidi, R.N.; Cuyckens, F.; Chen, J.; Scheers, E.; Kalamaridis, D.; Lin, R.; Silva, J.; Sha, S.; Evans, D.C.; Kelley, M.F.; et al. Metabolism and excretion of canagliflozin in mice, rats, dogs, and humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshall, S.F.; Burghaus, R.; Cosson, V.; Cheung, S.Y.; Chenel, M.; DellaPasqua, O.; Frey, N.; Hamrén, B.; Harnisch, L.; Ivanow, F.; et al. Good Practices in Model-Informed Drug Discovery and Development: Practice, Application, and Documentation. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2016, 5, 93–122. [Google Scholar]



| Treatment | Sampling Time (h) | Group1/4/7 (n = 6) | Group2/5/8 (n = 6) | Group3/6/9 (n = 6) | Sampling (µL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intravenous injection (IV, 0.3, 1, 3 mg/kg) | 0 | RO-right 1 | 80 | ||
| 0.083 | RO-right 1 | 80 | |||
| 0.25 | RO-right 1 | 80 | |||
| 0.5 | RO-left 2 | 80 | |||
| 1 | RO-left 2 | 80 | |||
| 2 | RO-left 2 | 80 | |||
| 4 | AA 3 | 80 | |||
| 8 | AA 3 | 100 | |||
| 24 | AA 3 | 100 | |||
| Treatment | Sampling Time (h) | Group10/13/16 (n =6) | Group11/14/17 (n =6) | Group12/15/18 (n =6) | Sampling (µL) |
| Per oral administration (PO, 0.3, 1, 3 mg/kg) | 0 | RO-right 1 | 80 | ||
| 0.083 | RO-right 1 | 80 | |||
| 0.25 | RO-right 1 | 80 | |||
| 0.5 | RO-left 2 | 80 | |||
| 1 | RO-left 2 | 80 | |||
| 2 | RO-left 2 | 80 | |||
| 4 | AA 3 | 80 | |||
| 8 | AA 3 | 100 | |||
| 24 | AA 3 | 100 |
| Parameter | Dose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 mg/kg | 1 mg/kg | 3 mg/kg | p Value | |
| IV administration | ||||
| AUClast (ng·h/mL) | 478.6 ± 33.6 | 1512.7 ± 282.3 | 4657.6 ± 998.0 | NC |
| AUC∞ (ng·h/mL) | 512.0 ± 30.7 | 1626.7 ± 335.6 | 5083.0 ± 1063 | NC |
| AUC∞/D | 1706.8 ± 102.3 | 1626.7 ± 335.6 | 1694.3 ± 354.5 | 0.810 |
| Co (ng/mL) | 125.0 ± 9.4 | 408.6 ± 103.2 | 1274.1 ± 186.6 | NC |
| Co/D | 416.8 ± 31.3 | 408.6 ± 103.2 | 424.7 ± 62.2 | 0.700 |
| CL (mL/min/kg) | 9.8 ± 0.6 | 10.7 ± 2.5 | 10.2 ± 2.1 | 0.810 |
| Vd,ss (L/kg) | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 3.1 ± 0.6 | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 0.755 |
| T1/2 (h) | 6.0 ± 1.3 | 6.5 ± 1.4 | 6.6 ± 0.5 | 0.484 |
| MRT (h) | 5.2 ± 0.4 | 4.9 ± 0.5 | 5.2 ± 0.8 | 0.459 |
| PO administration | ||||
| AUClast (ng·h/mL) | 487.8 ± 77.9 | 1363.6 ± 270.0 | 4735.8 ± 531.9 | NC |
| AUC∞ (ng·h/mL) | 497.7 ± 79.0 | 1373.8 ± 269.6 | 4761.0 ± 543.4 | NC |
| AUC∞/D | 1658.9 ± 263.5 | 1373.8 ± 269.6 | 1587.0 ± 181.1 | 0.191 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 72.1 ± 10.5 | 216.1 ± 94.1 | 942.8 ± 230.8 | NC |
| Cmax/D | 240.5 ± 35.0 | 216.1 ± 94.1 | 314.3 ± 76.9 | 0.077 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 0.7 ± 0.7 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.051 |
| T1/2 (h) | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 3.5 ± 0.2 | 3.3 ± 0.4 | 0.067 |
| MRT (h) | 5.7 ± 0.5 | 5.7 ± 0.5 | 5.3 ± 0.5 | 0.385 |
| BA (%) | 97.2 | 84.5 | 93.7 | - |
| Parameter | Dose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 mg/kg | 1 mg/kg | 3 mg/kg | p Value | |
| IV administration | ||||
| AUClast (ng·h/mL) | 784.5 ± 94.4 | 2508.8 ± 447.2 | 5614.1 ± 751.0 | NC |
| AUC∞ (ng·h/mL) | 849.5 ± 107.7 | 2798.6 ± 551.4 | 7387.3 ± 1288 | NC |
| AUC∞/D | 2831.6 ± 359.0 | 2798.6 ± 551.4 | 2462.4 ± 429.3 | 0.491 |
| Co (ng/mL) | 1269.4 ± 516.0 | 3956.4 ± 1028.2 | 10,258.1 ± 4094.5 | NC |
| Co/D | 4231.2 ± 1720.0 | 3956.4 ± 1028.2 | 3419.4 ± 1364.8 | 0.668 |
| CL (mL/min/kg) | 6.0 ± 0.8 | 6.2 ± 1.4 | 6.9 ± 1.2 | 0.491 |
| Vd,ss (L/kg) | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.4 | 0.053 |
| T1/2 (h) | 2.6 ± 0.4 | 2.9 ± 0.4 | 4.3 ± 0.6 | 0.021 |
| MRT (h) | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 2.9 ± 0.4 | 5.1 ± 1.1 | 0.015 |
| PO administration | ||||
| AUClast (ng·h/mL) | 489.2 ± 191.9 | 1348.0 ± 565.2 | 3254.2 ± 572.5 | NC |
| AUC∞ (ng·h/mL) | 527.3 ± 193.0 | 1649.3 ± 483.4 | 4156.3 ± 1085.3 | NC |
| AUC∞/D | 1757.6 ± 643.4 | 1649.3 ± 483.4 | 1385.4 ± 361.8 | 0.426 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 51.3 ± 15.0 | 183.0 ± 95.6 | 300.7 ± 108.2 | NC |
| Cmax/D | 171.2 ± 49.9 | 183.0 ± 95.6 | 100.2 ± 36.1 | 0.051 |
| Tmax (h) | 2.5 ± 2.4 | 2.5 ± 2.5 | 2.9 ± 2.1 | 0.690 |
| T1/2 (h) | 6.3 ± 2.3 | 6.9 ± 2.1 | 10.3 ± 7.5 | 0.625 |
| MRT (h) | 8.5 ± 3.2 | 9.9 ± 3.6 | 14.9 ± 10.6 | 0.762 |
| BA (%) | 62.1 | 58.9 | 56.3 | - |
| Dose | Time | Recovery (% of Dose) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg/kg (IV) | h | Feces | Urine |
| 0–24 | 36.3 ± 3.6 | 6.3 ± 0.8 | |
| 24–48 | 2.7 ± 1.3 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | |
| 48–72 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | ND | |
| 0–72 | 39.3 ± 3.5 | 6.6 ± 0.7 | |
| 1 mg/kg (PO) | h | Feces | Urine |
| 0–24 | 50.6 ± 11.1 | 6.6 ± 0.6 | |
| 24–48 | 0.72 ± 0.4 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | |
| 48–72 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | ND | |
| 0–72 | 51.4 ± 11.5 | 6.8 ± 0.6 | |
| Dose | Time | Recovery (% of Dose) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg/kg (IV) | h | Feces | Urine |
| 0–24 | 15.2 ± 6.2 | 6.6 ± 0.6 | |
| 24–48 | 0.7 ± 0.8 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | |
| 48–72 | ND | ND | |
| 0–72 | 15.9 ± 5.9 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | |
| 1 mg/kg (PO) | h | Feces | Urine |
| 0–24 | 44.5 ± 11.8 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | |
| 24–48 | 0.9 ± 0.4 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | |
| 48–72 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | |
| 0–72 | 50.3 ±8.3 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | |
| Tissue | K (h−1) | T1/2 (h) | AUC24 h (µg·h/mL for Plasma or µg·h/g Tissue) | AUC Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| plasma | 0.185 | 3.7 | 1.36 ± 0.26 | - |
| kidney | 0.024 | 29 | 54.5 ± 3.5 | 41.9 ± 7.7 |
| stomach | 0.206 | 3.4 | 15.1 ± 6.4 | 12.1 ± 7.0 |
| small intestine | 0.267 | 2.6 | 14.2 ± 3.4 | 10.8 ± 3.0 |
| large intestine | 0.204 | 3.4 | 11.1 ± 4.3 | 8.5 ± 4.5 |
| liver | 0.159 | 4.4 | 8.08 ± 1.1 | 5.8 ± 0.4 |
| lung | 0.072 | 9.6 | 3.04 ± 0.29 | 2.0 ± 0.2 |
| heart | 0.194 | 3.6 | 2.19 ± 0.35 | 1.7 ± 0.2 |
| spleen | 0.255 | 2.7 | 0.58 ± 0.11 | 0.4 ± 0.0 |
| testis | 0.031 | 22 | 0.95 ± 0.15 | 0.5 ± 0.1 |
| brain | NC | NC | NC | NC |
| Tissue | AUC48 h (µg·h/mL for Plasma or µg·h/g Tissue) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Dose | Repeated Dose for 7 Days | Repeated Dose for 14 Days | ||
| Plasma | 2.13 ± 0.27 | 2.09 ± 0.29 | 2.36 ± 0.69 | 0.358 |
| Kidney | 80.9 ± 5.1 | 77.2 ± 6.3 | 81.6 ± 4.8 | 0.610 |
| Liver | 10.2 ± 1.0 | 7.89 ± 2.1 | 8.85 ± 1.8 | 0.213 |
| Small intestine | 7.30 ± 0.77 | 9.39 ± 2.1 | 7.46 ± 2.3 | 0.228 |
| Large intestine | 5.68 ± 1.6 | 4.88 ± 1.1 | 4.90 ± 1.5 | 0.077 |
| Tissue | AUC Ratio | pValue | ||
| Single Dose | Repeated Dose for 7 Days | Repeated Dose for 14 Days | ||
| Kidney | 38.7 ± 6.3 | 37.6 ± 5.9 | 38.4 ± 18 | 0.444 |
| Liver | 4.85 ± 0.64 | 3.77 ± 0.73 | 4.37 ± 2.6 | 0.404 |
| Small intestine | 3.47 ± 0.49 | 4.50 ± 0.89 | 3.40 ± 1.5 | 0.251 |
| Large intestine | 3.24 ± 1.1 | 2.33 ± 0.34 | 2.20 ± 0.71 | 0.052 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, M.; Jeon, S.Y.; Choi, M.-K.; Jeon, J.-H.; Ji, H.-Y.; Choi, J.-S.; Song, I.-S. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Enavogliflozin in Mice and Rats. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061210
Pang M, Jeon SY, Choi M-K, Jeon J-H, Ji H-Y, Choi J-S, Song I-S. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Enavogliflozin in Mice and Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(6):1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061210
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Minyeong, So Yeon Jeon, Min-Koo Choi, Ji-Hyeon Jeon, Hye-Young Ji, Ji-Soo Choi, and Im-Sook Song. 2022. "Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Enavogliflozin in Mice and Rats" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 6: 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061210
APA StylePang, M., Jeon, S. Y., Choi, M.-K., Jeon, J.-H., Ji, H.-Y., Choi, J.-S., & Song, I.-S. (2022). Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Enavogliflozin in Mice and Rats. Pharmaceutics, 14(6), 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061210







