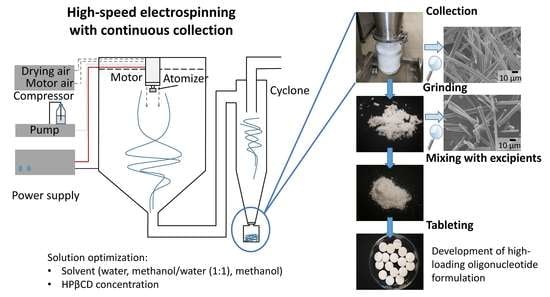
Oligonucleotide Formulations Prepared by High-Speed Electrospinning: Maximizing Loading and Exploring Downstream Processability
Abstract
Share and Cite
Hirsch, E.; Nacsa, M.; Pantea, E.; Szabó, E.; Vass, P.; Domján, J.; Farkas, A.; Nyíri, Z.; Eke, Z.; Vigh, T.; et al. Oligonucleotide Formulations Prepared by High-Speed Electrospinning: Maximizing Loading and Exploring Downstream Processability. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030855
Hirsch E, Nacsa M, Pantea E, Szabó E, Vass P, Domján J, Farkas A, Nyíri Z, Eke Z, Vigh T, et al. Oligonucleotide Formulations Prepared by High-Speed Electrospinning: Maximizing Loading and Exploring Downstream Processability. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(3):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030855
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirsch, Edit, Márió Nacsa, Eszter Pantea, Edina Szabó, Panna Vass, Júlia Domján, Attila Farkas, Zoltán Nyíri, Zsuzsanna Eke, Tamás Vigh, and et al. 2023. "Oligonucleotide Formulations Prepared by High-Speed Electrospinning: Maximizing Loading and Exploring Downstream Processability" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 3: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030855
APA StyleHirsch, E., Nacsa, M., Pantea, E., Szabó, E., Vass, P., Domján, J., Farkas, A., Nyíri, Z., Eke, Z., Vigh, T., Andersen, S. K., Verreck, G., Marosi, G. J., & Nagy, Z. K. (2023). Oligonucleotide Formulations Prepared by High-Speed Electrospinning: Maximizing Loading and Exploring Downstream Processability. Pharmaceutics, 15(3), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030855