Terahertz Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Solid-State Investigation of Norfloxacin in Paper Tablets after Wet Granulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Pure Substances
2.2.2. Physical Mixtures
2.2.3. smartFilms Loaded with Norfloxacin
2.2.4. Granulation of Norfloxacin-Loaded smartFilms
2.2.5. Production of Tablets
2.3. Solid-State Characterization
2.3.1. X-ray Powder Diffraction
2.3.2. Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy
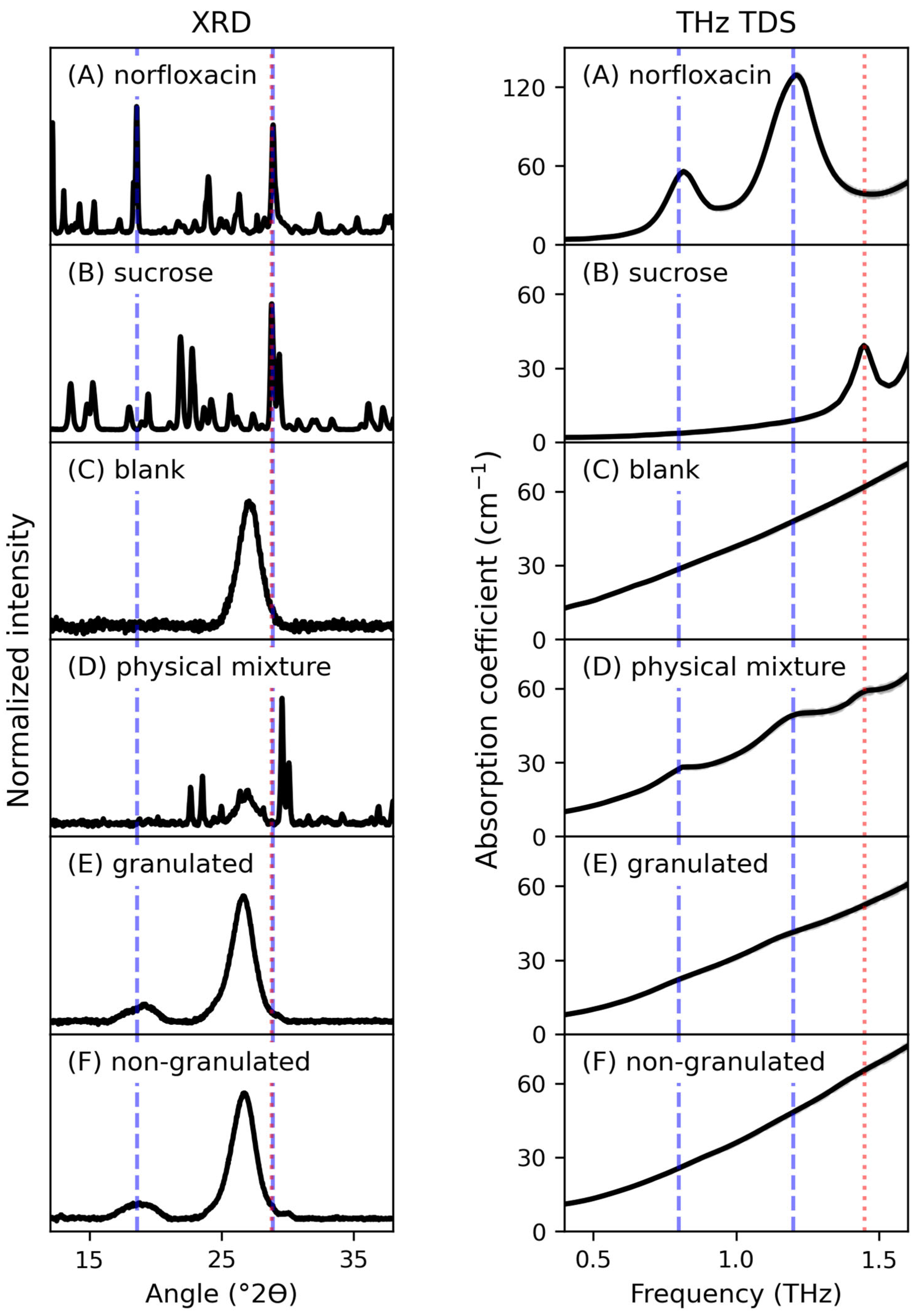
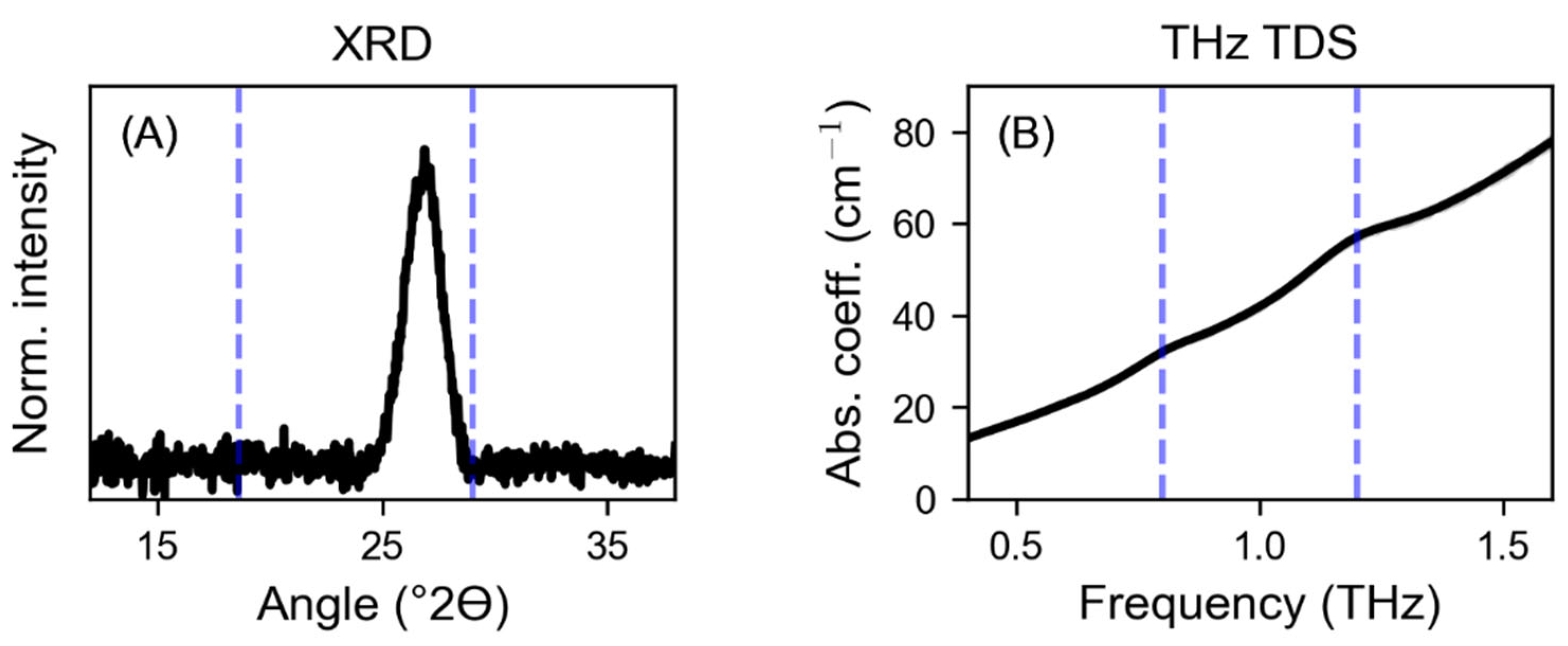
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sastry, S.V.; Nyshadham, J.R.; Fix, J.A. Recent technological advances in oral drug delivery—A review. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 2000, 3, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug solubility: Importance and enhancement techniques. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, F.L.O.; Marques, M.B.D.F.; Kato, K.C.; Carneiro, G. Nanonization techniques to overcome poor water-solubility with drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, B.J.; Bergström, C.A.S.; Vinarov, Z.; Kuentz, M.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P.; Brandl, M.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Shrestha, N.; Préat, V.; et al. Successful oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs both depends on the intraluminal behavior of drugs and of appropriate advanced drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, H.A.; Allam, A.; Elsabahy, M.; Fetih, G.; El-Badry, M. Nanostructured lipid carriers for improved oral delivery and prolonged antihyperlipidemic effect of simvastatin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 162, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, S.; Strätling, E.-J.; Hans-Peter; Keck, C.M. Cellulose fibre based support matrices for layered products for oral and peroral application and their preparation. European Patent Office EP3192499A1, 14 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, B.C.; Parks, M. What is the true solubility advantage for amorphous pharmaceuticals? Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornik, J.; Knoth, D.; Koch, M.; Keck, C.M. Terahertz-spectroscopy for non-destructive determination of crystallinity of L-tartaric acid in smartFilms® and tablets made from paper. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, F.; Keck, C.M. Tablets made from paper. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanyeswari, C.D.; Prasanth, Y.; Sameeda, R. Formulation and development of efavirenz tablets by paper technique using co-solvency method. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2019, 11, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornik, J.; Heidrich, L.; Schesny, R.; Castro-Camus, E.; Keck, C.M.; Koch, M. Non-destructive crystallinity assessment of indomethacin in tablets made from smartFilms® using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, A.; Moos, C.; Pelloux, A.; Pfeiffer, M.; Alter, C.; Kolling, S.; Keck, C.M. Tablets made from paper—An industrially feasible approach. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, A.; Nallbati, L.; Keck, C.M. Improving the Bioactivity of Norfloxacin with Tablets Made from Paper. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, F. Tablets Made from Paper for Oral Administration of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Ph.D. Thesis, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Marburg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa, N.F.; Daniels, R.; Fernandes, A.I.; Pinto, J.F. Amorphous and Co-Amorphous Olanzapine Stability in Formulations Intended for Wet Granulation and Pelletization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tank, D.; Karan, K.; Gajera, B.Y.; Dave, R.H. Investigate the effect of solvents on wet granulation of microcrystalline cellulose using hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as a binder and evaluation of rheological and thermal characteristics of granules. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdešič, P.; Sovány, T.; German Ilić, I. High-shear granulation of high-molecular weight hypromellose: Effects of scale-up and process parameters on flow and compaction properties. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 1770–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Han, J. Solid Form and Phase Transformation Properties of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride during Wet Granulation Process. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.A.; Zografi, G.; Gao, P.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, G.G.Z. Modeling Physical Stability of Amorphous Solids Based on Temperature and Moisture Stresses. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2932–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peltonen, L. Practical guidelines for the characterization and quality control of pure drug nanoparticles and nano-cocrystals in the pharmaceutical industry. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 131, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitler, J.A.; Taday, P.F.; Newnham, D.A.; Pepper, M.; Gordon, K.C.; Rades, T. Terahertz pulsed spectroscopy and imaging in the pharmaceutical setting—A review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, J.C.; Saraceno, C.J.; Koch, M.; Kaurav, P.; Pfeiffer, U.R.; Withayachumnankul, W.; Kurner, T.; Stohr, A.; El-Absi, M.; Abbas, A.A.-H.; et al. THz Systems Exploiting Photonics and Communications Technologies. IEEE J. Microw. 2023, 3, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Cardoso, G.G.; Rojas-Landeros, S.C.; Alfaro-Gomez, M.; Hernandez-Serrano, A.I.; Salas-Gutierrez, I.; Lemus-Bedolla, E.; Castillo-Guzman, A.R.; Lopez-Lemus, H.L.; Castro-Camus, E. Terahertz imaging for early screening of diabetic foot syndrome: A proof of concept. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mittleman, D.M. Perspective: Terahertz science and technology. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 230901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rau, J.V.; Fadeeva, I.V.; Forysenkova, A.A.; Davydova, G.A.; Fosca, M.; Filippov, Y.Y.; Antoniac, I.V.; Antoniac, A.; D’Arco, A.; Di Fabrizio, M.; et al. Strontium Substituted Tricalcium Phosphate Bone Cement: Short and Long-Term Time-Resolved Studies and In Vitro Properties. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2200803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitenstorfer, A.; Moskalenko, A.S.; Kampfrath, T.; Kono, J.; Castro-Camus, E.; Peng, K.; Qureshi, N.; Turchinovich, D.; Tanaka, K.; Markelz, A.; et al. The 2023 Terahertz Science and Technology Roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2023, 56, 223001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, P.U.; Cooke, D.G.; Koch, M. Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging—Modern techniques and applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2011, 5, 124–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine-Ostmann, T.; Wilk, R.; Rutz, F.; Koch, M.; Niemann, H.; Güttler, B.; Brandhorst, K.; Grunenberg, J. Probing noncovalent interactions in biomolecular crystals with terahertz spectroscopy. ChemPhysChem 2008, 9, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, M.; Fischer, B.M.; Uhd Jepsen, P. Noncovalent intermolecular forces in polycrystalline and amorphous saccharides in the far infrared. Chem. Phys. 2003, 288, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachan, C.J.; Rades, T.; Newnham, D.A.; Gordon, K.C.; Pepper, M.; Taday, P.F. Using terahertz pulsed spectroscopy to study crystallinity of pharmaceutical materials. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 390, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibik, J.; Zeitler, J.A. Direct measurement of molecular mobility and crystallisation of amorphous pharmaceuticals using terahertz spectroscopy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soltani, A.; Gebauer, D.; Duschek, L.; Fischer, B.M.; Cölfen, H.; Koch, M. Crystallization Caught in the Act with Terahertz Spectroscopy: Non-Classical Pathway for l-(+)-Tartaric Acid. Chemistry 2017, 23, 14128–14132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajito, K.; Kim, J.-Y.; Ueno, Y.; Song, H.-J.; Ueda, K.; Limwikrant, W.; Yamamoto, K.; Moribe, K. Nondestructive Multicomponent Terahertz Chemical Imaging of Medicine in Tablets. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, B171–B175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachan, C.J.; Taday, P.F.; Newnham, D.A.; Gordon, K.C.; Zeitler, J.A.; Pepper, M.; Rades, T. Using terahertz pulsed spectroscopy to quantify pharmaceutical polymorphism and crystallinity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, X.; Ochani, A.; Shen, S.; Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Ruggiero, M.T. Low-frequency vibrational spectroscopy: A new tool for revealing crystalline magnetic structures in iron phosphate crystals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 22241–22245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santitewagun, S.; Thakkar, R.; Zeitler, J.A.; Maniruzzaman, M. Detecting Crystallinity Using Terahertz Spectroscopy in 3D Printed Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 2380–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazuel, C. Norfloxacin. Anal. Profiles Drug Subst. 1991, 20, 557–600. [Google Scholar]
- Breda, S.A.; Jimenez-Kairuz, A.F.; Manzo, R.H.; Olivera, M.E. Solubility behavior and biopharmaceutical classification of novel high-solubility ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin pharmaceutical derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 371, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieweg, N.; Rettich, F.; Deninger, A.; Roehle, H.; Dietz, R.; Göbel, T.; Schell, M. Terahertz-time domain spectrometer with 90 dB peak dynamic range. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2014, 35, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Mittleman, D.M.; Ornik, J.; Castro-Camus, E. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Menlo Systems GmbH. TeraLyzer Terahertz Software. Available online: https://www.menlosystems.com/products/thz-time-domain-solutions/teralyzer-single/ (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Pupeza, I.; Wilk, R.; Koch, M. Highly accurate optical material parameter determination with THz time-domain spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 4335–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, M.; Jansen, C.; Koch, M. Analyzing sub-100-μm samples with transmission terahertz time domain spectroscopy. Opt. Commun. 2009, 282, 1304–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahvenainen, P.; Kontro, I.; Svedström, K. Comparison of sample crystallinity determination methods by X-ray diffraction for challenging cellulose I materials. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connor, B.H.; Li, D.Y.; Hunter, B.A. The importance of the specimen displacement correction in Rietveld pattern fitting with symmetric reflection-optics diffraction data. Adv. X-Ray Anal. 2001, 44, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.-K.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, C.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, T.; Son, J.-H.; Park, Q.-H.; Seo, M. Highly sensitive and selective sugar detection by terahertz nano-antennas. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heidrich, L.; Ornik, J.; Keck, C.M.; Castro-Camus, E.; Koch, M. Polyvinylpyrrolidone as co-inhibitor of crystallization of nifedipine in paper tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisazumi, J.; Suzuki, T.; Nakagami, H.; Terada, K. Quantification of pharmaceutical polymorphs and prediction of dissolution rate using theophylline tablet by terahertz spectroscopy. Chem. Pharm. Bull. Tokyo 2011, 59, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reyes-Reyes, E.S.; Carriles-Jaimes, R.; Castro-Camus, E. Algorithm for Determination of Cutoff Frequency of Noise Floor Level for Terahertz Time-Domain Signals. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2022, 43, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, C.-Y.; Richter, C. Sample Thickness Measurement with THz-TDS: Resolution and Implications. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2014, 35, 840–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline: ICH Topic Q 2 (R1) Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology, Step 5: Note for Guidance on Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology (CPMP/ICH/381/95). Validation of Analytical Procedures: Definitions and Methodology, London. 2006. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-q-2-r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-methodology-step-5_en.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Lee, S.L.; O’Connor, T.F.; Yang, X.; Cruz, C.N.; Chatterjee, S.; Madurawe, R.D.; Moore, C.M.V.; Yu, L.X.; Woodcock, J. Modernizing Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: From Batch to Continuous Production. J. Pharm. Innov. 2015, 10, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greco, S.; Authelin, J.-R.; Leveder, C.; Segalini, A. A practical method to predict physical stability of amorphous solid dispersions. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 2792–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmkemper, K.; Kyeremateng, S.O.; Heinzerling, O.; Degenhardt, M.; Sadowski, G. Impact of Polymer Type and Relative Humidity on the Long-Term Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4374–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.; Zografi, G. What We Need to Know about Solid-State Isothermal Crystallization of Organic Molecules from the Amorphous State below the Glass Transition Temperature. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1761–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, E.P.J.; Zeitler, J.A.; Friščić, T.; Pepper, M.; Jones, W.; Day, G.M.; Gladden, L.F. Testing the Sensitivity of Terahertz Spectroscopy to Changes in Molecular and Supramolecular Structure: A Study of Structurally Similar Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
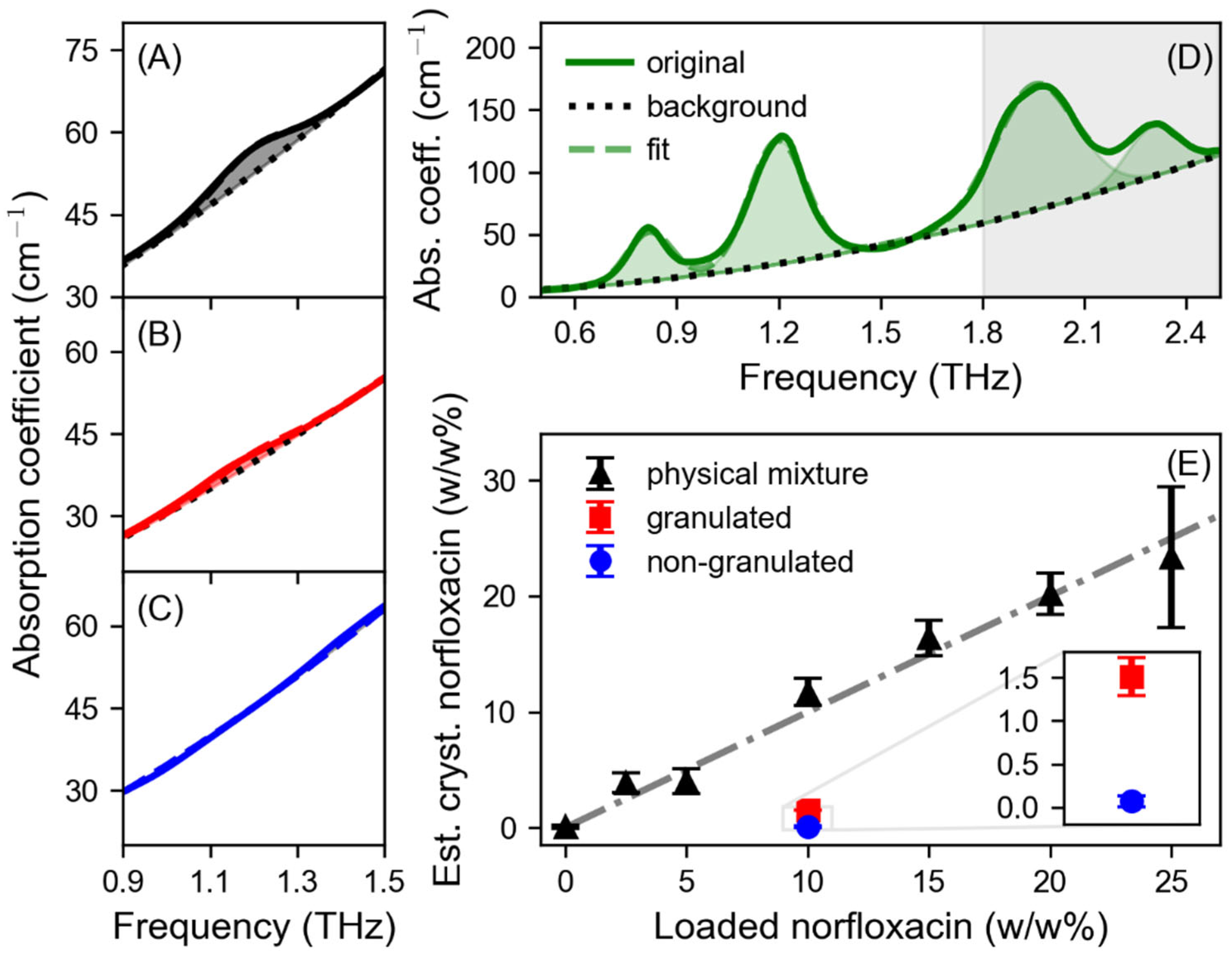
| Peak | G (cm−1) | v0 (THz) | Δv (THz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 39.32 | 0.82 | 0.06 |
| 2 | 99.11 | 1.20 | 0.08 |
| 3 | 100.56 | 1.96 | 0.12 |
| 4 | 40.00 | 2.30 | 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heidrich, L.; Abdelkader, A.; Ornik, J.; Castro-Camus, E.; Keck, C.M.; Koch, M. Terahertz Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Solid-State Investigation of Norfloxacin in Paper Tablets after Wet Granulation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071786
Heidrich L, Abdelkader A, Ornik J, Castro-Camus E, Keck CM, Koch M. Terahertz Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Solid-State Investigation of Norfloxacin in Paper Tablets after Wet Granulation. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(7):1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071786
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeidrich, Lara, Ayat Abdelkader, Jan Ornik, Enrique Castro-Camus, Cornelia M. Keck, and Martin Koch. 2023. "Terahertz Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Solid-State Investigation of Norfloxacin in Paper Tablets after Wet Granulation" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 7: 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071786
APA StyleHeidrich, L., Abdelkader, A., Ornik, J., Castro-Camus, E., Keck, C. M., & Koch, M. (2023). Terahertz Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Solid-State Investigation of Norfloxacin in Paper Tablets after Wet Granulation. Pharmaceutics, 15(7), 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15071786






