Head-to-Head Comparison of Novel Vaccine Technologies Comes with a Minefield of Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Vaccine Pharmacokinetics and Immune Responses
3. What to Think about When Designing Comparative Vaccine Technology Studies
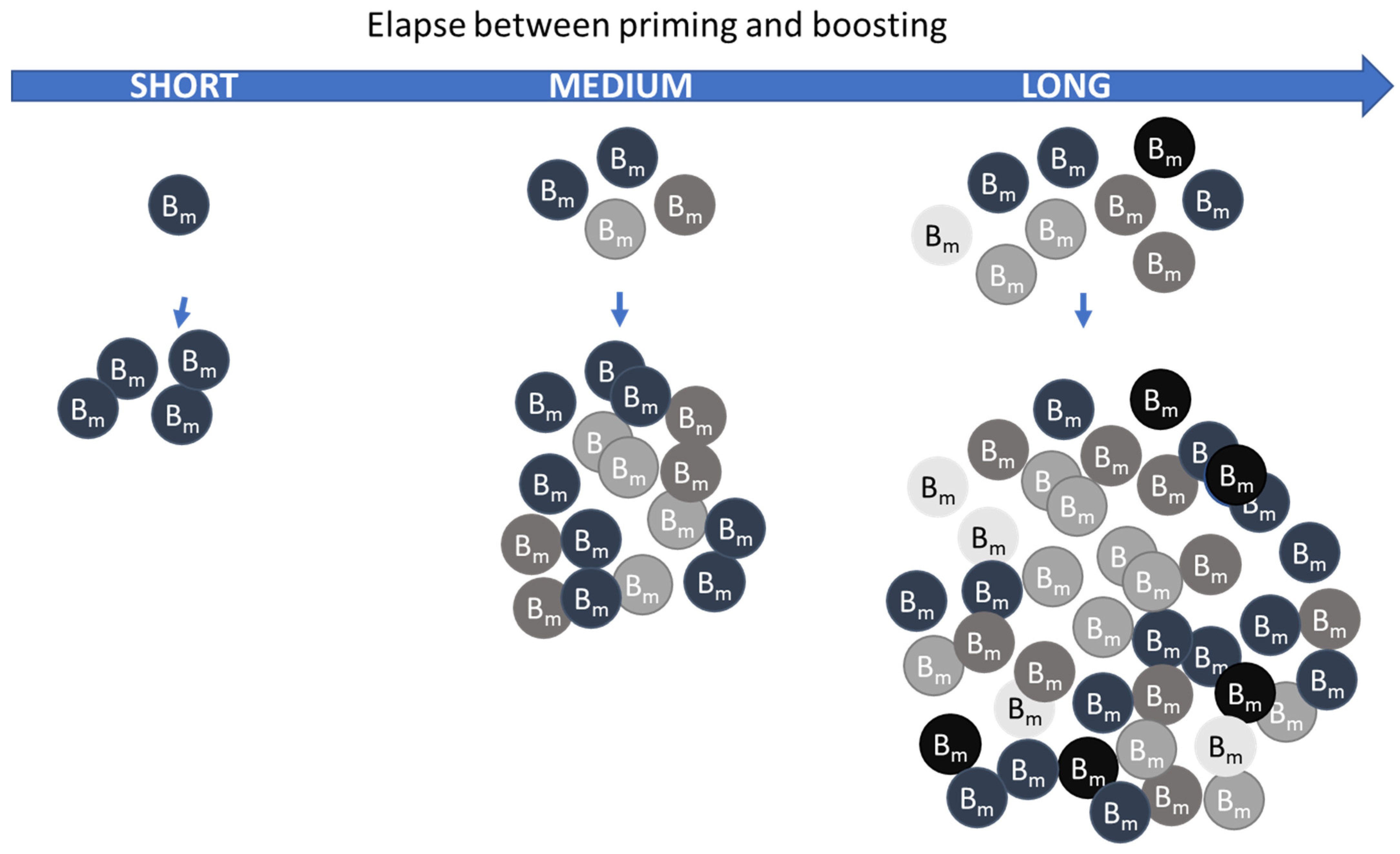
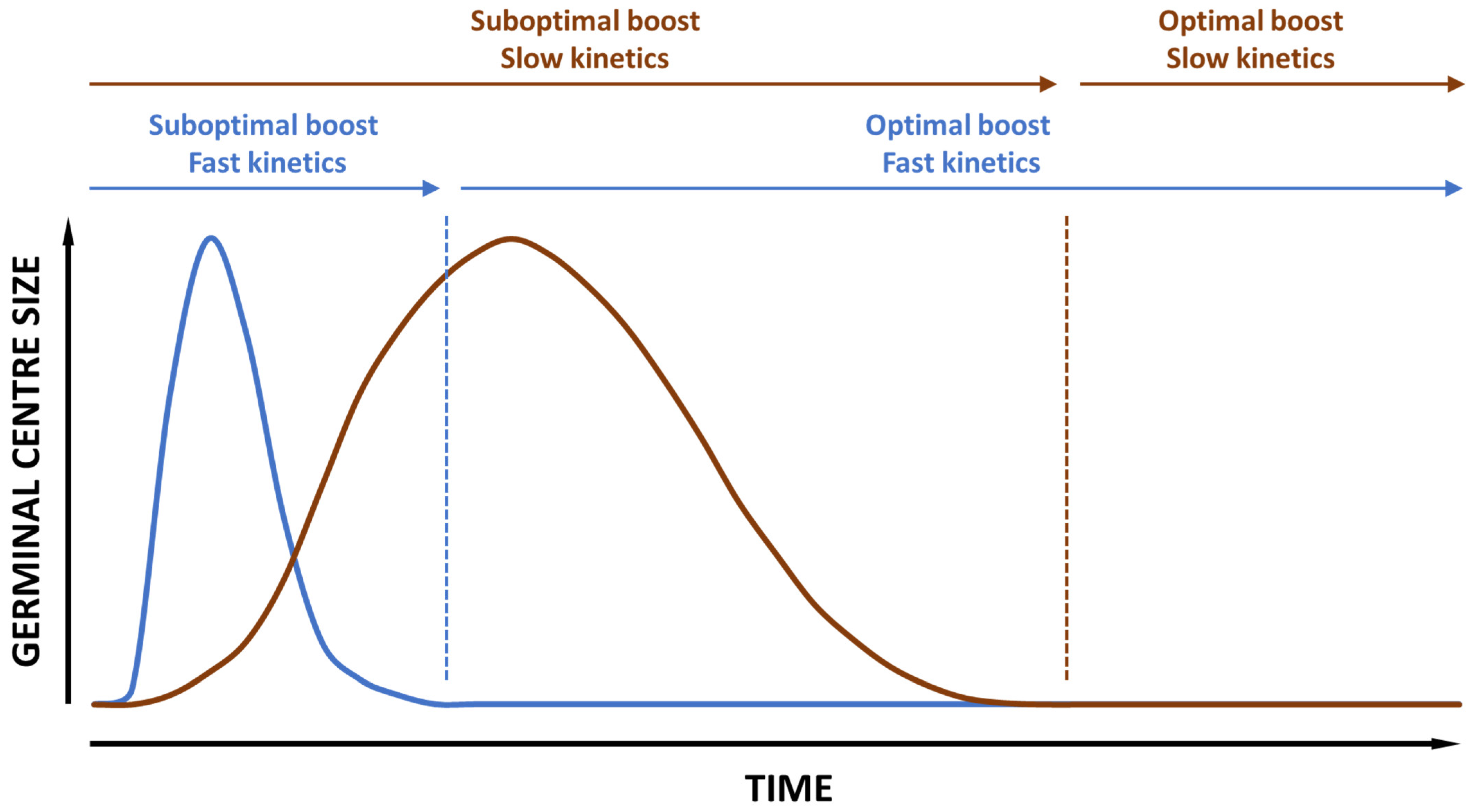
- Vaccine priming kinetics of the germinal centers in the draining lymph nodes. This is important for the determination of the optimal window for booster immunizations, especially when it comes to B cell boosting.
- Vaccine antigen dose. The optimal dose of an antigen, whether protein-, peptide- or nucleic-acid-based, varies from antigen to antigen and (unfortunately) from species to species. Most important, however, is that the optimum antigen dose is not the same for all vaccine technologies, and for some technologies, it has a major impact on the T/B cell induction balance, as illustrated with CAF01 by Wørzner et al. [38], meaning that antigen dose optimization should be linked to the expected correlates of protection for the vaccine.
- Sampling timepoint. With different pharmacokinetic windows for the different vaccine technologies, it is also clear that the optimal timeframe for test sampling will vary between technologies. These timepoints may also vary depending on the requested immune correlates; hence, it is important to make a thorough immune kinetic mapping of the B and T cell responses for each individual technology.
- Sampling sites. Different immune profiles not only lead to different timepoints for sample selection but also different optimal sampling sites. Strong effector T cell and plasma cell responses are best measured in the blood, whereas central memory B and T cell responses are better measured in the primary and secondary lymph nodes and spleen. Furthermore, unless a study is designed for investigating the effector immune responses for the individual vaccine technologies at their peak timepoint, it might be necessary to compare immune responses in different compartments.
4. Future Directions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, S.-T.; Zhang, X.-M.; Sun, P.-F.; Sun, L.-J.; Guo, X.; Tian, T.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Q.-Y.; Li, X.; Guo, L.-J.; et al. Intranasal Immunization Using Mannatide as a Novel Adjuvant for an Inactivated Influenza Vaccine and Its Adjuvant Effect Compared with MF59. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, N.P.H.; Olsen, A.; Buonsanti, C.; Follmann, F.; Zhang, Y.; Coler, R.N.; Fox, C.B.; Meinke, A.; D’Oro, U.; Casini, D.; et al. Different Human Vaccine Adjuvants Promote Distinct Antigen-Independent Immunological Signatures Tailored to Different Pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.; Kato, Y.; Melo, M.B.; Phung, I.; Freeman, B.L.; Li, Z.; Roh, K.; Van Wijnbergen, J.W.; Watkins, H.; Enemuo, C.A.; et al. A Particulate Saponin/TLR Agonist Vaccine Adjuvant Alters Lymph Flow and Modulates Adaptive Immunity. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabf1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.T.; Neustrup, M.A.; Harloff-Helleberg, S.; Korsholm, K.S.; Rades, T.; Andersen, P.; Christensen, D.; Foged, C. Systematic Investigation of the Role of Surfactant Composition and Choice of Oil: Design of a Nanoemulsion-Based Adjuvant Inducing Concomitant Humoral and CD4+ T-Cell Responses. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 1716–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvang, T.; Christensen, J.P.; Billeskov, R.; Thi Kim Thanh Hoang, T.; Holst, P.; Thomsen, A.R.; Andersen, P.; Dietrich, J. CD4 and CD8 T Cell Responses to the M. Tuberculosis Ag85B-TB10.4 Promoted by Adjuvanted Subunit, Adenovector or Heterologous Prime Boost Vaccination. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billeskov, R.; Christensen, J.P.; Aagaard, C.; Andersen, P.; Dietrich, J. Comparing Adjuvanted H28 and Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara Expressing H28 in a Mouse and a Non-Human Primate Tuberculosis Model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabro, S.; Tortoli, M.; Baudner, B.C.; Pacitto, A.; Cortese, M.; O’Hagan, D.T.; De Gregorio, E.; Seubert, A.; Wack, A. Vaccine Adjuvants Alum and MF59 Induce Rapid Recruitment of Neutrophils and Monocytes that Participate in Antigen Transport to Draining Lymph Nodes. Vaccine 2011, 29, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsdottir, T.A.; Lindqvist, M.; Nookaew, I.; Andersen, P.; Maertzdorf, J.; Persson, J.; Christensen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Anderson, J.; Khoomrung, S.; et al. Comparative Systems Analyses Reveal Molecular Signatures of Clinically Tested Vaccine Adjuvants. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.; Mortensen, R.; Rosenkrands, I.; Dietrich, J.; Andersen, P. Vaccine-Induced Th17 Cells Are Established as Resident Memory Cells in the Lung and Promote Local IgA Responses. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Pinto, F.E.; Hansen, H.S.; Andersen, P.; Christensen, D.; Janfelt, C.; Foged, C. Intrapulmonary (i.Pulmon.) Pull Immunization With the Tuberculosis Subunit Vaccine Candidate H56/CAF01 After Intramuscular (i.m.) Priming Elicits a Distinct Innate Myeloid Response and Activation of Antigen-Presenting Cells Than i.m. or i.Pulmon. Prime Immunization Alone. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodworth, J.S.; Christensen, D.; Cassidy, J.P.; Agger, E.M.; Mortensen, R.; Andersen, P. Mucosal Boosting of H56:CAF01 Immunization Promotes Lung-Localized T Cells and an Accelerated Pulmonary Response to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection without Enhancing Vaccine Protection. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, H.; Bruton, R.; Stephens, C.; Bentley, C.; Brown, K.; Amirthalingam, G.; Hallis, B.; Otter, A.; Zuo, J.; Moss, P. Extended Interval BNT162b2 Vaccination Enhances Peak Antibody Generation. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, H.; Bruton, R.; Ayodele, R.; Sylla, P.; McIlroy, G.; Logan, N.; Scott, S.; Nicol, S.; Verma, K.; Stephens, C.; et al. Vaccine Subtype and Dose Interval Determine Immunogenicity of Primary Series COVID-19 Vaccines in Older People. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, H.; Bruton, R.; Stephens, C.; Brown, K.; Amirthalingam, G.; Otter, A.; Hallis, B.; Zuo, J.; Moss, P. Differential Immunogenicity of BNT162b2 or ChAdOx1 Vaccines after Extended-Interval Homologous Dual Vaccination in Older People. Immun. Ageing 2021, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voysey, M.; Costa Clemens, S.A.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Single-Dose Administration and the Influence of the Timing of the Booster Dose on Immunogenicity and Efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) Vaccine: A Pooled Analysis of Four Randomised Trials. Lancet 2021, 397, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaxman, A.; Marchevsky, N.G.; Jenkin, D.; Aboagye, J.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Bibi, S.; Bittaye, M.; Cappuccini, F.; et al. Reactogenicity and Immunogenicity after a Late Second Dose or a Third Dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 in the UK: A Substudy of Two Randomised Controlled Trials (COV001 and COV002). Lancet 2021, 398, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirthalingam, G.; Bernal, J.L.; Andrews, N.J.; Whitaker, H.; Gower, C.; Stowe, J.; Tessier, E.; Subbarao, S.; Ireland, G.; Baawuah, F.; et al. Serological Responses and Vaccine Effectiveness for Extended COVID-19 Vaccine Schedules in England. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, T.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, G.; Saxena, S.K. Tracking the COVID-19 Vaccines: The Global Landscape. Human Vaccines Immunother. 2023, 19, 2191577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, D.; Khatami, A.; McKenna, J.; Campbell, D.; Attard-Montalto, S.; Birks, J.; Voysey, M.; White, C.; Finn, A.; Macloed, E.; et al. Immunogenicity of Reduced Dose Priming Schedules of Serogroup C Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccine Followed by Booster at 12 Months in Infants: Open Label Randomised Controlled Trial. BMJ 2015, 350, h1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.M.C.; Plotkin, S.A. The Influence of Interval between Doses on Response to Vaccines. Vaccine 2021, 39, 7123–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.; Sokolovska, A.; HogenEsch, H.; Hem, S.L. Relationship between the Strength of Antigen Adsorption to an Aluminum-Containing Adjuvant and the Immune Response. Vaccine 2007, 25, 6618–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morefield, G.L.; Jiang, D.; Romero-Mendez, I.Z.; Geahlen, R.L.; HogenEsch, H.; Hem, S.L. Effect of Phosphorylation of Ovalbumin on Adsorption by Aluminum-Containing Adjuvants and Elution upon Exposure to Interstitial Fluid. Vaccine 2005, 23, 1502–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.; HogenEsch, H.; Hem, S.L. Relationship between the Degree of Antigen Adsorption to Aluminum Hydroxide Adjuvant in Interstitial Fluid and Antibody Production. Vaccine 2003, 21, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noe, S.M.; Green, M.A.; HogenEsch, H.; Hem, S.L. Mechanism of Immunopotentiation by Aluminum-Containing Adjuvants Elucidated by the Relationship between Antigen Retention at the Inoculation Site and the Immune Response. Vaccine 2010, 28, 3588–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, T.J.; Kato, Y.; Abraham, W.; Chang, J.Y.H.; Kulp, D.W.; Watson, N.; Turner, H.L.; Menis, S.; Abbott, R.K.; Bhiman, J.N.; et al. Engineered Immunogen Binding to Alum Adjuvant Enhances Humoral Immunity. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabro, S.; Tritto, E.; Pezzotti, A.; Taccone, M.; Muzzi, A.; Bertholet, S.; De Gregorio, E.; O’Hagan, D.T.; Baudner, B.; Seubert, A. The Adjuvant Effect of MF59 Is Due to the Oil-in-Water Emulsion Formulation, None of the Individual Components Induce a Comparable Adjuvant Effect. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3363–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumjohann, D.; Preite, S.; Reboldi, A.; Ronchi, F.; Ansel, K.M.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Sallusto, F. Persistent Antigen and Germinal Center B Cells Sustain T Follicular Helper Cell Responses and Phenotype. Immunity 2013, 38, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.T.; Pedersen, G.K.; Christensen, D. Rational Design and In Vivo Characterization of Vaccine Adjuvants. ILAR J. 2018, 59, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coler, R.N.; Day, T.A.; Ellis, R.; Piazza, F.M.; Beckmann, A.M.; Vergara, J.; Rolf, T.; Lu, L.; Alter, G.; Hokey, D.; et al. The TLR-4 Agonist Adjuvant, GLA-SE, Improves Magnitude and Quality of Immune Responses Elicited by the ID93 Tuberculosis Vaccine: First-in-Human Trial. NPJ Vaccines 2018, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, M.; Collignon, C.; Hervé, C.; Chalon, A.; Welsby, I.; Detienne, S.; van Helden, M.J.; Dutta, S.; Genito, C.J.; Waters, N.C.; et al. Cellular and Molecular Synergy in AS01-Adjuvanted Vaccines Results in an Early IFNγ Response Promoting Vaccine Immunogenicity. NPJ Vaccines 2017, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didierlaurent, A.M.; Collignon, C.; Bourguignon, P.; Wouters, S.; Fierens, K.; Fochesato, M.; Dendouga, N.; Langlet, C.; Malissen, B.; Lambrecht, B.N.; et al. Enhancement of Adaptive Immunity by the Human Vaccine Adjuvant AS01 Depends on Activated Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didierlaurent, A.M.; Laupèze, B.; Di Pasquale, A.; Hergli, N.; Collignon, C.; Garçon, N. Adjuvant System AS01: Helping to Overcome the Challenges of Modern Vaccines. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2017, 16, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirelli, K.M.; Carnathan, D.G.; Nogal, B.; Martin, J.T.; Rodriguez, O.L.; Upadhyay, A.A.; Enemuo, C.A.; Gebru, E.H.; Choe, Y.; Viviano, F.; et al. Slow Delivery Immunization Enhances HIV Neutralizing Antibody and Germinal Center Responses via Modulation of Immunodominance. Cell 2019, 177, 1153–1171.e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, H.H.; Melo, M.B.; Kang, M.; Pelet, J.M.; Ruda, V.M.; Foley, M.H.; Hu, J.K.; Kumari, S.; Crampton, J.; Baldeon, A.D.; et al. Sustained Antigen Availability during Germinal Center Initiation Enhances Antibody Responses to Vaccination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6639–E6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, D.J.; Aung, A.; Silva, M. Controlling Timing and Location in Vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 158, 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, C.-A. 2—Vaccine Immunology. In Plotkin’s Vaccines, 7th ed.; Plotkin, S.A., Orenstein, W.A., Offit, P.A., Edwards, K.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 16–34.e7. ISBN 978-0-323-35761-6. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, G.K.; Wørzner, K.; Andersen, P.; Christensen, D. Vaccine Adjuvants Differentially Affect Kinetics of Antibody and Germinal Center Responses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 579761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wørzner, K.; Hvannastein, J.; Schmidt, S.T.; Foged, C.; Rosenkrands, I.; Pedersen, G.K.; Christensen, D. Adsorption of Protein Antigen to the Cationic Liposome Adjuvant CAF®01 Is Required for Induction of Th1 and Th17 Responses but Not for Antibody Induction. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 165, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christensen, D. Head-to-Head Comparison of Novel Vaccine Technologies Comes with a Minefield of Challenges. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16010012
Christensen D. Head-to-Head Comparison of Novel Vaccine Technologies Comes with a Minefield of Challenges. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristensen, Dennis. 2024. "Head-to-Head Comparison of Novel Vaccine Technologies Comes with a Minefield of Challenges" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16010012
APA StyleChristensen, D. (2024). Head-to-Head Comparison of Novel Vaccine Technologies Comes with a Minefield of Challenges. Pharmaceutics, 16(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16010012






