Controlling the Solubility, Release Rate and Permeation of Riluzole with Cyclodextrins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
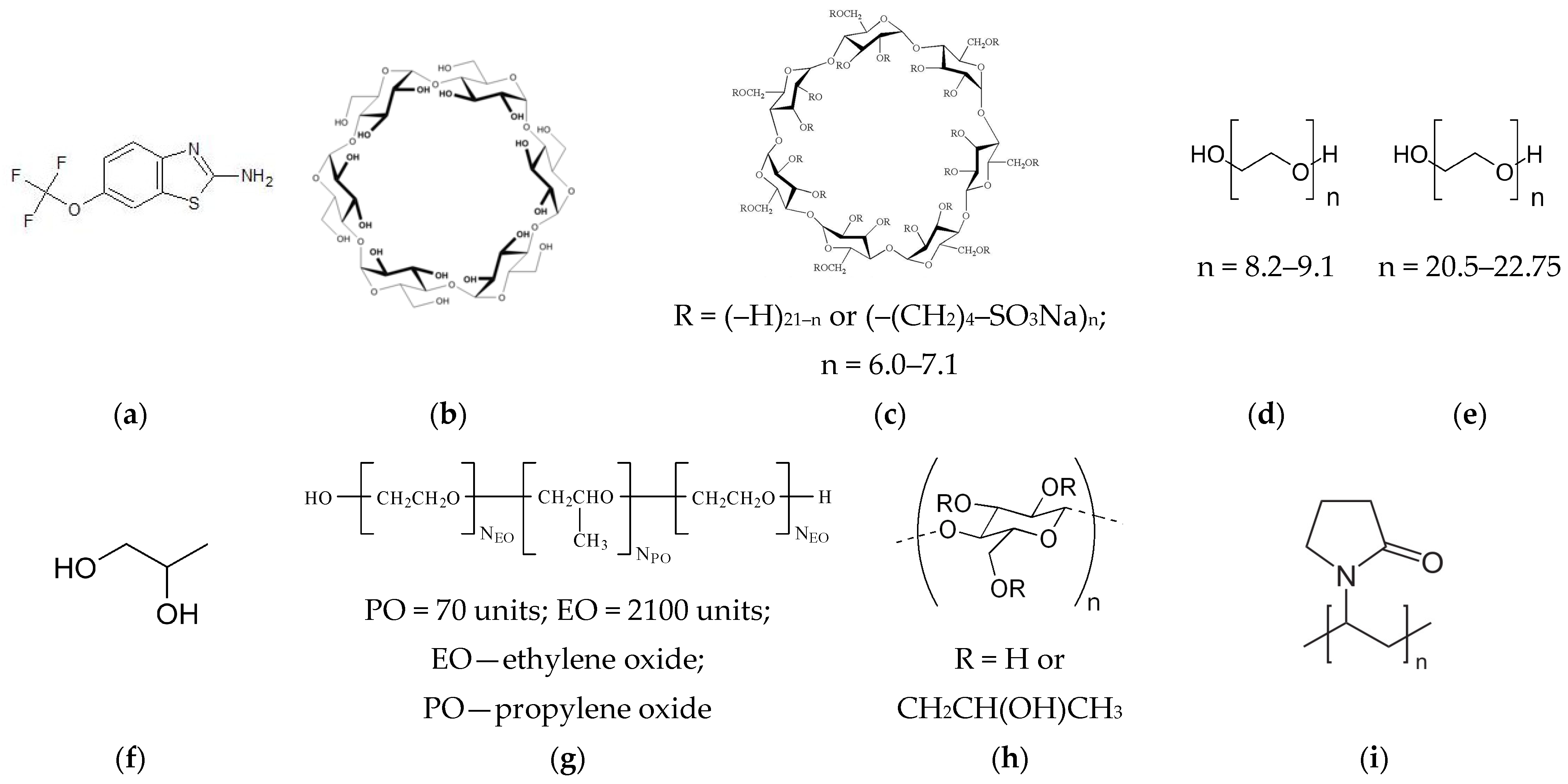
2.1. Materials
2.2. Determination of RLZ Equilibrium Solubility in CD Solutions
2.3. Estimation of RLZ/CD Stability Constant
2.4. Determinations of Thermodynamic Solubilization, Complexation and Solubility Parameters Using a Mole Fraction Scale
2.5. In Vitro Permeation Experiments under Static Conditions
2.6. Permeability Calculation Using a Quasi-Equilibrium Transport Model
2.7. Preparation of the Solid Samples by Mechanical Grinding Procedure
2.8. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.9. PXRD Analysis
2.10. Dissolution Experiments under Dynamic Conditions
2.11. Permeation Examinations under Dynamic Conditions
2.12. Dissolution/Permeation Quantitative Parameters Calculations
2.13. HPLC Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Solubility of RLZ in Cyclodextrin Solutions, Thermodynamic Considerations
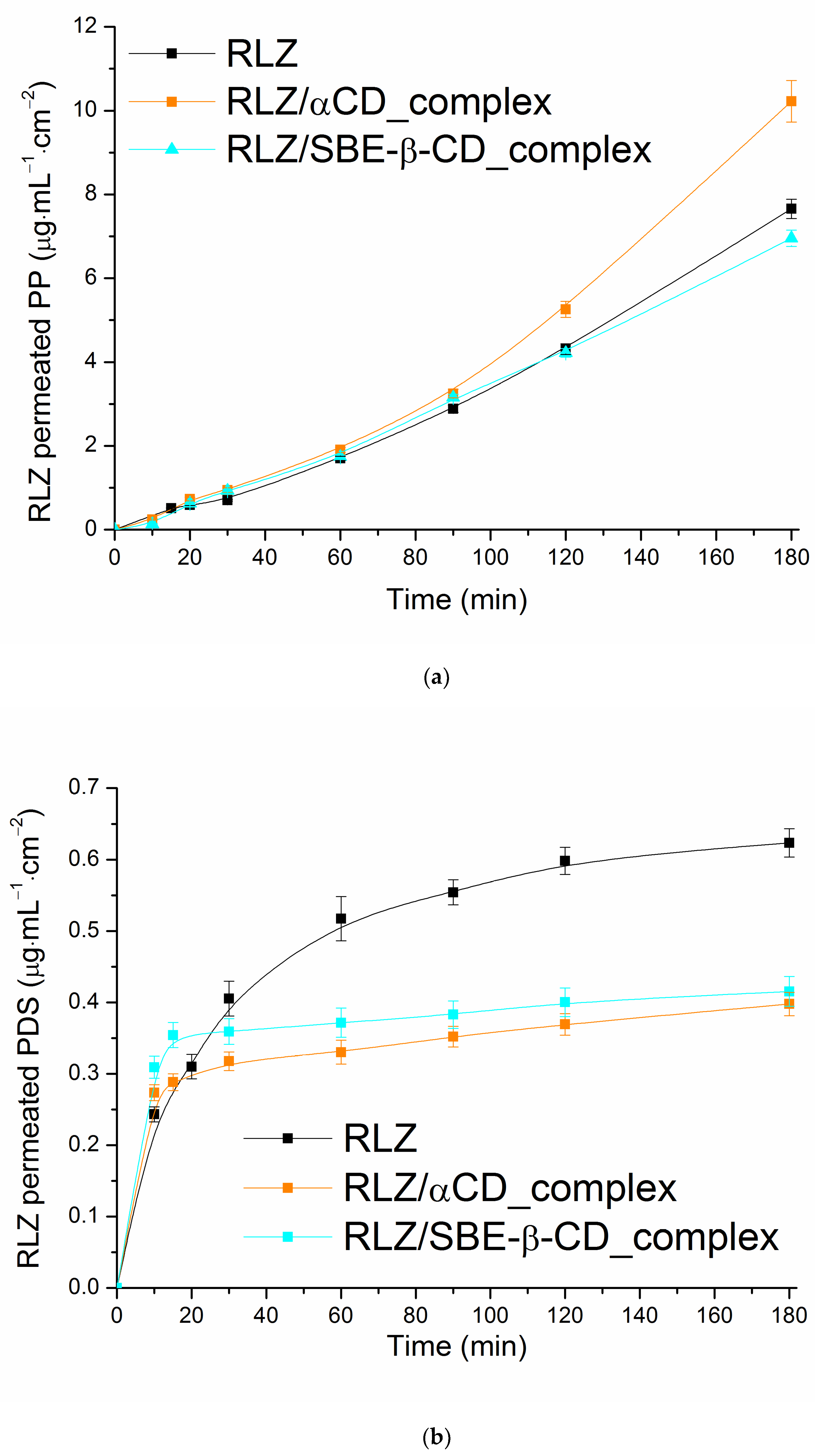
3.2. Permeability of RLZ in Static Conditions
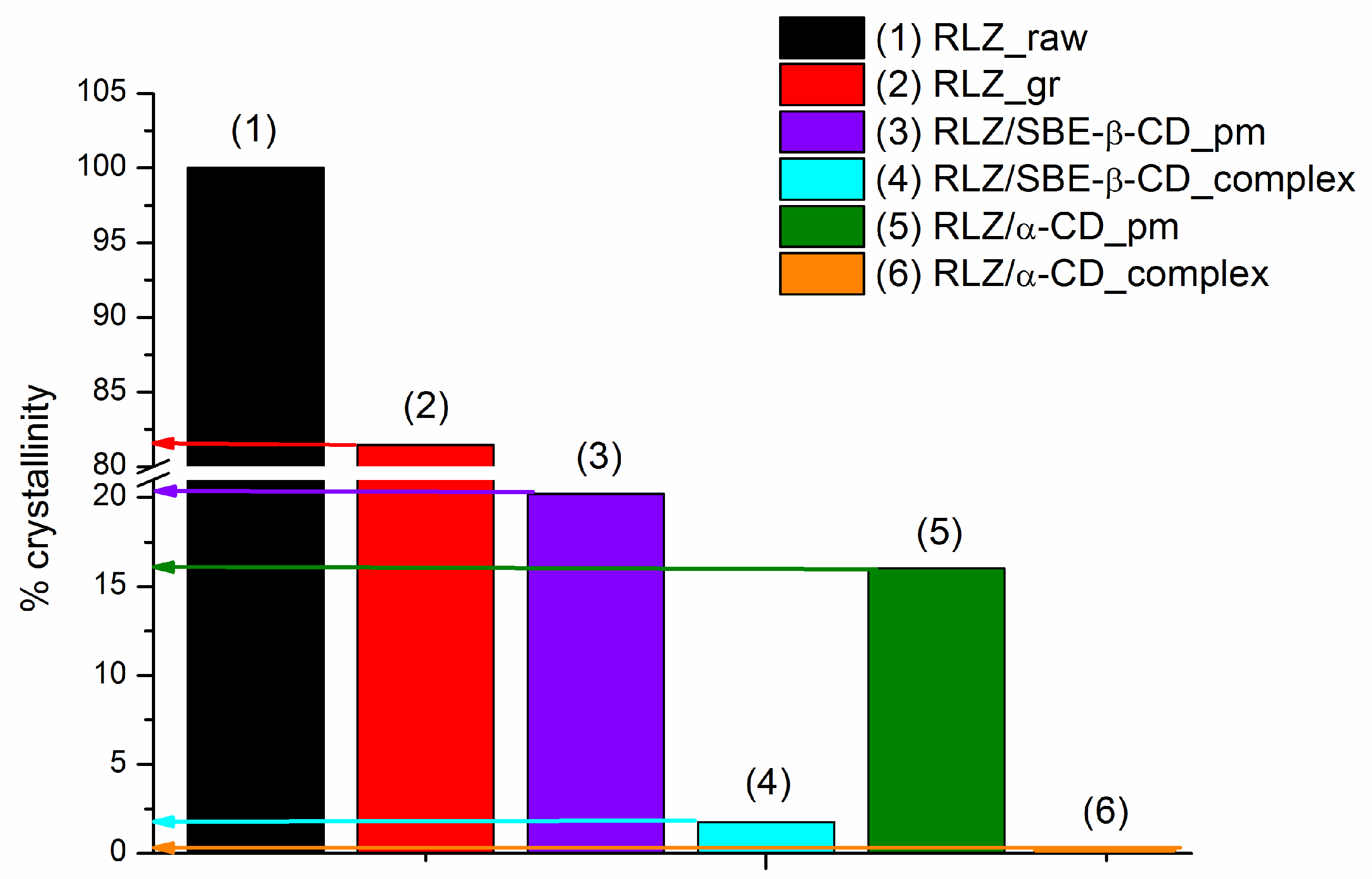
3.3. Preparation and Characterization of RLZ Solid Samples
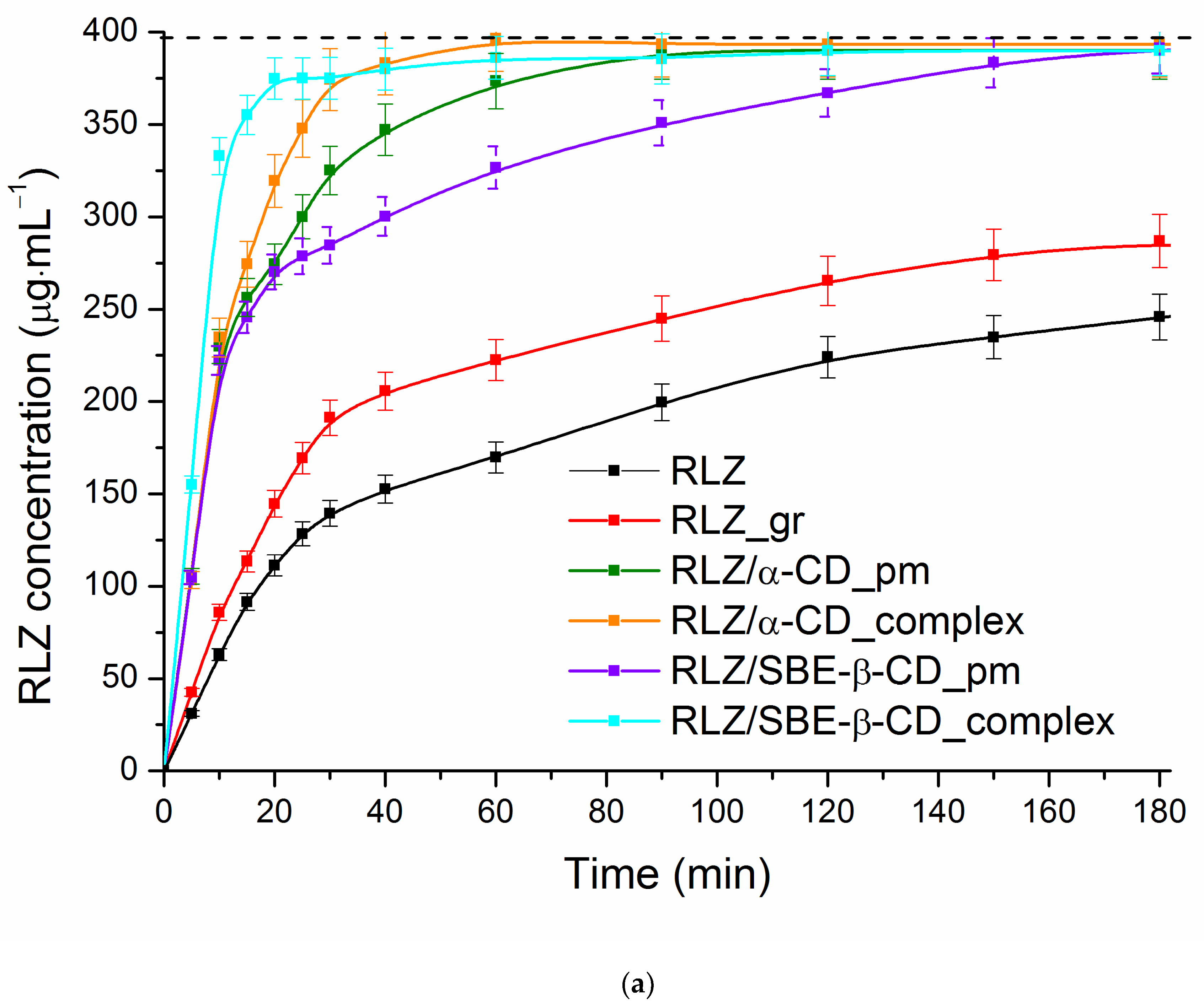
3.4. Dynamic Dissolution/Permeation Behavior of RLZ and Its Solid Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doble, A. The pharmacology and mechanism of action of riluzole. Neurology 1996, 47, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blyufer, A.; Lhamo, S.; Tam, C.; Tariq, I.; Thavornwatanayong, T.; Mahajan, S.S. Riluzole: A neuroprotective drug with potential as a novel anti-cancer agent (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zona, C.; Siniscalchi, A.; Mercuri, N.B.; Bernardi, G. Riluzole interacts with voltage-activated sodium and potassium currents in cultured rat cortical neurons. Neuroscience 1998, 85, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prickett, T.D.; Samuels, Y. Molecular pathways: Dysregulated glutamatergic signaling pathways in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4240–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, G.M. Riluzole oral suspension in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A guide to its use. Drugs Ther. Perspect. 2016, 32, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegemann, S.; Gosch, M.; Breitkreutz, J. Swallowing dysfunction and dysphagia is an unrecognized challenge for oral drug therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 430, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, A.M.; Smith, A. Riluzole 5 mg/ml oral suspension: For optimized drug delivery in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 11, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Product Monograph: Mylan-Riluzole Riluzole Tablets, USP 50 mg; Mylan Pharmaceuticals ULC, Control No.: 147961. Date of Preparation: 25 July 2012; Apotex Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2012.
- Product Monograph: PrAPO-Riluzole, Riluzole Tablets, USP Riluzole 50 mg; Submission Control No.: 127733, 154914. Date of Revision: 9 July 2012; Apotex Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2012.
- Williams, R.O., III; Watts, A.B.; Miller, D.A. Formulating Poorly Water Soluble Drugs; AAPS Press; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Khalipha, A.B.R.; Azad, M.A.K.; Hossain, S.; Haque, S. Methods of solubility and dissolution enhancement for poorly water soluble drugs: A Review. WJPPS 2014, 3, 107–130. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.K.; Joshi, A.; Singh, R.; Jana, S.; Dubey, K. An investigation into solubility and dissolution improvement of alectinib hydrochloride as a third-generation amorphous solid dispersion. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 81, 104259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.D.; Lee, P.I. Probing the mechanisms of drug release from amorphous solid dispersions in medium-soluble and medium-insoluble carriers. J. Control. Release 2015, 211, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huwaimel, B.; Alharby, T.N. Development of computational intelligence models for assessment of drug nanonization using green chemistry technique: Improvement of drug solubility. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 45, 103005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, F.; Esposito, T.; Mencherini, T.; Del Prete, F.; Cannoniere, A.L.; Aquino, R.P. Exploring microencapsulation potential: Multicomponent spray dried delivery systems for improvement of Chlorella vulgaris extract preservation and solubility. Powder Technol. 2023, 429, 118882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondoghdi, P.A.; Khorsandi, M.; Shekaari, H.; Mokhtarpour, M. Solubility improvement of indomethacin by novel biodegradable eutectic solvents based on protic ionic liquid monoethanolamine carboxylate/ethylene glycol. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 86, 104564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, D.; Yuan, H.; Li, C.; Yu, D.; Wang, G.; Li, S. Tertiary/quaternary amine derivatives of sophorolipid for baicalin solubility and antioxidating performance improvement: Solubilization or hydrotropy? J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 397, 124122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Lim, S.-J.; Choi, H.-G.; Lee, M.-K. Solid lipid nanoparticles as drug delivery system for water-insoluble drugs. J. Pharm. Investig. 2010, 40, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chadha, R.; Saini, A.; Arora, P.; Bhandari, S. Pharmaceutical cocrystals: A novel approach for oral bioavailability enhancement of drugs. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2012, 29, 183–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Hreinsdottir, D.; Masson, M. Evaluation of cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 302, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domańska, U.; Pelczarska, A.; Pobudkowska, A. Effect of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on solubility of sparingly soluble drug derivatives of anthranilic acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 2383–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puskás, I.; Varga, E.; Tuza, K.; Szemán, J.; Fenyvesi, É.; Sohajda, T.; Szente, L. Sulfobutylether cyclodextrins: Structure, degree of substitution and functional performance. In Cyclodextrins; Ramirez, F.G., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-63482-788-1. [Google Scholar]
- Green, A.R.; Guillory, J.K. Heptakis(2,6-di-O-methyl)-β-cyclodextrin complexation with the antitumor agent chlorambucil. J. Pharm. Sci. 1989, 78, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavone, C.; Bonagura, A.C.; Fiorentino, S.; Cimmaruta, D.; Cenami, R.; Torella, M.; Fossati, T.; Rossi, F. Efficacy and safety profile of diclofenac/cyclodextrin and progesterone/cyclodextrin formulations: A review of the literature data. Drugs R&D 2016, 16, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykaç, A.; Martos-Maldonado, M.C.; Casas-Solvas, J.M.; García-Fuentes, L.; Vargas-Berenguel, A. Binding ability properties of β-cyclodextrin dimers linked through their secondary faces towards cancer chemotherapeutic agent methotrexate. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E.; Brewster, M.E. Cyclodextrin-based pharmaceutics: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajewski, R.A.; Stella, V.J. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins, II: In vivo drug delivery. J Pharm Sci. 1996, 85, 1142Y1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdary, K.P.R.; Srinivas, S.V. Influence of hydrophilic polymers on celecoxib complexation with hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2006, 7, E184–E189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.M.; Dahan, A. Predicting the solubility–permeability interplay when using cyclodextrins insolubility-enabling formulations: Model validation. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 430, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins: Effects on drug permeation through biological membranes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 1119–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Cagno, M.P.; Stein, P.C. Studying the effect of solubilizing agents on drug diffusion through the unstirred water layer (UWL) by localized spectroscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 139, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkova, T.; Simonova, O.; Perlovich, G. Mechanistic insight in permeability through different membranes in the presence of pharmaceutical excipients: A case of model hydrophobic carbamazepine. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A. Construction of supramolecular structures from cyclodextrins and polymers. Carbohydr. Polym. 1997, 34, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, J.B.; Christensen, S.B.; Bauer-Brandl, A.; Brandl, M. Dissolution/permeation of albendazole in the presence of cyclodextrin and bile salts: A mechanistic in-vitro study into factors governing oral bioavailability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, T.; Simonova, O.; Perlovich, G. Modulation of distribution and diffusion through the lipophilic membrane with cyclodextrins exemplified by a model pyridinecarboxamide derivative. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, S.; Tang, P.; Li, H. The influence of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on the solubility, dissolution, cytotoxicity, and binding of riluzole with human serumalbumin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 117, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, S.; Tang, P.; Yan, J.; Xu, K.; Li, H. Characterization and evaluation of synthetic riluzole with β-cyclodextrin and 2,6-di-O-methyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 129, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, M.E.; Vandecruys, R.; Verreck, G.; Peeters, J. Supersaturating drug delivery systems: Effect of hydrophilic cyclodextrins and other excipients on the formation and stabilization of supersaturated drug solutions. Pharmazie 2008, 63, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, V.J.; Rajewski, R.A. Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 583, 119396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajewski, R.A.; Traiger, G.; Bresnahan, J.; Jaberaboansar, P.; Stella, V.J.; Thompson, D.O. Preliminary safety evaluation of parenterally administered sulfoalkylether β-cyclodextrin derivatives. J. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 84, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Campos, J.; Veiga, F.; Cardoso, C.; Paiva-Santos, A.C. Cyclodextrin-based delivery systems in parenteral formulations: A critical update review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 178, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhorov, D.A.; Kutyshenko, V.P.; Tarahovsky, Y.S.; Kukushkin, N.I.; Khrenov, M.O.; Kovtun, A.L.; Zakharova, N.M. Solid xenon carrier based on α-cyclodextrin: Properties, preparation, and application. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelb, R.I.; Schwartz, L.M. Complexation of carboxylic acids and anions by alpha and beta cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 1989, 7, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Connors, K. Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 1965, 4, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Avdeef, A.; Fuguet, E.; Llinàs, A.; Ràfols, C.; Bosch, E.; Völgyi, G.; Verbić, T.; Boldyreva, E.; Takács-Novák, K. Equilibrium solubility measurement of ionizable drugs-consensus recommendations for improving data quality. ADMET DMPK 2016, 4, 117–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, A.; Miller, J.M.; Dahan, A. The interaction of nifedipine with selected cyclodextrins and the subsequent solubility–permeability trade-off. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, P.; Maestrelli, F.; Cirri, M.; Furlanetto, S.; Pinzauti, S. Differential scanning calorimetry as an analytical tool in the study of drug-cyclodextrin interactions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2003, 73, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Su, C.; Hageman, M.; Hussain, M.; Haskell, R.; Stefanski, K.; Qian, F. Drug–polymer–water interaction and its implication for the dissolution performance of amorphous solid dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cugovčan, M.; Jablan, J.; Lovrić, J.; Cinčić, D.; Galić, N.; Jug, M. Biopharmaceutical characterization of praziquantel cocrystals and cyclodextrin complexes prepared by grinding. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 137, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.W.; Flanner, H.H. Mathematical comparison of dissolution profiles. Pharm. Technol. 1996, 20, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewster, M.E.; Loftsson, T. Complexation—Use of cyclodextrins to improve pharmaceutical properties of intramuscular formulations. In Injectable Drug Development. Techniques to Reduce pain and Irritation; Gupta, P.K., Brazeau, G.A., Eds.; Interpharm Press: Denver, CO, USA, 1999; pp. 307–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Másson, M.; Brewster, M.E. Self-association of cyclodextrins and cyclodextrin complexes. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrier, R.L.; Miller, L.A.; Ahmed, I. The utility of cyclodextrins for enhancing oral bioavailability. J. Control. Release 2007, 123, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.H.; Bashir, M.; Asghar, S.; Mallhi, T.H.; Khan, I.U. Effect of cyclodextrin derivatization on solubility and efficacy of drugs. In Colloid Science in Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology; Karakuş, S., Ed.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2019; pp. 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, V.; Rajewski, R.A.; Stella, V.J. Effect of cyclodextrin charge on complexation of neutral and charged substrates: Comparison of (SBE)7M-β-CD to HP-β-CD. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, V.; Rajewski, R.A.; Stella, V.J. Thermodynamics of binding of neutral molecules to sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrins (SBE-β-CD): The effect of total degree of substitution. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlovich, G.L.; Skara, M.; Bauer-Brandl, A. Driving forces and the influence of the buffer composition on the complexation reaction between ibuprofen and HPβ-CD. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 20, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, T.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Comparative analysis of solubilization and complexation characteristics for new antifungal compound with cyclodextrins. Impact of cyclodextrins on distribution process. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 154, 105531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkova, T.V.; Simonova, O.R.; Perlovich, G.L. Thiazolidine-2,4-dione derivative in 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin solutions: Complexation/solubilization, distribution and permeability. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 333, 115931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbah, C.J.; Onyekaba, T.C.; Uwakwe, A.O. Prediction of dermal permeability coefficient of nevirapine—Effect of cosolvents, anionic, nonionic and cationic surfactants. Pharm. Pharm. 2016, 7, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carrer, V.; Alonso, C.; Pont, M.; Zanuy, M.; Córdoba, M.; Espinosa, S.; Barba, C.; Oliver, M.A.; Martí, M.; Coderch, L. Effect of propylene glycol on the skin penetration of drugs. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 312, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, A.; Miller, J.; Hoffman, A.; Amidon, G. The solubility-permeability interplay in using cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers: Mechanistic modeling and application to progesterone. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Másson, M.; Loftsson, T.; Másson, G.; Stefánsson, E. Cyclodextrins as permeation enhancers: Some theoretical evaluations and in vitro testing. J. Control. Release 1999, 59, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Fri∂riksdóttir, H.; Gu∂mundsdóttir, T.K. The effect of water-soluble polymers on aqueous solubility of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 127, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, A.; Miller, J.M.; Dahan, A. Accounting for the solubility–permeability interplay in oral formulation development for poor water solubility drugs: The effect of PEG-400 on carbamazepine absorption. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, A.; Miller, J.M. The solubility–permeability interplay and its implications in formulation design and development for poorly soluble drugs. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, B.T.; Joyce, D.C.; Bhandari, B.R. Encapsulation of ethylene gas into alphacyclodextrin and characterisation of the inclusion complexes. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, L.; Loftsson, T.; Ferreira, D.; Veiga, F. Investigation and physicochemical characterization of vinpocetine-sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrin binary and ternary complexes. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Lai, Y.; He, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Chang, S.; Gu, Z. Supramolecular nanoparticles generated by the self-assembly of polyrotaxanes for antitumor drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5249–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.M.; Howes, T.; Bhandari, B.R. Characterization of crystalline and spray-dried amorphous α-cyclodextrin powders. Powder Technol. 2015, 284, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, P.; Langguth, P.; Kataoka, M.; Yamashita, S. IVIVC in oral absorption for fenofibrate immediate release tablets using a dissolution/permeation system. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, M.; Sugano, K.; Da Costa Mathews, C.; Wong, J.W.; Jones, K.L.; Masaoka, Y.; Yamashita, S. Application of dissolution/permeation system for evaluation of formulation effect on oral absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs in drug development. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, S.T.; Frank, K.J.; Fricker, G.; Brandl, M. Biopharmaceutical classification of poorly soluble drugs with respect to ‘‘enabling formulations’’. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, F.; Uekama, K. Cyclodextrin-based controlled drug release system. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 1999, 36, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, S.C. Companion animal physiology and dosage form performance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1383–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.H.S.; Patnala, S.; Löbenberg, R.; Kanfer, I. In vitro dissolution of generic immediate-release solid oral dosage forms containing BCS Class I drugs: Comparative assessment of metronidazole, zidovudine, and amoxicillin versus relevant comparator pharmaceutical products in South Africa and India. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014, 15, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Manuel, J.; Lobo, S. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profile. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.A.; Carrier, R.L.; Ahmed, I. Practical considerations in development of solid dosage forms that contain cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 1691–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, V.M.; Haslam, J.L.; Stella, V.J. Controlled and complete release of a model poorly watersoluble drug, prednisolone, from hydroxypropyl methylcellulose matrix tablets using (SBE)7m-β-cyclodextrin as a solubilizing agent. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaitanya Mannava, M.K.; Garai, A.; Nangia, A.K. Diffusion and flux improvement of drugs through complexation. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 2293–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berben, P.; Bauer-Brandl, A.; Brandl, M.; Faller, B.; Flaten, G.E.; Jacobsen, A.-C.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P. Drug permeability profiling using cell-free permeation tools: Overview and applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 119, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkova, T.V.; Simonova, O.R.; Perlovich, G.L. Impact of pH and membrane nature on distribution and permeability processes of nortriptyline hydrochloride. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 394, 123766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.Y.; Bala, S.; Škalko-Basnet, N.; di Cagno, M.P. Interpreting nonlinear drug diffusion data: Utilizing Korsmeyer-Peppas model to study drug release from liposomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 138, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missner, A.; Pohl, P. 110 years of the Meyer–Overton rule: Predicting membrane permeability of gases and other small compounds. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2009, 10, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, W. Permeability across lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 2254–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, M.M.; Raigorodskii, I.M.; Iordanskii, A.L.; Hadgraft, J. Modeling of percutaneous drug transport in vitro using skin-imitating Carbosil membrane. J. Control. Release 1998, 52, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| T (K) | RLZ Solubility (S2∙103 M) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBE-β-CD Concentration (CSBE-β-CD∙103 M) | |||||
| pH 6.8 | |||||
| 0 | 6.89 | 13.78 | 20.67 | 27.56 | |
| 298.15 | 1.71 | 6.32 | 10.86 | 15.27 | 19.92 |
| 303.15 | 1.98 | 6.77 | 11.47 | 16.09 | 21.01 |
| 310.15 | 2.31 | 7.19 | 12.09 | 17.06 | 22.02 |
| 313.15 | 2.47 | 7.56 | 12.87 | 17.54 | 22.80 |
| pH 4.0 | |||||
| 310.15 | 6.85 | 17.16 | 28.17 | 42.13 | 52.47 |
| pH 2.0 (final pH 2.7) | |||||
| 310.15 | 24.20 | 16.70 | 24.26 pH | 31.99 | 40.16 |
| α-CD concentration (Cα-CD∙103 M) | |||||
| 0 | 10.00 | 20.00 | 30.00 | 40.00 | |
| pH 6.8 | |||||
| 310.15 | 2.31 | 4.55 | 6.32 | 8.26 | 10.26 |
| pH 4.0 | |||||
| 310.15 | 6.85 | 10.61 | 14.26 | 18.00 | 22.28 |
| pH 2.0 (final pH 2.7) | |||||
| 310.15 | 24.20 | 29.34 | 32.28 | 33.94 | 34.72 |
| T (K) | 298.15 | 303.15 | 310.15 | 313.15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 6.8 | ||||
| RLZ/SBE-β-CD | 1116.0 ± 7.6 | 1110.6 ± 10.4 | 1103.6 ± 2.2 | 1100.9 ± 19.1 |
| RLZ/α-CD | - | - | 102.3 ± 2.1 | - |
| pH 4.0 | ||||
| RLZ/α-CD | - | - | 92.3 ± 2.5 | - |
| Solubility in Buffer pH 6.8 1 | |||
| (kJ·mol−1) | (kJ·mol−1) | (kJ·mol−1) | |
| 3.07∙10−5 | 25.8 ± 0.5 | 19.1 ± 0.7 | −6.7 ± 0.4 |
| Dissolution in 4% SBE-β-CD (pH 6.8) 2 | |||
| (kJ·mol−1) | (kJ·mol−1) | (kJ·mol−1) | |
| 3.60∙10−4 | 19.7 ± 0.4 | 7.0 ± 0.5 | −12.6 ± 1.2 |
| Solubilization in 4% SBE-β-CD (pH 6.8) 3 | |||
| (kJ·mol−1) | (kJ·mol−1) | (kJ·mol−1) | |
| 11.74 | −6.1 ± 0.1 | −12.1 ± 0.6 | −5.9 ± 0.4 |
| Complexation4 | |||
| (kJ·mol−1) | (kJ·mol−1) | (kJ·mol−1) | |
| 55,954.9 | −27.1 ± 0.5 | −1.2 ± 0.1 | 25.9 ± 2.7 |
| System | S2∙103 (M) | Papp∙106 (cm∙s−1) | ∙106 (cm∙s−1) | S2∙103 (M) | Papp∙106 (cm∙s−1) | ∙106 (cm∙s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-CD | SBE-β-CD | |||||
| Buffer | 2.31 | 11.96 ± 0.17 | - | 2.31 | 11.96 ± 0.17 | - |
| CD (0.01 M) | 4.55 | 8.86 ± 0.13 | 6.07 | 9.44 | 3.62 ± 0.08 | 2.93 |
| CD (0.02 M) | 6.32 | 7.96 ± 0.17 | 4.37 | 16.39 | 3.19 ± 0.13 | 1.69 |
| CD (0.03 M) | 8.26 | 7.34 ± 0.15 | 3.44 | 23.59 | n.d. 1 | 1.17 |
| CD (0.01 M)/PEG400 | 7.65 | 9.02 ± 0.26 | 3.61 | 10.59 | 2.56 ± 0.04 | 2.61 |
| CD (0.01 M)/PEG1000 | 6.12 | 8.63 ± 0.08 | 4.51 | 10.78 | 1.87 ± 0.06 | 2.56 |
| CD (0.01 M)/PG | 10.26 | 8.38 ± 0.14 | 2.69 | 10.09 | 2.84 ± 0.04 | 2.74 |
| CD (0.01 M)/F127 | 4.50 | 4.32 ± 0.09 | 6.14 | 9.94 | 2.88 ± 0.14 | 2.78 |
| CD (0.01 M)/PVP | 4.18 | 7.64 ± 0.10 | 6.61 | 9.44 | 3.77 ± 0.11 | 2.93 |
| CD (0.01 M)/HPMC | 4.17 | 8.84 ± 0.24 | 6.63 | 9.64 | 3.79 ± 0.05 | 2.87 |
| System | Q15 (%) | a DE60 (%) | b DE60 ratio | AUC (mg·min−1) | c DPP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RLZ_raw | 22.9 | 30.0 | - | 33.1 | 46.2 |
| RLZ_gr | 28.3 | 39.9 | 1.3 | 40.9 | 57.0 |
| RLZ/α-CD_pm | 64.1 | 72.1 | 2.4 | 63.8 | 89.0 |
| RLZ/α-CD_complex | 68.6 | 79.2 | 2.6 | 66.2 | 92.3 |
| RLZ/SBE-β-CD_pm | 61.4 | 64.9 | 2.2 | 59.3 | 82.7 |
| RLZ/SBE-β-CD_complex | 88.8 | 85.1 | 2.8 | 66.9 | 93.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volkova, T.; Simonova, O.; Perlovich, G. Controlling the Solubility, Release Rate and Permeation of Riluzole with Cyclodextrins. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060757
Volkova T, Simonova O, Perlovich G. Controlling the Solubility, Release Rate and Permeation of Riluzole with Cyclodextrins. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(6):757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060757
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolkova, Tatyana, Olga Simonova, and German Perlovich. 2024. "Controlling the Solubility, Release Rate and Permeation of Riluzole with Cyclodextrins" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 6: 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060757
APA StyleVolkova, T., Simonova, O., & Perlovich, G. (2024). Controlling the Solubility, Release Rate and Permeation of Riluzole with Cyclodextrins. Pharmaceutics, 16(6), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060757









