Expanded Nanofibrous Polymeric Mats Incorporating Tetracycline-Loaded Silica Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
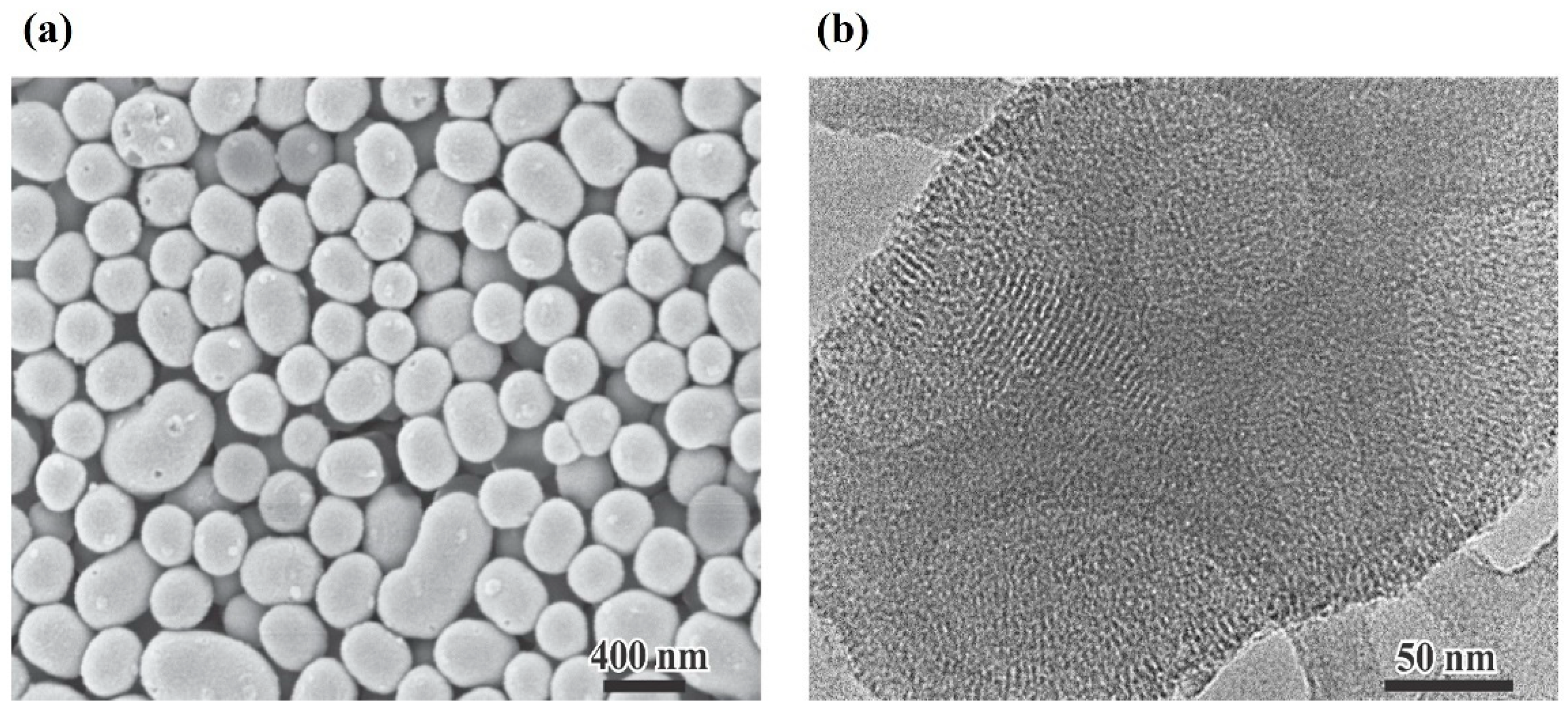
2.2.1. Synthesis of MSN
2.2.2. PVA Electrospinning
2.2.3. Characterization
Dynamic Light Scattering and Surface Z-Potential
Electronic Microscopy
Textural Properties
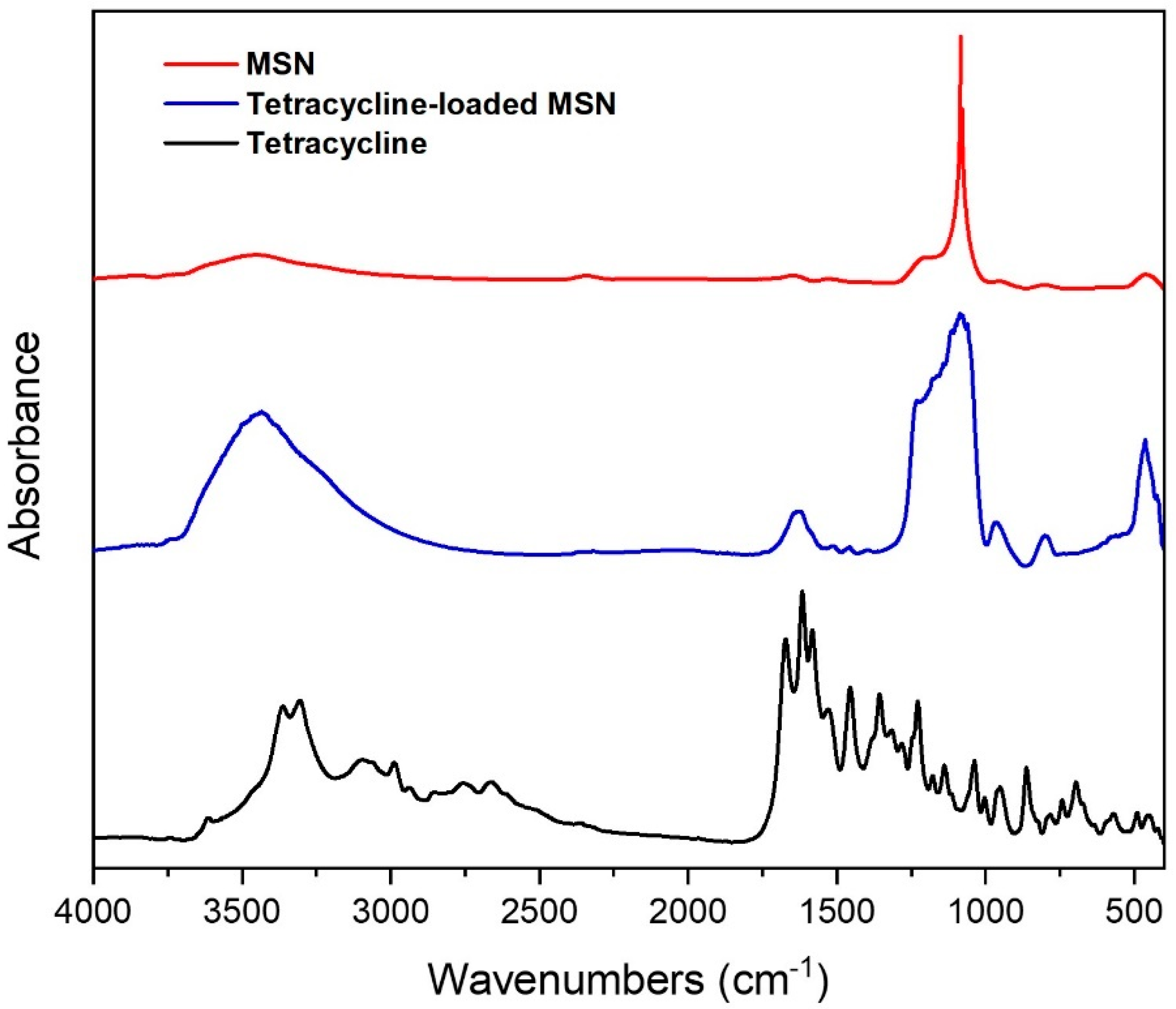
FTIR Spectroscopy
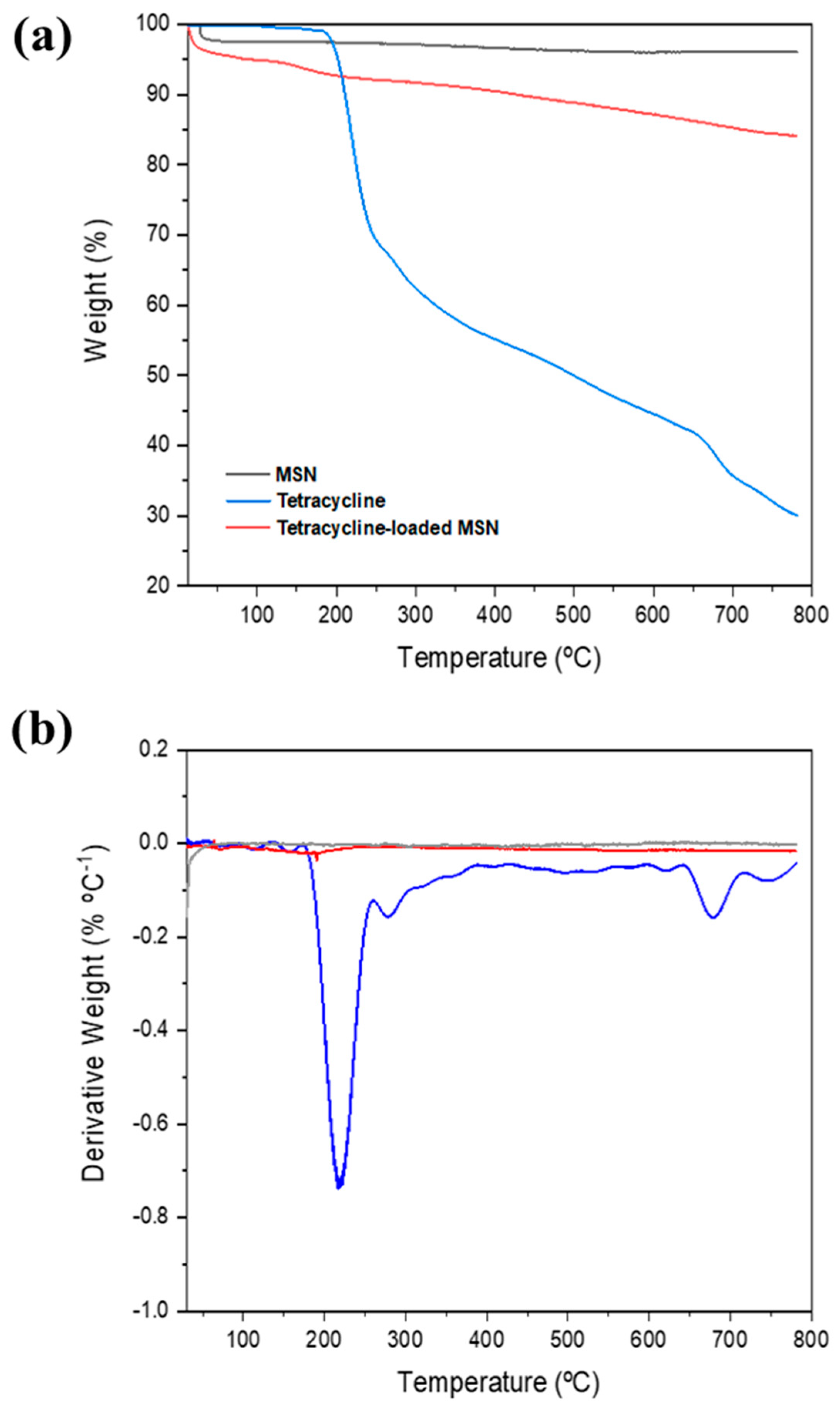
Thermal Analysis
Mechanical Analysis
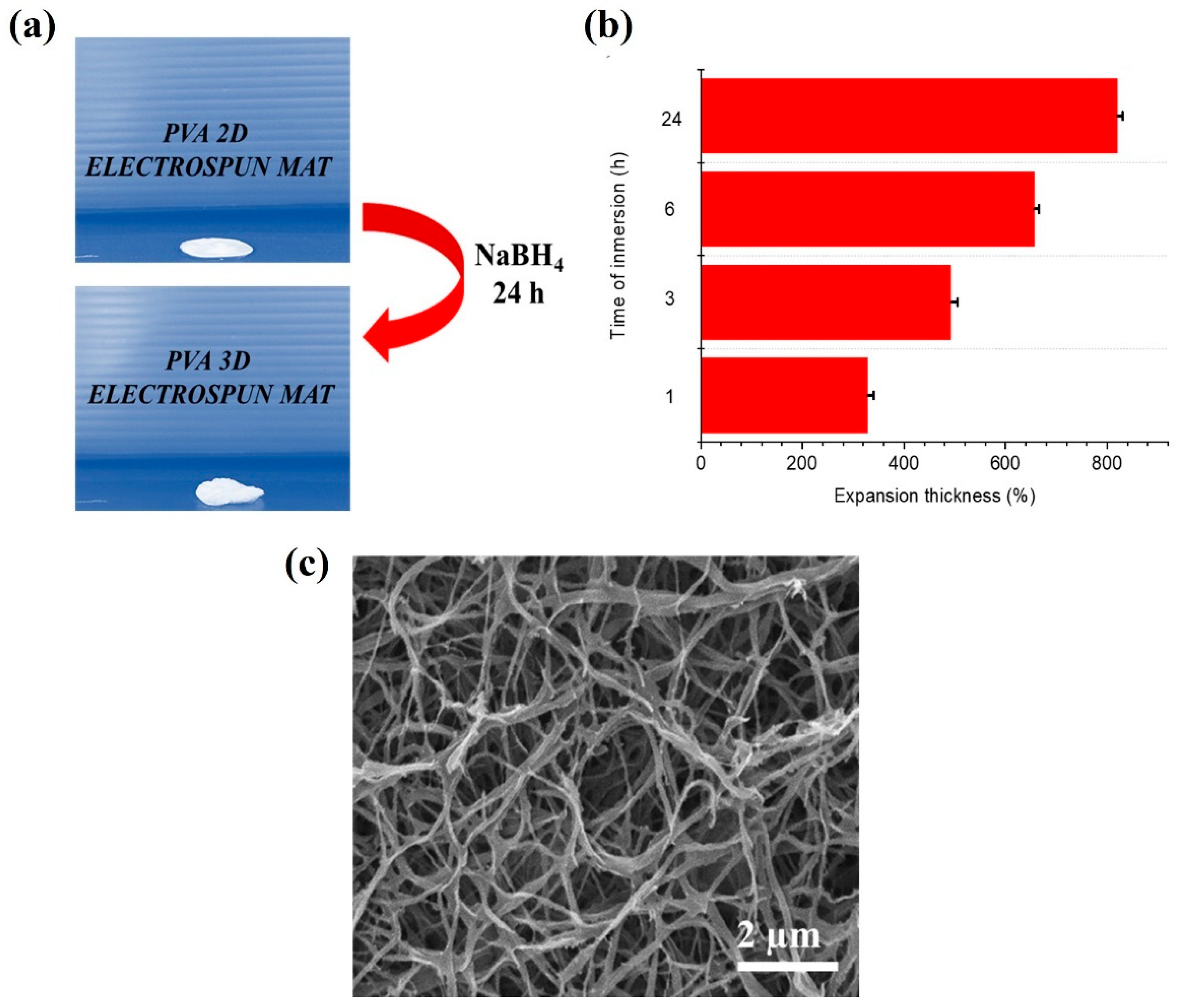
Gas-Foaming Procedure
Tetracycline Loading into MSN
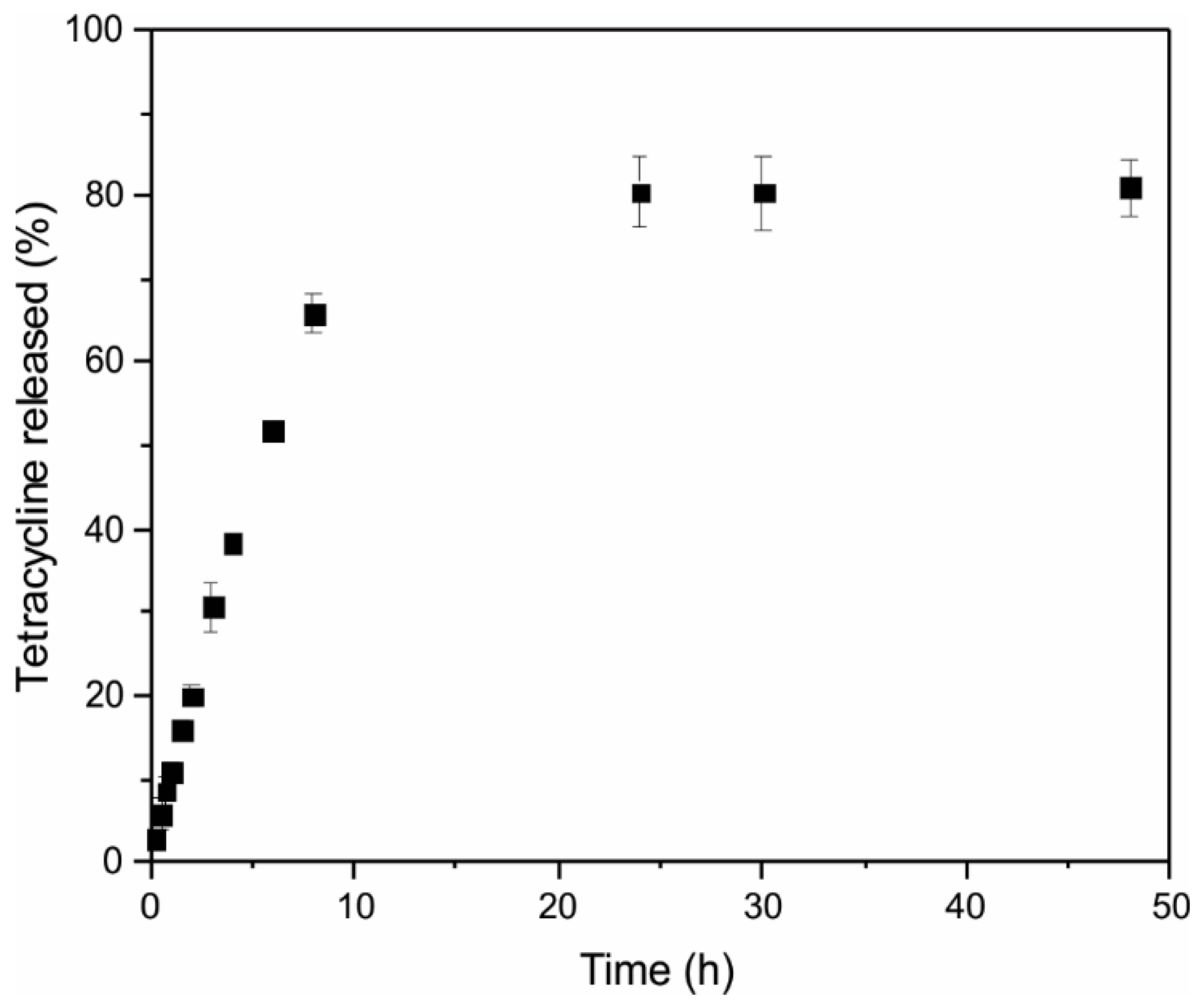
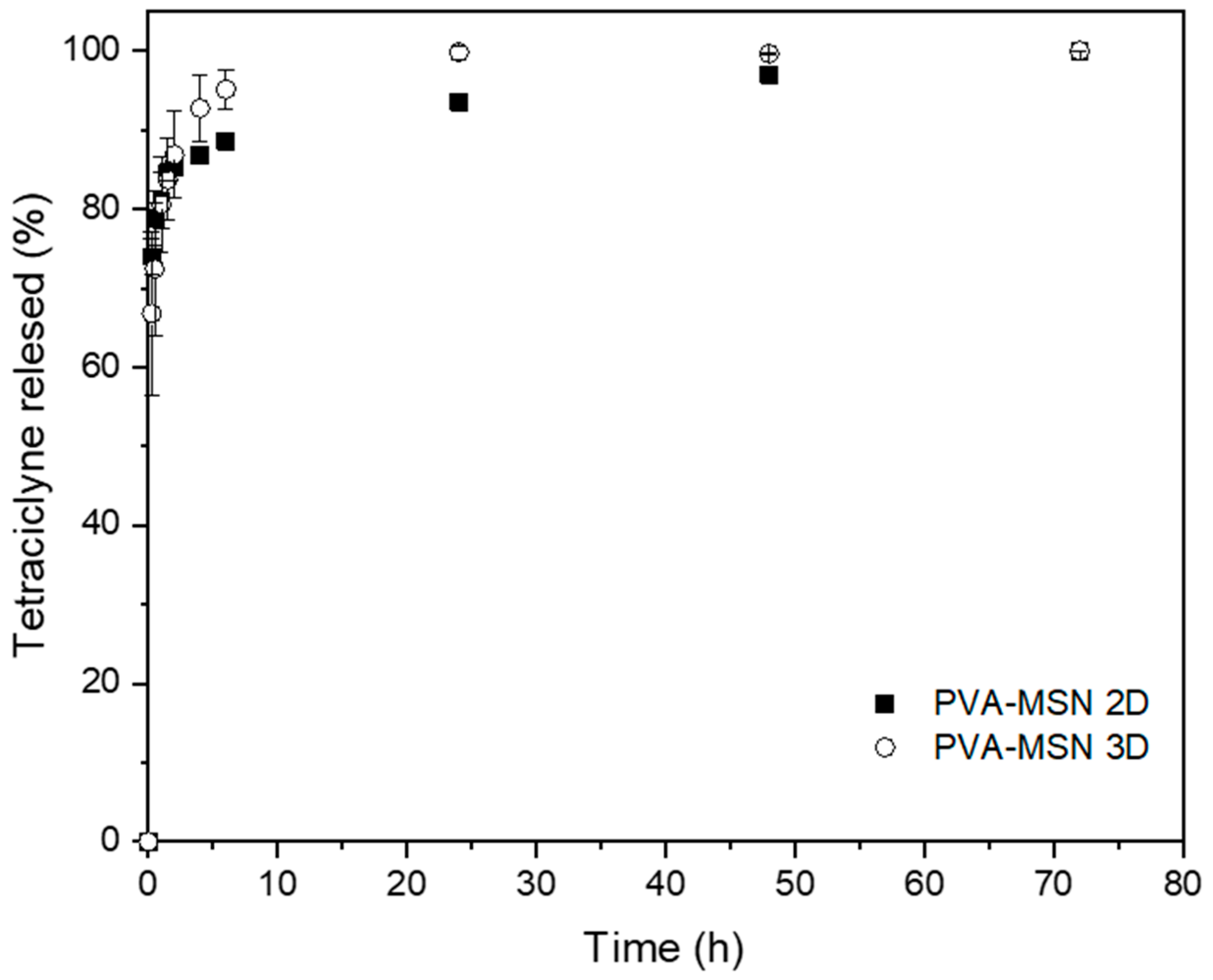
Tetracycline Release Assay
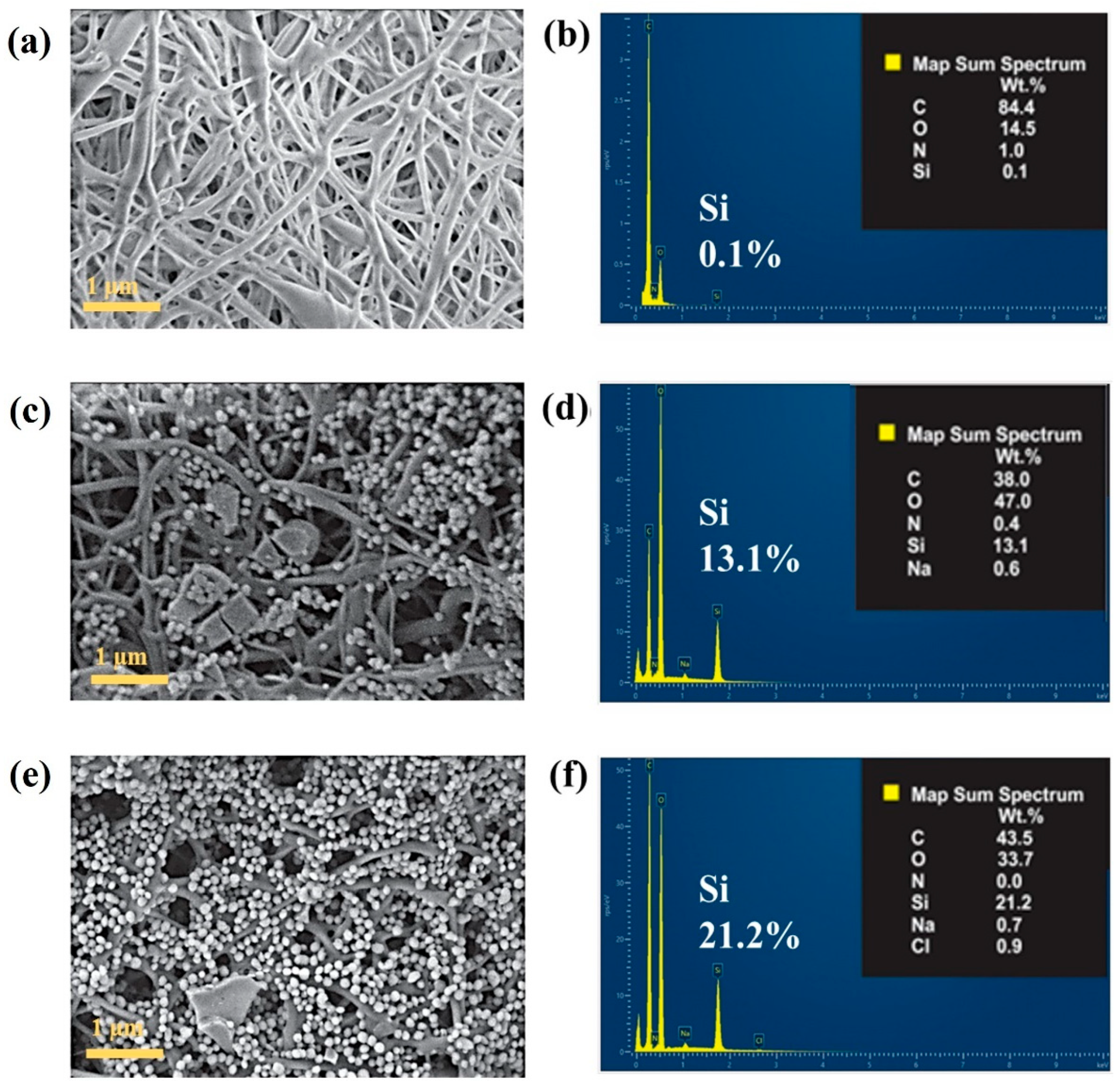
MSN Infiltration into PVA Mats
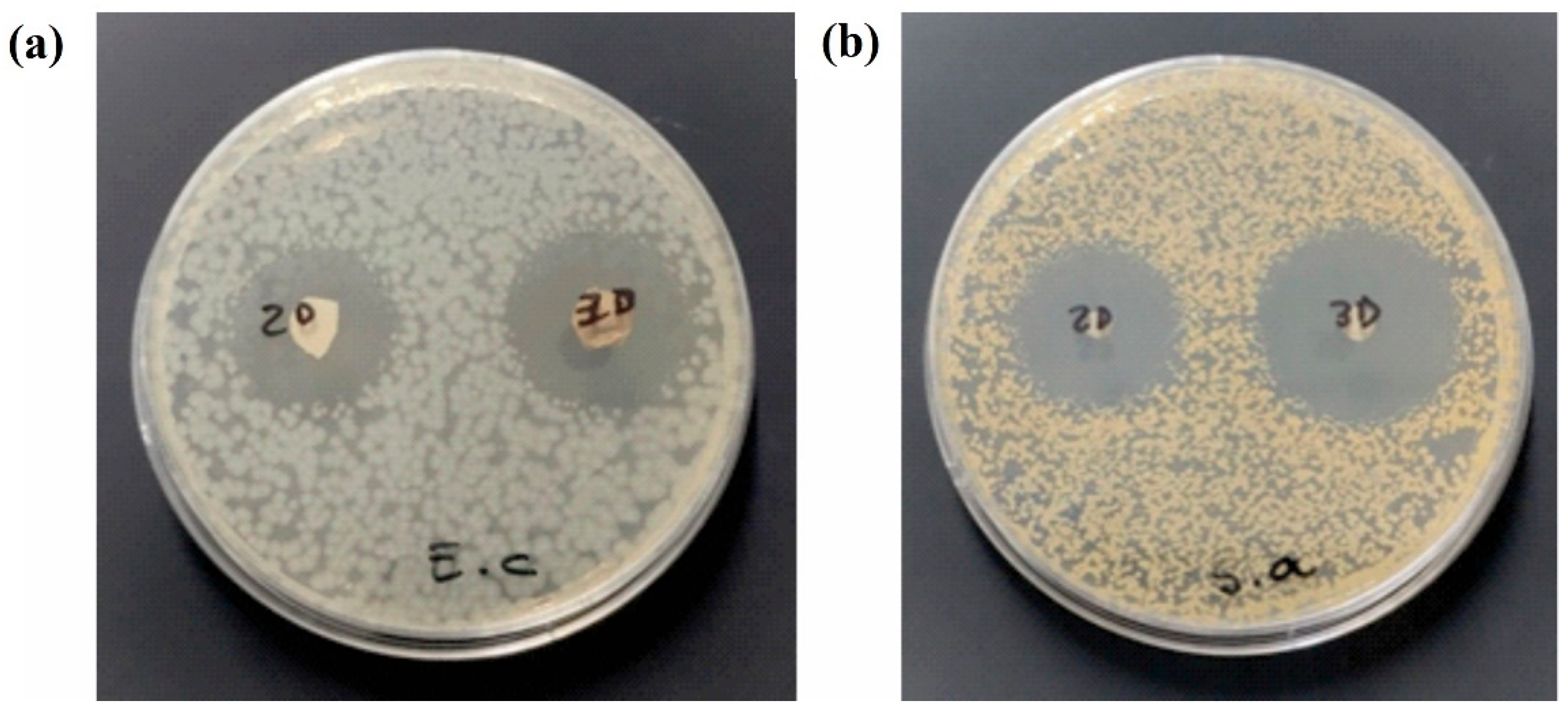
Antimicrobial Studies
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliveira, C.; Sousa, D.; Teixeira, J.A.; Ferreira-Santos, P.; Botelho, C.M. Polymeric biomaterials for wound healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1136077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luneva, O.; Olekhnovich, R.; Uspenskaya, M. Bilayer hydrogels for wound dressing and tissue engineering. Polymers 2022, 14, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, M.P. Wound Dressing Materials: Bridging Material Science and Clinical Practice. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talikowska, M.; Fu, X.; Lisak, G. Application of conducting polymers to wound care and skin tissue engineering: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 135, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, G.; Song, K.; Chen, A.; Xing, H.; Wu, J.; Sun, Q.; Li, G.; Cai, M. PLGA-based electrospun nanofibers loaded with dual bioactive agent loaded scaffold as a potential wound dressing material. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 231, 113570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Ni, N.; Huang, Y.; Lin, C. An advanced review: Polyurethane-related dressings for skin wound repair. Polymers 2023, 15, 4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikfarjam, S.; Aldubaisi, Y.; Swami, V.; Swami, V.; Xu, G.; Vaughan, M.B.; Wolf, R.F.; Khandaker, M. Polycaprolactone electrospun nanofiber membrane with skin graft containing collagen and bandage containing MgO nanoparticles for wound healing applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Sigen, A.; Gao, Y.; Guo, L.; Creagh-Flynn, J.; Zhou, D.; Greiser, U.; Dong, Y.; Wang, F.; Tai, H. A hybrid injectable hydrogel from hyperbranched PEG macromer as a stem cell delivery and retention platform for diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2018, 75, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froelich, A.; Jakubowska, E.; Wojtyłko, M.; Jadach, B.; Gackowski, M.; Gadziński, P.; Napierała, O.; Ravliv, Y.; Osmałek, T. Alginate-based materials loaded with nanoparticles in wound healing. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, C.S.; Graça, M.F.; Moreira, A.F.; de Melo-Diogo, D.; Correia, I.J. Chitin-and chitosan-based strategies in wound healing. In Natural Polymers in Wound Healing and Repair; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 333–380. [Google Scholar]
- Rajkumar, D.S.R.; Keerthika, K.; Vijayaragavan, V. Chitosan-based biomaterial in wound healing: A review. Cureus 2024, 16, e55193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew-Steiner, S.S.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K. Collagen in wound healing. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Wang, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhao, D. Gelatin-based biomaterials and gelatin as an additive for chronic wound repair. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1398939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Li, M.; Xu, A.; Zhuo, F. Recent applications and molecular mechanisms of hyaluronic acid in skin aging and wound healing. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2024, 23, 100320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Manna, S.; Roy, S.; Nandi, S.K.; Basak, P. Polymeric biomaterials-based tissue engineering for wound healing: A systemic review. Burn. Trauma 2023, 11, tkac058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, S.; Dattilo, M.; Patitucci, F.; Pezzi, G.; Parisi, O.I.; Puoci, F. Natural and synthetic polymeric biomaterials for application in wound management. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalva, S.N.; Augustine, R.; Al Mamun, A.; Dalvi, Y.B.; Vijay, N.; Hasan, A. Active agents loaded extracellular matrix mimetic electrospun membranes for wound healing applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinavel, S.; Korrapati, P.S.; Kalaiselvi, P.; Dharmalingam, S. Mesoporous silica incorporated PCL/Curcumin nanofiber for wound healing application. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 167, 106021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirouz, A.; Chung, M.; Kwon, J.; Fortunato, G.; Radacsi, N. 2D and 3D electrospinning technologies for the fabrication of nanofibrous scaffolds for skin tissue engineering: A review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Chen, F.; Wu, P.; Sun, G. Recent advances in bioengineered scaffolds for cutaneous wound healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 841583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jia, Z.; Shafiq, M.; Xie, X.; Xiao, X.; Castro, R.; Rodrigues, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, G.; Mo, X. Gas foaming of electrospun poly (L-lactide-co-caprolactone)/silk fibroin nanofiber scaffolds to promote cellular infiltration and tissue regeneration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 201, 111637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhang, E.; Huang, Y.; Tian, F.; Xue, J. 3D-printed electrospun fibres for wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2024, 32, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Ballarin, F.M.; Abraham, G.A. Combination of electrospinning with other techniques for the fabrication of 3D polymeric and composite nanofibrous scaffolds with improved cellular interactions. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 172002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradifar, F.; Sepahdoost, N.; Tavakoli, P.; Mirzapoor, A. Multi-functional dressings for recovery and screenable treatment of wounds: A review. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, M.M.; Heidari, R.; Keshavarzi, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Abedi, M.; Ranjbar, S.; Ghasemi, Y. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of electrospun PVA nanofiber containing ZnO/Curcumin for wound healing application. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2025, 197, 194–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinavel, S.; Indrakumar, J.; Korrapati, P.S.; Dharmalingam, S. Synthesis and fabrication of amine functionalized SBA-15 incorporated PVA/Curcumin nanofiber for skin wound healing application. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 637, 128185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, A.A.; Mohammed, R.S.; Hussein, Y.; Ali, A.S.; Khalil, A.A. Development of Lepidium sativum extracts/PVA electrospun nanofibers as wound healing dressing. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 20683–20695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Alizadeh, P.; Soltani, M. Wound healing performance of electrospun PVA/70S30C bioactive glass/Ag nanoparticles mats decorated with curcumin: In vitro and in vivo investigations. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 153, 213530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Li, S.; Shi, R.; Liu, H. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.; Gomte, S.S.; Prathyusha, E.; Agrawal, M.; Alexander, A. Biomedical applications of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery carrier. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, D.; Xia, D.; Liang, C.; Li, N.; Xu, R. Synergistic effect of co-delivering ciprofloxacin and tetracycline hydrochloride for promoted wound healing by utilizing coaxial PCL/gelatin nanofiber membrane. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Neumann, A.; Bremer, I.; Su, Y.; Dräger, G.; Kasper, C.; Behrens, P. Nanoporous silica nanoparticles as biomaterials: Evaluation of different strategies for the functionalization with polysialic acid by step-by-step cytocompatibility testing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Blachman, A.; Llarena, I.; Calabrese, G.; Moya, S.E.; Abraham, G.A. Gas-foamed poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers facilitate fibroblast infiltration. Mater. Lett. 2025, 389, 138356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M07-A9; Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically. Approved Standard—Ninth Edition. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012; Volume 32.
- Nairi, V.; Medda, S.; Piludu, M.; Casula, M.F.; Vallet-Regì, M.; Monduzzi, M.; Salis, A. Interactions between bovine serum albumin and mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with biopolymers. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, H.; Amiri, S.; Amiri, F.; Moradi, S.; Zarrintaj, P. Antibacterial biocomposite based on chitosan/pluronic/agarose noncovalent hydrogel: Controlled drug delivery by alginate/tetracycline beads system. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, R.; Assadollahi, V.; Manesh, M.H.S.; Mirzaei, S.A.; Elahian, F. Recent advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles formulations and drug delivery for wound healing. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 665, 124654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Carlson, M.A.; Teusink, M.J.; Wang, H.; MacEwan, M.R.; Xie, J. Expanding two-dimensional electrospun nanofiber membranes in the third dimension by a modified gas-foaming technique. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renkler, N.Z.; Babar, Z.U.D.; Barra, M.; Cruz-Maya, I.; De Santis, R.; Girolamo, R.d.; Marelli, M.; Ferretti, A.M.; Zaheer, A.; Iannotti, V. Optimizing Electrospun PVA Fibers with MXene Integration for Biomedical Applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2025, 310, 2400433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, S.; Moon, H.; Park, Y.; Jung, Y.M.; Koo, J.M.; Oh, D.X.; Hwang, D.S. Mechanical properties and thermal stability of intermolecular-fitted poly (vinyl alcohol)/α-chitin nanofibrous mat. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 244, 116476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabur, A.R.; Abdulmajeed, M.H.; Abd, S.Y. Effect of Cu nanoparticles addition on improving the electrical conductivity and mechanical properties of PVA electrospun polymeric film. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Beirut, Lebanon, 1–3 February 2018; p. 030016. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrasa, M.; Asadollahi, M.A.; Nasri-Nasrabadi, B.; Ghaedi, K.; Salehi, H.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Arpanaei, A. Incorporation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles into random electrospun PLGA and PLGA/gelatin nanofibrous scaffolds enhances mechanical and cell proliferation properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 66, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneru, B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chavala, S.H.; Miller, M.L.; Holbert, B.; Conson, M.; Ni, A.; Di Pasqua, A. Tetracycline-containing MCM-41 mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the treatment of Escherichia coli. Molecules 2015, 20, 19690–19698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, E.; Ruggeri, M.; Vigani, B.; Fila, C.T.; Cornaglia, A.I.; Boselli, C.; Viseras, C.; Rossi, S.; Sandri, G. Gas foamed scaffolds as smart 3D structures in skin tissue engineering. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkoğlu, G.C.; Khomarloo, N.; Mohsenzadeh, E.; Gospodinova, D.N.; Neznakomova, M.; Salaün, F. PVA-based electrospun materials—A promising route to designing nanofiber mats with desired morphological shape—A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Property | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| BET-specific surface area | m2 g−1 | 1143 |
| Micropore-specific surface area | m2 g−1 a | 0 |
| Mesopore-specific surface area | m2 g−1 | 1143 |
| Total pore volume | cm3 g−1 | 0.699 |
| Micropore volume | cm3 g−1 | 0 |
| Mesopore volume | cm3 g−1 a | 0.699 |
| Average mesopore diameter | nm | 2.87 |
| Material | E (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVA-2D | 93.11 ± 5.34 a | 12.70 ± 3.40 a | 6.10 ± 1.80 a |
| PVA-MSN 2D | 107.74 ± 5.54 b | 20.40 ± 3.0 b | 9.03 ± 1.12 b |
| PVA-MSN 3D | 34.11 ± 5.66 c | 3.95 ± 0.33 c | 1.98 ± 0.60 c |
| Material | E. coli | S. aureus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition Halos (mm) | MIC (cm2/mL) | MBC (cm2/mL) | Inhibition Halos (mm) | MIC (cm2/mL) | MBC (cm2/mL) | |
| 2D mat | 26. 7 ± 2.5 | 2.89 | 5.77 | 25.0 ± 1.0 | 0.72 | 1.45 |
| 3D mat | 27. 7 ± 2.1 | 1.26 | 2.52 | 29. 3 ± 2.2 | 0.31 | 0.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fookes, F.; Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Martucci, J.F.; Estenoz, D.; Abraham, G.A.; Busatto, C.A. Expanded Nanofibrous Polymeric Mats Incorporating Tetracycline-Loaded Silica Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101335
Fookes F, Bongiovanni Abel S, Martucci JF, Estenoz D, Abraham GA, Busatto CA. Expanded Nanofibrous Polymeric Mats Incorporating Tetracycline-Loaded Silica Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101335
Chicago/Turabian StyleFookes, Federico, Silvestre Bongiovanni Abel, Josefa F. Martucci, Diana Estenoz, Gustavo A. Abraham, and Carlos A. Busatto. 2025. "Expanded Nanofibrous Polymeric Mats Incorporating Tetracycline-Loaded Silica Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101335
APA StyleFookes, F., Bongiovanni Abel, S., Martucci, J. F., Estenoz, D., Abraham, G. A., & Busatto, C. A. (2025). Expanded Nanofibrous Polymeric Mats Incorporating Tetracycline-Loaded Silica Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101335









