Cluster Headache and Hypoxia: Breathing New Life into an Old Theory, with Novel Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Kudrow’s Carotid Body Theory
3. Hypoxia Signaling Cascade
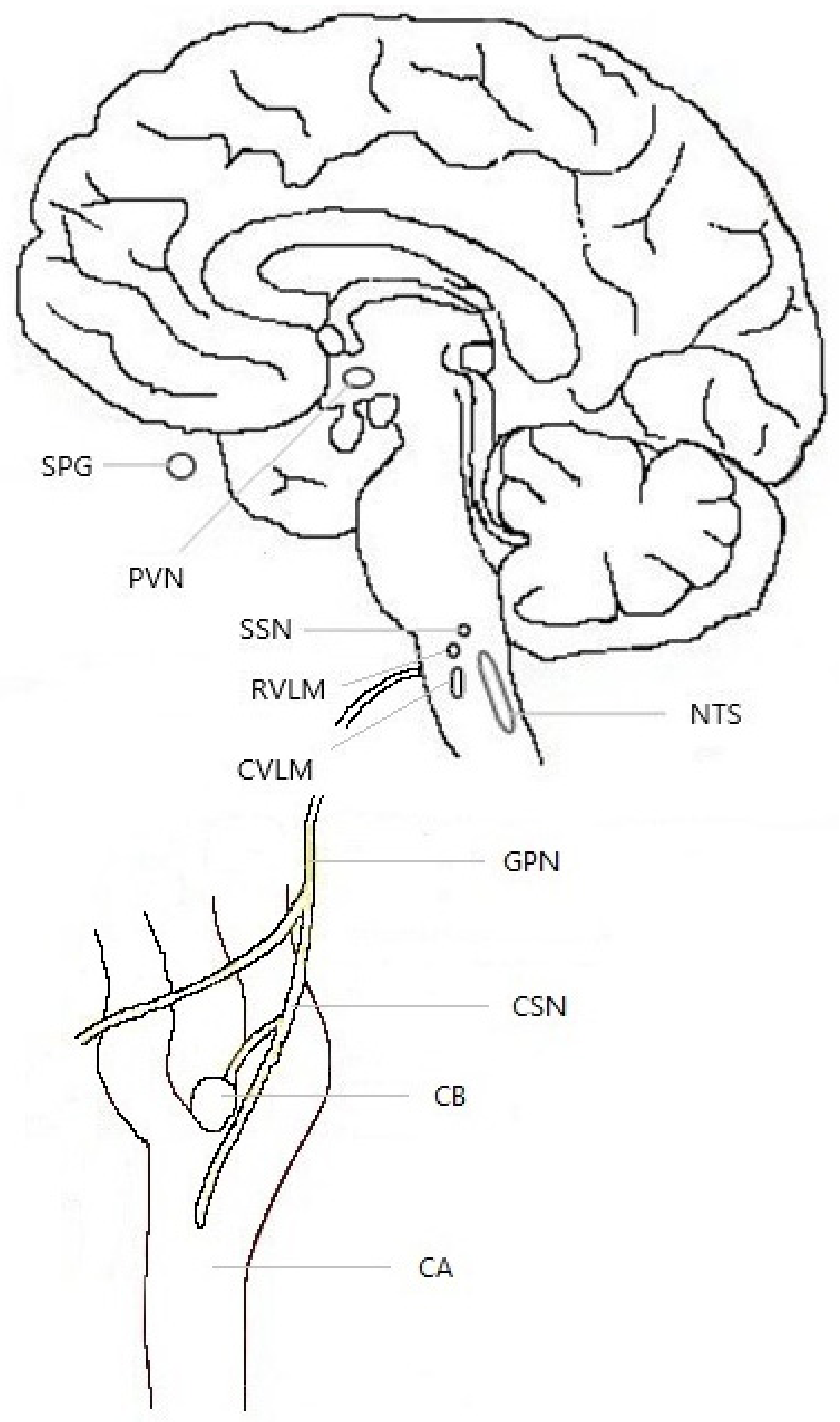
3.1. Anatomy
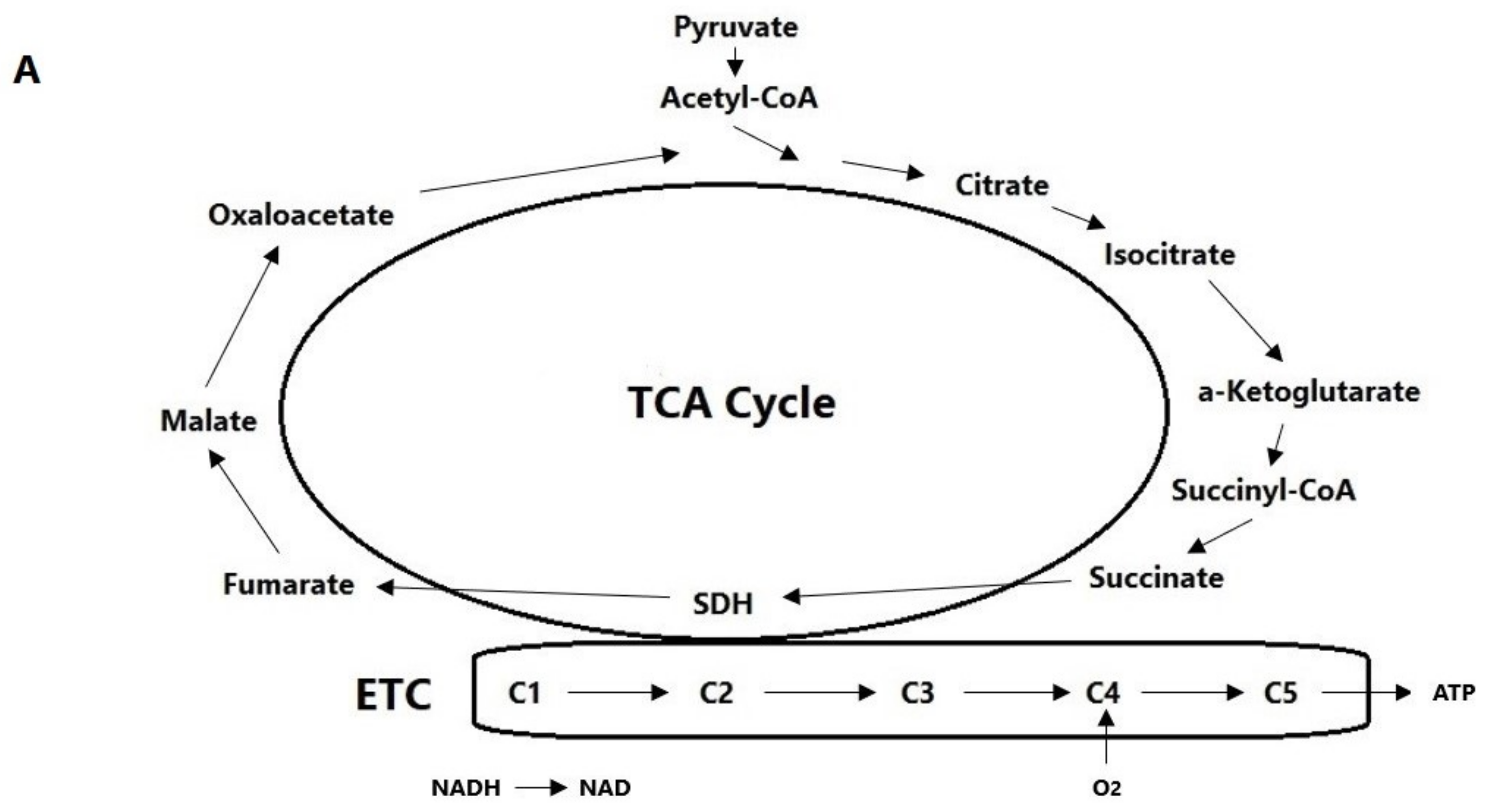
3.2. Mechanisms of Detection
3.3. Sensitization
4. Cluster Headache and Hypoxia: Neuroanatomy, Neurochemistry, and GWAS Genetic Studies
4.1. Neuroanatomical Overlap
4.2. Cluster Headache Genetics
4.3. Neurochemistry: Neurotransmitters and Neuropeptides
5. Cluster Headache and Hypoxia: Clinical Features
5.1. Behavioral Manifestations
5.2. Relationship to Cigarette Smoking
5.3. Triggers—Alcohol and Nitroglycerin
5.4. Circadian Patterning of Cluster Headache Attacks
5.5. Circannual Patterning of Cluster Bouts
5.6. Autonomic Features
5.7. Male–Female Ratio
5.8. Dietary Changes and Food Cravings
5.9. Comorbid Hypertension
6. Cluster Headache and Hypoxia: Current Pharmacology
6.1. Preventive Treatments
6.2. Acute Treatments
7. Limitations and Directions for Future Basic Research
8. Translational Research
8.1. Pharmacological Treatments
8.2. Nutraceutical Treatments
8.3. Behavioral Treatments
9. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHS | American Headache Society |
| CB | Carotid body |
| CGRP | Calcitonin gene-related peptide |
| CH | Cluster headache |
| CVLM | Caudal ventrolateral medulla |
| CYP2E1 | Cytochrome P450-2E1 |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ETC | Electron transport chain |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| HIF | Hypoxia-inducible factor |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-kappa B |
| NTS | Nucleus tractus solitarius |
| PACAP38 | Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide-38 |
| PHD | Prolyl hydrolase domain enzyme |
| pO2 | Partial pressure of oxygen |
| PVN | Paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RVLM | Rostral ventrolateral medulla |
| SCN | Suprachiasmatic nucleus |
| SDH | Succinate dehydrogenase |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| TNC | Trigeminal nucleus caudalis |
| VIP | Vasoactive intestinal peptide |
References
- Fischera, M.; Marziniak, M.; Gralow, I.; Evers, S. The incidence and prevalence of cluster headache: A meta-analysis of population-based studies. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The international classification of headache disorders, 3rd ed. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Membrilla, J.A.; Roa, J.; Díaz-de-Terán, J. Preventive treatment of refractory chronic cluster headache: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, T.D.; Fishman, R.S. Cluster headache in the United States of America: Demographics, clinical characteristics, triggers, suicidality, and personal burden. Headache 2012, 52, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, E.A.D.; Burish, M.J. Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of cluster headache. BMJ 2022, 376, e059577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burish, M.J.; Pearson, S.M.; Shapiro, R.E.; Zhang, W.; Schor, L.I. Cluster headache is one of the most intensely painful human conditions: Results from the International Cluster Headache Questionnaire. Headache 2021, 61, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji Lee, M.; Cho, S.J.; Wook Park, J.; Kyung Chu, M.; Moon, H.S.; Chung, P.W.; Myun Chung, J.; Sohn, J.H.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, B.S.; et al. Increased suicidality in patients with cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.M.; Lyngberg, A.; Jensen, R.H. Burden of cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, N.L.T.; Petersen, A.S.; Fronczek, R.; Tfelt-Hansen, J.; Belin, A.C.; Meisingset, T.; Tronvik, E.; Steinberg, A.; Gaul, C.; Jensen, R.H. Current treatment options for cluster headache: Limitations and the unmet need for better and specific treatments—A consensus article. J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.Y.; Goadsby, P.J. Cluster headache pathophysiology—Insights from current and emerging treatments. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanciullacci, M.; Alessandri, M.; Figini, M.; Geppetti, P.; Michelacci, S. Increase in plasma calcitonin gene-related peptide from the extracerebral circulation during nitroglycerin-induced cluster headache attack. Pain 1995, 60, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Edvinsson, L. Human in vivo evidence for trigeminovascular activation in cluster headache. Neuropeptide changes and effects of acute attacks therapies. Brain 1994, 117, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolodi, M.; Del Bianco, E. Sensory neuropeptides (substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide) and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in human saliva: Their pattern in migraine and cluster headache. Cephalalgia 1990, 10, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollesen, A.L.H.; Snoer, A.; Beske, R.P.; Guo, S.; Hoffmann, J.; Jensen, R.H.; Ashina, M. Effect of infusion of calcitonin gene-related peptide on cluster headache attacks: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, M.S.; Starling, A.J.; Pringsheim, T.M.; Becker, W.J.; Schwedt, T.J. Treatment of cluster headache: The American Headache Society evidence-based guidelines. Headache 2016, 56, 1093–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.S.; Lund, N.; Messlinger, K.; Christensen, S.L.; Barloese, M.; Jørgensen, N.R.; Kogelman, L.; Jensen, R.H. Reduced plasma calcitonin gene-related peptide level identified in cluster headache: A prospective and controlled study. Cephalalgia 2024, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Dodick, D.W.; Leone, M.; Bardos, J.N.; Oakes, T.M.; Millen, B.A.; Zhou, C.; Dowsett, S.A.; Aurora, S.K.; Ahn, A.H.; et al. Trial of galcanezumab in prevention of episodic cluster headache. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.W.; Goadsby, P.J.; Lucas, C.; Jensen, R.; Bardos, J.N.; Martinez, J.M.; Zhou, C.; Aurora, S.K.; Yang, J.Y.; Conley, R.R.; et al. Phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled study of galcanezumab in patients with chronic cluster headache: Results from 3-month double-blind treatment. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.; Evers, S.; Goadsby, P.J.; Leone, M.; Manzoni, G.C.; Pascual, J.; Carvalho, V.; Romoli, M.; Aleksovska, K.; Pozo-Rosich, P.; et al. European Academy of Neurology guidelines on the treatment of cluster headache. Eur. J. Neurol. 2023, 30, 2955–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenen, J.; Jensen, R.H.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; Láinez, M.J.A.; Gaul, C.; Goodman, A.M.; Caparso, A.; May, A. Stimulation of the sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) for cluster headache treatment. Pathway CH-1: A randomized, sham-controlled study. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.; Bahra, A.; Büchel, C.; Frackowiak, R.S.J.; Goadsby, P.J. Hypothalamic activation in cluster headache attacks. Lancet 1998, 352, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkink, E.B.; Schmitz, N.; Schoonman, G.G.; van Vliet, J.A.; Haan, J.; van Buchem, M.A.; Ferrari, M.D.; Kruit, M.C. The anterior hypothalamus in cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, S.; Nigri, A.; Bruzzone, M.G.; Carrion, J.P.M.; Fedeli, D.; Demichelis, G.; Chiapparini, L.; Ciullo, G.; Gonzalez, A.A.; Cecchini, A.P.; et al. Involvement of the ipsilateral-to-the-pain anterior-superior hypothalamic subunit in chronic cluster headache. J. Headache Pain 2024, 25, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S. Neural circuits regulating visceral pain. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.N.; Cao, S.; Song, X.L.; Pei, B.; Jin, C.Y.; Fan, B.F.; Jiang, H.; Xia, M. Glutamatergic neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus participate in the regulation of visceral pain induced by pancreatic cancer in mice. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2024, 13, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, M.; Tessitore, A.; Orologio, I.; Battista, G.; Siciliano, M.; Tedeschi, G.; Russo, A. Cluster headache pathophysiology: What we have learned from advanced neuroimaging. Headache 2022, 62, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holle, D.; Obermann, M. Cluster headache and the hypothalamus: Causal relationship or epiphenomenon? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistolesi, A.; Buonvicino, D.; Muzzi, M.; Urru, M.; Chiarugi, A. Effects of cluster headache preventatives on mouse hypothalamic transcriptional homeostasis. Cephalalgia 2022, 42, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudrow, L. A possible role of the carotid body in the pathogenesis of cluster headache. Cephalalgia 1983, 3, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudrow, L. The pathogenesis of cluster headache. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 1994, 7, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, S.D. Topical review: Cluster headache and sleep-related breathing disorders. J. Orofac. Pain 2011, 25, 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Graff-Radford, S.B.; Teruel, A. Cluster headache and obstructive sleep apnea: Are they related disorders? Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2009, 13, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobre, M.; Filho, P.; Dominici, M. Cluster headache associated with sleep apnoea. Cephalalgia 2003, 23, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudrow, L.; McGinty, D.J.; Phillips, E.R.; Stevenson, M. Sleep apnea in cluster headache. Cephalalgia 1984, 4, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malissart, P.; Ducros, A.; Labauge, P.; De Champfleur, N.M.; Carra-Dalliere, C. Carotid paraganglioma mimicking a cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candeloro, E.; Canavero, I.; Maurelli, M.; Cavallini, A.; Ghiotto, N.; Vitali, P.; Micieli, G. Carotid dissection mimicking a new attack of cluster headache. J. Headache Pain 2013, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, C. Cluster-like headache revealing polycythemia vera: A case report. Case Rep. Neurol. 2020, 12, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mampreso, E.; Maggioni, F.; Viaro, F.; Disco, C.; Zanchin, G. Efficacy of oxygen inhalation in sumatriptan refractory “high altitude” cluster headache attacks. J. Headache Pain 2009, 10, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.L.; Waldenlind, E.; Marcus, C. Diminished nocturnal lipolysis in cluster headache: A sign of central sympathetic dysregulation? Neurology 2003, 61, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudrow, L.; Kudrow, D.B. Association of sustained oxyhemoglobin desaturation and onset of cluster headache attacks. Headache 1990, 30, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-M.; Sand, T.; Sjaastad, O. Cluster headache: Oxygen saturation and end-tidal CO2 during and without attack. Headache 1992, 32, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hannerz, J.; Jogestrand, T. Provocation of unilateral pain in cluster headache patients by breathing CO2. Headache 1995, 35, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannerz, J.; Jogestrand, T. Chronic cluster headache: Provocation with carbon dioxide breathing and nitroglycerin. Headache 1996, 36, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.M.; Schaanning, J. Cluster headache: Pulse rate changes evoked by hyperoxia and hypoxia. Headache 1994, 34, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.M.; Schaanning, J.; Sjaastad, O. Cluster headache: The effect of low oxygen saturation. Headache 1990, 30, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.M.; Schaanning, J.; White, L.; Kruszewski, P.; Bjaanes, E.; Sjaastad, O. Cluster headache: The ventilatory response to transient hypoxia with pure nitrogen. Headache 1993, 33, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushi, I.; Yokota, S.; Okada, Y. The role of the hypothalamus in modulation of respiration. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2019, 265, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Sáenz, P.; Moreno-Dominguez, A.; Gao, L.; López-Barneo, J. Molecular mechanisms of acute oxygen sensing by arterial chemoreceptor cells. Role of Hif2α. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 614893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.M.; Takakura, A.C.; Moreira, T.S. Acute hypoxia activates hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus-projecting catecholaminergic neurons in the C1 region. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 285, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruyle, B.C.; Lima-Silveira, L.; Martinez, D.; Cummings, K.J.; Heesch, C.M.; Kline, D.D.; Hasser, E.M. Paraventricular nucleus projections to the nucleus tractus solitarii are essential for full expression of hypoxia-induced peripheral chemoreflex responses. J. Physiol. 2023, 601, 4309–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Pharmacologic targeting of hypoxia-inducible factors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 59, 379–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkum, J.M. The tricarboxylic acid cycle as a central regulator of the rate of aging: Implications for metabolic interventions. Adv. Biol. 2023, 7, 2300095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Prange-Barczynska, M.; Fielding, J.W.; Zhang, M.; Burrell, A.L.; Lima, J.D.C.C.; Eckardt, L.; Argles, I.L.A.; Pugh, C.W.; Buckler, K.J.; et al. Marked and rapid effects of pharmacological HIF-2α antagonism on hypoxic ventilatory control. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2237–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akman, M.; Belisario, D.C.; Salaroglio, I.C.; Kopecka, J.; Donadelli, M.; De Smaele, E.; Riganti, C. Hypoxia, endoplasmic reticulum stress and chemoresistance: Dangerous liaisons. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, H.A.; Andrade, D.C.; Toledo, C.; Schwarz, K.G.; Pereyra, K.V.; Díaz-Jara, E.; Marcus, N.J.; Del Rio, R. Inhibition of brainstem endoplasmic reticulum stress rescues cardiorespiratory dysfunction in high output heart failure. Hypertension 2021, 77, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, S.Z.; Lourie, R.; Das, I.; Chen, A.C.-H.; McGuckin, M.A. The interplay between endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation. Immunol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 90, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarce, M.P.; Iturriaga, R. Contribution of oxidative stress and inflammation to the neurogenic hypertension induced by intermittent hypoxia. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanduri, J.; Peng, Y.J.; Wang, N.; Khan, S.A.; Semenza, G.L.; Kumar, G.K.; Prabhakar, N.R. Epigenetic regulation of redox state mediates persistent cardiorespiratory abnormalities after long-term intermittent hypoxia. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmenter, M.E.; Carr, J.A.; Go, A.; Fu, Z.; Reid, S.G.; Powell, F.L. Glutamate receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarius contribute to ventilatory acclimatization to hypoxia in rat. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1839–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturriaga, R. Carotid body contribution to the physio-pathological consequences of intermittent hypoxia: Role of nitro-oxidative stress and inflammation. J. Physiol. 2023, 601, 5495–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, K.M.; Accorsi-Mendonça, D.; Moraes, D.J.A.; Machado, B.H. Evolution and physiology of neural oxygen sensing. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, H.-M.; Hu, K.; Zhou, X.-F.; Tang, S. Sensory plasticity of carotid body is correlated with oxidative stress in paraventricular nucleus during chronic intermittent hypoxia. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 13534–13543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Leyva, I.; Velez-Jimenez, M.-K.; García, S.; Nader-Kawachi, J.A.; Martínez-Mayorga, A.P.; Melo-Carrillo, A.; Juárez-Jimenez, H.; Martinez-Gurrola, M.; Gudiño-Castelazo, M.; Chiquete, E.; et al. Cluster headache: State of the art in treatment. Front. Pain Res. 2023, 4, 1265540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straube, A.; Eren, O. tVNS in the management of headache and pain. Auton. Neurosci. 2021, 236, 102875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Hernández, R.; Escobar, C.; Buijs, R.M. Suprachiasmatic nucleus-arcuate nucleus axis: Interaction between time and metabolism essential for health. Obesity 2020, 28 (Suppl. 1), s10–s17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.R.; Xu, Y.; Cassidy, R.M.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, D.-P.; Van Drunen, R.; Ribas-Latre, A.; Cai, Z.-L. Paraventricular hypothalamus mediates diurnal rhythm of metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condés-Lara, M.; Martínez-Lorenzana, G.; de los Monteros-Zúñiga, A.E.; López-Córdoba, G.; Córdova-Quiroga, A.; Flores-Bojórquez, S.A.; González-Hernández, A. Hypothalamic paraventricular stimulation inhibits nociceptive wide dynamic range trigeminocervical complex cells via oxytocinergic transmission. J. Neurosci. 2024, 44, e1501232024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Bourgeais, L.; Arreto, C.-D.; Condes-Lara, M.; Noseda, R.; Jay, T.; Villanueva, L. Paraventricular hypothalamic regulation of trigeminovascular mechanisms involved in headaches. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 8827–8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fitzgerald, M.E.; LeDoux, M.S.; Gong, S.; Ryan, P.; Del Mar, N.; Reiner, A. Projections from the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and the nucleus of the solitary tract to prechoroidal neurons in the superior salivatory nucleus: Pathways controlling rodent choroidal blood flow. Brain Res. 2010, 1358, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, H.; Sandor, P.S.; Michels, L.; Gantenbein, A.R. Cluster headache pathophysiology—A disorder of network excitability? Clin. Transl. Neurosci. 2021, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mifflin, S.W.; Cunningham, J.T.; Toney, G.M. Neurogenic mechanisms underlying the rapid onset of sympathetic responses to intermittent hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 119, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Song, Y.; Chong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Gastrodin alleviates NTG-induced migraine-like pain via inhibiting succinate/HIF-1α/TRPM2 signaling pathway in trigeminal ganglion. Phytomedicine 2024, 125, 155266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, D.; Messlinger, K. Transient activation of spinal trigeminal neurons in a rat model of hypoxia-induced headache. Pain 2021, 162, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mody, P.; Rukhadze, I.; Kubin, L. Rats subjected to chronic-intermittent hypoxia have increased density of noradrenergic terminals in the trigeminal sensory and motor nuclei. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 505, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fenik, P.; Zhan, G.; Mazza, E.; Kelz, M.; Aston-Jones, G.; Veasey, S.C. Selective loss of catechoaminergic wake active neurons in a murine sleep apnea model. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10060–10071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsvold, B.S.; Harder, A.V.E.; Ran, C.; Chalmer, M.A.; Dalmasso, M.C.; Ferkingstad, E.; Tripathi, K.P.; Bacchelli, E.; Børte, S.; Fourier, C.; et al. Cluster headache genomewide association study and meta-analysis identifies eight loci and implicates smoking as a causal risk factor. Ann. Neurol. 2023, 94, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Qin, X.; Zhu, Z.; Mu, J.; Zhu, L.; Wu, K.; Jiao, H.; Xu, X.; Ye, Q. FHL family members suppress vascular endothelial growth factor expression through blockade of dimerization of HIF1α and HIF1β. IUBMB Life 2012, 64, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, M.; Hua, J.; Zhou, T.; Chen, F.; Lv, X.; Huang, J.; Cai, Y. UFL1, a UFMylation E3 ligase, plays a crucial role in multiple cellular stress responses. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1123124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Ye, K.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, F. UFM1 inhibits hypoxia-induced angiogenesis via promoting proteasome degradation of HIF-1α. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2024, 479, 1833–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, J.A.; Gao, Y.; Hall, C.; Muller, W.J.; Gujral, T.S.; Greer, P.A. Genetic disruption of calpain-1 and calpain -2 attenuates tumorigenesis in mouse models of HER2+ breast cancer and sensitizes cancer cells to doxorubicin and lapatinib. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 33382–33395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Fan, G.-C.; Peng, T. Calpain-1 induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in promoting cardiomyocyte apoptosis following hypoxia-reoxygenation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhou, A.X.; Rouhi, P.; Uramoto, H.; Boren, J.; Cao, Y.; Pereira, T.; Akyurek, L.M.; Poellinger, L. Hypoxia-induced and calpain-dependent cleavage of filamin A regulates the hypoxic response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2560–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Xie, J.W.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y.; Cai, J.H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B.L.; An, L.; Wang, Z.Y. Hypoxia-triggered m-calpain activation evokes endoplasmic reticulum stress and neuropathogenesis in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2013, 19, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.P.; Seehra, R.S.; Heath, P.R.; Hall, B.P.C.; Bates, J.; Garwood, C.J.; Matuszyk, M.M.; Wharton, S.B.; Simpson, J.E. Transcriptomic analysis of human astrocytes in vitro reveals hypoxia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, modulation of metabolism, and dysregulation of the immune response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couasnay, G.; Bon, N.; Devignes, C.-S.; Sourice, S.; Bianchi, A.; Véziers, J.; Weiss, P.; Elefteriou, F.; Provot, S.; Guicheux, J.; et al. PiT1/Slc20a1 is required for endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis, chondrocyte survival, and skeletal development. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Li, Y.; Chu, Y.; Wu, W.M.; Yu, Q.H.; Zhu, X.B.; Wang, Q. PLCE1 promotes myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in H/R H9c2 cells and I/R rats by promoting inflammation. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, R.; Lang, R. Dual specificity phosphatases: From molecular mechanisms to biological function. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.-N.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Lin, G.-J.; Yin, X.-W.; Ma, C.-Y. DUSP10 alleviates ischemic stroke-induced neuronal damage by restricting p38/JNK pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2023, 450, 114478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turovsky, E.A.; Tarabykin, V.S.; Varlamova, E.G. Deletion of the neuronal transcription factors Satb1 induced disturbance of the kinome and mechanisms of hypoxic preconditioning. Biology 2023, 12, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Song, N.-N.; Lan, W.; Hu, L.; Su, C.-J.; Ding, Y.-Q.; Zhang, L. Expression of transcription factor Satb2 in adult mouse brain. Anat. Rec. 2013, 296, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, X.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Chu, Z.-Y.; Sun, Z.-H.; Zhang, J.-L.; Tang, Y.-F. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator attenuates oxidative stress-induced injury in diabetic retinopathy rats. Curr. Eye Res. 2023, 48, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-P.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Z.-B.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-B. CFTR prevents neuronal apoptosis following cerebral ischemia reperfusion via regulating mitochondrial oxidative stress. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 96, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Giunta, S.; Xia, S. Hypoxia in aging and age-related diseases: Mechanism and therapeutic strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvinsson, J.C.A.; Ran, C.; Olofsgård, F.J.; Steinberg, A.; Edvinsson, L.; Belin, A.C. MERTK in the rat trigeminal system: A potential novel target for cluster headache? J. Headache Pain 2024, 25, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zheng, J.; Xu, S.; Fang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Shao, A.; Shi, L.; Lu, J.; Mei, S.; et al. Mer regulates microglial/macrophage M1/M2 polarization and alleviates neuroinflammation following traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBerge, M.; Lantz, C.; Dehn, S.; Sullivan, D.P.; van der Laan, A.M.; Niessen, H.W.M.; Flanagan, M.E.; Brat, D.J.; Feinstein, M.J.; Kaushal, S.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors individually facilitate inflammatory myeloid metabolism and inefficient cardiac repair. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20200667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Bosco Ruganzu, J.; Jin, H.; Peng, X.; Ji, S.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yang, W. LRP1 knockdown aggravates Aβ1-42-stimulated microglial and astrocytic neuroinflammatory responses by modulating TLR4/NF-κB/MAPKs signaling pathways. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Feng, X.-W. Effects and relationship of intermittent hypoxia on serum lipid levels, hepatic low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1, and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Sleep Breath. 2016, 20, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, T. Extracellular interactions between fibulins and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β in physiological and pathological conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Dalpati, N.; Bhan, C.; Dash, S.P.; Kumar, P.; Sarangi, P.P. A C-terminal fragment of adhesion protein Fibulin7 regulates neutrophil migration and functions and improves survival in LPS induced systemic inflammation. Cytokine 2020, 131, 155113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalovski, M.; Hagopian, M.; Wang, M.; Brekken, R.A. Hypoxia and transforming growth factor β cooperate to induce fibulin-5 expression in pancreatic cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 22244–22252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Danielson, K.G.; Albert, T.J.; Shapiro, I.M.; Risbud, M.V. HIF-1α is a regulator of galectin-3 expression in the intervertebral disk. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikemori, R.Y.; Machado, C.M.L.; Furuzawa, K.M.; Nonogaki, S.; Osinaga, E.; Umezawa, K.; de Carvalho, M.A.; Verinaud, L.; Chammas, R. Galectin-3 up-regulation in hypoxic and nutrient deprived microenvironments promotes cell survival. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, B.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Battle, P.; Jessup, J.M.; Raz, A.; Kim, H.R. Galectin-3 protects human breast carcinoma cells against nitric oxide-induced apoptosis: Implication of galectin-3 function during metastasis. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buture, A.; Boland, J.W.; Dikomitis, L.; Ahmed, F. Update on the pathophysiology of cluster headache: Imaging and neuropeptide studies. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollesen, A.L.H.; Snoer, A.; Chaudhry, B.; Petersen, A.S.; Hagedorn, A.; Hoffmann, J.; Jensen, R.H.; Ashina, M. The effect of pituitary adenylate cycles-activating peptide-38 and vasoactive intestinal peptide in cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 1474–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellesi, L.; Al-Karagholi, M.A.; De Icco, R.; Chaudhry, B.A.; Lopez, C.L.; Snellman, J.; Hannibal, J.; Amin, F.M.; Ashina, M. Plasma levels of CGRP during a 2-h infusion of VIP in healthy volunteers and patients with migraine: An exploratory study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 871176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, Y.B.; Jia, N.; Sun, Q.R.; Ji, S.F. Endothelial protection of vasoactive intestinal peptide enhances angiogenesis mediated by eNOS pathway following focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2022, 28, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, G.; D’Amico, A.G.; Saccone, S.; Federico, C.; Cavallaro, S.; D’Agata, V. PACAP and VIP inhibit HIF-1α-mediated VEGF expression in a model of diabetic macular edema. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, G.; D’Amico, A.G.; Rasà, D.M.; Saccone, S.; Federico, C.; Cavallaro, S.; D’Agata, V. PACAP and VIP regulate hypoxia-inducible factors in neuroblastoma cells exposed to hypoxia. Neuropeptides 2018, 69, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonkowski, S. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the carotid body—A history of forty years of research. A mini review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuka, B.; Szabó, N.; Tóth, E.; Kincses, Z.T.; Párdutz, Á.; Szok, D.; Körtési, T.; Bagoly, T.; Helyes, Z.; Edvinsson, L.; et al. Release of PACAP-38 in episodic cluster headache patients—An exploratory study. J. Headache Pain 2016, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Liong, E.C.; Tipoe, G.L.; Fung, M.L. Upregulation of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide and its receptor expression in the rat carotid body in chronic and intermittent hypoxia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 758, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borkum, J.M. CGRP and brain functioning: Cautions for migraine treatment. Headache 2019, 59, 1339–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, G.; Bussone, G.; Di Fiore, P.; Perini, F.; Gucciardi, A.; Bolner, A.; Aguggia, M.; Saracco, G.; Galloni, E.; Giordano, G.; et al. Pathogenesis of chronic cluster headache and bouts: Role of tryptamine, arginine metabolism and α1-agonists. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38 (Suppl. 1), s37–s43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.R.; Sadik, A.; Sharma, S.; Poschet, G.; Gegner, H.M.; Lanz, T.V.; Lucarelli, P.; Klingmüller, U.; Platten, M.; Heiland, I.; et al. Hypoxia routes tryptophan homeostasis towards increased tryptamine production. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 590532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, G.; Gucciardi, A.; Perini, F.; Leon, A. Pathogenesis of cluster headache: From episodic to chronic form, the role of neurotransmitters and neuromodulators. Headache 2019, 59, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozal, E.; Shah, Z.A.; Pequignot, J.-M.; Pequignot, J.; Sachleben, L.R.; Czyzyk-Krzeska, M.F.; Li, R.C.; Guo, S.-Z.; Gozal, D. Tyrosine hydroxylase expression and activity in the rat brain: Differential regulation after long-term intermittent or sustained hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2005, 99, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, I.; Roskoski, R., Jr.; Carkaci-Salli, N.; Vrana, K.E. Complex molecular regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 1451–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, D.; Ferraris, A.; Leone, M.; Catania, A.; Carlin, A.; Grazzi, L.; Bussone, G. Increased plasma nitrites in migraine and cluster headache patients in interictal period: Basal hyperactivity of L-arginine-NO pathway? Cephalalgia 2002, 22, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, A.; Wiklund, N.P.; Brundin, L.; Remahl, A.I. Levels of nitric oxide metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid in cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Empl, M.; Förderreuther, S.; Schwarz, M.; Müller, N.; Straube, A. Soluble interleukin-2 receptors increase during the active periods in cluster headache. Headache 2003, 43, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelletti, P.; Granata, M.; Giacovazzo, M. Serum interleukin-1 beta is increased in cluster headache. Cephalalgia 1993, 13, 343–345 (Discussion 307–308). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umbrello, M.; Dyson, A.; Feelisch, M.; Singer, M. The key role of nitric oxide in hypoxia: Hypoxic vasodilation and energy supply-demand matching. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2013, 19, 1690–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britze, J.; Arngrim, N.; Schytz, H.W.; Ashina, M. Hypoxic mechanisms in primary headaches. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torelli, P.; Manzoni, G.C. Behavior during cluster headache. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2005, 9, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, P.; Pierangeli, G.; Cortelli, P. The primary headaches as a reflection of genetic Darwinian adaptive behavioral responses. Headache 2010, 50, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, G.C.; Terzano, M.G.; Bono, G.; Micieli, G.; Martucci, N.; Nappi, G. Cluster headache—Clinical findings in 180 patients. Cephalalgia 1983, 3, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.R. Some clinical and theoretical aspects of cluster headache. In Migraine and Related Headaches; Saxena, P.R., Ed.; Erasmus Universitet: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; pp. 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Spiacci, A.; de Oliveira Sergio, T.; da Silva, G.S.F.; Glass, M.L.; Schenberg, L.C.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Zangrossi, H. Serotonin the in the dorsal periaqueductal gray inhibits panic-like defensive behaviors in rats exposed to acute hypoxia. Neuroscience 2015, 307, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.G.; Ohtake, P.J.; Shipherd, J.C. Exaggerated anxiety is not unique to CO2 in panic disorder: A comparison of hypercapnic and hypoxic challenges. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1999, 108, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, T.D. Linking cigarette smoking/tobacco exposure and cluster headache: A pathogenesis theory. Headache 2018, 58, 1096–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, N.; Petersen, A.; Snoer, A.; Jensen, R.H.; Barloese, M. Cluster headache is associated with unhealthy lifestyle and lifestyle-related comorbid diseases: Results from the Danish Cluster Headache Survey. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esterbauer, H.; Schaur, R.J.; Zollner, H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1991, 11, 81–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argacha, J.F.; Xhaët, O.; Gujic, M.; Adamopoulos, D.; Beloka, S.; Dreyfuss, C.; Degaute, J.P.; Van De Borne, P. Nicotine increases chemoreflex sensitivity to hypoxia in non-smokers. J. Hypertens. 2008, 26, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, J.P.; da Cunha Dias, A.; Bettini, N.R.; Amancio de Sousa, S.A.B.; Durão, M.P.L.; de Castro Oliveira, L.V.; Monedeiro, F.; Ramalho, L.N.Z.; Branco, L.G.S.; Sabino, J.P.J.; et al. Cigarette smoke exposure causes systemic and autonomic cardiocirculatory changes in rats depending on the daily exposure dose. Life Sci. 2021, 277, 119498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Luo, C.; Long, J.; Wei, D.; Liu, J. Acrolein is a mitochondrial toxin: Effects on respiratory function and enzyme activities in isolated rat liver mitochondria. Mitochondrion 2006, 6, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, R.; Olschewski, A.; Heinemann, A. Succinate at the crossroad of metabolism and angiogenesis: Roles of SDH, HIF1α and SUCNR1. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, D.; Yang, L.; Gan, L.; Cederbaum, A. Cytochrome P450 2E1 potentiates ethanol induction of hypoxia and HIF-1alpha in vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 63, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzen, E.; Zhou, J.; Jelkmann, W.; Fandrey, J.; Brüne, B. Nitric oxide impairs normoxic degradation of HIF-1alpha by inhibition of prolyl hydroxylases. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 3470–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamovich, Y.; Dandavate, V.; Asher, G. Circadian clocks’ interactions with oxygen sensing and signalling. Acta Physiol. 2022, 2022, e13770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, C.M.; Czeisler, C.A.; Shea, S.A. An endogenous circadian rhythm of respiratory control in humans. J. Physiol. 2000, 526, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sennels, H.P.; Jorgensen, H.L.; Hansen, A.-L.S.; Goetze, J.P.; Fahrenkrug, J. Diurnal variation of hematology parameters in healthy young males: The Bispebjerg study of diurnal variations. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2011, 71, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristancho, E.; Riveros, A.; Sánchez, A.; Peñuela, O.; Böning, D. Diurnal changes of arterial oxygen saturation and erythropoietin concentration in male and female highlanders. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e12901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.A.; Marino, G.M.; Spears, A.R.; Arble, D.M. The molecular circadian clock of Phox2b-expressing cells drives daily variation of the hypoxic but not hypercapnic ventilatory response in mice. Function 2023, 4, zqad023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manella, G.; Aviram, R.; Bolshette, N.; Muvkadi, S.; Golik, M.; Smith, D.F.; Asher, G. Hypoxia induces a time- and tissue-specific response that elicits intertissue circadian clock misalignment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudrow, L. The cyclic relationship of natural illumination to cluster period frequency. Cephalalgia 1987, 7 (Suppl 6), 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.H.; Wang, P.J.; Fuh, J.L.; Lu, S.R.; Chung, C.T.; Tsou, H.K.; Wang, S.J. Cluster headache in the Taiwanese—a clinic-based study. Cephalalgia 2004, 24, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofte, H.K.; Berg, D.H.; Bekkelund, I.S.; Alstadhaug, K.B. Insomnia and periodicity of headache in an arctic cluster headache population. Headache 2013, 53, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmenko, N.V. Seasonal variations in atmospheric pressure, partial oxygen density, and geomagnetic activity as additional synchronizers of circannual rhythms. Biophysics 2019, 64, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, T.D.; Dempsey, J.A.; Thomas, K.N.; Ainslie, P.N.; Wilson, L.C.; Stothers, T.A.M.; Campbell, H.A.; Cotter, J.D. Carotid body hyperexcitability underlies heat-induced hyperventilation in exercising humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 133, 1394–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, J.B.; Livingstone, S.D.; Nolan, R.W.; Keefe, A.A. Respiratory heat loss during work at various ambient temperatures. Respir. Physiol. 1990, 79, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akerman, S.; Holland, P.R.; Lasalandra, M.P.; Goadsby, P.J. Oxygen inhibits neuronal activation in the trigeminocervical complex after stimulation of trigeminal autonomic reflex, but not during direct dural activation of trigeminal afferents. Headache 2009, 49, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Ruan, W.; Jiang, Y.; Smalling, R.; Yuan, X.; Eltzschig, H.K. Interplay of hypoxia-inducible factors and oxygen therapy in cardiovascular medicine. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barloese, M.C.J. A review of cardiovascular autonomic control in cluster headache. Headache 2016, 56, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loggia, M.L.; Juneau, M.; Bushnell, M.C. Autonomic responses to heat pain: Heart rate, skin conductance, and their relation to verbal ratings and stimulus intensity. Pain 2011, 152, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barloese, M.C.; Mehlsen, J.; Brinth, L.; Lundberg, H.I.; Jennum, P.J.; Jensen, R.H. Reduced baroreflex sensitivity in cluster headache patients. Headache 2015, 55, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkle, E.C.; Anderson, W.B. Dual mechanisms of eye signs in headache of cluster pattern. Trans. Am. Neurol. Assoc. 1960, 85, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Buchholz, B.; Kelly, J.; Bernatene, E.A.; Diodati, N.M.; Gelpi, R.J. Antagonistic and synergistic activation of cardiovascular vagal and sympathetic motor outflows in trigeminal reflexes. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, B.J.; Buchfelder, M. Trigemino-cardiac reflex: A recently discovered “oxygen-conserving” response? The potential therapeutic role of a physiological reflex. Arch. Med. Sci. 2006, 2, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, S. Sudden death and the oxygen-conserving reflex. Am. Heart J. 1966, 71, 840–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, V.; Behan, M.; Kinkead, R. Sex, hormones, and stress: How they impact development and function of the carotid bodies and related reflexes. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 185, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Dai, Y.; Bai, J.; Ren, B.; Xu, J.; Gao, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, R. 17β-oestradiol alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress injury induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion through the Haemoglobin/HIF 1α signalling pathway in ovariectomized rats. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 148, 105119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyner, M.J.; Limberg, J.K.; Wehrwein, E.A.; Johnson, B.D. Role of the carotid body chemoreceptors in glucose homeostasis and thermoregulation in humans. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 3079–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, A.; Schwedt, T.J.; Magis, D.; Pozo-Rosich, P.; Evers, S.; Wang, S.-J. Cluster headache. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, A.S.; Barloese, M.C.J.; Snoer, A.; Soerensen, A.M.S.; Jensen, R.H. Verapamil and cluster headache: Still a mystery. A narrative review of efficacy, mechanisms and perspectives. Headache 2019, 59, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, L.A.; Davies, G.F.; Xavier, I.J.; Ovsenek, N. L-carnosine and verapamil inhibit hypoxia-induced expression of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF-1α) in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts. Pharmacol. Res. 2002, 45, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, M.; Lucini, V.; D’Amico, D.; Grazzi, L.; Moschiano, F.; Fraschini, F.; Bussone, G. Abnormal 24-hour urinary excretory pattern of 6-sulphatoxymelatonin in both phases of cluster headache. Cephalalgia 1998, 18, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, M.; Lucini, V.; D’Amico, D.; Moschiano, F.; Maltempo, C.; Fraschini, F.; Bussone, G. Twenty-four-hour melatonin and cortisol plasma levels in relation to timing of cluster headache. Cephalalgia 1995, 15, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, O.; Beaumont, M.; Batejat, D.; Van Beers, P.; Charbuy, H. Hypoxic depression of melatonin secretion after simulated long duration flights in man. J. Pineal Res. 2004, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, M.; D’Amico, D.; Moschiano, F.; Fraschini, F.; Bussone, G. Melatonin versus placebo in the prophylaxis of cluster headache: A double-blind pilot study with parallel groups. Cephalalgia 1996, 16, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tjong, Y.-W.; Ip, S.-F.; Tipoe, G.L.; Fung, M.-L. Melatonin enhances the hypoxic response of the rat carotid body chemoreceptor. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 38, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vriend, J.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin and the von Hippel-Lindau/HIF-1 oxygen sensing mechanism: A review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1865, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecklenburg, J.; Sanchez Del Rio, M.; Reuter, U. Cluster headache therapies: Pharmacology and mode of action. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 13, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valvezan, A.J.; Klein, P.S. GSK-3 and Wnt signaling in neurogenesis and bipolar disorder. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, K.T.; Giulian, G.G.; Li, G.; Kao, J.P.; Marino, J.P. A molecular model for lithium’s bioactive form. Biophys. J. 2016, 111, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Rda, L.; Seibt, K.J.; Rico, E.P.; Bogo, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Inhibitory effect of lithium on nucleotide hydrolysis and acetylcholinesterase activity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) brain. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, E.A.; Powell, F.L. Serotonin and adenosine G-protein coupled receptor signaling for ventilatory acclimatization to sustained hypoxia. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussone, G.; Leone, M.; Peccarisi, C.; Micieli, G.; Granella, F.; Magri, M.; Manzoni, G.C.; Nappi, G. Double blind comparison of lithium and verapamil in cluster headache prophylaxis. Headache 1990, 30, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, B.T.; MacLean, A.R.; Craig, W.M. A new syndrome of vascular headache: Results of treatment with histamine: Preliminary report. Proc. Staff Meet. Mayo Clin. 1939, 14, 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Tepper, S.J.; Stillman, M.J. Cluster headache: Potential options for medically refractory patients (when all else fails). Headache 2013, 53, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, S.; Freitag, F.G.; Prager, J.; Gandhi, S. Treatment of intractable cluster. Headache 1986, 26, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, T.; Iwase, M.; Kanamaru, M.; Izumizaki, M.; Ohshima, Y.; Homma, I. Impaired ventilation and metabolism response to hypoxia in histamine H1 receptor-knockout mice. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2006, 154, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, B.T. Histaminic cephalgia. Lancet 1952, 72, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Haane, D.Y.P.; Dirkx, T.H.T.; Koehler, P.J. The history of oxygen inhalation as a treatment for cluster headache. Cephalalgia 2012, 32, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, A.E.; Huck, G.; Stiehl, D.P.; Jelkmann, W.; Hellwig-Bürgel, T. Dexamethasone impairs hypoxia-inducible factor-1 function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 372, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, M.S.; Robertson, C.E.; Kaplan, E.; Ailani, J.; Charleston, L., 4th; Kuruvilla, D.; Blumenfeld, A.; Berliner, R.; Rosen, N.L.; Duarte, R.; et al. The sphenopalatine ganglion: Anatomy, pathophysiology, and therapeutic targeting in headache. Headache 2016, 56, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Y.; Gong, P. Overexpression of calcitonin gene-related peptide protects mouse cerebral microvascular endothelial cells from high-glucose-induced damage via ERK/HIF-1/VEGF signaling. J. Physiol. Sci. 2019, 69, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, S.M.; Burish, M.J.; Shapiro, R.E.; Yan, Y.; Schor, L.I. Effectiveness of oxygen and other acute treatments for cluster headache: Results from the Cluster Headache Questionnaire, an international survey. Headache 2019, 59, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudrow, L. Response of cluster headache attacks to oxygen inhalation. Headache 1981, 21, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cittadini, E.; May, A.; Straube, A.; Evers, S.; Bussone, G.; Goadsby, P.J. Effectiveness of intranasal zolmitriptan in acute cluster headache: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind crossover study. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanaka, R.; Jin, H.; Aoe, T. Unraveling the connection: Pain and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ide, K. Acute hypoxia elicits prefrontal oxygenation asymmetry in young adults. Neurophotonics 2023, 10, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zohdi, H.; Scholkmann, F.; Wolf, U. Frontal cerebral oxygenation asymmetry: Intersubject variability and dependence on systemic physiology, season, and time of day. Neurophotonics 2020, 7, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzani, M.; Jahromi, S.R.; Ghorbani, Z.; Vahabizad, F.; Martelletti, P.; Ghaemi, A.; Sacco, S.; Togha, M.; School of Advanced Studies of the European Headache Federation (EHF-SAS). Gut-brain axis and migraine headache: A comprehensive review. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, X.; Jia, Q.; Xu, J.; Shi, J.; Li, X.; Xie, G.; Zhao, X.; He, K. Longitudinal multi-omics analysis uncovers the altered landscape of gut microbiota and plasma metabolome in response to high altitude. Microbiome 2024, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.A.; Wong, F.S.; Wen, L. Crosstalk between circadian rhythms and the microbiota. Immunology 2020, 161, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cantos, M.V.; Babu, A.F.; Hanhineva, K.; Kuipers, O.P. Identification of metabolites produced by six gut commensal Bacteroidales strains using non-targeted LC-MS/MS metabolite profiling. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 283, 127700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogal, A.; Louca, P.; Zhang, X.; Wells, P.M.; Steves, C.J.; Spector, T.D.; Falchi, M.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. Circulating levels of the short-chain fatty acid acetate mediate the effect of the gut microbiome on visceral fat. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 711359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, L.; Yuan, G.; Jia, J. New insights into the roles of olfactory receptors in cardiovascular disease. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2024, 479, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonasch, E.; Donskov, F.; Iliopoulos, O.; Rathmell, W.K.; Narayan, V.K.; Maughan, B.L.; Oudard, S.; Else, T.; Maranchie, J.K.; Welsh, S.J.; et al. Belzutifan for renal cell carcinoma in von Hippel-Lindau disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2036–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewinski, P.; Janczak, D.; Rucinski, A.; Tubek, S.; Engelman, Z.J.; Piesiak, P.; Jazwiec, P.; Banasiak, W.; Fudim, M.; Sobotka, P.A.; et al. Carotid body resection for sympathetic modulation in systolic heart failure: Results from first-in-man study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baby, S.M.; Gruber, R.B.; Young, A.P.; Macfarlane, P.M.; Teppema, L.J.; Lewis, S.J. Bilateral carotid sinus nerve transection exacerbates morphine-induced respiratory depression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 834, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strowd, R.; Ellingson, B.; Raymond, C.; Yao, J.; Wen, P.Y.; Ahluwalia, M.; Piotrowski, A.; Desai, A.; Clarke, J.L.; Lieberman, F.S.; et al. Activity of a first-in-class oral HIF2-alpha inhibitor, PT2385, in patients with first recurrence of glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 165, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zera, T.; Moraes, D.J.A.; da Silva, M.P.; Fisher, J.P.; Paton, J.F.R. The logic of carotid body connectivity to the brain. Physiology 2019, 34, 264–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, A.; Tiberi, M.; Zarletti, G.; Pala, M.I.; Trevi, E. Oral high-dose thiamine improves the symptoms of chronic cluster headache. Case Rep. Neurol. Med. 2018, 2018, 3901619. [Google Scholar]
- Tsepkova, P.M.; Artiukhov, A.V.; Boyko, A.I.; Aleshin, V.A.; Mkrtchyan, G.V.; Zvyagintseva, M.A.; Ryabov, S.I.; Ksenofontov, A.L.; Baratova, L.A.; Graf, A.V.; et al. Thiamine induces long-term changes in amino acid profiles and activities of 2-oxoglutarate and 2-oxoadipate dehydrogenases in rat brain. Biochemistry 2017, 82, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-J.; Feng, L.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mi, H.-F.; Zhou, X.-Q.; Jiang, W.-D. Hypoxia leads to gill endoplasmic reticulum stress and disruption of mitochondrial homeostasis in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): Mitigation effect of thiamine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, R.L.; Zastre, J.A. HIF1-α-mediated gene expression induced by vitamin B1 deficiency. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2013, 83, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zera, K.; Zastre, J. Thiamine deficiency activates hypoxia inducible factor-1α to facilitate pro-apoptotic responses in mouse primary astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lei, X.; Zheng, X.; Xie, Z.; Tang, G. Anticancer activity of natural flavonoids: Inhibition of HIF-1α signaling pathway. Curr. Org. Chem. 2019, 23, 2945–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonis, I.; Lakka, A.; Tsakalof, A.; Simos, G. The dietary flavonoid kaempferol effectively inhibits HIF-1 activity and hepatoma cancer cell viability under hypoxic conditions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafyllou, A.; Mylonis, I.; Simos, G.; Bonanou, S.; Tsakalof, A. Flavonoids induce HIF-1α but impair its nuclear accumulation and activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Chun, Y.S.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, M.S.; Park, J.W. Curcumin inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1 by degrading aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator: A mechanism of tumor growth inhibition. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Tang, L.; Shen, C.-L.; Wang, J.-S. Green tea polyphenols boost gut-microbiota-dependent mitochondrial TCA and urea cycles in Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 81, 108395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, J.M.; Hanson, B.E.; Asama, T.F.; Feider, A.J.; Hanada, S.; Aldrich, A.W.; Dyken, M.E.; Casey, D.P. Acute inorganic nitrate supplementation and the hypoxic ventilatory response in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 130, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugiani, M.; Lamantea, E.; Invernizzi, F.; Moroni, I.; Bizzi, A.; Zeviani, M.; Uziel, G. Effects of riboflavin in children with complex II deficiency. Brain Dev. 2006, 28, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, B.J.; Bates, M.L.; Del Rio, R.; Wang, Z.; Dopp, J.M. Oxidative stress augments chemoreflex sensitivity in rats exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2016, 234, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovine, B.; Oliviero, G.; Garofalo, M.; Orefice, M.; Nocella, F.; Borbone, N.; Piccialli, V.; Centore, R.; Mazzone, M.; Piccialli, G.; et al. The anti-proliferative effect of l-carnosine correlates with a decreased expression of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha in human colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, E.A.; Botusan, I.R.; Wang, J.; Peters, V.; Ansurudeen, I.; Brismar, K.; Catrina, S.B. Carnosine decreases IGFBP1 production in db/db mice through suppression of HIF-1. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 225, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.S.; Park, J.W.; Heo, H.; Park, J.S.; Park, S.W. The neuroprotective effect of carnosine (β-alanyl-L-histidine) on retinal ganglion cell following ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr. Eye Res. 2014, 39, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye, A.A.; Zhang, D.; Guo, L.; Zheng, Y.; Hoetker, D.; Zhao, J.; Posa, D.K.; Ng, C.K.; Zheng, H.; Kumar, A.; et al. Carnosine supplementation enhances post ischemic hind limb revascularization. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, L.; Gabutti, A.; Porta, C.; Spicuzza, L. Slow breathing reduces chemoreflex response to hypoxia and hypercapnia, and increases baroreflex sensitivity. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicuzza, L.; Gabutti, A.; Porta, C.; Montano, N.; Bernardi, L. Yoga and chemoreflex response to hypoxia and hypercapnia. Lancet 2000, 356, 1495–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, V.K.; Mark, A.L.; Abboud, F.M. Interaction of baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflex control of sympathetic nerve activity in normal humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 1953–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Zappaterra, M.; Righi, F.; Ciccarese, M.; Tiraferri, I.; Pini, L.A.; Guerzoni, S.; Cainazzo, M.M. Impact of continuing or quitting smoking on episodic cluster headache: A pilot survey. J. Headache Pain 2013, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, S.V.; Sacramento, J.F.; Guarino, M.P.; Gonzalez, C.; Obeso, A.; Diogo, L.N.; Monteiro, E.C.; Ribeiro, M.J. Carotid body, insulin, and metabolic diseases: Unraveling the links. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haane, D.Y.P.; Koehler, P.J. Nociceptive specific supraorbital nerve stimulation may prevent cluster headache attacks: Serendipity in a blink reflex study. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borkum, J.M. Cluster Headache and Hypoxia: Breathing New Life into an Old Theory, with Novel Implications. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 1691-1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060123
Borkum JM. Cluster Headache and Hypoxia: Breathing New Life into an Old Theory, with Novel Implications. Neurology International. 2024; 16(6):1691-1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060123
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorkum, Jonathan M. 2024. "Cluster Headache and Hypoxia: Breathing New Life into an Old Theory, with Novel Implications" Neurology International 16, no. 6: 1691-1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060123
APA StyleBorkum, J. M. (2024). Cluster Headache and Hypoxia: Breathing New Life into an Old Theory, with Novel Implications. Neurology International, 16(6), 1691-1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060123




