Internal Ophthalmoplegic Migraine During Pregnancy: A Clinical Case
Abstract
1. Introduction
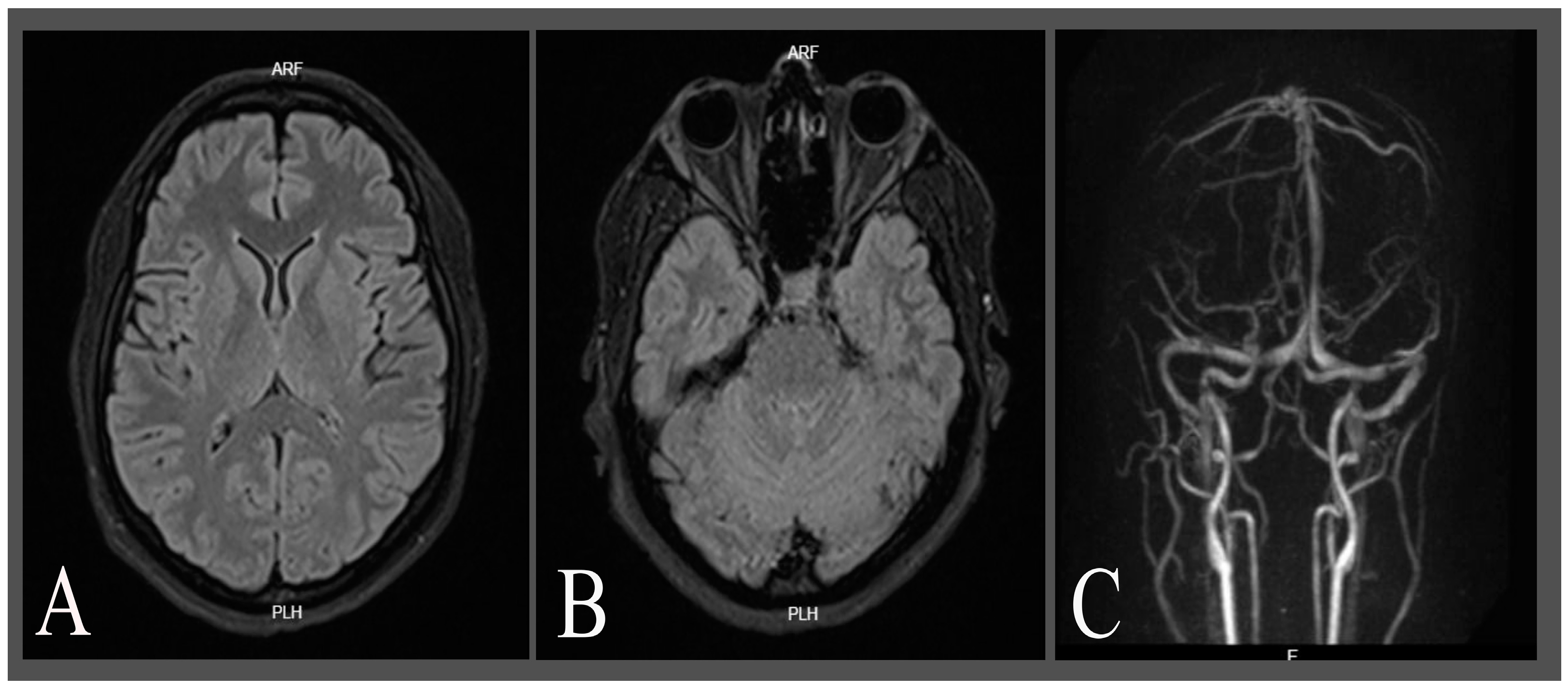
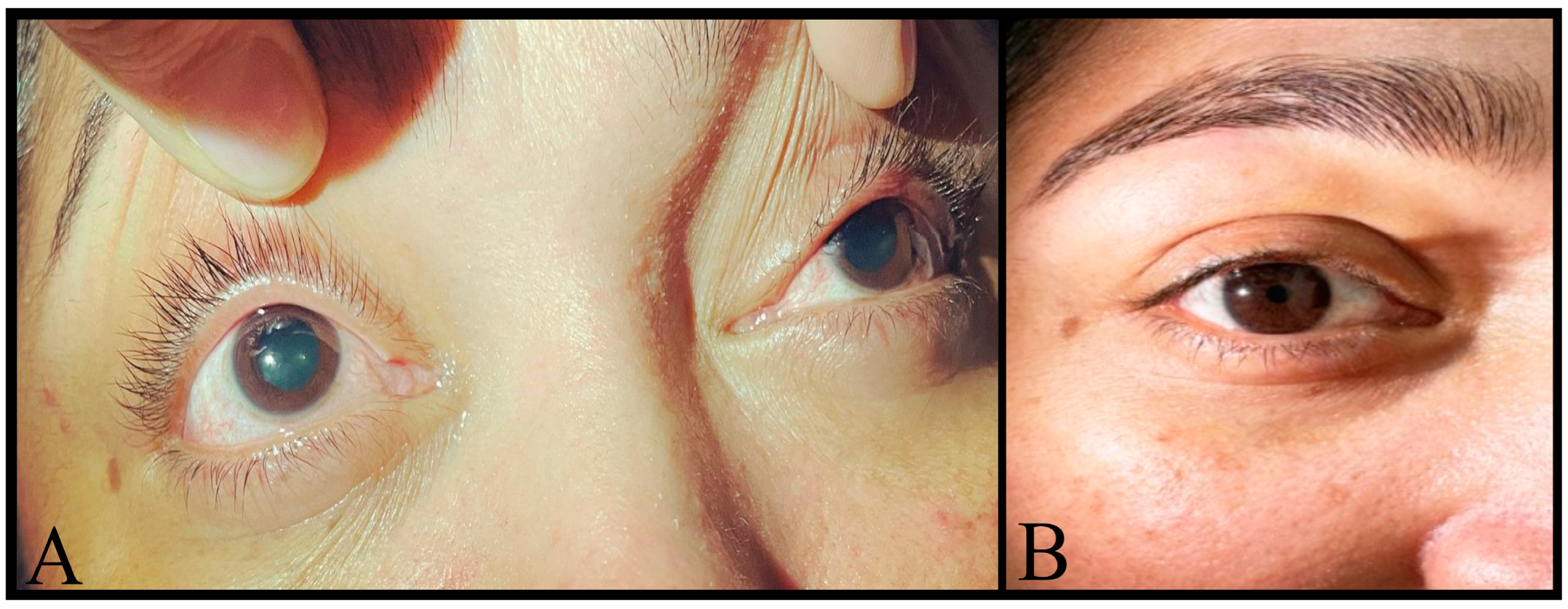
2. Case Description
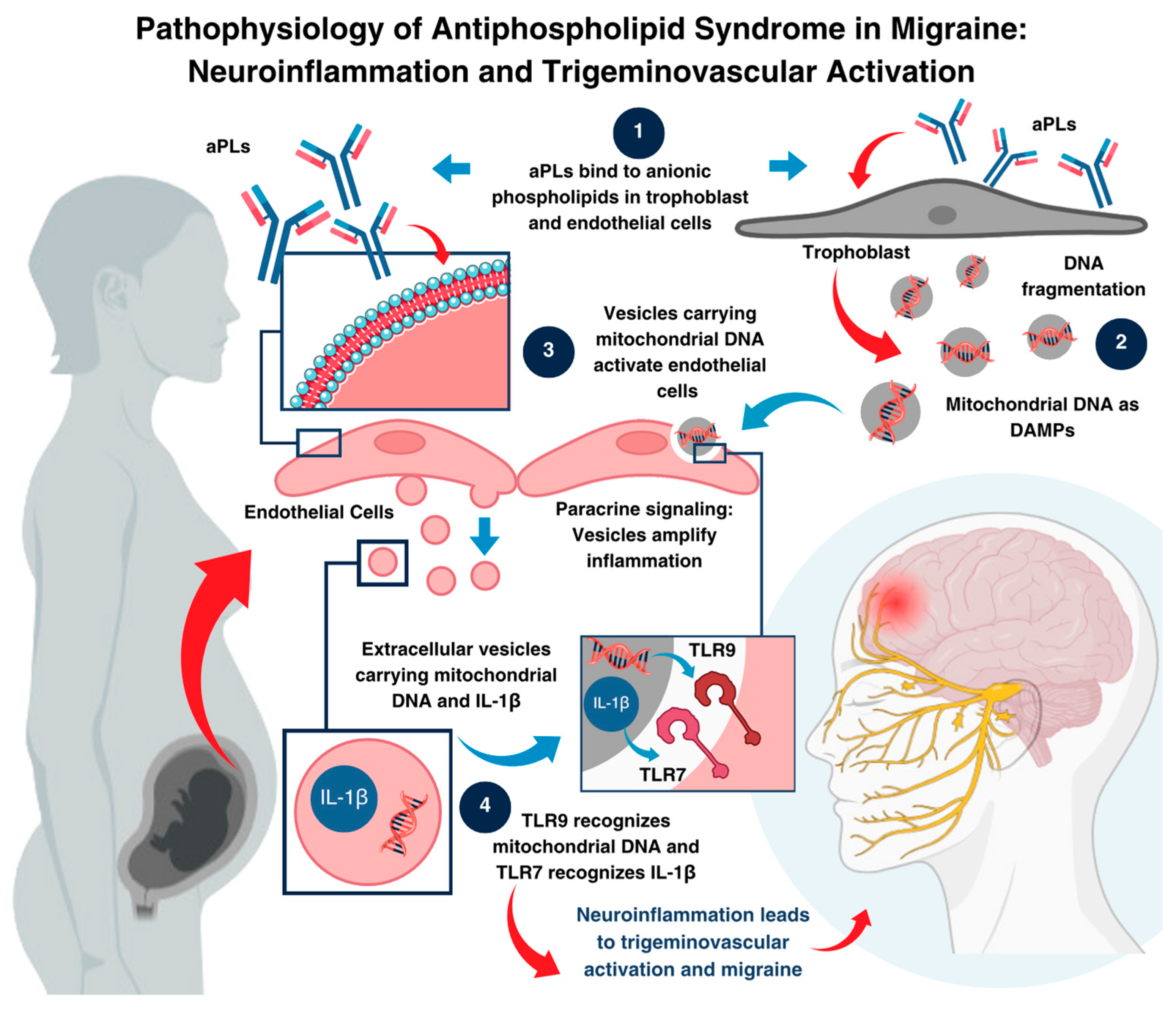
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karsan, N. Pathophysiology of Migraine. Continuum 2024, 30, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stovner, L.J.; Hagen, K.; Linde, M.; Steiner, T.J. The global prevalence of headache: An update, with analysis of the influences of methodological factors on prevalence estimates. J. Headache Pain 2022, 23, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.; Molina, E.; Rodriguez, A.; Woodford, S.; Nguyen, A.; Parker, G.; Lucke-Wold, B. Headache Disorders: Differentiating Primary and Secondary Etiologies. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2024, 23, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negro, A.; Delaruelle, Z.; Ivanova, T.A.; Martelletti, P.; Mitsikostas, D.D.; Reuter, U.; Mitsikostas, D.D. Headache and pregnancy: A systematic review. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafinia, F.; Kelley, E.L.; Meimand, H.E.; Iranmanesh, F.; Ghasemi, J.; Heydari, O. Headache characteristics in a sample of pregnant Iranian women with primary headache. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2024, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, D. The ophthalmoplegic migraines: A proposed classification. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 646–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noruzzadeh, R.; Modabbernia, A.; Aghamollaii, V.; Ghaffarpour, M.; Harirchian, M.H.; Salahi, S.; Nikbakht, N.; Noruzi, N.; Tafakhori, A. Memantine for prophylactic treatment of migraine without aura: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled study. Headache 2016, 56, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksic, D.; Drakulic, S.; Ljubisavljevic, S. Recurrent Painful Ophthalmoplegic Neuropathy: Migraine, Neuralgia, or Something Else? J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2020, 34, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorsby-Vargas, A.M.; Martínez-Maldonado, A.; Arellano-Martínez, C.L. Migraña oftalmopléjica con oftalmoplejia interna bilateral. Reporte de un caso. Rev. Mex. Oftalmol. 2022, 96, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, S.; Barbaro, G.; Paciullo, C.; Tersigni, C.; Scambia, G.; Di Simone, N. Antiphospholipid syndrome in pregnancy: New and old pathogenetic mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Rato, M.; Bandeira, M.; Romão, V.C.; Aguiar de Sousa, D. Neurologic Manifestations of the Antiphospholipid Syndrome—An Update. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2021, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherer, Y.; Hassin, S.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Levy, Y.; Livneh, A.; Ohry, A.; Langevitz, P. Transverse myelitis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies--the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. Clin. Rheumatol. 2002, 21, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervera, R.; Boffa, M.C.; Khamashta, M.A.; Hughes, G.R.V. The Euro-Phospholipid project: Epidemiology of the antiphospholipid syndrome in Europe. Lupus 2009, 18, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreoli, L.; Chighizola, C.B.; Banzato, A.; Pons-Estel, G.J.; Ramire de Jesus, G.; Erkan, D. Estimated frequency of antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with pregnancy morbidity, stroke, myocardial infarction, and deep vein thrombosis: A critical review of the literature. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 1869–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, J.F.; Pasoto, S.G.; Appenzeller, S. Seizures in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome: The Relevance of Smoking to Stroke. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 981519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelnik, C.M.; Kozora, E.; Appenzeller, S. Non-stroke Central Neurologic Manifestations in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2016, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzechowski, N.M.; Wolanskyj, A.P.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Kumar, N.; Moder, K.G. Antiphospholipid antibody-associated chorea. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 2165–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, C.; Franch, O.; Fernández-Paredes, L.; Oreja-Guevara, C.; Núñez-Beltrán, M.; Comins-Boo, A.; Reale, M.; Sánchez-Ramón, S. Antiphospholipid antibodies overlapping in isolated neurological syndrome and multiple sclerosis: Neurobiological insights and diagnostic challenges. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jeruc, J.; Popovic, M.; Vizjak, A.; Jurcić, V.; Lestan, B.; Ferluga, D. Multiple mononeuropathy due to vasculitis associated with anticardiolipin antibodies: A case report. Folia Neuropathol. 2006, 44, 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Cavestro, C.; Micca, G.; Molinari, F.; Bazzan, M.; DI Pietrantonj, C.; Aloi, R.; Pedemonte, E.; Iannini, R.; Frigeri, M.C.; Roccatello, D. Migraineurs show a high prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürks, M.; Rist, P.M.; Bigal, M.E.; Buring, J.E.; Lipton, R.B.; Kurth, T. Migraine and cardiovascular disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2009, 339, b3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.A.; Alam, F.; Wong, K.K. Comorbid association of antiphospholipid antibodies and migraine: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygiel-Górniak, B.; Rogacka, N.; Puszczewicz, M. Antinuclear antibodies in healthy people and non-rheumatic diseases—Diagnostic and clinical implications. Reumatologia 2018, 56, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanaugh, A.; Tomar, R.; Reveille, J.; Solomon, D.H.; Homburger, H.A. Guidelines for clinical use of the antinuclear antibody test and tests for specific autoantibodies to nuclear antigens. American College of Pathologists. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2000, 124, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinton, L.M.; Eystathioy, T.; Selak, S.; Chan, E.K.; Fritzler, M.J. Autoantibodies to protein transport and messenger RNA processing pathways: Endosomes, lysosomes, Golgi complex, proteasomes, assemblyosomes, exosomes, and GW bodies. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 110, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rau, J.C.; Dodick, D.W. Other Preventive Anti-Migraine Treatments: ACE Inhibitors, ARBs, Calcium Channel Blockers, Serotonin Antagonists, and NMDA Receptor Antagonists. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2019, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drugs.com. Memantine: Pregnancy Warnings. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/pregnancy/memantine.html#pregnancy-warnings (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- MacGregor, E.A. Headache in pregnancy. Neurol. Clin. 2012, 30, 835–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markey, K.A.; Mollan, S.P.; Jensen, R.H.; Sinclair, A.J. Understanding idiopathic intracranial hypertension: Mechanisms, management, and future directions. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, L.; Yang, X.G.; Lian, X.; Feng, Y.H.; Li, C.P.; Ma, H.C. Full-term pregnant women have higher lumbar epidural pressure than non-pregnant women: A preliminary report. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2013, 33, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Laboratory Test | June, 2022 (2nd Trimester) | September, 2022 (3rd Trimester) | February, 2024 (Follow-Up) | May, 2024 (Follow-Up) | Reference Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Beta2 Glicoprotein IgG | -- | -- | 0.19 U/mL | 0.18 U/mL | Negative: <0.8 U/mL Positive: >1.2 U/mL Undetermined: 0.8–1.2 U/mL |
| Anti-Beta2 Glicoprotein IgM | -- | -- | 0.47 U/mL | 0.31 U/mL | |
| Russell Viper Venom Test (LA1-TVVRD) | 56.4 s | 34.6 s | 55.9 s | 34.8 s | <1.20 |
| Control (Day) | 32.4 s | 33.1 s | -- | -- | -- |
| Confirmatory Test with Phospholipids (LA2) | -- | 36.4 s | 32.5 s | -- | -- |
| Silica Clotting Time (SCT) | -- | -- | 39.7 s | SCTSC: 33.7 s, Ratio: 0.86 | <1.16 |
| LA Ratio (LA1/LA2) | -- | 0.9 | 0.89 | 0.94 | >2: positive. 1.5–2: moderate 1.2–1.5: weak |
| Anti-Cardiolipin IgM | 8.94 MPL U/mL | -- | 4.3 MPL U/mL | 10.2 MPL U/mL | Negative: <12 MPL U/mL Positive: >18 MPL U/ml |
| Anti-Cardiolipin IgG | 2.86 GPL U/mL | -- | 2.9 GPL U/mL | 1.9 GPL U/mL | Negative: <12 GPL U/mL Positive: >18 GPL U/mL |
| ANA * | 1/160 patron lysosomal | 1/160 Discrete cytoplasmic granular pattern | 1/160 Discrete cytoplasmic granular pattern | 1/160 Discrete cytoplasmic granular pattern | Positive: >1/80 ACR-EULAR 2019 (LES) |
| COOMBS (Direct) | -- | Negative | -- | -- | -- |
| Anti-DNA Abs | -- | Negative | -- | -- | Negative: <1:10 Positive: >1:10 |
| C3 | -- | -- | 123 mg/dL | 115 mg/dL | 90.0–180.0 mg/dL |
| C4 | -- | -- | 17 mg/dL | 16 mg/dL | 10.0–40.0 mg/dL |
| RO/SSA antibodies | -- | 0.3 U/mL | -- | 0.2 U/mL | Negative <0.8 U/mL Positive >1.2 U/mL |
| Anti-LA/SSB antibodies | -- | 0.1 U/mL | -- | 0.0 U/mL | |
| SM antibody | -- | 0.6 U/mL | -- | 0.2 U/mL | |
| Anti-RNP antibodies | -- | 0.2 U/mL | -- | 0.3 U/mL | |
| ANCA C and P | -- | -- | Negative | Negative | -- |
| Factor V | 37% | -- | -- | -- | 50–150% |
| Test | Results at Week 25 (2022) | February, 2024 (Follow-Up) | May, 2024 (Follow-Up) | Reference Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 12.30 g/dL | 13.9 g/dL | 14.9 g/dL | 11.20–15.70 g/dL |
| Platelets | 260 ×103/μL | 203 ×103/μL | 244 ×103/μL | 140–400 ×103/μL |
| Leucocytes count | 10.04 ×103/mm3 | 7.88 ×103/mm3 | 7.59 ×103/mm3 | 4.00–10.04 ×103/mm3 |
| Proteinuria | Negative | -- | -- | Negative <150 mg/day or <10 mg/dL Positive >10 mg/dL or >150 mg/day |
| Urinary leucocytes | 0–3 cells/high-power field | -- | -- | 0–5 cells/high-power field |
| Urinary red cells | 0–2 cells/high-power field | -- | -- | 0–5 cells/high-power field |
| 24 h proteinuria | 231.00 mg/24 h | 10.00–140 mg/24 h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castillo-Guerrero, B.; Londoño-Juliao, G.; Pianetta, Y.; Gutiérrez-Rey, M.; Zuñiga, B.J.; Pestana, G.; Carbonell-Zabaleta, A.-K.; Rivera-Porras, D.; Bermúdez, V.; Vargas-Manotas, J. Internal Ophthalmoplegic Migraine During Pregnancy: A Clinical Case. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 1779-1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060128
Castillo-Guerrero B, Londoño-Juliao G, Pianetta Y, Gutiérrez-Rey M, Zuñiga BJ, Pestana G, Carbonell-Zabaleta A-K, Rivera-Porras D, Bermúdez V, Vargas-Manotas J. Internal Ophthalmoplegic Migraine During Pregnancy: A Clinical Case. Neurology International. 2024; 16(6):1779-1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060128
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastillo-Guerrero, Brenda, Gloria Londoño-Juliao, Yesenia Pianetta, Melissa Gutiérrez-Rey, Bley Jair Zuñiga, Gustavo Pestana, Ana-Karina Carbonell-Zabaleta, Diego Rivera-Porras, Valmore Bermúdez, and José Vargas-Manotas. 2024. "Internal Ophthalmoplegic Migraine During Pregnancy: A Clinical Case" Neurology International 16, no. 6: 1779-1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060128
APA StyleCastillo-Guerrero, B., Londoño-Juliao, G., Pianetta, Y., Gutiérrez-Rey, M., Zuñiga, B. J., Pestana, G., Carbonell-Zabaleta, A.-K., Rivera-Porras, D., Bermúdez, V., & Vargas-Manotas, J. (2024). Internal Ophthalmoplegic Migraine During Pregnancy: A Clinical Case. Neurology International, 16(6), 1779-1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16060128






